1. Introduction
The need to repair and fill bone defects is a reality in the medical and dental fields. The use of bone grafts aims to replace volumetric bone loss that often occurs due to bone defects resulting from conditions such as periodontal disease, trauma, tooth loss, alveolar ridge preservation after tooth extraction, bone grafts in the maxillary sinuses, ridge regeneration techniques for gaining bone height and thickness, extensive reconstructions of atrophic maxillae and mandibles, cleft palate treatments, bone defects in the oral, maxillofacial, cranial base, spinal fusion, and orthopedic (congenital malformations) regions [
1,
2,
3]. Bone tissue is the second most frequently transplanted tissue, with the United States and some European countries having the highest demand, accounting for about half a million cases of bone grafting needed annually [
4]. In the United States, allografts are the most used, while in Europe, bovine xenografts are more commonly employed [
5].
Bovine bone scaffolds are alternative to autogenous grafts that require a second surgical site. A second surgical procedures to obtain bone graft increases morbidity, risk of infection, hemorrhage and peripheral nerve lesions [
6]. Bovine bone grafts have a lower production cost than other grafts, are available on the market, have good osteoinduction, osteoconduction and mechanical stability characteristics [
5].
Several antibiotics and other molecules (e.g. bioglass or metals) have been used to impregnate the implant surface or even the bone graft. The antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) has been extensively investigated, including incorporating this metal into dental and orthopedic materials [
7]. The small size of the AgNP increases the contact area with the bacterial cell membrane, increasing the permeability and intracellular concentration of silver. Silver ions interferes with the mitochondrial respiratory chain causing oxidative reduction [
8].
In theory, the impregnation of bovine bone scaffolds can decrease trans and postoperative infection rates which leads to high risk of loss of bone volume and chronic infectious processes, such as osteomyelitis [
9]. However, the impregnation of bone graft with AgNP has been poorly investigated, and microbiological studies are lacking with focus biofilm, including multidrug resistant bacteria. The current literature about bone graft and AgNP focus in the development of implants, graft using hidroxiapatites and other synthetic materials. The use of bovine bone after processment and a cheap and easy method for AgNPs impregnation has been poorly evaluated.
The purpose of this investigation was to evaluate the in vitro antibiofilm activity of a bovine bone impregnated with AgNP in the most important clinical pathogens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bone processing
Spongy bone tissue discs were fabricated from adult bovine femur (metaphyseal portion), with dimensions of 6 mm in diameter and 3 mm in thickness, resulting in a volume of 84 mm³. This model was developed to facilitate the proposed analyses. Bovine bone tissue samples underwent a series of processing steps, including washing, agitation, sonication, centrifugation, and drying before impregnation with silver nanoparticles. These steps were carried out to remove various components such as bone marrow, blood cells, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each of these steps is detailed in a previous publication from our research group [
10]. For processing, the volume of each washing solution was calculated at a ratio of eight samples to 10 mL of washing solution. Throughout the process, washes were performed using deionized water (Direct-Q 3 UV water purification system, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Hydrogen peroxide was used at a concentration of 30% (Synth, Diadema, Brazil), and the concentration of sodium hydroxide used was 4% (Synth, Diadema, Brazil). The steps involved orbital agitation (shaker) at a constant temperature of 37°C and 120 rpm (New Brunswick Innova® 44, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Sonication was carried out at 35°C with a frequency of 40 kHz (Sanders Medical, Santa Rita da Sapucaí, Brazil). Centrifugation at 2000 g was used to assist in removing debris, such as blood cells and residual washing agents. This processing method was adapted from NHS Blood and Transplant in the United Kingdom (
Table 1) [
11].
2.1. Silver Nanoparticles
The procedure used to prepare 50 nm AgNPs was adapted from Dong et al. [
12]. Physical adsorption was used to incorporate the AgNPs in the bone matrix, based on an adaptation of the model reported by Becerril-Juárez et al. [
13]. For this purpose, bone models were added to the AgNPs solution at room temperature, for 60 minutes, protected from light. After the incorporation of AgNPs in the bone matrices, the samples were kept at a temperature of 70˚C for 60 minutes, in an oven with no air circulation system for drying, followed by lyophilization.
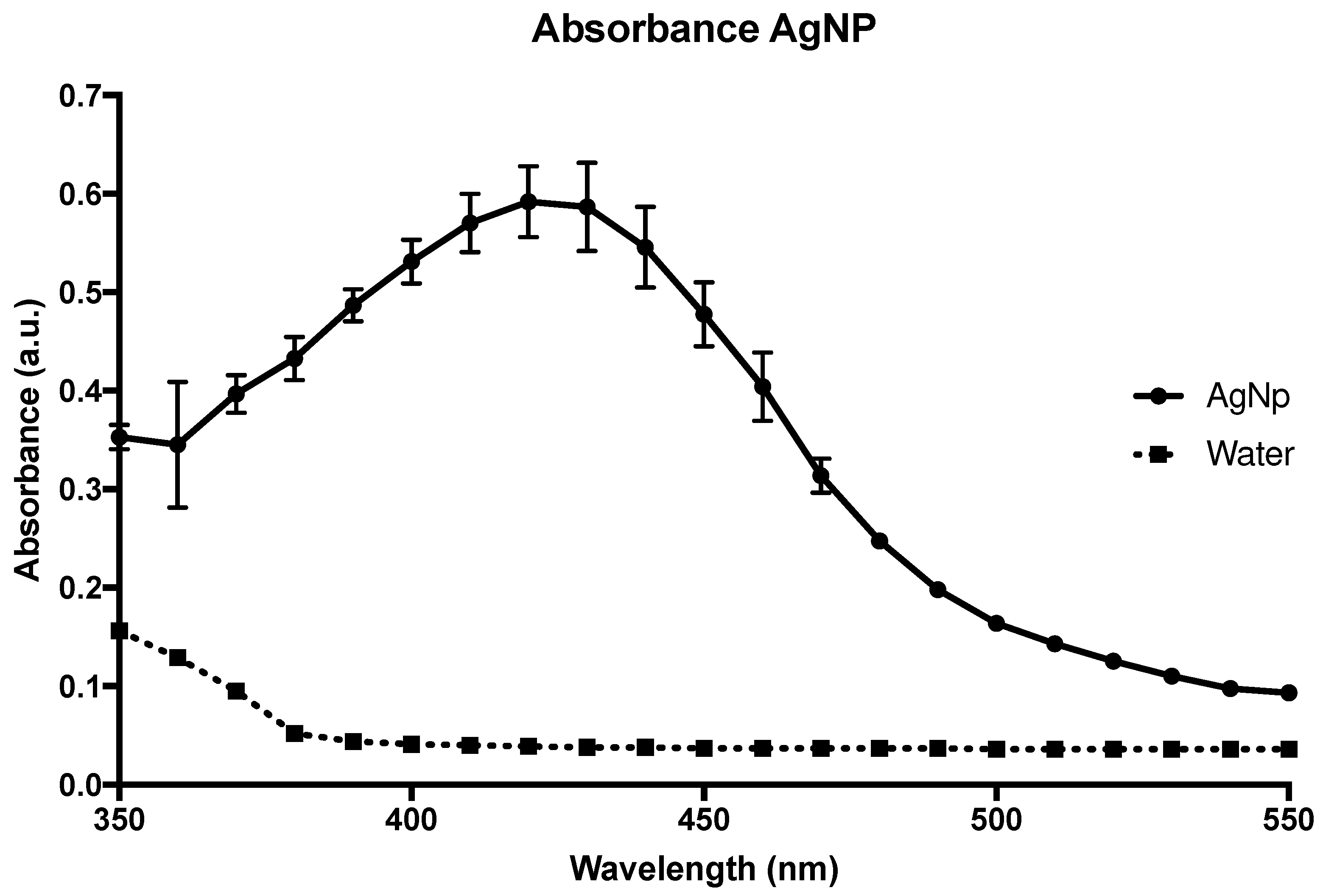
Figure 1, you can see the absorbance curve of the AgNPs solution measured using a Versamax spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA).
