Introduction
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) measures specific drug levels to guide treatment changes and helps clinicians in making decisions to adjust optimal drug frequency or dose administration, subsequently improving disease outcomes. The real long-term influences of in utero drug exposure on childhood development have yet to be fully determined and depend on the duration of in utero drug exposure and maternal drug levels. TDM during pregnancy may theoretically help limit fetal exposure while maintaining therapeutic drug levels in maternal blood. However, the consequences of drug exposure in utero on immune development and maturation in childhood are critical issues and are uncertain, present reassuring data have reported the absence of causal relationships between adverse events (including severe infection) in neonates and maternal drug exposure with biologics. Most antibody therapies used in patients with IBD are IgG molecules which are actively transported across the placenta, especially during the third trimester of the pregnancy. This review proposes here a clinical review to summarize the available findings of drug levels in infants, cord and maternal during pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding in IBD patients treated with biologics. Additionally, the usefulness of TDM in these patients during pregnancy will also be examined. In contrast with anti-TNFα agents, it is unsurprising that little data about pharmacokinetics (PK) of recently approved monoclonal antibodies (vedolizumad, ustekinumab) is available in relation to pregnancy and breastfeeding. A better understanding of drug pharmacokinetics during pregnancy and breastfeeding is of paramount interest for gastroenterologists to improve drug adjustment and to minimize risk of fetal exposure to the biologics and allow for optimal disease control in the mother.
Search strategy
This systematic review of the literature was performed in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines of 2023. A systematic search was conducted by using PubMed on 20th August 2023 to retrieve studies on the PK of IBD related drugs throughout different trimesters of pregnancy or in women at time of delivery and the offspring. Research was also done on studies analyzing PK in breastmilk. English articles or oral presentations during DDW, ECCO or UEGW, without limit to publication or presentation date, were also included. The search strategy consisted of five main keywords: “pharmacokinetics”, “IBD related drugs”, “pregnant women”, “offspring” and “lactation”. Studies including non-IBD participants were excluded. Studies not meeting the Research aim and inclusion criteria were excluded. Two investigators (MB and SN) independently conducted the search strategy and study selection. The results obtained were discussed, and in the case of disagreement, a third independent author (XR) was consulted.
Mechanisms of drug transport for antibody therapies across the human placenta
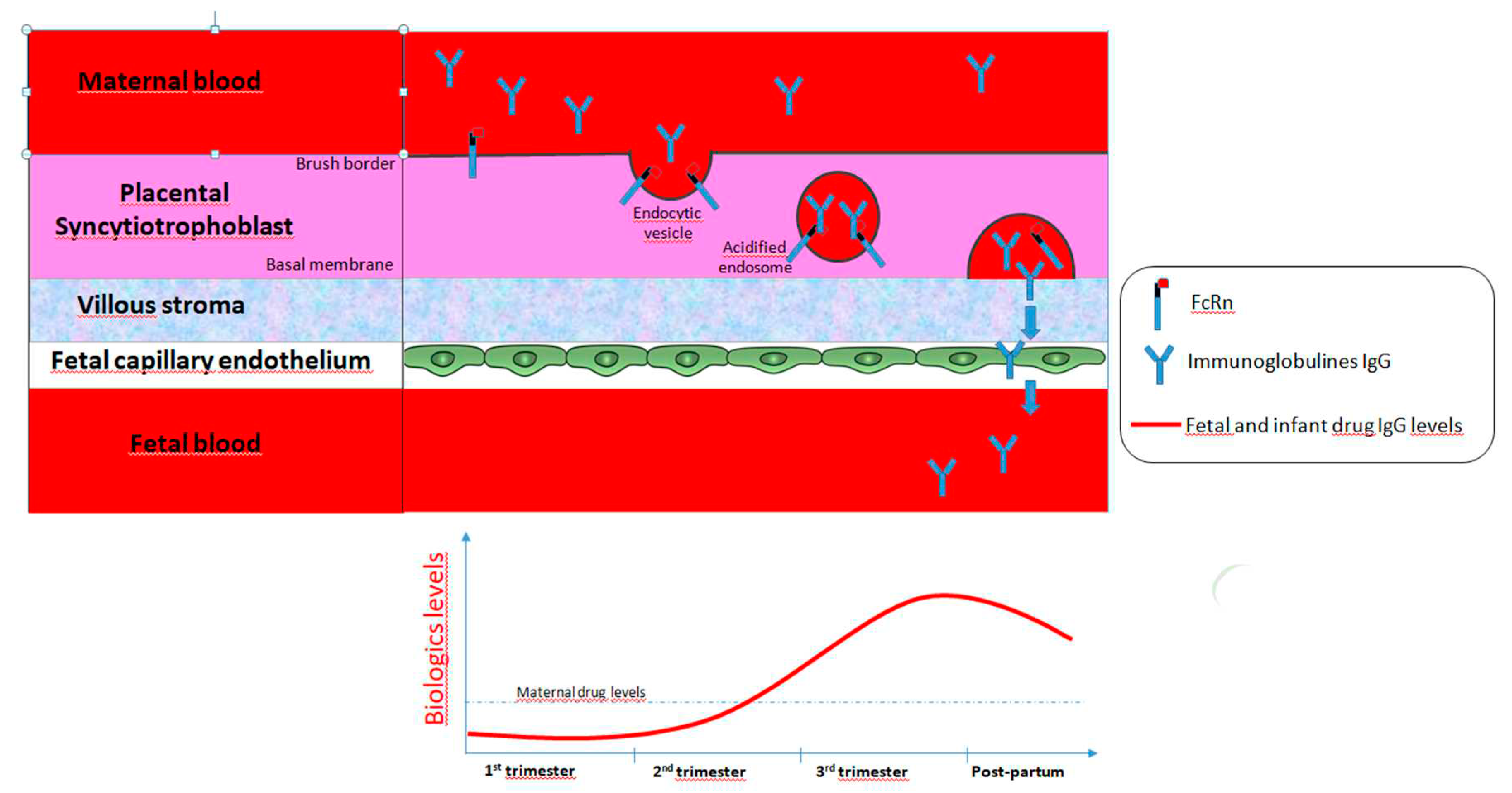
Most drugs cross the placenta by simple diffusion of the molecules driven by concentration and electrical gradients. However, beyond simple diffusion, various other mechanisms of drug exchanges between maternal and fetal blood are involved, such as transcellular transfer (via channels, facilitated diffusion or carrier-mediated active transport, endocytosis and exocytosis) (1). In contrast with small molecules, monoclonal antibody therapies, most of them being IgG1, are high molecular weight drugs and therefore cannot cross the placenta by simple diffusion (insignificant concentrations are detected in early pregnancy). In contrast, maternal transfer of IgG through the placenta is mediated by active transporters using a specific receptor-mediated binding Fcγ portion of IgG at the syncytiotrophoblast layers of the placenta. These layers represent the main site of exchange for nutrients, gases and drugs between the maternal blood and the fetus. IgG is then transported across the syncytiotrophoblast layers in coated vesicles that protect them from lysosome-mediated degradation. IgG transport from mother to neonate is mediated by the heterodimer fetal Fc receptor neonatal (FcRn) molecule, including an α-chain homologous to major histocompatibility complex class I molecules and β-2-microglobulin that both play a key role in placental IgG transport, catabolism and recycling (
