Submitted:
01 October 2023
Posted:
01 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Pharmacokinetic and safety of ellagitannin constituents
3. Catabolism of ellagitannins
4. Absorption and bioavailability of ellagitannins
5. Biodistribution and clearance of ellagitannins
6. Safety of pomegranate and pomegranate products
7. Pomegranate consumption and obesity
| Group | Population / disease induction | PG part or product | PG dose and duration | HDL | LDL | TC | VLDL | HDL-C | LDL-C | VLDL-C | TG | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical studies ( the values are expressed as mean ± SD) | ||||||||||||
| Treated group | Hypertensive subjects | PG juice | 150 ml/day, for 2 weeks | ni | ni | 218.73±42.81 a | ni | 49.27±8.06 a | 127.27±24.22 a | ni | 171.18±78.92 a | [41] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | ni | ni | 187.00±30.27 a | ni | 40.40±6.91 a | 109.40±25.82 a | ni | 165.60±124.32 a | ||
| Treated group | Dyslipidemic patients | PG-seed oil | 800 mg twice daily, for 4 weeks | ni | ni | ni | ni | 1.38±0.44 b | ni | ni | 2.75±1.40 b | [42] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | ni | ni | ni | ni | 1.25±0.26 b | ni | ni | 3.12±1.59 b | ||
| Treated group | COPD |
PG PG juice |
400 ml daily, for 5 weeks |
55.05 ±12.01 a | 130.48±32.29 a | 209.68±39.10 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 170.68±187.10 a | [43] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | 56.75±20.81 a | 116.06±29.14 a | 201.34±32.64 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 137.91±778.22 a | ||
| Treated group |
Obese patients obesity |
PG juice | 120 ml, for 1 month | ni | ni | 4.7±0.7 b | ni | 1.1±0.1 b | 2.9±0.8 b | ni | 1.3±0.3 b | [44] |
| Placebo group | _ | - | ni | ni | 4.8±0.6 b | ni | 1.2±0.2 b | 2.9±0.5 b | ni | 1.2±0.5 b | ||
| Treated group |
Hyper-cholesterolemic patients |
PGE + Simvastatin |
PGE: 1g/day Simvastatin :20mg/day, for 2 months |
ni | ni | 202±29 a | ni | 45 ± 11 a | 129±15 a | ni | 187±138 a | [45] |
| Placebo group | - | - | i | ni | 192±35 a | ni | 46±12 a | 123±27 a | ni | 110±19 a | ||
| Treated group |
PGE + Simvastatin |
PGE: 1g/day Simvastatin : 20 mg/day, for 1 month |
ni | ni | 208 ± 40 a | ni | 47±13 a | 135±37 a | ni | 129±43 a | ||
| Placebo group | _ | _ | ni | ni | 198 ±55 a | ni | 46 ±19 a | 123±38 a | ni | 144±71 a | ||
| Treated group | Hemodialysis patients | PG Juice |
0.7 mM of polyphenols, 3 times/week, for 1 year |
36.8 ± 10.8 a | 100 ± 33.1 a | 167.3 ± 43.5 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 167.3 ± 86.3 a | [46] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | 34.3 ± 15.4 a | 94.3 ± 27.2 a | 165.1 ± 35.8 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 206.1 ± 109.4 a | ||
| Treated group | CHD patients | PG juice |
240 ml/day, for 3 months |
48±11 a | 91±33 a | 170± 42 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 149±107 a | [47] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | 46 ± 12 a | 80±35 a | 157±32 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 155±102 a | ||
| Treated group | Volunteers at high CVD risk | PG Juice | 500 ml/day, for 4 weeks | ni | ni | 5.45±1.0 b | ni | 1.52±0.44 b | 3.31±0.73 b | ni | 1.147±0.39 b | [48] |
| Placebo group | _ | _ | ni | ni | 4.51±0.51 b | ni | 1.46±0.56 b | 2.54±0.79 b | ni | 1.14±0.51 b | ||
| Animal studies (data is reported as mean ± SEM/SE/SD) | ||||||||||||
| Treated group | by adding 10% of lipid in the basal diet | Hydroethanolic extract of PG | 50 mg/kg/day, for 23 days | 89 ± 11 a | 209 ± 23 a | 87 ± 9 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 381 ± 23 a | [49] |
| 100 mg/kg/day, for 23 days | 128 ± 5 a | 145 ± 29 a | 82 ± 5 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 325 ± 43 a | ||||