2.2. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS)
SEM was used for the analysis of morphology and microstructural characteristics before and after the impregnation of AgNPs in the bone matrix. The models were transferred to sterile glass Petri dishes with the primary fixing agent (0.68 g of 99.5% sucrose, 0.42 g of 98% sodium cacodylate, 0.6 mL of 30% glutaraldehyde (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) in 19.4 mL of deionized water, and left in contact for 45 minutes. After exposure to this primary fixing agent, the models were transferred every 10 minutes to the following solutions: buffer (composed of sucrose and sodium cacodylate at the concentrations mentioned above), 35% ethanol, 50% ethanol, 70% ethanol, 100% ethanol, and PA HMDS (hexamethyldisilazane) (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Following fixation, the models were kept in a desiccator until they were ready for observation in the SEM. They were pre-coated with gold particles in a metal coating equipment with a Q150R ES® rotary pump (Quorum Technologies, Lewes, United Kingdom) and subsequently mounted on a metal base for observation in the JEOL JSM 6010PLUS-LA scanning electron microscope at an acceleration voltage of 20 kV. Observations were made at magnifications ranging from 2,000 to 100,000 times, with AgNPs becoming visible at a magnification of 100,000x.
EDS is an analysis performed by an instrument coupled to the SEM, which allows for the measurement of the chemical elements present in the sample as well as the determination of their concentrations with great precision. The bone discs were characterized by EDS to verify the presence and distribution of silver on the bone tissue. The EDS analysis was conducted at the JEOL JSM 6010PLUS-LA Analysis Station with an acceleration voltage of 20 keV.
2.3. Nitrate silver minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
A silver nitrate solution in progressive titers from 0.25 to 512 mg/L was used [
14]. 200 µL aliquots of silver nitrate solution in Muller-Hinton broth in different concentrations were placed in a 96-well plate and 5 µL of the solution of each microorganism (
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC®25923™),
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC®25923™),
Candida albicans (ATCC®10231™),
Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC®29212™), multi-resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii OXA-23 (clinical isolate), and
Escherichia coli (ATCC®25922™)) were inoculated to reach a concentration of 10
6 colony forming units (cfu)/mL. After incubation for 24h at 36°C, the MIC was defined as the lowest concentration that did not show bacterial growth. All tests were performed in triplicate [
14].
2.4. Nitrate silver minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) and minimal fungicidal concentration (MFC)
MBC and MFC for AgNP were performed with the same microorganisms above, plating in triplicate 100 uL of all solutions over the MIC. The MBC and MFC were determined as the final concentration without bacterial or fungal growth.
2.5. Disc diffusion tests for AgNP susceptibility
Two bone models, one without impregnation (negative control) and one with AgNPs (test), were transferred to Muller-Hinton agar plates inoculated with the different bacteria and
C. albicans for 24 hours at 36°C to check for the presence of an inhibition halo. The analysis was quantitative by measuring the diameter of the halo formed on the agar plate. For this analysis, the process was adapted from the experiment by Saegeman et al. (2008), where the microorganisms described in the previous section were seeded on Mueller-Hinton agar plates (BD, Heidelberg, Germany), previously diluted to a turbidity standard equivalent to 0.5 McFarland [
15].
2.6. Quantification of biofilm production on plate
A suspension of 1.5x10
6 cfu/mL of each microorganism was prepared using TSA, then, 200ul were discharged into each well of a 96-well microplate (flat bottom). The microplate was incubated for 24 hours at 36
oC under shaking condition (120 rpm). After that, the biofilm of each tested strains was subjected to quantification by violet crystal (biomass) using Versa-Max microplate ELISA reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA) and a wavelength of 570 nm [
16].
2.7. Biofilm production on bone
From each microbe suspension, a 1:10 dilution was made in TSB broth until concentrations of 10
7 cfu/mL of bacteria and 10
5 cfu/mL of
C. albicans were achieved [
17]. Then, 10 mL of TSB broth was poured into sterile 12-well plates until it covered completely the bone discs (control and AgNP impregnated) for 2h under agitation (120 rpm). The specimens were transferred to a new sterile 12-well plate containing 0.9% NaCl to remove planktonic cells from the material. Then, specimens were transferred to another sterile 12-well plate and submerged in 10 mL of TSB broth at 37°C for 24h without agitation. During this step, the cells adhered to the device surface formed the biofilm. After this step, the specimens were submerged into 50 mL conical tubes filled with 10 mL of sterile 0.9% NaCl to remove the residues and unadhered/planktonic cells (step I). After this washing step, the specimens were allocated into 50 mL conical tubes filled with 10 mL of 0.9% NaCl for further processing (sonication), and the liquid of the last washing stored for planktonic cells analysis (step II).
2.8. Quantitative analysis of sessile cells from the biofilm
Five specimens of each group were transferred to sterile conical tubes with 10 mL of 0.9% NaCl and sonicated for 5 minutes in an ultrasonic bath using a Soniclean 15 (Sanders Medical, Santa Rita do Sapucaí, Brazil) at a frequency of approximately 40 kHz and temperature of 35°C [
18]. After the sonication step (step II), the supernatant (100 μL) was inoculated in TSA agar for growth evaluation and cells count (cfu/mL).
2.9. Cone Beam Computer Tomography (CBCT) and Digital Radiograph
For CBCT scans and digital radiograph, the bone scaffold was placed in a prepared and empty mandibular socket of the human dry mandible. This human dry mandible model was used previously [
19]. Moreover, for CBCT scans and digital radiographs, the mandible was fixed at the base of a plastic container filled with water to simulate soft tissue (Influence of exposure parameters on the detection of simulated root fractures in the presence of various intracanal materials [
20].
2.10. Direct Contact Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxicity of treated cancellous bovine bone tissue was tested according to ISO 10993/5 [
21]. 3T3 mouse cell line (ECACC – European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures, clone A31) was seeded in 24-well plates at a density of 4.4 x 10
4 cells/well. A total of 500 µL DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) (Gibco Invitrogen®) + 2 mM glutamine + 10% fetal bovine serum were dispensed into each well. The plates were incubated for 48 h at 37
oC in a humidified atmosphere with 5±1% CO
2. Growth media were removed from the wells and replaced with 1.8% agar with 0.01% neutral red dye. DMEM and SDS (200 µg/mL) were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. After incubation, the cells in contact with the tissue were viewed under a phase contrast microscope (Nikon Eclipse TS 100; Nikon) for qualitative morphological analysis.
2.11. Statistical analysis
For comparing the cell count in the groups, the median cfu/mL obtained with quantitative culture was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney test and presented with a median with interquartile range (25-75%). The difference in cfu/mL was significant when p<0.05. The data was calculated, analyzed, and plotted using Prism 7.0 (Graphpad, San Diego, CA).
3. Results
3.1. AgNP synthesis, EDS and SEM
The procedure used to obtain AgNPs was based on a green synthesis method that uses glucose, a nontoxic reducing agent, to convert Ag+ ions to Ag at zero oxidation state (Ag0). The final suspension presented a maximum absorption peak around 420 cm-1, measured by ultraviolet light spectra (
Figure 1), due to the plasmon band, confirming the formation of AgNPs of about 50 nm in diameter.
