1. Introduction
Acute respiratory failure caused by SARS-CoV-2 emerged at the end of 2019 in China, becoming a pandemic in a few months [
1]. The manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 vary depending on the patient’s condition, genetic variability and viral strain [
2]. Clinical presentations range from asymptomatic states to hypoxemic respiratory failure [
3], which requires a wide therapeutic range from conventional oxygen therapy, through non-invasive respiratory support (NIRS), invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), to ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) [
4]. Bilateral pneumonias are characteristic of SARS-CoV-2 which generate, in serious states, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although certain authors do not classify it within the classic entity of ARDS but in a new one called acute respiratory distress syndrome by SARS-CoV-2 (C-ARDS) based on certain pathophysiological differences and, also, divide them into two phenotypes (phenotype-L and phenotype-H) [
5]. In addition, we must remember the “happy hypoxemia” which are patients with objectified hypoxemia, but with a little clinic or almost asymptomatic. A final consensus on the pathophysiological mechanism has not been reached, but its association with the H-phenotype of C-ARDS has been demonstrated [
6]. However, other authors have proposed that this state of “happy hypoxemia” is caused by intrapulmonary shunts that they have named acute vascular distress syndrome (AVDS) [
7,
8]. All this can cause the SARS-CoV-2 clinic not to be early, but to develop three or four days after the onset of symptoms, hence the importance of its management in the Hospitalization ward [
9,
10].
At the beginning of the pandemic, given the speed of the spread of the virus [
11], patients have quickly filled the intensive care units (ICU), causing the need to apply non-invasive respiratory support therapies (NIRS) on the hospital ward, that is, high-flow therapies with nasal cannulas (HFNO), non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) either in CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) or Bilevel (two levels of airway pressure) or a combination therapy between HFNO and NIV, regardless of ventilatory mode. There is a debate about which NIRS modality generates less failure. In existing studies with NIRS, the failure rate is around 50% [
12,
13,
14,
15]. The therapy with the greatest failure is Bilevel but there is controversy as to whether CPAP and high-flow therapy are superior to each other [
16,
17,
18]. Although combination therapy is an increasingly used strategy in clinical practice, there is little literature on its use during the pandemic as well as its efficacy [
19]. The objective of our study is to assess the failure of different NIRS therapies (HFNO, CPAP, Bilevel or combined therapy) in patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure due to SARS-CoV-2.
2. Materials and Methods
An observational and retrospective study was designed of patients who came to the emergency room, through the respiratory circuit, for suspicious symptoms of SARS-CoV-2, of the Reina Sofía General University Hospital (RSGUH) of Murcia. The RSGUH attends an average of 93,000 emergencies per year, has 350 beds and a reference population of 250,000 people. The study covered the periods from March 8, 2020 to May 26, 2021. The inclusion criteria were SARS-CoV-2 positive patients who required NIRS during their hospital stay. Patients who required IMV prior to initiation of NIRS were excluded.
NIRS failure was defined as death or initiation of IMV during admission hospitable. The decision to start NIRS was the responsibility physician’s as well as the decision to discontinue, change, combine or initiate the IMV. The parameters programmed in the ventilator and the medication were at the discretion of the responsible physician. However, as of April 2020, an institutional protocol was established advising the start of NIRS in patients with PaO2/FiO2<200 mmHg, the need to use FiO2 greater than 40% to maintain adequate oxygenation or respiratory rate above 24 rpm. This protocol recommended the use of NIV in CPAP mode or HFNO as the first line of therapy.
The study followed current laws and regulations and was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of RSGUH and the Catholic University of San Antonio (UCAM).
During the study, demographic variables were collected: age and sex; comorbidities: arterial hypertension (HTN), diabetes mellitus type 2, dyslipidemia, obesity and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CPOD); treatments: home oxygen therapy (HOT), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) at home; clinical values in triage (Glasgow and vital signs); biochemical, haematimetric, gasometric, D-dimer and inflammatory biomarkers data; dexamethasone treatment; place of onset of NIRS (hospitalization draw or emergency room), duration of NIRS (hours), hospital stay and in-hospital mortality.
