Submitted:
02 October 2023
Posted:
03 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Bacteriophage Isolation
2.2. Purification and Large-Scale Amplification of Phage BIS08
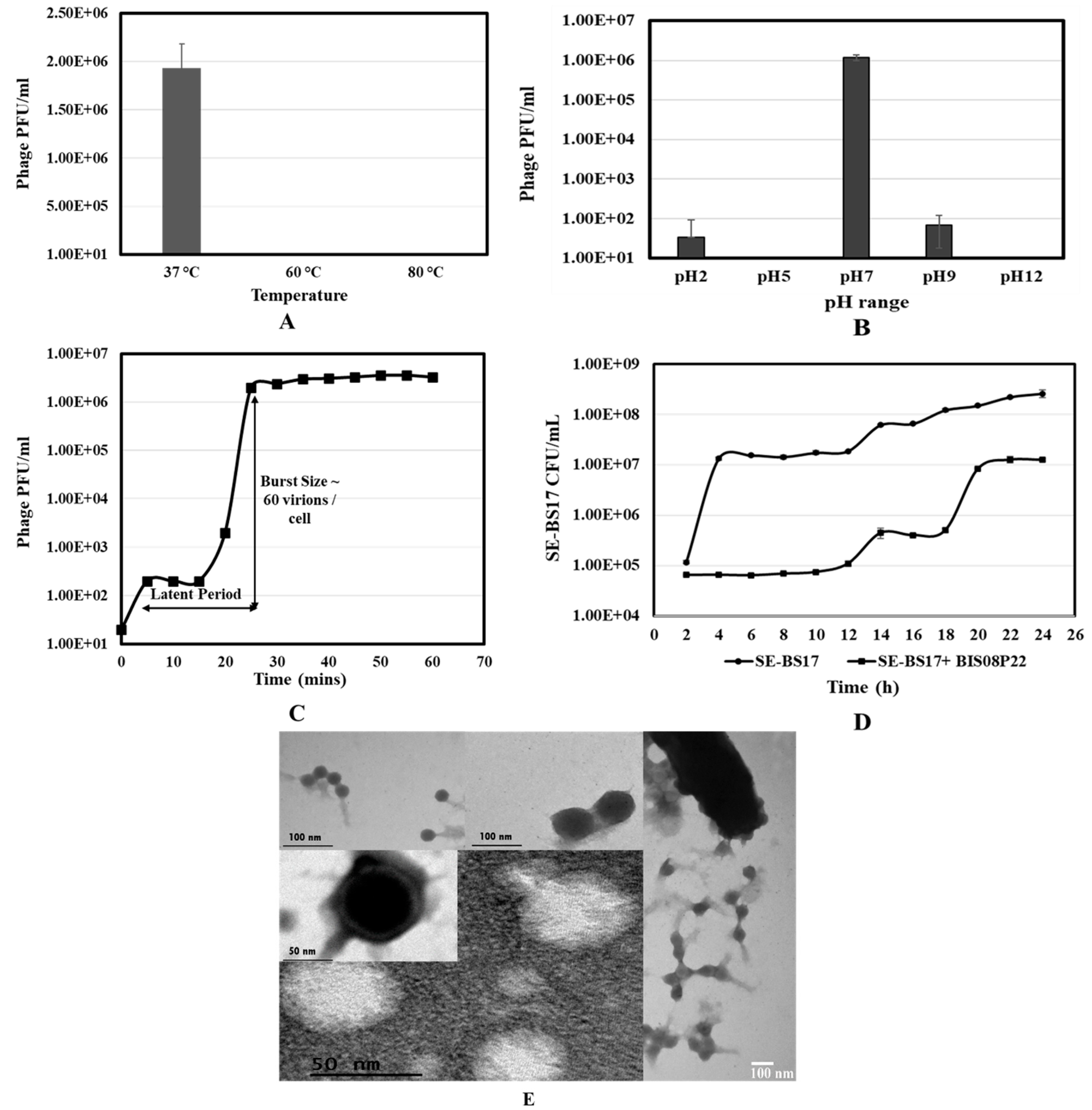
2.3. BIS08 Stability and Growth Curve
2.4. BIS08 Growth Impact on SE-BS17
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.6. BIS08 Genome Sequencing