Figure 1). Among the three subtypes of Fcγ receptors described in human placenta, the subtype III appears to contribute mostly to IgG transfer and its expression on the surface of the syncytiotrophoblast has been detected by 13 weeks of gestation. Therefore, the active transport of biologics across the placenta begins by week 13-17 and increases gradually as the pregnancy progresses, with the highest amounts of IgG being transferred from the maternal blood stream to the fetus during the third trimester (2) (3) (4). At 17-22 weeks gestation, the fetal levels of IgG represented only 5-10% of those found in maternal circulation. Acceleration of the transfer of all IgG subclasses, especially IgG1 has been reported during the third trimester. Moreover, the levels of exogenously administered IgG1 therapy in umbilical cords correlate with the timing of the last dose prior delivery (5). Around 26 weeks gestation, serum fetal IgG levels reached maternal concentrations and even exceeded it by threefold (sometimes higher) at term as assessed in cord blood levels in infants (4) (6).
Interestingly, the distribution of antibody therapies among the maternal, cord and fetual blood depends on multiple complex metabolic factors as well as on the maturation of the placenta (7). The magnitude of maternal IgG transport depends on the isotype of IgG, and IgG1 is preferentially transported to the fetus than in comparison with IgG4, IgG3 and IgG2, which is the least detected of all. For example, at 17-22 weeks gestation, the fetal levels of IgG1 were reported three fold higher than those of IgG2. Moreover, cord blood drug levels vary depending on the type of anti-TNF agents, with a fetal : maternal ratio of 2.6 and 1.5, respectively for IFX and for ADA. This active transfer of IgG during the second half of pregnancy is clinically relevant since it results in a strong exposure of antibody therapies in fetus in utero and in early life period, which represents a sensitive period for development, maturation and programming of the immune system. In addition, these high drug levels in neonates during pregnancy could be, at least theoretically, associated with higher susceptibility of infection.
Transfer of maternal biologics and drugs from breast tissue into breast milk
Serum drug concentrations directly affect drug transfer from breast tissue into breast milk and it is assumed that most drugs can be present in breast milk due to diffusion for small chemical molecules or active transport mediated by FcRn receptors for monoclonal antibodies (a mechanism similar to the placenta). However, beyond drug levels, other factors including breast milk pH, molecule size, protein binding, and breast inflammation might interfere with the transfer of drugs into breast milk. Historically, it was recommended that women receiving biologics avoid breastfeeding. However, secretory IgA represents the predominant immunoglobulin detected in breast milk and irrespective of the biologic, drug concentrations in breast milk are very low when compared with those found in maternal serum or in the umbilical cord, and peak concentrations were seen between 24-72 hours after drug administration. Although the mechanisms of intestinal absorption of immunoglobulin possibly involving FcRn remain unclear, a small fraction of ingested monoclonal antibodies by infants from breast feeding may be absorbed in the gut, as it has been well demonstrated in an infant who was not exposed to infliximab during pregnancy but was exposed to the drug during breastfeeding (8). In addition, breastfeeding while receiving biologics did not negatively affect the rate of infection or developmental milestones and hence, breastfeeding in women exposed to biologics is considered to be low risk.
Pharmacokinetics of anti-TNF agents in IBD during pregnancy
Study Selection
According to our study selection, 12 studies using biologics were included, nine concerning IFX, four ADA and one golimumab (GLM). The cumulative number of enrolled participants was 173. The number of Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and unspecified IBD were 112 (70%), 46 (29%) and 2 (1%), respectively.
