1. Introduction
With the intensification of coal mining, the dynamic disaster caused by coal rock is becoming increasingly severe. Rock burst poses a significant threat to the safe and efficient production of coal mines, given its rapid occurrence, high level of harm, and extensive damage range [1-3]. Rock burst is a dynamic event. It is caused by the sudden release of elastic energy stored in coal and rock formations. This phenomenon is influenced by the variation in coal thickness as well as the stress state of the coal seam and rock strata in the stopes [4-5]. Relevant research shows that the probability of rock burst is related to the change in coal thickness. During the mining period, the energy accumulation degree of the coal thickness change area is high, which can potentially lead to catastrophic events such as rock burst [6-7].
To investigate the impact of coal thickness variation on rock burst, several scholars utilize the coal-rock combination to conduct research. The impact of changes in coal thickness on the strength and deformation characteristics of coal-rock combinations was analyzed in studies [8-10]; results demonstrate that the strength of combinations is negatively correlated with coal thickness changes. Cheng Zhanbo et al. [
11] revealed the relationship between coal thickness changes, parameters at the coal-rock interface, and the strength of the combination. Zuo Jianping et al. [
12] compared the energy accumulation differences of various coal-rock combinations and identified a correlation with coal thickness variations. Chen Guangbo et al. [
13,
14] identified the key layer where energy for rock bursts accumulates within the coal seam. And the degree of energy accumulation was related to the change in coal thickness. The above-mentioned researchers have discussed the association between the strength and energy accumulation behavior characteristics of the combinations and the variation in coal thickness, but they have not sufficiently investigated the evolution of the surrounding rock stress and energy in the region of the variation in coal thickness.
To this end, Bai Xianxi et al. [
15] analyzed the surrounding rock’s stress and energy distribution characteristics in the roof thickness change area. They concluded that the greater the roof thickness change, the greater the initial stress in the coal seam thinning area. Wang Jianchao et al. [
16] analyzed the stress distribution characteristics of the surrounding rock of the coal thickness change area. They concluded that the working face was close to the parting area of the coal seam, and the abnormal stress in the parting area and the advance abutment pressure were superimposed, which was prone to rock burst. The stress distribution characteristics of the surrounding rock in the coal thickness change area of the longwall working face are analyzed. Reference [17-20] examines the impact of coal thickness fluctuations on rock stresses in the surroundings, revealing that coal thickness fluctuations can bring about atypical surrounding rock pressures; this achievement was accomplished by utilizing a highly accurate numerical calculation model. Wang Changbin et al. [
21] pointed out that high-stress concentrations in coal and rock strata will increase the possibility of rock burst. Zhao Tongbin et al. [
22] discussed the mechanical mechanism of mining rock burst in coal thickness change area.
The above scholars took the coal-rock combination layer as the object. Through indoor experiments and numerical simulation, they discussed the combined rock strata’s stress and energy distribution law in the coal thickness change area. However, the research on the relationship between the change of coal thickness and the stress and energy of the combined rock strata is relatively scarce. Therefore, this paper uses the weak impact tendency of 33 # layer coal seam in Jixi Pinggang Coal Mine as the research background. Taking the combined rock strata as the research object, the strata in the coal thickness change area are regarded as the change of the coal thickness, investigating how coal thickness and lithology impact the combination’s strength and energy accumulation characteristics. Based on our analysis, we have established a correlation between the stress and energy of the combined rock strata and the subsequent change in coal thickness, enabling us to identify the areas where stress and energy accumulate in the surrounding rock formations as the coal thickness changes. This valuable insight can serve as a guide to effectively prevent and manage rock bursts in the affected areas.
2. Uniaxial compression experiment of coal-rock combination
To thoroughly examine the combined structure’s stress and energy accumulation characteristics within the coal thickness change area, which change is regarded as the thickness change of the coal-rock combination. Therefore, in this experiment, the combination of different lithology and coal thickness was made, and the uniaxial compression experiment was carried out by using an RMT-150 testing machine to obtain the axial stress-axial strain curve of different combinations.
2.1. Samples making
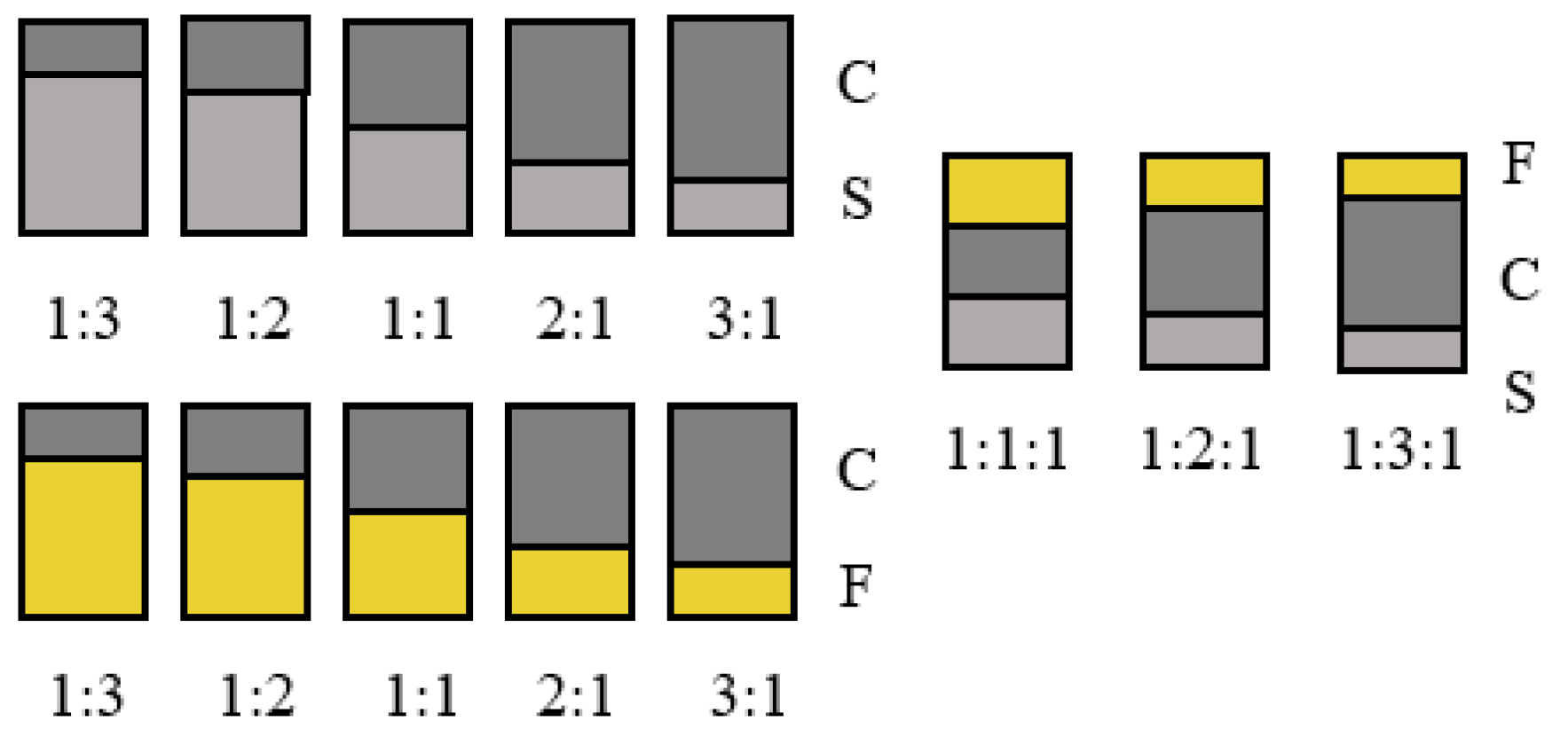
The samples taken in this experiment are from Pinggang Coal Mine in Jixi, Heilongjiang Province. According to the field conditions, the roof fine sandstone, floor shale, and coal seam of the working face are sampled. The samples are combined according to the experimental requirements, and the combination method is shown in
Figure 1. Among them are fine sandstone ( F ), shale ( S ), and coal ( C ). The size of coal and rock monomer and combination is a cylinder with a diameter of 50 mm and a height of 100 mm. To reduce the influence of the binder between the composite layers, the experiment was carried out by direct contact. The physical diagram of some samples is shown in
Figure 2.
