Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. History
3. Summary of Existing SED Reviews
4. Study Rationale
5. SED Theme Synthesis
5.1. Energy Financing towards the 1.5–2.0 °C Scenario
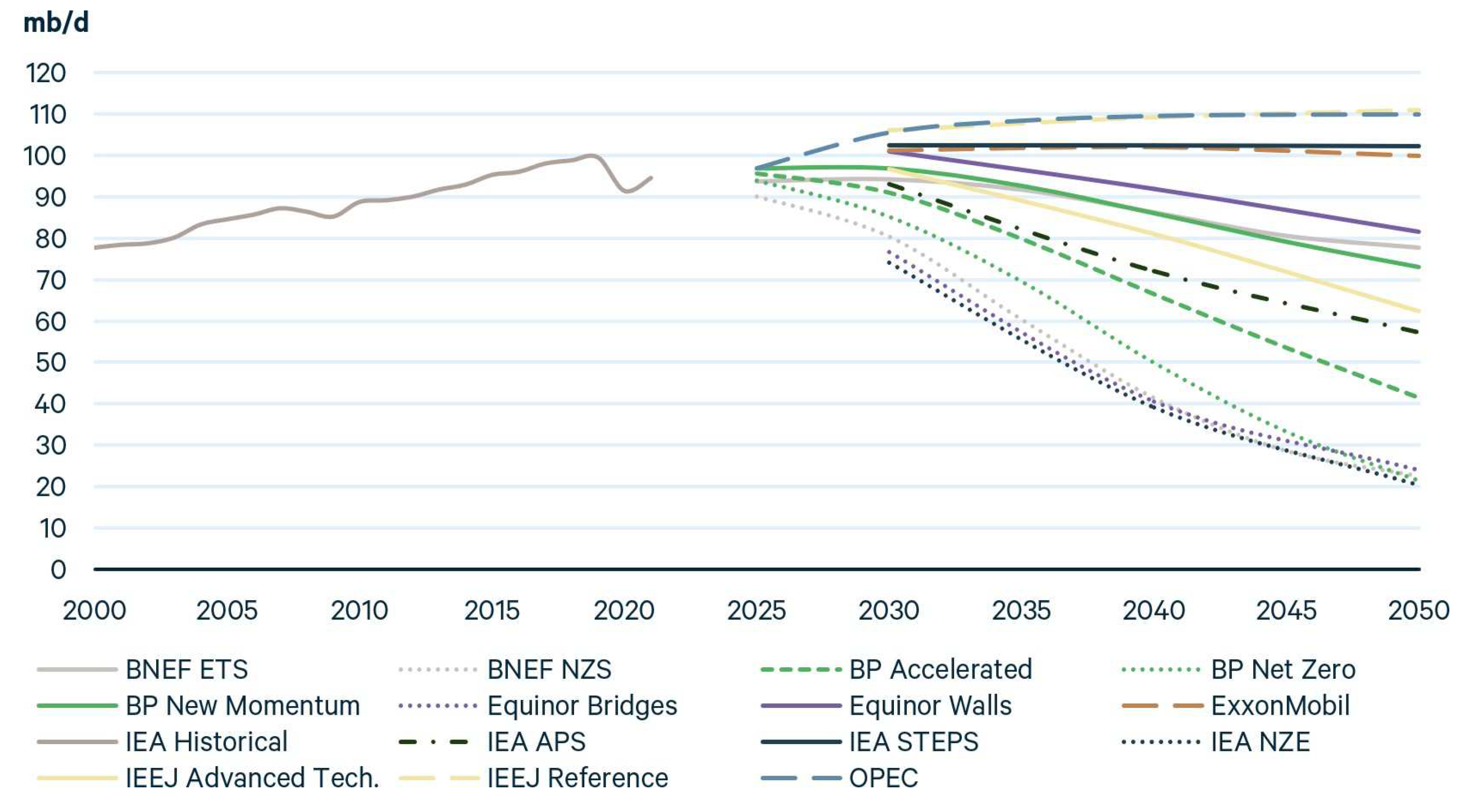
5.1.1. Proximity to Reaching the 1.5–2.0 °C Scenario
5.1.2. Response to the 1.5 °C Scenario Issues—Recent