1. Introduction
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) influenza surveillance data have shown a significant reduction in the global circulation of the influenza virus. Most countries have experienced historically low seasonal influenza virus circulation since April 2020, associated with non-pharmaceutical interventions such as travel restrictions, quarantine on arrival, societal distance, school and workplace closures, mask wearing, surface disinfection, and enhanced hand hygiene. Lack of exposure to influenza reduces population immunity and may increase the severity of major epidemics with the future global spread of new strains. In this regard, influenza vaccination is of great importance [
1].
Various approaches are used to prevent and reduce the incidence of seasonal and pandemic influenza, among them, vaccination is the most effective. Currently used seasonal influenza vaccines are usually available in trivalent or quadrivalent forms, including two subtypes of influenza A viruses – A/H1N1 and A/H3N2 - and influenza B virus of one or two antigenic lineages B/Victoria and B/Yamagata according to WHO’s annual vaccine recommendations. The production of quadrivalent vaccines reduces the risk of vaccine mismatch with epidemic strains [
2]. Nevertheless, recently, for the first time in 35 years, there has been observed the disappearance of influenza B/Yamagata antigenic lineage viruses from the circulation [
1].
Split and subunit inactivated influenza vaccines (IIVs) are mainly used for seasonal influenza prevention [
3]. In a split virion vaccine, the viral particles are destroyed with diethyl ether or detergents. Split vaccines contain 15 micrograms of HA antigen of each currently recommended influenza strain (A/H1N1pdm09, A/H3N2, B) [
4]. Subunit vaccines contain hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), which are purified by exclusion of viral RNP and several internal proteins. Vaccines must comply with WHO safety and efficacy requirements. The production of influenza vaccine in chick embryos is a highly productive and reliable technology that meets the quality criteria established by WHO and are set out in the guidelines for influenza vaccine production and control [
5]. Parenteral split or subunit influenza vaccines induce a strain-specific serum IgG antibody response and can be used to prevent influenza in children from 6 months of age, as well as in older people suffering from chronic diseases [
6,
7]. To enhance the immune response to vaccination, a search is being made for safe adjuvants that can enhance the immune response, increase its rate and duration [
8].
Seroconversions of hemagglutination inhibiting (HI) antibodies is traditionally used to assess the immunogenicity of influenza vaccines, representing the “gold standard” assay for this purpose. At the same time the WHO has repeatedly emphasized the importance of standardizing existing methods and developing new/improved ones for the detection of antibodies to NA [
9,
10]. In recent years, NA-inhibiting (NI) antibodies have been intensively studied due to their wide cross-reactivity, as well as neutralizing and protective properties [
11]. NA research can promote better understanding of how NA properties can help to develop new cross-reactive vaccines [
12].
Anti-NA antibodies can effectively limit transmission, reduce the severity of influenza infection, or prevent the development of secondary complications [
13,
14]. The fact that NI antibodies acquired after infection or prior vaccination demonstrate a broad spectrum associated with a reduction in the likelihood of influenza disease supports the inclusion of NA in next-generation vaccines aimed at better protection against drift variants [
15,
16]. Despite the recognized importance of NA-reactive antibodies in protection against influenza, the content of NA in seasonal influenza vaccines is currently not regulated and not measured by manufacturers [
16]. Since NA-based immunity may enhance protection against novel antigenic variants of the influenza virus [
17], the study of antibodies to NA has may play a role when predicting herd immunity against newly emerging influenza viruses, as well as estimating the protection of seasonal influenza vaccines in case of vaccine mismatch.
The aim of the study was to evaluate the production of NA-inhibiting (NI) antibodies after immunization with seasonal influenza vaccines, the duration of antibody persistence and the relationship with other quantitative parameters of the immune response to vaccination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vaccines
Study included three seasonal trivalent split or subunit adjuvanted IIV. The strain composition of the vaccines corresponded to the WHO recommendations for the northern hemisphere in the 2018-2019 season: A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus; A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 (H3N2)-like virus; and B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria/2/87 lineage) [
18]. All vaccines were produced according to Russian Pharmacopeia from purified egg-grown candidate vaccine viruses. HA content in vaccine formulations was indicated according to single-radial-immunodiffusion assay, NA content was not indicated. Split vaccine ‘Ultrix’ (produced by FORT LLC, Russia) contained 15 µg of HA of each strain in a 0.5 ml dose [
19]. Subunit vaccine ‘Grippol plus’ (produced by NPO ‘Petrovax Pharm’, Russia), contained 5 µg of HA of each strain (antigens produced by Abbott Biologicals B.V., the Netherlands) and 500 µg of Polyoxidonium
® adjuvant in a 0.5 ml dose [
20]. Another subunit vaccine ‘Sovigripp’ (produced by NPO ‘Microgen’, Russia) contained 5 µg of HA of influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 and A (H3N2) strains, 11 µg – of influenza B strain and 500 µg of Sovidon
® adjuvant in a 0.5 ml dose [
21].
2.2. Study Design
Serum samples were obtained within the framework of the serological survey. The study included healthy volunteers > 18 years old who had no contradictions to vaccination and who had signed the written informed consent. Vaccination was conducted in a specialized clinic of the Smorodintsev Research Institute of Influenza in open label regime. Blood samples were collected at the planned time points, including one point before vaccination (day 0) and 5 points after vaccination (day 7, day 21, 3 months, 6 months and 12 months). The study was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of the Smorodintsev Research Institute of Influenza, protocol #131 date 10 October 2018.
2.3. Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay
Assay was performed as recommended by WHO [
22] using inactivated influenza antigens (LLC “PPDP”, Russia). Sera were treated for 16-19 h at 37 °C with receptor destroying enzyme (RDE) from Vibrio cholerae NA extract (Denka Seiken Co., Tokyo, Japan) and then heat-inactivated at 56 °C for 30 min. Each serum (tested in duplicate) was 2-fold serially diluted in 96-well U-bottom polymer plates starting from 1:10 and mixed with 4 hemagglutination units (HAU) of influenza antigen. After 1 h incubation 0.5% chicken erythrocyte suspension was added. Antibody titers were expressed as the reciprocal of the highest serum dilution at which inhibition of agglutination was observed. A four-fold increase in HI antibody titer after vaccination was considered as antibody seroconversion.
2.4. Influenza Viruses
To assess NA antibodies in the enzyme-linked lectin assay (ELLA) we used purified reassortant influenza viruses which inherited HA from A/herring gull/Sarma/51c/2006 (H6N1) influenza virus and NA from A/South Africa/3626/13(H1N1)pdm09 or A/Hong Kong/2014/ (H3N2) strains. Viruses were obtained from the collection of Virology department, Institute of Experimental Medicine, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation. The viruses were propagated in 10-day old chicken embryos. Virus-containing allantoic fluid was first clarified by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min. Then virus was pelleted by ultracentrifugation at 17000 rpm for 3 hours (Beckman Optima TM L-100 XP Ultracentrifuge, Type 19 rotor). The supernatant was removed, the pellet was resuspended in 2.0 ml of ice-cold calcium borate buffer (pH = 7.2). The resuspended virus was applied to a 30/60% sucrose step gradient prepared in calcium borate buffer, followed by centrifugation at 20,000 rpm for 2.5 hours (SW 40 Ti rotor). The virus-containing layer at the interface of sucrose gradient was extracted and purified from sucrose by pelleting in calcium-borate buffer at 20,000 rpm for 2.5 hours (SW 40 Ti rotor). The pellet was resuspended in 1.0 ml calcium borate buffer. The antigen concentration was expressed in HAU.