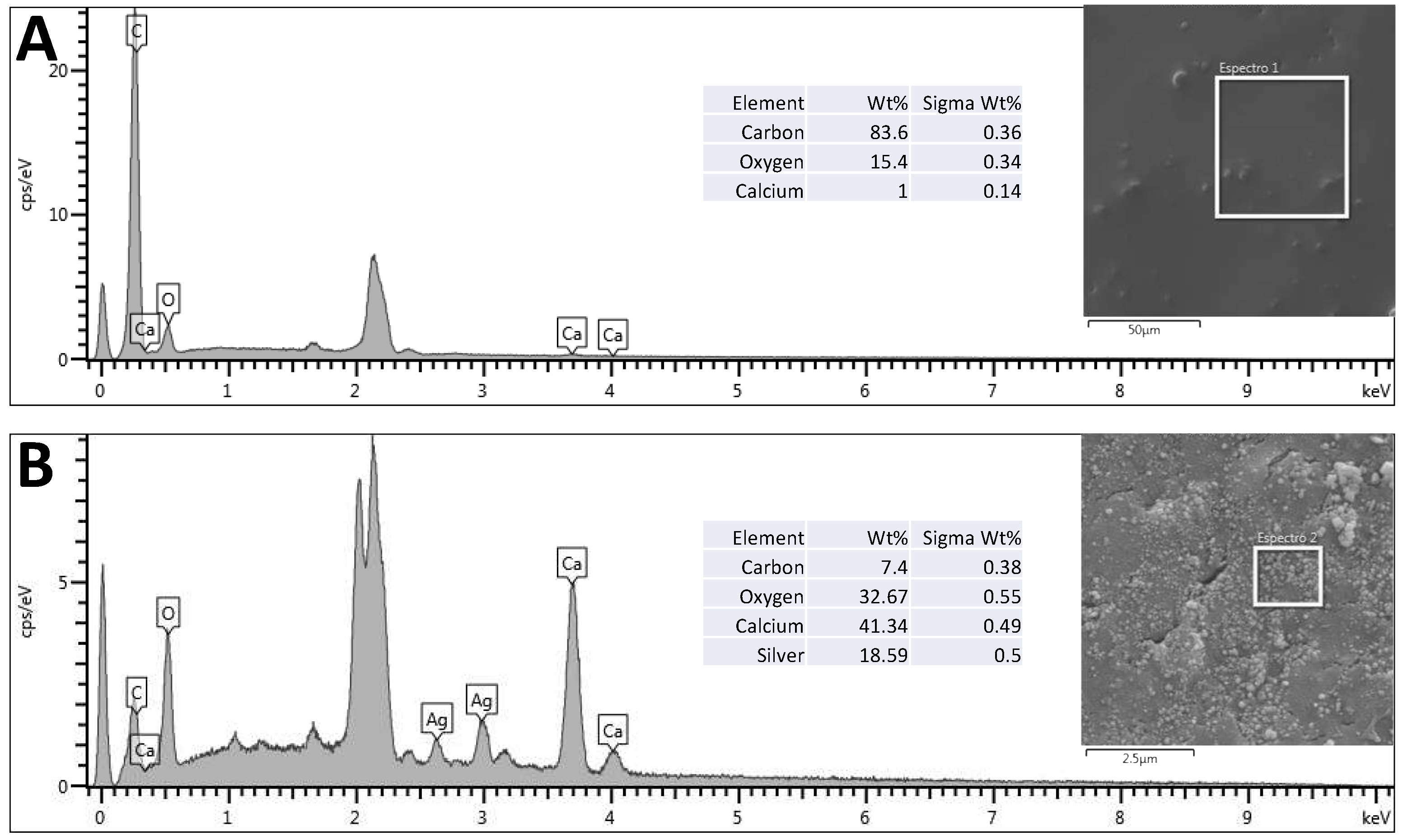
Using SEM and EDS, it is possible to observe the presence of nanoparticles impregnated in the bone scaffolds (
Figure 2) due to the presence of two characteristic peaks of silver atoms, corresponding to 18.59% (w/w) of the sample.
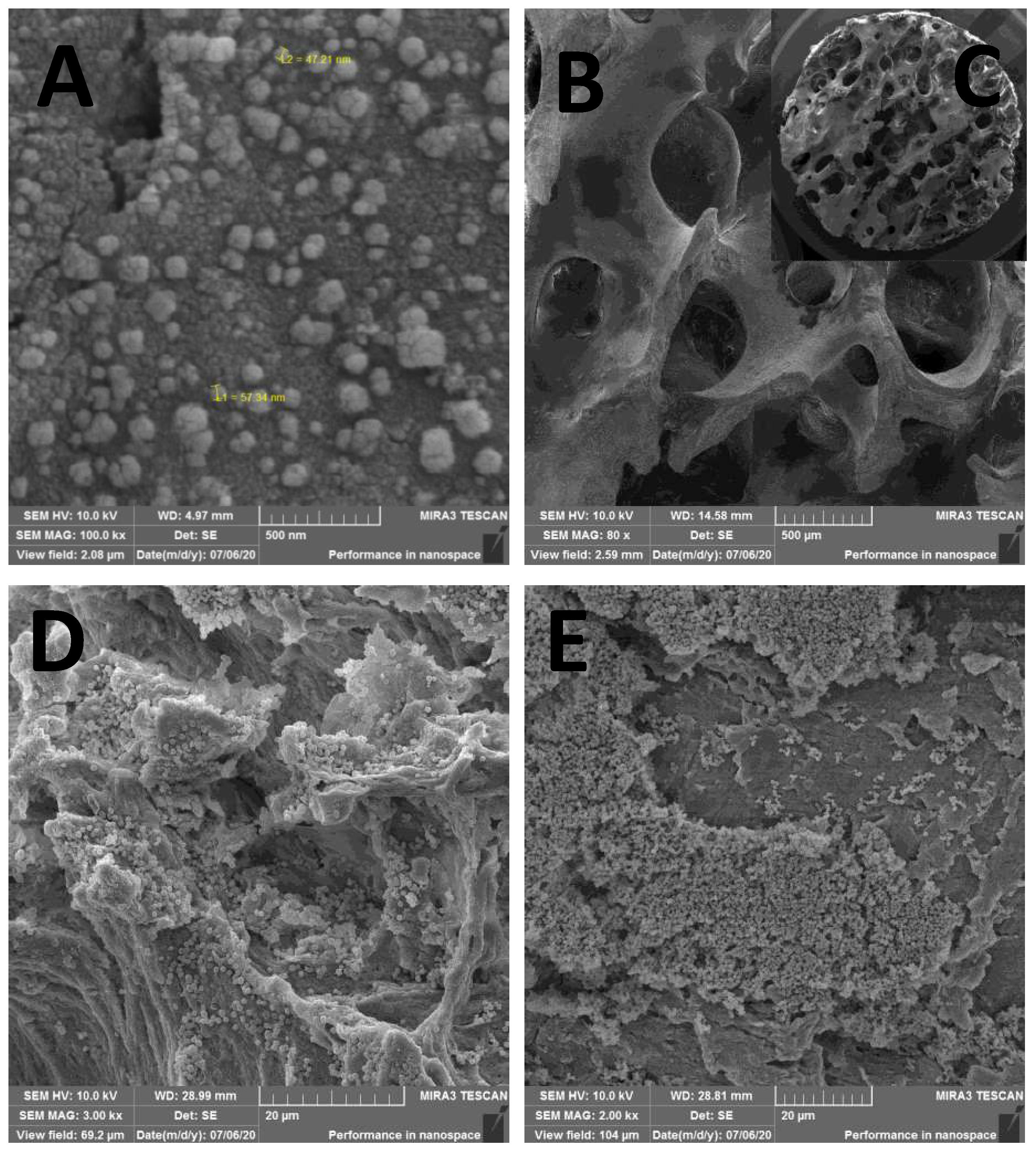
From SEM, one can confirm that the physical adsorption procedure used here was efficient in impregnating AgNPs and keeping them attached after drying the scaffolds (
Figure 3). The 80x magnification represents the bone tissue after processing, showing that all peribone tissue was removed, and in the
Figure 3B is represented the bone sample used for microbiological tests (
Figure 3C). In the
Figure 3A, the 100.000x amplification demonstrate the presence of AgNPs over bone tissue, allowing the measuring of the particles size, which ranged from 47 to 57 nm in several measure. However, other sizes were found in the scanning, suggest that the AgNP synthesis is not uniform. In the
Figure 3D and 3E is detailed the biofilm formation in AgNP and control group (non-impregnated bone) for microbiological studies.
