1. Introduction
T-cells are essential immune cell types and play a key role in adaptive immune responses, implicated in host defense against invading pathogens and antitumor immunity. The two main subtypes - CD4
+ helper T-cells and CD8
+ cytotoxic T-cells - continuously recirculate between blood and the secondary lymphoid organs in the naïve form, requiring a minimal metabolic activity. Thus, resting T-cells utilize an energy-efficient oxidative metabolism. Following antigen recognition and activation, T-cells exit this metabolically quiescent state and dynamically remodel themselves into an anabolic highly energetic effector phase, requiring immunological and microenvironmental signal-dependent rapid fine-tuning of metabolic programs [
1]. After antigen clearance, T-cells return to a quiescent state to support T-cell memory function.
Metabolic fitness of T-cells is not only essential to meet their bioenergetic demands for mounting an effective adaptive immune response, but also in determining their fate, antigen-specific activation, clonal expansion, differentiation, cytokine production, motility, and tissue recruitment. These immunological processes are ultimately driven by T-cells adopting an appropriate metabolic state to judicially meet cellular energy requirements. T-cells at each differentiation state require appropriate metabolic precursors, metabolism, and energy that are crucial for their effector functions. For example, certain subsets of effector T-cells (e.g., Th17 cells) utilize carbohydrate metabolism as the main energy source, while long-lived memory T-cells and regulatory T-cells (Tregs) utilize fatty acid oxidation to produce energy [
2]. Dysregulated metabolic adaptation in T-cells or inability of T-cells to appropriately tune metabolic needs can cause their overactivation leading to autoimmunity and self-tissue destruction frequently encountered in autoimmune diseases.
Here, we review the maladaptive mechanisms that impact T-cell metabolic fitness implicated in autoimmunity. We discuss abnormal carbohydrate, amino-acid, and lipid metabolisms, energy sensors, and age-related metabolic factors that drive T-cell malfunction and propose therapeutic strategies to target these abnormalities for managing and treating specific autoimmune conditions.
2. Dysregulated T-Cell Carbohydrate Metabolism in Autoimmunity
The most important carbohydrate metabolic adaptation of effector T-cells, immediately after the relay of activation or migration signals, is an accelerated glucose metabolism [
3]. For example, following engagement of the T-cell integrins (such as the lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 or LFA-1) with the ligands expressed on the inflamed endothelium (e.g., intercellular adhesion molecule 1 or ICAM-1), T-cells are stimulated to migrate [
4], which is crucial for T-cell entry into lymph nodes and inflamed tissues. The LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions also tune T-cell functional programs [
5,
6], which are implicated in adaptive immune response as well as in autoimmunity. The LFA-1 contact in actively migrating T-cells induces glucose uptake and increases extracellular acidification rates, which result in increased production of lactate [
7,
8]. Moreover, T-cell activation signals rapidly increase the expression, activity, and function of proteins and enzymes involved in metabolizing glucose. Specifically, T-cell activation signals increase the expression of glucose transporters (such as GLUT-1), which then translocate from cytoplasm to the cell surface, increasing cellular glucose uptake and glycolysis.
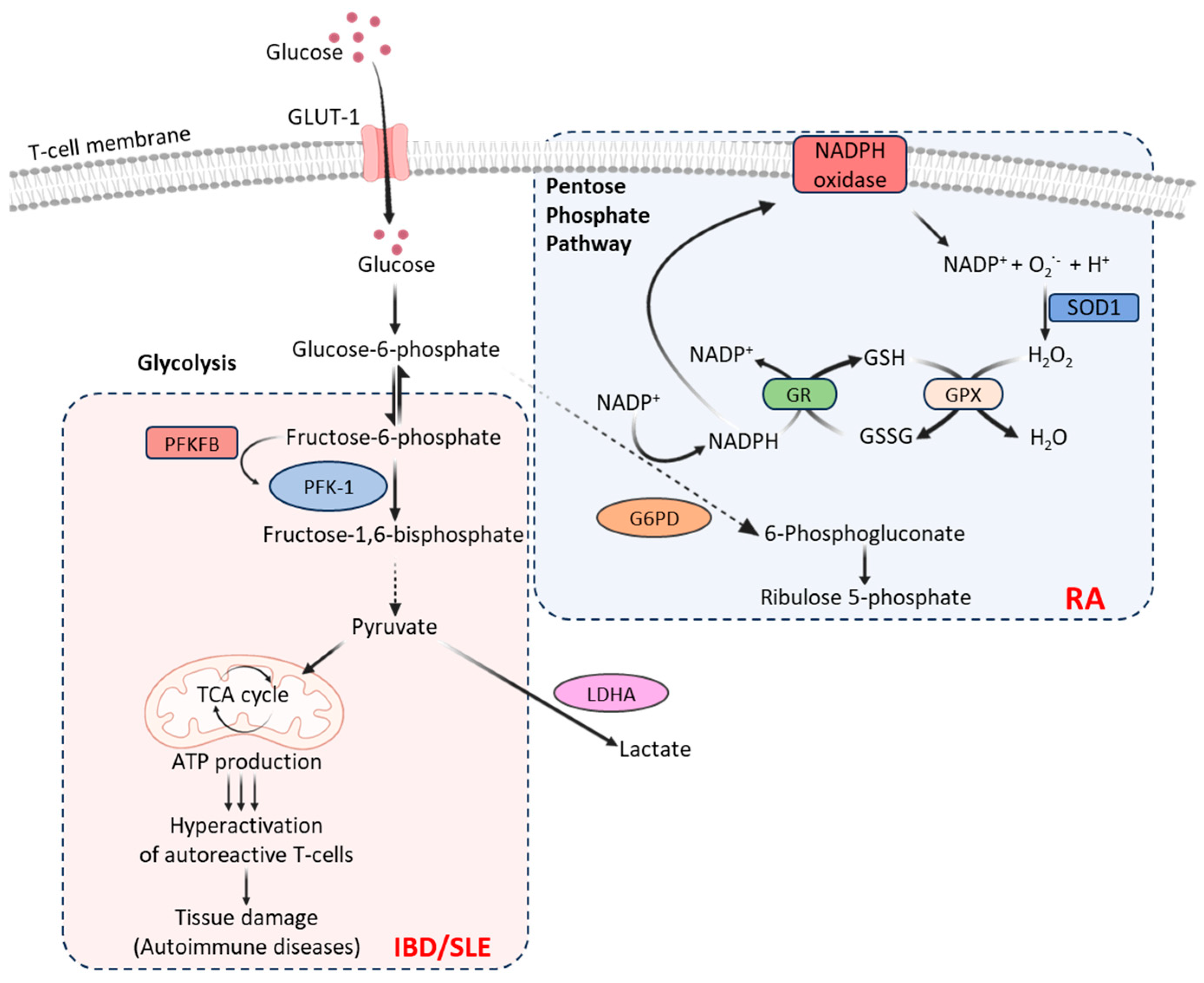
Autoimmunity-associated T-cells exhibit varying levels of dysregulation for carbohydrate metabolism, depending on disease presentation and T-cell bioenergetic demands. For instance, dysfunctional mitochondria in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patient’s T-cells produce relatively less lactate and ATP than healthy individuals [
9]. This is because, RA patients’ T-cells metabolize glucose
via the pentose phosphate pathway [
9] that generates excessive amounts of NADPH, which converts glutathione disulfide (GSSG) into glutathione (GSH) and thus diminishes intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) (
Figure 1). On the other hand, T-cells in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) exhibit increased glycolysis (