2.6.1. In silico Terminase Analysis of the BIS08 Large and Small Terminase Subunits
2.7. BIS08 Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Charecterization of BIS08
3.2. Genome analysis of Salmonella Phage BIS08
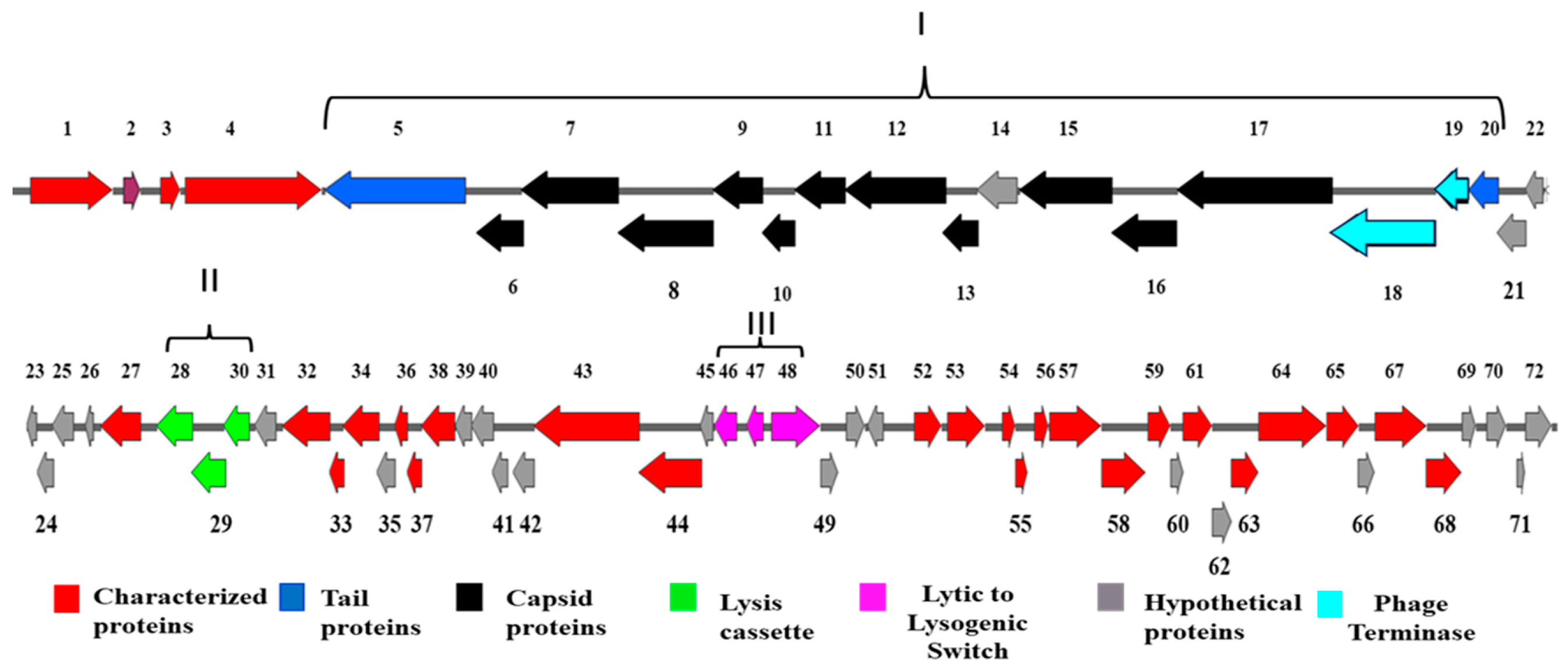
3.2.1. Structural ORFs
3.2.2. Phage Lysis Cassette