Policies of the top CO2 Emitters
5.2. Uprising in 100% Renewable Energy System Possibilities and SED
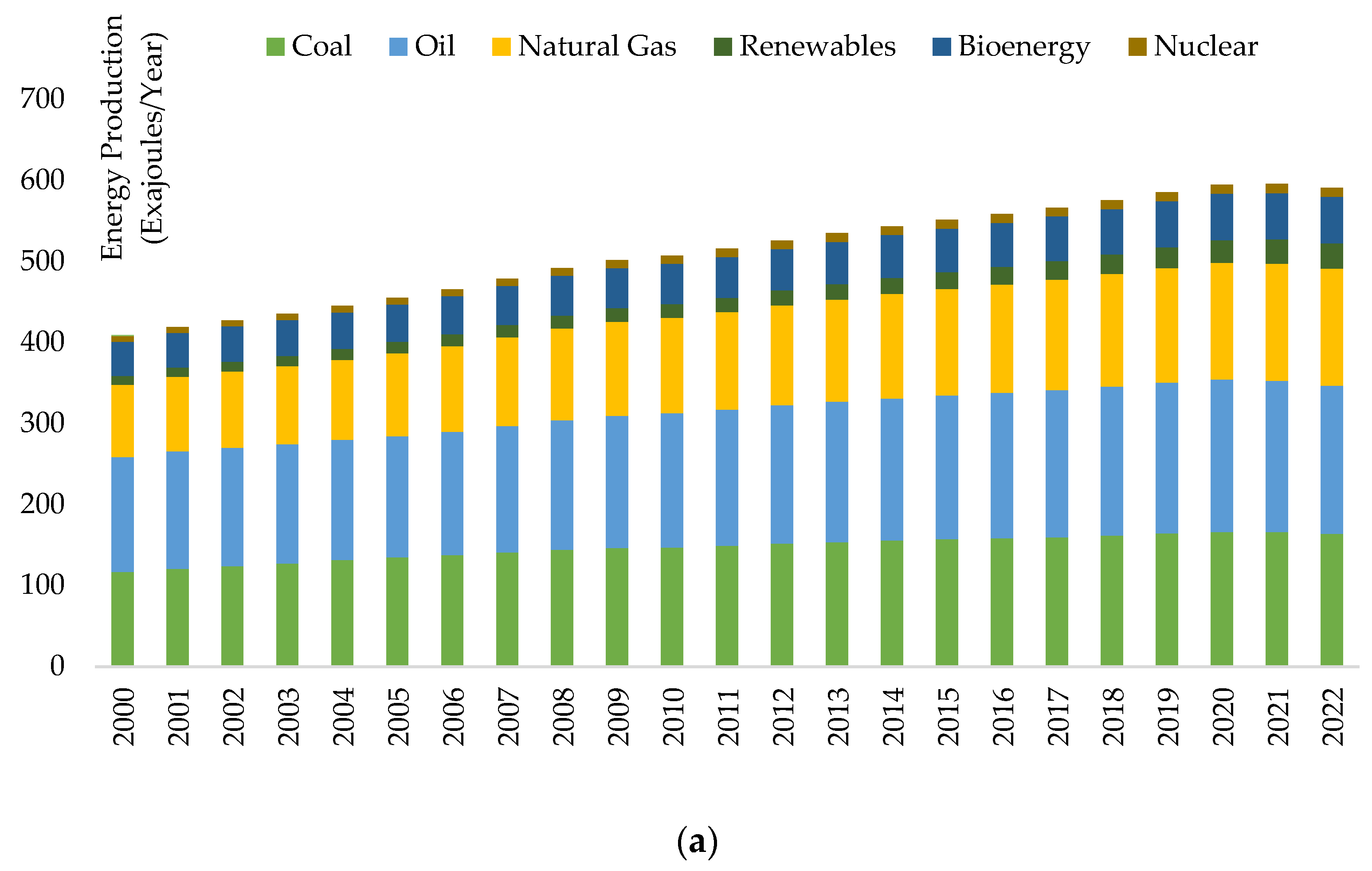
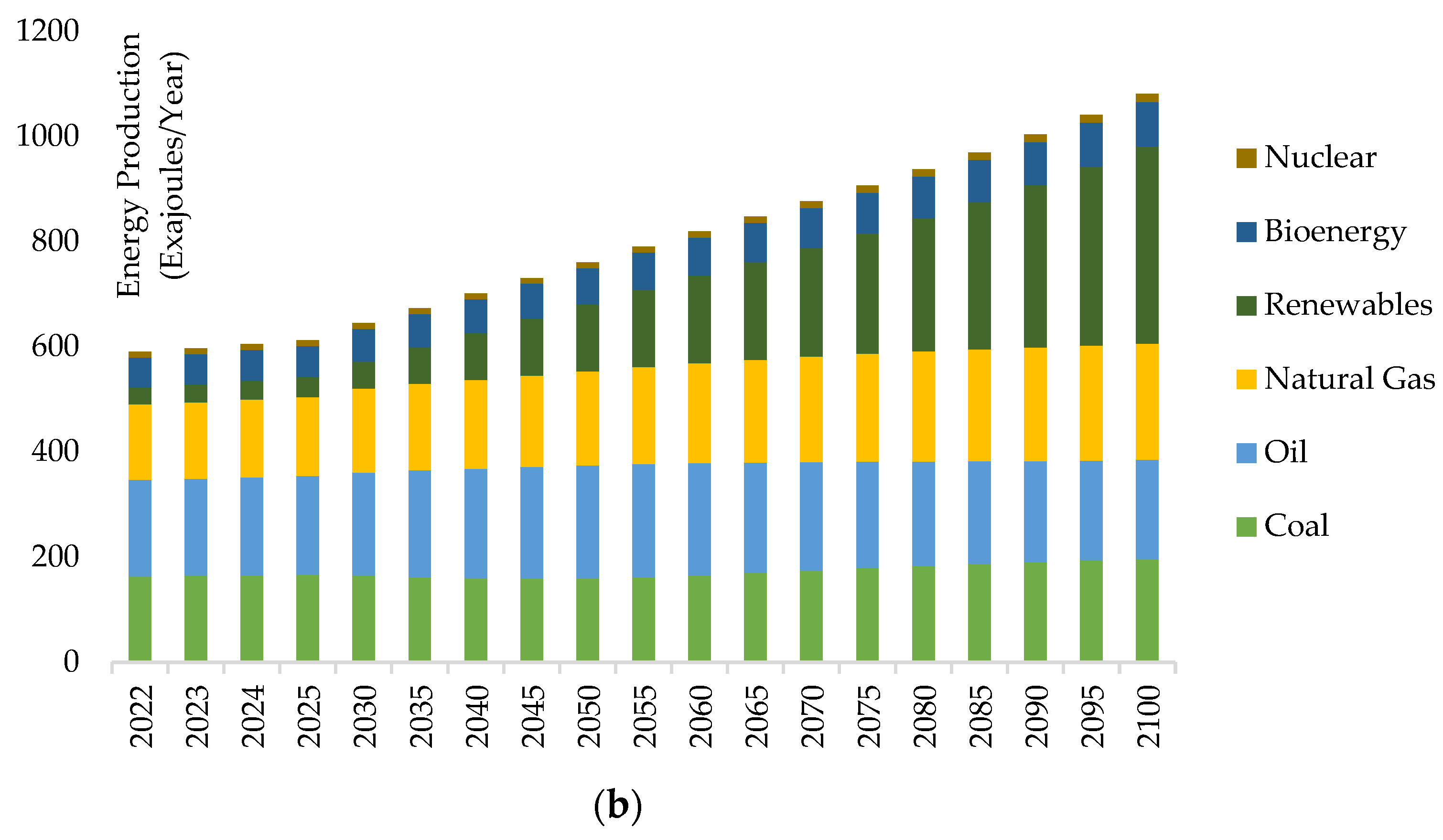
