Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
20 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Cerebral Morpho-Functional and Vascular Correlates of Hypnotizability
1.2. Functional Equivalence between Real and Imagined Perception/Action
1.3. Motor Cortex Excitability
1.4. Attention and Emotion
1.5. Paradoxical Pain Control by Cerebellar Stimulation
1.6. Interoception
1.7. Hypnotizability and Brain Injuries
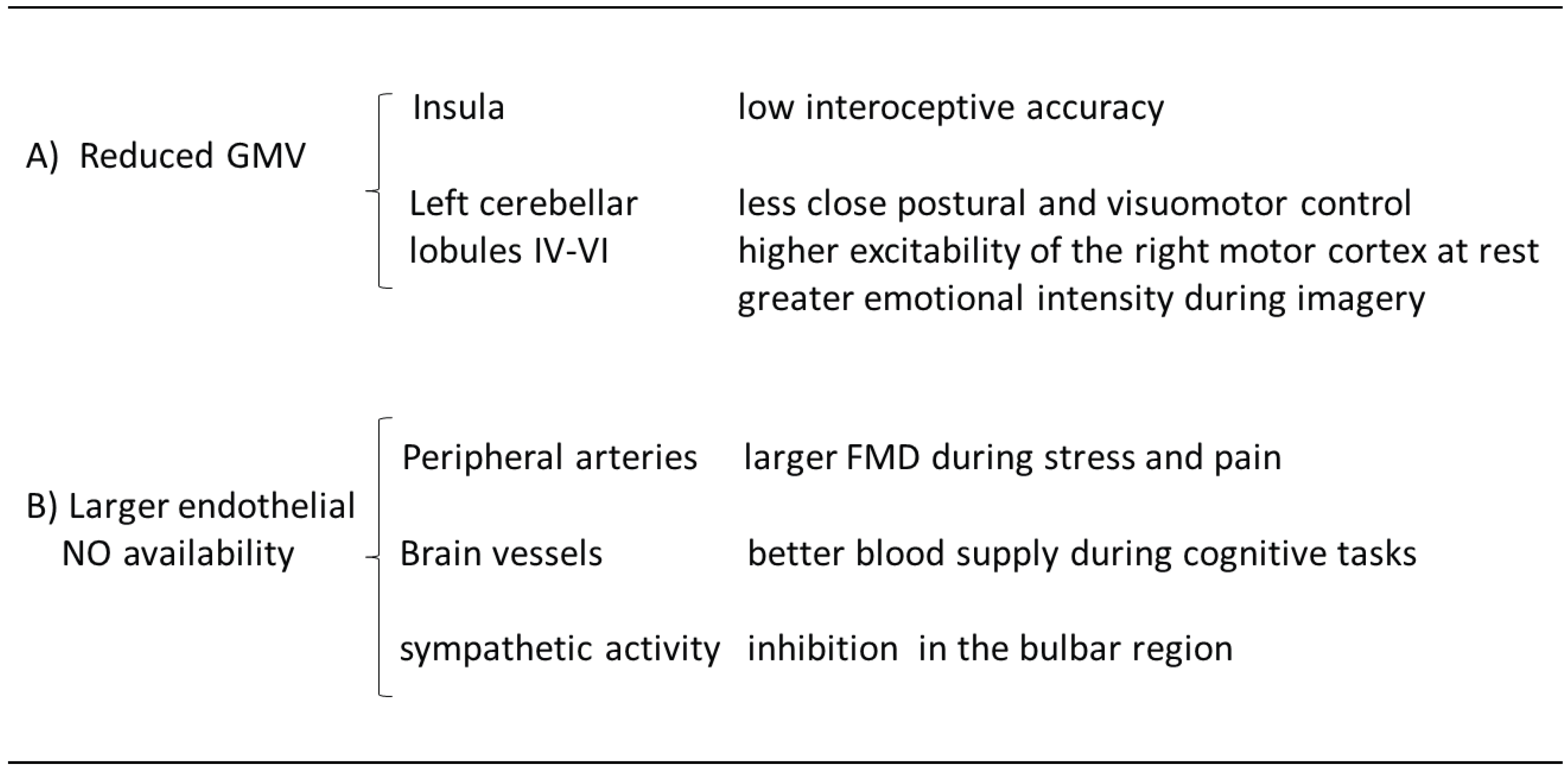
1.8. Cardiovascular Control
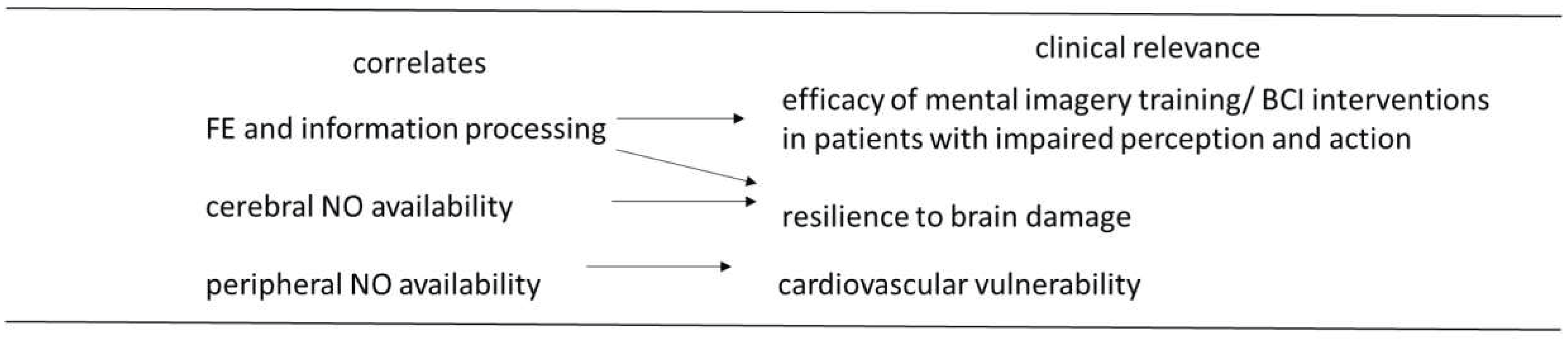
2. Limitations and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Acunzo, D. J., & Terhune, D. B. (2021). A Critical Review of Standardized Measures of Hypnotic Suggestibility. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 69(1), 50–71. [CrossRef]
- Acunzo, D.J., Oakley, D.A., & Terhune, D.B. (2021). The neurochemistry of hypnotic suggestion. American Journal of Clinical hypnosis, 63(4), 355-371. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B., Gill, I., Liblik, K., Uppal, J. S., & El-Diasty, M. (2023). The Role of Hypnotherapy in Postoperative Cardiac Surgical Patients, A Scoping Review of Current Literature. Current problems in cardiology, 48(9), 101787. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.O., Kramer, S., Hofman, N., Flynn, J., Hansen, M., Martin, V., Pillai, A., Buckley, P.F. (2021). A Meta-Analysis of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Effects on Brain Volume in Schizophrenia: Genotype and Serum Levels. Neuropsychobiology, 80(5), 411-424. [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, G., Nasrabadi, A.M. (2021a). Comparison of different EEG features in estimation of hypnosis susceptibility level. Comput Biol Med, 42(5), 590-7. [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, G. & Nasrabadi, A.M. (2012b). EEG phase synchronization during hypnosis induction. J Med Eng Technol, 36(4), 222-9. [CrossRef]
- Bastos, M.A.V. Jr, Oliveira Bastos, P.R.H., Foscaches Filho, G.B., Conde, R.B., Ozaki, J.G.O., Portella, R.B., Iandoli, D. Jr, Lucchetti, G. (2022). Corpus callosum size, hypnotic susceptibility and empathy in women with alleged mediumship: a controlled study. Explore (NY), 18(2), 217-225. [CrossRef]