3.2.3. Prophage Induction and Maintenance Proteins
3.2.4. Hypothetical and Characterized Proteins of BIS08
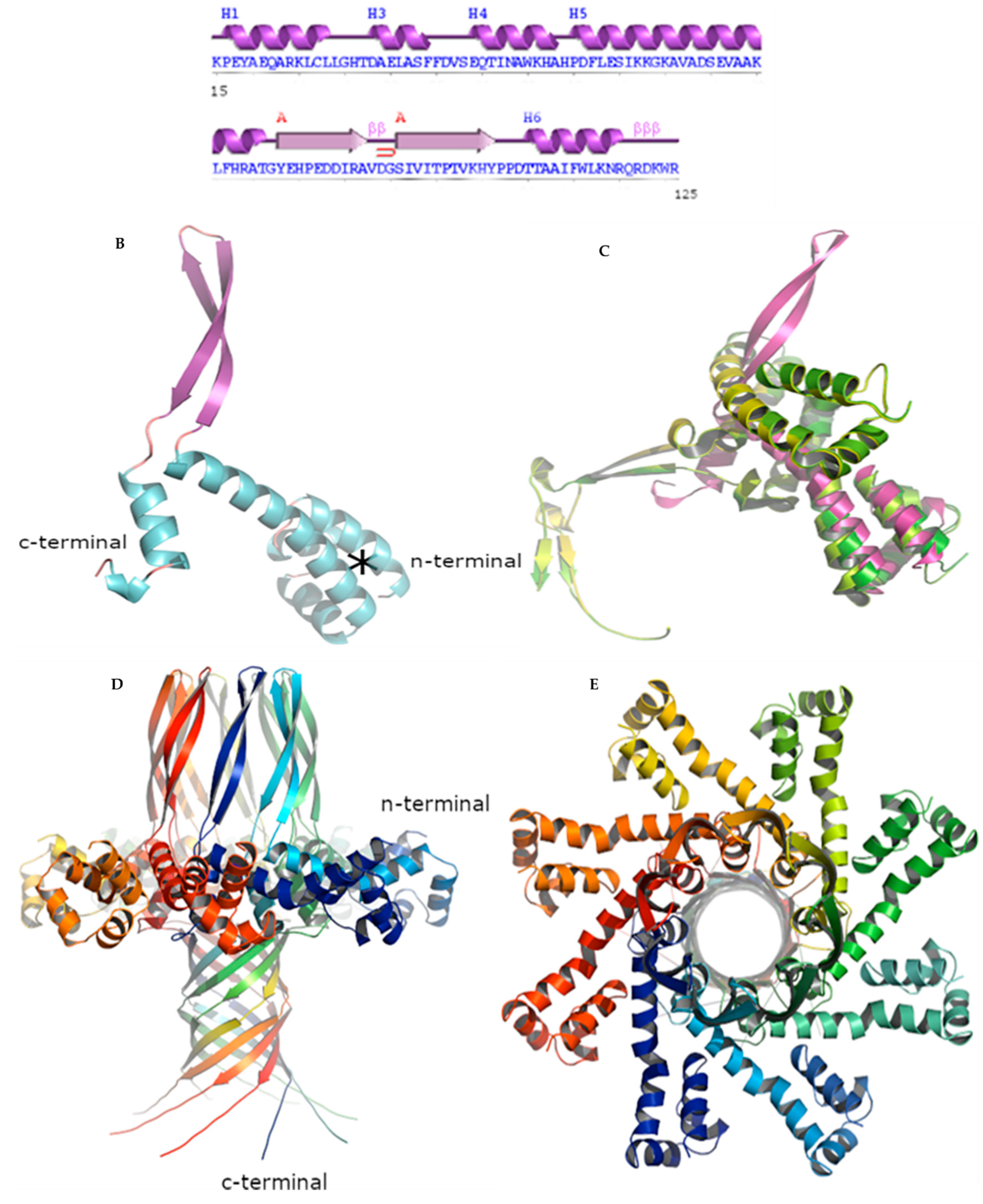
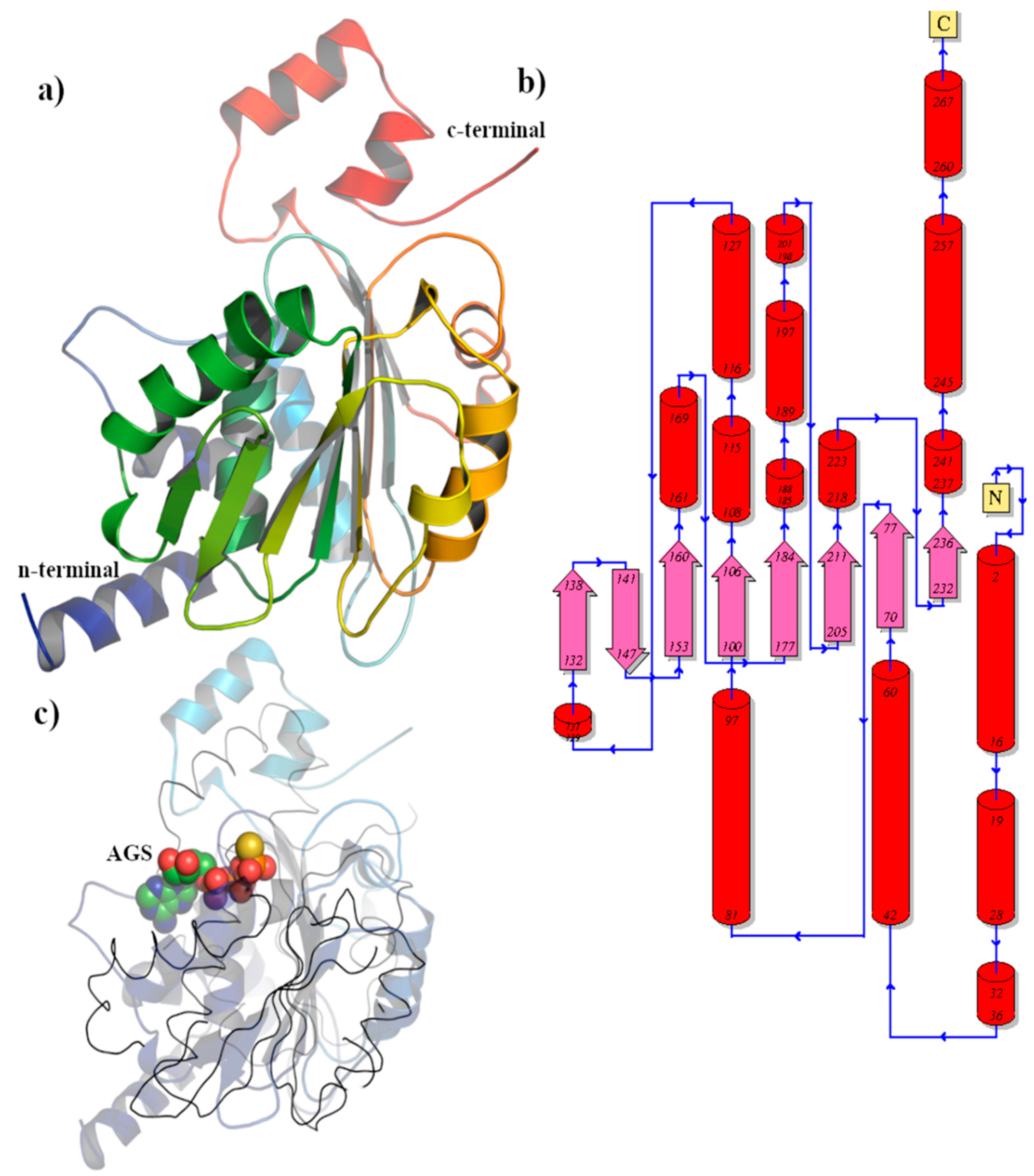
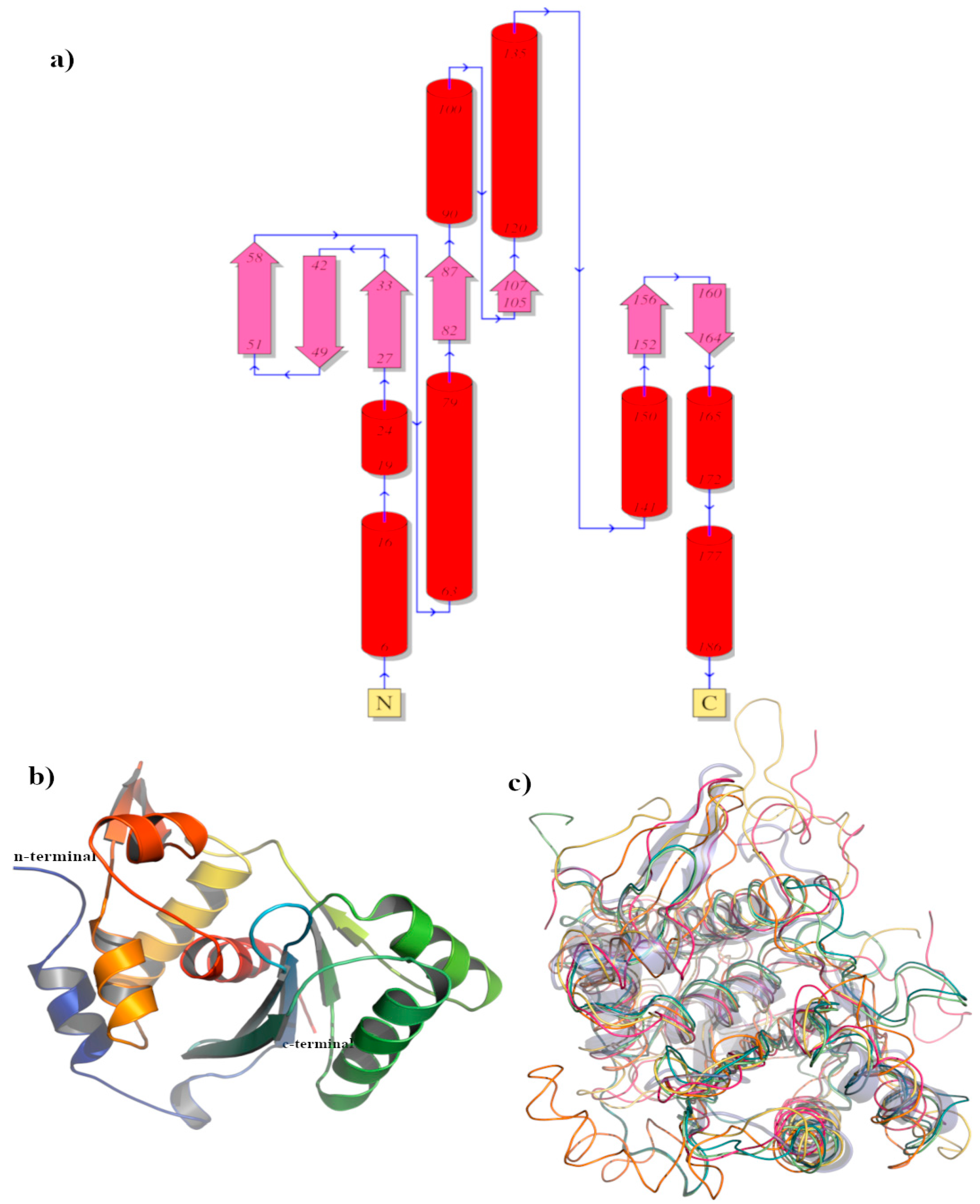
3.2.5. BIS08 Terminase Analysis
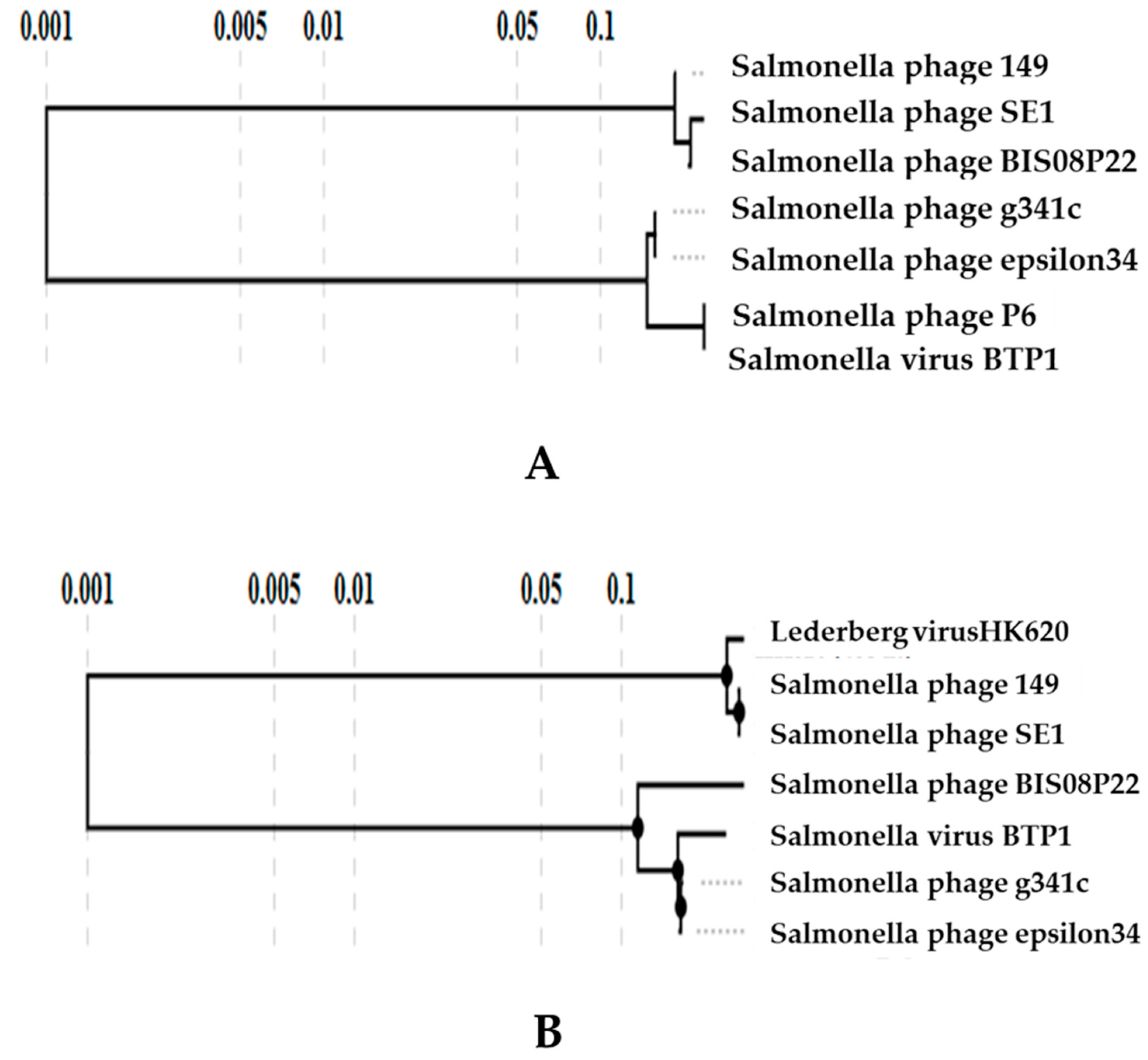
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of BIS08P22