| 200 mg/kg/day, for 23 days | 179 ± 18 a | 79 ± 8 a | 80 ± 9 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 302 ± 31 a | ||||
| 300 mg/kg/day, for 23 days | 185 ± 20 a | 61 ± 7 a | 81 ± 7 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 210 ± 27 a | ||||
| Control + | _ | _ | 98 ±9 a | 92 ±6 a | 73 ±8 a | ni | ni | ni | ni | 146 ± 21 a | ||
| Treated group | Hyper cholestrolemic diet | PG peel powder | (5%) | 38.40±5.18 a | 40.73±1.85 a | 92.33±4.76 a | 13.20±0.69 a | ni | ni | ni | 66±3.46 a | [50] |
| (10%) | 36.93±5.53 a | 46.67±1.97 a | 96.00±4.11 a | 12.40±0.84 a | ni | ni | ni | 62± 3.69 a | ||||
| (15%) | 41.50±5.98 a | 45.77±2.13 a | 97.67±4.52a | 10.40±0.59 a | ni | ni | ni | 52±3.99 a | ||||
|
PG peel extract |
(1%) | 41.40±5.18 a | 16.33±1.85 a | 75.00± 3.66 a | 17.27±0.79 a | ni | ni | ni | 86.33±4.78 a | |||
| (2%) | 42.93±5.53 a | 9.67±1.97 a | 69.00± 3.89 a | 16.40±0.67 a | ni | ni | ni | 82±4.11 a | ||||
| (3%) | 40.50±5.98 a | 12.77±2.13 a | 70.00± 3.92 a | 16.73±0.64 a | ni | ni | ni | 83.67±5.12 a | ||||
| Control + | _ | - | 41.93±5.53 a | 87.53±1.97 a | 154.33±5.13 a | 24.87±0.77 a | ni | ni | ni | 124.33± 3.70 a | ||
| Treated group | High fat diet | PG peel extract | 200 mg/kg, for 56 days | ni | ni | 172.3 ± 3.94 | ni | 40.03 ± 1.03 | 93.84 ± 3.69 | 38.49 ± 0.62 | 192.4 ± 3 | [51] |
| Control + | _ | - | ni | ni | 271.8 ± 3.94 | ni | 29.30 ± 1.03 | 185.3 ± 3.69 | 57.26 ± 0.62 | 285.5 ± 3 | ||
| Treated group |
Intraperitoneal injection of STZ (60 mg/kg) |
PG flowers extract |
250 mg/kg, for 21 dyas | ni | ni | 124.50 ± 8.62 a | ni | 45.17 ± 4.84 a | 61.67 ± 6.12 a | 17.67 ± 4.50 a | 88.17 ± 7.05 a | [52] |
| 500 mg/kg, for 21 days | ni | ni | 118.67 ± 9.60 a | ni | 48.67 ± 5.16 a | 54.67 ± 4.89 a | 14.34 ± 2.95 a | 72.83 ± 6.52 a | ||||
| Control+ | _ | 0 mg/kg, for 21 days | ni | ni | 292.33 ± 4.64 a | ni | 32.83 ± 4.22 a | 234.34 ± 6.12 a | 25.26 ± 0.93 a | 126.33 ± 4.64 a | ||
| Treated group | Intraperitonial injection of STZ (65 mg/kg) | PG leaves | 50 mg/kg, for 28 days | ni | ni | 162.25 ± 5.28 c | ni | 37.79 ± 1.92 c | 106.22 ± 6.14 c | 18.76 ±0.73 c | 93.845 ± 3.66 c | [53] |
| 100 mg/kg, for 28 days | ni | ni | 142.38 ± 2.70 c | ni | 63.32 ± 3.11 c | 80.36 ± 2.08 c | 15.99 ± 1.57 c | 84.53 ± 4.49 c | ||||
| 200 mg/kg, for28 days | ni | ni | 139.45 ± 1.98 c | ni | 44.54 ± 2.97 c | 60.41 ± 3.57 c | 15.71 ± 1.83 c | 76.25 ± 9.96 c | ||||
| Control+ | - | 0 mg/kg, for 28 days | ni | ni | 229.08 ± 7.51 c | ni | 20.47 ± 1.31 c | 179.50 ± 6.68 c | 29.09 ± 0.70 c | 145.46 ± 3.53 c | ||
| Treated group | Intraperitonial injection of poloxamer 407 | PG flowers | 500 mg/Kg, after 15 h | 6.23 ± 0.39 b | 8.56 ± 0.62 b | 16.9 ± 0.60 b | 2.11 ±0.23 b | ni | ni | ni | 10.57 ± 1.17 b | [54] |
| Control+ | _ | _ | 5.04 ± 0.20 b | 9.9 ± 0.67 b | 18.39 ± 0.63 b | 3.38 ±0.08 b | ni | ni | ni | 16.93 ± 0.75 b | ||
| Treated group | PG flowers | 500 mg/Kg, after 24 h | 6.06 ± 0.29 b | 10.74 ± 0.95 b | 19.72 ± 0.67 b | 2.91 ±0.09 b | ni | ni | ni | 14.56 ± 0.46 b | ||
| Control+ | _ | 0 mg/kg | 5.05 ± 0.17 b | 15.7 ± 0.80 b | 24.28 ± 0.89 b | 3.52 ±0.09 b | ni | ni | ni | 17.66 ± 0.46 b | ||
| Treated group | High cholesterol diet | PG juice |
0.2 mL/animal, for 30 days |
78.58±4.79 a | 19.38±10.34 a | 135.83 ± 13.9 b | 37.87±5.36 a | ni | ni | ni | 189.33 ± 26.81 a | [55] |
| Control + | _ | 67.70±2.34 a | 169.93± 31.90 a | 267 ±31.78 a | 29.37±1.18 a | ni | ni | ni | 146.83 ± 5.88 a | |||
| Treated group | High cholesterol diet | PGME | 200 mg, for 30 day | 1.54±0.208 | 0.58 ± 0.118 | 1.93 ± 0.191 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | ni | ni | ni | 1.05 ± 0.17 | [56] |
| 300 mg, for 30 day | 1.29 ± 0.68 | 0.21 ± 0.057 | 1.63 ± 0.125 | 0.10 ±0.028 | ni | ni | ni | 0.91 ± 0.12 | ||||