- Bocci, T., Barloscio, D., Parenti, L., Sartucci, F., Carli, G., & Santarcangelo, E.L. (2017). High Hypnotizability Impairs the Cerebellar Control of Pain. Cerebellum (London, England), 16(1), 55–61. [CrossRef]
- Callara, A. L., Fontanelli, L., Belcari, I., Rho, G., Greco, A., Zelič, Ž., Sebastiani, L., & Santarcangelo, E.L. (2023). Modulation of the heartbeat evoked cortical potential by hypnotizability and hypnosis. Psychophysiology, e14309. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Carli, G., Rendo, C., Sebastiani, L., Santarcangelo, E.L. (2006). Suggestions of altered balance: Possible equivalence of imagery and perception. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 54(2), 206-23. [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F.I., Cacace, I., Del Testa, M., Andre, P., Carli, G., De Pascalis, V., Rocchi, R., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2010). Hypnotizability-related EEG alpha and theta activities during visual and somesthetic imageries. Neuroscience letters, 470(1), 13–18. [CrossRef]
- Cesari, P., Modenese, M., Benedetti, S., Emadi Andani, M., & Fiorio, M. (2020). Hypnosis-induced modulation of corticospinal excitability during motor imagery. Scientific reports, 10(1), 16882. [CrossRef]
- Chiarucci, R., Madeo, D., Loffredo, M.I., Castellani, E., Santarcangelo, E.L., Mocenni, C. (2014). Cross-evidence for hypnotic susceptibility through nonlinear measures on EEGs of non-hypnotized subjects. Sci Rep, 8, 4-5610. [CrossRef]
- Colzato L. S., Waszak F., Nieuwenhuis S., Posthuma D., Hommel B. (2010). The flexible mind is associated with the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) Val158Met polymorphism: evidence for a role of dopamine in the control of task-switching. Neuropsychologia, 48, 2764–2768.
- Craig, A.D. (2002). How do you feel? Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nat Rev Neurosci, 3(8), 655-66. [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.D., Garfinkel, S.N. (2017). Interoception and emotion. Curr Opin Psychol, 17:7-14. [CrossRef]
- Crowson, J.J. Jr, Conroy, A.M., Chester, T.D. (1991). Hypnotizability as related to visually induced affective reactivity: a brief communication. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 39(3), 140-4. [CrossRef]