2.2. Stress-strain curve of coal-rock combination
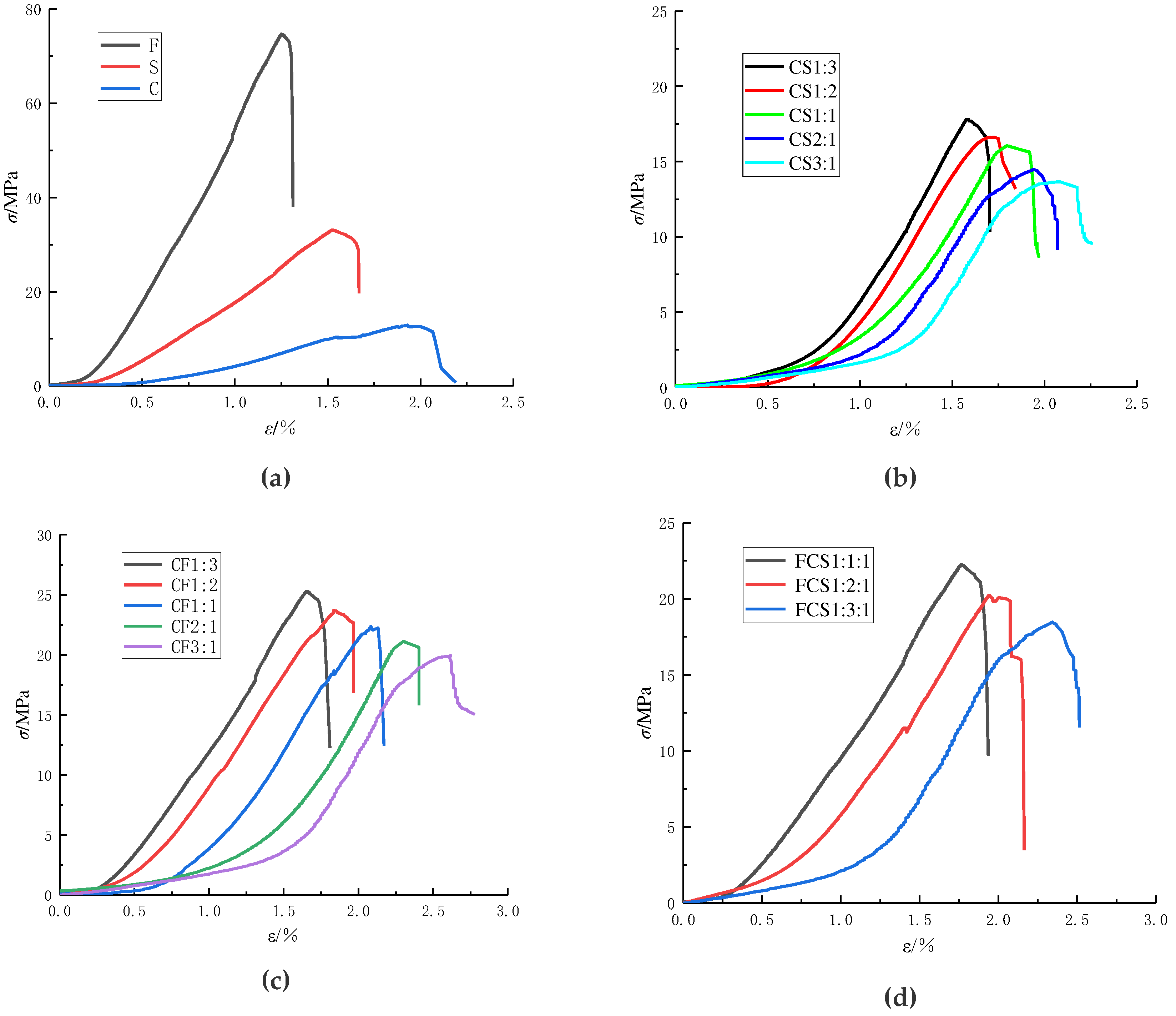
After the sample was made, the 0.05 mm / s loading rate was used to experiment, and the corresponding
σ-
ε curves of F, S, C monomers and CS, CF, and FCS combinations were obtained. The
σ-
ε curves for various structures formed from the combination of coal and rock are displayed in
Figure 3. Here,
σ is the axial stress, and
ε is the axial strain.
We extracted and compared the mechanical parameters of the monomer and combination in
Figure 3, resulting in
Table 1.
3. Strength and elastic modulus analysis of combination
The correlation between the strength and elastic modulus of the coal-rock monomer and combination can be ascertained through the analysis of the mechanical parameters outlined in
Table 1, which allows us to examine the effect of the coal thickness and lithology on the strength and modulus of the combination.
3.1. Relationship between strength and elastic modulus of coal-rock combination and coal-rock monomer
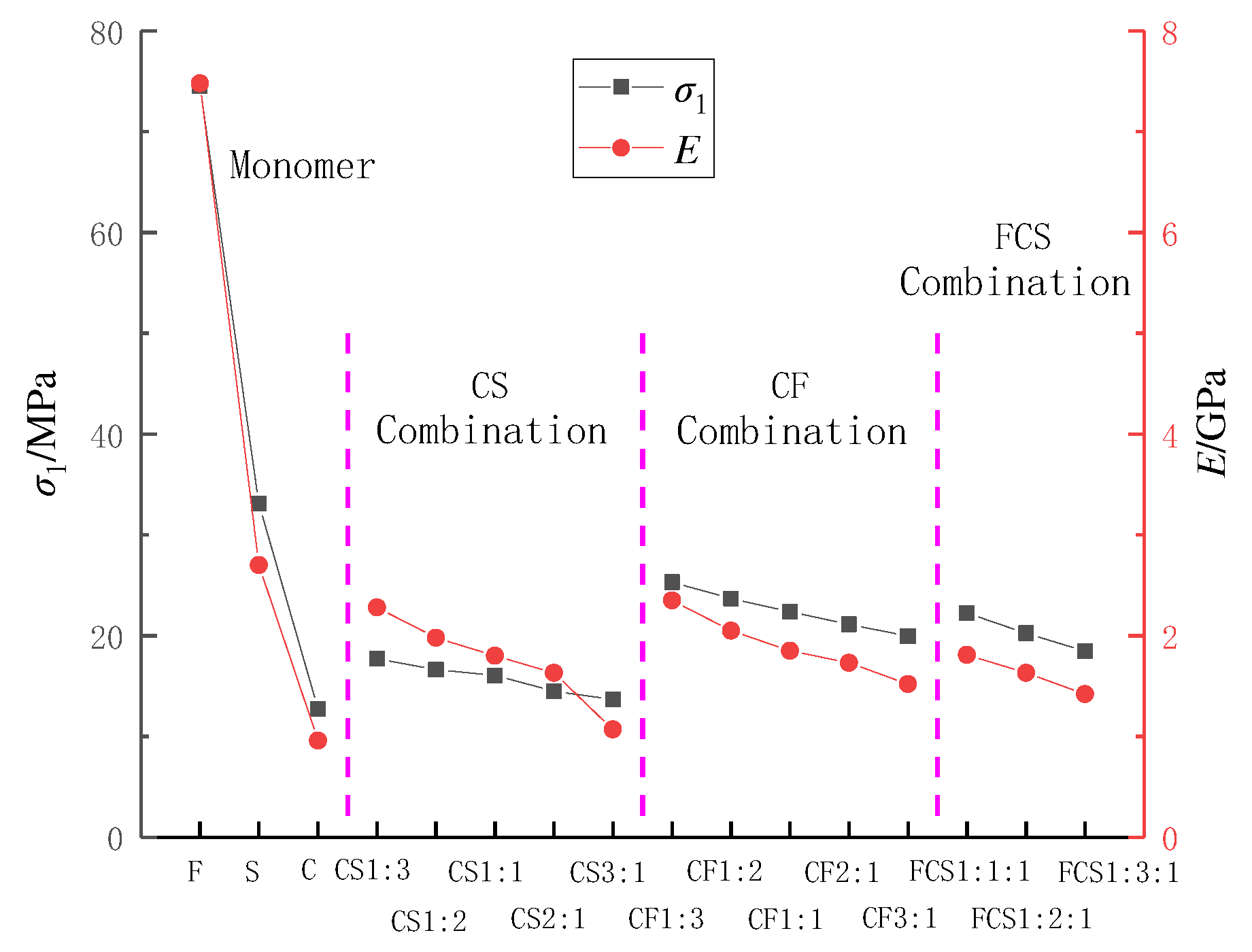
The peak strength and elastic modulus of various coal-rock combinations are displayed in
Figure 4, demonstrating their distribution characteristics. Here,
σ1 denotes the peak strength, and
E represents the elastic modulus.