Maternal infliximab trough concentrations during pregnancy
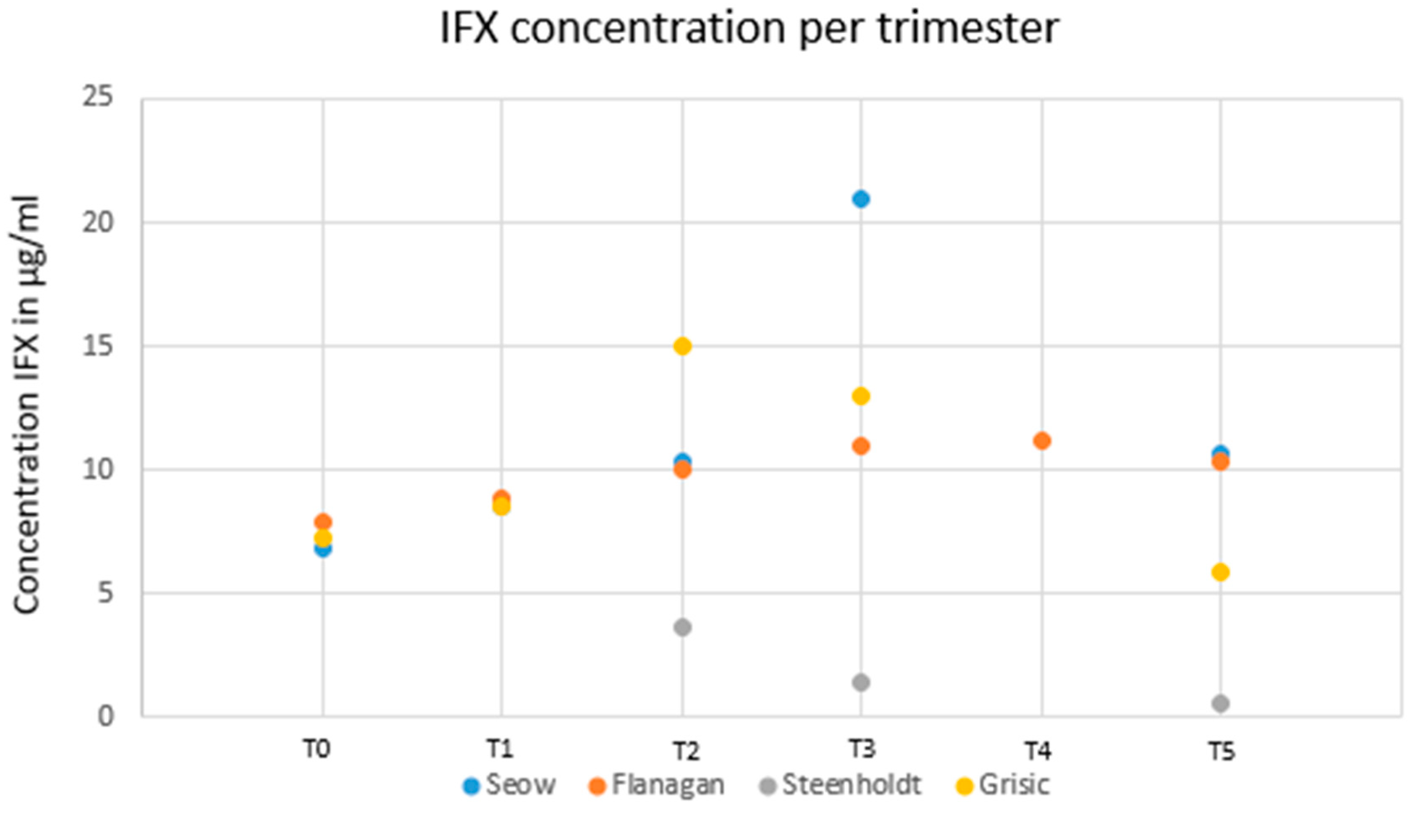
Four studies investigated serum drug trough levels in pregnant women with IBD treated with IFX. By pooling all patients (except those in the study from Bortlik M et al. (9)), infliximab was detected in all the womens’ serum, but not in the breast milk of nursing mothers or in the serum of breast-fed newborns in the first study analyzing this (10). Seow et al. (11) included twenty-five pregnant women treated with IFX or ADA maintenance therapies from the University of Calgary IBD pregnancy clinic. They were recruited prospectively with serum bio-banking performed each trimester. Fifteen women (8 CD , 7 UC) were treated with infliximab. In this cohort, the median serum trough infliximab concentrations were 8.50 μg/mL (IQR: 7.23-10.07 μg/mL), 10.31 μg/mL (IQR: 7.66-15.63 μg/mL) and 21.02 μg/mL (IQR: 16.01-26.70 μg/mL) during the first, second and third trimesters, respectively. After adjusting for albumin, body mass index and CRP, infliximab trough levels increased by 4.2 μg/mL per trimester during pregnancy (P = 0.02) (12). Maternal drug levels were measured pre-conception, in each trimester, at delivery and postpartum in 23 pregnant women with IBD under IFX therapy in a prospective observational study (Flanagan et al). Modelling showed an increase in infliximab levels of 0.16 µg/L/week (95% CI 0.08-0.24) (P < 0.001) similarly to the previous findings from Seow (11). Van Eliesen et al (13) assessed placental drug transfer and exposure to IFX (n = 3) and etanercept (n = 3) in women with autoimmune diseases (in which 2 CD). Healthy term placentas were infused with 100 µg/mL IFX (n = 4) or etanercept (n = 5) for 6 hours. In 3 pregnant women, IFX was detected in the cord blood and entered the placenta (cord-to-maternal ratio of 1.6 ± 0.4, placenta-to-maternal ratio of 0.3 ± 0.1). In ex-vivo placenta drug infusion, the magnitude of placental drug transfer did not differ between the drugs. Final concentrations in the fetal blood compartment for IFX and etanercept were 0.3 ± 0.3 µg/mL and 0.2 ± 0.2 µg/mL, respectively. However, in placental tissue, IFX levels exceeded those of etanercept (19 ± 6 µg/g vs. 1 ± 3 µg/g, P < 0.001). Therefore, tissue drug exposure was higher under IFX than under etanercept both in vivo as well as in ex-vivo drug infused placentas. In line with previous studies, a retrospective study enrolling 23 pregnant IBD patients with IFX showed that drug clearance decreased significantly during the second and third trimesters, leading to increasing maternal IFX concentrations irrespective of the drug regimen (14).