3.3. Nitrate silver MIC and MBC
All pathogens were susceptible to silver with low MIC (0.25–4 mg/L). The MIC of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa were 4 mg/L; 2mg/L to E. coli, E. faecalis, and A. baumannii; and 0.25 to C. albicans. The susceptibility to silver allows the correct interpretation of the AgNP activity on biofilm, avoiding false-negative results.
The MBC was the same of the MIC for E. coli, S. aureus and A. baumannii (4 mg/L, 4 mg/L, and 8 mg/L, respectively). For P. aeruginosa the MBC was twice the MIC (8 mg/L) and four times for E. faecalis (16 mg/L). For C. albicans, silver nitrate did not achieve fungicidal concentration, only fungistatic (>128 mg/L).
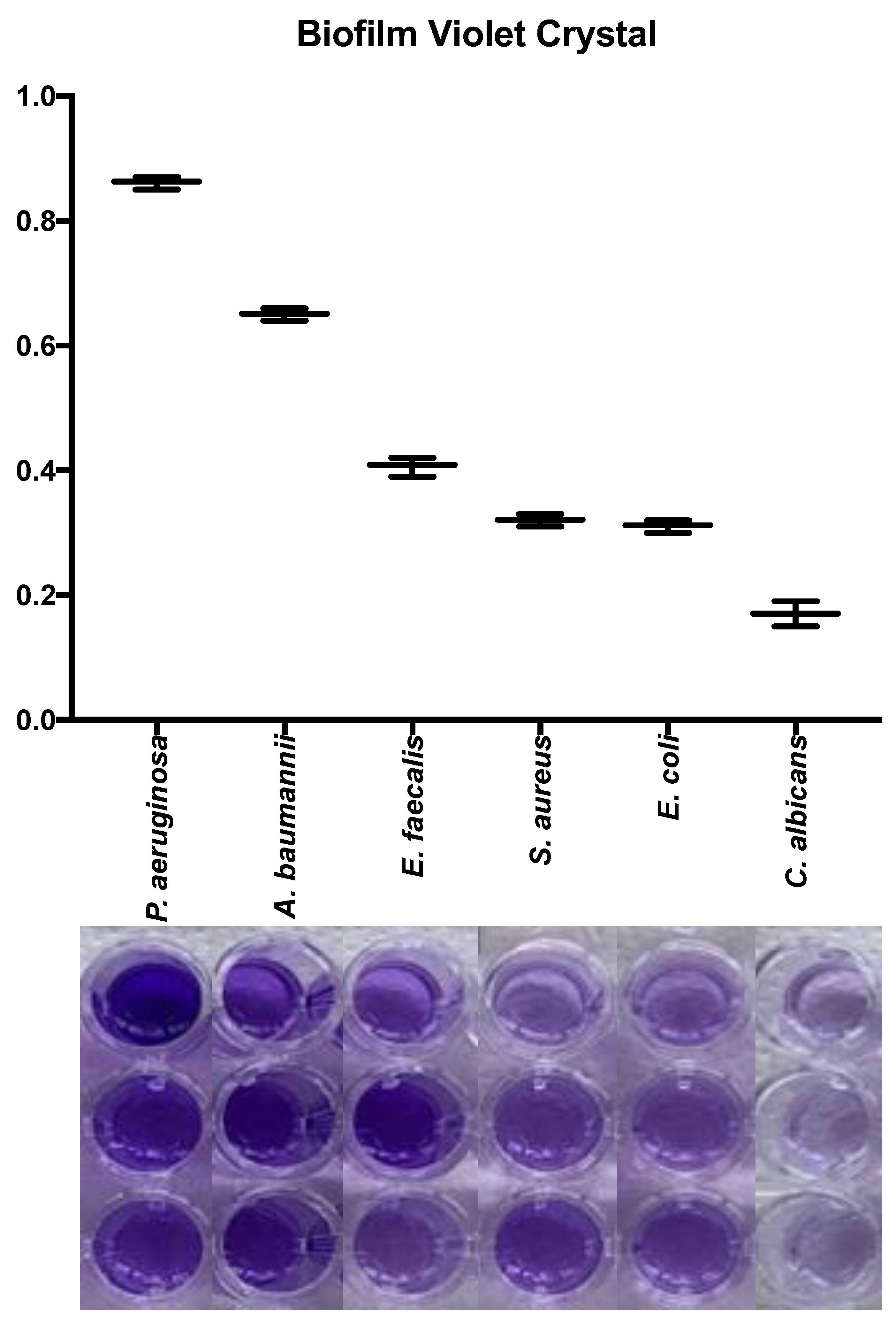
3.4. Quantification of biofilm production on plate
All microorganisms produced biofilm in the plate test. The biomass of each microorganism varied significantly.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
A. baumannii were the most biofilm producer microorganism. In the
Figure 4 is detailed the macroscopic aspect of the biomass using violet crystal assay and the absorbance results using microplate ELISA reader. The biomass evaluation by crystal violet showed a higher biofilm production in
P. aeruginosa, implants an absorbance of 0.86±0.01, followed by
A. baumannii (0.61±0.01),
E. faecalis (0.40±0.01),
S. aureus (0.32±0.01),
E. coli (0.31±0.01),
and C. albicans (0.17±0.01). All microorganisms showed differences between them in biofilm production (p<0.05), except for