Figure 1) that contributes to pro-inflammatory responses, causing hyperactivation of autoreactive T-cells leading to tissue damage [
10,
11]. T-cells in patients with hyperplasia-associated diseases, including psoriasis, exhibit uncontrolled cell proliferation associated with increased GLUT-1 levels [
12]. These suggest that inhibiting GLUT-1 or T-cell glycolysis by glucose import inhibitors could be exploited as a potential therapeutic approach to limit inflammation and achieve immune tolerance in these autoimmune diseases. Indeed, GLUT-1 inhibition in effector T-cells has been found to reduce disease symptoms in a mouse model of SLE [
13].
The rate of glycolysis is controlled by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase (PFKFB), most potent allosteric activator of the enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1) that converts the first glycolysis-committed fructose-6-phosphate into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and thus regulates cellular glycolytic flux. The PFKFB3 deficiency limits the production of ATP, pyruvate, and lactate, shifting glucose towards the pentose phosphate pathway. Human T-cells express PFKFB3, and its expression is rapidly increased (>20-fold) following T-cell receptor engagement and activation signals. T-cells in patients with SLE and IBD express relatively higher levels of PFKFB3 than that in a healthy human [
13]. In RA patients, T-cells express relatively high levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), favoring pentose phosphate pathway of glucose metabolism [
9]. By shifting the PFKFB3/G6PD ratio, T-cells in RA patients skew glucose metabolism from ATP production towards NADPH biosynthesis that generates inflammation-inducing effector cells [
9]. In a human tissue-mouse chimera model, the restoration of PFKFB3 expression in adoptively transferred RA T-cells has been shown to reduce synovial tissue inflammation [
14].
The monosaccharide carbohydrate N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), a monomeric unit of the polymer chitin and the second most abundant carbohydrate after cellulose, plays an important role in T-cell function [
15]. T-cell activation signals trigger the
MGAT-5 gene, leading to N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V-mediated glycosylation of TCR and consequently skew T-cell Th1/Th2 balance [
16]. Mutated MGAT5 can trigger a hyperimmune response [
16] increasing host susceptibility towards IBD by heightened TCR clustering and CD4
+ T-cell differentiation [
17]. Metabolic supplementation of mucosal T-cells from patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) with GlcNAc has been found to enhance branched N-glycosylation in the TCR, resulting in the suppression of T-cell growth, inhibition of the Th1/Th17 immune response, and controlled T-cell activity [
17]. GlcNAc supplementation therapy alone or combined with anti-inflammatory therapies can therefore be suggested as a potential approach for treating IBD and UC.
Lactate is another important carbon source needed for T-cell metabolic fitness [
18]. However, cellular accumulation of lactate in the synovial joints can cause functional impairment of T-cells [
19]. The conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) has an important role in safeguarding the proinflammatory and cytolytic effector functions [
20]. Thus, remodeling glucose metabolism in T-cells by regulating LDHA activity is an attractive approach to potentially reduce chronic inflammation and autoimmunity.
3. Imbalanced T-Cell Lipid Metabolism in Autoimmunity
Lipid species and lipid mediators drive important biological processes in T-cell functional programs, including migration, proliferation, and differentiation [
21]. Excessive levels of saturated fatty acids in the extracellular environment skew T-cells towards pro-inflammatory phenotypes, while polyunsaturated fatty acids promote anti-inflammatory responses [
22]. An imbalance in T-cell lipid metabolism and pathways result in processes implicated autoimmune disorders. For instance, metabolic alterations in the mTORC1 pathway cause intracellular cholesterol accumulation that can hyperactivate CD4
+ T-cells leading to autoimmunity [
23]. Inhibiting mTORC1 therefore could be exploited to control hyperactive T-cells as a therapeutic approach in these diseases.