Table 1 and
Figure 4 demonstrate that the monomer's peak strength and elastic modulus follow the order of F > S > C. The binary combination of peak strength and elastic modulus demonstrates that CS is greater than C and less than S, and CF is greater than C and less than F. The ternary combination FCS peak strength and elastic modulus as a whole is greater than C and less than F and S. This indicates that the coal-rock combination peak strength and elastic modulus are both between the coal and the rock strengths but are closer to the coal monoliths.
3.2. Influence of coal thickness on the strength of combinations
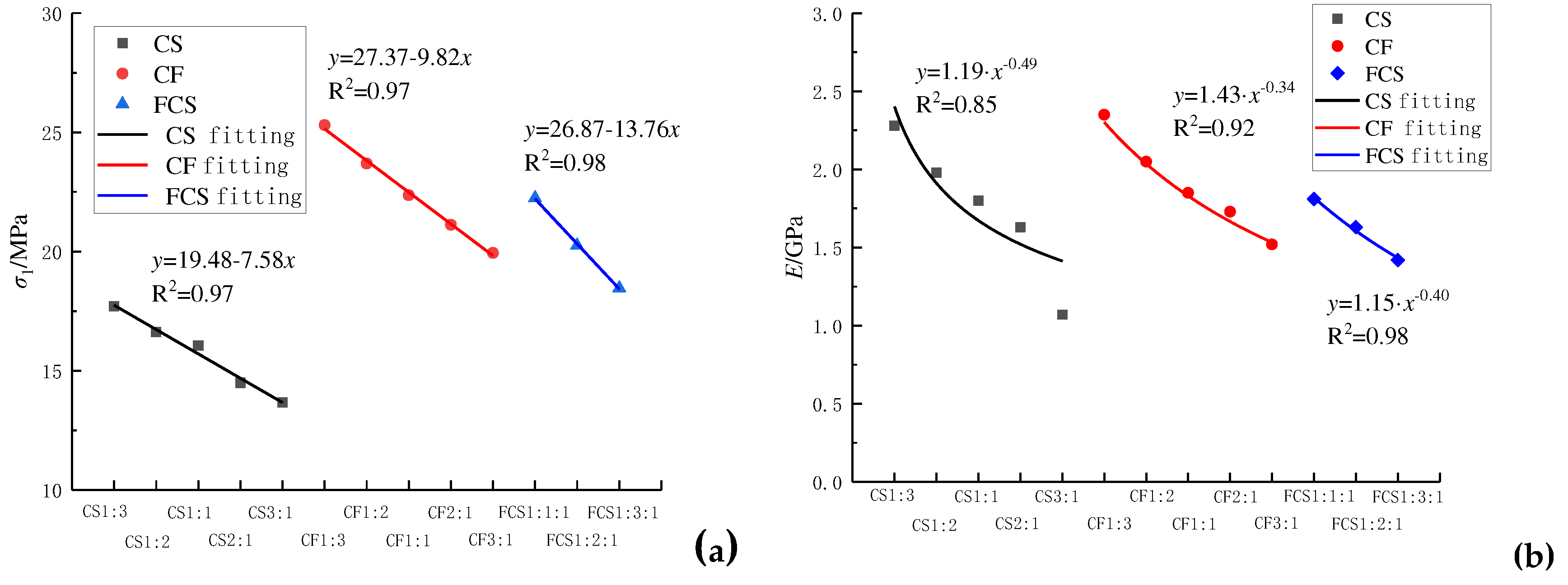
To analyze the impact of the coal thickness on the strength of the combination, we extracted the combination's peak strength and elastic modulus data in
Table 1. We established the correlation between the peak strength, elastic modulus, and height ratio of the coal-rock combination, as illustrated in
Figure 5.
The data presented in
Figure 5 shows that as the C thickness ratio increases, the peak strength and elastic modulus of CS, CF, and FCS decrease. The peak strength and C thickness of the combination CS, CF, and FCS are in accordance with the expressions
y=19.48-7.58
x,
y=27.37-9.82
x, and
y=26.87-13.76
x, respectively, and the elastic modulus of the combination CS, CF, and FCS are in accordance with the ratios of the thicknesses of the combinations to the thicknesses of the C. The CS, CF, and FCS to the thicknesses of the C are in accordance with the expressions
y=1.19
x-0.49,
y=1.43
x-0.34, and
y=1.15
x- 0.40 expressions; this is mainly because the larger the proportion of C in the combinations, the smaller the axial pressure required for the combinations to undergo axial deformation, and thus the smaller the peak strength and modulus of elasticity of the combinations. Therefore, it can be concluded that the peak strength of the combination is directly linked to the proportion of coal thickness. At the same time, the elastic modulus exhibits an inverse relationship with the ratio of coal thickness.
3.3. Influence of lithology on the strength of combinations
From
Figure 5, it can be seen that the ratio of CS, CF peak strength, and C thickness of the combination conforms to the expressions of
y = 19.48-7.58
x and
y = 27.37-9.82
x, respectively; the ratio of CS and CF elastic modulus to C thickness of the composite conforms to the expressions of
y = 1.19
x-0.49 and
y = 1.43
x-0.34, respectively. The variations in peak strength and elastic modulus reduction rate of combinations are primarily due to differing rock strength and elastic modulus of various lithologic combinations. When the coal thickness is constant, the peak strength and elastic modulus of CS and CF combinations are as follows: CF1 : 3 > CS1 : 3, CF1: 2 > CS1: 2, CF1: 1 > CS1: 1, CF2: 1 > CS2: 1, CF3: 1 > CS3: 1. This demonstrates that the more significant the strength and modulus of elasticity of the rock, the more significant the peak strength and modulus of elasticity of the combination of various combinations of equal coal thickness.
4. Energy accumulation law of coal-rock combination body
The patterns of variation in pre-peak energy, post-peak energy, and impact energy index were examined to determine the influence of lithology and coal thickness on the energy accumulation behavior of the combination.
