Submitted:
02 October 2023
Posted:
02 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
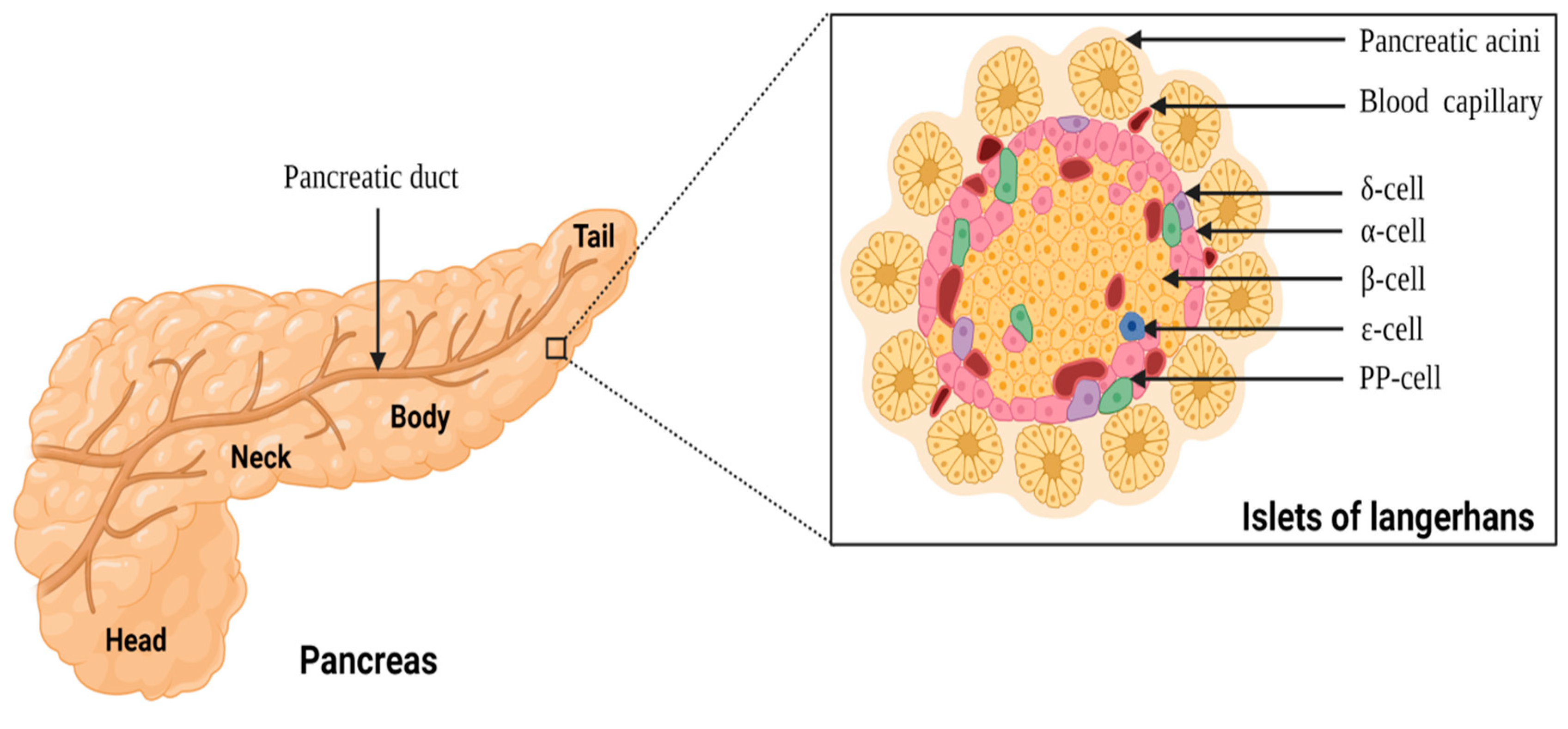
Anatomy of pancreas and the islets of Langerhans
A brief overview of type 1 diabetes
Current treatment options towards management of T1DM
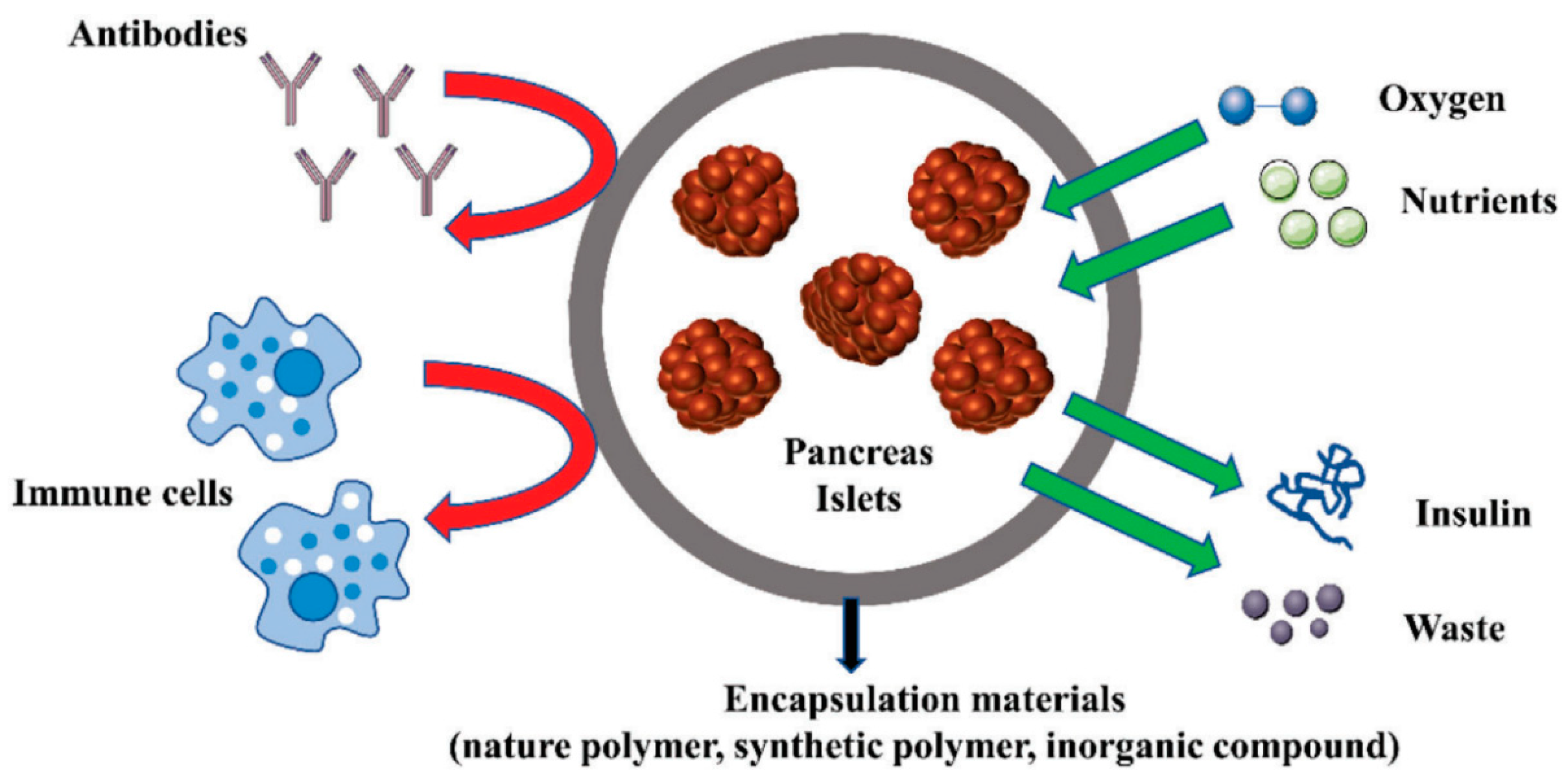
Islet encapsulation and the need for 3D bioprinting technology
3D bioprinting and types of bioprinting
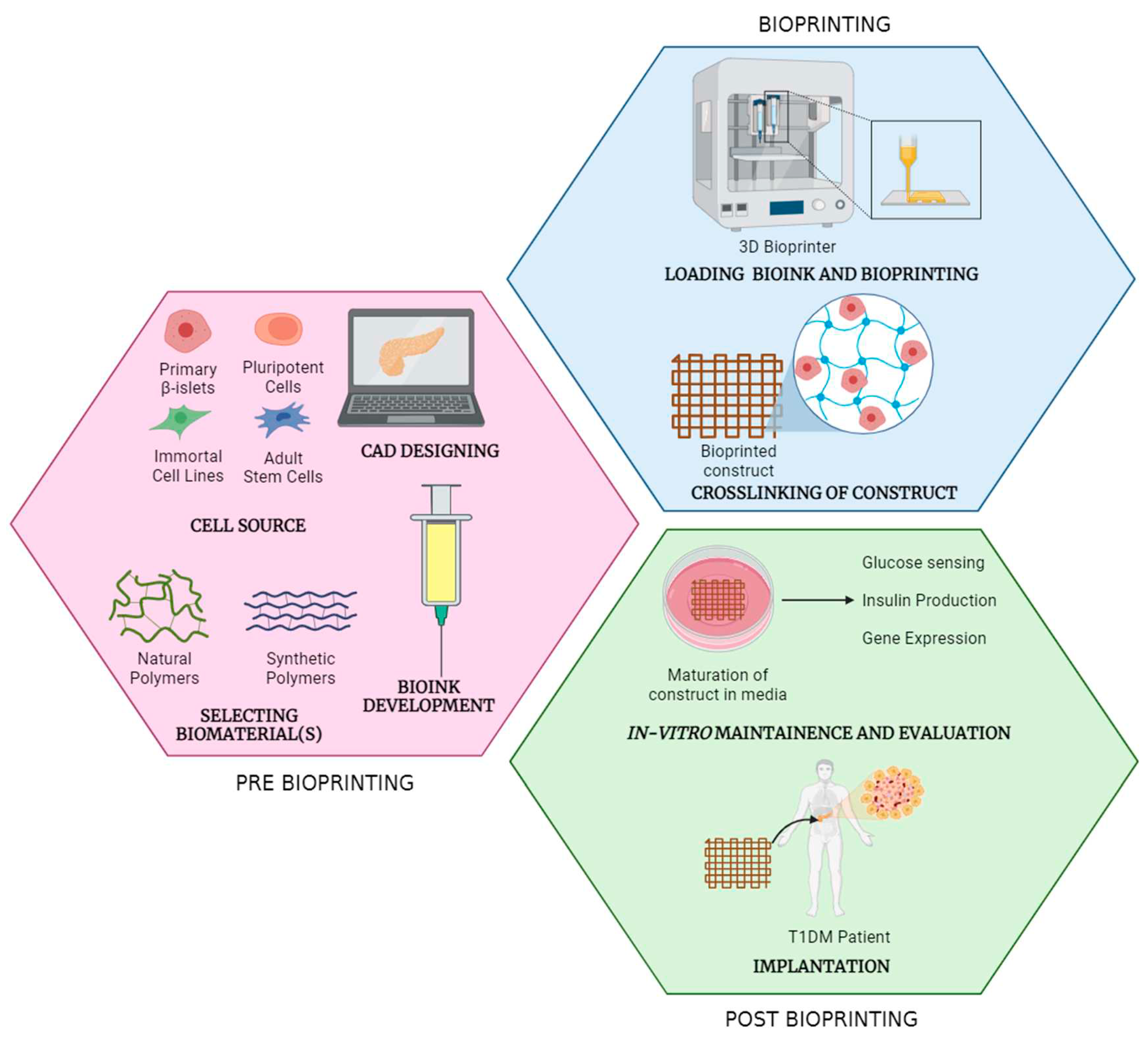
Stages of bioprinting process
Pre-bioprinting
Bioprinting
Post-bioprinting
Types of bioprinting
Extrusion-based bioprinting
Inkjet-based bioprinting
Laser-assisted bioprinting
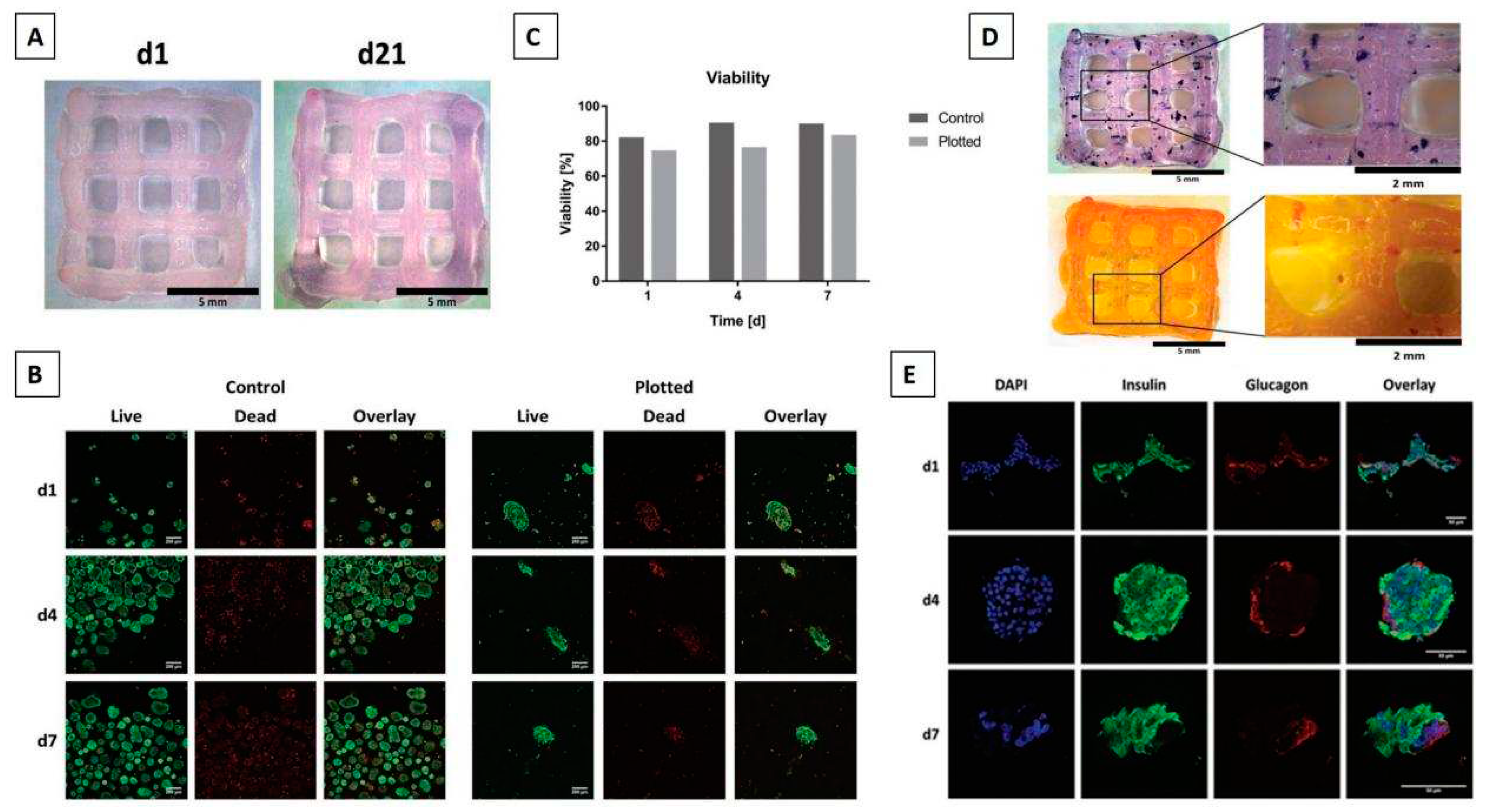
3D bioprinting of pancreas
Essential considerations in bioink development
Cells: the building blocks of bioartificial pancreas
Main cells
Supporting cells
Biopolymers used for bioink development
Alginate
Gelatin
pdECM
Hyaluronic acid
PLA
PCL
Growth factors
Strategies to recapitulate pancreatic function in bioprinted tissue
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical approval
Consent to participate
Consent to publication
Availability of data and materials
Conflicts of Interest
Copyright
Abbreviations
| 3D | three dimensional |
| ADSCs | adipose-derived stem cells |
| ASCs | adult stem cells |
| CAD | computer-assisted designing |
| dECM | decellularized extracellular matrix |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| DTZ | dithizone |
| EBB | extrusion-based bioprinting |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| FDA | Food Drug Administration |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| GelMA | gelatin methacroyl |
| HAMA | hyaluronic acid methacrylate |
| hiPSCs | human induced pluripotent stem cells |
| HUVECs | human umbilical vein-derived endothelial cells |
| iPSCs | induced pluripotent stem cells |
| LAB | laser-assisted bioprinting |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stem cells |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| pdECM | pancreatic-derived extracellular matrix |
| PLA | polylactic acid |
| PP-cells | pancreatic protein cells |
| RGD | arginine-glycine-aspartic acid |
| T1DM | type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| Tregs | regulatory T-cells |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Standring, S. Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Am J Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 2703–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Kulenović, A.; Sarač-Hadžihalilović, A. Blood vessels distribution in body and tail of pancreas- a comparative study of age related variation. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010, 10, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.R.; Daniel, P.M.; Fraser, P.A. The pancreas as a single organ: the influence of the endocrine upon the exocrine part of the gland. Gut. 1981, 22, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarles, H. The exocrine pancreas. Int Rev Physiol. 1977, 12, 173–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karpińska, M.; Czauderna, M. Pancreas—its functions, disorders, and physiological impact on the mammals’ organism. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 807632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, Xavier G. The cells of the islets of Langerhans. J Clin Med. 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, S.J.; Hauge-Evans, A.C.; Jones, P.M. Insulin-secreting cell lines: potential for research and diabetes therapy. In Cellular endocrinology in health and disease; Ulloa-Aguirre, A., Conn, P.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 239–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, O.; Berman, D.M.; Kenyon, N.S.; Ricordi, C.; Berggren, P.O.; Caicedo, A. The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissova, M.; Fowler, M.J.; Nicholson, W.E.; Chu, A.; Hirshberg, B.; Harlan, D.M.; et al. Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005, 53, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromada, J.; Franklin, I.; Wollheim, C.B. α-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr Rev. 2007, 28, 84–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, K.S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.A.; et al. Role of insulin in health and disease: an update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrojo e Drigo, R.; Jacob, S.; García-Prieto, C.F.; Zheng, X.; Fukuda, M.; Nhu, H.T.T.; et al. Structural basis for delta cell paracrine regulation in pancreatic islets. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, N.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Kodama, S. Development and characteristics of pancreatic epsilon cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zielinski, M.C.; Misawa, R.; Wen, P.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, C.Z.; et al. Quantitative analysis of pancreatic polypeptide cell distribution in the human pancreas. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e55501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichii, H.; Inverardi, L.; Pileggi, A.; Molano, R.D.; Cabrera, O.; Caicedo, A.; et al. A novel method for the assessment of cellular composition and beta-cell viability in human islet preparations. Am J Transplant. 2005, 5, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, D.; Meda, P.; Morel, P.; Matthey-Doret, D.; Caille, D.; Toso, C.; et al. Expression and secretion of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor are regulated by proinflammatory cytokines in human pancreatic islet cells. Diabetologia. 2005, 48, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, L.; Unger, R.H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975, 306, 1243–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsen, S.L.; Hegre, O.D.; Parsons, J.A.; McEvoy, R.C.; Elde, R.P. Pancreatic islet cell hormones distribution of cell types in the islet and evidence for the presence of somatostatin and gastrin within the D cell. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976, 24, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, L. The microanatomy of the islets of Langerhans. Metabolism. 1976, 25, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, M.; Santos, C.; Rorsman, P. The vascular architecture of the pancreatic islets: a homage to August Krogh. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2021, 252, 110846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Thompson, M.; Butterworth, E.A.; Boatwright, J.L.; Nair, M.A.; Nasif, L.H.; Nasif, K.; et al. Islet sympathetic innervation and islet neuropathology in patients with type 1 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, K.; Drogemuller, C.J.; Wallace, G.G.; Coates, P.T. Bioprinting an artificial pancreas for type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2019, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Metabolic factors, genetics factors, and lifestyle in relation to diabetes: a cross-sectional study using NHANES 2017-March 2020 pre-pandemic. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Medical Imaging, Sanitation and Biological Pharmacy (MISBP 2022), Chengdu, China., 9–10 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mobasseri, M.; Shirmohammadi, M.; Amiri, T.; Vahed, N.; Hosseini Fard, H.; Ghojazadeh, M. Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Promot Perspect. 2020, 10, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.B.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, D.Y. 3D bioprinting for artificial pancreas organ. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018, 1064, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero-Piloña, A.; Raskin, P. Idiopathic type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2001, 15, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.G.; Hummel, M.; Schenker, M.; Bonifacio, E. Autoantibody appearance and risk for development of childhood diabetes in offspring of parents with type 1 diabetes: the 2-year analysis of the German BABYDIAB Study. Diabetes. 1999, 48, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilonen, J.; Hammais, A.; Laine, A.P.; Lempainen, J.; Vaarala, O.; Veijola, R.; et al. Patterns of β-cell autoantibody appearance and genetic associations during the first years of life. Diabetes. 2013, 62, 3636–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, R.A.; Dunne, J.L.; Atkinson, M.A.; Chiang, J.L.; Dabelea, D.; Gottlieb, P.A.; et al. Staging presymptomatic type 1 diabetes: a scientific statement of JDRF, the Endocrine Society, and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, A.; Bruin, J.E.; Arora, P.; Rubin, A.; Batushansky, I.; Asadi, A.; et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troppmann, C. Complications after pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010, 15, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, M.; Parkin, E.; Gruessner, C.; Rodriguez Rilo, H.L. Pancreas vs. islet transplantation: a call on the future. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010, 15, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.P. Islet transplantation as a treatment for diabetes — a work in progress. N Engl J Med. 2004, 350, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, P.J.; Holmes-Walker, D.J.; Goodman, D.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Loudovaris, T.; Gunton, J.E.; et al. Australian Islet Transplant Consortium. Multicenter Australian trial of islet transplantation: improving accessibility and outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2013, 13, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, P.E.; Walker, M.M.; Fink, C.J. Perifusion of isolated rat islets in vitro. Participation of the microtubular system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes. 1972, 21, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.P.; Lanz, K.J.; Sutherland, D.E.; Kendall, D.M. Prevention of diabetes for up to 13 years by autoislet transplantation after pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Diabetes. 2001, 50, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, P.O.; Palm, F.; Andersson, A.; Liss, P. Markedly decreased oxygen tension in transplanted rat pancreatic islets irrespective of the implantation site. Diabetes. 2001, 50, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, W.; Sundberg, B.; Groth, C.G.; Brendel, M.D.; Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; et al. Incompatibility between human blood and isolated islets of Langerhans: a finding with implications for clinical intraportal islet transplantation? Diabetes. 1999, 48, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, L.; Johansson, H.; Lukinius, A.; Berne, C.; Foss, A.; Källen, R.; et al. Production of tissue factor by pancreatic islet cells as a trigger of detrimental thrombotic reactions in clinical islet transplantation. Lancet. 2002, 360, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, W.; Groth, C.G.; Larsson, R.; Nilsson, B.; Korsgren, O. Isolated human islets trigger an instant blood mediated inflammatory reaction: implications for intraportal islet transplantation as a treatment for patients with type 1 diabetes. Ups J Med Sci. 2000, 105, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, C.B.; Cure, P.; Tharavanij, T.; Baidal, D.A.; Alejandro, R. Current challenges in islet transplantation. Curr Diab Rep. 2008, 8, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, T.; Shea, L.D. Advances in islet encapsulation technologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Barr, G.; Faucher, K.M.; Sun, X.L.; Safley, S.A.; Weber, C.J.; et al. A Membrane-mimetic barrier for islet encapsulation. Transplant Proc. 2004, 36, 1206–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, M.; Storrs, R.; Li, S.; Liang, O.; Laugenour, K.; Dorian, R.; et al. Function and viability of human islets encapsulated in alginate sheets: in vitro and in vivo culture. Transplant Proc. 2011, 43, 3265–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Z.L.; Kerby, A.; King, A.J.; Jones, P.M.; Pickup, J.C. Nano-scale encapsulation enhances allograft survival and function of islets transplanted in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012, 55, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Chiu, A.; Sahay, G.; Doloff, J.C.; Dholakia, N.; Thakrar, R.; et al. Core–shell hydrogel microcapsules for improved islets encapsulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2013, 2, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, H.A.; Kendall, W.F., Jr.; Darrabie, M.; Opara, E.C. Prevention of morphological changes in alginate microcapsules for islet xenotransplantation. J Investig Med. 2001, 49, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.N.; Rosenberg, L. Maintenance of beta-cell function and survival following islet isolation requires re-establishment of the islet-matrix relationship. J Endocrinol. 