Cholesterol flux is critical in maintaining cellular cholesterol homeostasis. Alterations in the activity of genes involved in T-cell cholesterol uptake, biosynthesis, and signaling (e.g.,
LRRD1, CYP51A1, PASK, and
Yes1) have been associated with MS pathogenesis [
24]. Acyl-CoA acyltransferase (ACAT)-1 and ACAT-2 are main cholesterol esterification enzymes that convert free cholesterol to cholesteryl esters, which are stored in the cell [
25]. ACAT-1 is expressed in CD8
+ T-cells and is upregulated upon CD8
+ T-cell activation [
26]. ACAT-1 deficiency by genetic ablation or its pharmacological inhibition reduces cholesterol esterification but promotes cholesterol biosynthesis in T-cells [
26], which can increase cholesterol levels in the T-cell plasma membrane. The plasma membrane cholesterol directly binds to the TCR causing nano-clustering that enhances TCR interactions with specific antigen, and thus disrupts T-cell homeostasis [
27,
28]. These altered processes provide a setting for hypercholesterolemia that can lead to the development of T-cell-mediated inflammatory diseases [
27,
28]. For example, the downregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes (LDLR, HMGCS1, FDFT1, and DHCR7) has been observed during 25-hydroxycholesterol supplementation (25-HC, an oxysterol known to control cholesterol flux) that aided in suppressing IL-10 in RA patients [
29].
CD4
+ T-cells can switch from an IFN-γ
+ effector to an IL-10
+ anti-inflammatory subtype. Inhibiting the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway with statins during this IFN-γ
+ to IL-10
+ switching process has been found to create a block in immune resolution, resulting in substantial decrease in the IL-10 production [
30], which is implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE. An altered distribution of sphingolipid-cholesterol-enriched membrane microdomains (lipid rafts) and associated signaling molecules proximal to the antigen receptor have been observed in SLE. These include reduced expression of the lymphocyte-specific protein kinase (Lck) that regulates T-cell development and homeostasis [
31].
In MS, the immune system attacks the lipid-rich myelin sheath of neurons that release a deluge of lipids. A shift from the normal cholesterol biosynthesis pathway to a pathway that produces pro-inflammatory fatty acids has been observed in MS patients. The long chain fatty acids (LCFAs) promote the production of IFN-γ and IL-17 that can exacerbate the acute encephalitis, while short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) exert protection by inducing FOX3P expression, which repress the differentiation of Th17 subsets implicated in autoimmune reactions [
32].
The major autoimmune/autoinflammatory skin diseases, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, are characterized by T-cell hyperproliferation in the skin that depends on cholesterol synthesis and de novo fatty acid synthesis. T-cells with defects in fatty acid oxidation will have an impaired T-cell formation as they are fueled
via fatty acid oxidation happening in endoplasmic reticulum. The resident memory T-cells present in the skin are functionally specialized in fatty acid uptake from cutaneous environment. The defect in fatty acid oxidation can be attributed to promotion of mitochondrial function that increases the proliferation of memory T-cells in T-cell-mediated skin diseases [
33,
34].
Glycosphingolipids (GSL) that consist of glycans linked to C-1 hydroxyl group of ceramides are expressed in cellular plasma membranes. An altered GSL profile influences the balance between stimulatory and inhibitory signals transmitted during T-cell activation, skewing the T-cell function. Peripheral CD4
+ T-cells in SLE patients exhibit an increased levels of lipid raft-associated GSL compared to that in healthy individuals. This elevated levels of GSLs in SLE patients is due to increased expression of the nuclear receptor LXRβ that regulates cellular lipid metabolism and trafficking. LXRβ antagonists can therefore be used to normalize GSL metabolism, correct CD4
+ T-cell signaling, and restore T-cell function in SLE patients [
35].
4. Dysregulated T-Cell Amino Acid Metabolism in Autoimmunity
In addition to glucose and lipid metabolisms, activated T-cells are also dependent on amino acids and their metabolism. Certain essential amino acids are crucial for T-cell functioning and they serve as metabolic fuels for mitochondrial oxidation and ATP production. For instance, leucine is critical for the efficient activation of T-cells. The L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) mediates the transport of amino acids including leucine, tryptophan, arginine, tyrosine, and phenylalanine. A deficiency in LAT1 or mTORC1 can result in a dysregulated amino acid metabolism by impairing the T-cell differentiation thereby causing autoimmunity. Defective amino-acid metabolism in T-cells causing hyperactivation of T-cells has been observed in MS patients [
36].
T-cells utilize significantly high amounts of glutamine, which is the most abundant amino acid in serum. After entering T-cells, glutamine is hydrolyzed by glutaminase into glutamate, which is then converted to α-ketoglutarate with the simultaneous release of the amino group. During the process of T-cell differentiation, enzymes glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 1 (GOT-1) and 2 (GOT-2) catalyze the amino group into aspartate via a reductive amination reaction. The aminooxy-acetic acid, a GOT-1 selective inhibitor, reduces the formation of α-ketoglutarate which is metabolized to 2-hydroxyglutaratein. Consequently, cellular levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate are significantly reduced in differentiated Th17 cells. This reduces the hypermethylation of the FOXP3 gene increasing FOXP3 expression, which is one of the major transcriptional factors driving and maintaining the Treg phenotype and functioning. Increased Tregs exert an antagonistic effect on ROR-γt (a master transcription factor essential for Th17 differentiation), thus repressing Th17 differentiation [
37]. Methionine metabolism tunes T-cell adaptive immune response through regulation of epigenic reprogramming. In this context, dietary restriction of methionine has been found to reduce the severity of multiple sclerosis (MS) disease symptoms by limiting the expansion of Th17 cells in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model [
38].