Altogether, maternal IFX levels may be maintained as constant in a de-intensified regimen by therapeutic drug monitoring guidance in inflammatory bowel disease.
Infliximab and maternal trough concentration before, during and after pregnancy
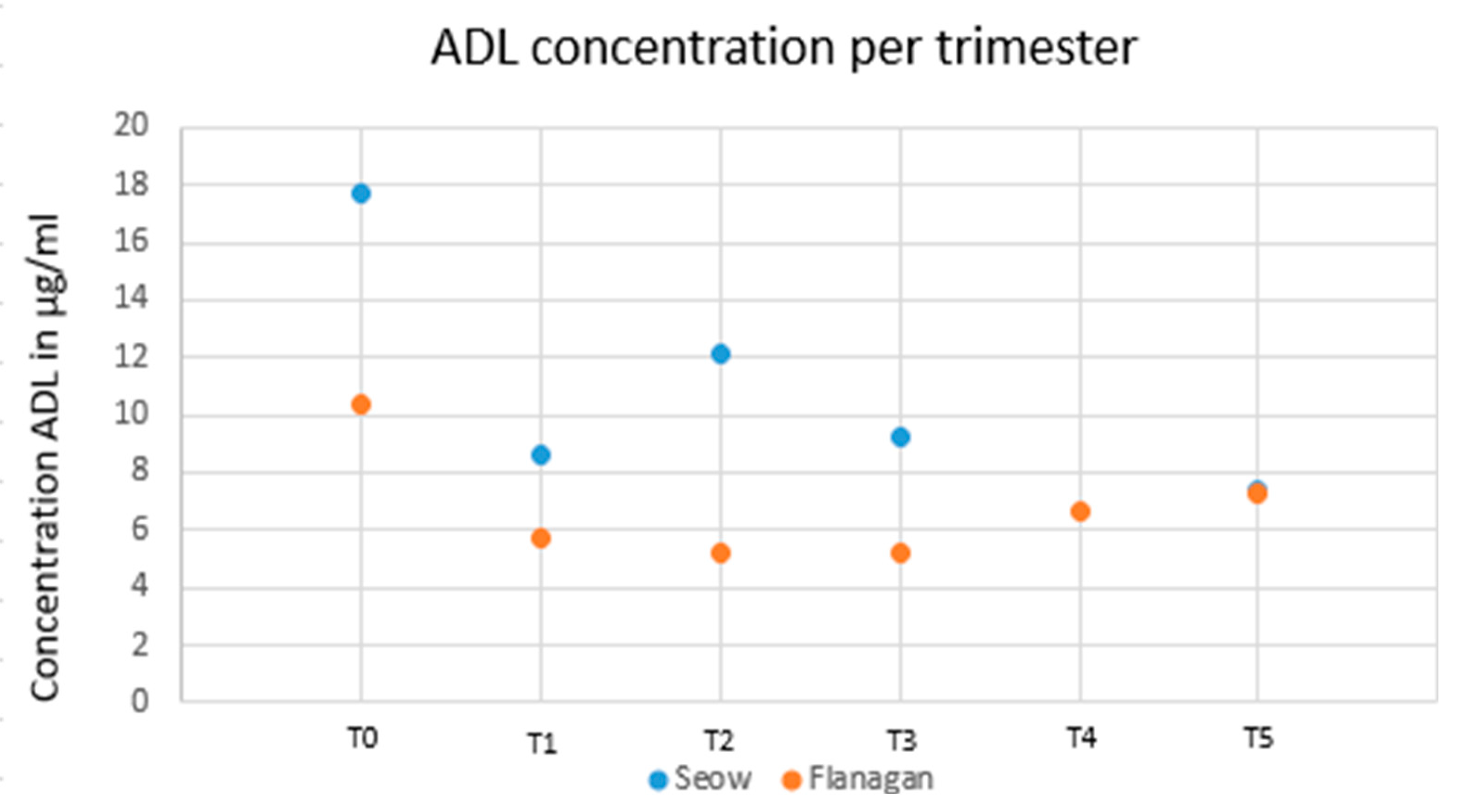
The IFX levels after delivery compared to pre-pregnancy levels were higher in studies conducted by Seow et al. (11) and Flanagan et al. (12) (10.17 µg/mL versus 6.9 µg/mL and 10.3 versus 7.9 µg/mL, respectively) and were lower in the study of Grišic et al. (14) (5.9 µg/mL versus 7.3 µg/mL). Overall, the IFX levels after pregnancy were all lower than those during pregnancy.
Figure 2 reports the dynamics of drug levels before, during and after pregnancy.