| 400 mg, for 30 day | 0.91±0.117 | 0.17 ± 0.049 | 1.04 ±0.159 | 0.07 ±0.026 | ni | ni | ni | 0.46 ± 0.15 | ||||
| Control + | _ | 0 mg | 2.16 ±0.150 | 0.68 ± 0.050 | 2.55 ± 0.211 | 0.27 ±0.072 | ni | ni | ni | 1.17 ± 0.13 | ||
8. Type 2 diabetes and pomegranate consumption
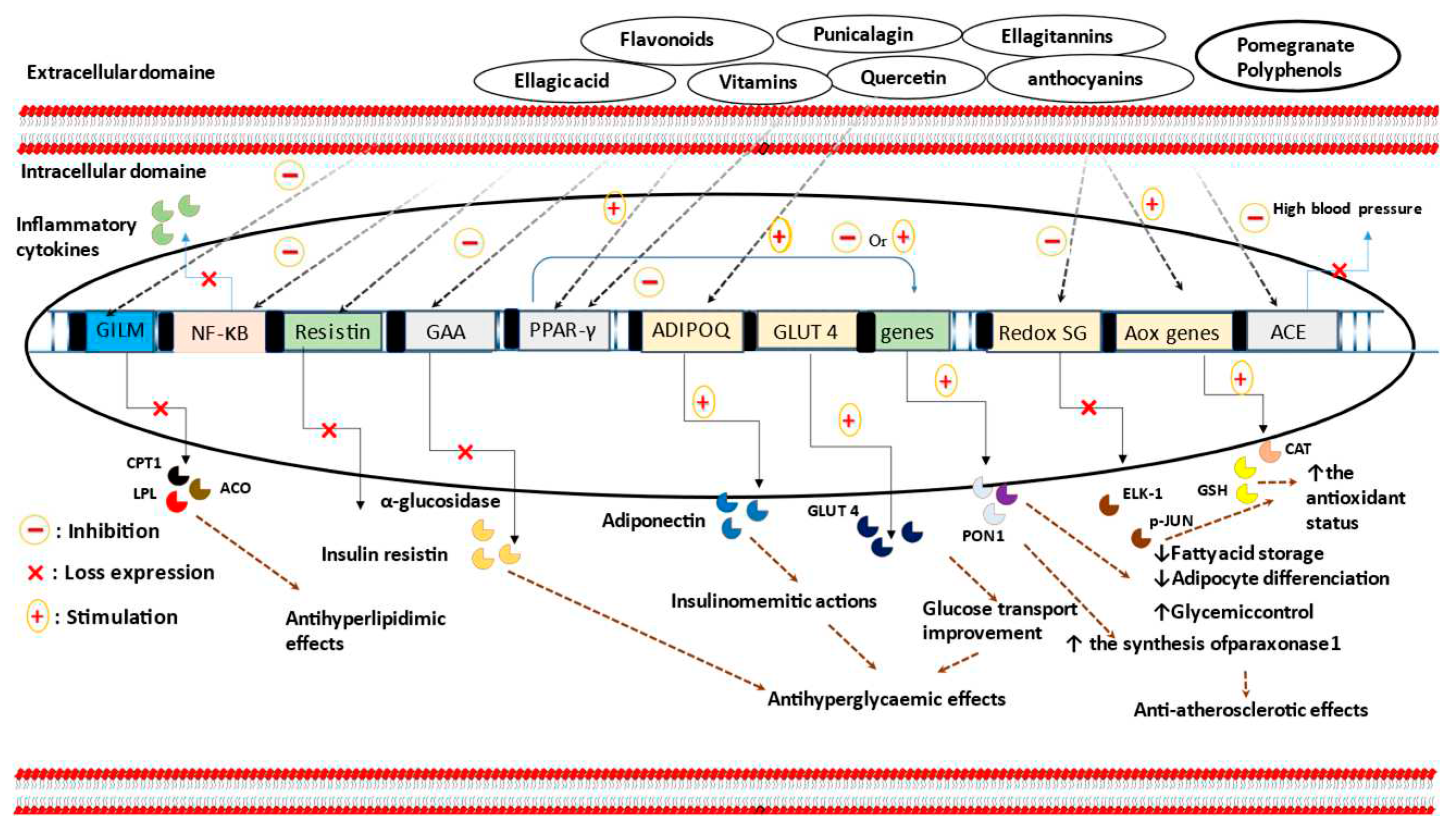
| Animal model/ population/ cell line |
Disease or induction of the disease | PG part or product | Dose and period of treatment | Findings | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG intake effect on obesity and diabetes mellitus | |||||
| Male C57Bl/J6 mice | High-fat diet | PG-seed oil | 1%, for 12 weeks | ↓ body weight; ↓ body fat mass; ↔ liver insulin sensitivity; ↑ peripheral insulin sensitivity; ↔ food intake; ↔ energy expenditure. | [35] |
| Male CD-1 mice | High-fat diet | PG-seed oil | 61.79 mg/day, for 14 weeks | ↓ weight gain; ↓ body weight; ↓ absolute weight gain; ↓ percentage of weight gain; ↔ lean mass; ↔ cholesterol profile; ↓ leptin; ↑ adiponectin. | [62] |
| Zucker diabetic fatty rats | Genetic manipulation |
PG flower extract |
500 mg/kg/day, for 6-weeks | ↓ plasma glucose; ↔ fasting serum glucose; ↑ cardiac PPAR-γ mRNA expression; ↑ GLUT-4 mRNA; ↑ mRNA expression of inhibitor-kBα. |
[59] |
| Zucker lean rats | - | ↔ plasma glucose; ↔ fasting plasma glucose. | |||
| Human THP-1-derived macrophage cells | - | 50µg/ml, for 48 h | ↑ PPAR-γ gene expression; ↑ PPAR-γ-dependent mRNA expression. ↑ lipoprotein lipase activity. |
||
| Swiss albino male mice | Alloxan injection | PG peel extract | 200 mg/kg/day, for 10 days | ↓ plasma glucose; ↓ α-amylase activity; ↓ water consumption; ↓ lipid peroxidation; ↑ plasma insulin. | [63] |
| Male albino rats | Alloxan injection | PG peel aqueous extract | 0.43g/kg BW, for 4-weeks | ↓ blood glucose; ↑ insulin level; ↑ β-cells regeneration. | [65] |
| Male Sprague Dawley rats | Alloxan injection | PG seed | 60 g/ kg/day, for 15 days | ↔ serum glucose; ↔ fasting blood glucose; ↔ size of islets; ↔ islets density; ↔ percent of β-cells in each islet; ↔ number of islets. |
[67] |
| albino rats | Alloxan injection | PG flower extract | 300 or 400or 500 mg/kg. Sampling time: at 1 and 2 h. |
↓ blood glucose. |
[82] |
| Zucker diabetic fatty rats | Genetic manipulation |
PG flower extract |
250,500, and 1000 mg/kg/day, for 2 weeks. 200 µl, for 5 min for the in vitro assay. |
↓ postprandial hyperglycemia; ↓ α-glucosidase activity (IC50: 1.8 µg/ml); ↓ plasma glucose levels after sucrose loading. |
[64] |
| Adult albino rats | Streptozotocin treatment | PG seed extract | 150, 300 and 600 mg/kg, for 2, 4, 8 and 12 h |
↓ blood glucose in time and dose-dependent manner. | [83] |
| 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes |
- |
Punicic acid | 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 µM | ↑ PPAR-α and γ activity; ↓ fasting plasma glucose; ↑ glucose normalizing capabilities; ↓ NF-κB activation; ↓ TNF-α expression. | [84] |
| ovariectomized mice | Surgical intervention |
PG fruit extract |
30 mg/kg/day, for 12 weeks | ↓ serum resistin concentrations. |
[61] |
| 3T3-L1 adipocytes | - | 50 and 100 µg/mL, for 9 and 12 h | ↓ resistin protein secretion; ↔ resistin mRNA expression; ↑ intracellular resistin degradation; ↔ adiponectin secretion. | ||
| Ellagic acid | 20, 40, and 70 µM, for 12h | ↓ resistin protein secretion; ↔ adiponectin secretion; ↓ intracellular resistin time-dependently. | |||
| Punicic acid | 5 and 10 µM, for 9h | ↔ resistin molecule secretion. | |||
| C57BL/6J obese mice | High-fat diet | Catalpic acid | 1g/100g, for 78 days | ↓ insulin; ↓ fasting blood glucose; ↑ glucose normalizing ability; ↓ abdominal white adipose tissue storage; ↑ PPAR-α expression; ↑ HDL-C; ↓ TG. |
[72] |
| male and female ICR mice | High-fat diet | PG leaf extract | 400 or 800 mg/kg daily, for 5 weeks | ↓ body weight; ↓ energy intake; ↓ TC; ↓ TG; ↓ TC/HDL-C ratio; ↓ glucose; ↓ fat absorption; ↓ appetite. |
