Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
29 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Silage Preparation
2.2. Analysis of chemical composition, fermentation characteristics and microbial composition
2.3. Antioxidant capacity analysis
2.4. Microbial community analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and microbial compositions of CK before ensiled
3.2. Effect of FT on the fermentation quality of CK silage
3.3. Effect of FT on the chemical composition of CK silage
3.4. Effect of FT on the antioxidant capacity of CK silage
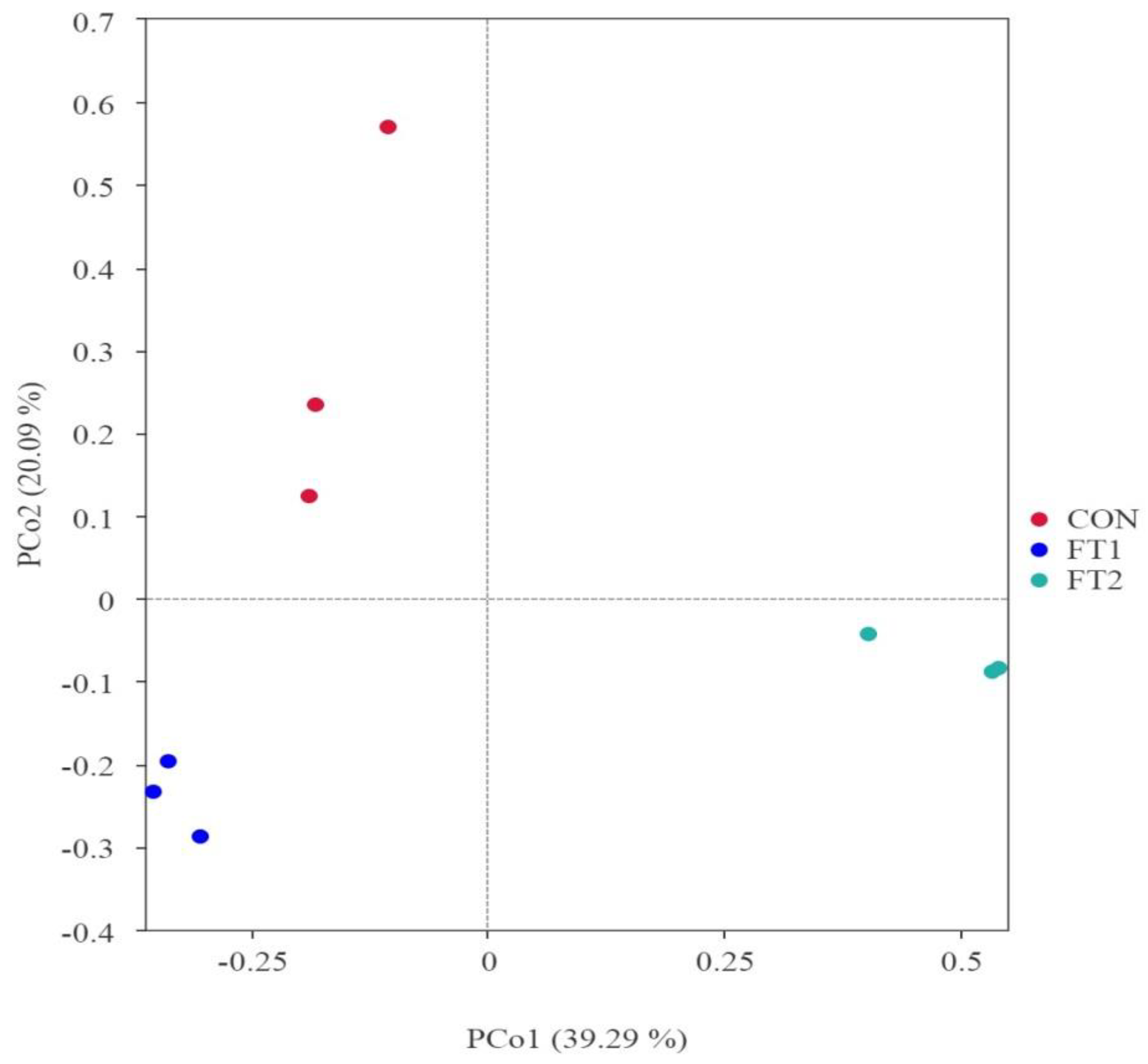
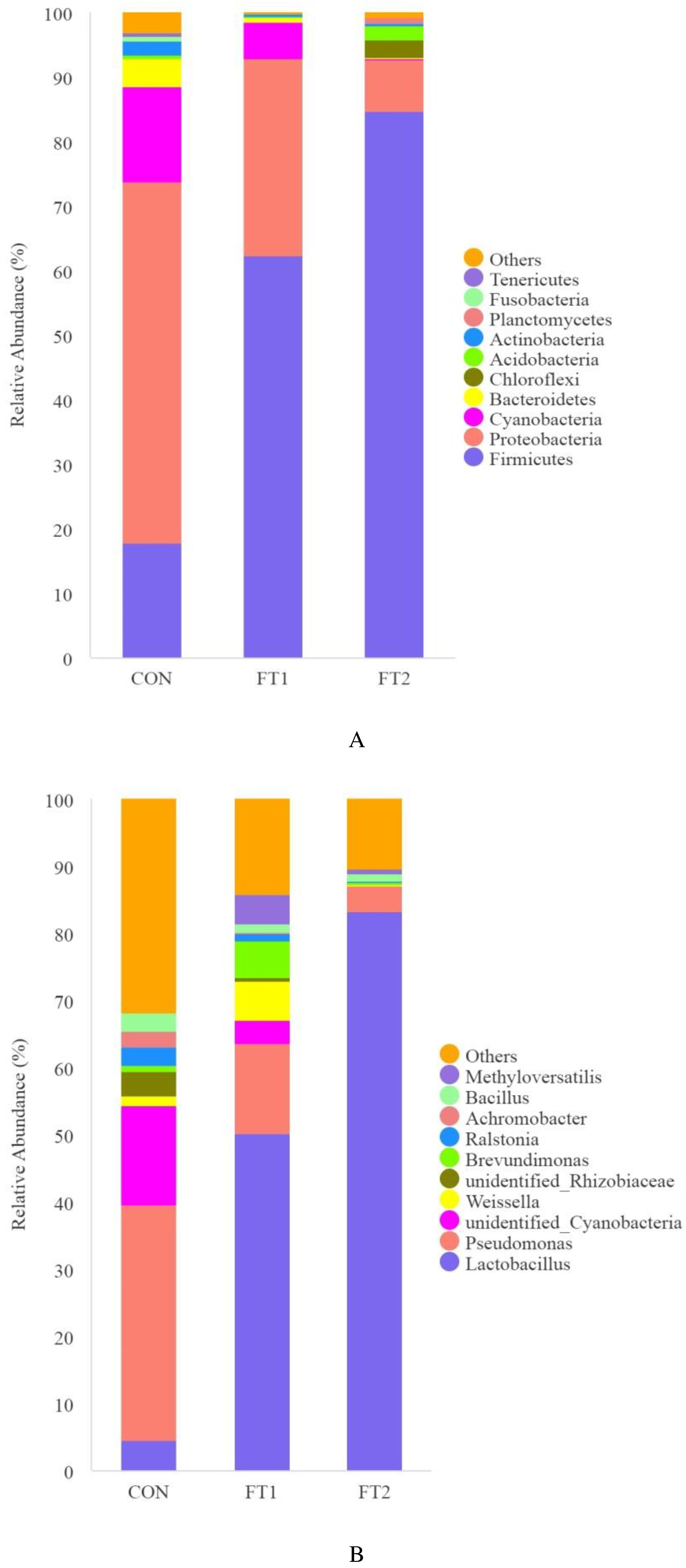
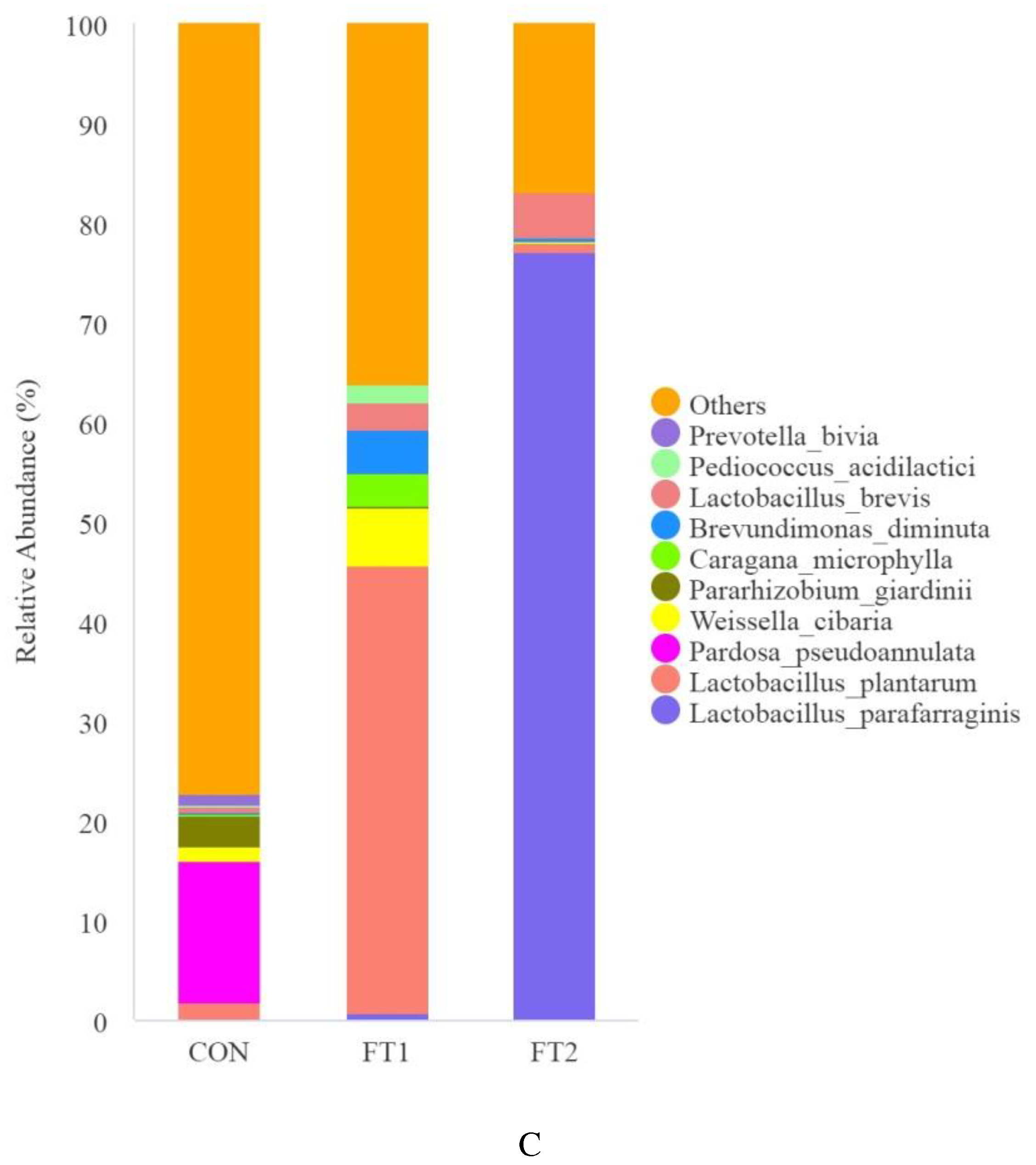
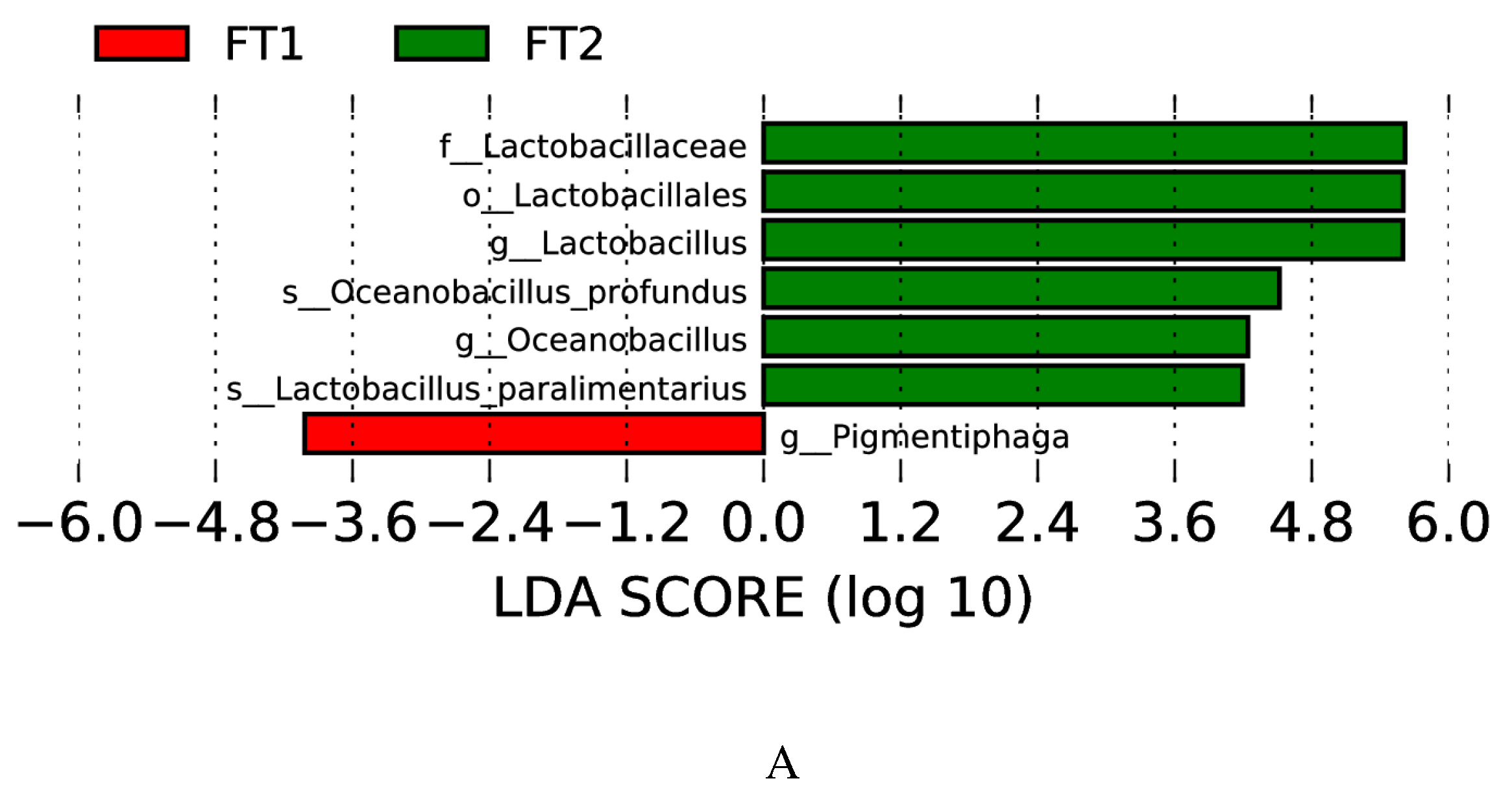
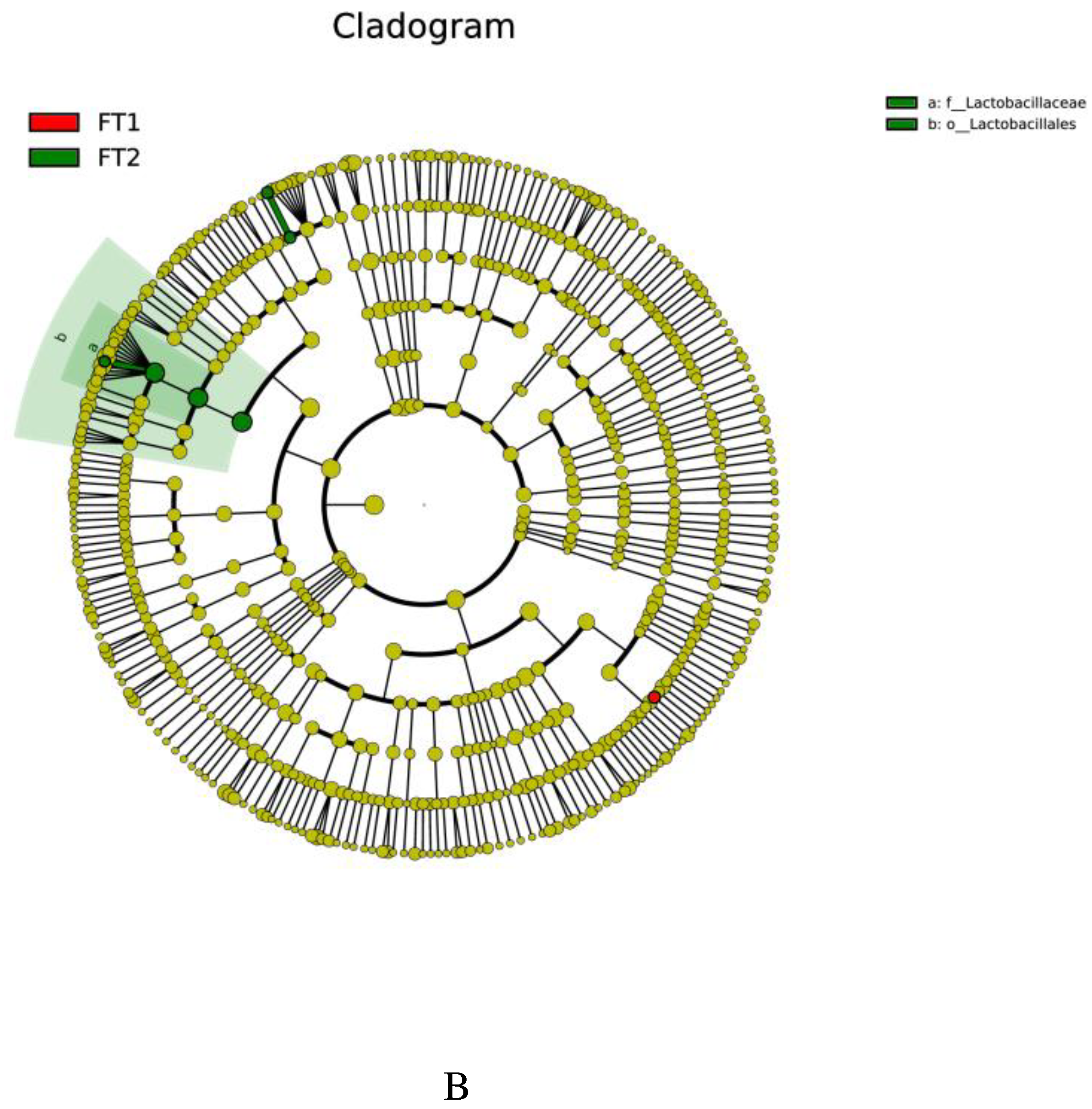
3.5. Effect of FT on the microbial communities of CK silage
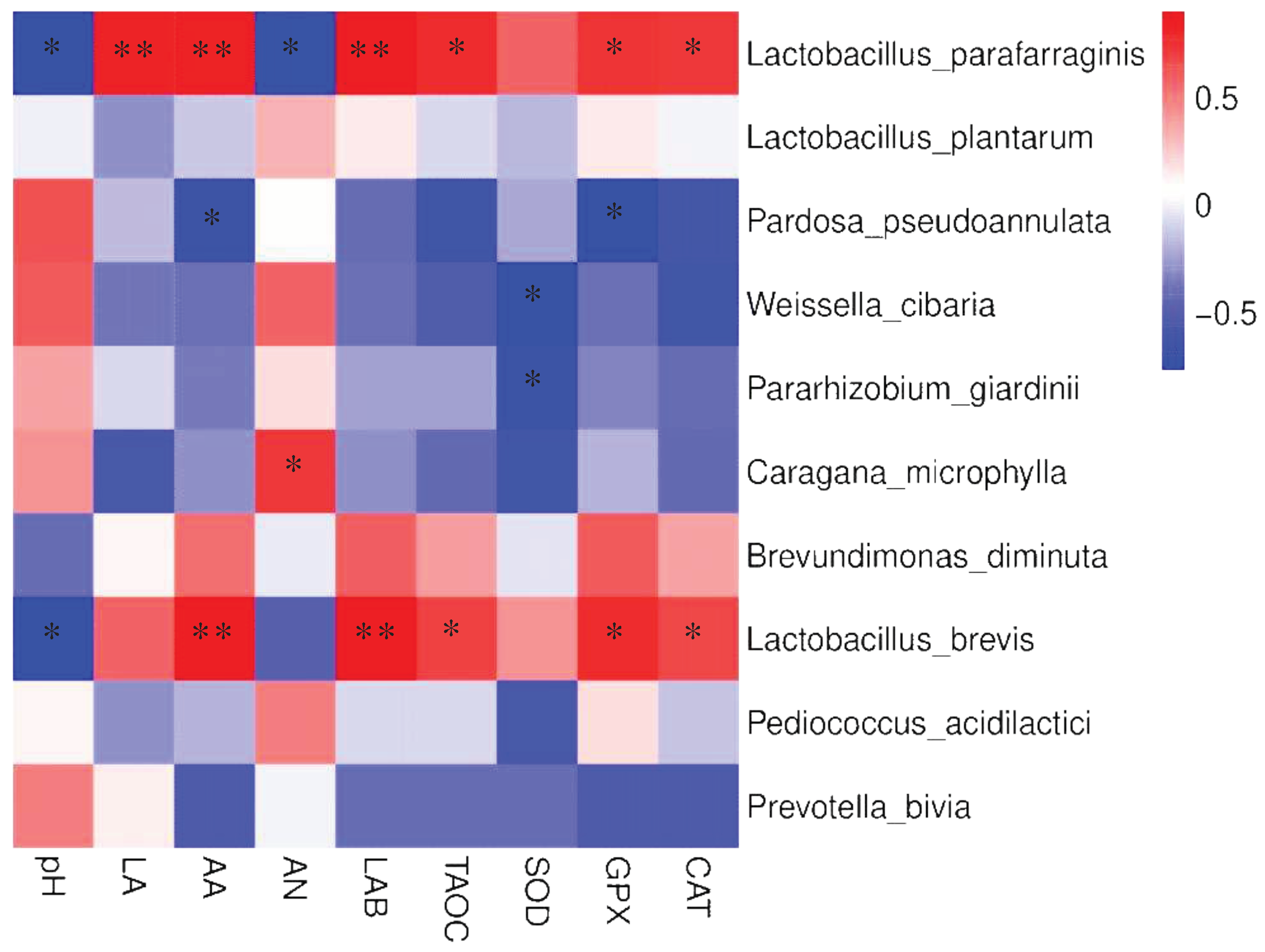
3.6. The correlation between microorganisms and fermentation parameters, antioxidant capacity of CK silage
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of FT on the chemical composition of fresh CK and Silage
4.2. Effect of FT on the fermentation quality of CK silage
4.3. Effect of FT on the antioxidant capacity of CK silage
4.4. Effect of FT on the microbial communities of CK silage
4.5. The correlation between microorganisms and fermentation parameters, antioxidant capacity of CK silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.J.; Chaudhry, A.S.; Osman, A.; Shi, C.Q.; Edwards, G.R.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Cheng, L. Associative effects of ensiling mixtures of sweet sorghum and alfalfa on nutritive value, fermentation and methane characteristics. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 206, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.R. Effects of planting Caragana shrubs on soil nutrients and stoichiometries in desert steppe of Northwest China. Catena. 2019, 183, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, T.Z.; Shen, Y.Q.; Han, L.J.; Peng, Z.J.; Xie, Z.X.; Zhong, C.; Jia, S.R. Bacterial cellulose production from ethylenedi-amine pretreated Caragana korshinskii Kom. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 164, 113340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Chen, Z.X.; Shen, Y.Y.; Yang, X.L. Efficient prediction of profile mean soil water content for hillslope-scale Caragana korshinskii plantation using temporal stability analysis. Catena, 2021, 206, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Du, Z.M.; Yamasaki, S.; Nguluve, D.; Tinga, B.; Macome, F.; Oya, T. Community of natural lactic acid bacteria and silage fermentation of cornstover and sugarcane tops in Africa. Asian-Australasian. J. Animal. Sci. 2020, 33, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.T.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.F.; Xue, Y.L.; Cai, Y.M.; Zhang, G.J. Microbial community, fermentation quality, and in vitro degradability of ensiling Caragana with lactic acid bacteria and rice bran. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 804429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.C.; Wang, Y.; Rinne, M.; Franco, O.M.; Li, F.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y.M.; Zhang, G.J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses on the fermentation quality, in vitro dry matter digestibility, and microbial community of Korshinsk peashrub (Caragana korshinskii Kom.) silages harvested at two growth stages. Grass. Forage. Sci 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bao, X.Y.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q. Treatment of alfalfa silage with tannin acid at different levels modulates ensiling characteristics, methane mitigation, ruminal fermentation patterns and microbiota. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 278, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Oh, J.; Firkins, J.L.; Dijkstra, J.; Kebreab, E.; Waghorn, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Adesogan, A.T.; Yang, W.; Lee, C.; Gerber, P.J.; Henderson, B.; Tricarico, J.M. Special topics-Mitigation of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from animal operations: I. A review of enteric methane mitigation options. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5045–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertenat, D.; Cero, M.D.; Vogl, C.R.; Ivemeyer, S.; Meier, B.; Maeschli, A.; Hamburger, M.; Walkenhorst, M. Ethnoveterinary knowledge of farmers in bilingual regions of Switzerland—Is there potential to extend veterinary options to reduce antimicrobial use? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 246, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.F.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.A.