Submitted:
02 October 2023
Posted:
03 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Intoduction
2. Problem formulation
3. Control design
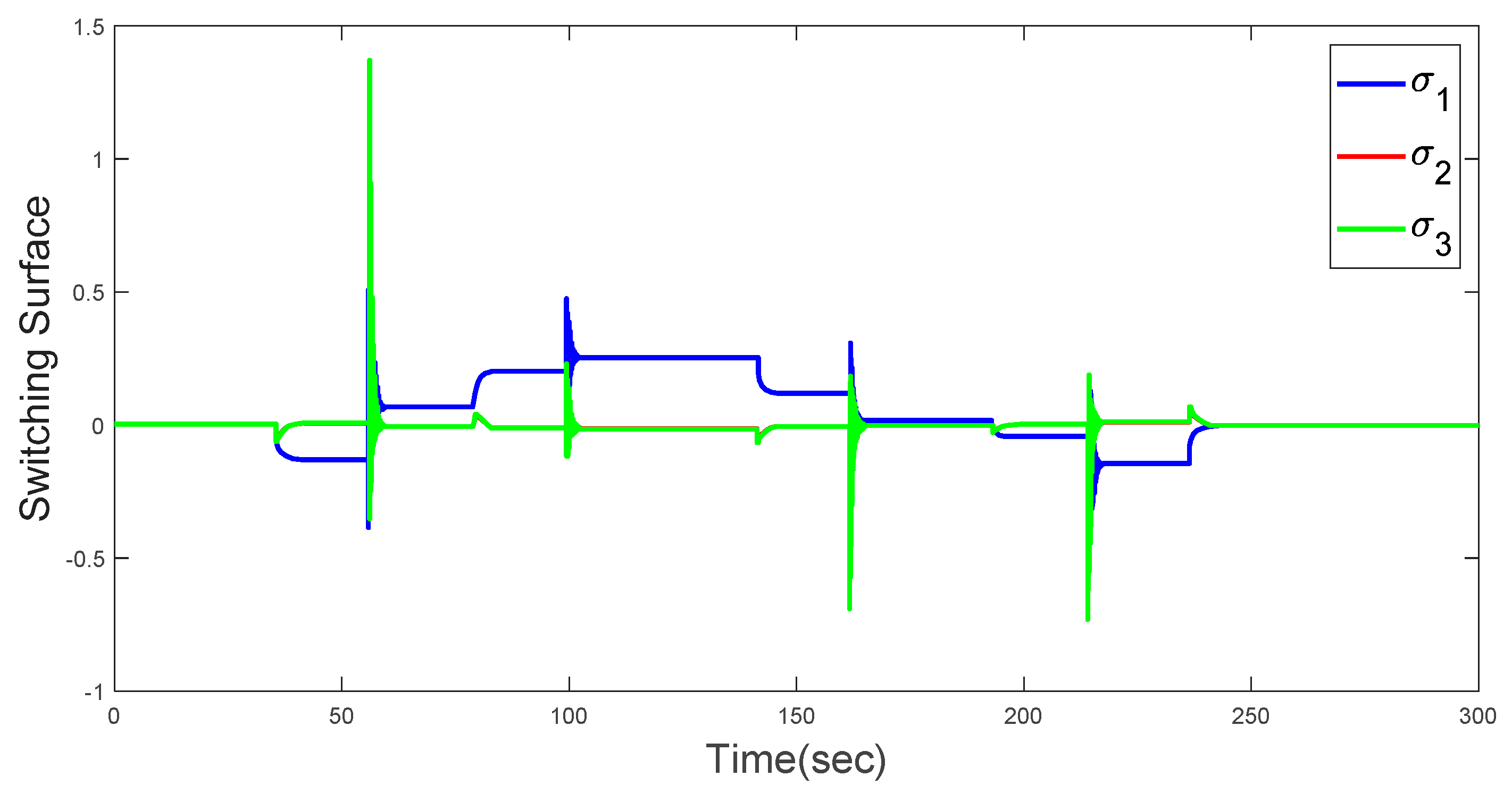
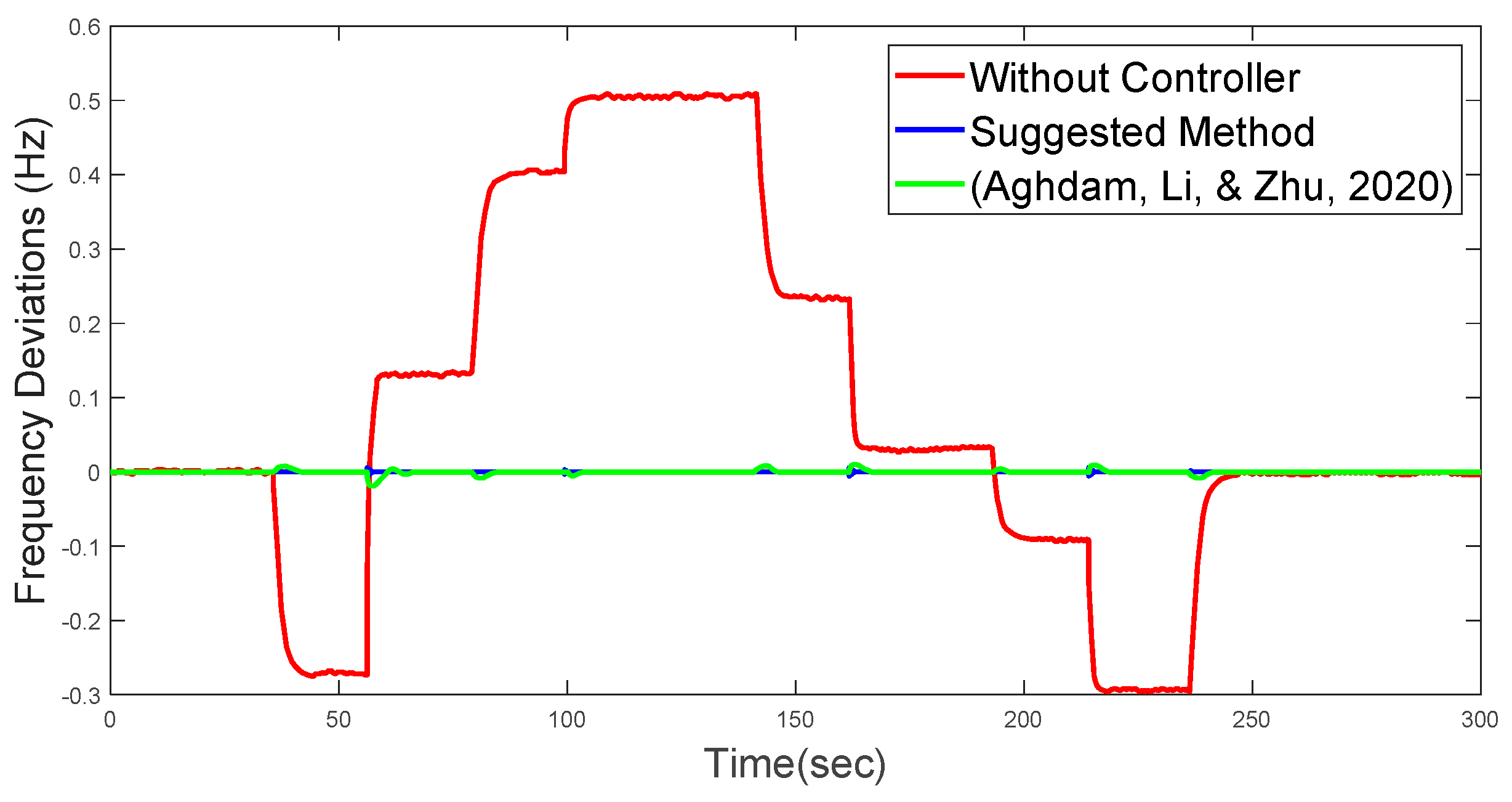
4. Simulation results
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Wind Turbine | States of the system | ||
| Fuel Cell | Control signals | ||
| Photovoltaic Units | External disturbances | ||
| Diesel Engine Generator | Upper bound of | ||
| Flywheel Energy Storage System | Constant for switching manifold | ||
| Battery Energy Storage System | Constant for switching manifold | ||
| Micro-Grid | Estimation of | ||
| Switching Manifold | Constant for adaptation law | ||
| Scaler parameter | Positive odd integer | ||
| Settling time | The candidate Lyapunov’s function | ||
| Initial time | Constant for barrier function |
References
- Isidori, A. Nonlinear control systems II; Springer: 2013.
- Mohler, R.R. Nonlinear systems (vol. 2) applications to bilinear control; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: 1991.
- Sepestanaki, M.A.; Barhaghtalab, M.H.; Mobayen, S.; Jalilvand, A.; Fekih, A.; Skruch, P. Chattering-Free Terminal Sliding Mode Control Based on Adaptive Barrier Function for Chaotic Systems With Unknown Uncertainties. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103469–103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-W.; Liaw, D.-C.; Lee, T.-C. Reliable control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2000, 45, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, S.; Michailidis, I.; Kosmatopoulos, E.B.; Papachristodoulou, A.; Ioannou, P.A. Convex Design Control for Practical Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2014, 59, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Zong, G.; Xu, N. Hierarchical Sliding-Mode Surface-Based Adaptive Actor–Critic Optimal Control for Switched Nonlinear Systems With Unknown Perturbation. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.M.; Ebeed, M.; Alhejji, A.; Refai, A. A Robust Cascaded Controller for Load Frequency Control in Renewable Energy Integrated Microgrid Containing PEV. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2023, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooban, M.H.; Niknam, T.; Blaabjerg, F.; Dragičević, T. A new load frequency control strategy for micro-grids with considering electrical vehicles. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, P.; Weiss, G. Saturating PI Control of Stable Nonlinear Systems Using Singular Perturbations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2022, 68, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, L. Towards a theoretical foundation of PID control for uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 2022, 142, 110360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerkpreedapong, D.; Hasanovic, A.; Feliachi, A. Robust load frequency control using genetic algorithms and linear matrix inequalities. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccagli, M.; Andrieu, V.; Tarbouriech, S.; Astolfi, D. LMI conditions for contraction, integral action, and output feedback stabilization for a class of nonlinear systems. Automatica 2023, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sumarmad, K.A.; Sulaiman, N.; Wahab, N.I.A.; Hizam, H. Energy Management and Voltage Control in Microgrids Using Artificial Neural Networks, PID, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers. Energies 2022, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, R.T.; Agarwal, V. Fuzzy logic control of the ultracapacitor interface for enhanced transient response and voltage stability of a DC microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2018, 55, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.H.; Choi, H.-K.; Moon, J.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Hybrid Koopman model predictive control of nonlinear systems using multiple EDMD models: An application to a batch pulp digester with feed fluctuation. Control. Eng. Pr. 2021, 118, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasingam, A.; Son, S.H.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Data-driven feedback stabilisation of nonlinear systems: Koopman-based model predictive control. Int. J. Control. 2022, 96, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morstyn, T.; Savkin, A.V.; Hredzak, B.; Agelidis, V.G. Multi-Agent Sliding Mode Control for State of Charge Balancing Between Battery Energy Storage Systems Distributed in a DC Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 4735–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Jabbari, A.; Mobayen, S. An intelligent ABC-based terminal sliding mode controller for load-frequency control of islanded micro-grids. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 64, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Tang, Y.; He, H. Observer-based sliding mode frequency control for micro-grid with photovoltaic energy integration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM); 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Alnuman, H.; Hsia, K.-H.; Sepestanaki, M.A.; Ahmed, E.M.; Mobayen, S.; Armghan, A. Design of Continuous Finite-Time Controller Based on Adaptive Tuning Approach for Disturbed Boost Converters. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.H.; Abbaszadeh, E.; Sepestanaki, M.A.; Mobayen, S.; Su, C.-L.; Nemati, A. Adaptive Finite-Time Tracking Control of Fractional Microgrids Against Time-Delay Attacks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Makrini, I.; Guerrero, C.R.; Lefeber, D.; Vanderborght, B. The Variable Boundary Layer Sliding Mode Control: A Safe and Performant Control for Compliant Joint Manipulators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 2, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Wang, C.; Chu, Y.; Fei, J. Neural-Observer-Based Terminal Sliding Mode Control: Design and Application. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 4800–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorshedy, M.F.; Selvam, S.; Mahajan, S.B.; Almakhles, D. Investigation of high-gain two-tier converter with PI and super-twisting sliding mode control. ISA Trans. 2023, 138, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shen, X.; Alcaide, A.M.; Yin, Y.; Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Wu, L.; Franquelo, L.G. Sliding Mode Control of Grid-Connected Neutral-Point-Clamped Converters Via High-Gain Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamayun, M.T.; Edwards, C.; Alwi, H.; Hamayun, M.T.; Edwards, C.; Alwi, H. Integral Sliding Mode Control; Springer: 2016.