1999, 163, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; You, X.; Wu, J. Advances in encapsulation and delivery strategies for islet transplantation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021, 10, e2100965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V., Atala. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Yu, Y. Bioprinting toward organ fabrication: challenges and future trends. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013, 60, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygili, E.; Dogan-Gurbuz, A.A.; Yesil-Celiktas, O.; Draz, M.S. 3D bioprinting: a powerful tool to leverage tissue engineering and microbial systems. Bioprinting. 2020, 18, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Yue, K.; Aleman, J.; et al. 3D Bioprinting for Tissue and Organ Fabrication. Ann Biomed Eng 2017, 45, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, K.; Norotte, C.; Marga, F.; Murphy, K.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Forgacs, G. Tissue engineering by self-assembly and bio-printing of living cells. Biofabrication. 2010, 2, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.; Yang, Y.Y. Building blocks to the future of regenerative medicine: organoid bioprinting. Matter. 2021, 4, 2659–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Li, C.W.; Kuo, C.L.; Shih, T.L.; Chen, J.J. Improved synthesis of asymmetric curcuminoids and their assessment as antioxidants. Molecules. 2022, 27, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Barui, A.; Wu, Y.; Ozbolat, V.; Moncal, K.K.; Ozbolat, I.T. Essential steps in bioprinting: from pre-to post-bioprinting. Biotechnol Adv. 2018, 36, 1481–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GhavamiNejad, A.; Ashammakhi, N.; Wu, X.Y.; Khademhosseini, A. Crosslinking strategies for 3D bioprinting of polymeric hydrogels. Small. 2020, 16, 2002931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, B.A.; Mulyasasmita, W.; Su, J.; Lampe, K.J.; Heilshorn, S.C. Improving viability of stem cells during syringe needle flow through the design of hydrogel cell carriers. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012, 18, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Nam, J.; Sun, W. Effects of dispensing pressure and nozzle diameter on cell survival from solid freeform fabrication-based direct cell writing. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008, 14, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Basu, B. An overview of hydrogel-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting of soft tissues. J Indian Inst Sci. 2019, 99, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Boland, T.; D’Lima, D.D.; Lotz, M.K. Thermal inkjet printing in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2012, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Dean, D.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Boland, T. Cell damage evaluation of thermal inkjet printed Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010, 106, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkan, U.A.; El Assal, R.; Yildiz, S.E.; Sung, Y.; Trachtenberg, A.J.; Kuo, W.P.; et al. Engineering anisotropic biomimetic fibrocartilage microenvironment by bioprinting mesenchymal stem cells in nanoliter gel droplets. Mol Pharm. 2014, 11, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudapati, H.; Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I. A comprehensive review on droplet-based bioprinting: past, present and future. Biomaterials. 2016, 102, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, C.J.; Gilmore, K.J.; Beirne, S.; McCallum, D.; Wallace, G.G.; In Het Panhuis, M. Bio-ink for on-demand printing of living cells. Biomater Sci. 2013, 1, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Yildiz, A.; El Assal, R.; Chen, P.; Guven, S.; Inci, F.; Demirci, U. Towards artificial tissue models: past, present, and future of 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016, 8, 14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, B.; Guillemot, F. Cell patterning technologies for organotypic tissue fabrication. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.; Deiwick, A.; Schlie, S.; Michael, S.; Gruene, M.; Coger, V.; et al. Skin tissue generation by laser cell printing. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skardal, A.; Atala, A. Biomaterials for integration with 3-D bioprinting. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015, 43, 730–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiele, N.R.; Corr, D.T.; Huang, Y.; Raof, N.A.; Xie, Y.; Chrisey, D.B. Laser-based direct-write techniques for cell printing. Biofabrication 2010, 2, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Pamfil, D.; Stoleru, E.; Baican, M. New developments in medical applications of hybrid hydrogels containing natural polymers. Molecules. 2020, 25, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, J.M.; Rajotte, R.V.; Zimmerman, M.; Rezania, A.; Kin, T.; Dixon, D.E.; et al. Development of an ectopic site for islet transplantation, using biodegradable scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C. Weir, Susan Bonner-Weir, John L Leahy; Islet Mass and Function in Diabetes and Transplantation. Diabetes 1990, 39, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, L. Functional hydrogel bioink, a key challenge of 3D cellular bioprinting. APL Bioeng. 2020, 4, 030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview. Biomater Sci. 2018, 6, 915–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Tan, J.; Huang, L.; Luo, B.; Lu, L.; et al. 3D bioprinting of gellan gum and poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate based hydrogels to produce human-scale constructs with high-fidelity. Mater Des. 2018, 160, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, A.; Levato, R.; D’Este, M.; Piluso, S.; Eglin, D.; Malda, J. Printability and shape fidelity of bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Chem Rev. 2020, 120, 11028–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting. 2020, 20, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Heinrich, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Akpek, A.; Hu, N.; Liu, X.; et al. Extrusion bioprinting of shear-thinning gelatin methacryloyl bioinks. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017, 6, 1601451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzl, K.; Lin, S.; Tytgat, L.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Gu, L.; Ovsianikov, A. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016, 8, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Q.L.; Choong, C. Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: role of porosity and pore size. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulghani, S.; Morouço, P.G. Biofabrication for osteochondral tissue regeneration: bioink printability requirements. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019, 30, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Taneja, M.; Weir, G.C.; Tatarkiewicz, K.; Song, K.H.; Sharma, A.; et al. In vitro cultivation of human islets from expanded ductal tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000, 97, 7999–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
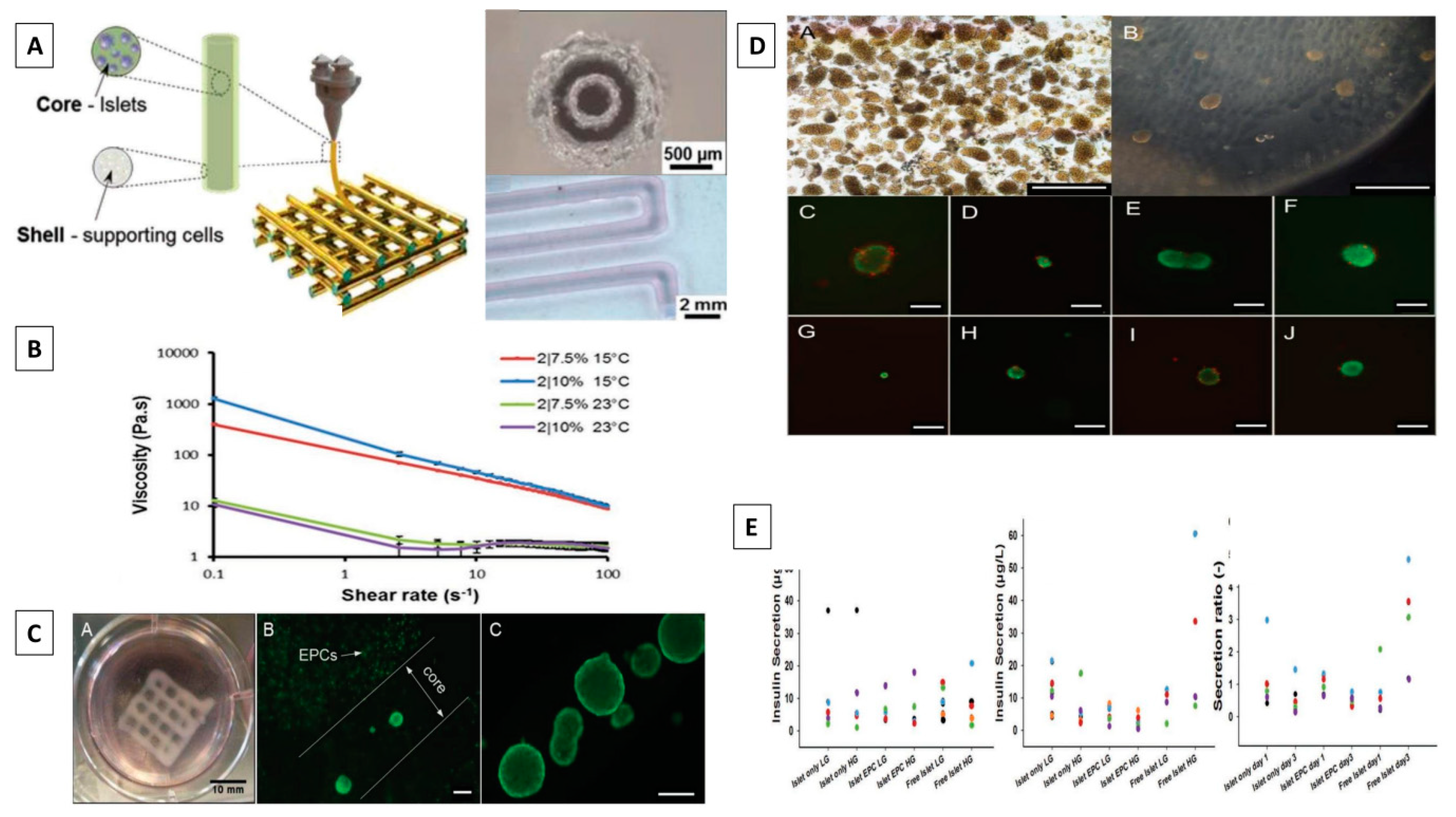
- Hu, S.; Martinez-Garcia, F.D.; Moeun, B.N.; Burgess, J.K.; Harmsen, M.C.; Hoesli, C.; et al. An immune regulatory 3D-printed alginate-pectin construct for immunoisolation of insulin producing β-cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021, 123, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salg, G.A.; Poisel, E.; Neulinger-Munoz, M.; Gerhardus, J.; Cebulla, D.; Bludszuweit-Philipp, C.; et al. Toward 3D-bioprinting of an endocrine pancreas: a building-block concept for bioartificial insulin-secreting tissue. J Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 20417314221091033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cardona, Y.; Echeverri-Cuartas, C.E.; López, M.E.L.; Moreno-Castellanos, N. Chitosan/Gelatin/PVA scaffolds for beta pancreatic cell culture. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Dufour, J.M. Cell lines: valuable tools or useless artifacts. Spermatogenesis. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.G.; Millman, J.R. Applications of iPSC-derived beta cells from patients with diabetes. Cell Rep Med. 2021, 2, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, B.; Parham, L. Ethical issues in stem cell research. Endocr Rev. 2009, 30, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintus, E.; Baldassarri, M.; Perazzo, L.; Natali, S.; Ghinelli, D.; Buda, R. Stem cells in osteochondral tissue engineering. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018, 1058, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala-Cuellar, A.P.; Kang, J.H.; Jeung, E.B.; Choi, K.C. Roles of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue regeneration and immunomodulation. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019, 27, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, A.; Aich, A.; Sanyal, A.; Chandra, A.; Goswami, S. Current landscape of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in COVID induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Acta Sci Microbiol. 2022, 5, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.M.; Bishop, A.E. Stem cells and tissue engineering: past, present, and future. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006, 1068, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavathuparambil Abdul Manaph, N.; Sivanathan, K.N.; Nitschke, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Coates, P.T.; Drogemuller, C.J. An overview on small molecule-induced differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into beta cells for diabetic therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wszoła, M.; Nitarska, D.; Cywoniuk, P.; Gomółka, M.; Klak, M. Stem cells as a source of pancreatic cells for production of 3D bioprinted bionic pancreas in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Cells. 2021, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraza, E.; Coronel, M.M.; Fraker, C.A.; Ricordi, C.; Stabler, C.L. Preventing hypoxia-induced cell death in beta cells and islets via hydrolytically activated, oxygen-generating biomaterials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109, 4245–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifson, N.; Lassa, C.V.; Dixit, P.K. Relation between blood flow and morphology in islet organ of rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1985, 249, E43–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, Å.; Lau, J.; Sandberg, M.; Borg, L.A.H.; Magnusson, P.U.; Carlsson, P.O. Endothelial cell signalling supports pancreatic beta cell function in the rat. Diabetologia. 2009, 52, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafii, S.; Lyden, D. Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003, 9, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, M.D.; Magee, C.C.; Sayegh, M.H. Immunosuppressive strategies in transplantation. Lancet. 1999, 353, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kuhr, C.S.; Zheng, X.X.; Carper, K.; Thomson, A.W.; Reyes, J.D.; et al. New insights into mechanisms of spontaneous liver transplant tolerance: the role of Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Am J Transplant. 2008, 8, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidt, S.; Wood, K.J. Biomarkers of operational tolerance in solid organ transplantation. Expert Opin Med Diagn. 2012, 6, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann N, Sawitzki B. Treg therapy in transplantation: How and when will we do it? Curr Transplant Rep. 2015, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurchy, A.N.; Bushell, A.; Levings, M.K.; Wood, K.J. Moving to tolerance: clinical application of T regulatory cells. Semin Immunol. 2011, 23, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Ma, L.; Zhao, M.; Huang, G.; Mirenda, V.; Dorling, A.; et al. Ex vivo expanded human regulatory T cells delay islet allograft rejection via inhibiting islet-derived monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production in CD34+ stem cells-reconstituted NOD-scid IL2rγnull mice. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e90387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.C.; Hester, J.; Nadig, S.N.; Zhang, W.; Trzonkowski, P.; Gray, D.; et al. Ex vivo expanded human regulatory T cells can prolong survival of a human islet allograft in a humanized mouse model. Transplantation. 2013, 96, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, E.; Barzad, M.S.; Mohamadnia, S.; Tavakoli, O.; Mehrdadfar, A. A review on alginate-based bioinks, combination with other natural biomaterials and characteristics. J Biomater Appl. 2022, 37, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axpe, E.; Oyen, M.L. Applications of alginate-based bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2016, 17, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, B.S.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Bechtel, P.J.; Jafri, H.; Narayan, R.; Imam, S.H.; et al. Cold water fish gelatin films: effects of cross-linking on thermal, mechanical, barrier, and biodegradation properties. Eur Polym J. 2008, 44, 3748–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, S.; Tabish, T.A.; Liaqat, U.; Ozbolat, I.T.; Rizwan, M. Advances in gelatin bioinks to optimize bioprinted cell functions. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023, 12, e2203148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; San, B.H.; Turner, N.J.; White, L.J.; Faulk, D.M.; Badylak, S.F.; et al. Molecular assessment of collagen denaturation in decellularized tissues using a collagen hybridizing peptide. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Midha, S.; Sharma, A.; Ghosh, S. Silk-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018, 7, 1701204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Highley, C.B.; Rodell, C.B.; Sun, W.; Burdick, J.A. 3D printing of shear-thinning hyaluronic acid hydrogels with secondary cross-linking. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016, 2, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, J.; Luo, X.S. Hyaluronic acid: a versatile biomaterial in tissue engineering. Plast Aesthet Res. 2017, 4, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabek, O.M.; Farina, M.; Fraga, D.W.; Afshar, S.; Ballerini, A.; Filgueira, C.S.; et al. Three-dimensional printed polymeric system to encapsulate human mesenchymal stem cells differentiated into islet-like insulin-producing aggregates for diabetes treatment. J Tissue Eng. 2016, 7, 2041731416638198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, B.; Gullotti, D.; Mangraviti, A.; Utsuki, T.; Brem, H. Polylactic acid (PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016, 107, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhabelal, V.J.; Ray, S.S. Poly (ε-caprolactone) nanocomposite scaffolds for tissue engineering: a brief overview. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Irie, S. Preparation of stable alginate gel beads in electrolyte solutions using Ba2+ and Sr2+. Biotechnol Tech. 1988, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Alginate as immobilization matrix for cells. Trends Biotechnol. 1990, 8, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, P.; Faas, M.M.; Strand, B.; Calafiore, R. Alginate-based microcapsules for immunoisolation of pancreatic islets. Biomaterials. 2006, 27, 5603–5617. [Google Scholar]
- Draget, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of alginates and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkai, U.; Rotem, A.; de Vos, P. Survival of encapsulated islets: more than a membrane story. World J Transplant. 2016, 6, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicheportiche, D.; Reach, G. In vitro kinetics of insulin release by microencapsulated rat islets: effect of the size of the microcapsules. Diabetologia. 1988, 31, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsgren, O. Islet encapsulation: physiological possibilities and limitations. Diabetes. 2017, 66, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, P.; Marchetti, P. Encapsulation of pancreatic islets for transplantation in diabetes: the untouchable islets. Trends Mol Med. 2002, 8, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshimoto, H.; Imamura, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Tanaka, K. Paracrine effects of adipose-derived stem cells promote lymphangiogenesis in irradiated lymphatic endothelial cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019, 143, 1189e–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, L.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Natural polymers for the microencapsulation of cells. J R Soc Interface. 2014, 11, 20140817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Yao, R.; Ge, Y. An cell-assembly derived physiological 3D model of the metabolic syndrome, based on adipose-derived stromal cells and a gelatin/alginate/fibrinogen matrix. Biomaterials. 2010, 31, 3868–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, R.; Hübner, U.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Mülhaupt, R. Rapid prototyping of scaffolds derived from thermoreversible hydrogels and tailored for applications in tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2002, 23, 4437–4447. [Google Scholar]
- Grassl, E.D.; Oegema, T.R.; Tranquillo, R.T. A fibrin-based arterial media equivalent. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003, 66A, 550–561. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.; Sun, W. Bioprinting endothelial cells with alginate for 3D tissue constructs. J Biomech Eng. 2009, 131, 111002. [Google Scholar]
- Marchioli, G.; van Gurp, L.; van Krieken, P.P.; Stamatialis, D.; Engelse, M.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; et al. Fabrication of three-dimensional bioplotted hydrogel scaffolds for islets of Langerhans transplantation. Biofabrication. 2015, 7, 025009. [Google Scholar]