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food. Chem. 2022, 383, 132531–132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.; Davoodi, H. Herbal plants and their derivatives as growth and health promoters in animal nutrition. Vet. Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaziz, F.; Helbert, C.B.; Romdhane, M.B.; Koubaa, M.; Bhiri, F.; Kallel, F.; Chaari, F.; Driss, D.; Buon, L.; Chaabouni, S.E. Structural data and biological properties of almond gum oligosaccharide: Application to beef meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.K.; Wang, X.K.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Li, X.M.; Yang, F.Y. Exploring the silage quality of alfalfa ensiled with the residues of astragalus and hawthorn. Bioresource. Technol. 2020, 297, 122249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.C.; Yang, F.Y.; Undersander, D.J.; Guo, X.S. Fermentation characteristics, aerobic stability, proteolysis and lipid composition of alfalfa silage ensiled with apple or grape pomace. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 202, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitrytė, V.; Povilaitis, D.; Kraujalienė, V.; Šulniūtė, V.; Pukalskas, A.; Venskutonis, P.R. Fractionation of sea buckthorn pomace and seeds into valuable components by using high pressure and enzyme-assisted extraction methods. LWT-Food. Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Qu, H.; Bai, S.Q.; Yan, L.J.; You, M.H.; Gou, W.L.; Li, P.; Gao, F.Q. Effect of wet sea buckthorn pomace utilized as an additive on silage fermentation profile and bacterial community composition of alfalfa. Bioresource. Technol. 2020, 314, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castejón, M.; Visioli, F.; Rodriguez-Casado, A. Diverse biological activities of dandelion. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, Y.Z.; Guo, L.; Donato, P.D.; Silvestri, B. Comparison of bioactive phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of different parts of Taraxacum mongolicum. Molecules. 2020, 25, 3260–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K.; Carle, R.; Schieber, A. Taraxacum-A review on its phytochemical and pharmacological profile. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D. S.; Wu, X.G. , Yi, Q.J. Mulberry and dandelion water extracts prevent alcohol-induced steatosis with alleviating gut microbiome dysbiosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Song, M.; Wang, N.F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.F.; An, X.P.; Qi, J.W. The effects of solid-state fermentation on the content, composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids from dandelion. Plos. One. 2020, 15, e0239076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.R.