- Császár-Nag, N., & Bókkon, I. (2022). Hypnotherapy and IBS: Implicit, long-term stress memory in the ENS. Heliyon, 9(1), e12751. [CrossRef]
- De Benedittis, G. (2022). Hypnobiome: A New, Potential Frontier of Hypnotherapy in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome-A Narrative Review of the Literature. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 70(3), 286–299. [CrossRef]
- Dell P. F. (2010). Involuntariness in hypnotic responding and dissociative symptoms. Journal of trauma & dissociation: the official journal of the International Society for the Study of Dissociation (ISSD), 11(1), 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, S. W., Whalley, M. G., & Oakley, D. A. (2009). Fibromyalgia pain and its modulation by hypnotic and non-hypnotic suggestion: an fMRI analysis. European journal of pain (London, England), 13(5), 542–550. [CrossRef]
- Elkins G. (2022). From Research to Clinical Practice. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 70(3), 209–211. [CrossRef]
- Escobar Cervantes, C., Esteban Fernández, A., Recio Mayoral, A., Mirabet, S., González Costello, J., Rubio Gracia, J., Núñez Villota, J., González Franco, Á., & Bonilla Palomas, J. L. (2023). Identifying the patient with heart failure to be treated with vericiguat. Current medical research and opinion, 39(5), 661–669. [CrossRef]
- Facco, E., Testoni, I., Ronconi, L., Casiglia, E., Zanette, G., & Spiegel, D. (2017). Psychological Features of Hypnotizability: A First Step Towards Its Empirical Definition. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 65(1), 98–119. [CrossRef]
- Fiorio, M., Modenese, M., & Cesari, P. (2020). The rubber hand illusion in hypnosis provides new insights into the sense of body ownership. Scientific reports, 10(1), 5706. [CrossRef]
- Fontanelli, L., Spina, V., Chisari, C., Siciliano, G., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2022). Is hypnotic assessment relevant to neurology?. Neurological sciences: official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology, 43(8), 4655–4661. [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z., Li, H., Naser, P.V., Oswald, M.J., Kuner, R. (2021). Suppression of Neuropathic Pain and Comorbidities by Recurrent Cycles of Repetitive Transcranial Direct Current Motor Cortex Stimulation in Mice. Sci. Rep., 11, 9735.