S. aureus and
E. coli (p=0.93).
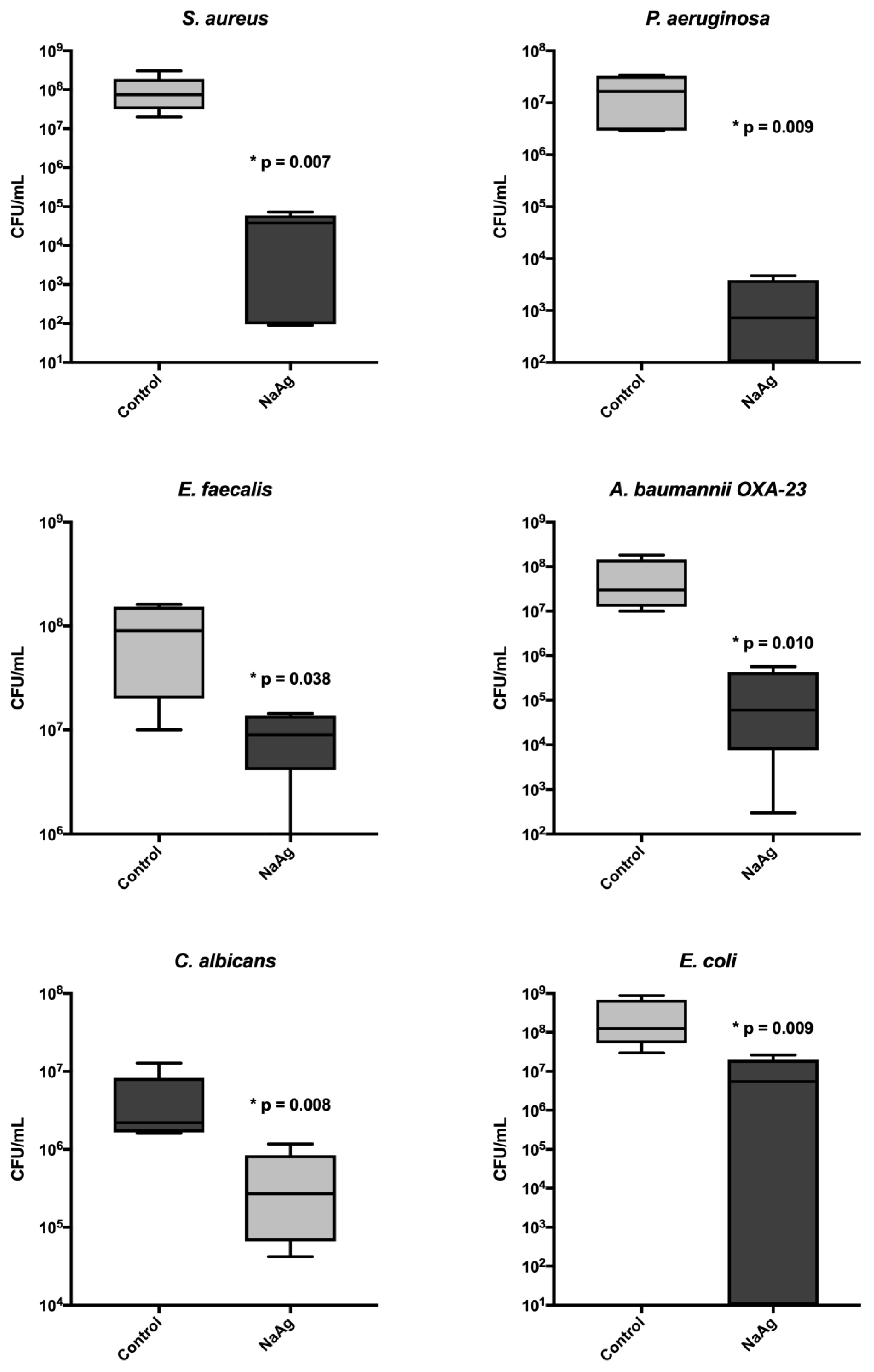
3.5. Quantitative analysis of sessile cells from the biofilm
The scaffold impregnated with AgNP presented a significant reduction in the biofilm cells for all microorganisms, reducing more than 3 logs in cfu count per mL. We evaluated the correlation of silver MIC with biomass and sessile cell count; however, no correlation was found (
Figure 5 and
Table 2).
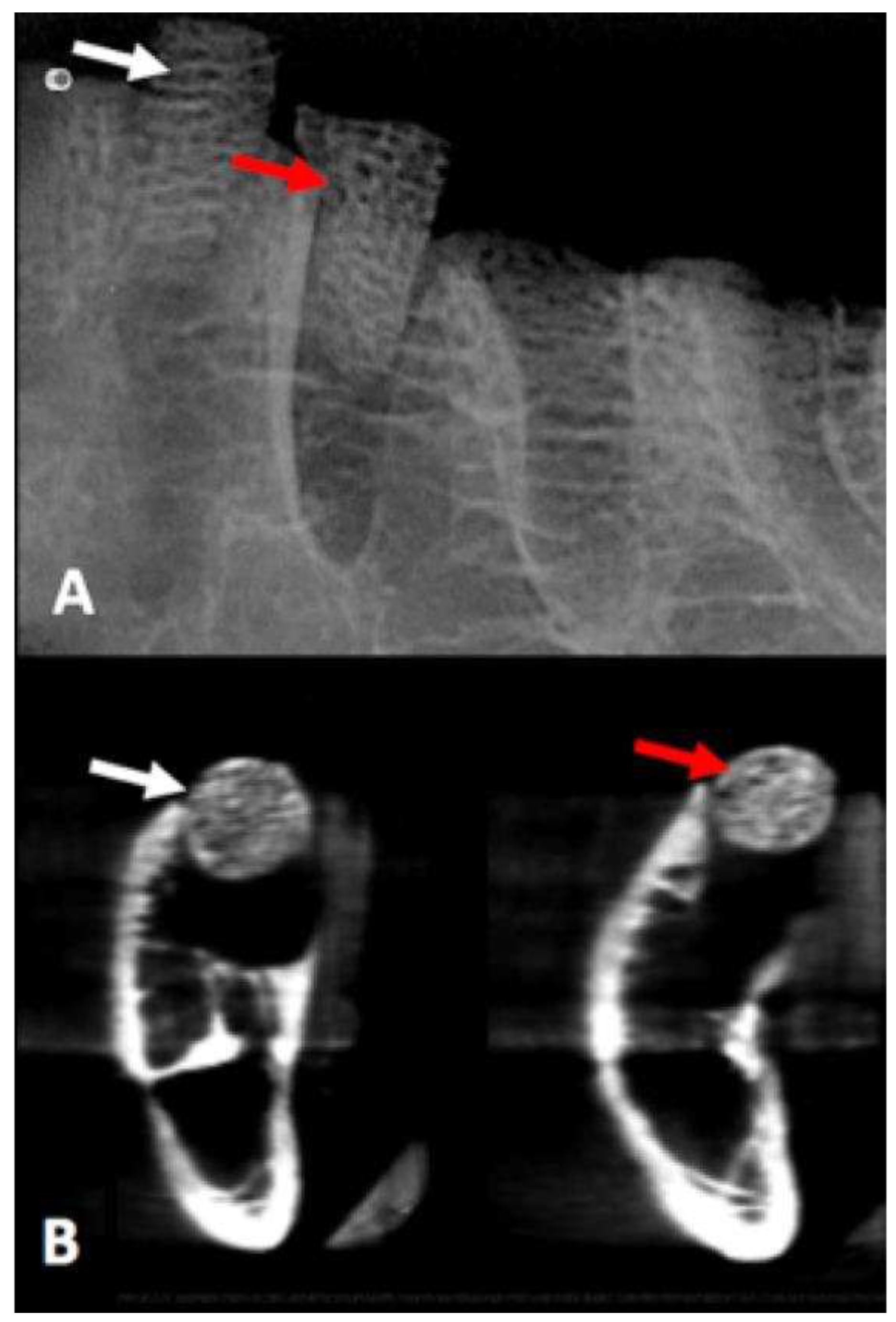
3.6. CBCT and Digital Radiograph
Values obtained to compare probability distributions of radiopacity bone disc, with and without AgNP impregnation, indicated that there were no different distributions of variables under the experimental conditions (p = 0.531) (
Figure 6).