Branched chain amino transferases (BCAT) are isoenzymes responsible for the first step of degradation of branched chain amino acids (BCAAs). The role played by BCAT isoenzymes within the immune cells is still not clear. Among all the BCAAs, leucine is significantly important as loss of BCATc expression can increase the supply of leucine to mTORC1. This can result in T-cell hyperactivation and autoimmunity. A localized depletion of leucine by inducing amino acid-consuming enzymes, such as BCATc, promotes the induction of T-cell anergy [
3].
The non-essential amino acid serine, synthesized from a glycolysis intermediate, 3-phosphoglycerate, is also important for T-cell proliferation and effector function [
39]. In addition, intermediate metabolic products derived from other amino acids, such as nitric oxide (NO) from L-Arginine, mediate changes in T-cell function. For example, NO enhances differentiation of Th1, Th17 and Th9 cells and therefore exacerbates autoimmune inflammation. Increased NO is a well-established inflammatory factor in RA and IBD. Therefore, limiting soluble NO in the serum could be a potential therapeutic approach to control autoimmunity [
40].
5. T-Cell Energy Sensors Implicated in Autoimmunity
T-cells utilize energetic and biosynthetic precursors in order to maintain homeostasis and perform effector functions. For example, T-cell motility is regulated by mitochondria activity and metabolic mediators that precisely co-ordinate receptor-ligand interactions, signal transduction, and cytoskeletal remodeling. [
41]. An actively migrating T-cell localize mitochondria to the uropod to fuel cytoskeletal rearrangements. T-cell energy sensors, such as the AMPK-activated kinase (AMPK), sense changes in energy levels and activate signaling pathways to maintain cellular energy balance. Thus, environmental, and immunological stimuli can activate catabolic pathways in T-cells
via AMPK to generate ATP. The AMPK pathways crosstalk with T-cell lipid and glucose metabolisms [
3]. When the energy stores are low in T-cells AMPK is activated, which phosphorylates the components of cellular energetic pathways. AMPK also inhibits the mTORC1. During low energy levels, the AMPK and mTORC1 are connected to each other and AMPK tends to inactivate the mTORC1 to decelerate the cellular replication and growth. All these processes simultaneously restore T-cell energy balance for appropriate functions [
42]. In RA patients, T-cells exhibit defective mitochondria and altered recruitment of AMPK, causing hyperproliferation and proinflammatory effector functions [
14]. Similarly, T-cells in patients with SLE have dysfunctional mitochondria [
43].
N-myristylation is required for the lysosomal translocation of AMPK. However, a defective N-myristylation has been observed in RA T-cells due to reduced concentrations of N-myristoyltransferase (NMT1). This causes an increased differentiation rate of T helper cells into Th1 and Th17. Loss of the NMT1 enzyme or its genomic alterations causes synovial inflammation and can prevent the lysosomal recruitment of AMPK, resulting in the activation of mTORC1 [
44].
In autoimmune skin diseases, T-cells are unable to meet high energy demands, resulting in T-cell dysfunction. While AMPK and mTORC1 are recognized as crucial players in controlling the cellular metabolic state, their detailed mechanisms are not fully understood. The mTORC1 protein can sense the need for metabolic factors (e.g., amino acids), oxygen, energy requirements, growth factors, etc. required for cell division and growth and can also transmit this information in the regulation of various metabolic processes. However, under hypoxia or ATP limiting inflammatory conditions, mTORC1 does not get activated, but the AMPK helps T-cells to adapt to the local metabolic microenvironment [
34].
Kynurenic acid, a potent immunomodulatory metabolite, is an endogenous ligand for aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) complex and promotes Treg differentiation. In SLE, kynurenine accumulates intracellularly and activate the mTORC1 complex in T-cells skewing the T-cell lineage development. On the contrary, SLE T-cells exhibit diminished cysteine production because of an impaired pentose phosphate pathway. This results in reduced glutathione synthesis and cystine accumulation [
45]. Metformin can indirectly inhibit the activation of mTOR and HIF1α and thus reduce Th17 and increase Treg differentiation, decreasing EAE clinical presentations [
46].