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Lectin Assay (ELLA)
We used ELLA to evaluate NA inhibiting antibodies as described previously [
23]. Briefly, 96-well plates (Greiner Bio-One, Kremsmünster, Austria) were coated overnight with 150 μl of 50 μg/ml fetuin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA). Next, 60 μl of serum was heated at 56 °C for 30 min, serially diluted with PBS-BSA, and then incubated with an equal volume of pre-diluted virus for 30 min at 37 °C. The content of influenza viruses was 128-256 HAU/0.1 ml which gave OD450 in the range of 0.4–0.6. After incubation, 100 μl of the mixtures was applied to the fetuin-coated wells. After incubation for 1 hour at 37 °C, the plates were washed, before assessing NA activity by incubating with peroxidase-labeled peanut lectin (2.5 μg/ml, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by washing and addition of 100 μl of the peroxidase substrate 3,3’, 5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). The reaction was stopped after 5 min by adding 100 μl of 1 N sulfuric acid. Optical density (OD) values were measured at 450 nm using a universal microplate reader (Elx800, Bio-Tek Instruments Inc., USA). The titer of serum antibodies against NA was determined as the reverse dilution of the sample with 50% inhibition of NA activity which was defined as two-fold decrease in optical density in comparison with the virus control wells. A two-fold increase in NI antibody titer after vaccination was considered as antibody seroconversion.
2.6. NA Activity of Influenza Viruses and Influenza Vaccines
The NA activity of influenza viruses and influenza vaccines was measured by ELLA using high molecular substrate fetuin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Lous, USA). Virus or vaccine 2-fold dilutions were prepared in phosphate-buffered saline containing bovine serum albumin (PBS-BSA) starting from 256 HAU in triplicate.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical data analysis and visualization were performed using MS Excel 2016, RStudio 2022.12.0 and GraphPad Prizm 8.4.3. A number of group descriptive statistics including proportion (%), mean, median, interquartile range (IQR) and geometric mean were calculated. Confidence interval for geometric mean was calculated by transforming the titers to logarithms, then calculating 95% CI and then taking antilog of the interval limits. Confidence interval (95%CI) for proportion were calculated by Clopper-Pearson method. Statistical analysis was exploratory and was performed post-hoc, particular statistical tests are indicated in the text. For statistical analysis the logarithmic values of antibody titers were used. The difference was considered statistically significant at p-value < 0.05. Regression analyses was performed with ‘glm’ function from ‘stats’ package in RStudio using binomial family model. Correlation matrix and heatmap were generated by Spearman correlation analysis for multiple variables as implemented in Prism 8.4.3 (GraphPad).
2.8. Study Limitations
The present study included participants 18 years and older with unknown history of previous vaccination and infection, both seropositive and seronegative. The study was open label and no special inclusion criteria were used except for eligibility to vaccination, so the study cohort does not represent any specific population. The study aimed to analyze humoral immune response to HA and NA influenza antigens, and did not include the analyses of cell mediated response after vaccination as well as the protection rate in vaccinated groups. The study focuses on antibody analysis at one time point before vaccination and five time points within a year after vaccination with inactivated influenza vaccine, and presents the data from 73 subjects with complete specimen set.
3. Results
3.1. Antibody Levels throughout the Year after Vaccination
Assessment of NA and HA inhibiting antibodies was performed in serum samples, obtained from 73 healthy individuals (aged 20 to 87) before and throughout the year after influenza vaccination. Among the study group, 46 participants were immunized with a subunit adjuvanted vaccine, and 27 volunteers were immunized using a split vaccine. The main demographic characteristics of the study population are presented in
Table 1.
The majority of subjects had a previously unknown history of influenza vaccination. Overall level of seropositivity to HA and NA antigens at the moment of vaccination varied from middle (37% against N2) to high (85% against H1pdm09).
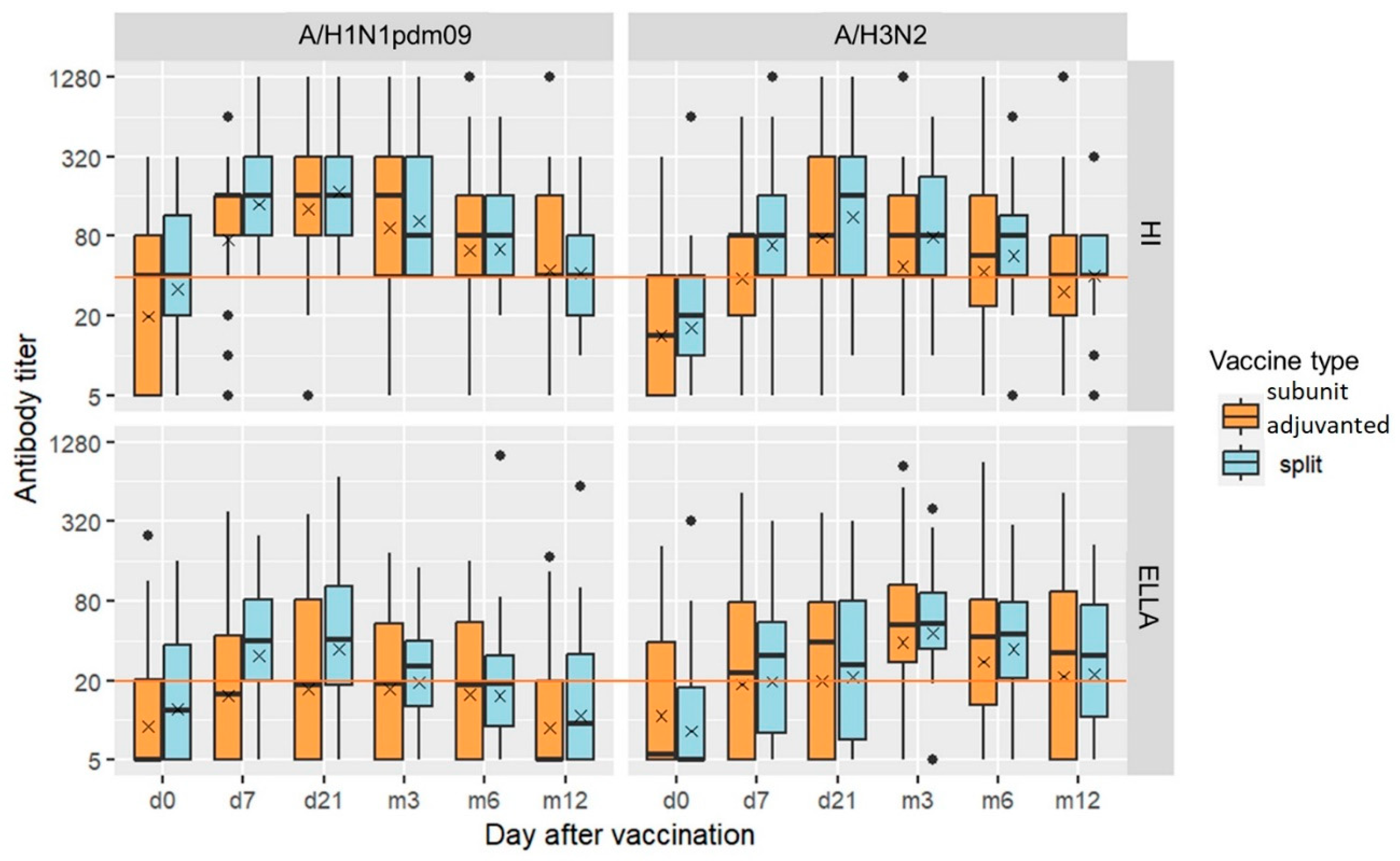
The levels of NI and HI antibodies throughout one year after vaccination showed expected according to earlier studies and similar dynamics. With the exception of anti-N2 antibodies, the rise of geometric mean antibody titers (GMTs) was detected already at day 7 after vaccination, continued till day 21 and fell down 3 months after vaccination (
Figure 1, Suppl
Table 1). Slower dynamics was observed for N2 specific antibodies, with the maximum GMT observed at 3 months after vaccination. Overall NI antibody titers before and after vaccination using both split IIV and adjuvanted IIVs were noticeably lower than the HI antibody titers.