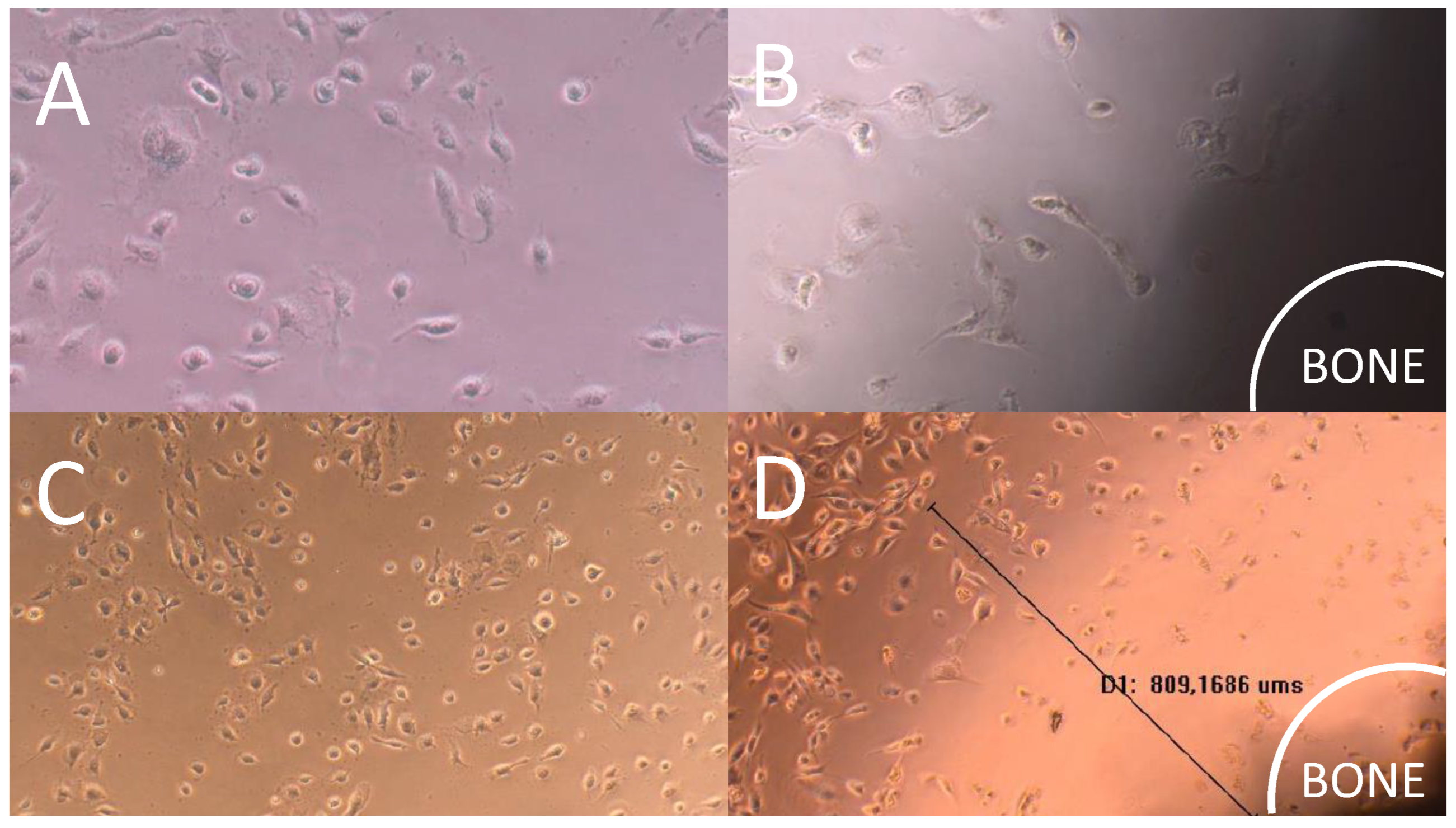
3.7. Direct Contact Cytotoxicity Assay
Direct contact cytotoxicity assay revealed that the cell monolayer next to the impregnated bone with AgNP was destroyed. The presence of a halo around the sample indicating cell death was verified through the analysis of images under 10x (
Figure 7). Furthermore, the presence of evident morphological changes and round cells during lysis were observed (
Figure 3B). The monolayer was not completely destroyed, indicating moderate reactivity and degree of toxicity. Halo of 922.6±236.5 μm diameter indicated moderate reactivity and degree of toxicity.
4. Discussion
The development of a bone substitute with the potential for antimicrobial activity has always been important in orthopedics and dentistry. In orthopedics, it serves the purpose of filling spaces that may be associated with biofilms, while in dentistry, it addresses the potential risk of contamination in the field of implantology. The choice of silver as a potential antimicrobial agent was based on its broad spectrum of activity against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, its ability to be transformed into nanoparticles to enhance its activity, a theoretical potential for improved osteointegration, and furthermore, its lack of chemical relation to antibiotics used in treatments, thereby avoiding the induction of resistance or the selection of multidrug-resistant bacteria through microbiota modification [
22].
In our study, all pathogens were susceptible to silver with low MICs. These values were obtained by silver nitrate, differently from other authors who defined MIC by AgNPs, showing divergent results [
23]. The test was conducted using free silver since its reproducibility is possible, whereas with AgNPs, it is not possible to assess the silver concentration, only an estimate based on formulas. Therefore, to enable comparability between microorganisms as well as reproducibility at different time points, free silver was used. Due to potential variations in nanoparticle preparation during production, we do not rely on the MIC test for nanoparticles. Mathur et al. described the antibacterial action of AgNPs through penetration into the microorganism's cell membrane, increasing its permeability, leading to the rupture of this structure and consequent cell death [
24]. Another mechanism described is the formation of free radicals that damage the cell membrane, causing porosity and cell lysis [
25]. Toxicity doesn't just pertain to bacterial cells but also to eukaryotic cells, as nanoparticles may exhibit some degree of cytotoxicity. [
26,
27] The cytotoxicity assay showed moderate toxicity in the AgNPs impregnated bone scaffold we developed, similar with previous cited publications. Another issue with the use of silver is its discoloration, which can stain teeth or skin when applied directly to these tissues [
28]. However, in our study, it is used as an implant, which would not cause aesthetic damage.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in studies using AgNPs with antibiofilm activity. These studies have assessed the antibiofilm activity of AgNPs in combination with metallic surfaces such as titanium compounds, aiming to prevent infections associated with orthopedic prostheses as well as dental implants [
29]. In the context of dentistry, the combination of AgNPs with restorations has shown activity against
Streptococcus biofilms, the primary pathogen associated with dental biofilm and subsequent caries formation [
30]. Another antibiofilm strategy involving the use of AgNPs is their combination with other biocompatible materials like chitosan, enabling their integration into hydrogels or 3D printing using bioprinters, facilitating the development of therapeutic or preventive wound dressings [
31,
32].
Smaller particles have higher surface area that allows the release of a higher amount of silver ions, responsible for the most acceptable mechanism of bactericidal action [
33]. In this sense, smaller particles are expected to present a greater antimicrobial effect than bigger particles and particle aggregates. This can be explication for the maintenance of viable bacterial cells after scaffold impregnation, mainly E. faecalis and E. coli. Bacteria with high capacity of multiplication and biofilm-producing, like
P. aeruginosa,
S. aureus and
A. baumannii showed higher susceptibility to AgNPs.
Olson et al. highlighted that
P. aeruginosa,
E. coli, and
S. aureus produce biofilms in a short period of time and without great nutritional requirements, data similar to those obtained in our study [
34]. However, in our study, the broth used in the biofilm model present abundant nutrients, which can differ the biofilm pattern and bacterial redox system, which can affect silver activity [
35]. Anuj et al. evaluated the association of silver nanoparticles with linezolid as a bactericidal agent on
E. coli MTCC®443™, where the resistance mechanism of drug efflux of this microorganism was inactivated by AgNP [
36]. This is an important issue, considering that AgNPs can be an important molecule to be used in combination with antibiotics.
This study had some limitations because we evaluated a few bacteria, which could include multidrug-resistant isolates. Biomechanical evaluation can be important for a structural scaffold if used for large bone defects. The shelf life was not determined beyond six months. Thus, as a product, a more extended time (12 months) would be important. The cone beam tomography showed no difference distributions of variables under the experimental conditions, suggesting that AgNP does not interfere in the radiological exam, an important characteristic for scaffolds in dental implants. Even though the literature is broad of impregnated materials, microbiological studies with biofilm on bovine scaffolds were not reported yet.