[36] |
| Zucker diabetic fatty rats | Genetic manipulation | PG flower extract | 500 mg/ kg daily, for 6 weeks | ↓ TG; ↓ TC; ↓ fatty acids; ↓ fatty acids transport proteins; ↓ PPAR-; ↓ acyl-CoA oxidase; ↓ 5 -AMP-activated protein kinase-α-2; ↓ carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; ↓ acetyl-CoA carboxylase mRNA. |
[85] |
| Zucker diabetic fatty rats |
Genetic manipulation |
PG flower extract |
500 mg/kg/day, for 6 weeks | ↓ TG; ↓ lipid droplets; ↑ PPAR-α; ↑ acyl-CoA oxidase; ↑ carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; ↓ gene expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; ↔ fatty acids and TG synthesis; ↔ fatty acids and TG hydrolysis; ↔ fatty acids and TG uptake. |
[37] |
| HepG2 cell line | - | 10, 50 and 100 µg/ml, for 48h | ↑ PPAR-α; ↑ Acyl-CoA oxidase mRNA. | ||
| Type 2 diabetic and hyperlipidemic patients | Diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia | PG juice | 40 g/day of concentrated PG juice, for 8 weeks | ↓ TC; ↓ LDL-C; ↓ LDL-C/HDL-C; ↓ TC/HDL-C; ↔TG; ↔ HDL-C. |
[86] |
|
Calves |
- |
Polyphenols PG extract | 5 or 10 g/day (0,15, and 30 mg of gallic acid equiv/kg/day), for 70 days | ↔ on body weight or intake, during the first 30 postnatal days, but are ↓ after this period; ↔ glucose concentration; ↔ 3-hydroxybutyrate; ↓ fat digestion; ↔ dry matter; ↔ starch digestibility; ↔ organic matter. |
[38] |
| Calves | - | PG peel | Ad libitum, for 2 months | ↑ feed intake; ↑ weight gain tendency. | [39] |
| Balb/c mice | High-fat feeding | PG peel extract | 0.2% (6 mg/day/mouse), for 4 weeks | ↔ weight gain; ↔ glycaemia; ↔ glucose tolerance; ↓ TC; ↓ LDL-C; ↔ IL-1β, IL-6 and COX-2 in the liver; ↓ IL-1β, IL-6 and COX-2 both in in the gastrointestinal tract and visceral adipose tissue. |
[40] |
|
Male wistar rats |
High lipid diet | PG peel extract | 50, 100, 200, and 300mg/kg, for 23 days | ↓ body weight; ↓ TC; ↓ LDL-C; ↓ alkaline phosphatase; ↓ TG; ↑ HDL-C; ↓ AST; ↓ ALT. |
[49] |
| Pomegranate intake and cardiovascular diseases | |||||
| J774.A1 macrophages |
- |
PG juice | 75 mmol/L, for 90 min | ↑ Ox-LDL degradation by 40%; ↔ on macrophage degradation of native LDL; ↔ macrophage cholesterol efflux capacities; ↓ macrophage cholesterol biosynthesis (by 50%). | [87] |
|
Human coronary artery endothelial cells |
High shear stress | PG juice | 7–14 µl of PG juice, for 24h. | ↓ the activation of redox-sensitive genes (ELK-1 and p-JUN); ↑ eNOS expression. |
[88] |
| Low-density-lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice (LDLR_/_ mice) | Genetic manipulation and high-cholesterol diet |
PG juice |
31 µl/day (0.875 µmol of total polyphenols), for 24 weeks | ↓ the activation of redox-sensitive genes (ELK-1 and p-JUN); ↑ eNOS expression; ↓ the progression of atherosclerosis lesions in mice. | [88] |
| Carotid artery stenosis subjects | carotid artery stenosis |
PG juice |
50 ml, for 1 or 3 years |
↓ carotid intima-media thickness; ↑ PON 1 activity; ↓ LDL basal oxidative state; ↓ LDL susceptibility to oxidation; ↓ antibodies against ox-LDL; ↑ total antioxidant status; ↓ antibodies against oxidized LDL; ↓ systolic blood pressure. |
[89] |
| Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice | Genetic manipulation | PG juice | 31 µL of PJ/d (0.875 mmol of total polyphenols/d ), for 2 months | ↑ PON1 activity; ↓ MPM lipid peroxide; ↓ Ox-LDL MPM uptake; ↓ MPM cholesterol esterification; ↑ macrophage cholesterol efflux; ↓ macrophage Ox-LDL uptake; ↓ cholesterol esterification; ↓ atherosclerosis lesions size. |
[90] |
| Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice | Genetic manipulation |
PG byproduct |