Compared to baseline, a statistically significant increase in the average HI and NI titers was observed at almost all time points starting from day 7 after vaccination for both split and subunit adjuvanted vaccine groups. All p- values are given in the supplementary data (Suppl.
Table 2). A year after immunization with the split IIV a statistically significant increase in antibody titers to both antigens of the A/H3N2 influenza virus still persisted. A year after immunization with adjuvanted IIVs, the level of antibodies significantly differed from the pre-vaccination level only for H1 specific HI antibodies and NI antibodies to N2 (Suppl.
Table 2).
Exploratory analysis of variance did not find statistically significant differences between the split and subunit adjuvant vaccine groups in HI and NI antibody titers at any of the time points (not shown). Stratification by high or low baseline antibody titers (<1:40 for HI antibodies and <1:20 for NI antibodies) also showed no statistically significant difference between split and subunit adjuvanted vaccine groups (Suppl.
Figure S1, Suppl.
Figure S2).
3.2. Antibody Seroconversion Rates after Vaccination
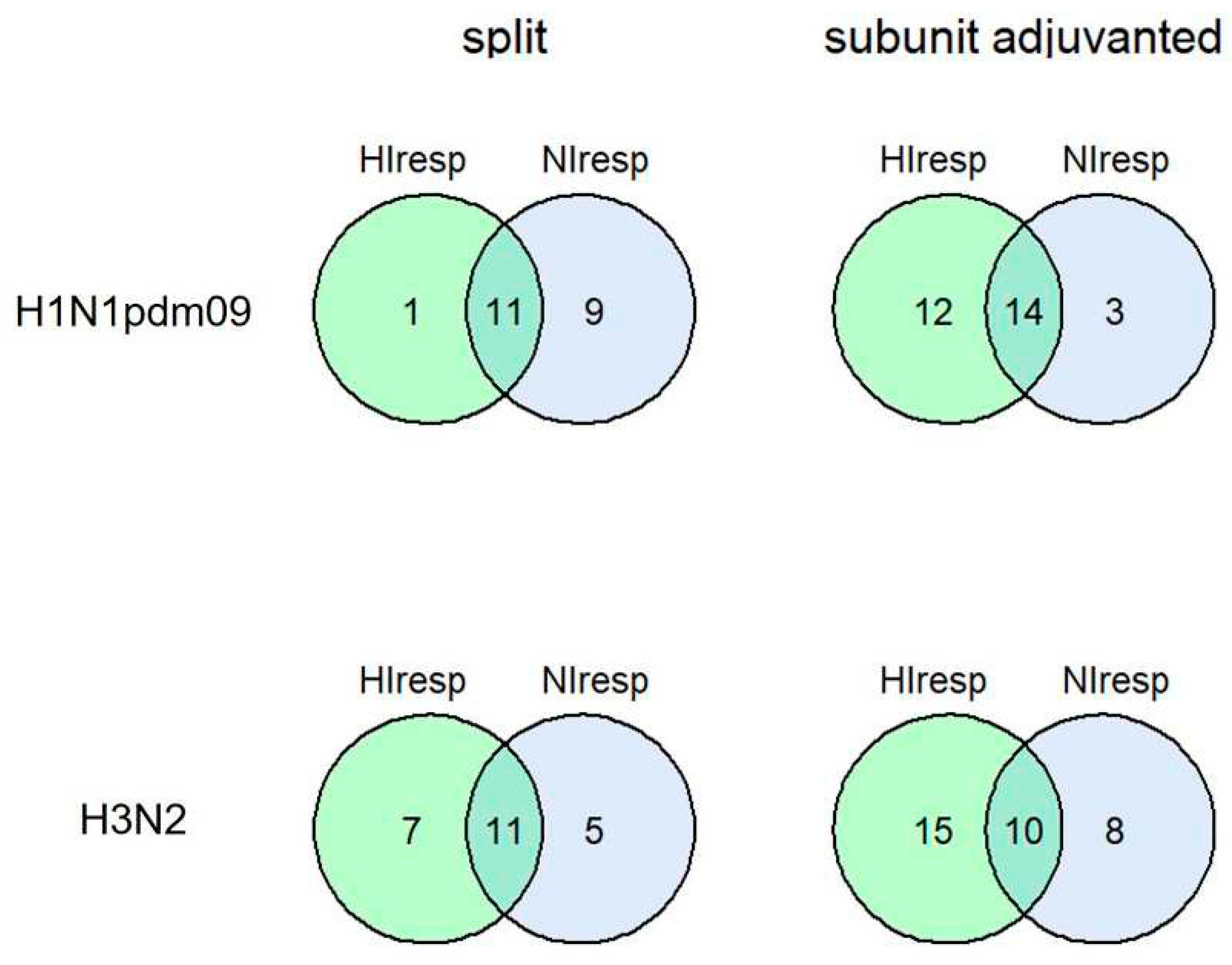
To compare HA and NA-specific antibody response we compared the seroconversion rates of HI and NI antibodies on day 21 after vaccination. Split IIV caused significantly more NI antibody conversions to the A/H1N1 influenza virus compared to adjuvanted IIVs (
Table 2).
Same trend was observed for A/H3N2 virus NI antibodies; however, the difference was not statistically significant. Worth noted both vaccines met the Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP) criteria on the number of HI antibodies seroconversions which exceeded the 40% threshold [
24]. Regression analyses performed for the probability of positive seroconversion outcome confirmed statistically significant impact of vaccine type factor on the response to N1 neuraminidase and show no impact of age, sex or initial antibody titer (
Supplementary Table S3).To demonstrate neutralization properties of the sera we used microneutralization assay. A strong correlation between HI and MNA antibody titers and the same dynamics of antibodies after vaccination is shown (Suppl.