Qualitative variables were analyzed using absolute and relative frequencies. The quantitative variables were described by mean and standard deviation if they presented parametric distribution and by median and interquartile range in case of nonparametric distribution. With the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test the type of distribution was checked. Using Pearson’s chi-square test or Fisher’s test, as specified, comparisons between qualitative variables were made. Among the quantitative variables with normality criteria, the Student’s t test (in comparisons of one variable with two categories) or the analysis of variance: ANOVA test (comparison of a variable with more than two categories) and those that did not meet normality criteria, the Mann-Whitney U or the Kruskal-Wallis test, as appropriate. All significant factors were included in the univariate analysis. All analyses were performed in 2 tails and statistical significance was accepted if p < 0.05 or 95% CI. The SPSS Statistics v-21 program (IBM, New Castle, NY, USA) was used.
3. Results
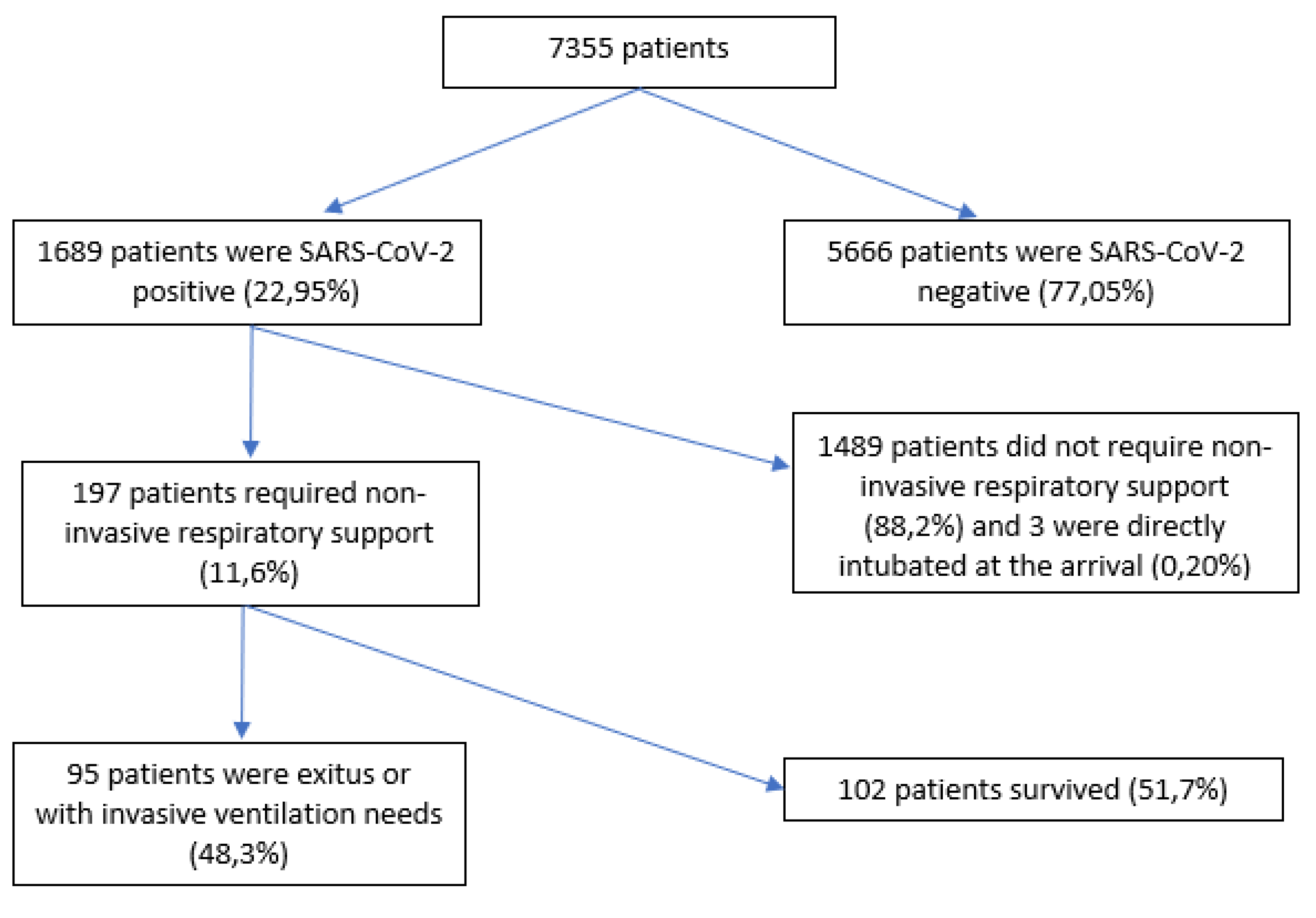
Of 7355 patients, 197 (11.6%) were included. A total of 5666 (77%) patients were excluded because they were SARS-CoV-2 negative, 3 because of early orotracheal intubation (0.2%) and 1489 were SARS-CoV-2 positive patients (88%) who did not require NIRS. Of the 197 patients who required NIRS, 95 of them failed this therapy (48.3%) (
Figure 1).