Deficient Tregs, excessive effector T-cells and the elevated proinflammatory cytokines can induce intestinal inflammation thereby exacerbating the symptoms of IBD. In IBD, the metabolic sensor AMPK plays an important role in maintaining the gut barrier function and suppressing the inflammation in Tregs. Activation of AMPK can create a pseudo-starving condition that can favour oxidative metabolism and suppress the intestinal inflammation. Additionally, AMPK can alter cellular metabolism by shifting the proinflammatory cytokine production to anti-inflammatory by promoting T-cell differentiation that support epithelial barrier function and autophagy. Hence, activating the AMPK can be exploited as a potential therapeutic option for treating IBD. Similarly, another significant metabolic sensor mTORC1 is highly activated in the IBD patients’ the gut mucosa. Thus, inhibiting the mTORC1 signaling can also be considered as a potential therapeutic approach for IBD treatment. The mTORC1 inhibitors including Tacrolimus, Everolimus, and Sirolimus are being tested in clinical trials for IBD treatment [
10]. Mesalamine (5-aminosalicylate), an immunosuppressant that inhibits the mTORC1 signaling has pleiotropic effects on various energy metabolic pathways including NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, PPAR-γ, MAPK and PI3K/Akt responsible for colonic inhibition [
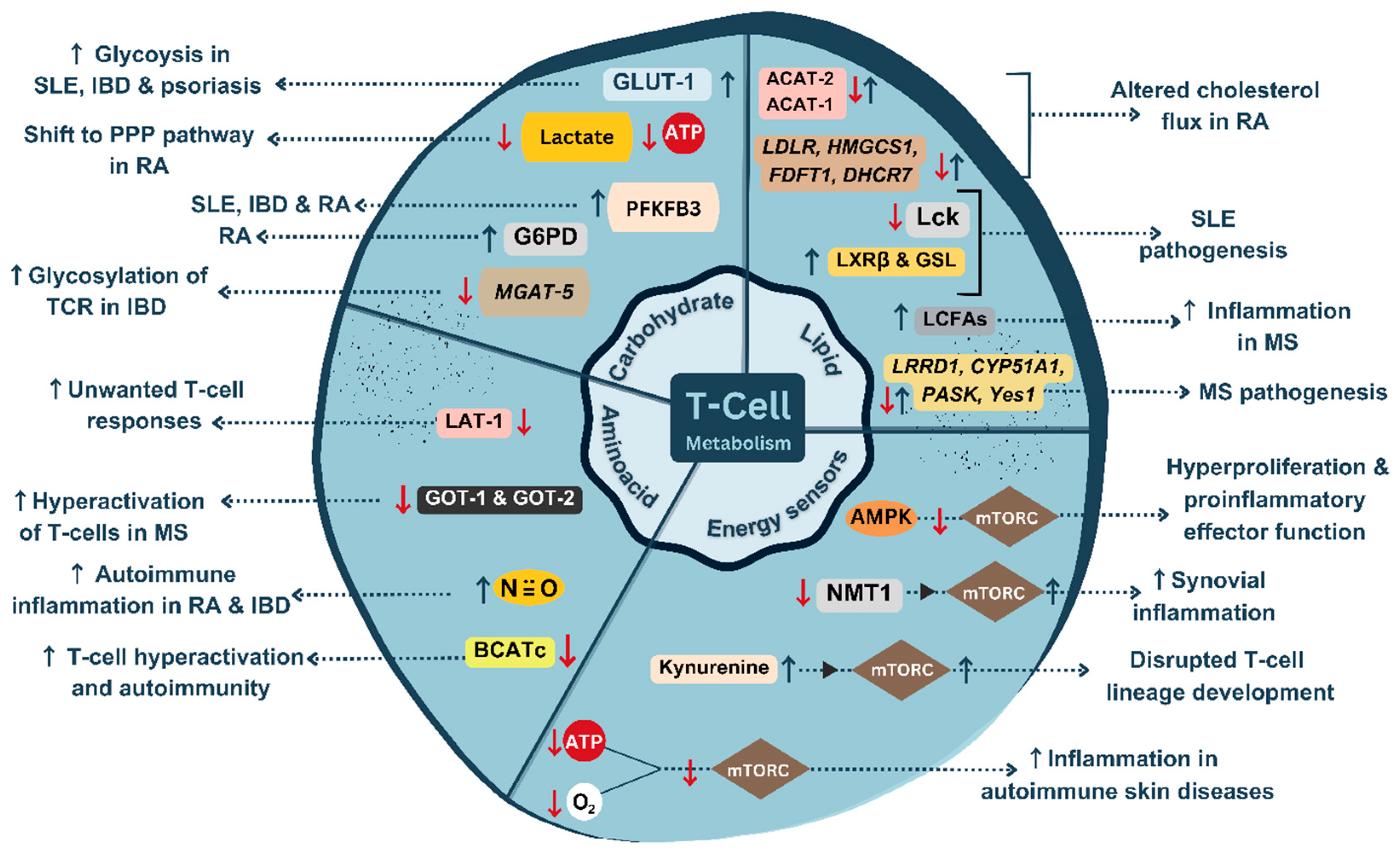
47]. The metabolic maladaptation occurring in T-cells which can lead to autoimmunity are summarized in
Figure 2.
6. Progressive Deterioration of T-Cell Metabolic Fitness with Age and Autoimmunity
There is a strong connection between ageing and T-cell metabolic pathways. Thymic ageing mainly starts with the T-cells, adapting dynamically to the new organization, as the production of new T-cells stops, and the existing T-cells has to deal with the foreign antigens and the chronic infections brought about by it. The other major events in immunological senescence include damaging of DNA and accumulation of proteins. However, the changes taking place in individuals with specific autoimmune diseases may vary as their T-cells would have already undergone functional transition and became more innate, tissue invasive and pro-inflammatory in nature [
48]. This creates a T-cell aging associated phenotype (TASP) combined with gain of new functions and loss of existing regulatory and cytotoxic effector functions. The TASP can drive tissue inflammation in autoimmune diseases [
49].
T-cell homeostatic signaling, mainly the IL-7 signaling, declines with ageing, challenging the metabolic fitness of T-cells. The availability of cytokines and costimulatory molecules can further impact the metabolic profile of ageing T-cells. The young naïve T-cells are constantly exposed to nutrient-rich environment. With ageing, the number of naïve T-cell population reduces, and the activity of T-cells deteriorates. Trophic signals, including TCR downstream signaling, and homeostatic cytokines regulate the glucose uptake and glycolysis through multiple enzymes. In the absence of these tropic signals, aging associated T-cells are not able to maintain glucose metabolism resulting in reduced mitochondrial membrane potential of T-cells that eventually die. These T-cells give rise to less efficient effector T-cells with impaired cytokine production [
50,
51]. However, it remains unclear whether these alterations are the survival adaptations by the aged T-cells requiring more detailed investigation to understand aged T-cell functioning that may help to manipulate the metabolism in order to prevent T-cell exhaustion.