- Duin, S.; Schütz, K.; Ahlfeld, T.; Lehmann, S.; Lode, A.; Ludwig, B.; et al. 3D Bioprinting of functional islets of Langerhans in an alginate/methylcellulose hydrogel blend. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019, 8, 1801631. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Lim, M.; et al. Three-dimensional dynamic fabrication of engineered cartilage based on chitosan/gelatin hybrid hydrogel scaffold in a spinner flask with a special designed steel frame. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015, 55, 384–392. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, A.; Vu, D.; Larsen, G.F.; Lin, H.Y. Preparation and evaluation of the electrospun chitosan/PEO fibers for potential applications in cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2005, 16, 861–873. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Joisher, H.; Ganguly, A. Polymeric scaffolds for pancreatic tissue engineering: a review. Rev Diabet Stud. 2018, 14, 334–353. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yue, K.; Zhu, K.; Liu, W.; et al. Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink. Biomaterials. 2016, 106, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Carter, S.D.; Renes, M.J.; Kim, J.; Rojas-Canales, D.M.; Penko, D.; et al. Development of a coaxial 3D printing platform for biofabrication of implantable islet-containing constructs. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019, 8, e1801181. [Google Scholar]
- Blomeier, H.; Zhang, X.; Rives, C.; Brissova, M.; Hughes, E.; Baker, M.; Powers, A.C.; Kaufman, D.B.; Shea, L.D.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Polymer scaffolds as synthetic microenvironments for extrahepatic islet transplantation. Transplantation. 2006, 82, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brissova, M.; Powers, A.C. Revascularization of transplanted islets: Can it be improved? Diabetes. 2008, 57, 2269–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, A.R.; Gala-Lopez, B.; Ziff, O.; Shapiro, A.M.J. Revascularization of transplanted pancreatic islets and role of the transplantation site. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013, 2013, 352315. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Smyth, C.A.; Eckstein, C.; Bilbao, G.; Mays, J.; Eckhoff, D.E.; et al. Cytoprotection of PEG-modified adult porcine pancreatic islets for improved xenotransplantation. Biomaterials. 2005, 26, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Sackett, S.D.; Tremmel, D.M.; Ma, F.; Feeney, A.K.; Maguire, R.M.; Brown, M.E.; et al. Extracellular matrix scaffold and hydrogel derived from decellularized and delipidized human pancreas. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 10452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rana, D.; Zreiqat, H.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ramalingam, M. Development of decellularized scaffolds for stem cell-driven tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017, 11, 942–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, H.; Hu, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, C. Decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds: recent trends and emerging strategies in tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2022, 10, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pati, F.; Jang, J.; Ha, D.H.; Won Kim, S.; Rhie, J.W.; Shim, J.H.; et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat Commun. 2014, 5, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, G.S.; Dziki, J.L.; Badylak, S.F. Extracellular matrix-based materials for regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mater. 2018, 3, 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Hwang, D.G.; Shim, I.K.; Kim, S.C.; Jang, J. Pancreatic tissue-derived extracellular matrix bioink for printing 3D cell-laden pancreatic tissue constructs. J Vis Exp. 2019, e60434. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.G.; Jo, Y.; Kim, M.; Yong, U.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.M.; et al. A 3D bioprinted hybrid encapsulation system for delivery of human pluripotent stem cell-derived pancreatic islet-like aggregates. Biofabrication. 2021, 14, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idaszek, J.; Volpi, M.; Paradiso, A.; Nguyen Quoc, M.; Górecka, Ż.; Klak, M.; et al. Alginate-based tissue-specific bioinks for multi-material 3D-bioprinting of pancreatic islets and blood vessels: a step towards vascularized pancreas grafts. Bioprinting. 2021, 24, e00163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemshekhar, M.; Thushara, R.M.; Chandranayaka, S.; Sherman, L.S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Emerging roles of hyaluronic acid bioscaffolds in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016, 86, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, B.; Zhou, D.; Shao, M.; Xu, W.; Zhou, Y. Photocrosslinking maleilated hyaluronate/methacrylated poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous mats for hydrogel wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 155, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szychlinska, M.A.; Bucchieri, F.; Fucarino, A.; Ronca, A.; D’Amora, U. Three-dimensional bioprinting for cartilage tissue engineering: insights into naturally-derived bioinks from land and marine sources. J Funct Biomater. 2022, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
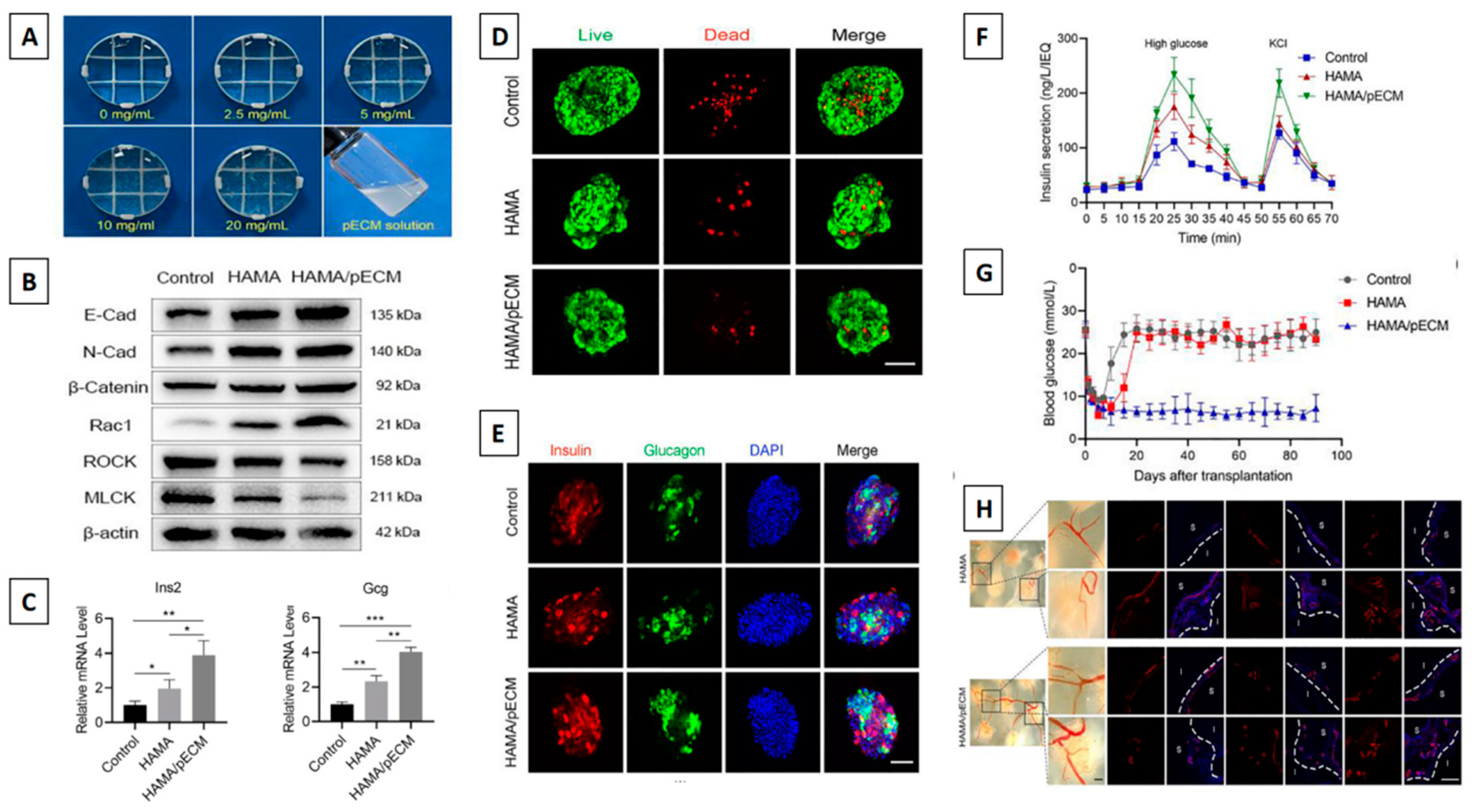
- Cañibano-Hernández, A.; Saenz del Burgo, L.; Espona-Noguera, A.; Orive, G.; Hernández, R.M.; Ciriza, J.; et al. Hyaluronic acid enhances cell survival of encapsulated insulin-producing cells in alginate-based microcapsules. Int J Pharm. 2019, 557, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, S.; Williams, J.; Rawal, S.; Ramachandran, K.; Stehno-Bittel, L. Hyaluronic acid/collagen hydrogel as an alternative to alginate for long-term immunoprotected islet transplantation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017, 23, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velten, F.; Laue, C.; Schrezenmeir, J. The effect of alginate and hyaluronate on the viability and function of immunoisolated neonatal rat islets. Biomaterials. 1999, 20, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Johnson, M.; Creagh-Flynn, J.; Xu, Q.; Tai, H.; et al. Green synthetic approach for photo-cross-linkable methacryloyl hyaluronic acid with a tailored substitution degree. Biomacromolecules. 2020, 21, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.H.Y.; Kade, J.C.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Ruberu, K.; Mukherjee, P.; Yue, Z.; et al. 3D hybrid printing platform for auricular cartilage reconstruction. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2020, 6, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, F.; Xue, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Hyaluronic acid methacrylate/pancreatic extracellular matrix as a potential 3D printing bioink for constructing islet organoids. Acta Biomater. 2022, 165, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices — a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, T.; Declercq, H.; De Geyter, N.; Cornelissen, R.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; et al. Plasma surface modification of polylactic acid to promote interaction with fibroblasts. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012, 24, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.T.; Martins, A.; Dias, I.R.; Viegas, C.A.; Neves, N.M.; Gomes, M.E.; et al. Synergistic effect of scaffold composition and dynamic culturing environment in multilayered systems for bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012, 6, e24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