Table 1 shows the relationship between the variables studied and the type of NIRS. The median age of patients treated with NIRS was 66 years with an interquartile range (IQR) of 21, gender (male) were 129 patients (65.5%). The most frequent personal history were: hypertension (58.9%), diabetes mellitus type 2 (34%), dyslipidemia (44.7%) and obesity (22.3%). 8.1% used home CPAP and 5.1% HOT. The SOFA on arrival at the emergency room of the patients was 2 (IQR 1) and the SpO
2/FiO
2 423 (IQR 52). Regarding the frequency of use of each type of NIRS therapy, we found that HFNO was used in 18 patients (9.1%), followed by combined HFNO therapy with CPAP in 24 patients (12.2%), CPAP was used in 28 patients (14.2%), combined HFNO therapy with Bilevel in a total of 45 patients (22.8%) and Bilevel in 82 patients (41.7%). The time of initiation NIRS from arrival at the emergency room was 24 (IQR 96) hours. Breaking down this result, the time of initiation HFNO from arrival at the emergency room was 36 (RIQ 93) hours, the combined therapies of HFNO with CPAP 72 (RIQ 60) hours, CPAP was 48 (RIQ 99) hours, HFNO with Bilevel 5 (RIQ 95) hours and Bilevel 24 (RIQ 90) hours (p=0.014). The median duration of the different respiratory therapies was 107 (IQR 164) hours, broken down by type of NIRS: HFNO had a median duration of 48 (IQR 117) hours, combination therapy of HFNO with CPAP had a median duration of 96 (IQR 90) hours, CPAP had a median duration of 120 (IQR 120) hours, combination therapy with HFNO and Bilevel had a median duration of 156 (IQR 201) hours and Bilevel a median duration of 96 (IQR 192) hours (p=0.057).
55 (27.9%) patients required IMV. The percentage of need for IMV according to the type of therapy was 22.2%, 16.7%, 32.1%, 33.3% and 28% for HFNO, CPAP+HFNO, CPAP, Bilevel+HFNO and Bilevel respectively (p=0.611). Overall intrahospitalary mortality was 64 patients (32.5%), with therapy mortality of 16.7%, 4.2%, 21.4%, 37.8% and 45.1% for HFNO, CPAP+HFNO, CPAP, Bilevel+HFNO and Bilevel respectively (p=0.001).
Overall NIRS failure was 48.3% (95 patients). The failure according to the type of NIRS is shown in
Table 2. 70 patients (35.5%) received an NIRS with HFNO, CPAP or CPAP+HFNO, of which the technique failed in 23 patients (24.2%). The remaining 127 patients (64.5%) were treated with Bilevel or Bilevel+HFNO, with a failure of the technique in 72 patients (56.6%); (OR: 0.374; CI 95%: 0.203-0.688. p=0.001). The analysis between NIRS failure in CPAP mode (46.5%) and HFNO (27.7%) showed no statistically significant relationship (OR: 2.253; CI 95%: 0.632-8.032. p=0.206).