3.3.1. Comparative Genome Analysis with Prophages
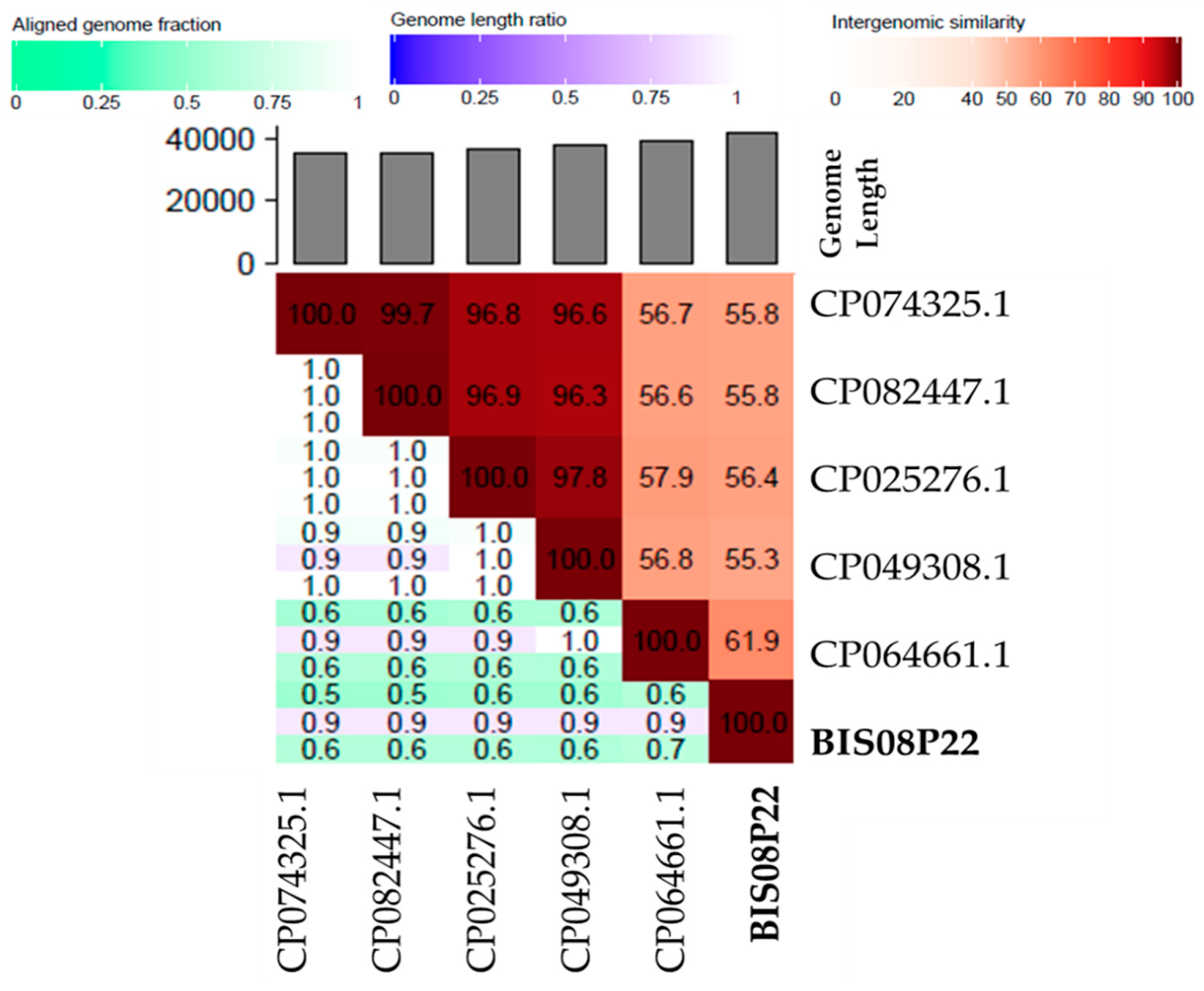
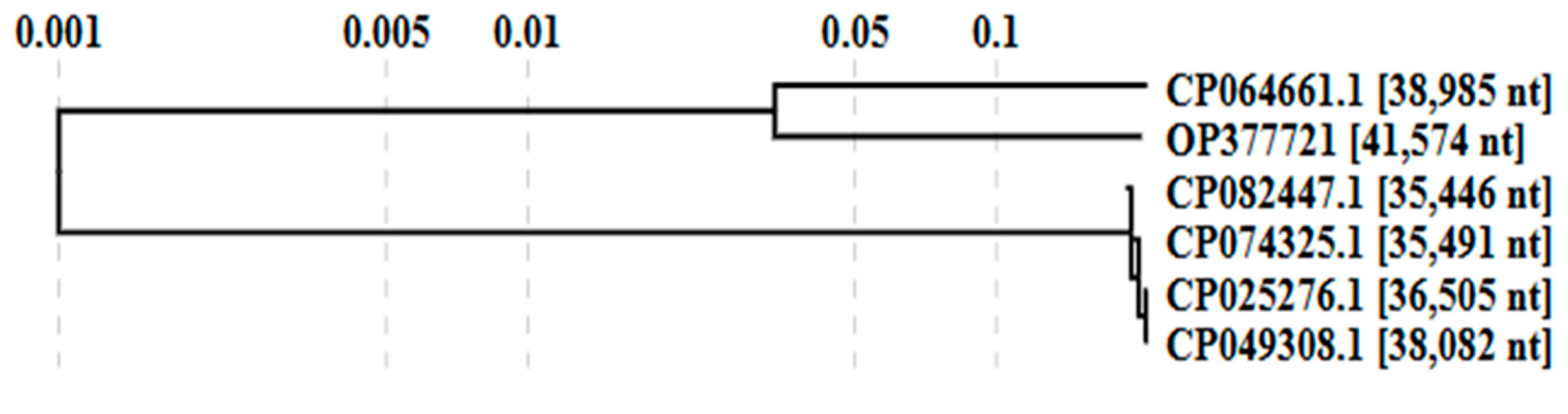
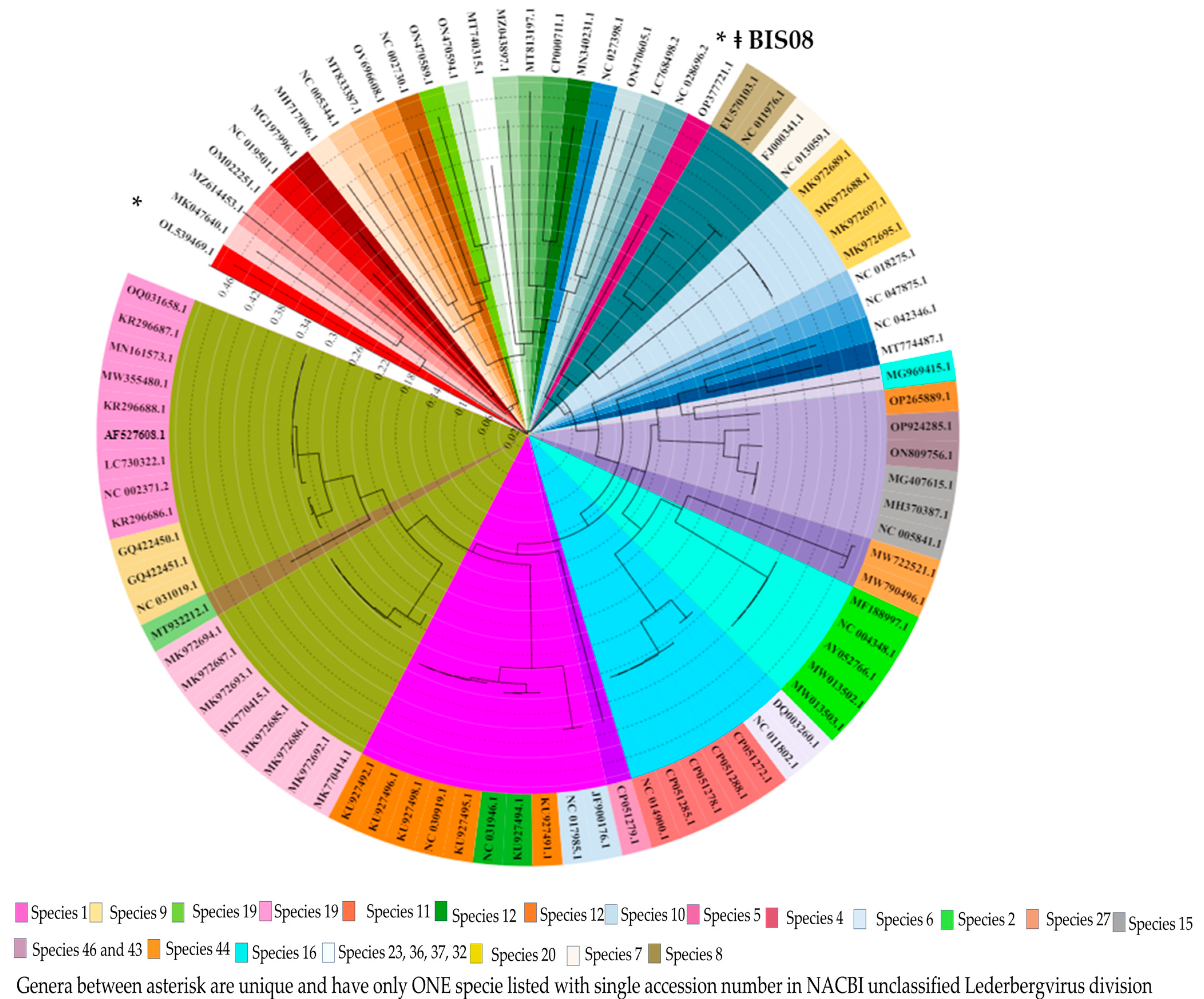
3.3.2. Comparative Genome Analysis with Phage Homologs in NCBI
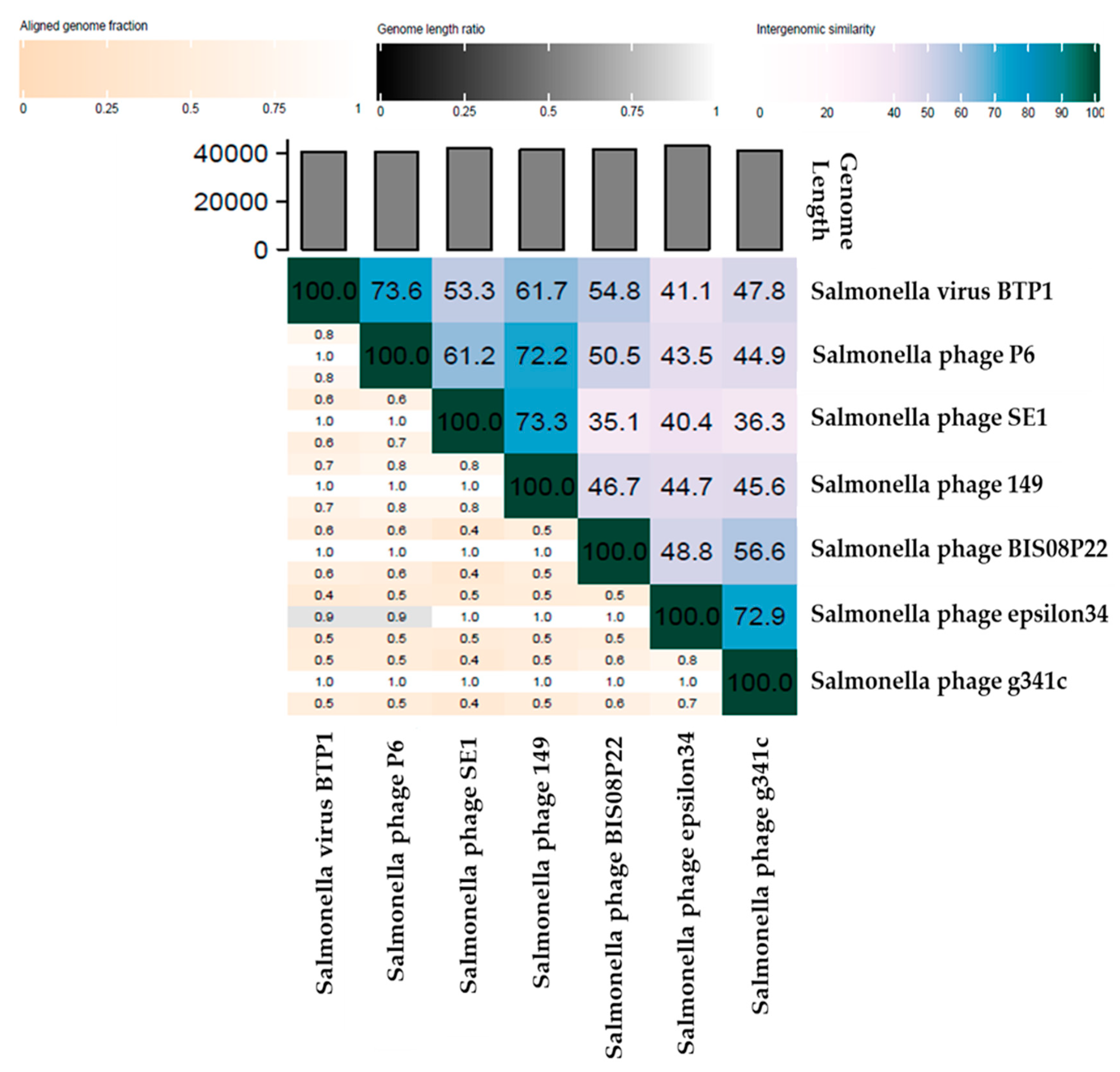
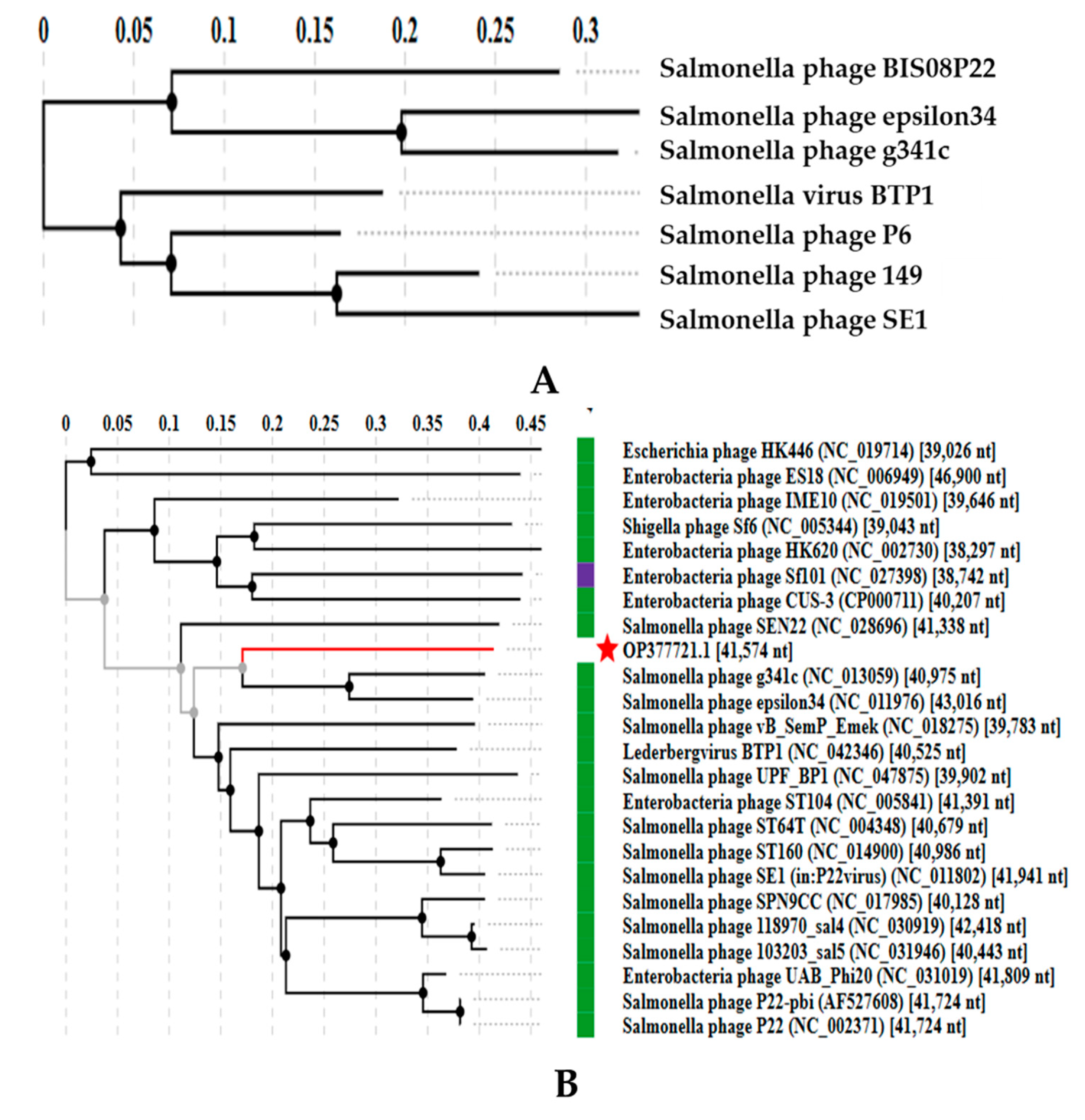
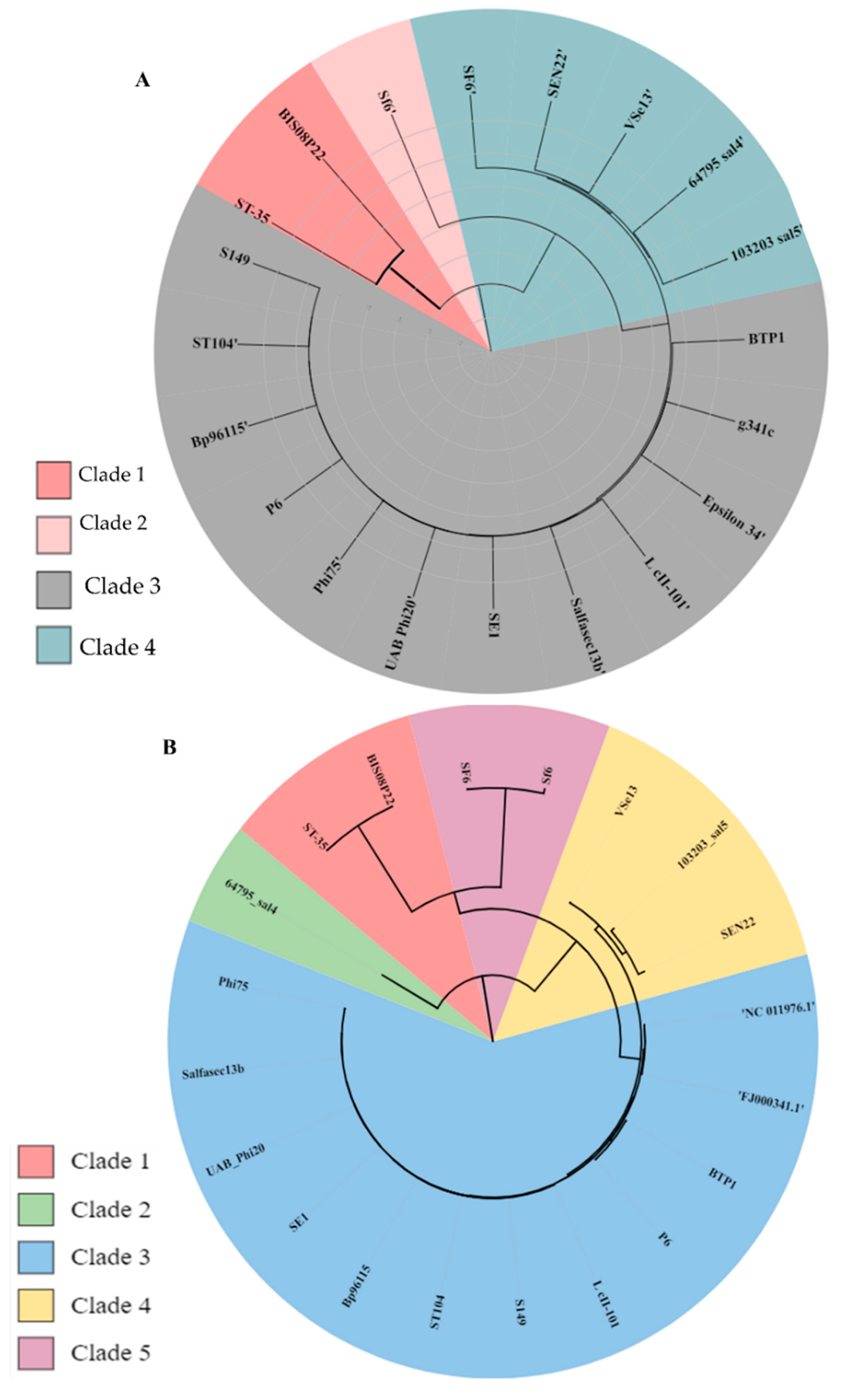
3.3.3. Comparative Analysis of All Lederbergvirus Phages in Relation to BIS08
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- J. E. S. Strange, P. Leekitcharoenphon, F. D. Møller, and F. M. Aarestrup, “Metagenomics analysis of bacteriophages and antimicrobial resistance from global urban sewage,” Sci Rep, vol. 11, no. 1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, “The language of phages,” Nat Rev Microbiol, vol. 15, no. 3, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Howard-Varona, K. R. Hargreaves, S. T. Abedon, and M. B. Sullivan, “MINI REVIEW Lysogeny in nature: mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages Why study lysogeny?,” Nature Publishing Group, vol. 11, 2017.