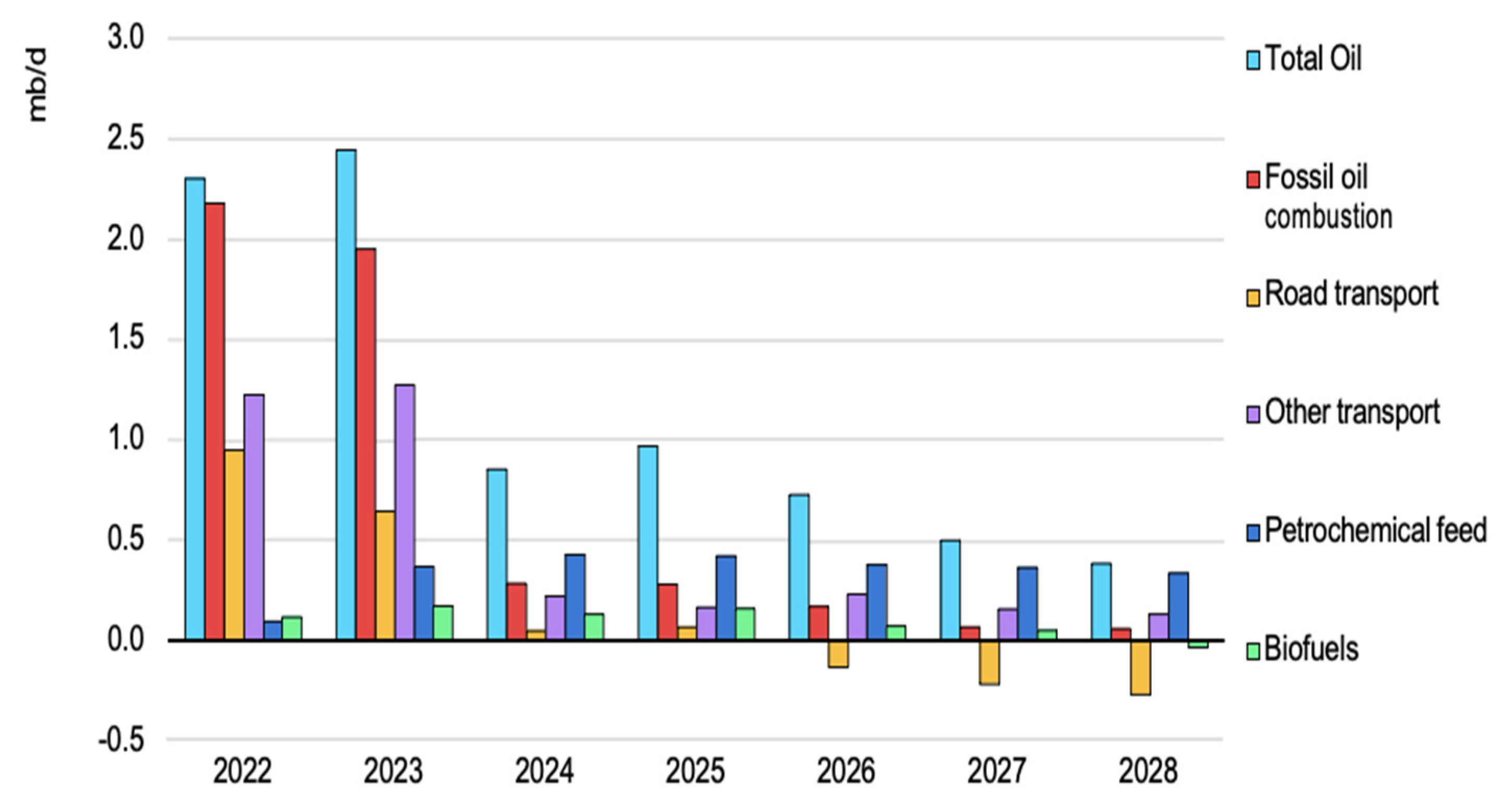
- Energy-related global CO2 emissions climbed by 0.9%, or 321 Mt, hitting a new high of more than 36.8 Gt.