Placenta drug transfer in pregnant women treated with infliximab
Two studies have reported some small case reports investigating drug levels in the blood of breast-fed infants from mothers exposed to IFX. In the first case, the breast-fed infant’s serum IFX level was 39.5 microg/mL at 6 weeks after birth (15). In this case, a last infusion of IFX (10mg/kg) was administered to the mother two weeks before delivery. In another study, a 26 year-old woman with UC was treated with regular IFX infusions until gestation week 31 and gave birth to a healthy child at gestation week 37 (16). Maternal IFX trough level was relatively high during pregnancy. In the infant’s blood, drug levels were detectable at week 16 after birth, but not at reassessment at week 28. In 11 IBD pregnant patients treated with IFX, drug concentrations in the blood cord and in the blood of the infant at birth were compared with those of the mother (15). The median level of IFX in the cord was 160 % higher than that of the mother and IFX could be detected in the infants for as long as 6 months. In a study including 32 CD pregnant patients treated with IFX, the authors found a positive correlation between IFX cord levels and gestational week of last exposure as well as maternal serum levels (9). In fact, anti-TNF drug levels in the cord blood at birth depend on the type of anti-TNF type. In a recent prospective single center study, the authors included 131 pregnancies that resulted in a live birth [73 IFX, 58 ADA]. At birth, 94 cord blood samples were obtained [52 IFX, 42 ADA], showing significantly higher levels of IFX than ADA [p < 0.0001]. Anti-TNF type and time to treatment withdrawn were used in the linear regression model. During the third trimester, IFX transportation across the placenta increased exponentially, however, ADA transportation was limited and increased in a linear fashion (18).
IFX drug levels during breastfeeding
A large prospective multicenter study analyzed the drug concentrations in breast milk samples (n = 72) from patients receiving biologic therapy from October 2013 to November 2015. IFX was detected in breast milk samples in 19 out of 29 exposed women (with a maximum drug concentration of 0.74 μg/mL) (19).
Duration of IFX detection in newborn
In a large, prospective multicentric study involving 44 pregnant women treated with IFX, the authors investigated the drug concentrations in umbilical cord blood of newborns, the rates of drug clearance after birth, and how these parameters correlated with drug concentrations in mothers at birth and the subsequent risk of infection in infants during the first year of life. The time from the last exposure to IFX during pregnancy correlated inversely with the concentration of the drug in the umbilical cord (IFX: r = -0.77, P < .0001) and in mothers at time of birth (IFX, r = -0.80; P < .0001 for both). The median ratio of infant:mother drug concentration at birth was 1.97 (95% CI, 1.50-2.43). The mean drug clearance time in infants was 7.3 months (95% CI, 6.2-8.) In this study, bacterial infections developed in 4 infants (5%) and non-serious viral infections occurred in 16 infants (20%). The relative risk of infection was 2.7-fold higher in infants whose mothers received the combination of an anti-TNF agent and thiopurine, compared with those under anti-TNF monotherapy (95% CI, 1.09-6.78; P = .02). Drugs were not detected in infant blood after the age of 12 months (5). In a prospective study including 107 infants exposed to anti-TNF during pregnancy (in which 66 were under IFX), the authors aimed to develop a pharmacokinetic model to predict time to drug clearance after birth in infants exposed during pregnancy. All infants with detectable drug levels in blood cord at birth and with at least one additional blood sample within the first year were included. Anti-TNFα was detectable in 25 infants (23%) at 6 months. At 12 months, IFX was detected in 3 infants (4%) whereas ADA was undetectable. A Bayesian forecasting method was developed using a one-compartment pharmacokinetic model. The model proposes that the predicted clearing time was in accordance with the measured observations (20). In a recent study (21), the authors aimed to determine the optimal timing for the last dosing of anti-TNF agents (IFX, ADA and golimumab) in pregnant women with IBD, as well as to investigate the recommended vaccine schedules for infants exposed to these drugs. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model of anti-TNF agents was built for adults and extrapolated to pregnant patients, fetuses, and infants. The main results are reported in
Table 1 and
Table 2 and are of interest for clinical practice. The timing of the last dosing of IFX and ADA was determined by the lowest limit of the therapeutic range. Optimal IFX trough concentrations were considered between 3-7 μg/ml (22). However, IFX trough concentrations over 15 μg/ml augment the risk of infection (23). For pregnant women exposed to ADA, several studies have reported that the risks of infection were not related to ADA trough concentration. Hence, to achieve therapy level, it is recommended to take blood samples throughout pregnancy, as for Mahadevan et al. (24).
TNF-α Inhibitors—Adalimumab and maternal trough concentration during pregnancy
Two studies analyzed adalimumab serum levels during pregnancy in IBD patients. Seow et al. analyzed 11 pregnant patients with IBD treated with ADA. After adjusting for albumin, BMI and CRP, drug levels remained stable (P > 0.05) during pregnancy (11). Flanagan et al. (12) included 15 IBD patients (23 on IFX, 15 on ADA and 12 on vedolizumab) with at least two intrapartum observations. Conversely to IFX, modelling showed no change of ADA levels. These results are reported in
Figure 2.
Figure 3.
Adalimumab concentrations per trimester from 2 available studies.
Figure 3.
Adalimumab concentrations per trimester from 2 available studies.
Placental transfer of ADA
Two studies analyzed placental transfer of adalimumab. Mahadevan et al. (17) studied 10 pregnant women with IBD receiving adalimumab. Serum concentrations of the drugs were measured at birth in the mother, infant, and in cord blood, and then monthly in the infant until the drugs were undetectable. Drug concentrations in the cord and the infant at birth were compared with those of the mother. The median level of ADA in the cord was 153% than that of the mother. ADA could be detected in the infants for as long as 6 months. Borthlik et al. (9) have analyzed the relationship of neonatal and maternal anti-TNF-α levels at delivery with gestational age at the last exposure. Conversely to IFX, no correlation was found in the case of ADA for this.
ADA and breast milk
In a large and prospective multicenter study, the authors analyzed breast milk samples (n = 72) from patients receiving biologic therapy from October 2013 to November 2015 (19). They detected adalimumab in 2 of the 21 treated women (maximum, 0.71 μg/mL). As with IFX, maternal use of ADA appears to be compatible with breastfeeding.