- Green, J.P., Lynn, S.J. (2011). Hypnotic responsiveness: expectancy, attitudes, fantasy proneness, absorption, and gender. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 59(1), 103-21. [CrossRef]
- Grześk, G., Witczyńska, A., Węglarz, M., Wołowiec, Ł., Nowaczyk, J., Grześk, E., & Nowaczyk, A. (2023). Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Activators-Promising Therapeutic Option in the Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 28(2), 861. [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A., Di Rienzo, F., Macintyre, T., Moran, A., & Collet, C. (2012). Imagining is Not Doing but Involves Specific Motor Commands: A Review of Experimental Data Related to Motor Inhibition. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 6, 247. [CrossRef]
- Han, K., Liu, J., Tang, Z., Su, W., Liu, Y., Lu, H., Zhang, H. (2023). Effects of excitatory transcranial magnetic stimulation over the different cerebral hemispheres dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurosci, 17, 1102311. PMID: 37260845; PMCID: PMC10228699. [CrossRef]
- Henschke, J. U., & Pakan, J. M. P. (2023). Engaging distributed cortical and cerebellar networks through motor execution, observation, and imagery. Frontiers in systems neuroscience, 17, 1165307. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.W., Benson, H., Arns, P.A., Stainbrook, G.L., Landsberg, G.L., Young, J.B., Gill, A. (1982). Reduced sympathetic nervous system responsivity associated with the relaxation response. Science, 215(4529), 190-2. [CrossRef]
- Hoiland, R. L., Caldwell, H. G., Howe, C. A., Nowak-Flück, D., Stacey, B. S., Bailey, D. M., Paton, J. F. R., Green, D. J., Sekhon, M. S., Macleod, D. B., & Ainslie, P. N. (2020). Nitric oxide is fundamental to neurovascular coupling in humans. The Journal of physiology, 598(21), 4927–4939. [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.E., Crawford, H.J., Harrington, G., Downs, J.H. 3rd. (2004). Increased anterior corpus callosum size associated positively with hypnotizability and the ability to control pain. Brain, 127(Pt 8), 1741-7. [CrossRef]
- Huerta de la Cruz, S., Santiago-Castañeda, C. L., Rodríguez-Palma, E. J., Medina-Terol, G. J., López-Preza, F. I., Rocha, L., Sánchez-López, A., Freeman, K., & Centurión, D. (2022). Targeting hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide to repair cardiovascular injury after trauma. Nitric oxide: biology and chemistry, 129, 82–101. [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A. J., & Boe, S. G. (2022). Imagining the way forward: A review of contemporary motor imagery theory. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 16, 1033493. [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Marcelo, E., Campioni, L., Manzoni, D., Santarcangelo, E. L., & Petri, G. (2019). Spectral and topological analyses of the cortical representation of the head position: Does hypnotizability matter?. Brain and behavior, 9(6), e01277. [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Marcelo, E., Campioni, L., Phinyomark, A., Petri, G., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2019a). Topology highlights mesoscopic functional equivalence between imagery and perception: The case of hypnotizability. NeuroImage, 200, 437–449. [CrossRef]
- Incognito, O., Menardo, E., Di Gruttola, F., Tomaiuolo, F., Sebastiani, L., Santarcangelo, E.L. (2019). Visuospatial imagery in healthy individuals with different hypnotizability levels. Neurosci Lett, 690, 158-161. [CrossRef]