4.1. Energy accumulation characteristics of combination body
The data were extracted from
Table 1 and subsequently utilized to derive the energy distribution law of various combinations. The derived law is illustrated in
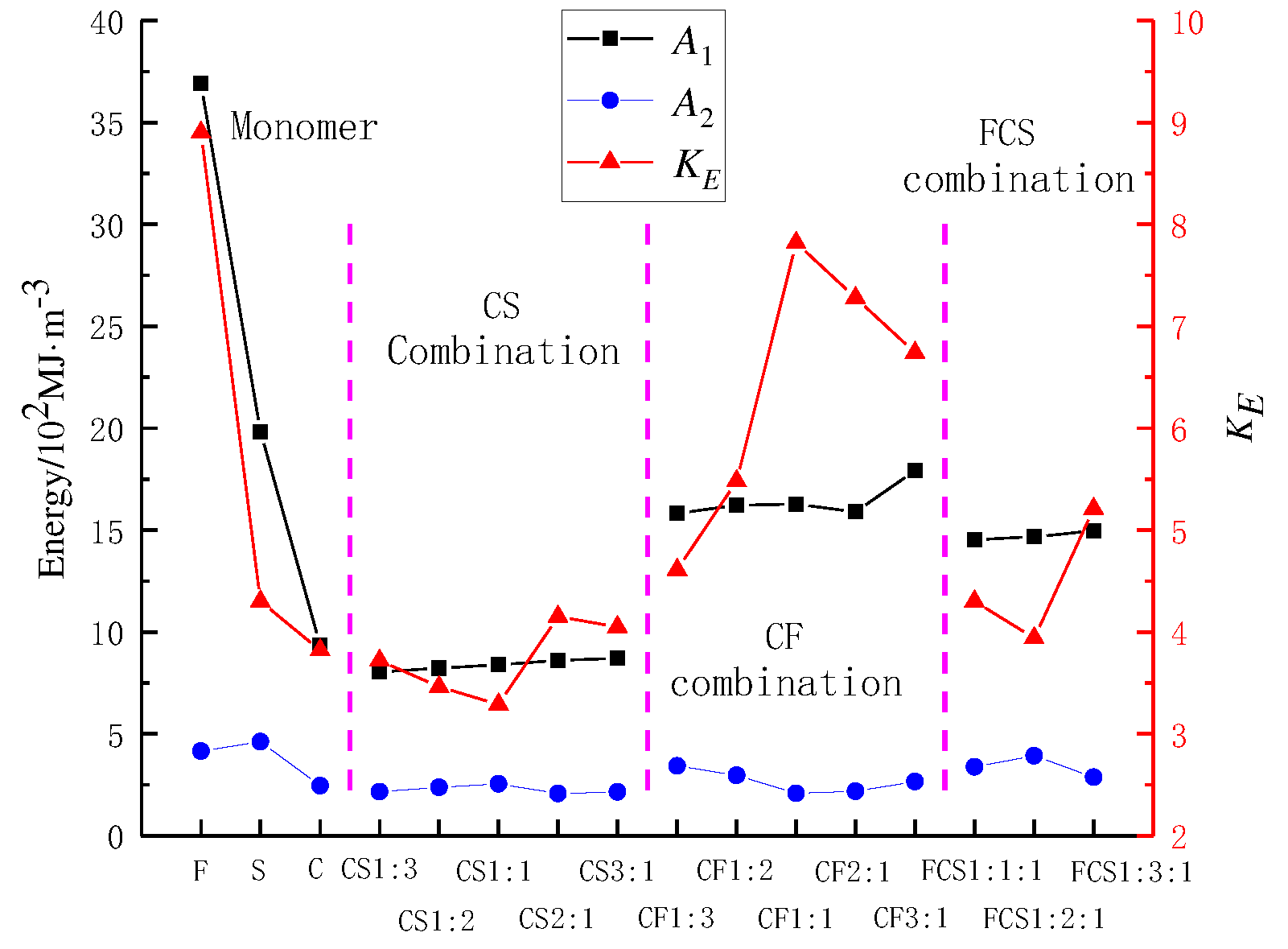
Figure 6. The abbreviations used in the graph are
A1 for pre-peak energy,
A2 for post-peak energy, and
KE for impact energy index.
From the data presented in
Figure 6, it is evident that the energy accumulation of the monomers is different from that of the combinations, and the pre-peak energy of the monomers is F>S>C, indicating that the pre-peak energy accumulation of the rock is more significant than that of the coal. The pre-peak energy exhibited by binary combinations suggests that CS exceeds C and is below S, while CF surpasses C and is lower than F. These findings indicate that the lithology significantly impacts the pre-peak energy of the combination. The peak energy of the ternary combination of FCS is greater than that of C but less than that of S and greater than that of CS. It is slightly less than that of CF, indicating that F has a certain effect on the buildup of pre-peak energy in the ternary combination of FCS. Furthermore, due to F's significant strength and modulus of elasticity compared to S and C, F can be considered a hard rock layer, suggesting that the hard rock layer plays a role in the buildup of pre-peak energy in the combination.
No apparent pattern is discernible in the post-peak energy of the combinations. The energy impact index of the combinations shows that CF is more significant than CS, and FCS is greater than CS, indicating that the greater the rock strength and elastic modulus, the more significant the energy impact index of the combination.
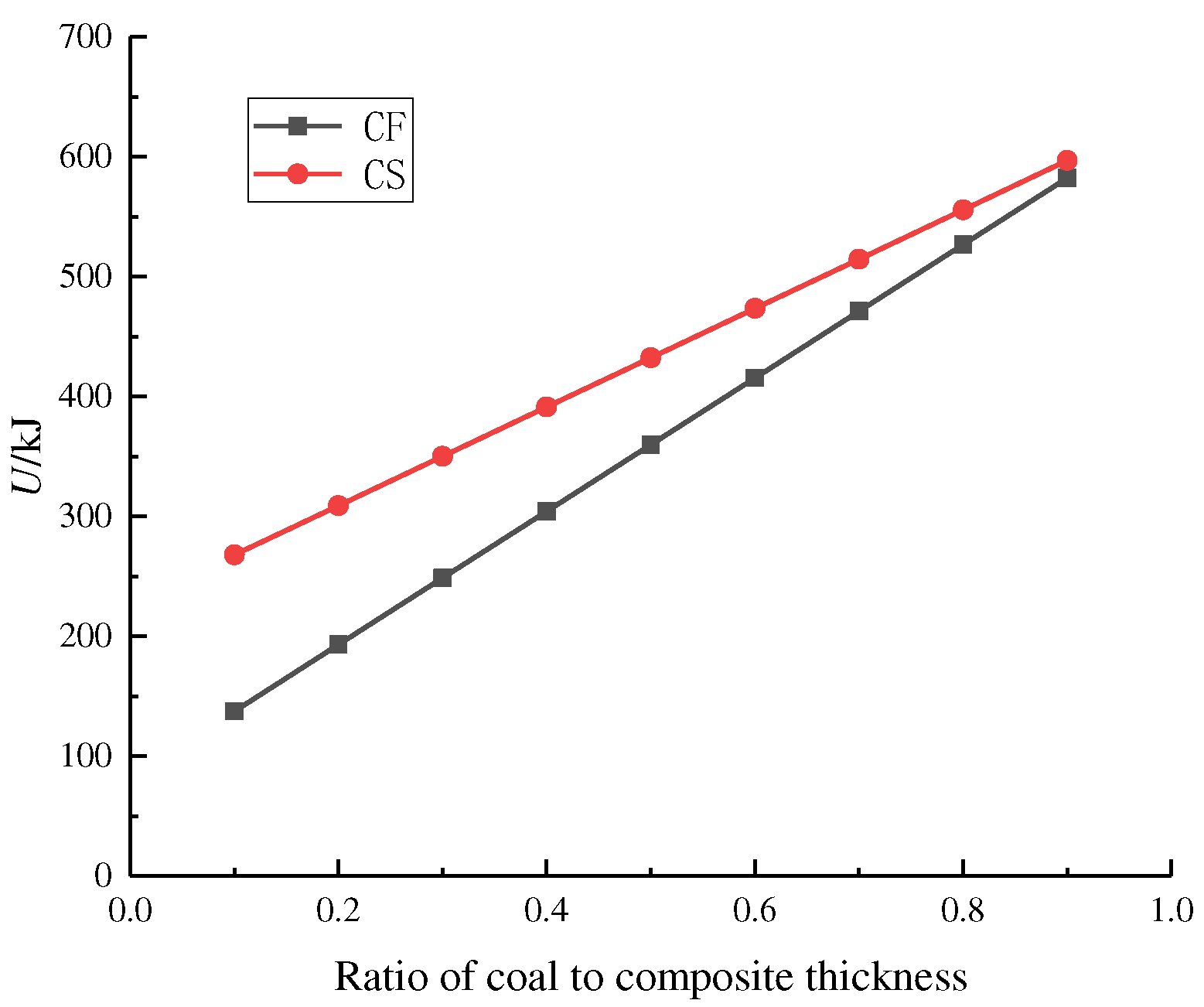
4.2. The influence of coal thickness on the energy accumulation characteristics of the combination
When the coal thickness varies, we extract the relevant data from
Table 1 and depict the resulting energy change profile for different combinations of coal thickness, as shown in
Figure 7.