17 or 51.5 µg of gallic acid equiv/kg/day, for 3 months | ↓ atherosclerotic lesion size; ↓ cellular lipid peroxide; ↓ glutathione levels; ↑ POM-2 lactonase activity; ↓ Ox-LDL uptake. |
[91] |
| J774A.1 macrophage | - | 10 or 50 µmol/L of total polyphenols, for 18 h | ↓ cellular total peroxide; ↓ Ox-LDL uptake. | ||
| J774A.1 macrophage | - | PG juice | 10–50 µM of total polyphenols, for 18 h | ↑ expression and enzymatic activity of PON-2; ↑ PPAR-γ and AP-1 activation; ↓ macrophage oxidative status; ↓ Ox-LDL uptake. | [58] |
| Wistar albino rats |
High-fat diet |
PG peel extract | 50 or 100 mg/kg, for 6 weeks |
↓ TC; ↓ LDL-C; ↓ VLDL-C; ↓ TAGs; ↑ HDL-C ; ↑ GR; ↑ SOD; ↑ CAT; ↑ GSH; ↓ MDA; ↑ PON-1 activities; ↓ LDH activity; ↑ TNF-α; ↑ CD36. |
[92] |
| Ellagic acid | 1mg/kg, for 6 weeks | ||||
| Punicalagin | 7mg/kg, for 6 weeks | ||||
| Zucker diabetic fatty rats | Genetic manipulation |
PGF extract |
500 mg/kg, for 6 weeks |
↓ cardiac fibronectin expression; ↓ collagen I and III mRNAs; ↓ expression of endothelin -1; ↓ endothelin receptor a; ↓ c-jun and inhibitor-kBβ expression; ↑ inhibitor-kBα; ↓ LPS-induced NF-kB activation. | [93] |
9. Atheroprotective activities and antidyslipidemic effects of pomegranate consumption
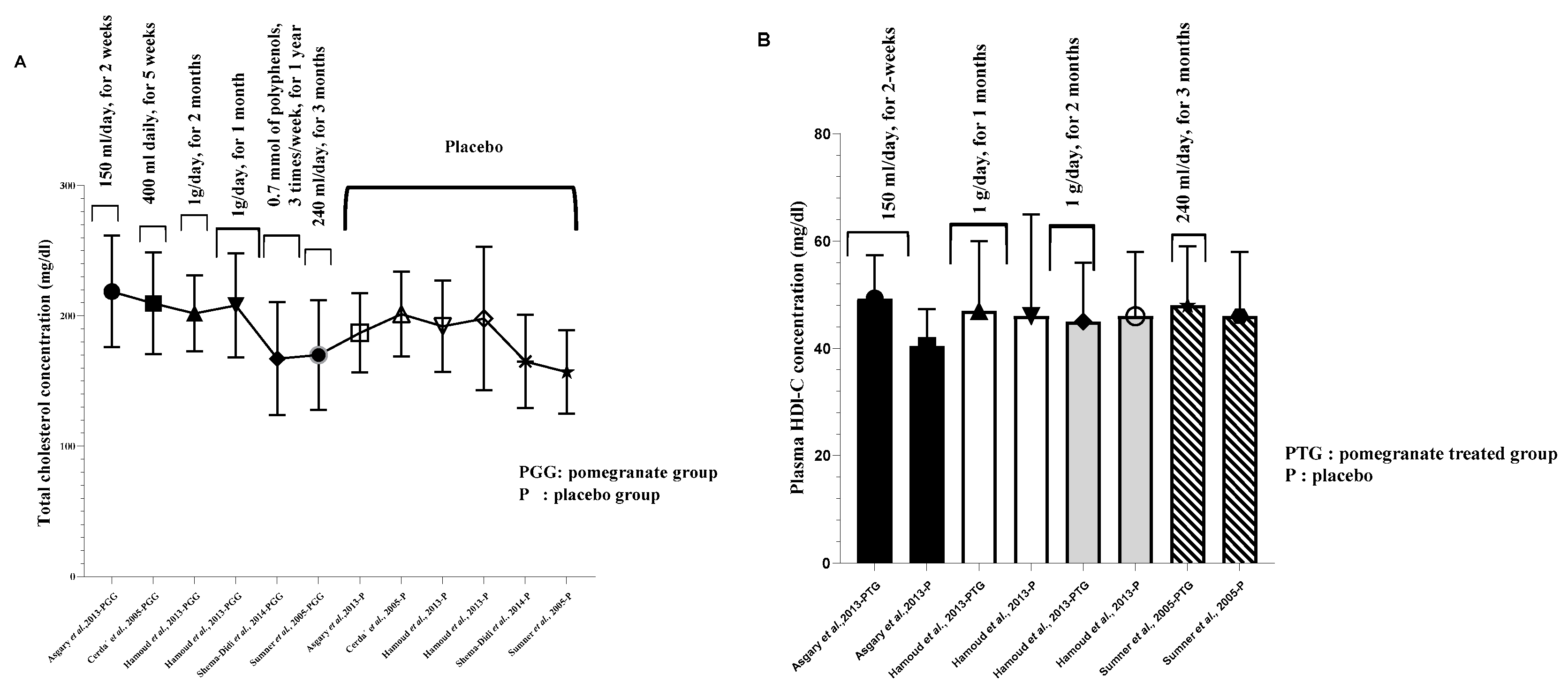
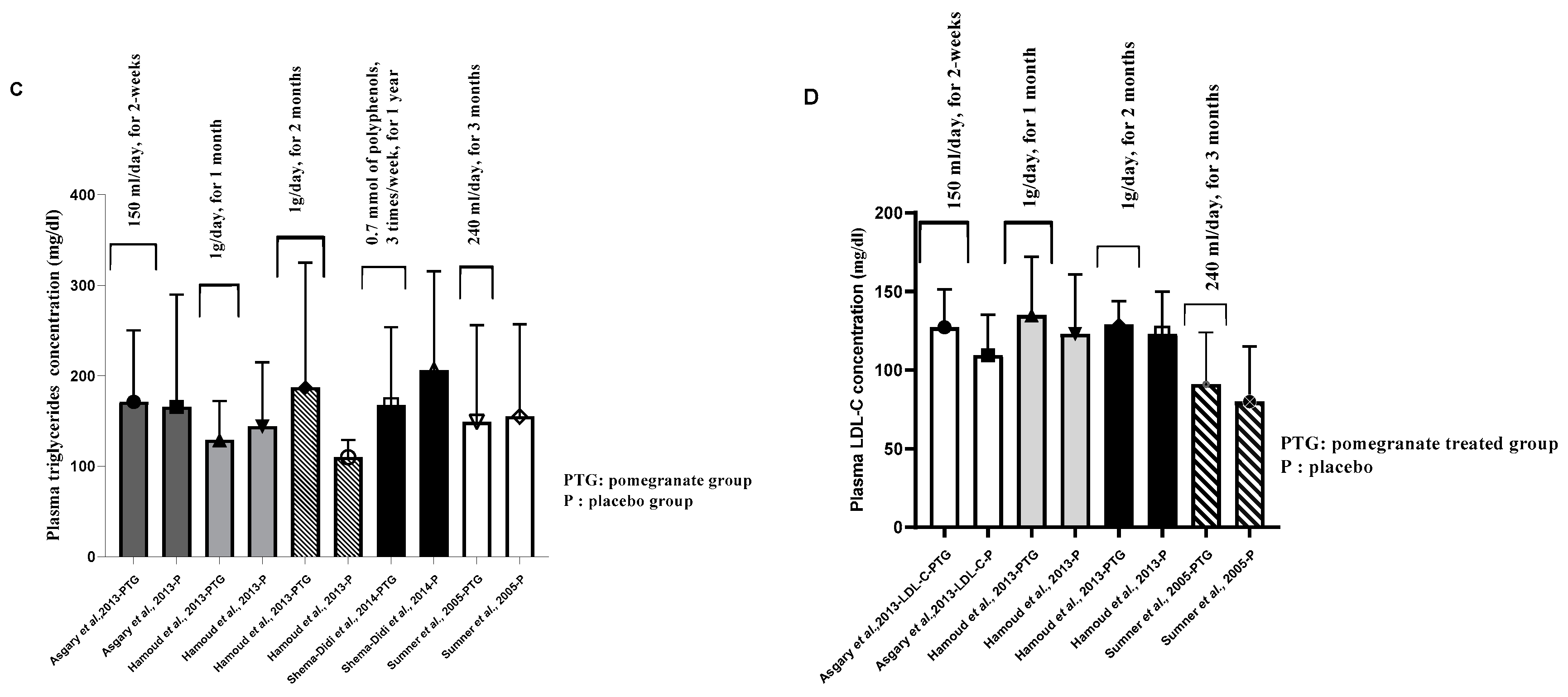
10. Antidyslipidemic effects of pomegranate and pomegranate products
11. Insulin resistance, blood pressure, and pomegrnate consumption
12. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization: “Obesity and overweight,” 2021.
- S. Webber, International Diabetes Federation, vol. 102, no. 2. 2013.
- F. Meuleneire, Management of diabetic foot ulcers using dressings with Safetac®: A review of case studies, vol. 4, no. 4. 2008.
- C. Bommer et al., “The global economic burden of diabetes in adults aged 20–79 years: a cost-of-illness study,” Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol., vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 423–430, 2017. [CrossRef]
- H. Dysfunction, “Associated with Troglitazone,” New Engl. J. Med. Corresp., vol. 338, no. 13, pp. 916–917, 1998.
- A. Muthukumar, M. Sridevi, R. Gayathri, S. Muthukumar, S. R. M. S, and A. Muthukumar, “A Pharmacovigilance Study of antidiabetic Drugs in Hypertensive Patients in a Territory Hospital in Coimbatore Zone,” Sch. Reasearch Libr., vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 70–76, 2017.
- C.J. Rosen, “Revisiting the Rosiglitazone Story — Lessons Learned,” N. Engl. J. Med., vol. 363, no. 9, pp. 803–806, 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. Viberti et al., “A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT),” Health Care (Don. Mills)., vol. 25, no. 10, pp. 1737–1743, 2002.
- S. E. Kahn et al., “Glycemic Durability of Rosiglitazone, Metformin, or Glyburide Monotherapy,” N. Engl. J. Med., vol. 355, no. 23, pp. 2427–2443, 2006. [CrossRef]
- A.D. Wright, C. A. Cull, K. M. Macleod, and R. R. Holman, “Hypoglycemia in Type 2 diabetic patients randomized to and maintained on monotherapy with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin for 6 years from diagnosis: UKPDS73,” J. Diabetes Complications, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 395–401, 2006. [CrossRef]
- A.N. Jacob, K. Salinas, B. Adams-Huet, and P. Raskin, “Weight gain in type 2 diabetes mellitus,” Diabetes, Obes. Metab., vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 386–393, 2007. [CrossRef]
- P. Raskin, M. RENDELL, M. C. RIDDLE, and J. F. DOLE, “A Randomized Trial of Rosiglitazone,” 2001.
- S. R. et al Mehta, “Effect of Rosiglitazone on the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Death from Cardiovascular Causes.,” N. Engl. J. Med., pp. 687–696, 2015.
- J. Ludvigsson, “Novel therapies in the management of type I diabetes mellitus,” Panminerva Med., vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 257–270, 2012.