- ambrik, Z., Santarcangelo, E. L., Ghelarducci, B., Picano, E., & Sebastiani, L. (2004). Does hypnotizability modulate the stress-related endothelial dysfunction?. Brain research bulletin, 63(3), 213–216. [CrossRef]
- Jambrik, Z., Santarcangelo, E. L., Rudisch, T., Varga, A., Forster, T., & Carli, G. (2005). Modulation of pain-induced endothelial dysfunction by hypnotisability. Pain, 116(3), 181–186. [CrossRef]
- Jeannerod, M., & Frak, V. (1999). Mental imaging of motor activity in humans. Current opinion in neurobiology, 9(6), 735–739. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P., Adachi, T., Tomé-Pires, C., Lee, J., Osman, Z.J., Miró, J. (2015). Mechanisms of hypnosis: toward the development of a biopsychosocial model. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 63(1), 34-75. Erratum in: Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 63(2), 247. [CrossRef]
- Kallio, S., Revonsuo, A., Hämäläinen, H., Markela, J., & Gruzelier, J. (2001). Anterior brain functions and hypnosis: a test of the frontal hypothesis. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 49(2), 95–108. [CrossRef]
- Kirenskaya, A. V., Novototsky-Vlasov, V. Y., Chistyakov, A. N., & Zvonikov, V. M. (2011). The relationship between hypnotizability, internal imagery, and efficiency of neurolinguistic programming. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 59(2), 225–241. [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, I., & Lynn, S. J. (1997). Hypnotic involuntariness and the automaticity of everyday life. The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 40(1), 329–348. [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, I., & Lynn, S. J. (1998). Dissociation theories of hypnosis. Psychological bulletin, 123(1), 100–115. [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T. (2013). Regulation of the sympathetic nervous system by nitric oxide and oxidative stress in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: 2012 Academic Conference Award from the Japanese Society of Hypertension. Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension, 36(10), 845–851. [CrossRef]
- Landry, M., Lifshitz, M., & Raz, A. (2017). Brain correlates of hypnosis: A systematic review and meta-analytic exploration. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews, 81(Pt A), 75–98. [CrossRef]
- Laricchiuta, D., Picerni, E., Cutuli, D., & Petrosini, L. (2022). Cerebellum, Embodied Emotions, and Psychological Traits. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 1378, 255–269. [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, P., Bachner-Melman, R., Gritsenko, I., Ebstein, R.P. (2000). Exploratory association study between catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) high/low enzyme activity polymorphism and hypnotizability. Am J Med Genet, 96(6), 771-4. [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, M., Howells, C., & Raz, A. (2012). Can expectation enhance response to suggestion? De-automatization illuminates a conundrum. Consciousness and cognition, 21(2), 1001–1008. [CrossRef]
- Lynn, S. J., & Green, J. P. (2011). The sociocognitive and dissociation theories of hypnosis: toward a rapprochement. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 59(3), 277–293. [CrossRef]
- Lynn, S. J., Green, J. P., Zahedi, A., & Apelian, C. (2023). The response set theory of hypnosis reconsidered: toward an integrative model. The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 65(3), 186–210. [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, V. U., Seitz, J., Schönfeldt-Lecuona, C., Höse, A., Abler, B., Hole, G., Goebel, R., & Walter, H. (2015). The neural correlates of movement intentions: A pilot study comparing hypnotic and simulated paralysis. Consciousness and cognition, 35, 158–170. [CrossRef]