Figure S3). The combined seroconversions to HA and NA were observed on average in half of the participants (
Figure 2).
The distribution of the numbers for participants who seroconverted for all four components (H1-HA, N1-NA, H3-HA and N2-NA), and seroconverted for 3 of 4 components presented in Suppl.
Figure S4.
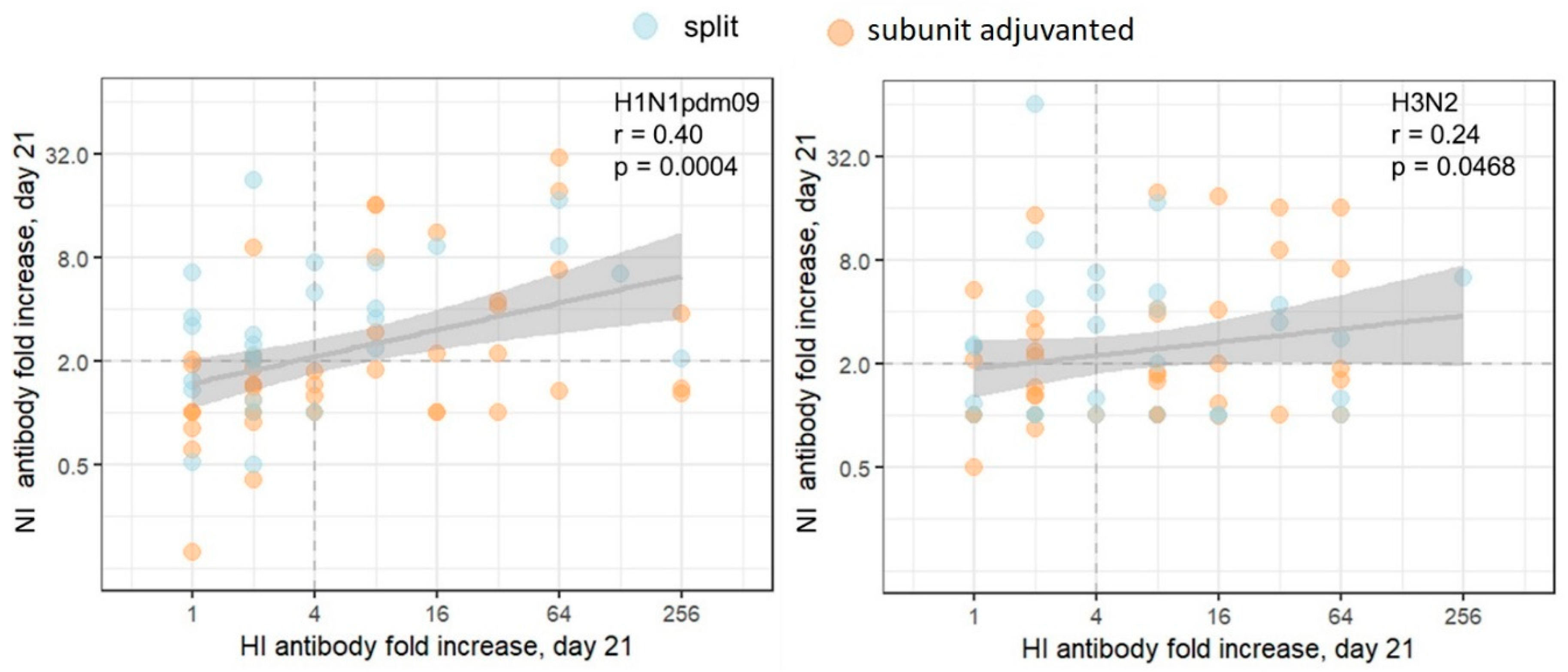
Figure 3 represents the correlation analysis of post-vaccination HI and NI antibody titers fold-increase for all subjects in the cohort including all study participants, both seronegative and seropositive on day 21 after immunization. The total number of seropositive/negative participants are presented in
Table 1. A poor to moderate correlation between HI and NI post-vaccination antibody titers fold increase (
Figure 3) assumes some degree of independence in the response to different antigens of the same virus.
3.3. Preexisting Immunity Impact and Correlation Analysis of HI and NI Antibody Titers
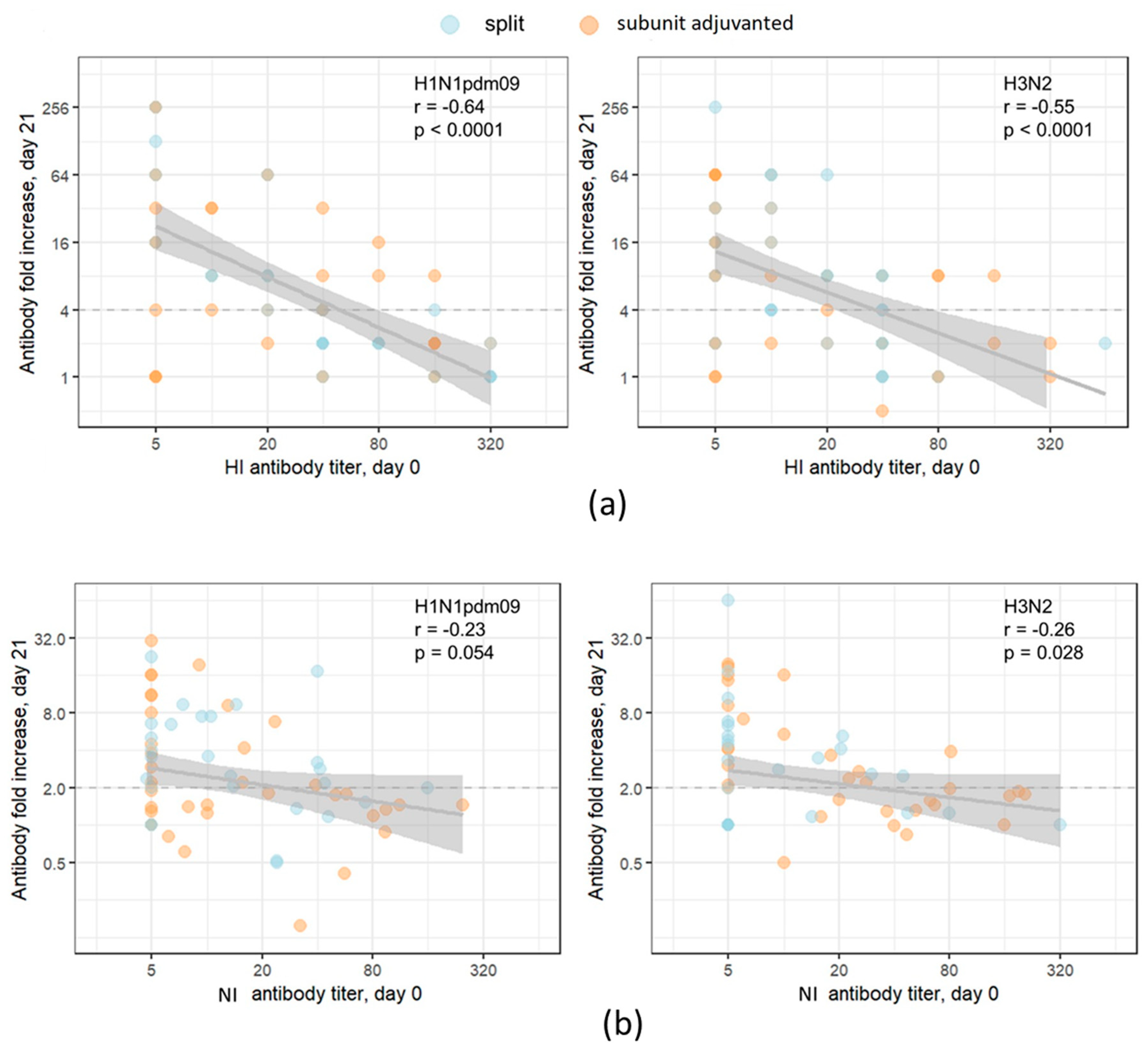
Next, we analyzed the dependence of the response to vaccination on the preexisting level of HI and NI antibodies.