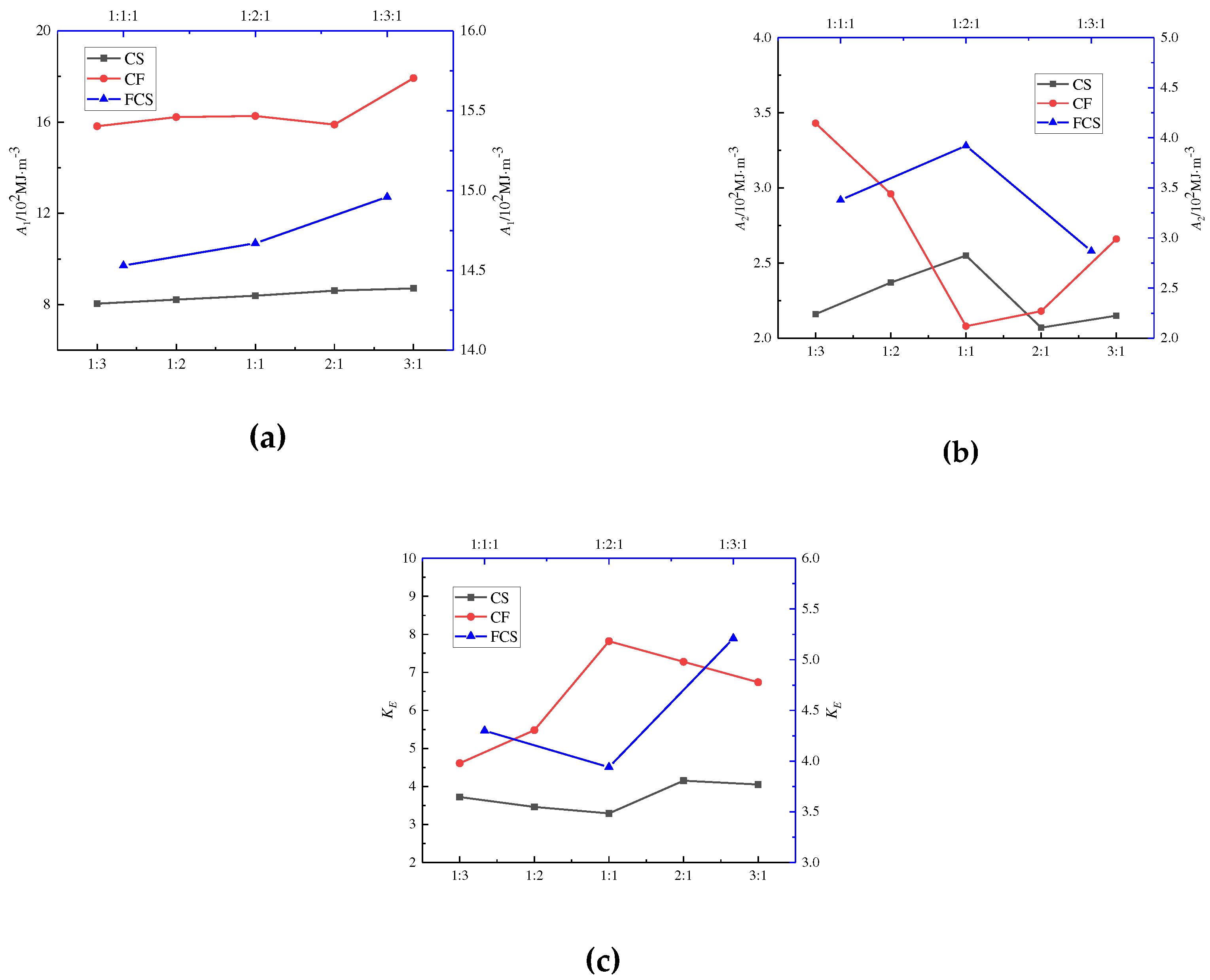
Figure 7(a) demonstrates that the CS and CF pre-peak energy of the binary combinations are arranged in descending order as CS1:3 < CS1:2 < CS1:1 < CS2:1 < CS3:1 and CF1:3 < CF1:2 < CF1:1 < CF2:1 < CF3:1, respectively. In addition, the FCS pre-peak energy of the ternary combination is arranged in descending order as FCS1:1:1 < FCS1:2:1 < FCS1:3.1. This observation suggests a gradual increase in the pre-peak energy of the combination as the percentage of C thickness is augmented.
As indicated in
Figure 7(b), as the C thickness percentage increases, the post-peak energy of the combination shows the trend of CS and FCS increasing and then decreasing; on the contrary, CF shows the direction of decreasing and then expanding, and the fluctuation range of post-peak energy of the combination CS, CF and FCS are 2.07~2.55 (10
2MJ·m
-3), 2.08~3.43 (10
2MJ·m
-3), and 2.87~3.43 (10
2MJ·m
-3), respectively. There is no apparent regularity in the post-peak energy of the combination with the more significant coal thickness percentage; the range of post-peak energy fluctuation of the CF combination is larger than that of the CS combination, which shows that the larger the rock strength and elastic modulus are, the larger the range of post-peak energy fluctuation of the combination.
According to
Figure 7(c), binary combination CS and CF exhibit a fluctuation range of impact energy index between 3.29 to 4.15 and 4.61 to 7.82, respectively. Additionally, ternary combination FCS shows a fluctuation range of impact energy index between 3.94 and 5. 21. The impact energy index of combination is affected by the lithology, with greater peak strength and modulus of elasticity in rocks resulting in a wider fluctuation range. The lithology affects the combination's impact energy index, with greater peak strength and modulus of elasticity in rocks, resulting in a wider fluctuation range. Generally, an increasing trend in the impact energy index of the combination is observed with a more significant proportion of coal thickness.
The results suggest that a higher percentage of coal thickness in the combination leads to an increase in the pre-peak energy accumulation. The post-peak energy displays no clear patterns, while the impact energy index indicates a rising trend.