- C. Groth and M. P. Calos, “Phage integrases: Biology and applications,” Journal of Molecular Biology, vol. 335, no. 3. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Casjens and J. H. Grose, “Contributions of P2- and P22-like prophages to understanding the enormous diversity and abundance of tailed bacteriophages,” Virology, vol. 496, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Z. Hibstu, H. Belew, Y. Akelew, and H. M. Mengist, “Phage Therapy: A Different Approach to Fight Bacterial Infections,” Biologics: Targets and Therapy, vol. 16. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Harrison and M. A. Brockhurst, “Ecological and Evolutionary Benefits of Temperate Phage: What Does or Doesn’t Kill You Makes You Stronger,” BioEssays, vol. 39, no. 12. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. L. W. Zajdowicz and R. K. Holmes, “Phage Conversion and the Role of Bacteriophage and Host Functions in Regulation of Diphtheria Toxin Production by Corynebacterium diphtheriae,” 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Sakaguchi et al., “The genome sequence of Clostridium botulinum type C neurotoxin-converting phage and the molecular mechanisms of unstable lysogeny,” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 102, no. 48, 2005. [CrossRef]
- E. F. Boyd, M. R. Carpenter, and N. Chowdhury, “Mobile effector proteins on phage genomes,” Bacteriophage, vol. 2, no. 3, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Mirold et al., “Isolation of a temperate bacteriophage encoding the type III effector protein SopE from an epidemic Salmonella typhimurium strain,” 1999. [Online]. Available: www.pnas.org.
- P. L. Wagner and M. K. Waldor, “MINIREVIEW Bacteriophage Control of Bacterial Virulence,” Society, vol. 70, no. 8, 2002. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Miao and S. I. Miller, “Bacteriophages in the evolution of pathogen-host interactions,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 96, no. 17. 1999. [CrossRef]
- C. Wendling et al., “Tripartite species interaction: eukaryotic hosts suffer more from phage susceptible than from phage resistant bacteria,” BMC Evol Biol, vol. 17, no. 1, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Turner et al., “Abolishment of morphology-based taxa and change to binomial species names: 2022 taxonomy update of the ICTV bacterial viruses subcommittee,” Arch Virol, vol. 168, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. N. Chiang, J. R. Penadés, and J. Chen, “Genetic transduction by phages and chromosomal islands: The new and noncanonical,” PLoS Pathog, vol. 15, no. 8, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. J. Walker et al., “Changes to virus taxonomy and the Statutes ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2020),” Arch Virol, vol. 165, no. 11, 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. J. Walker et al., “Changes to virus taxonomy and to the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2021),” Arch Virol, vol. 166, no. 9, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhu, J. Shang, C. Peng, and Y. Sun, “Phage family classification under Caudoviricetes: A review of current tools using the latest ICTV classification framework,” Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 13. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Catalano, “Viral Genome Packaging Machines,” in Viral Genome Packaging Machines: Genetics, Structure, and Mechanism, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Susskind and D. Botstein, “Molecular genetics of bacteriophage P22,” Microbiological Reviews, vol. 42, no. 2. 1978. [CrossRef]
- Botstein, “Synthesis and maturation of phage P22 DNA. I. Identification of intermediates,” J Mol Biol, vol. 34, no. 3, 1968. [CrossRef]
- V. B. Rao and M. Feiss, “The bacteriophage DNA packaging motor,” Annual Review of Genetics, vol. 42. 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. Sattar et al., “Phenotypic characterization and genome analysis of a novel Salmonella Typhimurium phage having unique tail fiber genes,” Sci Rep, vol. 12, no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Seul, J. J. Müller, D. Andres, E. Stettner, U. Heinemann, and R. Seckler, “Bacteriophage P22 tailspike: Structure of the complete protein and function of the interdomain linker,” Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, vol. 70, no. 5, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Steinbacher et al., “Phage P22 tailspike protein: Crystal structure of the head-binding domain at 2.3 Å, fully refined structure of the endorhamnosidase at 1.56 Å resolution, and the molecular basis of O-antigen recognition and cleavage,” J Mol Biol, vol. 267, no. 4, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Y. Te Liao, F. Liu, X. Sun, R. W. Li, and V. C. H. Wu, “Complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli phage vB_EcoS Sa179lw, isolated from surface water in a producegrowing area in northern California,” Genome Announc, vol. 6, no. 27, 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Jerse and J. B. Kaper, “The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid,” Infect Immun, vol. 59, no. 12, 1991. [CrossRef]
- M. Mirdita, K. Schütze, Y. Moriwaki, L. Heo, S. Ovchinnikov, and M. Steinegger, “ColabFold: making protein folding accessible to all,” Nat Methods, vol. 19, no. 6, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhao et al., “Crystal structure of the DNA-recognition component of the bacterial virus Sf6 genome-packaging machine,” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 107, no. 5, 2010. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhao, Y. N. Kamau, T. E. Christensen, and L. Tang, “Structural and functional studies of the phage Sf6 terminase small subunit reveal a DNA-spooling device facilitated by structural plasticity,” J Mol Biol, vol. 423, no. 3, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Jumper et al., “Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold,” Nature, vol. 596, no. 7873, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Holm, “Using Dali for Protein Structure Comparison,” in Methods in Molecular Biology, 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. J. Hilbert, J. A. Hayes, N. P. Stone, C. M. Duffy, B. Sankaran, and B. A. Kelch, “Structure and mechanism of the ATPase that powers viral genome packaging,” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 112, no. 29, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhao, T. E. Christensen, Y. N. Kamau, and L. Tang, “Structures of the phage Sf6 large terminase provide new insights into DNA translocation and cleavage,” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 110, no. 20, 2013. [CrossRef]
- L. Holm, “DALI and the persistence of protein shape,” Protein Science, vol. 29, no. 1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Laskowski, J. Jabłońska, L. Pravda, R. S. Vařeková, and J. M. Thornton, “PDBsum: Structural summaries of PDB entries,” Protein Science, vol. 27, no. 1, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Sun et al., “The Structure of the Phage T4 DNA Packaging Motor Suggests a Mechanism Dependent on Electrostatic Forces,” Cell, vol. 135, no. 7, 2008. [CrossRef]
- H. K. H. Fung et al., “Structural basis of DNA packaging by a ring-type ATPase from an archetypal viral system,” Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 50, no. 15, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhao et al., “Two distinct modes of metal ion binding in the nuclease active site of a viral DNA-packaging terminase: Insight into the two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism,” Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 43, no. 22, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Dong et al., “Structural basis of nucleosome deacetylation and DNA linker tightening by Rpd3S histone deacetylase complex,” Cell Res, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Daudén, J. Martín-Benito, J. C. Sánchez-Ferrero, M. Pulido-Cid, J. M. Valpuesta, and J. L. Carrascosa, “Large terminase conformational change induced by connector binding in bacteriophage T7,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 288, no. 23, pp. 16998–17007, 2013.