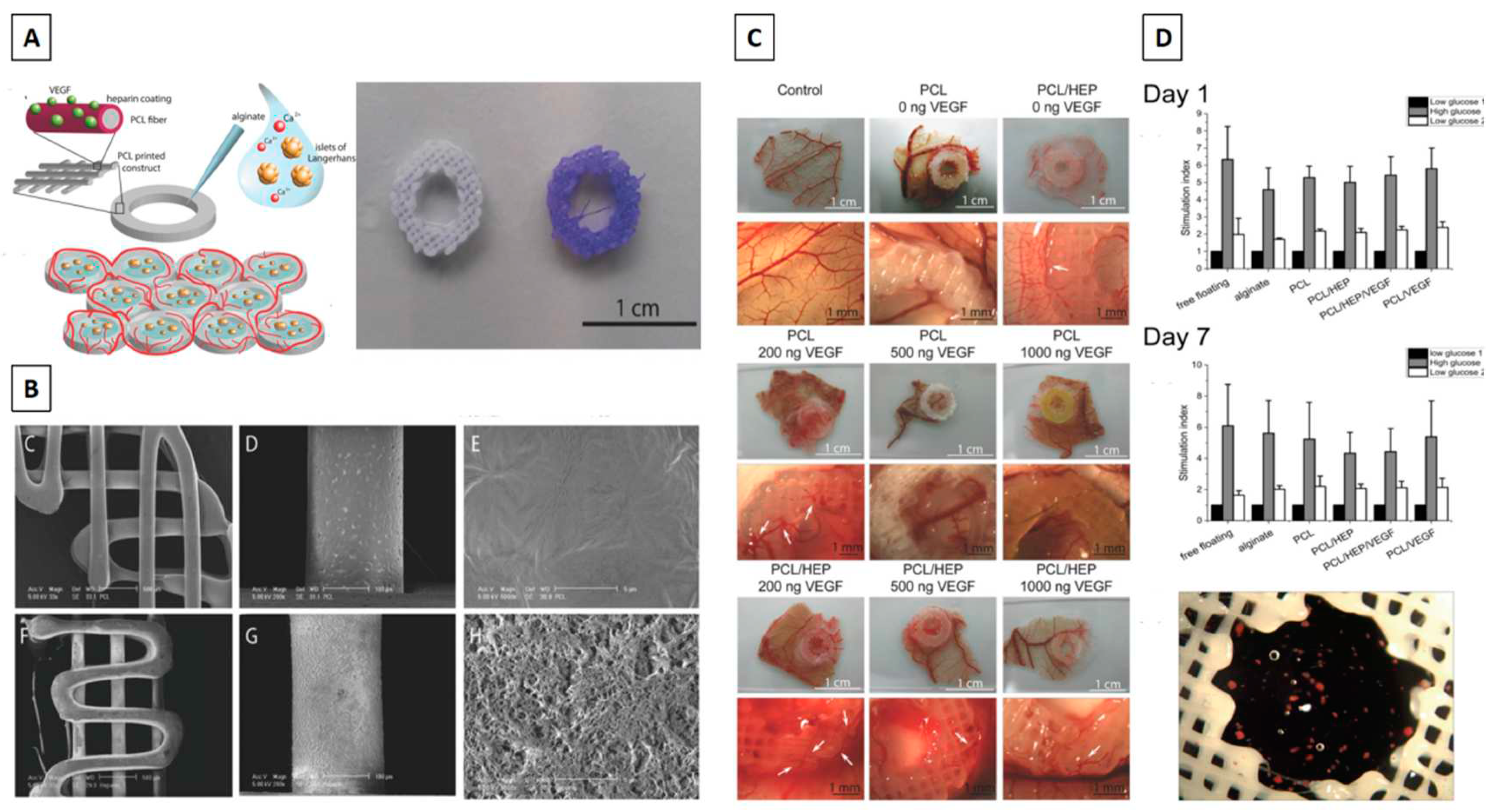
- Sabek, O.M.; Farina, M.; Fraga, D.W.; Afshar, S.; Ballerini, A.; Filgueira, C.S.; et al. Three-dimensional printed polymeric system to encapsulate human mesenchymal stem cells differentiated into islet-like insulin-producing aggregates for diabetes treatment. J Tissue Eng. 2016, 7, 2041731416638198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Millman, J.R. Economic 3D-printing approach for transplantation of human stem cell-derived β-like cells. Biofabrication. 2016, 9, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Ballerini, A.; Fraga, D.W.; Nicolov, E.; Hogan, M.; Demarchi, D.; et al. 3D printed vascularized device for subcutaneous transplantation of human islets. Biotechnol J. 2017, 12, 1700169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, E.; Gu, G.; McLaughlin, M.; Brown, D.; Brekken, R.; Murtaugh, L.C.; et al. Role of VEGF-A in vascularization of pancreatic islets. Curr Biol. 2003, 13, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, F.; Samiei, M.; Adibkia, K.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S. Biodegradable and biocompatible polymers for tissue engineering application: a review. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.M.; Lakey, J.R.; Ryan, E.A.; Korbutt, G.S.; Toth, E.; Warnock, G.L.; et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000, 343, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioli, G.; Luca, A.D.; de Koning, E.; Engelse, M.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; et al. Hybrid polycaprolactone/alginate scaffolds functionalized with VEGF to promote de novo vessel formation for the transplantation of islets of Langerhans. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016, 5, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koons, G.L.; Mikos, A.G. Progress in three-dimensional printing with growth factors. J Control Release. 2019, 295, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bras, S.; Miralles, F.; Basmaciogullari, A.; Czernichow, P.; Scharfmann, R. Fibroblast growth factor 2 promotes pancreatic epithelial cell proliferation via functional fibroblast growth factor receptors during embryonic life. Diabetes. 1998, 47, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlund, H. Pancreatic organogenesis — developmental mechanisms and implications for therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2002, 3, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawdon, B.B.; Andrew, A. Effects of tri-iodothyronine (T3), insulin, insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFβ1) on the proportion of insulin cells in cultured embryonic chick pancreas. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1998, 198, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapf, J.; Schmid, C.H.; Froesch, E.R. Biological and immunological properties of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984, 13, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, J.; Arany, E.; McDonald, T.J.; Hill, D.J. Apoptosis in the pancreatic islet cells of the neonatal rat is associated with a reduced expression of insulin-like growth factor II that may act as a survival factor. Endocrinology. 1998, 139, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.J.; Strutt, B.; Arany, E.; Zaina, S.; Coukell, S.; Graham, C.F. Increased and persistent circulating insulin-like growth factor II in neonatal transgenic mice suppresses developmental apoptosis in the pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 2000, 141, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: a crucial target for anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes Cancer. 2011, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissova, M.; Shostak, A.; Shiota, M.; Wiebe, P.O.; Poffenberger, G.; Kantz, J.; Powers, A.C. Pancreatic islet production of vascular endothelial growth factor-a is essential for islet vascularization, revascularization, and function. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2974–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, W.; Liu, M.; Sui, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Highly efficient differentiation of human ES cells and iPS cells into mature pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russ, H.A.; Parent, A.V.; Ringler, J.J.; Hennings, T.G.; Nair, G.G.; Shveygert, M.; et al. Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, G.G.; Liu, J.S.; Russ, H.A.; Tran, S.; Saxton, M.S.; Chen, R.; et al. Recapitulating endocrine cell clustering in culture promotes maturation of human stem-cell-derived β cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliuca, F.W.; Millman, J.R.; Gürtler, M.; Segel, M.; Van Dervort, A.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell. 2014, 159, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.Y.; Chan, V.W.; Leung, K.T.; Zhang, X.B.; Wong, A.S.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals that CD9 is a negative marker of glucose-responsive pancreatic β-like cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2020, 15, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, A.; Beattie, G.M.; Cirulli, V.; Lopez, A.D.; Ricordi, C.; Rubin, J.S. Growth factor/matrix-induced proliferation of human adult β-cells. Diabetes. 1995, 44, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumida, Y.; Aoki, T.; Yasuda, D.; Koizumi, T.; Suganuma, C.; Saito, K.