Duration of ADA in newborns
Thorough a large and prospective multicenter study including 44 pregnant women treated with ADA, the authors investigated concentrations of infliximab in umbilical cord blood of newborns and rates of clearance after birth, and how these correlated with drug concentrations in mothers at birth and risk of infection during the infant’s first year of life (5). The time from last exposure to ADA during pregnancy correlated inversely with the concentration of the drugs in the umbilical cord (r = -0.64, P = .0003) and in mothers at time of birth (ADA, r = -0.80; P < .0001). The median ratio of infant:mother drug concentration at birth was 1.21 for ADA (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.94-1.49). The mean time of drug clearance in infants was 4.0 months for ADA (95% CI, 2.9-5.0), conversely to IFX which was cleared slower than ADA.
TNF-α Inhibitors—golimumab maternal trough concentration during pregnancy breast milk and golimumab in children
Very little data about maternal drug trough concentration is available with GLM therapy during pregnancy. Only one case reports study (25) covered GLM with data exclusively at delivery were reported (6.6 mcg/mL). For GLM, no advice on dosage was given by the authors. Currently, no data is published about evolution of serum levels of GLM during pregnancy and thus, we do not know if the pharmacokinetics are similar to that of IFX or ADA.
Few information is available on the clinical use of GLM therapy during breastfeeding. As golimumab is a large protein molecule with a molecular weight of approximately 150,000 Da, the amount in milk is likely to be very low. It is also likely to be partially destroyed in the infant's gastrointestinal tract and absorption by the infant is most likely minimal. Until more data becomes available, GLM should be used with caution during breastfeeding, especially if nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Waiting for at least 2 weeks postpartum to resume therapy may minimize drug transfer to the infant. Matro et al. (19) did not detect GLM in breast milk from the one mother exposed to this drug.
No publication is available about the exposure duration of GLM in children from mothers using GLM during pregnancy. Based on very little data reporting very low drug concentration in the children born, we can speculate similar management of live vaccines in newborns as with the other anti-TNF drugs.
Outcomes of pregnancy and children when using anti-TNF during pregnancy
In a recent meta-analysis, a total of 8 studies included 527 pregnant women with IBD. Of these patients, 343 received therapy with IFX and 184 with ADA (26). Compared to ADA, adverse pregnancy outcomes including congenital malformations and spontaneous abortion were not increased in case of exposure to IFX. Another meta-analysis was performed for adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs), congenital abnormalities (CAs), preterm birth (PTB) and low birth weight (LBW) to assess the risks associated with anti-TNFα therapy for pregnancy outcomes (27). Anti-TNFα therapy does not increase the risk of APOs, CAs, PTB or LBW compared with disease-matched controls. Furthermore, the risk of CAs was not increased when published prevalence data was compared with data for the general population. These findings may offer some reassurance to women and physicians regarding the safety profile of anti-TNFα therapy during pregnancy in IBD. Finally, a separate recent meta-analysis (28) included 48 studies to estimate the prevalence of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with IBD exposed to biologic therapy. Adverse pregnancy outcomes amongst pregnant IBD women using biologics are comparable with that of the general population. In all studies, TDM was not analyzed to identify an association between serum drug levels and adverse events.
Moreover, some studies analyzed the impact of monoclonal antibody therapy use during pregnancy and the response to vaccination in newborns. In a large study including 179 women, vaccination of infants against HiB and tetanus toxin, based on antibody titers measured when infants were at least 7 months old does not appear to be affected by in utero exposure to biologic therapy (29). Julssgaard et al. (5) analyzed the concentrations of anti-TNFα in mothers and newborns and reported risk of infections during the time. Bacterial infections developed in 4 infants (5%) and viral infections developed in 16 (20%), all with benign courses. The relative risk for infection was 2.7 in infants whose mothers received the combination of an anti-TNF agent and thiopurine, compared with anti-TNF monotherapy (95% CI, 1.09-6.78; P = .02). In a large prospective cohort study (30) including 191 children (IFX (67 [35%] of 191), ADA (49 [26%])), the authors aimed to examine whether live rotavirus vaccine could be administered safely to infants exposed to biologic agents, as assessed in the Canadian Special Immunization Clinic (SIC) Network. No serious adverse events after immunization were reported, but three (2%) infants required medical attention. So, according to the authors, rotavirus vaccination can be offered to infants exposed to anti-TNF agents in utero. A systematic bibliographic search was performed recently to review the effectiveness and safety of vaccines in children exposed to biological drugs in utero and/or those whose mothers received biological agents during lactation (31). Vaccines appear to be effective in infants exposed to biologics in utero. Inactivated vaccines are likely safe, whereas live-attenuated vaccines should be avoided while the children have detectable levels of biological drugs. Vaccines (non-live and live) are possibly safe in children breastfed by mothers treated with biologics. However, drug levels during pregnancy or in blood cord were not concomitantly measured in this study in order to look for an association with those very low drug concentrations found in breast milk.
When can we resume IFX and ADA during pregnancy?
Firstly, studies have reported increased levels of IFX concentrations during the third trimester of pregnancy, conversely to ADA. So, using TDM, we can speculate the possibility of decreasing the dose of IFX during this time to obtain therapeutic levels. The IFX levels in
Figure 2 show discrepancies at T5 for two studies (15) (10). The discrepancies at T5 may possibly be related to the time of measurement after delivery. The latest measurement performed by Kane et al. and Vasilauskas et al., was at 14 weeks. Seow et al. (11) and Flanagan et al. (12) defined post-pregnancy as up to 6 months [
14,
15]. Grisic et al. (14) showed measurements up to 250 weeks after conception, and Steenholdt et al. (16) made their last measurement at 28 weeks after delivery. However, we think that it would be interesting to measure TDM of IFX and ADA after delivery, using a proactive strategy.