Figure 4 represents the dependence of the post-vaccination antibody fold-increase on the baseline (preexisting) antibody level for all subjects in the cohort. On the left side of the graph X axis are participants with low baseline titers (including seronegative), on the right side - those with high baseline titers (seropositive). This type of analysis does not presume grouping by the baseline titer. As expected, the post-vaccination HI antibody fold increase strongly negatively correlated with initial antibody titers (
Figure 4a). Poor negative correlation was found for post-vaccination NI antibody titers fold increase and preexisting NI antibody level (
Figure 4b).
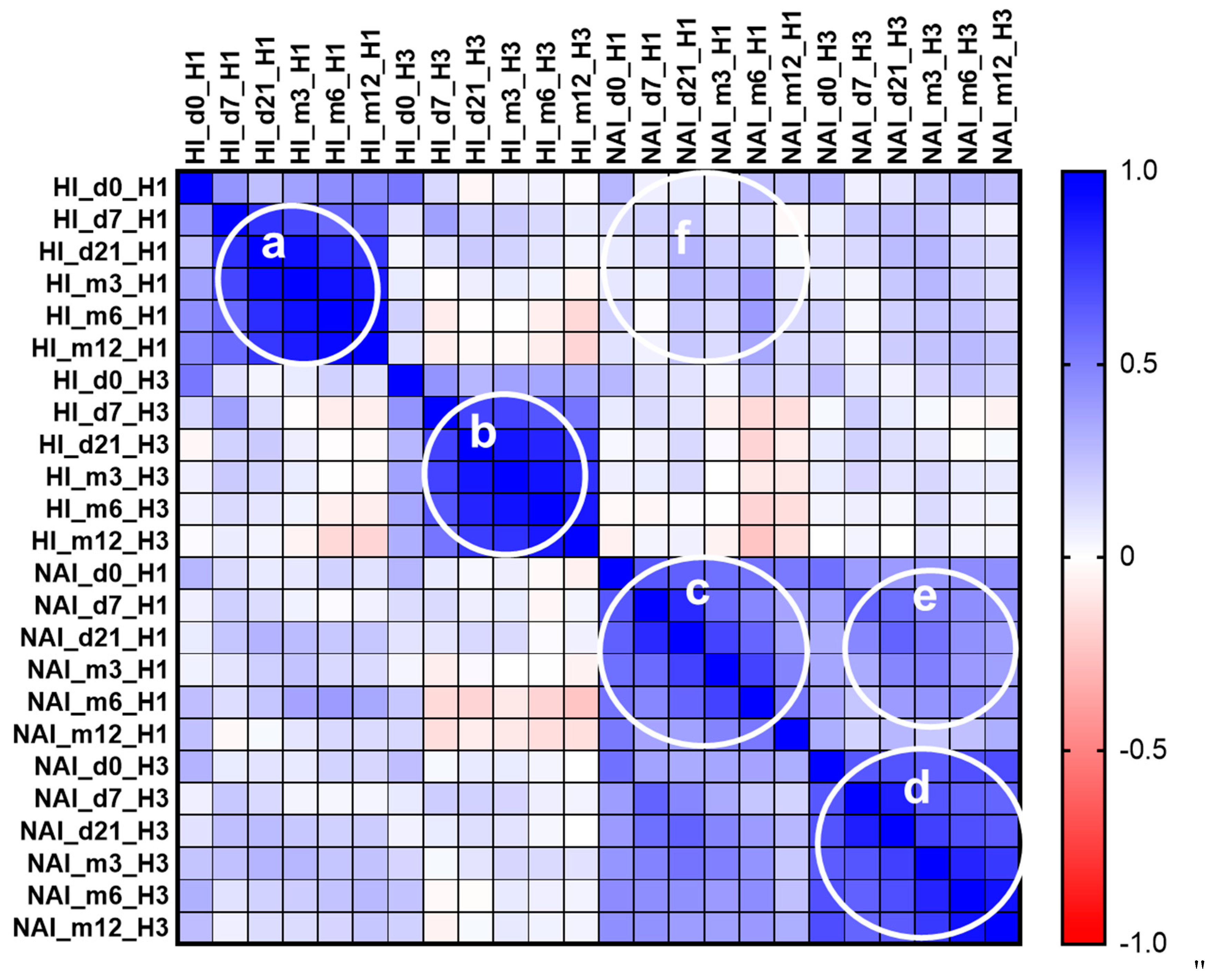
Further, we performed the rough correlation matrix analyses of HI and NI antibody titers to A/H1N1pdm09 and A/H3N2 influenza viruses before, shortly after vaccination and throughout a year (
Figure 5). Analysis of HI antibody titers have shown that the higher was the response after vaccination the higher will be the titer during the whole year (
Figure 5a,b). Analyses of NI antibody titers have shown that the higher was the initial NI antibody titer before vaccination, the higher it will be during the year after vaccination (
Figure 5c,d). Some level of correlation was found between anti-NA antibody titers against two influenza A subtypes (
Figure 5e) and almost no correlation between anti-HA and anti-NA antibody titers (
Figure 5f).