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, J.; Ke, W.C.; Zhou, J.W.; Zhu, J.X.; Guo, X.S.; Long, R.J. Characterization of antioxidant properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from spontaneously fermented yak milk in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 35, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Z.; Paengkoum, P.; Paengkoum, S.; Chumpawadee, S.; Ban, C.; Thongpea, S. Short communication: purple corn (Zea mays L.) stover silage with abundant anthocyanins transferring anthocyanin composition to the milk and increasing antioxidant status of lactating dairy goats. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 102, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.P.; Yu, Y.D.; Yu, Z.; Shao, T.; Na, R.S.; Zhao, M.M. Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and cellulase on fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of Leymus chinensis silage. Grassland. Sci. 2014, 60, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy. Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R. P. A method for the extraction of plant samples and the determination of total soluble carbohydrates. J. Sci. Food. Agr. 1958, 9, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Association of Analytical Communities: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.M.; Ding, W.R.; Ke, W.C.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.S. Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.K.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, B.G.; Yang, J.X.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresoure. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.F.; Scott, M.B.; Tweed, J.K.S.; Minchin, F.R.; Davies, D.R. Effects of polyphenol oxidase on lipolysis and proteolysis of red clover silage with and without a silage inoculant (Lactobacillus plantarum L54). Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2008, 144, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh-Cigari, F.; Khorvash, M.; Ghorbani, G.R.; Ghasemi, E.; Taghizadeh, A.; Kargar, S.; Yang, W.Z. Interactive effects of molasses by homofermentative and heterofermentative inoculants on fermentation quality, nitrogen fractionation, nutritive value and aerobic stability of wilted alfalfa (Medicago sativa L) silage. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, B.D.; Meeske, R.; van der Merwe, H.J.; Groenewald, I.B. Effects of homofermentative and heterofermentative bacterial silage inoculants on potato hash silage fermentation and digestibility in rams. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2010, 157, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, K.A.; Muck, R.E. Proteolysis in ensiled forage legumes that vary in tannin concentration. Crop. Sci. 1991, 31, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu. Y.R.; Foo L.Y. The polyphenol constituents of grape pomace. Food. Chem. 1999, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.D.; Valles, B.S.; Lobo, A.P. Phenolic and antioxidant composition of by-products from the cider industry: apple pomace. Food. Chem. 2009, 117, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Okada, S. Lactobacillus farraginis sp. nov. and Lactobacillus parafarraginis sp. nov., heterofermentative lactobacilli isolated from a compost of distilled shochu residue. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Yang, F.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Shao, T. Characteristics of Lactobacillus parafarraginis ZH1 and its role in improving the aerobic stability of silages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.K.; Brzezinska-Slebodzinska, E.; Madsen, F.C. Oxidative stress, antioxidants, and animal function. J. Dairy. Sci. 1993, 76, 2812–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Shao, T.; Bai, Y.F. The effect of fibrolytic enzyme, Lactobacillus plantarum and two food antioxidants on the fermentation quality, alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene of high moisture napier grass silage ensiled at different temperatures. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2016, 221, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsampasi, B.; Christodoulou, C.; Tsiplakou, E.; Mavrommatis, A.; Mitsiopoulou, C.; Karaiskou, C.; Dotas, V.; Robinson, P.H.; Bampidis, V.A.; Christodoulou, V.; Zervas, G. Effects of dietary pomegranate pulp silage supplementation on milk yield and composition, milk fatty acid profile and blood plasma antioxidant status of lactating dairy cows. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Rezaei, M.; Rezaei, J. Total replacement of corn silage with sorghum silage improves milk fatty acid profile and antioxidant capacity of Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 101, 10953–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Z.; Paengkoum, P.; Paengkoum, S.; Chumpawadee, S.; Ban, C.; Thongpea, S. Purple corn (Zea mays L.) stover silage with abundant anthocyanins transferring anthocyanin composition to the milk and increasing antioxidant status of lactating dairy goats. J. Dairy. Sci. 2019, 102, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Ke, W.C.; Bai, J.; Li, F.H.; Xu, D.M.; Ding, Z.T.; Guo, X.S. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici J17 with high-antioxidant activity on antioxidant, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, fatty acids, and fermentation profiles of alfalfa silage ensiled at two different dry matter contents. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 268, 114614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Huang, Z.P.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T.; Franco, M.; Ke, W.C.; Li, F.H.; Bai, J.; Ding, Z.T.; Guo, X.S. Antioxidant status, chemical composition and fermentation profile of alfalfa silage ensiled at two dry matter contents with a novel Lactobacillus plantarum strain with high-antioxidant activity. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 272, 114751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M. , Akinloye, O.A.. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Xu, Y.; Gowd, V.; Zhao, J.C.; Xie, J.H.; Liang, W.K.; Chen, W. Systematic study on phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of some new and common mulberry cultivars in China. J. Funct. Foods. 2016, 25, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakub, T. , Karel, Š. Flavonoids as potent scavengers of hydroxyl radicals. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. F. 2016, 15, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; He, H.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Kong, J. Effects of inoculants Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus parafarraginis on the fermentation characteristics and microbial communities of corn stover silage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.H.; Li, J.F.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.R.; Shao, T. Effects of freeze-thaw event on microbial community dynamics during red clover ensiling. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, X.J.