The pathogenic T-cells in RA patients could be a consequence of the premature thymic aging, making it a crucial risk determinant in case of RA patients. The shortening of telomeric DNA and the instability of mitochondrial DNA can produce metabolites that can expand T-cell endoplasmic reticulum membranes and induce production of proinflammatory cytokines. Eventually, these T-cells became tissue invasive and activate the inflammasome. RA T-cells easily transform into mobile T-cells which can easily enter the synovial tissue causing tissue inflammation. This rapid transformation of T-cells can be attributed to the cell’s altered lipid metabolism [
52].
Mitochondrial malfunction is another feature of aged T-cells. Aged naïve T-cells show lower calcium influx, impaired calcium buffering capacity, reduction in ATP production, increased ROS generation, and reduced clonal expansion compared to the younger T-cells. These changes can affect T-cell metabolism. Reduced oxidative phosphorylation in aged T-cells could be due to many factors, for example, decline in the activity of respiratory enzymes, proton leakage, or a decrease in membrane potential [
53,
54]. However, mitochondrial malfunction associated with aging and association with autoimmunity are not well understood. Future studies should be necessary to understand the role of mitochondrial metabolism in ageing T-cells that will pave way to develop therapeutic interventions that can improve the immune responses in aged individuals.
A reduction in the suppressive functions of Tregs can make the host cells susceptible to inflammatory diseases and on the other hand, the loss of function of Tregs can be due to the exposure with inflammatory environment. Most of the abnormalities that are seen in RA T-cells are connected with the defects in mitochondrial DNA which can have a direct effect on tissue inflammation. The failure of mitochondrial electron transport chain leads low levels of metabolites and reduced production of ROS which creates reductive stress. A decrease in aspartate production has also been observed which triggers ER membrane expansion and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [
55]. However, how the inflammation influence the Treg functions remains unknown. A better understanding about the thymic ageing mechanism can help to understand the events causing tissue inflammation.
7. Future Research and Conclusions
Activated T-cells can adjust their reliance on various metabolic pathways depending on available nutrients in the surrounding tissue microenvironment. However, many questions pertaining to T-cell metabolic flexibility remain to be answered. How do T-cells dynamically to perform specific effector functions? Metabolic status of T-cell subtypes is likely to vary in various tissues, and among patients with various levels of tissue destructive autoimmunity due to diverse temporal and spatial coordination of local metabolite microenvironment. Whether and how metabolic pathways are compartmentalized to support T-cell function in diverse tissues under varying microenvironments, such as those encountered in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues, and in inflamed peripheral tissues in patients with autoimmune diseases need further research. A vital function of T-cells is their migration to tissue sites, which is an energetically demanding process. How do a T-cell and its intracellular signaling components regulate metabolic activity depending on specific energetic demands for T-cell motility? Unravelling the molecular basis of the role of cellular metabolism and T-cell migration will expand our understanding of host immunity and autoimmunity. Metabolic pathway regulators, including glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), and several adaptor proteins control T-cell metabolism and motility [
56,
57]. Can metabolic modulators be combined with LFA-1-targeted therapeutics for safe clinical outcomes? It would be imperative to understand how local nutrient availability affects T-cell function. Role of diet and dietary restriction in shaping T-cell metabolic fitness needs to be examined, which will shed light on whether specific aspects of host nutrition can be targeted to tackle autoimmune tissue damage.
Therapeutic approaches to manage and treat autoimmune diseases continue to evolve. At the same time, extensive innovations are necessary to improve clinical outcomes. In this context, targeting T-cell metabolic fitness could be an ideal approach to tackle autoimmunity. There is a need to understand various maladaptive mechanisms associated with T-cell metabolic fitness, which are responsible for controlling the T-cell function in a diverse range of autoimmune conditions. Current strategies to regulate T-cell metabolic fitness need to be combined with genetic approaches to selectively manipulate metabolism of specific T-cell subtypes. Therefore, it would be imperative to develop novel techniques and test in the clinic to control T-cell metabolism to improve the outcomes of autoimmune diseases.