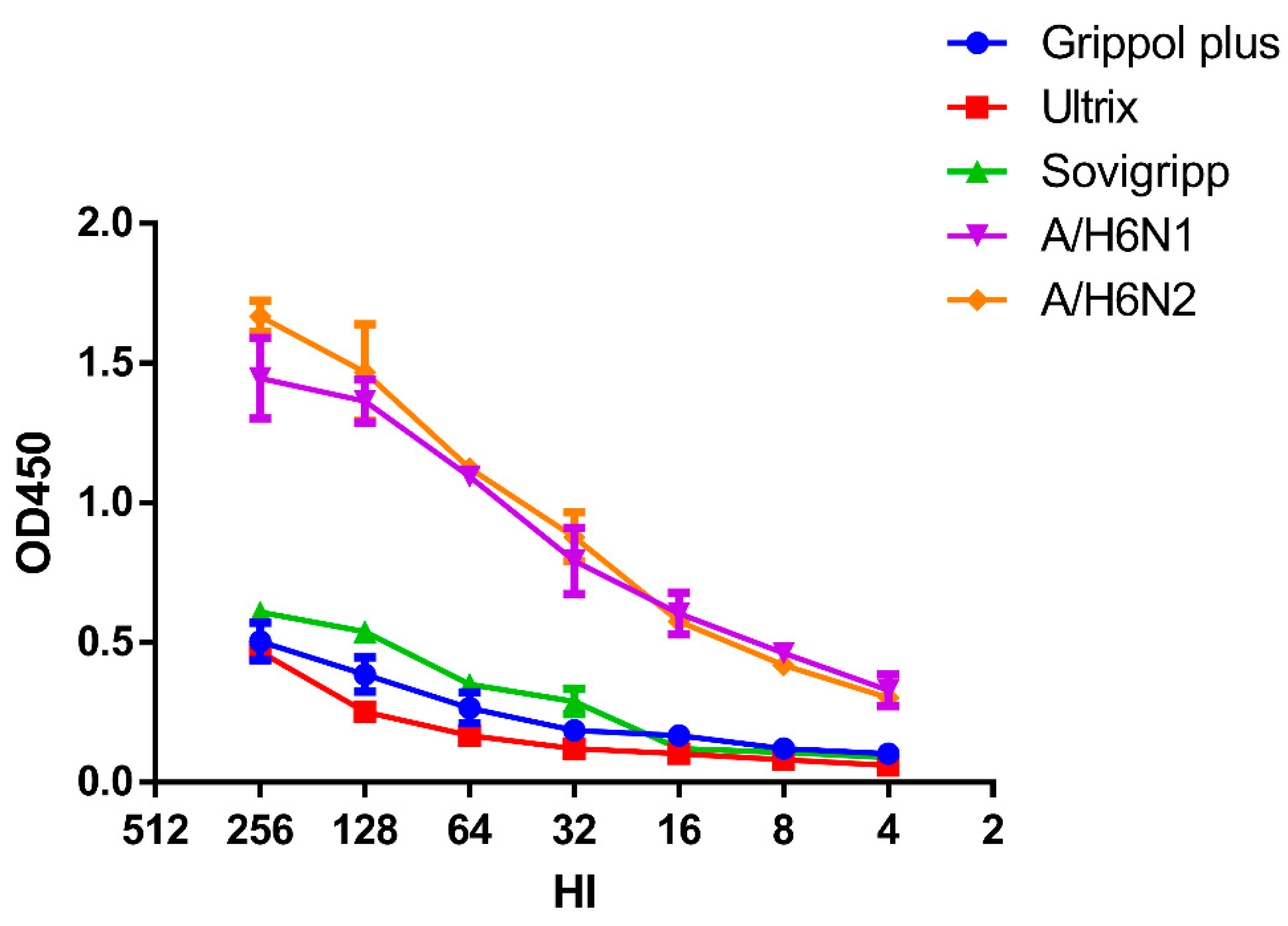
3.4. Neuraminidase Functional Activity in the Vaccine Formulation
So finally, we tried to evaluate if the NA included in the vaccine preparations is functionally active. The sialidase activity of the vaccine preparations used in this study was compared with that of the reassortant influenza viruses containing NA of the N1 or N2 subtype (
Figure 6).
It turned out that all three vaccines exhibit enzymatic activity, although significantly lower than whole influenza viruses with the same hemagglutination activity (P=0.0009, Kruskal-Wallis test). Therefore, the increase in antibody titers to NA may well be specific rather than non-specific steric hiding of the NA active site by antibodies attached to the highly conserved HA stem region [
25].
4. Discussion
Vaccination is the most effective and scientifically proven way to prevent influenza infection. Current influenza vaccines have been optimized and standardized specifically to induce high titers of anti-HA antibodies, and the production of anti-NA antibodies is not considered as a criterion for immunogenicity. There is evidence that NA can make an additional contribution to the protective efficacy of influenza vaccination [
25]; therefore, the study of NI antibody seroconversion may be important for assessing the immunogenicity of influenza vaccines, and this issue has repeatedly attracted the attention of experts from the World Health Organization [
9,
10]. Since NI antibodies block the enzymatic function of NA [
26], this determines the possible mechanisms of their protective action, such as preventing the release of viral progeny from the cell [
27]. At the initial stage of the infectious cycle of the influenza virus, NI antibodies can prevent the attachment of HA to sialic receptors by steric shielding [
28]. In addition, by attaching to the cell surface, NA antibodies can promote the induction of Fc receptor-mediated effector functions, such as ADCC [
29], and mediate the activation of the complement system in the process of complement-dependent cytotoxicity [
30].
Animal models have shown that NA-directed antibodies do not completely prevent infection with the influenza virus, but reduce the lethality and reproduction of the virus in the lungs [
31,
32,
33]. In humans, NI antibodies are not inferior to HI antibodies in protecting against influenza infection and in preventing the development or reducing the severity of the disease [
34]. Natural influenza infection results in high seroconversion rates against both HA and NA [
27]. A number of studies have shown that the induction of antibodies towards NA after immunization with seasonal vaccines are substantially reduced when compared to influenza infection [
35] and varies widely between manufacturers [
34,
36,
37,
38,
39]. After a natural influenza infection, the number of NA-reactive B cells was equal to or exceeded HA-reactive B cells, while seasonal influenza vaccines rarely induce NA-reactive B cells [
35]. In addition, widely cross-reactive anti-NA antibodies acquired from natural infection did not bind several inactivated vaccines available, suggesting that vaccines lack the NA epitopes targeted by these antibodies [
35]. The NA enzymatic activity is an excellent indicator of the native structure and correlates well with immunogenicity [
40]. Quite often, it is believed that during production of IIVs, NA loses its structure and, consequently, its enzymatic activity and immunogenicity [
41]. The stability and immunogenicity of NA in a vaccine may depend on the method of virus inactivation and also varies between manufacturers. In our study, it was shown that both split and subunit IIVs exhibited similar enzymatic activity albeit lower than whole viruses.
The antigenic competition between HA and NA has been postulated, which is mainly due to the larger number of HA proteins found on the virion surface and its amplified presentation to the antigen-recognition cells of the immune system [
42]. The amount of NA in vaccines also differs depending on the proportions of HA and NA in each strain. Thus, in the whole virus, the ratio of HA to NA is usually 4-5:1 [
43]. Seasonal inactivated vaccines usually contain 15 µg of the HA of each component [
38]. In the present study, we used seasonal IIVs: the split vaccine contained 15 μg of HA of each vaccine strain, and both subunit adjuvant vaccines contained 5 μg of HA, NA content of vaccines was unknown. In our study NI antibody titers after vaccination using both split IIV and subunit adjuvanted IIVs were noticeably lower than the HI antibody titers, which can partly be explained in terms of the differences in the tests used to detect these antibodies. At the same time, we have demonstrated a statistically significant antibody increase for both HI and NI antibodies to A/H1N1 and A/H3N2 influenza viruses starting from day 7 after vaccination with both the split and subunit adjuvant IIVs. Besides, the increase in average titers compared with the pre-vaccination level persisted during 12 months in relation to both HI and NI antibodies.