- Yao, Q.; Jahanshahi, H.; Moroz, I.; Bekiros, S.; Alassafi, M.O. Indirect neural-based finite-time integral sliding mode control for trajectory tracking guidance of Mars entry vehicle. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 71, 3723–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Song, Q.; Ma, S.; Ma, W.; Yin, C.; Cao, D.; Yu, H. A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lai, G. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control of Robot Manipulators with System Failures. Mathematics 2022, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.S.; Singh, P.; Swarnkar, P. Intelligent fuzzy logic-based sliding mode control methodologies for pick and drop operation of robotic manipulator. International Journal of Computational Vision and Robotics 2022, 12, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepestanaki, M.A.; Bahmani, H.; Ali, M.A.; Jalilvand, A.; Mobayen, S.; Fekih, A. Fuzzy Estimator Indirect Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Nonlinear Systems Based on Adaptive Continuous Barrier Function. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 34296–34305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Salhi, I.; Laghrouche, S.; Ait-Amirat, Y.; Djerdir, A. Nonlinear Disturbance Observer-based sliding mode control of interleaved boost converter for fuel cell used in microgrids. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ning, B.; Dong, H. Adaptive neural control with intercepted adaptation for time-delay saturated nonlinear systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 26, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabah, K.; Ladaci, S. A Fractional Adaptive Sliding Mode Control Configuration for Synchronizing Disturbed Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 39, 1244–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Song, J.; Zuo, L.; Yang, P. Neural Adaptive Sliding-Mode Control of a Vehicle Platoon Using Output Feedback. Energies 2017, 10, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, D.; Hedrick, J.; Yip, P.; Gerdes, J. Dynamic surface control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2000, 45, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Xu, D. Prescribed Performance-Based Adaptive Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Virtual Synchronous Generators. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Feng, Y.; Man, Z. Terminal sliding mode control–an overview. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society 2020, 2, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyaalaoui, K.; Labbadi, M.; Ouassaid, M.; Cherkaoui, M.; Bouzi, M. High-order sliding-mode control using integral terminal sliding manifold for a wind turbine under grid faults. Int. J. Control. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, H.; Yu, X. Practical Terminal Sliding-Mode Control and Its Applications in Servo Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; He, H. Dynamic Behavior of Terminal Sliding Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 3480–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihong, M.; Paplinski, A.; Wu, H. A robust MIMO terminal sliding mode control scheme for rigid robotic manipulators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1994, 39, 2464–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Moreno, J.A.; Chalanga, A.; Bandyopadhyay, B.; Fridman, L.M. Continuous terminal sliding-mode controller. Automatica 2016, 69, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepestanaki, M.A.; Jalilvand, A.; Mobayen, S.; Zhang, C. Design of adaptive continuous barrier function finite time stabilizer for TLP systems in floating offshore wind turbines. Ocean Eng. 2022, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekoukar, V.; Erfanian, A. A Decentralized Modular Control Framework for Robust Control of FES-Activated Walker-Assisted Paraplegic Walking Using Terminal Sliding Mode and Fuzzy Logic Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, H.; Fridman, L.M.; Laghrouche, S.; Harmouche, M. Barrier function-based adaptive sliding mode control. Automatica 2018, 93, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plestan, F.; Shtessel, Y.; Brégeault, V.; Poznyak, A. New methodologies for adaptive sliding mode control. Int. J. Control 2010, 83, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.E. Design analysis: mathematical modeling of nonlinear systems; Cambridge University Press: 1999.