- Difficulties in 2022 had an impact on the rise in emissions. Overall, 60 Mt CO2 of the 321 Mt CO2 increase is attributable to the requirement for cooling and heating during severe weather, while another 55 Mt CO2 is associated with the shutdown of nuclear power plants.
- Energy combustion emissions increased by 423 Mt, while emissions from industrial processes decreased by 102 Mt.
- The increased usage of sustainable energy technologies, including heat pumps, electric vehicles, and renewable energy sources, helped prevent an extra 550 Mt of CO2 emissions.
- Oil emissions climbed by 2.5%, or 268 Mt, compared to coal emissions, to reach 11.2 Gt.
- Despite the switch from petrol to coal in many countries, the global growth in emissions was less than expected in a year marked by energy price shocks, rising inflation, and disruptions to conventional fuel trading patterns.
- Due to supply issues made worse by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, natural gas emissions declined by 1.6%, or 118 Mt. The highest decrease in petrol emissions (−13.5%) was seen in Europe. Significant drops (−1.8%) were also noted in the Asia-Pacific region.
- A significant growth in renewable energy sources significantly decreased the revival in coal power emissions. Last year, renewable energy sources generated 90% of the additional electricity used worldwide. A new annual record was set by an increase in wind and solar PV generation of almost 275 TWh each.
- Except for China, emissions from emerging markets and developing economies in Asia increased by 4.2% or 206 Mt CO2 in 2022, outpacing emissions from all other regions. The region’s emissions increased by more than half because of coal-fired power generation.
- The combined production of wind and solar PV electricity surpassed gas or nuclear power for the first time.
6. SED Progress
6.1. Emerging Issues and Directions in SED
6.1.1. Energy War
6.1.2. Energy Storage
6.1.3. Decarbonization Strategies for SED in Power and Other Sectors
7. Discussion
7.1. Sustainable Energy Development Tracking and Assessment
7.2. Energy, Climate Change, and Sustainable Development
7.3. Energy Security in the Context of Sustainable Development
7.4. Energy Innovation, Financing, and Sustainable Development
8. Conclusions and Prospects for Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, R.; Yuqi, Z.; Richard, G.N.; Brian, C.P.; Aaron, B. Global Energy Outlook 2023: Sowing the Seeds of an Energy Transition; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- IEA. Oil 2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/oil-2023 (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- World Commission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future: Towards Sustainable Development; World Commission on Environment and Development: Oslo, Norway, 1987. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5987our-common-future.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Climate Interactive. Available online: https://www.climateinteractive.org (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- IEA. World Energy Outlook 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2022 (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- EI. Statistical Review of World Energy 2022. 2023. Available online: https://www.energyinst.org/statistical-review (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Goldemberg, J.; United Nations Development Programme, United Nations; Department of Economic and Social Affairs; World Energy Council. World Energy Assessment: Energy and the Challenge of Sustainability; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Gunnarsdottir, I.; Davidsdottir, B.; Worrell, E.; Sigurgeirsdottir, S. Sustainable energy development: History of the concept and emerging themes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110770. [CrossRef]
- Akpan, J.; Olanrewaju, O. Towards a Common Methodology and Modelling Tool for 100% Renewable Energy Analysis: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 6598. [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Environmental Law Guidelines and Principles 1-Stockholm Declaration; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 1972. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/29567/ELGP1StockD.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- IEA. Global Energy and Climate Model-Techno-Economic Inputs. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-and-climate-model (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- IEA. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Energy Highlights; IEA: Paris, France, 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-product/greenhouse-gas-emissions-from-energy-highlights (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Available online: https://www.iea.org/ (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- IPCC. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/reports/ (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Background of the UNFCCC. Available online: https://unfccc.int/files/essential_background/background_publications_htmlpdf/application/pdf/conveng.