The variables associated with failure are shown in
Table 3. Sex stands out, with a failure of 72.6% of men compared to 27.4% of women (OR: 1.858; CI 95%:1,020-3,382. p=0.042); the median age at failure was 69.8 (IQR 14.3) years versus success which was 64.5 (IQR 12.2) years (p=0.006) and as antecedents diabetes mellitus type 2 which was present in failure in 41.1% of patients versus 27.5% who were successful (p=0.074). Upon arrival at the emergency room, the median SpO2/FiO2 in failure was 414 (IQR 90) versus success which was 428 (IQR 33) (p=0.013). The median lactic acid levels at failure were 1.8 (IQR 1.3) mg/dl versus 1.4 (IQR 1.1) mg/dl (p=0.001). The time of onset of NIRS in failure was 24 (IQR 96) hours, being earlier than in success whose onset was 48 (IQR 95) hours, (p=0.758). The median duration of NIRS was 96 (IQR 168) hours at failure and at success was 126 (IQR 144) hours (p=0.176). The median stay in the hospitalization ward was 12 (IQR 9.8) days in success and failure was 10 (IQR 12) days (p=0.016). NIRS was started in the hospitalization ward in 121 patients (61.4%) compared to 76 patients who started in the emergency room (38.6%) and NIRS failure started in the ward was 51 patients (42.2%) compared to success in 70 patients (57.8%) (p=0.031).
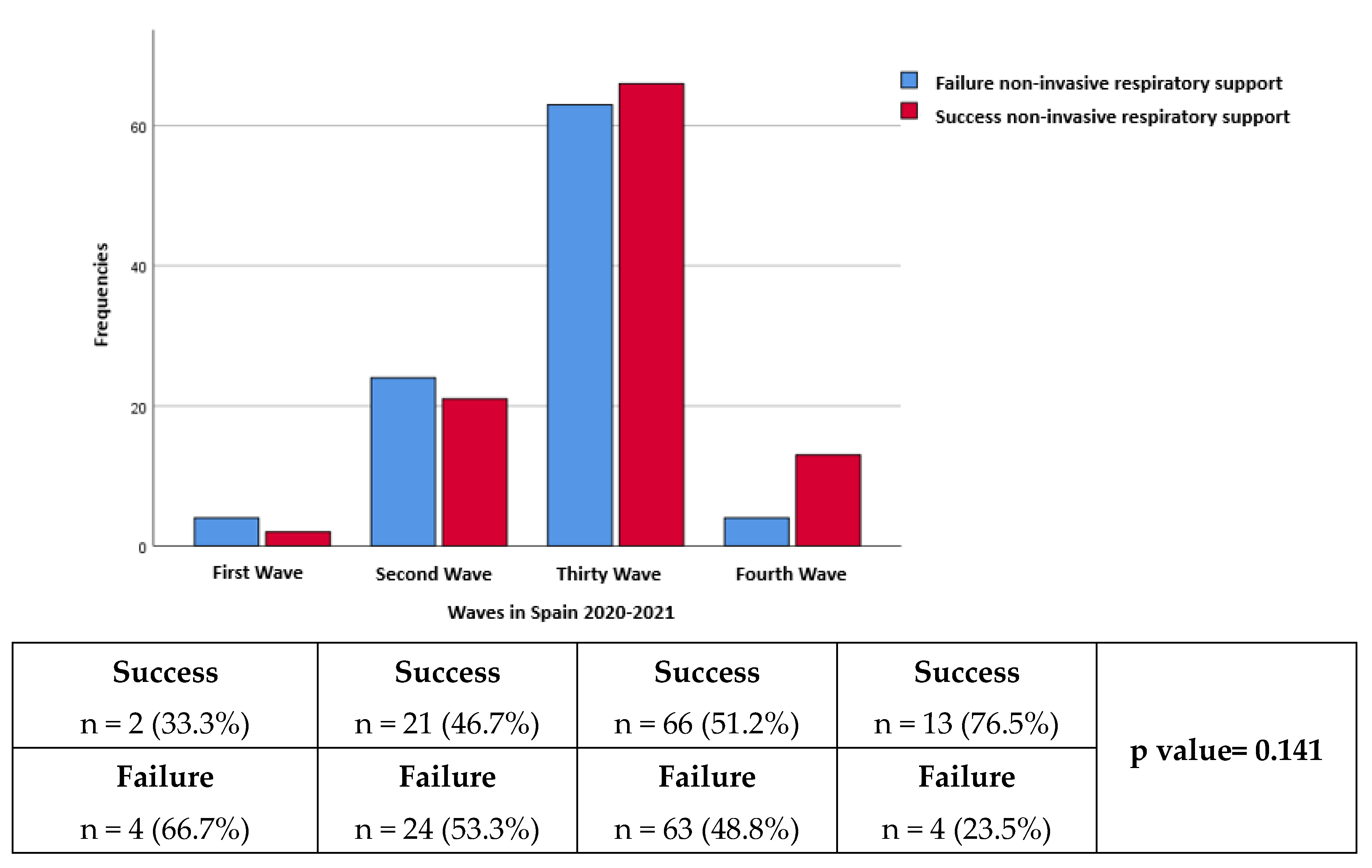
Regarding the distribution according to waves, the number of patients in the first, second, third and fourth waves respectively was 6 (3%), 45 (22.8%), 129 (65.5%) and 17 (8.6%). The failure rate was 66.7%, 53.3%, 48.8% and 23.5% in the first, second, third and fourth waves respectively (p=0.141) (
Figure 2).
4. Discussion
NIRS is a fundamental pillar in the treatment of respiratory failure secondary to SARS-CoV-2. The particularities of overloading the health system in the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic have definitively opened the doors to the use NIRS in conventional hospitalization wards.
In our study, it was observed that the most frequently used therapy was Bilevel followed by Bilevel+HFNO combined therapy, between both with almost two-thirds of patients. However, when analyzing the strategies of CPAP and/or HFNO, as recommended by the consensus, they presented a markedly lower failure rate being statistically significant. In this sense, it is important to highlight that the strategy with the least failure was combined therapy with CPAP + HFNO. A noteworthy finding of our data is the lower failure of the NIRS when it starts in the conventional hospitalization ward with respect to the start in the emergency room. Finally, despite not being statistically significant, our study observed a lower failure rate in successive waves, probably due to a combination of a greater multidisciplinary approach and experience in the doctors of the hospital.