Previously, it was shown that the most pronounced rise in the levels of NA-specific antibodies was observed on the 21st day after immunization with IIV and after 180 days the average levels of antibodies to NA were still significantly different from those before vaccination [
43]. In our study the levels of NI antibodies increased already on day 7 after immunization and it can be noted that they did not differ significantly from those on day 21 while the level of antibodies to HA almost always increased from 7 to 21 days after vaccination (Suppl. Tables S1, S2).
The weak correlation of immune responses to HA and NA on day 21 post vaccination shown in our study coincides with previously obtained data [
34] and once again emphasizes that NI antibodies can be independent indicators of post-vaccination immunity to influenza. Multivariate analyzes performed in earlier studies have shown that serum HI and NI antibodies independently correlated with resistance to infection and infection-associated disease. Notably, only serum NI antibodies independently predicted a reduction in incidence among infected subjects [
44].
A number of studies have focused on the effect of pre-existing antibody levels on the immune response after vaccination. So, during the 2007-2008 influenza season it was shown that individuals with high HI or NI titers before vaccination, the inactivated vaccine may not induce antibody increases due to natural immunity and may not provide additional protection and/or immune response [
45]. At the same time, it has recently been shown that infection with the A(H3N2) virus prior to vaccination can increase the number and spectrum of A(H3N2)-reactive antibodies induced by vaccination [
46].Our study showed that the formation of HI antibodies after immunization depended on a low pre-vaccination level of these antibodies, then no such dependence was found with respect to NI antibodies.
In conclusion, it should be said that that studying the immunogenicity of NA in seasonal vaccines will help to improve the effectiveness of influenza vaccination. This can be facilitated by studying the properties of NA when selecting candidates for vaccine strains, standardizing the content of NA in vaccine preparations, and optimizing the manufacturing process to preserve the antigenic structure of NA [48]. Adding a known quantity of conformationally correct NA to current seasonal vaccines may improve efficacy and, potentially, cross-reactivity against drifted strains of influenza [
16].
5. Conclusions
Immunization with inactivated influenza vaccines led to a significant increase in serum anti-NA antibody titers, slowly waning during one year after vaccination.
The dynamics of anti-NA antibody titers differed depending on the virus subtype: antibodies to A/H3N2 virus NA increased later than antibodies to subtypes A/H1N1pdm09 and persisted longer. The increase in antibody titers to NA of influenza A viruses after vaccination did not depend on their preexisting level.
The values of NA antibody titers after vaccination directly correlated with titers before vaccination in contrast to antibodies to HA.
The split vaccine was more immunogenic in relation to NI antibodies seroconversion rate.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
DYA, SMA, SMV - conceptualization; REA, KVZ, KPA, PNN, KKS - acquisition, methodology, analysis, and interpretation of data; DYA, SMV - drafting of the manuscript; SMA, LDA - critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; SMV - statistical analysis; SMA, LDA - obtained funding; DYA, SMA - project administration. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted. The corresponding author is responsible for the overall content and conduct of the study, and the decision to publish.
Funding
The study was done within the framework of the project “Assessment of population immunity and epidemiological efficacy of flu vaccines in the Russian Federation” funded by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (2019-2021). The work was partially supported from the budget of the Institute of Experimental Medicine, within the framework of the theme of fundamental scientific research FGWG-2022-0001.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Particular datasets are available on reasonable request to corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no financial interests/personal relationships related to this manuscript.
References
- Dhanasekaran, Vijaykrishna, Sheena Sullivan, Kimberly M. Edwards, Ruopeng Xie, Arseniy Khvorov, Sophie A. Valkenburg, Benjamin J. Cowling, and Ian G. Barr. Human seasonal influenza under COVID-19 and the potential consequences of influenza lineage elimination. Nature communications 2022, 13, 1721.
- Ambrose, C.S.; Levin, M.J. The rationale for quadrivalent influenza vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhaus, A.; Lavanchy, D. Recommendations for the use of inactivated influenza vaccines and other preventive measures. Vaccine 2001, 19, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, Theone C., Adrian Onu, Laurentiu Berbecila, Emilia Lupulescu, Alina Ghiorgisor, Gideon F. Kersten, Yi-Qing Cui, Jean-Pierre Amorij, and Leo Van der Pol. Influenza vaccine manufacturing: effect of inactivation, splitting and site of manufacturing. Comparison of influenza vaccine production processes. PloS one 2016, 11, e0150700.
- Hendriks, J., Holleman, M., de Boer, O., de Jong, P. and Luytjes, W. An international technology platform for influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2011, 29, A8–A11.
- Iorio, A. M., P. Rivosecchi, T. Zei, M. Neri, and L. Merletti. Immune response to trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine in young and elderly subjects. Vaccine 1989, 7, 341–344.
- World Health Organization. Influenza vaccines: recommendations for the use of inactivated influenza vaccines and other preventive measures. Weekly Epidemiological Record= Relevé épidémiologiquehebdomadaire 2000, 75, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Tregoning, J.S.; Russell, R.F.; Kinnear, E. Adjuvanted influenza vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 14, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.A.; Neuzil, K.M.; Pervikov, Y.; Palkonyay, L. WHO meeting on the role of neuraminidase in inducing protective immunity against influenza infection, Vilamoura, Portugal, September 14, 2008. Vaccine 2009, 27, 6366–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Eichelberger, M.C.; Webby, R.J.; Shaw-Saliba, K.; Wan, H.; Wilson, P.C.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Monto, A.S. NAction! How Can Neuraminidase-Based Immunity Contribute to Better Influenza Virus Vaccines? Mbio 2018, 9, e02332–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgea, L.T.; Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Memoli, M.J. Influenza Neuraminidase: A Neglected Protein and Its Potential for a Better Influenza Vaccine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F.; Palese, P. Advances in the development of influenza virus vaccines //Nature reviews Drug discovery. – 2015. – Т. 14. – №. 3. – С. 167-182.
- Maier H., E. et al. Pre-existing antineuraminidase antibodies are associated with shortened duration of influenza A (H1N1) pdm virus shedding and illness in naturally infected adults //Clinical Infectious Diseases. – 2020. – Т. 70. – №. 11. – С. 2290-2297.
- McCullers, J.A.; Huber, V.C. Correlates of vaccine protection from influenza and its complications. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, C.D.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Billings, M.; Eick-Cost, A.; Couzens, L.; Sanchez, J.L.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Seguin, P.; Myers, C.A.; et al. Neutralizing and Neuraminidase Antibodies Correlate With Protection Against Influenza During a Late Season A/H3N2 Outbreak Among Unvaccinated Military Recruits. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-J.; Crank, M.C.; Shiver, J.; Graham, B.S.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Next-generation influenza vaccines: opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichelberger M., C. , Monto A. S. Neuraminidase, the forgotten surface antigen, emerges as an influenza vaccine target for broadened protection //The Journal of infectious diseases. – 2019. – Т. 219. – №. Supplement_1. – С. S75-S80.
- World Health Organization. 22 February 2018. Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2018-2019 northern hemisphere influenza season. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/recommended-composition-of-influenza-virus-vaccines-for-use-in-the-2018-2019-northern-hemisphere-influenza-season.