- M. Adriaenssens and J. Rodney Brister, “How to name and classify your phage: An informal guide,” Viruses, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Letunic and P. Bork, “Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation,” Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 49, no. W1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- “An investigation on the nature of ultra-microscopic viruses by Twort FW, L.R.C.P. Lond., M.R.C.S. (From the Laboratories of the Brown Institution, London) ,” Bacteriophage, vol. 1, no. 3, 2011. [CrossRef]
- V. S. Gummalla, Y. Zhang, Y. Te Liao, and V. C. H. Wu, “The Role of Temperate Phages in Bacterial Pathogenicity,” Microorganisms, vol. 11, no. 3. 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. V. Davies, C. Winstanley, J. L. Fothergill, and C. E. James, “The role of temperate bacteriophages in bacterial infection,” FEMS Microbiology Letters, vol. 363, no. 5. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Q. Chen et al., “Bacteriophage and Bacterial Susceptibility, Resistance, and Tolerance to Antibiotics,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 14, no. 7. 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. Turner, A. M. Kropinski, and E. M. Adriaenssens, “A Roadmap for Genome-Based Phage Taxonomy.,” Viruses, vol. 13, no. 3, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L.-M. Bobay, E. P. C. Rocha, and M. Touchon, “The adaptation of temperate bacteriophages to their host genomes.,” Mol Biol Evol, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 737–751, Apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, Y. Te Liao, A. Salvador, X. Sun, and V. C. H. Wu, “Prediction, Diversity, and Genomic Analysis of Temperate Phages Induced From Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains,” Front Microbiol, vol. 10, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Jeon and J. Ahn, “Evaluation of phage adsorption to Salmonella Typhimurium exposed to different levels of pH and antibiotic,” Microb Pathog, vol. 150, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Gildea, J. A. Ayariga, B. K. Robertson, and R. Villafane, “P22 Phage Shows Promising Antibacterial Activity under Pathophysiological Conditions,” Archives of Microbiology & Immunology, vol. 06, no. 01, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Moraru, A. Varsani, and A. M. Kropinski, “VIRIDIC—A novel tool to calculate the intergenomic similarities of prokaryote-infecting viruses,” Viruses, vol. 12, no. 11, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Xiao et al., “Assembly and Capsid Expansion Mechanism of Bacteriophage P22 Revealed by High-Resolution Cryo-EM Structures,” Viruses, vol. 15, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- King, D. Botstein, S. Casjens, W. Earnshaw, S. Harrison, and E. Lenk, “Structure and assembly of the capsid of bacteriophage P22.,” Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, vol. 276, no. 943, 1976. [CrossRef]
- E. B. Gilcrease, D. A. Winn-Stapley, F. C. Hewitt, L. Joss, and S. R. Casjens, “Nucleotide sequence of the head assembly gene cluster of bacteriophage L and decoration protein characterization,” J Bacteriol, vol. 187, no. 6, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Roy, A. Bhardwaj, P. Datta, G. C. Lander, and G. Cingolani, “Small terminase couples viral DNA binding to genome-packaging ATPase activity,” Structure, vol. 20, no. 8, 2012. [CrossRef]
- G. Fermin, S. Mazumdar-Leighton, and P. Tennant, “Chapter 9 - Viruses of Prokaryotes, Protozoa, Fungi, and Chromista,” in Viruses, P. Tennant, G. Fermin, and J. E. Foster, Eds., Academic Press, 2018, pp. 217–244. [CrossRef]
- S. Sattar et al., “Genome Analysis and Therapeutic Evaluation of a Novel Lytic Bacteriophage of Salmonella Typhimurium: Suggestive of a New Genus in the Subfamily Vequintavirinae,” Viruses, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 241, 2022.
- H. Bao, H. Zhang, and R. Wang, “Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages of Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum,” Poult Sci, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Y. E. Gencay, T. Birk, M. C. H. Sørensen, and L. Brøndsted, “Methods for isolation, purification, and propagation of bacteriophages of Campylobacter jejuni,” in Methods in Molecular Biology, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Yamamoto, B. M. Alberts, R. Benzinger, L. Lawhorne, and G. Treiber, “Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification,” Virology, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 734–744, 1970. [CrossRef]
- M. Kropinski, “Practical Advice on the One-Step Growth Curve.,” Methods Mol Biol, vol. 1681, pp. 41–47, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Capra, A. Quiberoni, and J. Reinheimer, “Phages of Lactobacillus casei/paracasei: Response to environmental factors and interaction with collection and commercial strains,” J Appl Microbiol, 2006. [CrossRef]
- G. O’Flynn, A. Coffey, G. F. Fitzgerald, and R. P. Ross, “The newly isolated lytic bacteriophages st104a and st104b are highly virulent against Salmonella enterica,” J Appl Microbiol, 2006. [CrossRef]
- P. Bryant, G. Pozzati, and A. Elofsson, “Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2,” Nat Commun, vol. 13, no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. C. Schrödinger, “The PyMOL molecular graphics system, version 1.3 r1.” August, 2010.
- P. Meier-Kolthoff and M. Göker, “VICTOR: genome-based phylogeny and classification of prokaryotic viruses,” Bioinformatics, vol. 33, no. 21, pp. 3396–3404, 2017.
- Y. Nishimura, T. Yoshida, M. Kuronishi, H. Uehara, H. Ogata, and S. Goto, “ViPTree: the viral proteomic tree server,” Bioinformatics, vol. 33, no. 15, pp. 2379–2380, 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Davis, D. Seto, and P. Mahadevan, “CoreGenes5.0: An Updated User-Friendly Webserver for the Determination of Core Genes from Sets of Viral and Bacterial Genomes,” Viruses, vol. 14, no. 11, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Yukgehnaish et al., “PhageLeads: Rapid Assessment of Phage Therapeutic Suitability Using an Ensemble Machine Learning Approach,” Viruses, vol. 14, no. 2, 2022. [CrossRef]
| Organism | CHAIN | Z-scorea | R.M.S.D.b | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oshimavirus P7426 | 4ZNK-A | 20.9 | 2.8 | Phage terminase large subunit Gene Names: P74p84 EC: 3.6.4 (UniProt), 3.1.21 (UniProt) |
| Byrnievirus HK97 | 6Z6D-A | 20.1 | 3.1 | Terminase large subunit |
| Lederbergvirus Sf6 | 4IEE-A | 18.4 | 2.7 | Gene 2 protein |
| Tequatrovirus T4 | 3CPE-A | 18.3 | 3.1 | Large subunit terminase EC : 3.6.4 (UniProt), 3.1.21 (UniProt) |
| Organism | CHAIN | Z-scorea | R.M.S.D.b | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas phage | 8DKR-B | 22.5 | 1.9 | Large terminase protein Gene names: vbpaeme217_00005 EC : 3.1 |
| Lederbergvirus Sf6 | 4IEE-A | 21.2 | 2.2 | Gene 2 protein |
| Byrnievirus HK97 | 6Z6D-A | 16.3 | 2.8 | Terminase large subunit |
| Tequatrovirus T4 | 3CPE-A | 16.0 | 2.6 | DNA packaging protein gp17 |
| Escherichia phage T7 | 4BIL-A | 16.0 | 2.6 | DNA maturase b, Gene Names: 19 EC: 3.6.4 (UniProt), 3.1.21 (UniProt) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