The consensus recommendations lean towards HFNO or CPAP mode over Bilevel [
20]. The caution when ventilating with two levels of pressure (Bilevel), and therefore using a support pressure, is associated with the directly proportional relationship between the support pressure and the tidal volume. It has been demonstrated that tidal volumes, mainly above 10 cc/kg ideal weight, present a higher probability of VILI (ventilator-induced lung injury) [
21] and, therefore, a higher probability of failure. The problem of pressure ventilation in the patient with spontaneous breathing, usual in NIV, is the impossibility of programming or limiting the tidal volume performed by the patient. That is, by not being able to control the tidal volume, which is the result of the programmed support pressure plus the patient’s own respiratory effort, there is a greater probability of failure of the technique by VILI. For this reason, the recommendations advise using support pressure as low as possible, and therefore using HFNO and/or CPAP (without support pressure) are the most advisable modalities [
12,
17,
22].
The overall failure of the NIRS in other series varies between 40 and 60% [
13,
14,
17,
19], so our data are within the average of these margins. Focusing on mortality, the overall 32.5% is higher than the 26.6% of Franco et al., a study similar to ours, but lower than the 40.5% of the study by Perkins et al. [
14]. However, if we analyze only the therapies of HFNO and/or CPAP in the failure between the study of Franco et al. and ours we observe very similar figures between both studies (47.7% vs. 46.5%) if we talk about CPAP but lower in our case when referring to HFNO (38% vs. 27.7%). Our study is pioneering in analyzing combination therapies, so it is not possible to make a comparison between these therapies and other articles. However, it should be noted that the lowest failure rates (20.9%) are found in the combined therapy between CPAP + HFNO. The reason for these results is difficult to define. Probably the fact that they are younger patients and the earlier start of therapy, which may have meant a later onset of respiratory failure, have influenced the good results. However, the better tolerance of a combined therapy, which entails longer CPAP times without requiring sedation or the need to remove the support due to patient intolerance should not be ruled out as a key point for the greater success of the joint technique over the individual ones [
15].