- Xiu, C.; Guo, P. Global Terminal Sliding Mode Control With the Quick Reaching Law and Its Application. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49793–49800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Rajab, Z.; Alfergani, A.; Mohamed, O. The impact of the time delay on the load frequency control system in microgrid with plug-in-electric vehicles. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazari, A.; Monsef, H.; Wu, B. Coordination strategies of distributed energy resources including FESS, DEG, FC and WTG in load frequency control (LFC) scheme of hybrid isolated micro-grid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 109, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooban, M.-H.; Niknam, T.; Blaabjerg, F.; Davari, P.; Dragicevic, T. A robust adaptive load frequency control for micro-grids. ISA Trans. 2016, 65, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooban, M.-H. Secondary Load Frequency Control of Time-Delay Stand-Alone Microgrids With Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 7416–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.; Das, S. Fractional Order AGC for Distributed Energy Resources Using Robust Optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 7, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.M.; Li, L.; Zhu, J. Comprehensive study of finite control set model predictive control algorithms for power converter control in microgrids. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
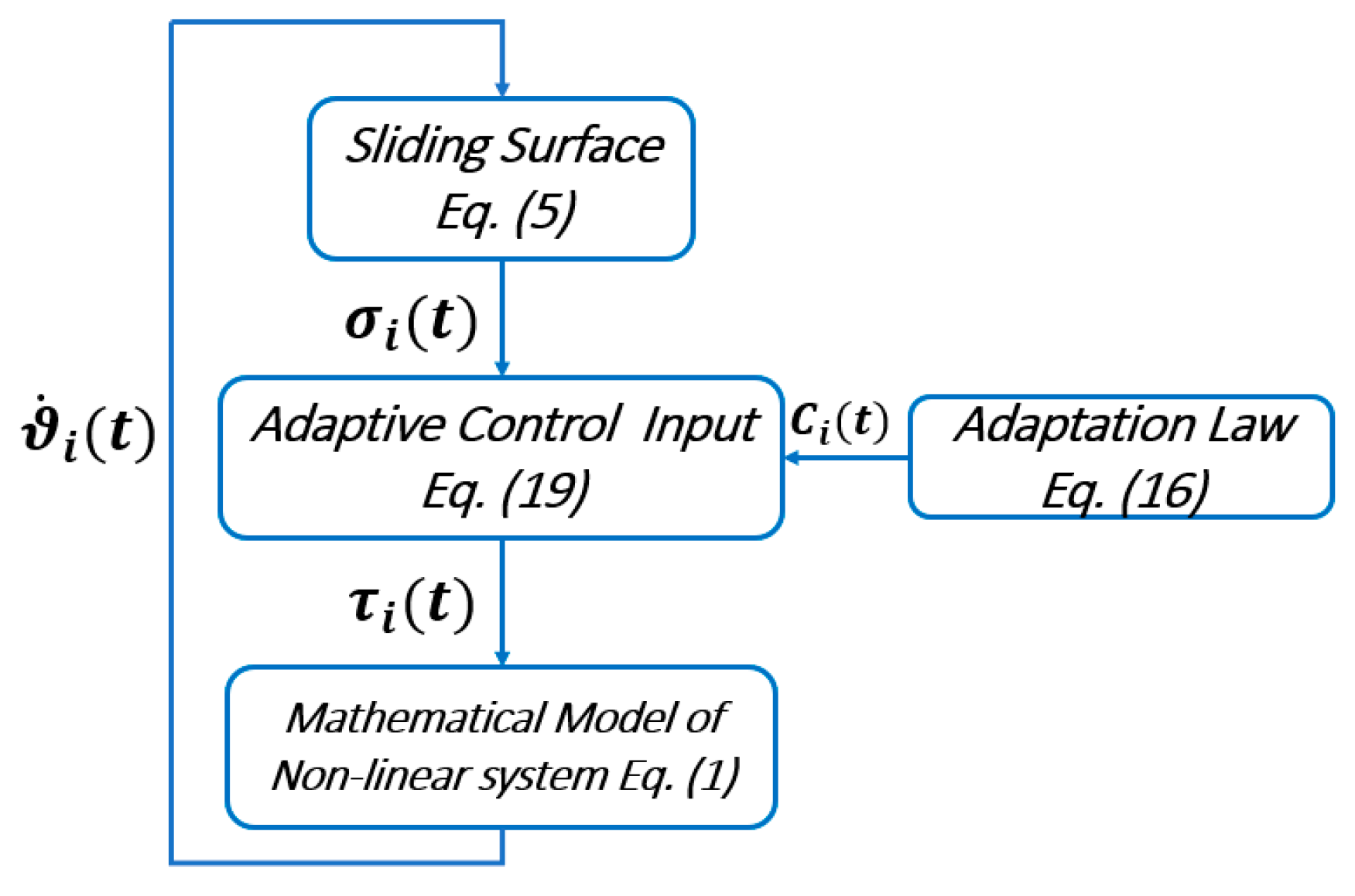
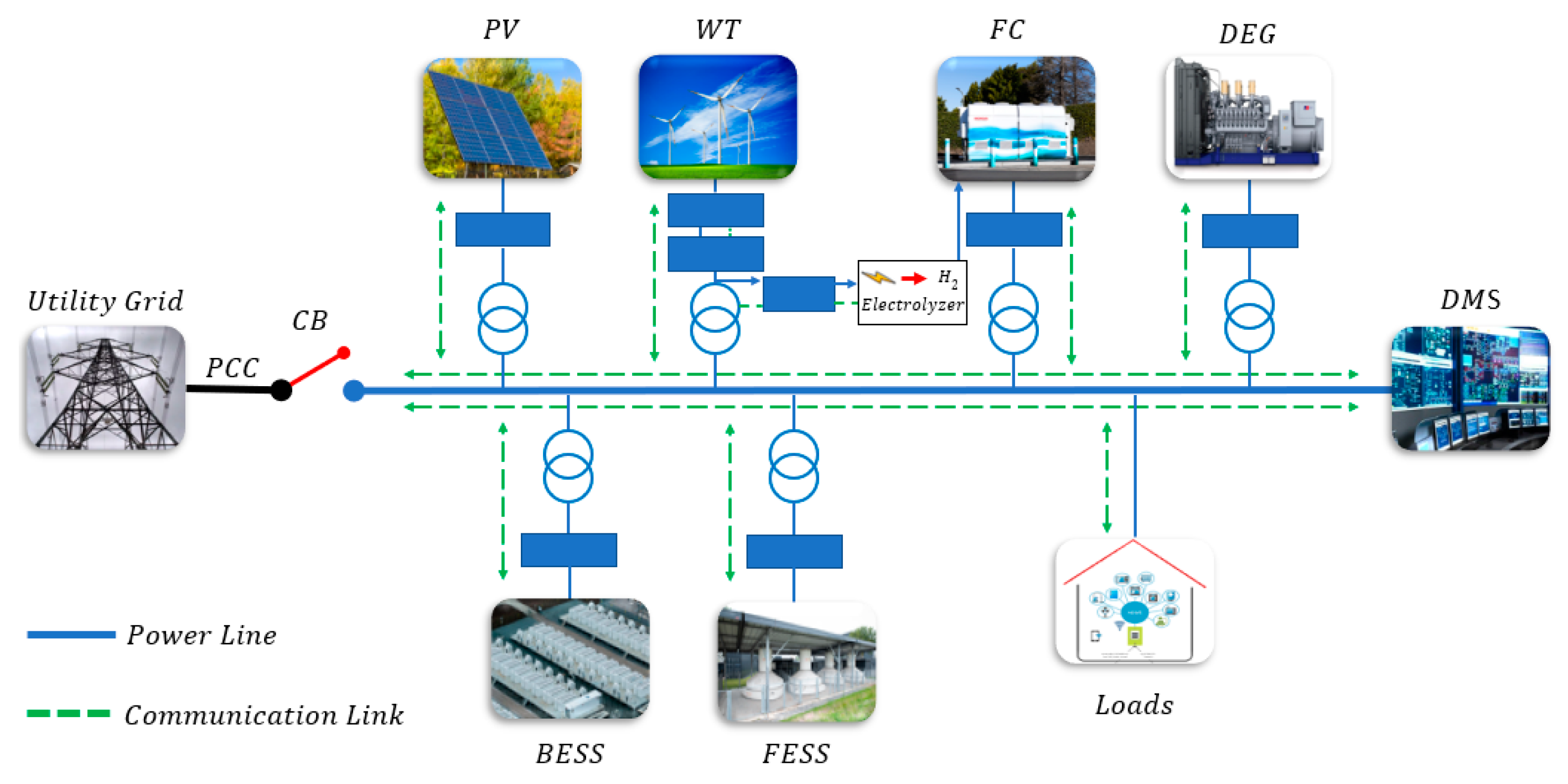
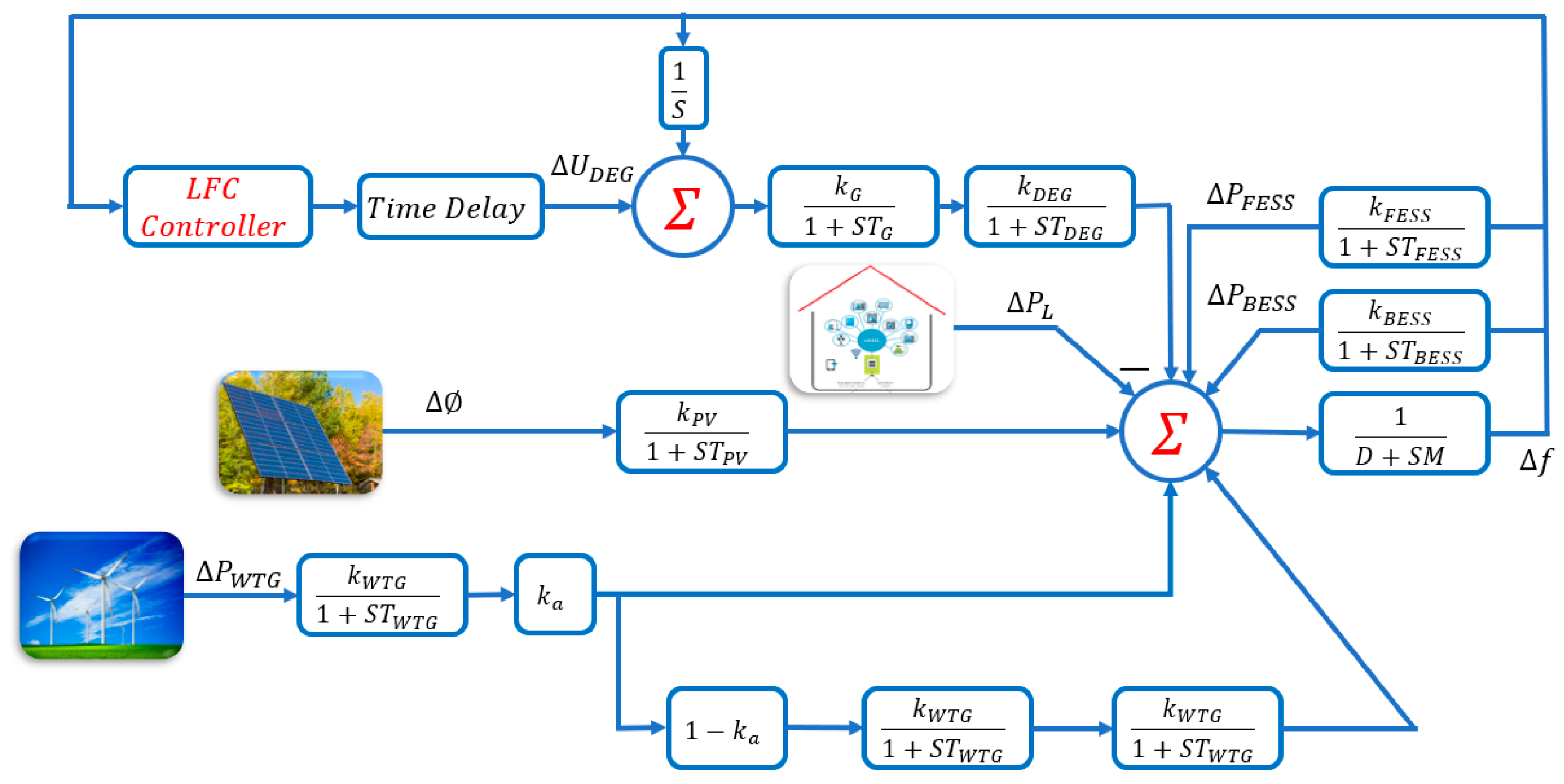
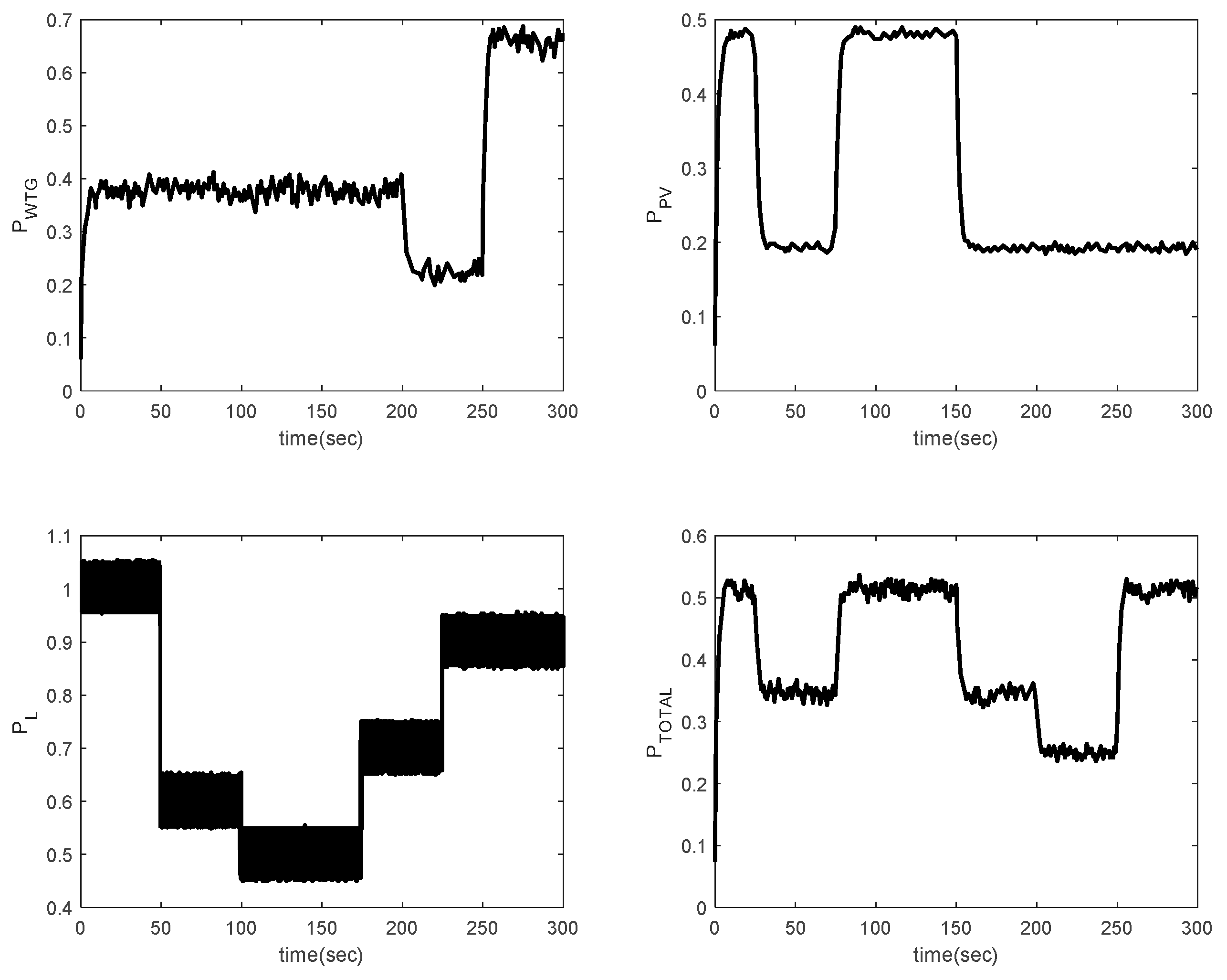
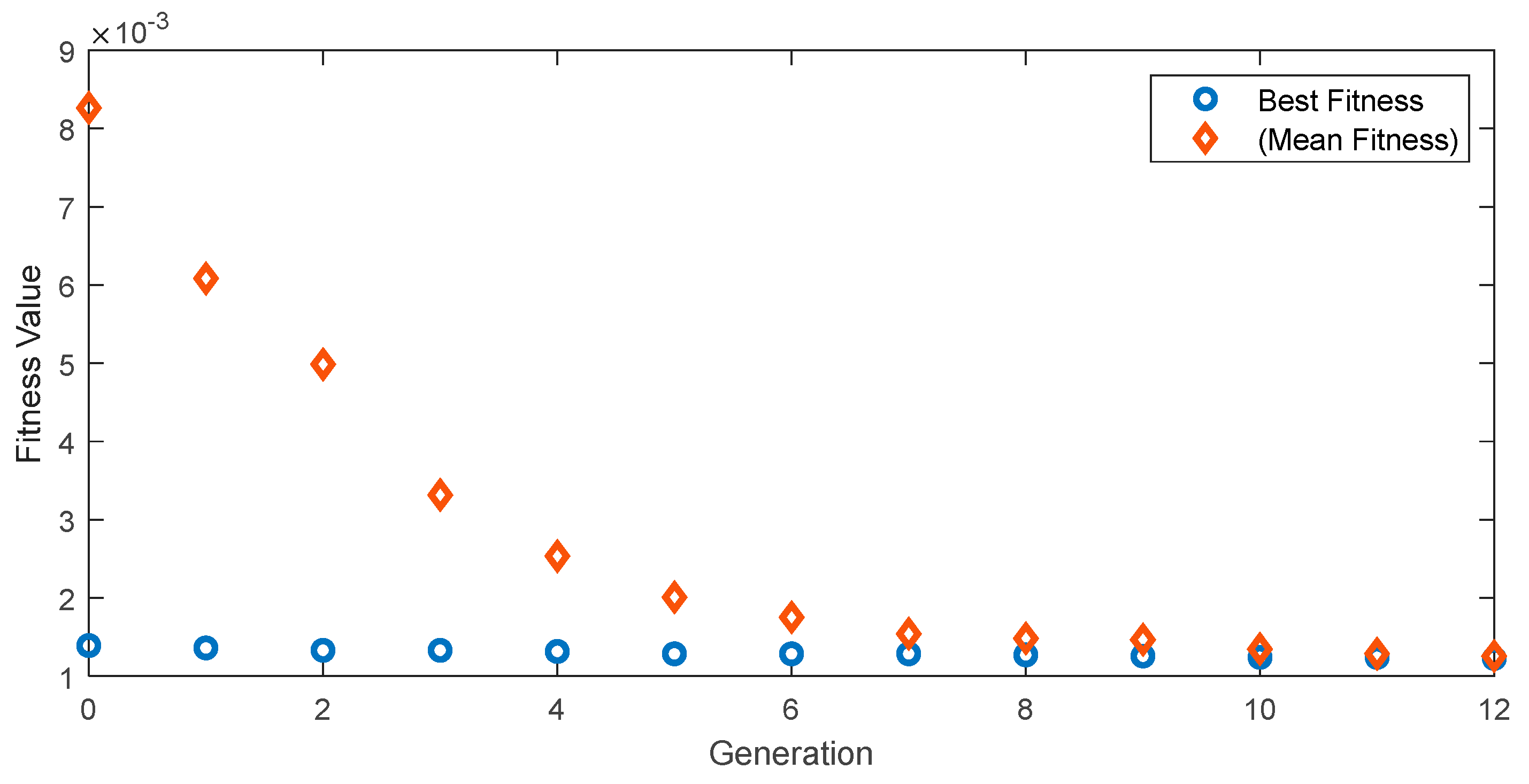
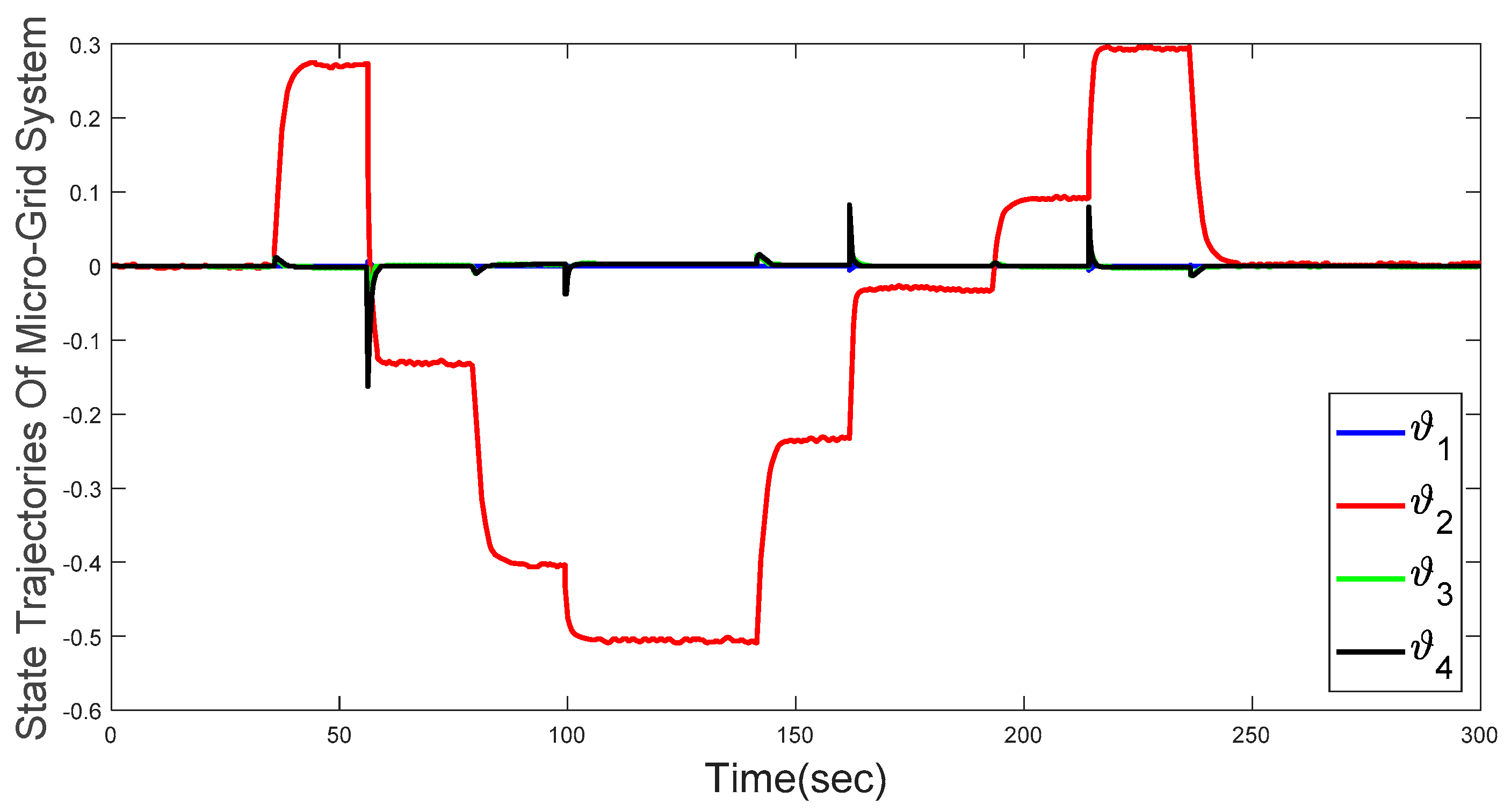
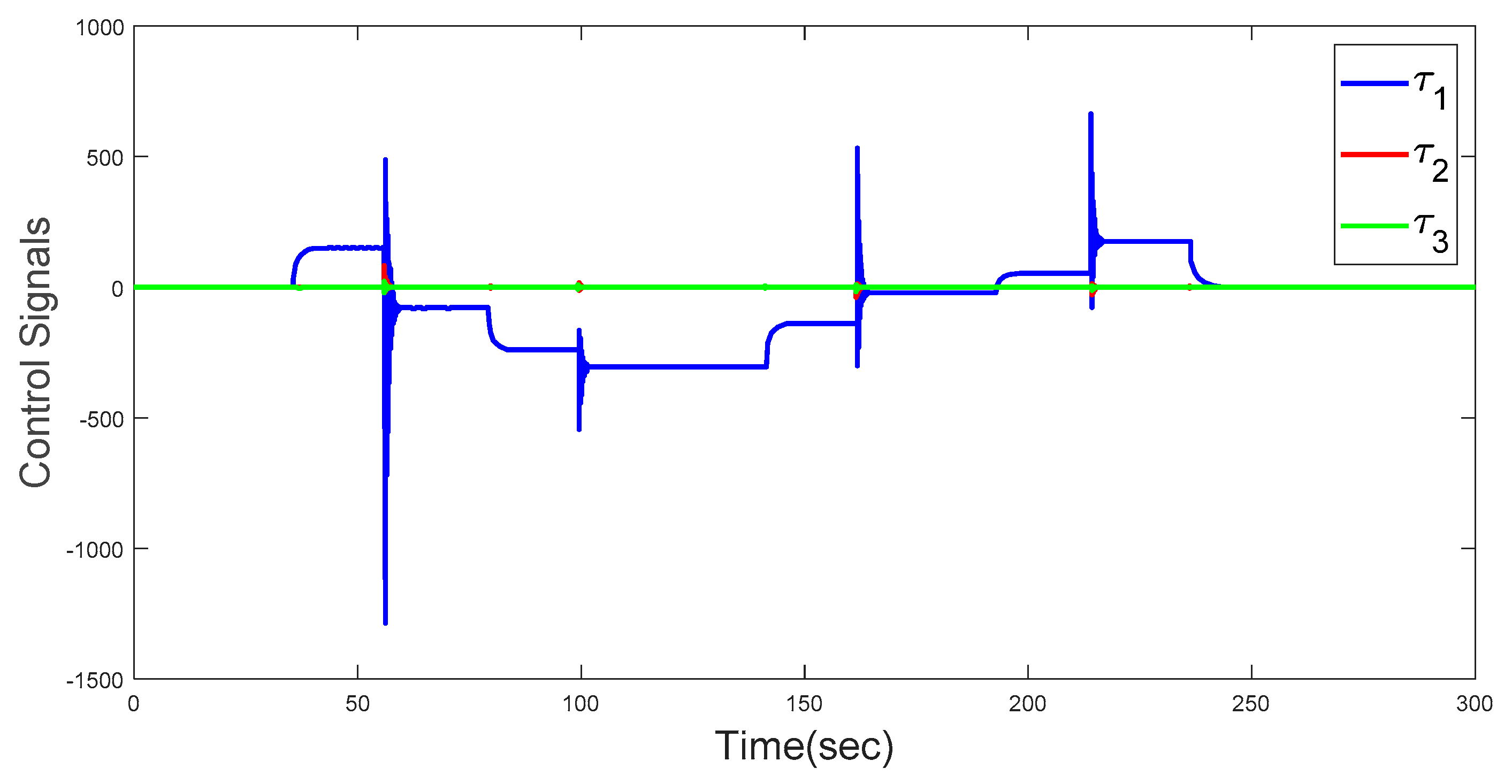
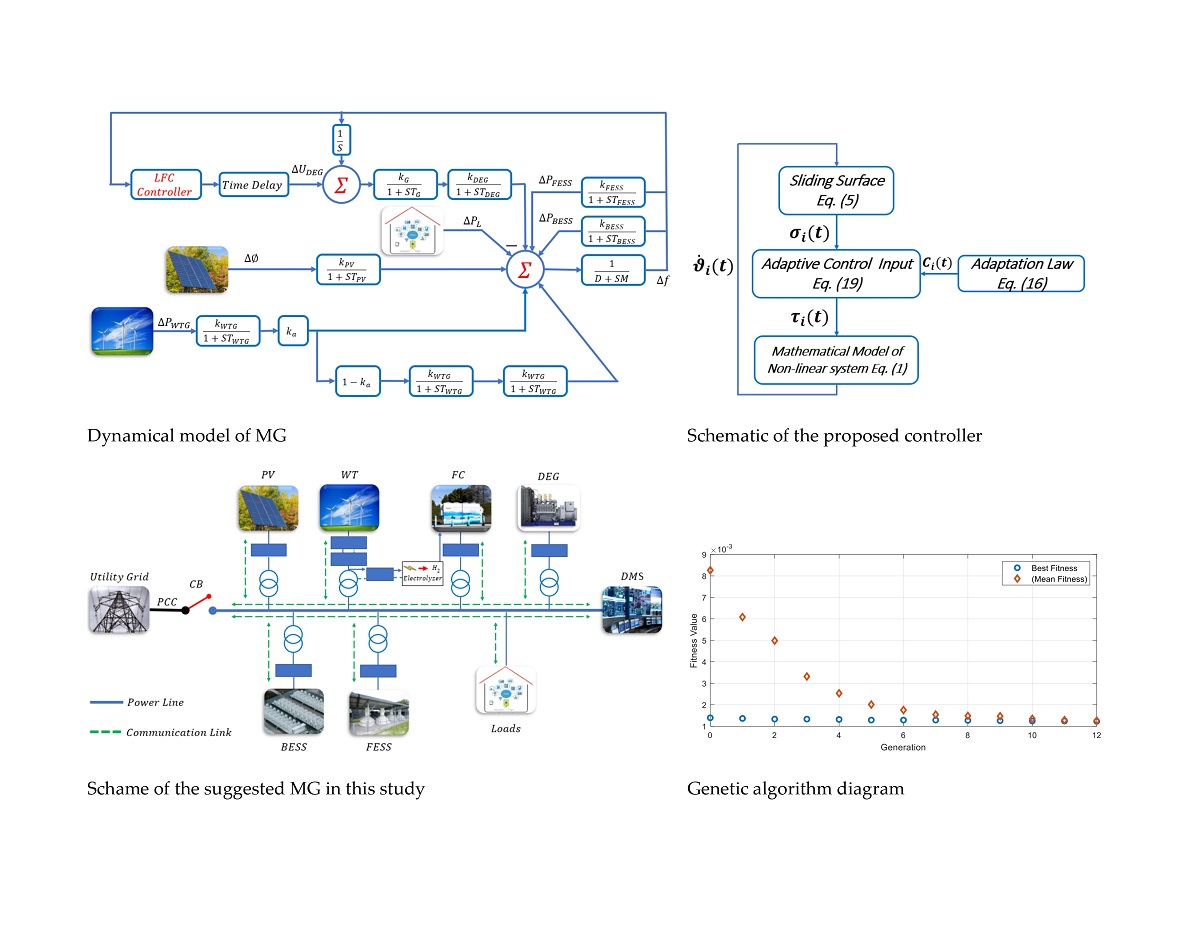
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.1 | ||
| (Diesel generator time constant) | 1 | 0.1 | |
| 2 | 1/300 | ||
| 1.8 | 1 | ||
| (The time constant of the aqua electrolyzer) | 0.5 | 1 | |
| 4 | 1/500 | ||
| (DG speed regulation) | 3 | 1/100 | |
| (Damping coefficient) | 0.012 | -1/100 | |
| (Inertia constant) | 0.2 | -1/300 |
| Symbol | Title | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Constants of Eq. (5) | ||
| Constants of Eq. (5) | ||
| 2 | 1/300 | |
| 1.8 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