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lv, R.L.; Zhou, H.L.; Tang, J. Effects of citric acid and Lactobacillus plantarum on silage quality and bacterial diversity of king grass silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.H.; Lindow, S.E.; Zhang, J.G. Lactobacillus parafarraginis ZH1 producing anti-yeast substances to improve the aerobic stability of silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberline, J.A. Cyanobacteria: omics and manipulation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2017, 36, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Ni, K.K.; Zhang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, F.Y. Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition and microbial community of tropical forage silage under different temperatures. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.W.; Lv, H.J.; Xing, Y.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q. Intrinsic tannins affect ensiling characteristics and proteolysis of Neolamarckia cadamba leaf silage by largely altering bacterial community. Bioresource. Technol. 2020, 311, 123496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunière, L.; Sindou, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Chevallier, I.; Sergentet, D. Silage processing and strategies to prevent persistence of undesirable microorganisms. Animal. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Pech Cervantes, A.A.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: effects of Escherichia coli. O157:H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, L.W.; Xing, Y.Q.; Zhou, W.; Pian, R.Q.; Yang, F.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q. Bacterial diversity and fermentation quality of Moringa oleifera leaves silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria inoculants and stored at different temperatures. Bioresource. Technol. 2019, 284, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Yuan, X.J.; Li, J.F.; Dong, Z.H.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresource. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, H.; Holzer, M.; Mayrhuber, E.; Braun, R. Acetic acid increases stability of silage under aerobic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items1 | CK |
|---|---|
| DM (g/kg FM) | 426.21 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 64.79 |