4.3. The influence of lithology on the energy accumulation characteristics of the combination
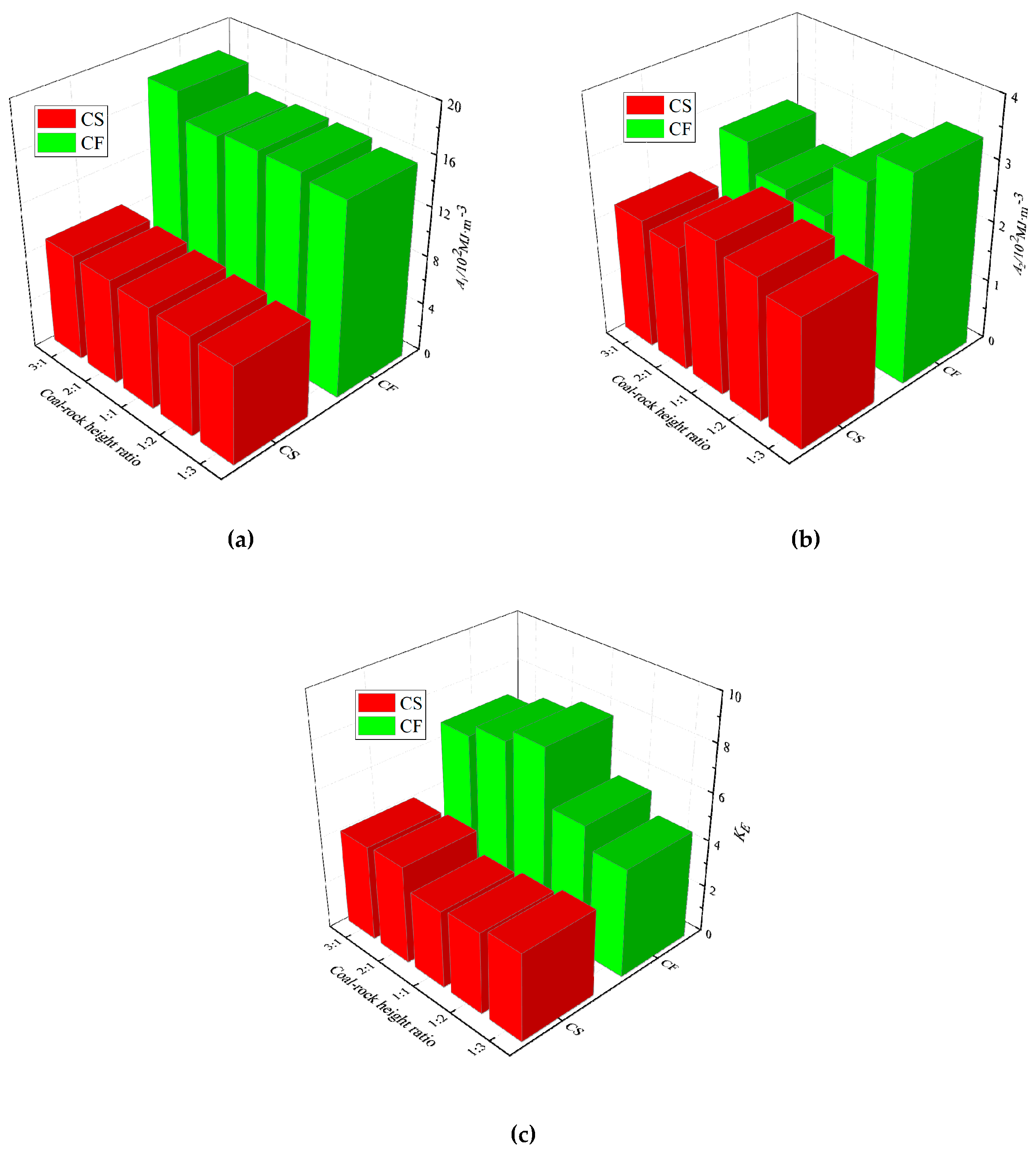
We extracted energy data from CS and CF combinations of equal coal thickness and plotted different combination energy change curves,
Figure 8.
When the coal thickness is constant,
Figure 8(a) shows that the pre-peak energy of CS and CF vary as follows: CF1:3>CS1:3, CF1:2>CS1:2, CF1:1>CS1:1, CF2:1>CS2:1, and CF3:1>CS3:1. In addition, the pre-peak energy of the CF combination is more significant than that of the CS combination. As the F peak strength and elastic modulus are more significant than the S, this indicates that the more significant the peak rock strength and elastic modulus, the greater the pre-peak energy build-up of the combination.
Figure 8 ( b ) shows that the post-peak energy of the combination CS fluctuates in the range of 2.07 ~ 2.55 ( 10
2 MJ · m
-3 ). The CF post-peak energy of the combination fluctuates in the range of 2.08 ~ 3.43 ( 10
2 MJ · m
-3 ). The post-peak energy fluctuation range of the CS combination is significantly smaller than that of the CF combination. It shows that the larger the rock monomer's peak strength and elastic modulus, the larger the post-peak energy fluctuation range of the combination.
As shown in
Figure 8(c), when the coal thickness is equal, the CS and CF impact energy index of the combinations are CF1:3>CS1:3, CF1:2>CS1:2, CF1:1>CF1:1, CF2:1>CS2:1 and CF3:1>CS3:1, and the fluctuation range of the CS and CF impact energy index of the assemblage is 3.29~4.15, respectively, 4.61~7.82. In addition, the rock's peak strength and elastic modulus directly affect the impact energy index, with larger values suggesting a higher impact potential.
5. Coal-rock combination structure model
5.1. Mechanical model of coal-rock combination structure
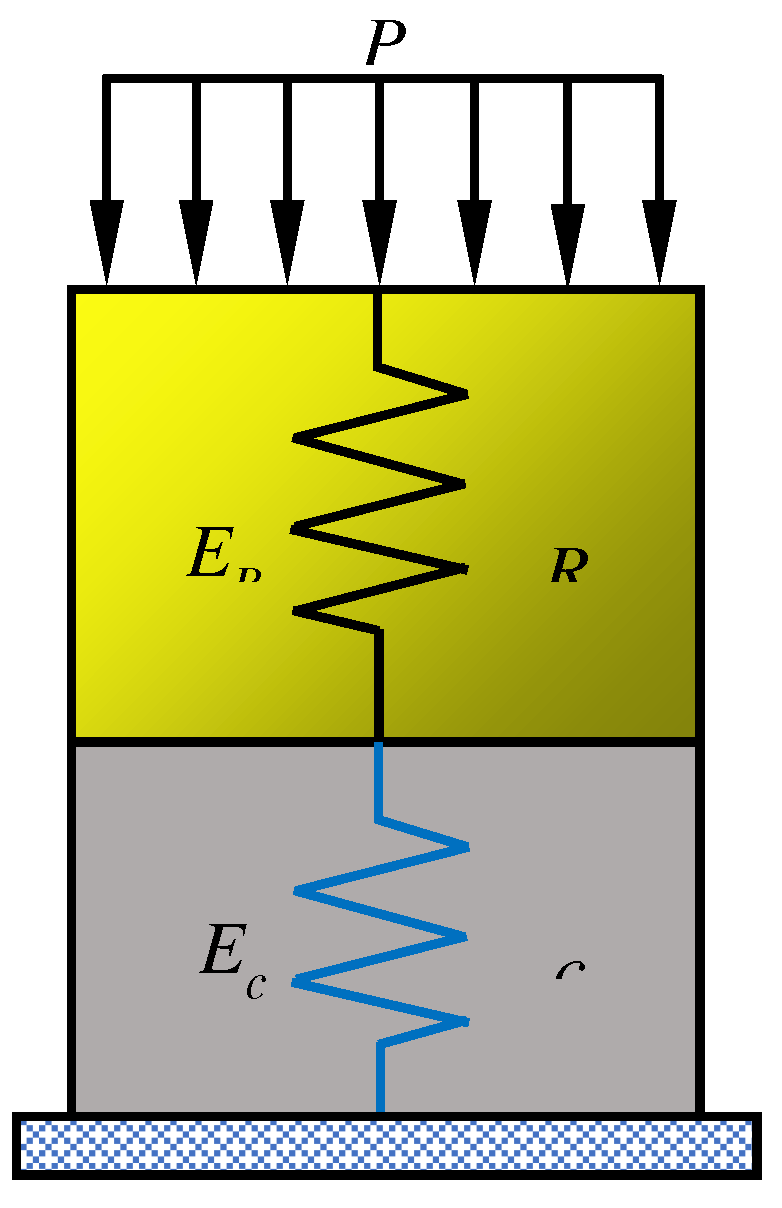
Under the assumption that the coal-rock structure is in an elastic state before the damage occurs, the coal-rock structure is represented as a spring structure consisting of two elastic elements connected in series[
16], as the model shown in
Figure 9.