Looking at breast milk, anti-TNF concentrations are very low, and breast feeding while under IFX or ADA is recommended to be safe. The more important point is about serum levels concentrations in the newborns. Mahadevan et al. suggested performing biologic therapy for weeks before delivery. Indeed, no effects in pregnant women and newborns were reported in all studies, except for serum anti-TNF concentrations in the newborn. Finally, the essential question is to determine the optimal timing for the last dosage of anti-TNF agents (infliximab, adalimumab, and golimumab) in pregnant women with IBD, as well as to investigate the recommended vaccine schedules for infants exposed to these drugs. Liu et al. (20) developed a pharmacokinetic model to predict time-to-clearance in infants exposed to biologics during pregnancy. Infants with a detectable anti-TNF at umbilical cord level and in at least one other blood sample during the first year of life were included. According to their results online, they can predict the duration of anti-TNF in the child and can adapt the date of live vaccination. Chen et al. (34) recommend more stringent points for timing the last dose and vaccine according to the regimen used for pregnant women. However, for practitioners not using TDM, it would be easier to time live vaccines at one year for the child or to discuss vaccination ebefore in case of no drug detection in blood.
Figure 4.
Pharmacokinetics of in pregnant women with IBD.
Figure 4.
Pharmacokinetics of in pregnant women with IBD.
Serum ustekinumab levels during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Ustekinumab is an entirely humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody blocking the p40 subunit of interleukin (IL) IL-12 and IL-23 and is currently approved in the treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Interleukin-12 targeted by ustekinumab contributes to uterine physiology (uterine angiogenesis), in regulation of trophoblast invasion and in local vascular remodeling during implantation of an embryo (35). Notably, both high and low levels of IL-12 in pregnancy have been associated with early spontaneous abortions. In addition, IL-23 regulates the critical functions of human decidual immune cells, which play a key role in the tolerance of genetically different (allogenic) cells while aiding the mother’s immune function in early pregnancy (36). These findings raise the concern of potential interference of ustekinumab exposure on pregnancy. However, clinical results from a large registry comparing the pregnancy events occurring in IBD patients exposed and not exposedto ustekinumab are reassuring and did not show unexpected adverse outcomes of pregnancy and child growth. Data in the literature on ustekinumab pharmacokinetics during pregnancy remains unclear, limited to small case series and concern exclusively drug measurement in maternal, cord and infant blood and not on drug concentrations in intestinal tissues. Sako M et al. investigated drug concentrations at delivery in maternal peripheral and cord blood from a patient with CD treated with ustekinumab and in infants’ blood at six months (37). Similar to anti-TNF agents, the level of ustekinumab in cord blood was 2.8-fold higher compared with that measured in maternal serum, but drug concentration was undetectable in the baby’s bloodstream after six months (37) (38) (39). Similar findings were reported in three other case reports, one in a pregnant women with CD treated until 33 weeks of gestation with dose interval of ustekinumab shortened to every 4 weeks another in a woman with refractory CD treated with ustekinumab until week 30 of pregnancy (38) and finally, in a patient with UC under usual maintenance therapy with a 2-2.5 times higher drug concentration in blood cord than in contemporaneous maternal serum. In the last case, the drug was yet detectable in infant serum more than 2 months after the last maternal dose (40). Interestingly, maternal drug serum trough levels which were monitored at induction therapy and throughout pregnancy were found stable (41).
Recently, several larger prospective observational cohort studies investigated the pharmacokinetics of ustekinumab during pregnancy. The first one from Mitrova K et al. reported drug levels in 15 infant-mother pairs during pregnancy in IBD patients (42). At the time of delivery, drug levels in the cord and in the maternal blood were strongly correlated with a median infant-to-maternal ratio of 1.7, concordant with those previously observed in precedent small case series. The second study presented during the last ECCO Congress which was not yet published reported the australian experience of PK of ustekinumab and vedolizumab in pregnant women with IBD. This multicenter prospective cohort study included 35 pregnant patients treated with maintenance dose of ustekinumab. They investigated both infant and maternal drug levels at delivery, as well as drug concentrations in infants at various time points until drug clearance. They reported a strong positive correlation between drug levels in maternal and infant serum at time of delivery and the infant:maternal drug level ratio was 1.74 (IQR 1.24-3.5) in accordance with those previously reported in previous case series (43). Time to drug clearance in infants was 13 weeks (IQR 9-22) and serum ustekinumab was not detected 15 weeks after delivery in two-third of infants. Interestingly, in this cohort, time to clearance in infants did not differ between women who received the last dose of ustekinumab during the second and those that received it during the third trimester of pregnancy. The third prospective study included 15 women with CD under ustekinumab treatment and confirmed previous data with infant drug levels at delivery 1.79 (IQR 1.26-3.1) fold higher than maternal levels with a median clearance time of 9 weeks (range 6-19) in 9 infants in whom drugs levels were measured over time (39). In the Pregnancy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Neonatal Outcomes – PIANO registry, a prospective observational study that enrolled pregnant women with IBD in 30 US centers, similar pharmacokinetics findings of ustekinumab during pregnancy were observed in a small subgroup of patients (6).
Altogether, few studies show ustekinumab PK during pregnancy, however, their results are in line with overall stable concentrations of maternal serum drug levels throughout pregnancy, and in the infant. A lack of correlation was seen between ustekinumab levels in the umbilical cord blood with the gestational week during which the drug was administered In addition, drug clearance time was not different regardless of the time of the last ustekinumab injection during the second half of pregnancy.