- Erofeeva, М.К.; Nickonorov, I.; Maksakova, V.; Stukova, M.; Konshina, O.; Okhapkina, E.; Voicehovskaya, E.; Korovkin, S.; Melnikhov, S.; Kiselev, O. Protective Properties of Inactivated Virosomal Influenza Vaccine. Procedia Vaccinol. 2014, 8, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talayev, V.; Zaichenko, I.; Svetlova, M.; Matveichev, A.; Babaykina, O.; Voronina, E.; Mironov, A. Low-dose influenza vaccine Grippol Quadrivalent with adjuvant Polyoxidonium induces a T helper-2 mediated humoral immune response and increases NK cell activity. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6645–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erofeeva, M.K. Stukova, M. A., Shakhlanskaya, E. V., Buzitskaya, Z. V., Maksakova, V. L., Krainova, T. I., ... &Lioznov, D. A. (2021). Evaluation of the Preventive Effectiveness of Influenza Vaccines in the Epidemic Season 2019–2020 in St. Petersburg. Epidemiology and Vaccinal Prevention, 20(5), 52-60.
- World Health Organization. (2011). Manual for the laboratory diagnosis and virological surveillance of influenza. World Health Organization. 2.F Serological diagnosis of influenza by haemagglutination inhibition testing. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44518.
- Desheva, Y. A. , Smolonogina, T. A., &Sychev, I. A. (2018). Peroxidase-linked lectin assay to determine neuraminidase-inhibiting antibodies using reassortant influenza viruses.
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, 1997. Note for guidance on harmonisation of requirements for influenza vaccines. European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Brussels, Belgium.
- Rajendran, M.; Nachbagauer, R.; Ermler, M.E.; Bunduc, P.; Amanat, F.; Izikson, R.; Cox, M.; Palese, P.; Eichelberger, M.; Krammer, F. Analysis of Anti-Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Antibodies in Children, Adults, and the Elderly by ELISA and Enzyme Inhibition: Evidence for Original Antigenic Sin. Mbio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Webby, R.J. Contribution of antibody production against neuraminidase to the protection afforded by influenza vaccines. Rev. Med Virol. 2012, 22, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbherr, S.J.; Ludersdorfer, T.H.; Ricklin, M.; Locher, S.; Rentsch, M.B.; Summerfield, A.; Zimmer, G. Biological and Protective Properties of Immune Sera Directed to the Influenza Virus Neuraminidase. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1550–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, M.; Krammer, F.; McMahon, M. The Human Antibody Response to the Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Following Infection or Vaccination. Vaccines 2021, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wurtzer, S.; Rameix-Welti, M.-A.; Dwyer, D.; van der Werf, S.; Naffakh, N.; Clavel, F.; Labrosse, B. Enhancement of the Influenza A Hemagglutinin (HA)-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion and Virus Entry by the Viral Neuraminidase (NA). PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Podolsky, K.A.; Chromikova, V.; Kirkpatrick, E.; Falconieri, V.; Meade, P.; Amanat, F.; Tan, J.; Tenoever, B.R.; Tan, G.S.; et al. Broadly protective murine monoclonal antibodies against influenza B virus target highly conserved neuraminidase epitopes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Sheng, Z.; Sreenivasan, C.C.; Wang, D.; Li, F. Influenza A Virus Antibodies with Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Function. Viruses 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliasas, V.C.; Menne, Z.; Aida, V.; Yin, J.-H.; Naskou, M.C.; Neasham, P.J.; North, J.F.; Wilson, D.; Horzmann, K.A.; Jacob, J.; et al. A Novel Neuraminidase Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Offers Protection Against Heterologous H3N2 Influenza Virus Infection in the Porcine Model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 915364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desheva, Y.; Petkova, N.; Losev, I.; Guzhov, D.; Go, A.; Chao, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H. Establishment of a Pseudovirus Platform for Neuraminidase Inhibiting Antibody Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desheva, Y.; Losev, I.; Petkova, N.; Kudar, P.; Donina, S.; Mamontov, A.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chao, Y.-C. Antigenic Characterization of Neuraminidase of Influenza A/H7N9 Viruses Isolated in Different Years. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S.; Petrie, J.G.; Cross, R.T.; Johnson, E.; Liu, M.; Zhong, W.; Levine, M.; Katz, J.M.; Ohmit, S.E. Antibody to Influenza Virus Neuraminidase: An Independent Correlate of Protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Wohlbold, T.J.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Huang, M.; Huang, Y.; Neu, K.E.; Lee, J.; Wan, H.; Rojas, K.T.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. Influenza Infection in Humans Induces Broadly Cross-Reactive and Protective Neuraminidase-Reactive Antibodies. Cell 2018, 173, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.C.; Kilbourne, E.D.; E Johansson, B. Neuraminidase-specific antibody responses to inactivated influenza virus vaccine in young and elderly adults. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, T.R.; Rayford, Y.; Niño, D.; Winokur, P.; Brady, R.; Belshe, R.; Chen, W.; Atmar, R.L.; Couch, R.B. A high dosage influenza vaccine induced significantly more neuraminidase antibody than standard vaccine among elderly subjects. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, R.B.; Atmar, R.L.; Keitel, W.A.; Quarles, J.M.; Wells, J.; Arden, N.; Niño, D. Randomized comparative study of the serum antihemagglutinin and antineuraminidase antibody responses to six licensed trivalent influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2012, 31, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito H, Nishimura H, Kisu T, Hagiwara H, Watanabe O, Kadji FMN, et al. Low Response in Eliciting Neuraminidase Inhibition Activity of Sera Among Recipients of a Split, Monovalent Pandemic Influenza Vaccine During the 2009 Pandemic. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233001. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana I, Yang K, Getie-Kebtie M, Couzens L, Markoff L, Alterman M, Eichelberger MC: Stability of neuraminidase in inactivated influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2225–2230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanko, A. Shuklina, M., Kovaleva, A., Zabrodskaya, Y., Vidyaeva, I., Shaldzhyan, A., ... &Katlinski, A. Comparative immunological study in mice of inactivated influenza vaccines used in the Russian immunization program. Vaccines 2020, 8(4), 756. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson BE, Moran TM, Kilbourne ED. Antigen-presenting B cells and helper T cells cooperatively mediate intravirionic antigenic competition between influenza A virus surface glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987, 84, 6869–6873. [CrossRef]
- Couch, R.B.; Atmar, R.L.; Franco, L.M.; Quarles, J.M.; Wells, J.; Arden, N.; Niño, D.; Belmont, J.W. Antibody Correlates and Predictors of Immunity to Naturally Occurring Influenza in Humans and the Importance of Antibody to the Neuraminidase. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Fong, Y.; Juraska, M.; Carpp, L.N.; Monto, A.S.; Martin, E.T.; Petrie, J.G. HAI and NAI titer correlates of inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccine efficacy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auladell, M.; Phuong, H.V.M.; Mai, L.T.Q.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Carolan, L.; Wilks, S.; Thai, P.Q.; Price, D.; Duong, N.T.; Hang, N.L.K.; et al. Influenza virus infection history shapes antibody responses to influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creytens, S.; Pascha, M.N.; Ballegeer, M.; Saelens, X.; de Haan, C.A.M. Influenza Neuraminidase Characteristics and Potential as a Vaccine Target. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 786617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).