- Madeo, D., Castellani, E., Santarcangelo, E.L., Mocenni, C. (2013). Hypnotic assessment based on the recurrence quantification analysis of EEG recorded in the ordinary state of consciousness. Brain Cogn, 83(2), 227-33. [CrossRef]
- Malinski T. (2007). Nitric oxide and nitroxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD, 11(2), 207–218. [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y., Kwon, T.G., Lennon, R.J., Lerman, L.O., Lerman, A. (2015). Prognostic Value of Flow-Mediated Vasodilation in Brachial Artery and Fingertip Artery for Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Heart Assoc, 4(11), e002270. [CrossRef]
- McGeown, W.J., Mazzoni, G., Vannucci, M., & Venneri, A. (2015). Structural and functional correlates of hypnotic depth and suggestibility. Psychiatry Reseach, 28, 231(2), 151-9. [CrossRef]
- Mecacci, G., Menzocchi, M., Zeppi, A., Carli, G., & Santarcangelo, E.L(2013). Body sway modulation by hypnotizability and gender during low and high demanding postural conditions. Archives Italilennes de Biologie, 151(3), 99-105. [CrossRef]
- Mehling, W.E., Acree, M., Stewart, A., Silas, J., Jones, A. (2018). The Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness, Version 2 (MAIA-2). PLoS One, 13(12), e0208034. [CrossRef]
- Mućka, S., Miodońska, M., Jakubiak, G. K., Starzak, M., Cieślar, G., & Stanek, A. (2022). Endothelial Function Assessment by Flow-Mediated Dilation Method: A Valuable Tool in the Evaluation of the Cardiovascular System. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(18), 11242. [CrossRef]
- Ohira, K., Yokota, H., Hirano, S., Nishimura, M., Mukai, H., Horikoshi, T., Sawai, S., Yamanaka, Y., Yamamoto, T., Kakeda, S., Kuwabara, S., Tanaka, T., Uno, T. (2022). DRD2 Taq1A Polymorphism-Related Brain Volume Changes in Parkinson’s Disease: Voxel-Based Morphometry. Parkinsons Dis, 2022, 8649195. [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y., Stohler, C.S., Herr, D.R. (2019). Role of the Prefrontal Cortex in Pain Processing. Mol Neurobiol, 56(2), 1137-1166. [CrossRef]
- Parris, B.A. & Dienes, Z. (2013). Hypnotic suggestibility predicts the magnitude of the imaginative word blindness suggestion effect in a non-hypnotic context. Conscious Cogn, 22(3), 868-74. [CrossRef]
- Parris, B. A., Hasshim, N., & Dienes, Z. (2021). Look into my eyes: Pupillometry reveals that a post-hypnotic suggestion for word blindness reduces Stroop interference by marshalling greater effortful control. The European journal of neuroscience, 53(8), 2819–2834. [CrossRef]
- Peters, B., Eddy, B., Galvin-McLaughlin, D., Betz, G., Oken, B., & Fried-Oken, M. (2022). A systematic review of research on augmentative and alternative communication brain-computer interface systems for individuals with disabilities. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 16, 952380. [CrossRef]
- Piccione, C., Hilgard, E. R., & Zimbardo, P. G. (1989). On the degree of stability of measured hypnotizability over a 25-year period. Journal of personality and social psychology, 56(2), 289–295. [CrossRef]
- Picerni, E., Santarcangelo, E. L., Laricchiuta, D., Cutuli, D., Petrosini, L., Spalletta, G., & Piras, F. (2019). Cerebellar Structural Variations in Participants with Different Hypnotizability. Cerebellum (London, England), 18(1), 109–118. [CrossRef]
- Porges, S.W. Body Perception Questionnaire. Laboratory of Developmental Assessment, University of Maryland; College Park, MD, USA: 1993.