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- UNFCCC. Conference of the Parties (COP). Available online: https://unfccc.int/process/bodies/supreme-bodies/conference-of-the-parties-cop (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- UN. UN General Assembly; UN: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1997. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/conferences/environment/newyork1997 (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- UN. Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change United Nations; UN: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1998. Available online: https://unfccc.int/kyoto_protocol (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- United Nations. A/RES/55/2: United Nations Millennium Declaration; UN: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/generalassembly/docs/globalcompact/A_RES_55_2.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Guidelines for Major Groups on CSD 9. 2000. Available online: http://www.un.org/esa/sustdev/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- United Nations. Report of the World Summit on Sustainable Development: Johannesburg; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. https://documents-dds-ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N02/636/93/PDF/N0263693.pdf?OpenElement (accessed on 25 June 2023 ).
- IAEA; UNDESA; IEA; Eurostat; EEA. United Nations Environment Programme. 2005. Available online: http://www.iaea.org/Publications/index.html (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Available online: https://www.irena.org/ (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- The Secretary-General’s Advisory Group on Energy and Climate Change (AGECC). Energy for a Sustainable Future (Reports and Recommendations); AGECC: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- Sustainable Energy for All (SE4All). Available online: https://www.seforall.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (A/RES/70/1); UN: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Moreno, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C. SDG Index and Dashboards Detailed Methodological Paper. 2018. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiOvMSihuuBAxXSQ94KHVXZChkQFnoECBMQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fraw.githubusercontent.com%2Fsdsna%2F2018GlobalIndex%2Fmaster%2F2018GlobalIndexMethodology.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0-qrSw18nJJVyQhkpFzAZf&opi=89978449 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Ritchie, R.; Mispy, O.-O. SDG Tracker-Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sdg-tracker.org/energy (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- UNFCCC. Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). Available online: https://unfccc.int/NDCREG (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- UNFCCC. The Paris Agreement. 2016. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/parisagreement_publication.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- UNFCCC. Global Stocktake. Available online: https://unfccc.int/topics/global-stocktake (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Guzović, Z.; Duic, N.; Piacentino, A.; Markovska, N.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Lund, H. Recent advances in methods, policies and technologies at sustainable energy systems development. Energy 2022, 245, 123276. [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Sustainable Energy Transition for Renewable and Low Carbon Grid Electricity Generation and Supply. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 743114. [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Nuclear Power and Sustainable Development; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2016. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/11084/nuclear-power-and-sustainable-development (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Łukasiewicz, K.; Pietrzak, P.; Kraciuk, J.; Kacperska, E.; Cieciora, M. Sustainable Energy Development—A Systematic Literature Review. Energies 2022, 15, 8284. [CrossRef]
- Morea, D.; El Mehtedi, M.; Buonadonna, P. Energy Context: Analysis of Selected Studies and Future Research Developments. Energies 2023, 16, 1423. [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shao, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q. Energy and sustainable development nexus: A review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2023, 47, 101078. [CrossRef]