| EE (g/kg DM) | 25.20 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 10.12 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 801.81 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 664.81 |
| LAB (log10 cfu/g FM) | 3.19 |
| Yeasts (log10 cfu/g FM) | 0.00 |
| Molds (log10 cfu/g FM) | 3.86 |
| Items1 | Treatments2 | SEM3 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 1% FT | 2% FT | |||
| pH | 3.78 a | 3.77 a | 3.72 b | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | 37.02 b | 37.32 b | 44.69 a | 1.23 | <0.01 |
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | 2.90 b | 4.02 b | 12.28 a | 1.05 | <0.01 |
| Propanoic acid (g/kg DM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | - |
| Butyrate (g/kg DM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | - |
| NH3-N (g/kg TN−1) | 14.65 a | 14.40 a | 11.65 b | 0.48 | <0.01 |
| LAB (log 10 cfu/g FM) | 2.49 c | 3.72 b | 4.50 a | 0.22 | <0.01 |
| Yeasts (log 10 cfu/g FM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | - |
| Molds (log 10 cfu/g FM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | - |
| Items1 | Treatments2 | SEM3 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 1% FT | 2% FT | |||
| DM (g/kg FM) | 417.14 c | 423.53 b | 428.10 a | 1.20 | <0.01 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 65.85 b | 66.13 b | 67.40 a | 0.18 | <0.01 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 3.50 | 3.62 | 3.57 | 0.06 | 0.73 |
| EE (g/kg DM) | 44.39 | 43.58 | 42.28 | 0.54 | 0.28 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 760.98 a | 758.31 a | 737.85 b | 3.71 | <0.05 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 647.40 a | 643.68 a | 603.86 b | 5.27 | <0.01 |
| Items1 | Treatments2 | SEM3 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 1% FT | 2% FT | |||
| T-AOC (mmol/g Prot) | 72.74 c | 84.51 b | 90.45 a | 2.66 | <0.01 |
| SOD (U/g FW) | 173.19 b | 172.67 b | 215.11 a | 7.80 | <0.01 |
| GSH-Px (U/g FW) | 210.41 b | 320.27 a | 334.14 a | 19.94 | <0.01 |
| CAT (U/g FW) | 8.08 c | 16.22 b | 21.73 a | 1.99 | <0.01 |
| Items | Treatments1 | SEM2 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 1% FT | 2% FT | |||
| Ace | 378.95 | 215.13 | 199.38 | 80.02 | 0.66 |
| Chao1 | 364.49 | 197.63 | 188.53 | 77.34 | 0.64 |
| Simpson | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.52 |
| Shannon | 3.89 | 3.26 | 1.85 | 0.75 | 0.59 |
| Coverage | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