Ustekinumab levels during breastfeeding
Limited data on breast milk transfer of ustekinumab from women to their infants is available. Drug exposure of infants to ustekinumab during breastfeeding and whether drug exposure in infants has an impact on t risk of infection and developmental milestones remains unclear s and controversial. A recent case report of a 36-yearold female with UC treated with a maintenance regimen of ustekinumab (90 mg/ 8weeks) has provided information on drug concentrations in breast milk which were substantially lower compared with those found in cord blood (ratio 1 to 100) or in maternal serum (ration 1 to 20) and decreased gradually thereafter. When comparing serum maternal ustekinumab levels with those in breast milk, the ratio of areaunder the time-concentration curves of the drug was very low (0.0008) (40). Ustekinumab was also detected in low concentration in breast milk from a small case report including 3 nursing mothers with Crohn’s disease exposed to treatment (90 mg/8 weeks for 2 of them and intensified dose of 90 mg/4 weeks for the latter) (44).
Notably, the low drug concentrations measured in breast milk samples collected one hour after the completion of drug administration were two-fold lower compared with pre-dose serum levels. A multicenter prospective observational study investigated breast milk samples from 6 women with IBD treated with ustekinumab. Low levels of ustekinumab in breast milk were detected in 4 out of 6 patients with a peak concentration of 1.57 μg/mL (ranging from 0.72-1.57). This was seen 12-72 hours post injection and was followed by a gradual decrease thereafter. In addition, infection rates and developmental delay at 12 months did not differ between drug exposed and non-exposed breastfed infants (19).
Altogether, our knowledge on the usefulness of monitoring serum ustekinumab or vedolizumab maternal levels during pregnancy remains unclear and is currently not recommended in patients with IBD. Therapeutic drug monitoring during pregnancy and proactive dose adjustment are not necessary since its impact for making clinical decisions has not been demonstrated in routine clinical practice. Overall, drug concentrations at birth in blood infant cord and in serum after birth, due to placental drug transfer, may have a greater impact on the risk of infection and development outcomes than drug transfer during lactation.
Serum vedolizumab trough levels during pregnancy
Vedolizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody that selectively antagonizes α4β7 gastrointestinal integrin receptors that was approved for treatment of IBD patients. The receptor targeted by vedolizumab inhibits leukocyte trafficking into the gut and subsequently reduces the recruitment of immune and inflammatory cells. It is also involved in placental development which has caused apprehension about its use in pregnant women. Data about the potential impact of vedolizumab exposure during pregnancy is limited and results from the European retrospective multicenter case-control observational CONCEIVE study. The study reports pregnancy and child developmental outcomes in 73 IBD women exposed to vedolizumab. Additionally, a retrospective cohort study from the GETAID including 44 drug-exposed women with IBD during pregnancy and a few cases from the PIANO registry also contribute to the available data (45) (46). There was no clear evidence of a negative safety signal although further larger, prospective and dedicated studies are required to confirm these reassuring findings.
At time of delivery, vedolizumab was detectable in the serum of infants. Although the mechanisms of transfer of vedolizumab across the placenta to the fetal blood stream are similar to the IgG antibodies, placental pharmacokinetic studies have reported substantial differences between vedolizumab and other biologics including anti-TNF agents and ustekinumab. A comparative study investigating the placental pharmacokinetics of vedolizumab and ustekinumab in IBD women (15 exposed to ustekinumab and 16 to vedolizumab) found lower drug concentrations of vedolizumab in the cord blood than in the maternal blood. This is in contrast with concentrations measured in mothers exposed to ustekinumab during pregnancy. In this cohort, the median vedolizumab concentrations in maternal and in cord blood samples from mothers with IBD was 7.3 mg/L and 4.5 mg/L with a median infant-to-maternal ratio of 0.66 (compared with 1.7 in the cohort of pregnant mothers exposed to ustekinumab) (42). Moreover, there was a positive relationship between drug levels in the cord blood and the gestational week of the last vedolizumab infusion.
Serum vedolizumab trough levels during breastfeeding
There is limited data regarding the impact of vedolizumab exposure in women with IBD during breastfeeding on infant outcomes. All data available during pregnancy and breastfeeding concerns intravenous vedolizumab administration and no data isavailable with the recently approved subcutaneous injection of vedolizumab.
Vedolizumab is detected in breast milk at low concentrations. Drug levels in breast milk from 5 vedolizumab treated lactating women with IBD were investigated in a short report. Breast milk samples were collected prior to infusion, 30 minutes post infusion and then twice daily for up to 14 days. Vedolizumab was detected in all breast milk samples with varying concentrations which were very low based on the corresponding serum concentration (less than 1%). The peak drug concentration was 0.318 μg/mL in this cohort and was raised from 3-7 days after infusion.Taking in account the maximal vedolizumab concentrations in milk samples and the overall amount of milk ingested by the infants (around 150 mL per kilogram of body weight), it is estimated that the infants could receive 0.048 mg per kilogram body weight per day (5).
Altogether, we should keep in mind that vedolizumab is detected in maternal and cord blood, and drug concentrations in the cord blood are lower than in maternal blood in majority of cases, contrasting to those measured under ustekinumab. Safety data on the use of vedolizumab during pregnancy and breastfeeding does not indicate any negative effects. Ustekinumab and vedolizumab exposure during pregnancy and lactation are both considered low risk by the recent ECCO guidelines despite limited available data (32). However, we require more prospective, real-life and larger dedicated studies to confirm these reassuring findings.