5. Conclusions
Considering the current results of our study, this bone scaffold had both antimicrobial and anti-biofilm properties. AgNP incorporation was effective, with moderate toxicity, which must be confirmed in in vivo models. Bone scaffold impregnated with AgNP decreased biofilm synthesis by reducing the viability of sessile cells, being a promising material in the clinical use of dental and orthopedic procedures. In vivo studies are needed to assess osseointegration, anti-biofilm efficacy and safety.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.T. and L.D.; methodology, F.T.; validation, G.G., L.K. and V.R.; formal analysis, F.T.; investigation, M.W.; resources, F.T.; data curation, E.C.; writing—original draft preparation, F.T. and E.C; writing—review and editing, L.D.; visualization, F.T. and L.D.; supervision, F.T.; project administration, F.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available under request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Dr Francisco Carlos Serbena and technician Vanessa with the FEG in the C-LABMU from Universidade Estadual de Ponta Grossa. We thank Laborclin for culture media donation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Manrique, N.; Pereira, C.C.; Garcia, L.M.; Micaroni, S.; Carvalho, A.A.; Perri, S.H.; Okamoto, R.; Sumida, D.H.; Antoniali, C. Alveolar bone healing process in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). A radiographic densitometry study. J Appl Oral Sci 2012, 20, 222-227. [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Ramachandra, S.S.; Lahori, M.; Singhal, R.; Jithendra, K.D. Combined soft and hard tissue augmentation for a localized alveolar ridge defect. Contemp Clin Dent 2013, 4, 556-558. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.F.; Bucchi, C.; Navarro, P.; Beltran, V.; Borie, E. Bone grafts utilized in dentistry: an analysis of patients' preferences. BMC Med Ethics 2015, 16, 71. [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.R.; Laurencin, C.T.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 2012, 40, 363-408. [CrossRef]
- Haugen, H.J.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Rossi, F.; Perale, G. Bone grafts: which is the ideal biomaterial? J Clin Periodontol 2019, 46 Suppl 21, 92-102. [CrossRef]
- Iviglia, G.; Kargozar, S.; Baino, F. Biomaterials, Current Strategies, and Novel Nano-Technological Approaches for Periodontal Regeneration. J Funct Biomater 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Allaker, R.P. The use of nanoparticles to control oral biofilm formation. J Dent Res 2010, 89, 1175-1186. [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.; Ho, C.M.; Lok, C.N.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.M.; Chiu, J.F.; Tam, P.K. Topical delivery of silver nanoparticles promotes wound healing. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 129-136. [CrossRef]
- Kose, N.; Asfuroglu, Z.M.; Kose, A.; Sahinturk, V.; Gurbuz, M.; Dogan, A. Silver ion-doped calcium phosphate-based bone-graft substitute eliminates chronic osteomyelitis: An experimental study in animals. J Orthop Res 2021, 39, 1390-1401. [CrossRef]
- Dantas, L.R.; Wollmann, L.C.; Suss, P.H.; Kraft, L.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; Tuon, F.F. Disinfection protocol for human musculoskeletal allografts in tissue banking using hydrogen peroxide 30. Cell Tissue Bank 2021, 22, 643-649. [CrossRef]
- Eagle, M.J.; Man, J.; Rooney, P.; Hogg, P.; Kearney, J.N. Assessment of an improved bone washing protocol for deceased donor human bone. Cell Tissue Bank 2015, 16, 83-90. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.W., D.; Sun, G.; Hinestroza, J. Assembly of Metal Nanoparticles on Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofibers by Control of Interfacial Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions. Chem. Mater. 2015, 20, 5.
- Becerril-Juáres, I.G.M.-L., R.A.; Ureña-Nuñez, F.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.A.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V. . Silver micro-, submicro- and nano-crystals using bovine bone as template. Formation of a silver/bovine bone composite. Mat. Lett. 2012, 85, 4.
- Sutterlin, S.; Tano, E.; Bergsten, A.; Tallberg, A.B.; Melhus, A. Effects of silver-based wound dressings on the bacterial flora in chronic leg ulcers and its susceptibility in vitro to silver. Acta Derm Venereol 2012, 92, 34-39. [CrossRef]
- Saegeman, V.; Ectors, N.; Lismont, D.; Verduyckt, B.; Verhaegen, J. Bacteriostasis testing on allograft tissue inoculated in Wilkins-Chalgren broth. J Hosp Infect 2008, 70, 278-283. [CrossRef]
- Kharidia, R.; Liang, J.F. The activity of a small lytic peptide PTP-7 on Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Microbiol 2011, 49, 663-668. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.J.; Chang, C.; Akiyama, T.; Bothner, B. New Technologies for Studying Biofilms. Microbiol Spectr 2015, 3, 10.1128. [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Piper, K.E.; Jacobson, M.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Unni, K.K.; Osmon, D.R.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Greenleaf, J.F.; et al. Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N Engl J Med 2007, 357, 654-663. [CrossRef]
- Segato, A.V.K.; Piasecki, L.; Felipe Iparraguirre Nunovero, M.; da Silva Neto, U.X.; Westphalen, V.P.D.; Gambarini, G.; Carneiro, E. The Accuracy of a New Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Software in the Preoperative Working Length Determination Ex Vivo. J Endod 2018, 44, 1024-1029. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.G.O.; Rabelo, K.A.; Sousa Melo, S.L.; Campos, P.S.F.; Oliveira, L.; Bento, P.M.; Melo, D.P. Influence of exposure parameters on the detection of simulated root fractures in the presence of various intracanal materials. Int Endod J 2017, 50, 586-594. [CrossRef]
- Kraft, L.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; de Nazareno Wollmann, L.C.F.; Suss, P.H.; Tuon, F.F. Determination of antibiotics and detergent residues in decellularized tissue-engineered heart valves using LC-MS/MS. Cell Tissue Bank 2020, 21, 573-584. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, R.; Ji, Z.; Mu, H.; Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, R.; Zhang, S.; et al. Balancing the antibacterial and osteogenic effects of double-layer TiO(2) nanotubes loaded with silver nanoparticles for the osseointegration of implants. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 2911-2923. [CrossRef]
- John, M.S.; Nagoth, J.A.; Ramasamy, K.P.; Ballarini, P.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Mancini, A.; Telatin, A.; Lio, P.; Giuli, G.; Natalello, A.; et al. Horizontal gene transfer and silver nanoparticles production in a new Marinomonas strain isolated from the Antarctic psychrophilic ciliate Euplotes focardii. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 10218. [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Jha, S.; Ramteke, S.; Jain, N.K. Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2018, 46, 115-126. [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, E.; Banerjee, R. Hybrid silver-gold nanoparticles suppress drug resistant polymicrobial biofilm formation and intracellular infection. J Mater Chem B 2020, 8, 4890-4898. [CrossRef]
- Kumah, E.A.; Fopa, R.D.; Harati, S.; Boadu, P.; Zohoori, F.V.; Pak, T. Human and environmental impacts of nanoparticles: a scoping review of the current literature. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1059. [CrossRef]
- Bellisario, D.; Santo, L.; Quadrini, F.; Hassiba, M.; Bader, N.; Chowdhury, S.H.; Hassan, M.K.; Zughaier, S.M. Cytotoxicity and Antibiofilm Activity of Silver-Polypropylene Nanocomposites. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Vollu, A.L.; Rodrigues, G.F.; Rougemount Teixeira, R.V.; Cruz, L.R.; Dos Santos Massa, G.; de Lima Moreira, J.P.; Luiz, R.R.; Barja-Fidalgo, F.; Fonseca-Goncalves, A. Efficacy of 30% silver diamine fluoride compared to atraumatic restorative treatment on dentine caries arrestment in primary molars of preschool children: A 12-months parallel randomized controlled clinical trial. J Dent 2019, 88, 103165. [CrossRef]
- Salaie, R.N.; Hassan, P.A.; Meran, Z.D.; Hamad, S.A. Antibacterial Activity of Dissolved Silver Fractions Released from Silver-Coated Titanium Dental Implant Abutments: A Study on Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Formation. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dhawan, P.; Rajpal, S.K.; Sharma, R. A Comparison of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Silver-based Preventive Restorations (Silver Nitrate, Silver Diamine Fluoride, and Silver Nanoparticles) against Streptococcus mutans Monospecies Biofilm Model. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2023, 16, S13-S19. [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, G.; Ivanova, K.; Torrent-Burgues, J.; Tzanov, T. Multimodal silver-chitosan-acylase nanoparticles inhibit bacterial growth and biofilm formation by Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. J Colloid Interface Sci 2023, 646, 576-586. [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Malakooti, M.H.; Paisana, H.; Ohm, Y.; Marques, D.G.; Alhais Lopes, P.; Piedade, A.P.; de Almeida, A.T.; Majidi, C. EGaIn-Assisted Room-Temperature Sintering of Silver Nanoparticles for Stretchable, Inkjet-Printed, Thin-Film Electronics. Adv Mater 2018, e1801852. [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D.J.; Shah, S.I. Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2005, 5, 244-249. [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Ceri, H.; Morck, D.W.; Buret, A.G.; Read, R.R. Biofilm bacteria: formation and comparative susceptibility to antibiotics. Can J Vet Res 2002, 66, 86-92.