- F.-Y. Hsiao, W.-F. Huang, Y.-W. Wen, P.-F. Chen, K. N. Kuo, and Y.-W. Tsai, “Thiazolidinediones and Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus,” Drug Saf., vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 675–690, 2009. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Floyd, E. Barbehenn, P. Lurie, M. Sidney, and Wolfe, “Case series of liver failure associated with rosiglitazone and pioglitazone,” Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf., vol. 18, pp. 1238–1243, 2009. [CrossRef]
- A. Singh, S. R. Sarkar, L. W. Gaber, and M. A. Perazella, “Acute Oxalate Nephropathy Associated With Orlistat, a Gastrointestinal Lipase Inhibitor,” Am. J. Kidney Dis., vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 153–157, 2007. [CrossRef]
- N. P. Seeram, R. Lee, and D. Heber, “Bioavailability of ellagic acid in human plasma after consumption of ellagitannins from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice,” Clin. Chim. Acta, vol. 348, no. 1–2, pp. 63–68, 2004. [CrossRef]
- B. Cerdá, R. Llorach, J. J. Cerón, J. C. Espín, and F. A. Tomás-Barberán, “Evaluation of the bioavailability and metabolism in the rat of punicalagin, an antioxidant polyphenol from pomegranate juice,” Eur. J. Nutr., vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 18–28, 2003. [CrossRef]
- B. Cerdá, P. Periago, J. C. Espín, and F. A. Tomás-Barberán, “Identification of urolithin A as a metabolite produced by human colon microflora from ellagic acid and related compounds,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 53, no. 14, pp. 5571–5576, 2005. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Espín, R. González-Barrio, B. Cerdá, C. López-Bote, A. I. Rey, and F. A. Tomás-Barberán, “Iberian pig as a model to clarify obscure points in the bioavailability and metabolism of ellagitannins in humans,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 55, no. 25, pp. 10476–10485, 2007. [CrossRef]
- L. A. L. H. Ingorani and H. A. D. Erendorf, “Absorption , Metabolism , and Antioxidant Effects of Pomegranate ( Punica granatum L .) Polyphenols after Ingestion of a Standardized Extract in Healthy Human Volunteers,” pp. 8956–8961, 2006. [CrossRef]
- R. González-Barrio, G. Borges, W. Mullen, and A. Crozier, “Bioavailability of anthocyanins and ellagitannins following consumption of raspberries by healthy humans and subjects with an ileostomy,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 3933–3939, 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. P. Seeram et al., “Pomegranate ellagitannin-derived metabolites inhibit prostate cancer growth and localize to the mouse prostate gland,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 55, no. 19, pp. 7732–7737, 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Tripathi and D. K. Singh, “Molluscicidal activity of Punica granatum bark and Canna indica root,” Brazilian J. Med. Biol. Res., vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 1351–1355, 2000. [CrossRef]
- A. Sánchez-Lamar et al., “Assessment of the genotoxic risk of Punica granatum L. (Punicaceae) whole fruit extracts,” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 115, no. 3, pp. 416–422, 2007. [CrossRef]
- E. P. Vale, L. R. do Rego, D. D. N. Pureza, P. G. de B. Silva, F. F. O. de Sousa, and M. de A. B. Monteiro Neto, “Cytogenetic and toxicological effects of Punica granatum Linnaeus fruit peel hydroethanolic extract in mice,” South African J. Bot., vol. 130, pp. 465–470, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Vidal et al., “Studies on the toxicity of Punica granatum L. (Punicaceae) whole fruit extracts,” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 89, no. 2–3, pp. 295–300, 2003. [CrossRef]
- S. B. Jahromi et al., “Punica granatum peel extract toxicity in mice,” Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 4–9, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Tasaki et al., “Safety assessment of ellagic acid, a food additive, in a subchronic toxicity study using F344 rats,” Food Chem. Toxicol., vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 1119–1124, 2008. [CrossRef]
- B. Cerdá, J. J. Cerón, F. A. Tomás-Barberán, and J. C. Espín, “Repeated oral administration of high doses of the pomegranate ellagitannin punicalagin to rats for 37 days is not toxic,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 51, no. 11, pp. 3493–3501, 2003. [CrossRef]
- K. Pathakoti, L. Goodla, M. Manubolu, and T. Tencomnao, “Metabolic Alterations and the Protective Effect of Punicalagin Against Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Toxicity in HT22 Cells,” Neurotox. Res., vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 521–531, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Ye, L. Zhang, Y. Yan, and H. Lin, “Punicalagin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced toxicity through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling,” Biosci. Rep., vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 1–8, 2019. [CrossRef]
- I. A. T. M. Meerts et al., “Toxicological evaluation of pomegranate seed oil,” Food Chem. Toxicol., vol. 47, no. 6, pp. 1085–1092, 2009. [CrossRef]
- I. O. C. M. Vroegrijk et al., “Pomegranate seed oil, a rich source of punicic acid, prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice,” Food Chem. Toxicol., vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 1426–1430, 2011. [CrossRef]
- F. Lei et al., “Evidence of anti-obesity effects of the pomegranate leaf extract in high-fat diet induced obese mice,” Int. J. Obes., vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 1023–1029, 2007. [CrossRef]
- K. Z. Y. Xu, C. Zhu, M. S. Kim, J. Yamahara, and Y. Li, “Pomegranate flower ameliorates fatty liver in an animal model of type 2 diabetes and obesity,” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 123, no. 2, pp. 280–287, 2009. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Oliveira et al., “Effects of feeding polyphenols from pomegranate extract on health, growth, nutrient digestion, and immunocompetence of calves,” J. Dairy Sci., vol. 93, no. 9, pp. 4280–4291, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. Shabtay et al., “Nutritive and antioxidative potential of fresh and stored pomegranate industrial byproduct as a novel beef cattle feed,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 56, no. 21, pp. 10063–10070, 2008. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Neyrinck, V. F. Van Hée, L. B. Bindels, F. De Backer, P. D. Cani, and N. M. Delzenne, “Polyphenol-rich extract of pomegranate peel alleviates tissue inflammation and hypercholesterolaemia in high-fat diet-induced obese mice: Potential implication of the gut microbiota,” Br. J. Nutr., vol. 109, no. 5, pp. 802–809, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Asgary, A. Sahebkar, M. R. Afshani, M. Keshvari, S. Haghjooyjavanmard, and M. Rafieian-Kopaei, “Clinical evaluation of blood pressure lowering, endothelial function improving, hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects of pomegranate juice in hypertensive subjects,” Phyther. Res., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 193–199, 2014. [CrossRef]
- G. Asghari et al., “Effect of pomegranate seed oil on serum TNF-α level in dyslipidemic patients,” Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr., vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 368–371, 2012. [CrossRef]
- B. Cerdá et al., “Pomegranate juice supplementation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A 5-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial,” Eur. J. Clin. Nutr., vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 245–253, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. González-Ortiz, E. Martínez-Abundis, M. C. Espinel-Bermúdez, and K. G. Pérez-Rubio, “Effect of pomegranate juice on insulin secretion and sensitivity in patients with obesity,” Ann. Nutr. Metab., vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 220–223, 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. Hamoud et al., “Pomegranate extract (POMx) decreases the atherogenicity of serum and of human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDM) in simvastatin-treated hypercholesterolemic patients: A double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, prospective pilot study,” Atherosclerosis, vol. 232, no. 1, pp. 204–210, 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. Shema-Didi, B. Kristal, S. Sela, R. Geron, and L. Ore, “Does Pomegranate intake attenuate cardiovascular risk factors in hemodialysis patients?,” Nutr. J., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 2–9, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Sumner et al., “Effects of pomegranate juice consumption on myocardial perfusion in patients with coronary heart disease,” Am. J. Cardiol., vol. 96, no. 6, pp. 810–814, 2005. [CrossRef]
- C. Tsang, N. F. Smail, S. Almoosawi, I. Davidson, and E. A. S. Al-Dujaili, “Intake of polyphenol-rich pomegranate pure juice influences urinary glucocorticoids, blood pressure and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in human volunteers,” J. Nutr. Sci., vol. 1, pp. 1–9, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. Sadeghipour, M. Eidi, A. Ilchizadeh Kavgani, R. Ghahramani, S. Shahabzadeh, and A. Anissian, “Lipid lowering effect of punica granatum L. Peel in high lipid diet fed male rats,” Evidence-based Complement. Altern. Med., vol. 2014, 2014. [CrossRef]
- F. L. A. Hossin, “Effect of pomegranate (Punica granatum) peels and it’s extract on obese hypercholesterolemic rats,” Pakistan J. Nutr., vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 1251–1257, 2009. [CrossRef]
- A. E. El-Hadary and M. F. Ramadan, “Phenolic profiles, antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, and antioxidant properties of pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel extract,” J. Food Biochem., vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 1–9, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Bagri, M. Ali, V. Aeri, M. Bhowmik, and S. Sultana, “Antidiabetic effect of Punica granatum flowers: Effect on hyperlipidemia, pancreatic cells lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in experimental diabetes,” Food Chem. Toxicol., vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 50–54, 2009. [CrossRef]
- A. N. Patel, D. D. Bandawane, and N. K. Mhetre, “Pomegranate (Punica granatum Linn.) leaves attenuate disturbed glucose homeostasis and hyperglycemia mediated hyperlipidemia and oxidative stress in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats,” Eur. J. Integr. Med., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 307–321, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. Sarker, Z. A. Mahmud, S. K. Saha, N. S. Tithi, M. S. Ali, and S. C. Bachar, “Antihyperlipidemic activity of flowers of punica granatum in poloxamer-407 induced hyperlipidemic mice model,” Pharmacogn. J., vol. 4, no. 27, pp. 66–70, 2012. [CrossRef]
- K. G. Al-Fartosi, R. J. Tuama, A. B. Roomi, & Saad, and H. Jasim, “Effect of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L) Juice on Lipid Profile of Hyperlipidemic Female Mice,” Int. J. Res. Applied, Nat. Soc. Sci., vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 2321–8851, 2015.