Under mining stress P, coal and rock are subject to deformation to a certain extent, while their stress distribution is equivalent. Assuming that the overall elastic modulus of the combination is E, the height of coal and rock is
hc and
hR, respectively, the deformation is Δ
hc and Δ
hR, respectively, and the elastic modulus is
Ec and
ER, respectively.
Formula (4) can be obtained by substituting formula (1) and (2) into formula (3). It can be seen that when the total height of the coal-rock combination remains unchanged and the elastic modulus of coal and rock remains unchanged, the overall elastic modulus of the combinations decreases with the increase of coal thickness hc.
5.2. Relationship between combinations stress and coal thickness
Assuming that the same strain
ε occurs after the coal and coal rock structures are stressed, it can be seen from the elasticity [
24] :
The stress of coal-rock structure is compared with that of coal [16, 25], that is
As can be seen from formula (7), Ec<ER, Ec/ER<1, hc/H<1, Ec/ER+(1-Ec/ER)hc/H<1, that is, Pc<PcR. When the coal and rock strain is the same, the stress on the coal-rock structure is more significant than that on coal. Meanwhile, the stress of surrounding rock in the coal thickness thinning region is more significant than that in the coal thickness changing region, and the more significant the proportion of coal thickness, the smaller the stress in the coal thickness changing region.
5.3. Relationship between combinations of energy and coal thickness
There is a commonly held belief that the coal body is destroyed when mining stress reaches its maximum and the stress of the coal-rock combination reaches its peak. The minimum energy theory of rock mass failure posits that the energy consumed by coal and rock mass failure is the energy under a unidirectional stress state. The energy expended during coal and rock mass failure is typically associated with a unidirectional stress state[
26].
From the laboratory determination of mechanical parameters and the field test of Pinggang Coal Mine and the results, the elastic modulus of coal, fine sandstone, and shale are 0.96GPa, 7.48GPa, and 2.70GPa, respectively, and the stress concentration coefficients under the influence of mining are 2~2.5, corresponding to stresses of 35.0MPa and 43.75MPa. The graph in
Figure 10 demonstrates the correlation between energy accumulation and coal thickness.
Equation (8) and
Figure 10 show that for constant coal and rock elastic modulus, the energy accumulated before the destruction of the formation is directly related to the coal thickness hc. In the case of constant coal and rock thickness, the greater the modulus of elasticity of the rock, the more energy is accumulated and the greater the possibility of impact hazard. These observations corroborate the results of the experiment.
6. Discussion
In coal mining, rock bursts occur due to the stress state of the coal seam and rock stratum and their occurrence conditions. The thickness of the coal seam varies significantly in the local area, and the stress state of the surrounding rock in this area is correlated with the variation in coal thickness and the mechanical properties of the roof and floor.
The above 4.2 research shows that the surrounding rock stress is negatively correlated with the percentage of coal thickness, and the surrounding rock stress is more significant than that in the area of thinning coal thickness than in the area of thickening, which indicates that during the process of coal seam changing from thick to thin, the degree of concentration of surrounding rock stress in the area of coal thickness change gradually increases, which is easily induced the rock burst.
The law of energy accumulation in combined strata is influenced by coal thickness, rock strength, and elastic modulus. Higher coal thickness proportion increases energy accumulation before the combination peak. A thick coal seam area accumulates more energy compared to a thinner one and thus is more likely to experience rock burst. The positive correlation between the combined rock strata's energy accumulation and the rock's strength and elastic modulus indicates that the bigger the strength of the roof and floor, the more the combined rock strata's energy accumulation is, and the more prone to rock burst.
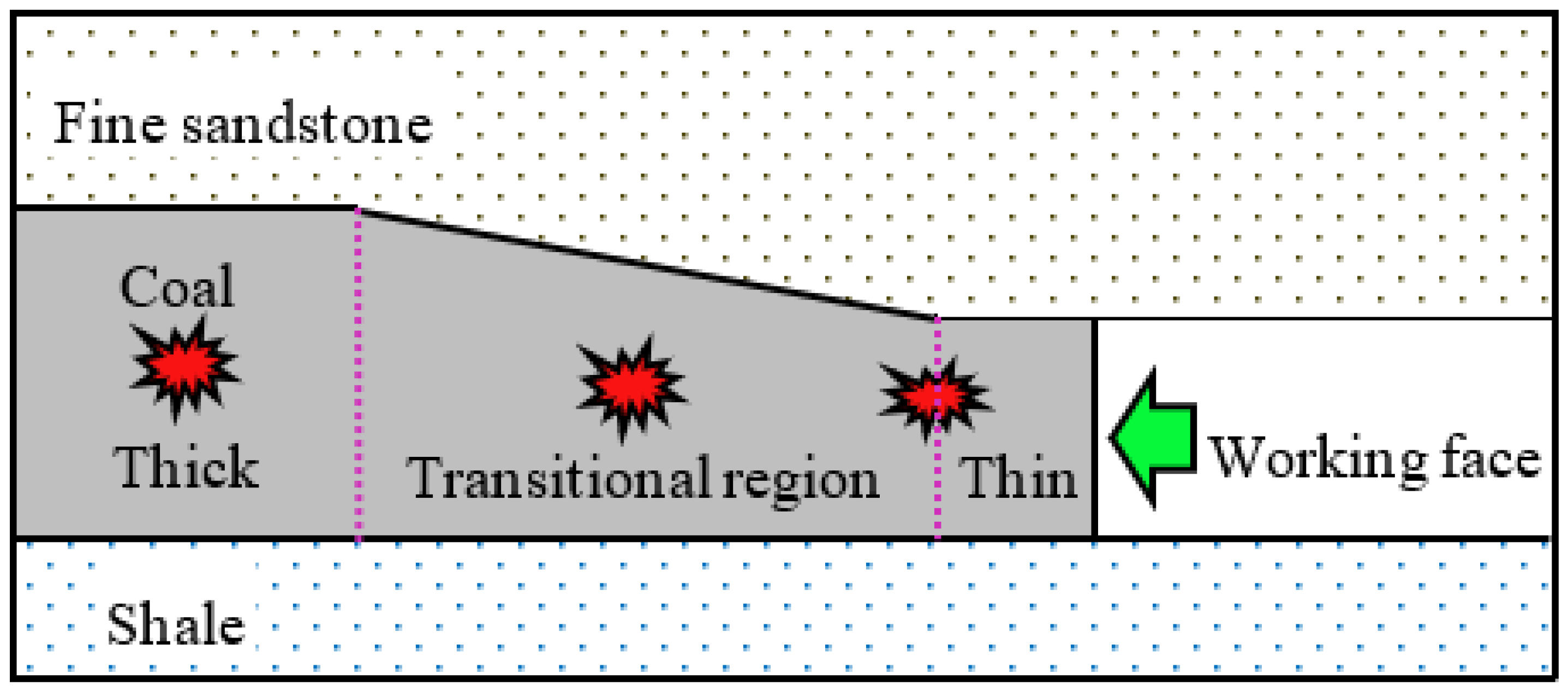
In summary, the stress distribution in the area where the thickness of coal changes shows abnormality. There is a significant stress concentration in the region where the coal thickness is thinning. The energy accumulation in thick coal seams is higher than in thin coal seams. Consequently, the surrounding rock where the thickness of the coal changes and in the thick coal seam area is more likely to accumulate energy, leading to dynamic disasters such as rock bursts, as illustrated in
Figure 11.