- Presciuttini, S., Gialluisi, A., Barbuti, S., Curcio, M., Scatena, F., Carli, G., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2014). Hypnotizability and Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT) polymorphysms in Italians. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 7, 929. [CrossRef]
- Quarti-Trevano, F., Dell’Oro, R., Cuspidi, C., Ambrosino, P., & Grassi, G. (2023). Endothelial, Vascular and Sympathetic Alterations as Therapeutic Targets in Chronic Heart Failure. Biomedicines, 11(3), 803. [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V., Chai, Y. L., Poh, L., Selvaraji, S., Fann, D. Y., Jo, D. G., De Silva, T. M., Drummond, G. R., Sobey, C. G., Arumugam, T. V., Chen, C. P., & Lai, M. K. P. (2023). Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a critical feature in unravelling the etiology of vascular cognitive impairment. Acta neuropathologica communications, 11(1), 93. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A., Santarcangelo, E. L., & Roatta, S. (2022a). Does hypnotizability affect neurovascular coupling during cognitive tasks?. Physiology & behavior, 257, 113915. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A., Santarcangelo, E. L., & Roatta, S. (2022b). Cerebrovascular reactivity during visual stimulation: Does hypnotizability matter?. Brain research, 1794, 148059. [CrossRef]
- Raz A., Fan J., & Posner M. I. (2006). Neuroimaging and genetic associations of attentional and hypnotic processes. Journal of Physiology (Paris), 99, 483–491. [CrossRef]
- Rominger, C., Weiss, E.M., Nagl, S., Niederstätter, H., Parson, W., Papousek, I. (2014). Carriers of the COMT Met/Met allele have higher degrees of hypnotizability, provided that they have good attentional control: a case of gene-trait interaction. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 62(4), 455-82. [CrossRef]
- Rosati, A., Belcari, I., Santarcangelo, E. L., & Sebastiani, L. (2021). Interoceptive Accuracy as a Function of Hypnotizability. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 69(4), 441–452. [CrossRef]
- Ruggirello, S., Campioni, L., Piermanni, S., Sebastiani, L., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2019). Does hypnotic assessment predict the functional equivalence between motor imagery and action?. Brain and cognition, 136, 103598. [CrossRef]
- Ruzyla-Smith, P., Barabasz, A., Barabasz, M. & Warner, D. (1995). Effects of hypnosis on the immune response: B-cells, T-cells, helper and suppressor cells. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis, 38, 71-79.
- Santarcangelo, E. L., & Carli, G. (2021). Individual Traits and Pain Treatment: The Case of Hypnotizability. Frontiers in neuroscience, 15, 683045. [CrossRef]
- Santarcangelo, E.L., Cavallaro, E., Mazzoleni, S., Marano, E., Ghelarducci, B., Dario, P., Micera, S., & Sebastiani, L. (2005). Kinematic strategies for lowering of upper limbs during suggestions of heaviness: a real-simulator design. Experimental Brain Research, 162(1),35-45. [CrossRef]
- Santarcangelo, E. L., Scattina, E., Carli, G., Ghelarducci, B., Orsini, P., & Manzoni, D. (2010). Can imagery become reality?. Experimental Brain Research, 206(3), 329–335. [CrossRef]
- Santarcangelo, E. L., & Scattina, E. (2016). Complementing the Latest APA Definition of Hypnosis: Sensory-Motor and Vascular Peculiarities Involved in Hypnotizability. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 64(3), 318–330. [CrossRef]
- Santarcangelo, E. L., Balocchi, R., Scattina, E., Manzoni, D., Bruschini, L., Ghelarducci, B., & Varanini, M. (2008). Hypnotizability-dependent modulation of the changes in heart rate control induced by upright stance. Brain research bulletin, 75(5), 692–697. [CrossRef]
- Santarcangelo, E. L., Paoletti, G., Balocchi, R., Carli, G., Morizzo, C., Palombo, C., & Varanini, M. (2012). Hypnotizability modulates the cardiovascular correlates of participantive relaxation. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 60(4), 383–396. [CrossRef]