In summary, current review explains how certain metabolic maladaptation in T-cells could provide a setting for the incidence or progression of autoimmune diseases. We draw attention to the identified risk genes and defective genes involved in T-cell maladaptive metabolic program. Understanding the myriad ways in which metabolic dysfunctions can occur in T-cells can help to devise novel therapeutic strategies or further optimize existing strategies to treat autoimmune diseases.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, I.R.A. and N.K.V; writing—review and editing, B.H.S.W., D.K. and NKV; resources, N.K.V.; funding acquisition, N.K.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported, in part, by the Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) under its MOE Academic Research Fund (AcRF) Tier 1 Grants (RG26/20 and RG94/22), and the National Research Foundation Singapore under its Open Fund Large Collaborative Grant (OFLCG18May-0028) and administered by the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council (NMRC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank India@NTU Connect Program for facilitating this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Varanasi, S.K.; Kumar, S.V.; Rouse, B.T. Determinants of tissue-specific metabolic adaptation of T cells. Cell Metab 2020, 32, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewicz, M.; Ronowska, A.; Zieliński, M.; Jankowska-Kulawy, A.; Trzonkowski, P. T regulatory cells metabolism: The influence on functional properties and treatment potential. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1122063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyer, J.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Bailis, W. Metabolic signaling in T cells. Cell Res 2020, 30, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.K.; Kelleher, D. An introduction to LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions in T-cell motility. Methods Mol Biol 2019, 1930, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Kelleher, D. Not just an adhesion molecule: LFA-1 contact tunes the T lymphocyte program. J Immunol 2017, 199, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Fazil, M.H.; Ong, S.T.; Chalasani, M.L.; Low, J.H.; Kottaiswamy, A.; Prasannan, P.; Kizhakeyil, A; Kumar, S.; Panda, A.K.; Freeley, M.; Smith, S.M.; Boehm, B.O.; Kelleher, D. LFA-1/ICAM-1 ligation in human T cells promotes Th1 polarization through a GSK3β signaling-dependent Notch pathway. J Immunol 2016, 197, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli-Berg, F.M.; Jangani, M. Metabolic regulation of leukocyte motility and migration. J Leukoc Biol 2018, 104, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, M.; Cheung, K.C.P.; Fu, H.; Bonacina, F.; Wang, G.; Coe, D.; Ward, E.J.; Colamatteo, A.; Jangani, M.; Baragetti, A.; Matarese, G.; Smith, D.M.; Haas, R.; Mauro, C.; Wraith, D.C.; Okkenhaug, K.; Catapano, A.L.; De Rosa, V.; Norata, G.D.; Marelli-Berg, F.M. Regulatory T cell migration is dependent on glucokinase-mediated glycolysis. Immunity 2017, 47, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, C.M.; Wu, B.; Goronzy, J.J. The metabolic signature of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2020, 32, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, V.Z.; Jones, F.; Doherty, G.; Ryan, E.J. Targeting immune cell metabolism in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2021, 27, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelic, M.; Kono, M.; Tsokos, G.C. T cell metabolism in lupus. Immunometabolism 2020, 2, e200009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pålsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A. Targeting immunometabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy. Cell Res 2020, 30, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Qu, G.; Choi, S.C.; Cornaby, C.; Titov, A.; Kanda, N.; Teng, X.; Wang, H.; Morel, L. Targeting T cell activation and lupus autoimmune phenotypes by inhibiting glucose transporters. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, C.; Goronzy, J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, A.; Slawson, C.; Fields, P.E. The role of O-GlcNAcylation in immune cell activation. Front Endocrinol 2021, 12, 596617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Gao, G.; Pawling, J.; Dennis, J.W.; Demetriou, M.; Li, B. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V (Mgat5)-mediated N-glycosylation negatively regulates Th1 cytokine production by T cells. J Immunol 2004, 173, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.M.; Correia, A.; Pereira, M.S.; Almeida, C.R.; Alves, I.; Pinto, V.; Catarino, T.A.; Mendes, N.; Leander, M.; Oliva-Teles, M.T.; Maia, L.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Taniguchi, N.; Lima, M.; Pedroto, I.; Marcos-Pinto, R.; Lago, P.; Reis, C.A.; Vilanova, M.; Pinho, S.S. Metabolic control of T cell immune response through glycans in inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018, 115, E4651–E4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Veliça, P.; Gameiro, P.A.; Cunha, P.P.; Foskolou, I.P.; Rullman, E.; Bargiela, D.; Johnson, R.S.; Rundqvist, H. Lactate exposure shapes the metabolic and transcriptomic profile of CD8+ T cells. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J. Lactate rewires synovial T cells in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Dou, X.; Chen, R.; Ge, Y.; Lin, Y. LDHA as a regulator of T cell fate and its mechanisms in disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 158, 114164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Kanno, T.; Nakajima, T. Fatty acid metabolism in T-cell function and differentiation. Int Immunol 2022, 32, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubler, M.J.; Kennedy, A.J. Role of lipids in the metabolism and activation of immune cells. J Nutr Biochem 2016, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Urbano, M.; Quintero-González, D.C.; Vasquez, G. T cell metabolism and possible therapeutic targets in systemic lupus erythematosus: a narrative review. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2022, 44, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrastelj, J.; Andrews, R.; Loveless, S.; Morgan, J.; Bishop, S.M.; Bray, N.J.; Williams, N.M.; Robertson, N.P. CSF-resident CD4+ T-cells display a distinct gene expression profile with relevance to immune surveillance and multiple sclerosis. Brain Commun 2021, 3, fcab155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, S.; Yu, C.; Li, B.L.; Miyazaki, A. Roles of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 and -2. Curr Opin Lipidol 2001, 12, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Bai, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Meng, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Yan, C.; Wang, L.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, T.Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, P.; Song, B.L.; Liu, W.; Sun, S.C.; Liu, X.; Li, B.L.; Xu, C. Potentiating the antitumour response of CD8(+) T cells by modulating cholesterol metabolism. Nature 2016, 531, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, E.; Taheri, F.; Gheibi Hayat, S.M.; Montecucco, F.; Carbone, F.; Rostami, D.; Montazeri, A.; Sahebkar, A. The atherogenic role of immune cells in familial hypercholesterolemia. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Jin, S.; Chen, G. The effect of lipid metabolism on CD4+ T cells. Mediators Inflamm 2021, 5, 6634532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.; Perucha, E. Cholesterol metabolism: a new molecular switch to control inflammation. Clin Sci 2021, 135, 1389–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucha, E.; Melchiotti, R.; Bibby, J.A.; Wu, W.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Roberts, C.A.; Hall, Z.; LeFriec, G.; Robertson, K.A.; Lavender, P.; Gerwien, J.G.; Taams, L.S.; Griffin, J.L.; de Rinaldis, E.; van Baarsen, L.G.M.; Kemper, C.; Ghazal, P.; Cope, A.P. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway regulates IL-10 expression in human Th1 cells. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kashyap, A.; Silakari, O. Exploration of the therapeutic aspects of Lck: a kinase target in inflammatory mediated pathological conditions. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 108, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompura, S.L.; Hafler, D.A.; Dominguez-Villar, M. Fatty acid metabolism and T cells in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 869197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.; Kupper, T. T cells and the skin: from protective immunity to inflammatory skin disorders. Nat Rev Immunol 2019, 19, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Meyenn, L.; Bertschi, N.L.; Schlapbach, C. Targeting T cell metabolism in inflammatory skin disease. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, P.; Cai, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y. Lipid metabolism: immune regulation and therapeutic prospectives in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 860586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Luo, Q.; Chen, L. Amino acid solute carrier transporters in inflammation and autoimmunity. Drug Metab Dispos 2021, DMD-AR-2021-000705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, S.; Mickael, M.E.; Moran, M.; Spell, M.; Basu, R. RORγt promotes Foxp3 expression by antagonizing the effector program in colonic regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2021, 207, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.G.; Chen, J.; Mamane, V.; Ma, E.H.; Muhire, B.M.; Sheldon, R.D.; Shorstova, T.; Koning, R.; Johnson, R.M.; Esaulova, E.; Williams, K.S.; Hayes, S.; Steadman, M.; Samborska, B.; Swain, A.; Daigneault, A.; Chubukov, V.; Roddy, T.P.; Foulkes, W.; Pospisilik, J.A.; Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.C.; Artyomov, M.N.; Witcher, M.; Krawczyk, C.M.; Larochelle, C.; Jones, R.G. Methionine metabolism shapes T helper cell responses through regulation of epigenetic reprogramming. Cell Metab 2020, 31, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolan, S.S.; Li, G.; Wik, J.A.; Malachin, G.; Guo, S.; Kolan, P.; Skålhegg, B.S. Cellular metabolism dictates T cell effector function in health and disease. Scand J Immunol 2020, 92, e12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rizvi, Z.A.; Awasthi, A. Metabolic checkpoints in differentiation of helper T cells in tissue inflammation. Front Immunol 2019, 9, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Liu, K.; Kondo, Y.; Slubowski, C.J.; Dertnig, T.; Denicoló, S.; Arbab, M.; Hubner, J.; Konrad, K.; Fakhari, M.; Lederer, J.A.; Robson, S.C.; Visner, G.A.; Junger, W.G. Purinergic P2X4 receptors and mitochondrial ATP production regulate T cell migration. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 3583–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, N.R.; Whitfield, J.; Hoffman, N.J. Interactive roles for AMPK and glycogen from cellular energy sensing to exercise metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergely, P.Jr.; Grossman, C.; Niland, B.; Puskas, F.; Neupane, H.; Allam, F.; Banki, K.; Phillips, P.E.; Perl, A. Mitochondrial hyperpolarization and ATP depletion in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2002, 46, 175–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Jin, K.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Tian, L.; Shoor, S.; Roche, N.E.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. N-myristoyltransferase deficiency impairs activation of kinase AMPK and promotes synovial tissue inflammation. Nat Immunol 2019, 20, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gong, N.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y. Immunometabolomics provides a new perspective for studying systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 118, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Bonner, J.A.; Shi, L.Z. Metabolic checkpoints in neurodegenerative T helper 17 (TH17) and neuroregenerative regulatory T (Treg) cells as new therapeutic targets for multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen Res 2020, 15, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, V.; Krnjic, A.; Frick, A.; Gmainer, C.; Asboth, M.; Jimenez, K.; Lang, M.; Baumgartner, M.; Evstatiev, R.; Gasche, C. Mesalamine and azathioprine modulate junctional complexes and restore epithelial barrier function in intestinal inflammation. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyahu, Y.; Monsonego, A. Thymus involution sets the clock of the aging T-cell landscape: Implications for declined immunity and tissue repair. Ageing Res Rev 2021, 65, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.V.; Sato, Y.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. T-cell aging-associated phenotypes in autoimmune disease. Front Aging 2022, 3, 867950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, K.M.; Palchaudhuri, R.; Palmer, C.S.; La Gruta, N.L. The clock is ticking: the impact of ageing on T cell metabolism. Clin Transl Immunology 2019, 8, e01091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes, R.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Weyand, C.; Goronzy, J. Metabolic reprogramming in memory CD4 T cell responses of old adults. Clin Immunol 2019, 207, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Immunometabolism in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 2020, 294, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callender, L.A.; Carroll, E.C.; Bober, E.A.; Akbar, A.N.; Solito, E.; Henson, S.M. Mitochondrial mass governs the extent of human T cell senescence. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, A.; Schurman, S.H.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Dunn, C.A.; Singh, A.K.; Macian, F.; Cuervo, A.M.; Sen, R.; Ferrucci, L. Age-associated changes in human CD4+ T cells point to mitochondrial dysfunction consequent to impaired autophagy. Aging 2019, 11, 9234–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, T.; Jin, K.; Hu, Z.; Abdel, M.; Warrington, K. Mitochondrial aspartate regulates TNF biogenesis and autoimmune tissue inflammation. Nat Immunol 2021, 22, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Kelleher, D. Adaptor regulation of LFA-1 signaling in T lymphocyte migration: Potential druggable targets for immunotherapies? Eur J Immunol 2014, 44, 3484–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazil, M.H.U.T.; Prasannan, P.; Wong, B.H.S.; Kottaiswamy, A.; Salim, N.S.B.M.; Sze, S.K.; Verma, N.K. GSK3β interacts with CRMP2 and Notch1 and controls T-cell motility. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 680071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).