If we assess the place of onset of the NIRS we find that its onset in the conventional hospitalization ward (61%), in all its modalities, is more frequent with respect to the hospital emergency service (39%). This may be due to the syndrome of “happy hypoxemia” or a few advanced conditions on arrival at the emergency room that would cause the need for no initiation of NIRS. Thus, the greater failure of NIRS in emergency service (57.9%) could be caused by more severe conditions or more advanced disease, and therefore with later initiation of therapy, which requires an immediate initiation of NIRS. The fact that in the conventional hospitalization ward there is less failure of the NIRS indicates that it is possible to perform NIRS safely and effectively, mainly by providing adequate monitoring and training of health personnel. In this sense, it is important to highlight that, at the end of the second wave, all patients with respiratory support were in the same conventional hospitalization ward, which included centralized monitoring and after training medical and nursing staff. It is difficult to measure the impact of these actions, but from the third wave onwards, a greater number of successes than global failure is observed.
As limitations of the study, we found that, first, despite an acceptable sample size, it decreases substantially when analyzed by group, especially those treated purely with HFNO. Secondly, the NIV parameters have not been assessed. Third, despite the existence of an institutional protocol, it only focused on non-combined therapies, or NIV or HFNO, so the times between the different types of NIRS in combination therapies were different in each patient. Fourth, the results obtained may have been because NIV was used in patients who, upon arrival at the emergency room, were more severe than others who opted for other types of therapies. Although it is true that many of them were admitted with conventional oxygen therapy and in the plant started the NIRS due to a subsequent worsening of SpO2/FiO2. Fifth, the experience of the physician responsible for the management of NIRS could influence the success or failure of patients, either by prolonging HFNO over time instead of an earlier onset of NIV or by the inadequate choice of modes and/or ventilatory parameters.
5. Conclusions
The use of NIRS in conventional hospitalization is safe and effective in patients with respiratory failure secondary to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The therapeutic strategy with Bilevel increases the probability of failure. The combined therapy strategy with CPAP and HFNO could be the most promising option.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Flowchart of patient inclusion.; Figure S2: Success and failure by waves of SARS-CoV-2 in Spain; Table S1: Clinical-analytical characteristics and evolution of the global sample and study according to the type of therapy used; Table S2 Success or failure of patients according to the modality of NIRS; Table S3: Clinical-analytical characteristics and univariate study depending on the success or failure of NIRS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, García-Fernández JJ, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA; methodology, García-Fernández JJ, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA; software, García-Fernández JJ; validation, Bernal-Morell E and Cinesi-Gómez C; formal analysis, García-Fernández JJ, Cinesi-Gómez C; investigation, García-Fernández JJ, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA; resources, García-Fernández JJ, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA; data curation, Galicia-Puyol S, Guerras Conesa JJ, Gil-Rosa I; writing—original draft preparation, García-Fernández JJ; writing—review and editing, García-Fernández JJ; visualization,García-Fernández JJ; supervision, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA, Bernal-Morell E; project administration, Cinesi-Gómez C, Sánchez-Nicolás JA; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Reina Sofia General University Hospital. Protocol code CE042207 approved in September 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because the study was retrospective, and the patients are not identified.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
PubMed, UpToDate, IBM SPSS Statistics v-21 program (IBM, New Castle, NY, USA)
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Malik YA. Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Malays J Pathol. abril de 2020;42(1):3-11.
- Ochani R, Asad A, Yasmin F, Shaikh S, Khalid H, Batra S, et al. COVID-19 pandemic: from origins to outcomes. A comprehensive review of viral pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Infez Med. 1 de marzo de 2021;29(1):20-36.