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor is constitutively produced by donor-derived bone marrow cells and promotes regeneration of pancreatic β-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005, 333, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipeleers, D.; In’t Veld, P.; Maes, E.; Van De Winkel, M. Glucose-induced insulin release depends on functional cooperation between islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982, 79, 7322–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.; Menegaz, D.; Caicedo, A. Deciphering the complex communication networks that orchestrate pancreatic islet function. Diabetes. 2021, 70, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Singh, Y.P.; Datta, P.; Ozbolat, V.; O’Donnell, A.; Yeo, M.; et al. Strategies for 3D bioprinting of spheroids: a comprehensive review. Biomaterials. 2022, 291, 121881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Chen, S.T.; Malliaras, G.G.; Barone, D.G. Foreign body reaction to implanted biomaterials and its impact in nerve neuroprosthetics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 622524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareta, R.; Sanders, B.; Babbar, P.; Soker, T.; Booth, C.; Mcquilling, J.; et al. Immunoisolation: where regenerative medicine meets solid organ transplantation. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014, 8, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Lee, E.; Ryu, G.R.; Ko, S.H.; Ahn, Y.B.; Song, K.H. Hypoxia increases β-cell death by activating pancreatic stellate cells within the islet. Diabetes Metab J. 2020, 44, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Endo, H.; Okuyama, H.; Takeda, T.; Iwahashi, H.; Imagawa, A.; et al. Cellular hypoxia of pancreatic β-cells due to high levels of oxygen consumption for insulin secretion in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286, 12524–12532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, C.; Campo, F.; Neroni, A.; Piemonti, L.; Citro, A. Bioengineering the vascularized endocrine pancreas: a fine-tuned interplay between vascularization, extracellular-matrix-based scaffold architecture, and insulin-producing cells. Transpl Int. 2022, 35, 10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, J.M.; Jung, J.W.; Shim, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Cho, D.W. 3D printing of composite tissue with complex shape applied to ear regeneration. Biofabrication. 2014, 6, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, H.A.; Moss, S.M.; Hoying, J.B. Methods for vascularization and perfusion of tissue organoids. Mamm Genome. 2022, 33, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, D.T.; Song, W.; Wang, L.H.; Ma, M. Engineering the vasculature for islet transplantation. Acta Biomater. 2019, 95, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankajakshan, D.; Agrawal, D.K. Mesenchymal stem cell paracrine factors in vascular repair and regeneration. J Biomed Technol Res. 2014, 1, 1019104/jbtr2014107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Krishnan, L.; Nunes, S.S.; Church, K.H.; Edgar, L.T.; Boland, E.D.; et al. Determinants of microvascular network topologies in implanted neovasculatures. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012, 32, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Song, D.; Wang, X. 3D Bioprinting for pancreas engineering/manufacturing. Polymers. 2022, 14, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I.T. 3D bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.E.; Beenken-Rothkopf, L.N.; Mirsoian, A.; Kojic, N.; Kaplan, D.L.; Barron, A.E.; et al. Enhanced function of pancreatic islets co-encapsulated with ECM proteins and mesenchymal stromal cells in a silk hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2012, 33, 6691–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, S.G.; Park, J.H.; Nam, H.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, Y.S.; et al. Silk fibroin hydrolysate exerts an anti-diabetic effect by increasing pancreatic β cell mass in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. J Vet Sci. 2012, 13, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, D.G.; Yaneva, Z.L. Antioxidant properties and redox-modulating activity of chitosan and its derivatives: biomaterials with application in cancer therapy. Biores Open Access. 2020, 9, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Gao, X. Antioxidant activity and cytoprotective effect of kappa-carrageenan oligosaccharides and their different derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006, 16, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Phang, S.J.; Kamaruzaman, N.; Salleh, A.; Zawani, M.; Sanyal, A.; et al. Antioxidant biomaterials in cutaneous wound healing and tissue regeneration: a critical review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, C.; Mazumder, I.; Marrazzo, P. Revolutionizing the Use of Honeybee Products in Healthcare: A Focused Review on Using Bee Pollen as a Potential Adjunct Material for Biomaterial Functionalization. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2023, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y. Bee pollen polysaccharide From Rosa rugosa Thunb.(Rosaceae) promotes pancreatic β-cell proliferation and insulin secretion. Frontiers in pharmacology 2021, 12, 688073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomaterial | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate |
|
|
[110,111] |
| Gelatin |
|
|
[112,113] |
| pdECM |
|
|
[114,115] |
| Hyaluronic acid |
|
1. It cannot be utilised in its pure form for bioink development since it lacks printability and is unstable due to its high-water absorption.2. It rapidly gets absorbed in vivo. Hence chemical crosslinking is necessary. | [116,117] |
| PLA |
|
|
[118,119] |
| PCL |
|
|
[120] |
| Sl. No. | Growth factors | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) |
|
[178,179,180] |
| 2. | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) |
|
[181,182] |
| 3. | Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) |
|
[183] |
| 4. | Epidermal growth factor(EGF) |
|
[184,185] |
| 5. | Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) |
|
[185,186,187] |
| 6. | Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) |
|
[188,189] |
| 7. | Transforming growth factor(TGF) |
|
[185] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