- Energy Policy Tracker. Track Public Money for Energy in Recovery Packages. IISD, IGES, OCI, ODI, SEI and Columbia University. 2023. Available online: https://www.energypolicytracker.org (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2020/Jun/Renewable-Power-Costs-in-2019 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- IEA. World Energy Investment 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2023 (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- International Renewable Energy Agency. World Energy Transitions Outlook 2023: 1.5 °C Pathway; Preview. 2023. Available online: https://www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Jun/World-Energy-Transitions-Outlook-2023 (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers in Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Government of China. China Nationally Determined Contribution (Reducing Greenhouse Gases in China: A 2030 Emissions Target). 2022. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/China%E2%80%99s%20Achievements%2C%20New%20Goals%20and%20New%20Measures%20for%20Nationally%20Determined%20Contributions.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Government of USA. The USA Nationally Determined Contribution (Reducing Greenhouse Gases in the United States: A 2030 Emissions Target). 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/United%20States%20NDC%20April%2021%202021%20Final.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Government of India. India’s Updated First Nationally Determined Contribution Under Paris Agreement (2021–2030). 2022. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-08/India%20Updated%20First%20Nationally%20Determined%20Contrib.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Germany (on behalf of Europe). Europe Nationally Determined Contribution (Reducing Greenhouse Gases in the Europe: A 2030 Emissions Target). 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/EU_NDC_Submission_December%202020.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Government of Canada. Canada Nationally Determined Contribution under the Paris Agreement. 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/Canada%27s%20Enhanced%20NDC%20Submission1_FINAL%20EN.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Government of the Republic of South Africa. South Africa’s Just Energy Transition Investment Plan (JET IP). 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/27s-just-energy-transition-investment-plan-jet-ip-2023-2027 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Government of Egypt. Egypts Updated First Nationally Determined Contribution 2030 (Second Update). 2023. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2023-06/Egypts%20Updated%20First%20Nationally%20Determined%20Contribution%202030%20%28Second%20Update%29.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Federal Government of Nigeria. Nigeria’s Energy Transition Plan. Available online: https://energytransition.gov.ng (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Government of Morocco. Morocco Contributions Determined at the National Level—Updated. 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/Moroccan%20updated%20NDC%202021%20_Fr.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A. Providing all global energy with wind, water, and solar power, Part I: Technologies, energy resources, quantities and areas of infrastructure, and materials. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 154–1169. [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A.; Cameron, M.A.; Mathiesen, B.V. Matching demand with supply at low cost in 139 countries among 20 world regions with 100% intermittent wind, water, and sunlight (WWS) for all purposes. Renew Energy 2018, 123, 236–248. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Breyer, C.; Lund, H. Status and perspectives on 100% renewable energy systems. Energy 2019, 175, 471–480. [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. ; Rosado P. Our World in Data; 2023. Renewable Energy. Available online: https https://ourworldindata.org/renewable-energy (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/co2-emissions-in-2022 (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- World Bank. World Development Indicators. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/ (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Aniebo, I.N.; Akpan, J.S. Energy Transition: Implications, Considerations, and Roadmap Development for Sub-Saharan Africa. In Proceedings of the SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria, 1–3 August 2022; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Green Hydrogen in China: A Roadmap for Progress. 2023. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/whitepapers/green-hydrogen-in-china-a-roadmap-for-progress (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, D. The future of hydrogen energy: Bio-hydrogen production technology. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 33677–33698. [CrossRef]
- Valente, A.; Iribarren, D.; Dufour, J. Life cycle assessment of hydrogen energy systems: A review of methodological choices. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 346–363. [CrossRef]
- Afgan, N.H.; Carvalho, M.G. Sustainability assessment of hydrogen energy systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 1327–1342. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xiang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xue, P.; Sun, W.; Cai, H.; Gu, C.; Liu, J. Resilience Assessment of Hydrogen-Integrated Energy System for Airport Electrification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 2812–2824. [CrossRef]