- Scacchia, P., & De Pascalis, V. (2020). Effects of Prehypnotic Instructions on Hypnotizability and Relationships Between Hypnotizability, Absorption, and Empathy. The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 62(3), 231–266. [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, L., D’Alessandro, L., Menicucci, D., Ghelarducci, B., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2007). Role of relaxation and specific suggestions in hypnotic emotional numbing. International journal of psychophysiology, 63(1), 125–132. [CrossRef]
- Seminowicz, D.A., & Moayedi, M. (2017). The Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Acute and Chronic Pain. J Pain, 18(9), 1027-1035. [CrossRef]
- Spina, V., Chisari, C., & Santarcangelo, E. L. (2020). High Motor Cortex Excitability in Highly Hypnotizable Individuals: A Favourable Factor for Neuroplasticity?. Neuroscience, 430, 125–130. [CrossRef]
- Srzich, A. J., Byblow, W. D., Stinear, J. W., Cirillo, J., & Anson, J. G. (2016). Can motor imagery and hypnotic susceptibility explain Conversion Disorder with motor symptoms?. Neuropsychologia, 89, 287–298. [CrossRef]
- Strick, P.L., Dum, R.P., & Fiez, J.A. (2009). Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annual Reviews of Neuroscience, 32, 413-34. [CrossRef]
- Szekely, A., Kovacs-Nagy, R., Bányai, E.I., Gosi-Greguss, A.C., Varga, K., Halmai, Z., Ronai, Z., Sasvari-Szekely, M. (2010). Association between hypnotizability and the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) polymorphism. Int J Clin Exp Hypn, 58(3), 301-15. [CrossRef]
- Terhune, D.B., Cardeña, E., Lindgren, M. (2011). Dissociated control as a signature of typological variability in high hypnotic suggestibility. Conscious Cogn, 20(3), 727-36. [CrossRef]
- Terreni, C. Efficacia di un training immaginativo sul movimento: studio sperimentale. Master thesis, Pisa University, 2023.
- Tsakiris, M., & Critchley, H. (2016). Interoception beyond homeostasis: affect, cognition and mental health. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 371(1708), 20160002. [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M. T., Maki, T., Ihara, M., Lee, V. M. Y., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2020). Brain Microvascular Pericytes in Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 12, 80. [CrossRef]
- Weber, C., Dilthey, A., & Finzer, P. (2023). The role of microbiome-host interactions in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 13, 1151021. [CrossRef]
- Wieder, L., Brown, R., Thompson, T., & Terhune, D. B. (2021). Suggestibility in functional neurological disorder: a meta-analysis. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry, 92(2), 150–157. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T. G., Faerber, K. A., Rummel, C., Halsband, U., & Campus, G. (2022). Functional Changes in Brain Activity Using Hypnosis: A Systematic Review. Brain sciences, 12(1), 108. [CrossRef]
- Yargholi, E., & Nasrabadi, A.M. (2015). Chaos-chaos transition of left hemisphere EEGs during standard tasks of Waterloo-Stanford Group Scale of hypnotic susceptibility. J Med Eng Technol, 39(5), 281-5. [CrossRef]
- Yao, W. X., Ge, S., Zhang, J. Q., Hemmat, P., Jiang, B. Y., Liu, X. J., Lu, X., Yaghi, Z., & Yue, G. H. (2023). Bilateral transfer of motor performance as a function of motor imagery training: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 1187175. [CrossRef]
- Zambach, S.A., Cai, C., Helms, H.C.C., Hald, B.O., Dong, Y., Fordsmann, J.C., Nielsen, R.M., Hu, J., Lønstrup, M., Brodin, B., et al. (2021). Precapillary sphincters and pericytes at first-order capillaries as key regulators for brain capillary perfusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 118, e2023749118.
- Zeng, J., Wang, L., Cai, Q., Wu, J., & Zhou, C. (2022). Effect of hypnosis before general anesthesia on postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing minor surgery for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gland surgery, 11(3), 588–598. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Ku, Y. (2018). Hypnotic and non-hypnotic suggestion to ignore pre-cues decreases space-valence congruency effects in highly hypnotizable individuals. Conscious Cogn, 65, 293-303. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