- M. F. Saleh and F. H. Mohammed, “ANTI HYPERLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PUNICA GRANATUM L . MESOCARP IN HYPERLIPIDEMIC RATS,” vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 8989–8994, 2020.
- M. Mueller and A. Jungbauer, “Culinary plants, herbs and spices - A rich source of PPARγ ligands,” Food Chem., vol. 117, no. 4, pp. 660–667, 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. Shiner, B. Fuhrman, and M. Aviram, “Macrophage paraoxonase 2 (PON2) expression is up-regulated by pomegranate juice phenolic anti-oxidants via PPARγ and AP-1 pathway activation,” Atherosclerosis, vol. 195, no. 2, pp. 313–321, 2007. [CrossRef]
- T. H. W. Huang et al., “Anti-diabetic action of Punica granatum flower extract: Activation of PPAR-γ and identification of an active component,” Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., vol. 207, no. 2, pp. 160–169, 2005. [CrossRef]
- H. Kohno, R. Suzuki, Y. Yasui, M. Hosokawa, K. Miyashita, and T. Tanaka, “Pomegranate seed oil rich in conjugated linolenic acid suppresses chemically induced colon carcinogenesis in rats,” Cancer Sci., vol. 95, no. 6, pp. 481–486, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Y. Makino-Wakagi, Y. Yoshimura, Y. Uzawa, N. Zaima, T. Moriyama, and Y. Kawamura, “Ellagic acid in pomegranate suppresses resistin secretion by a novel regulatory mechanism involving the degradation of intracellular resistin protein in adipocytes,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., vol. 417, no. 2, pp. 880–885, 2012. [CrossRef]
- B. K. McFarlin, K. A. Strohacker, and M. L. Kueht, “Pomegranate seed oil consumption during a period of high-fat feeding reduces weight gain and reduces type 2 diabetes risk in CD-1 mice,” Br. J. Nutr., vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 54–59, 2009. [CrossRef]
- H. S. Parmar and A. Kar, “Antidiabetic potential of Citrus sinensis and Punica granatum peel extracts in alloxan treated male mice,” BioFactors, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 17–24, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li et al., “Punica granatum flower extract, a potent α-glucosidase inhibitor, improves postprandial hyperglycemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats,” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 99, no. 2, pp. 239–244, 2005. [CrossRef]
- E. A. M. Khalil, “Antidiabetic effect of an aqueous extract of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peels in normal and alloxan diabetic rats,” Egypt. J. Hosp. Med., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 92–99, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Y. A., S. E.Y., F. I., S. F., and K. A. I., “Antiobesity, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of senna (senna alexandrina mill.) and pomegranate (punica granatum l.) leaves extracts and its fractions,” Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharm. Res., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 18–24, 2018.
- G. Jelodar, M. Maleki, and S. Sirus, “EFFECT OF WALNUT LEAF, CORIANDER AND POMEGRANATE ON BLOOD GLUCOSE AND HISTOPATHOLOGY OF PANCREAS OF ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS,” Afr. J. Trad., vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 299–305, 2007. [CrossRef]
- B. Hosseini, A. Saedisomeolia, L. G. Wood, M. Yaseri, and S. Tavasoli, “Effects of pomegranate extract supplementation on inflammation in overweight and obese individuals: A randomized controlled clinical trial,” Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract., vol. 22, pp. 44–50, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Khajebishak, L. Payahoo, M. Alivand, and B. Alipour, “Punicic acid: A potential compound of pomegranate seed oil in Type 2 diabetes mellitus management,” J. Cell. Physiol., vol. 234, no. 3, pp. 2112–2120, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Ö. Akarca Dizakar, G. S. Saribas, and A. Tekcan, “Effects of ellagic acid in the testes of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats,” Drug Chem. Toxicol., vol. 0, no. 0, pp. 1–8, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, Y. Cao, J. Chen, H. Qin, and L. Yang, “A New Possible Mechanism by Which Punicalagin Protects against Liver Injury Induced by Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Upregulation of Autophagy via the Akt/FoxO3a Signaling Pathway,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 67, no. 50, pp. 13948–13959, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Hontecillas, M. Diguardo, E. Duran, M. Orpi, and J. Bassaganya-Riera, “Catalpic acid decreases abdominal fat deposition, improves glucose homeostasis and upregulates PPAR α expression in adipose tissue,” Clin. Nutr., vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 764–772, 2008. [CrossRef]
- L. Fajas et al., “The organization, promoter analysis, and expression of the human PPARγ gene,” J. Biol. Chem., vol. 272, no. 30, pp. 18779–18789, 1997. [CrossRef]
- A. Chawla and A. Lazar, “Peroxisome Expression In Adipocyte Differentiation Receptor ( WAR ) y : And Induction,” Endocrinology, vol. 135, no. 2, pp. 798–800, 1994.
- P. Tontonoz, E. Hu, and B. M. Spiegelman, “Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPARγ2, a lipid-activated transcription factor,” Cell, vol. 79, no. 7, pp. 1147–1156, 1994. [CrossRef]
- J. Berger and D. E. Moller, “THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF PPARs.,” Annu. Rev. Med, vol. 53, pp. 409–435, 2002. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Rangwala and M. A. Lazar, “Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in diabetes and metabolism,” Trends Pharmacol. Sci., vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 331–336, 2004. [CrossRef]
- R. S. Farag, M. S. Abdel-Latif, S. Emam, and S. Tawfeek, “Phytochemical screening and polyphenol constituents of pomegranate peels and leave juices,” Agric. Soil Sci., vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 86–93, 2014.
- J.-H. EokLee, S.-D. Kim, J.-Y. Lee, K.-N. Kim, and H.-S. Kim, “Analysis of Flavonoids in Concentrated Pomegranate extract by HPLC with Diod Array Detection.,” Food Sci. Biotechnol, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 171–174, 2005.