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Liao, S.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, G.; Dai, G.; Chen, L. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. J Proteome Res 2020. [CrossRef]
- Anuj, S.A.; Gajera, H.P.; Hirpara, D.G.; Golakiya, B.A. Bacterial membrane destabilization with cationic particles of nano-silver to combat efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Life Sci 2019, 230, 178-187. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Absorbance curve of the nanoparticle, showing a peak at 420 nm, confirming a size of 50 nm.
Figure 1.
Absorbance curve of the nanoparticle, showing a peak at 420 nm, confirming a size of 50 nm.
Figure 2.
EDS with corresponding element identification in bone withoutimpregnation (A), and AgNP impregnated bone (B).
Figure 2.
EDS with corresponding element identification in bone withoutimpregnation (A), and AgNP impregnated bone (B).
Figure 3.
SEM of AgNP impregnated bone with nanoparticles size between 47 and 57nm (A x100.000); the processed bone sample before impregnation and before biofilm (B x80 and C x22); (D) biofilm in AgNP impregnated bone (x3.000); and biofilm in the control sample, showing a higher population of microorganisms (E x2.000).
Figure 3.
SEM of AgNP impregnated bone with nanoparticles size between 47 and 57nm (A x100.000); the processed bone sample before impregnation and before biofilm (B x80 and C x22); (D) biofilm in AgNP impregnated bone (x3.000); and biofilm in the control sample, showing a higher population of microorganisms (E x2.000).
Figure 4.
Quantification of biofilm on plate of different microorganisms used in the AgNP impregnated bone model. Measure of the absorbance biomass for each microorganism after violet crystal assay. Biomass of each microorganism used in the biofilm model in the 96-well plate, before measure of the absorbance.
Figure 4.
Quantification of biofilm on plate of different microorganisms used in the AgNP impregnated bone model. Measure of the absorbance biomass for each microorganism after violet crystal assay. Biomass of each microorganism used in the biofilm model in the 96-well plate, before measure of the absorbance.
Figure 5.
Cell count (CFU/mL) of biofilm in bone with AgNP and without impregnation (control).
Figure 5.
Cell count (CFU/mL) of biofilm in bone with AgNP and without impregnation (control).
Figure 6.
The white arrow shows the bone disc without AgNP impregnation, and the red arrow shows the bone disc with AgNP impregnation at periapical digital radiograph and CBCT scan.
Figure 6.
The white arrow shows the bone disc without AgNP impregnation, and the red arrow shows the bone disc with AgNP impregnation at periapical digital radiograph and CBCT scan.
Figure 7.
Cytotoxicity assay images of bone scaffold with silver nanoparticles under different magnifications (A and B: 10x; C and D: 20x). A and C represent the negative control and B and D the cytotoxicity assay results of the treated bone. The black line represents the distance between the bone sample and viable cells zone.
Figure 7.
Cytotoxicity assay images of bone scaffold with silver nanoparticles under different magnifications (A and B: 10x; C and D: 20x). A and C represent the negative control and B and D the cytotoxicity assay results of the treated bone. The black line represents the distance between the bone sample and viable cells zone.
Table 1.
These steps were part of the bone tissue processing procedure to prepare the bone discs for further analyses, involving washing, centrifugation, sonication, and chemical treatments to remove various components such as bone marrow, blood cells, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids from the bovine bone samples.
Table 1.
These steps were part of the bone tissue processing procedure to prepare the bone discs for further analyses, involving washing, centrifugation, sonication, and chemical treatments to remove various components such as bone marrow, blood cells, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids from the bovine bone samples.
| Process |
Duration |
| 1. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 2. Centrifugation at 2000g at 22°C |
15 minutes |
| 3. Deionized water at 35°C with sonication |
15 minutes |
| 4. Centrifugation at 2000g at 22°C |
15 minutes |
| 5. 30% Hydrogen Peroxide at 35°C with sonication |
15 minutes |
| 6. Deionized water at 35°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 7. Centrifugation at 2000g at 22°C |
15 minutes |
| 8. 4% Sodium Hydroxide at 35°C with sonication |
15 minutes |
| 9. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 10. Centrifugation at 2000g at 22°C |
15 minutes |
| 11. 70% Alcohol at 35°C with sonication |
15 minutes |
| 12. Deionized water at 35°C with sonication |
15 minutes |
| 13. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 14. Centrifugation at 2000g at 22°C |
15 minutes |
| 15. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 16. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 17. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 18. Deionized water at 37°C with agitation |
10 minutes |
| 19. Heating to 70°C |
60 minutes |
Table 2.
Correlations of biofilm on plate, MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration in mg/L) and biofilm on bone (control and with silver nanoparticles [AgNP]) with respective Log reduction. Absorbance of biofilm on plate was used as comparative for p value.
Table 2.
Correlations of biofilm on plate, MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration in mg/L) and biofilm on bone (control and with silver nanoparticles [AgNP]) with respective Log reduction. Absorbance of biofilm on plate was used as comparative for p value.
| |
Biofilm on plate |
|
MIC |
|
Bone Biofilm |
| Microoganism |
Absorbance (ƛ)
|
ƛ/Negative control
|
|
|
|
Control |
AgNP |
Log Reduction |
| P. aeruginosa |
0.86 |
15.7 |
|
4 |
1.6x107
|
7.3x102
|
4.35 |
| E. coli |
0.31 |
5.7 |
|
2 |
1.3x108
|
5.4x106
|
1.36 |
| S. aureus |
0.32 |
5.8 |
|
4 |
7.5x107
|
3.7x104
|
3.30 |
| E. faecalis |
0.41 |
7.4 |
|
2 |
9.0x107
|
9.1x106
|
1.00 |
|
A. baumannii OXA-23 |
0.65 |
11.8 |
|
2 |
3.0x107
|
6.0x104
|
2.70 |
| C. albicans |
0.17 |
3.1 |
|
0.25 |
2.2x106
|
2.7x105
|
0.91 |
| Negative Control |
0.06 |
1.0 |
|
- |
|
- |
- |
- |
| P value |
|
|
0.240 |
|
0.983 |
0.629 |
0.078 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).