- Rahimi Pordanjani S, Hasanpour A, Askarpour H, Bastam D, Rafiee M, Khazaei Z, et al. Aspects of Epidemiology, Pathology, Virology, Immunology, Transmission, Prevention, Prognosis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review. Int J Prev Med. 2021;12:38. [CrossRef]
- Coleman MH, Aldrich JM. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Ventilator Management and Rescue Therapies. Crit Care Clin. octubre de 2021;37(4):851-66. [CrossRef]
- Meyer NJ, Gattinoni L, Calfee CS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet. 2021;398(10300):622-37. [CrossRef]
- Chiumello D, Busana M, Coppola S, Romitti F, Formenti P, Bonifazi M, et al. Physiological and quantitative CT-scan characterization of COVID-19 and typical ARDS: a matched cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(12):2187-96. [CrossRef]
- Jounieaux V, Rodenstein DO, Mahjoub Y. On Happy Hypoxia and on Sadly Ignored “Acute Vascular Distress Syndrome” in Patients with COVID-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1 de diciembre de 2020;202(11):1598-9. [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub Y, Rodenstein DO, Jounieaux V. Severe Covid-19 disease: rather AVDS than ARDS? Crit Care. 11 de junio de 2020;24:327.
- Redberg RF, Katz M, Steinbrook R. Internal Medicine and COVID-19. JAMA. 22 de septiembre de 2020;324(12):1135-6. [CrossRef]
- Sharrack S, Zollinger-Read CA, Cox MF, Shiha MG, Song SH. UK internal medicine training in the time of COVID-19. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. junio de 2021;51(2):177-83. [CrossRef]
- Umakanthan S, Sahu P, Ranade AV, Bukelo MM, Rao JS, Abrahao-Machado LF, et al. Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Postgraduate Medical Journal. 1 de diciembre de 2020;96(1142):753-8. [CrossRef]
- Franco C, Facciolongo N, Tonelli R, Dongilli R, Vianello A, Pisani L, et al. Feasibility and clinical impact of out-of-ICU noninvasive respiratory support in patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 5 de noviembre de 2020;56(5):2002130. [CrossRef]
- Luján M, Sayas J, Mediano O, Egea C. Non-invasive Respiratory Support in COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Front Med (Lausanne). 4 de enero de 2022;8:788190. [CrossRef]
- Durr KM, Yadav K, Rosenberg H. Effect of noninvasive respiratory strategies on intubation or mortality among patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and COVID-19: The RECOVERY-RS randomized clinical trial. CJEM. 2022;24(6):582-4. [CrossRef]
- Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S, et al. High-flow oxygen through nasal cannula in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 4 de junio de 2015;372(23):2185-96. [CrossRef]
- García-Pereña L, Ramos Sesma V, Tornero Divieso ML, Lluna Carrascosa A, Velasco Fuentes S, Parra-Ruiz J. Benefits of early use of high-flow-nasal-cannula (HFNC) in patients with COVID-19 associated pneumonia. Med Clin (Engl Ed). 10 de junio de 2022;158(11):540-2. [CrossRef]
- Grieco DL, Maggiore SM, Roca O, Spinelli E, Patel BK, Thille AW, et al. Non-invasive ventilatory support and high-flow nasal oxygen as first-line treatment of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(8):851-66. [CrossRef]
- Rochwerg B, Einav S, Chaudhuri D, Mancebo J, Mauri T, Helviz Y, et al. The role for high flow nasal cannula as a respiratory support strategy in adults: a clinical practice guideline. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(12):2226-37. [CrossRef]
- Fernández R, González de Molina FJ, Batlle M, Fernández MM, Hernandez S, Villagra A, et al. [Non-invasive ventilatory support in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A Spanish multicenter registry]. Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2021;45(5):315-7. [CrossRef]
- Cinesi Gómez C, Peñuelas Rodríguez Ó, Luján Torné M, Egea Santaolalla C, Masa Jiménez JF, García Fernández J, et al. Recomendaciones de consenso respecto al soporte respiratorio no invasivo en el paciente adulto con insuficiencia respiratoria aguda secundaria a infección por SARS-CoV-2. Arch Bronconeumol. julio de 2020;56:11-8. [CrossRef]
- Beitler JR, Malhotra A, Thompson BT. Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. Clin Chest Med. diciembre de 2016;37(4):633-46.
- Mauri T, Turrini C, Eronia N, Grasselli G, Volta CA, Bellani G, et al. Physiologic Effects of High-Flow Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1 de mayo de 2017;195(9):1207-15. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).