- N. Parsaeyan, H. Mozaffari-Khosravi, and M. R. Mozayan, “Effect of pomegranate juice on paraoxonase enzyme activity in patients with type 2 diabetes,” J. Diabetes Metab. Disord., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 2–5, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Jandari, E. Hatami, R. Ziaei, A. Ghavami, and A. M. Yamchi, “The effect of pomegranate (Punica granatum) supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis,” Complement. Ther. Med., vol. 52, p. 102478, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Jafri, M. Aslam, K. Javed, and S. Singh, “Effect of punica granatum Linn. (flowers) on blood glucose level in normal and alloxan- induced diabetic rats,” J. Ethnopharmacol., pp. 309–314, 2000. [CrossRef]
- A. K. Das, S. C. Mandal, S. K. Banerjee, S. Sinha, B. P. Saha, and M. Pal, “Studies on the hypoglycaemic activity of Punica granatum seed in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats,” Phyther. Res., vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 628–629, 2001. [CrossRef]
- R. Hontecillas, M. O’Shea, A. Einerhand, M. Diguardo, and J. Bassaganya-Riera, “Activation of ppar γ and α by punicic acid ameliorates glucose tolerance and suppresses obesity-related inflammation,” J. Am. Coll. Nutr., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 184–195, 2009. [CrossRef]
- T. H. W. Huang et al., “Pomegranate flower improves cardiac lipid metabolism in a diabetic rat model: Role of lowering circulating lipids,” Br. J. Pharmacol., vol. 145, no. 6, pp. 767–774, 2005. [CrossRef]
- A. Esmaillzadeh, F. Tahbaz, I. Gaieni, H. Alavi-Majd, and L. Azadbakht, “Concentrated pomegranate juice improves lipid profiles in diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia,” J. Med. Food, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 305–308, 2004. [CrossRef]
- B. Fuhrman, N. Volkova, and M. Aviram, “Pomegranate juice inhibits oxidized LDL uptake and cholesterol biosynthesis in macrophages,” J. Nutr. Biochem., vol. 16, no. 9, pp. 570–576, 2005. [CrossRef]
- F. De Nigris et al., “Beneficial effects of pomegranate juice on oxidation-sensitive genes and endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity at sites of perturbed shear stress,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 102, no. 13, pp. 4896–4901, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Aviram et al., “Pomegranate juice consumption for 3 years by patients with carotid artery stenosis reduces common carotid intima-media thickness, blood pressure and LDL oxidation,” Clin. Nutr., vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 423–433, 2004. [CrossRef]
- M. Kaplan et al., “Pomegranate juice supplementation to atherosclerotic mice reduces macrophage lipid peroxidation, cellular cholesterol accumulation and development of atherosclerosis,” J. Nutr., vol. 131, no. 8, pp. 2082–2089, 2001. [CrossRef]
- M. Rosenblat, N. Volkova, R. Coleman, and M. Aviram, “Pomegranate byproduct administration to apolipoprotein E-deficient mice attenuates atherosclerosis development as a result of decreased macrophage oxidative stress and reduced cellular uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 1928–1935, 2006. [CrossRef]
- E. ElHussieny, R. Soliman, and N. ElBeih, “Ameliorative Effects of Pomegranate Peel Extract and Some of its Bioactive Components against Hyperlipidemia-Induced Atherosclerosis in Male Rats,” Egypt. J. Exp. Biol., vol. 14, no. 1, p. 85, 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. H. W. Huang et al., “Pomegranate flower extract diminishes cardiac fibrosis in zucker diabetic fatty rats: Modulation of cardiac endothelin-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways,” J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 856–862, 2005. [CrossRef]
- J. N. Losso, R. R. Bansode, A. Trappey, H. A. Bawadi, and R. Truax, “In vitro anti-proliferative activities of ellagic acid,” J. Nutr. Biochem., vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 672–678, 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. Khateeb, A. Gantman, A. J. Kreitenberg, M. Aviram, and B. Fuhrman, “Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) expression in hepatocytes is upregulated by pomegranate polyphenols: A role for PPAR-γ pathway,” Atherosclerosis, vol. 208, no. 1, pp. 119–125, 2010. [CrossRef]
- E. Burgermeister, D. Chuderland, T. Hanoch, M. Meyer, M. Liscovitch, and R. Seger, “Interaction with MEK Causes Nuclear Export and Downregulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ,” Mol. Cell. Biol., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 803–817, 2007. [CrossRef]
- W. Rock, M. Rosenblat, R. Miller-Lotan, A. P. Levy, M. Elias, and M. Aviram, “Consumption of Wonderful variety pomegranate juice and extract by diabetic patients increases paraoxonase 1 association with high-density lipoprotein and stimulates its catalytic activities,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 56, no. 18, pp. 8704–8713, 2008. [CrossRef]
- F. Hadaegh, D. Khalili, A. Ghasemi, M. Tohidi, F. Sheikholeslami, and F. Azizi, “Triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol ratio is an independent predictor for coronary heart disease in a population of Iranian men,” Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis., vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 401–408, 2009. [CrossRef]
- P. Mirmiran, M. R. Fazeli, G. Asghari, A. Shafiee, and F. Azizi, “Effect of pomegranate seed oil on hyperlipidaemic subjects: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial,” Br. J. Nutr., vol. 104, no. 3, pp. 402–406, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. Esmaillzadeh, F. Tahbaz, I. Gaieni, H. Alavi-Majd, and L. Azadbakht, “Cholesterol-lowering effect of concentrated pomegranate juice consumption in type II diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia,” Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res., vol. 76, no. 3, pp. 147–151, 2006. [CrossRef]
- J. M. McKenney, “Pharmacotherapy of dyslipidemia,” Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther., vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 413–422, 2001. [CrossRef]
- A. Sahebkar, L. E. Simental-Mendía, P. Giorgini, C. Ferri, and D. Grassi, “Lipid profile changes after pomegranate consumption: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,” Phytomedicine, vol. 23, no. 11, pp. 1103–1112, 2016. [CrossRef]
- F. de Nigris et al., “The influence of pomegranate fruit extract in comparison to regular pomegranate juice and seed oil on nitric oxide and arterial function in obese Zucker rats,” Nitric Oxide - Biol. Chem., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 50–54, 2007. [CrossRef]
- K. B. Arun, P. Jayamurthy, C. V. Anusha, S. K. Mahesh, and P. Nisha, “Studies on Activity Guided Fractionation of Pomegranate Peel Extracts and Its Effect on Antidiabetic and Cardiovascular Protection Properties,” J. Food Process. Preserv., vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 1–12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Mohan, H. Waghulde, and S. Kasture, “Effect of pomegranate juice on angiotensin II-induced hypertension in diabetic wistar rats,” Phyther. Res., vol. 24, no. SUPPL. 2, pp. 196–203, 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. L. dos Santos et al., “Pomegranate peel extract attenuates oxidative stress by decreasing coronary angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity in hypertensive female rats,” J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. - Part A Curr. Issues, vol. 79, no. 21, pp. 998–1007, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Davidson et al., “Effects of Consumption of Pomegranate Juice on Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Men and Women at Moderate Risk for Coronary Heart Disease,” Am. J. Cardiol., vol. 104, no. 7, pp. 936–942, 2009. [CrossRef]
- A. Lynn, H. Hamadeh, W. C. Leung, J. M. Russell, and M. E. Barker, “Effects of Pomegranate Juice Supplementation on Pulse Wave Velocity and Blood Pressure in Healthy Young and Middle-aged Men and Women,” Plant Foods Hum. Nutr., vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 309–314, 2012. [CrossRef]
- G. Sohrab et al., “Effects of pomegranate juice consumption on oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes: a single-blind, randomized clinical trial,” Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr., vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 249–255, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Sahebkar, C. Ferri, P. Giorgini, S. Bo, P. Nachtigal, and D. Grassi, “Effects of pomegranate juice on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,” Pharmacol. Res., vol. 115, pp. 149–161, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Aviram and L. Dornfeld, “Pomegranate juice consumption inhibits serum angiotensin converting enzyme activity and reduces systolic blood pressure,” Atherosclerosis, vol. 158, no. 1, pp. 195–198, 2001. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