7. Conclusions
This paper takes the coal-rock combination as the object, analyses the impact of different coal thickness and lithology on the mechanical parameters and energy accumulation behavior of the combination, reveals the change of coal thickness and the combination of rock layer stress and energy between, and reaches the following conclusions:
- (1)
The coal-rock combinations' peak strength and elastic modulus are between coal and rock but closer to the coal monomer. As the coal thickness ratio increases, the peak strength and elastic modulus of combinations gradually decrease, except for strength, which has a clear linear relationship to the coal thickness ratio, and elastic modulus, which has a clear inverse relationship to the coal thickness ratio. The combination's strength and modulus of elasticity with the equal percentage of coal thickness are positively correlated with the rock's strength and elastic modulus.
- (2)
The pre-peak energy lies between coal and rock, while the post-peak energy and impact energy index does not show any apparent regularities with coal and rock. The combination's pre-peak energy and impact energy index shows an apparent positive correlation with coal thickness, while post-peak energy shows no obvious regular pattern.
- (3)
Coal thickness accounted for the same percentage, the pre-peak energy of the combination, impact energy index, and rock strength and modulus of elasticity showed a positive correlation, the post-peak energy and coal thickness changes have no obvious regularity and hard rock stratum help the combination pre-peak energy accumulation, the greater the likelihood of its occurrence of impact.
- (4)
The stress distribution of surrounding rock in coal thickness variation is abnormal. Surrounding rock stress shows a negative correlation with percent coal thickness, and surrounding rock energy shows a positive correlation with percent coal thickness, indicating that surrounding rock stress is more significant in the thinning coal thickness region than in the thickening coal thickness region and surrounding rock energy accumulation is less in the thinning coal thickness region than in the thickening coal thickness region. The abnormal stress distribution and high energy accumulation of surrounding rock in the area of coal thickness change are easy to induce dynamic disasters such as rock burst.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z.; validation, Z.L.; formal analysis and investigation, Z.L.; data curation, Z.L., Y.L. and W. Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.L., Y.L.; supervision, G.L., T.Q., L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Key Project of “Revealing the List and Taking Command” in Heilongjiang Province (2021ZXJ02A03, 2021ZXJ02A04) and the National Natural Science Foundation (51774122).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- YUAN Liang,WANG Enyuan,MA Yankun,et al. Research progress of coal and rock dynamic disasters and scientific and technological problems in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(5):1825-1845.
- DOU Linming,TIAN Xinyuan,CAO Anye,et al. Present situation and problems of coal mine rock burst prevention and control in China [J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):152-171.
- Cao Jinrong, Dou Linming, Konietzky Heinz, et al. Failure mechanism and control of the coal bursts triggered by mining-induced seismicity: a case study[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2023, 82(7): 168. [CrossRef]
- PAN Yishan,XIAO Yonghui,LUO Hao,et al. Study on safety of rockburst mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(5):1846-1860.
- JIANG Fuxing,ZHANG Xiang,ZHU Sitao. Discussion on key problems in prevention and control system.
- of coal mine rock burst[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 203-213.
- PAN Yishan,SONG Yimin,ZHU Chenli,et al. Localization method of coal rock deformation for rock burst prediction [J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(1):185-198.
- NAN Cunquan,DING Weibo,Lv Jinguo,et al. Numerical simulation for the changing regularity of the leading support pressure in the coal seam variety region under the mining impact [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18(6): 2200-2204.
- ZUO Jianping,XIE Heping,WU Aimin,et al. Investigation on failure mechanisms and mechanical behaviors of deep coal-rock single body and combined body [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(1): 84-92.
- Pan Bao, Yu Weijian, Shen Wenbing. Experimental Study on Energy Evolution and Failure Characteristics of Rock-Coal-Rock Combination with Different Height Ratios [J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2021, 39(1): 425-35. [CrossRef]
- Guo Dongming, Zhang Wei, Chen Qiyu, et al. Failure Mechanism and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Coal-Rock Samples[J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2022, 58(3): 390-397. [CrossRef]
- Cheng Zhanbo, Li, LiangHui, Zhang, YaNing. Laboratory investigation of the mechanical properties of coal-rock combined body[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(4): 1947-1958. [CrossRef]
- ZUO Jianping,SONG Hongqiang. Energy evolution law and differential energy instability model of coal-rock combined body [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(8) : 3037-3051.
- CHEN Guangbo, ZHANG Junwen, HE Yongliang, et al. Derivation of pre-peak energy distribution formula and energy accumulation tests of coal-rock combined body [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43 (S2) : 130-143+154.
- CHEN Guangbo, QIN Zhongcheng, ZHANG Guohua, et al. Law of energy distribution before failure of a loaded coal-rock combined body [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41 (6): 2021-2033.
- Bai Xianxi, Cao Anye, Cai Wu, et al. Rock burst mechanism induced by stress anomaly in roof thickness variation zone: a case study[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2022, 13(1): 1805-1830. [CrossRef]
- Wang Jianchao, Jiang Fuxing, Meng Xiangjun, et al. Mechanism of Rock Burst Occurrence in Specially Thick Coal Seam with Rock Parting[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(5): 1953-1965. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Guangan, Dou Linming, Li Zhenlei, et al. Mining-induced stress changes and rock burst control in a variable-thickness coal seam[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2016, 9(5): 365. [CrossRef]
- WANG Yong , YANG Bi , DENG Chuan, et al. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Influence of Coal Thickness Change on Rock Burst [J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(5): 198-201.
- SHEN Tengfei, GU Shitan, LEI Ruide, et al. Distribution Laws and Influence Factors of Elastic Strain Energy in Thickness Variation of Coal Seam [J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2015, 46(6): 187-189.
- REN Zhongping, WANG Chunqiu, JIANG Bangyou, et al. Numerical Simulation on Influence of Coal Seam Thickness Variation on Rock Burst Danger [J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45(12): 51-53+57.
- Wang Changbin, Cao Anye, Zhu Guangan, et al. Mechanism of rock burst induced by fault slip in an island coal panel and hazard assessment using seismic tomography: a case study from Xuzhuang colliery, Xuzhou, China[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2017, 21(3): 469-481. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Tongbin, Guo Weiyao, Tan Yunliang, et al. Mechanics mechanism of rock burst caused by mining in the variable region of coal thickness [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(7) : 1659-1666.
- Xu Zhilun. A concise course in elasticity [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Advanced Education Press, 2002. (in Chinese).
- CHEN Guangbo, WANG Eryu, WANG Wencai, et al. Experimental study on the influence of lithology and rock-coal height ratio on mechanical properties and impact effect of combined body [J]. Energy Sources Part A-recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2019: 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Yangsheng, Feng Zengchao, Wan Zhijun. Least energy priciple of dynamical failure of rock mass [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(11): 1781-1783.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).