- Afgan, N.H.; Veziroglu, A.; Carvalho, M.G. Multi-criteria evaluation of hydrogen system options. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3183–3193. [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Electricity Storage Valuation Framework: Assessing System Value and Ensuring Project Viability. 2020. Available online:https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2020/Mar/IRENA_Storage_valuation_2020.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Saha, P.; Akash, F.A.; Shovon, S.M.; Monir, M.U.; Ahmed, M.T.; Khan, M.F.H.; Sarkar, S.M.; Islam, M.K.; Hasan, M.M.; Vo, D.V.N.; et al. Grey, blue, and green hydrogen: A comprehensive review of production methods and prospects for zero-emission energy. Int. J. Green Energy 2023, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Calise, F. Recent Advances in Green Hydrogen Technology. Energies 2022, 15, 5828. [CrossRef]
- Varvoutis, G.; Lampropoulos, A.; Mandela, E.; Konsolakis, M.; Marnellos, G.E. Recent Advances on CO2 Mitigation Technologies: On the Role of Hydrogenation Route via Green H2. Energies 2022, 15, 4790. [CrossRef]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Adan, A.B.; Dabar, O.A.; Jalludin, M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Guirreh, I.A. Economic feasibility of green hydrogen production by water electrolysis using wind and geothermal energy resources in asal-ghoubbet rift (Republic of Djibouti): A comparative evaluation. Energies 2021, 15, 138. [CrossRef]
- Al-Badi, A.; Al Wahaibi, A.; Ahshan, R.; Malik, A. Techno-Economic Feasibility of a Solar-Wind-Fuel Cell Energy System in Duqm, Oman. Energies 2022, 15, 5379. [CrossRef]
- Bahlawan, H.; Losi, E.; Manservigi, L.; Morini, M.; Spina, P.R.; Venturini, M. Analysis of a Multi-Generation Renewable Energy System With Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbine. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2022, 144, 111020. [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; von Krauland, A.-K.; Song, K.; Krull, A.N. Impacts of green hydrogen for steel, ammonia, and long-distance transport on the cost of meeting electricity, heat, cold, and hydrogen demand in 145 countries running on 100% wind-water-solar. Smart Energy 2023, 11, 100106. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghussain, L.; Ahmad, A.D.; Abubaker, A.M.; Hassan, M.A. Exploring the feasibility of green hydrogen production using excess energy from a country-scale 100% solar-wind renewable energy system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 21613–21633. [CrossRef]
- Akpasi, S.O.; Isa, Y.M. Review of Carbon Capture and Methane Production from Carbon Dioxide. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1958. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Abdulateef, A.M.; Hafedh, S.A.; Al-Samari, A.; Abdulateef, J.; Sameen, A.Z.; Salman, H.M.; Al-Jiboory, A.K.; Wieteska, S.; Jaszczur, M. Renewable energy-to-green hydrogen: A review of main resources routes, processes and evaluation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17383–17408. [CrossRef]
- Babin, A.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Iliuta, M.C. Potential and challenges of bioenergy with carbon capture and storage as a carbon-negative energy source: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 146, 105968. [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.R.; Rezk, H.; Abd-Elbary, H.; Ziedan, H.A.; Elnozahy, A. Experimental investigation to improve the energy effciency of solar PV panels using hydrophobic SiO2 nanomaterial. Coatings 2020, 10, 503. [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.; Godina, R.; Azevedo, S.G.; Matias, J.C.O. A comprehensive review of industrial symbiosis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119113. [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, M.; Pilorgé, H.; Davids, J.; Psarras, P. Opportunities for cement decarbonization. lean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 15, 100667. [CrossRef]
- Lejda, K.; Jaworski, A.; Savostin-Kosiak, D.; Mądziel, M.; Balawender, K.; Ustrzycki, A. Assessment of petrol and natural gas vehicle carbon oxides emissions in the laboratory and on-road tests. Energies 2021, 14, 1631. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Acquah, M.A. (Eds.) Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V) and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technologies. 2021. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/books/book/3495 (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Akpan, J.; Effiong, E.; Akanni, O.; Okorie, V. Experimental Testing and Numerical Modelling Validation for Ranque-Hilsch Vortex Cooling Tube Design. In Proceedings of the 5th European International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Rome, Italy, 26–28 July 2022; IEOM Society: Rome, Italy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yebiyo, M.; Chaer, I. A review of recent advances in emerging alternative heating and cooling technologies. Energies 2021, 14, 502. [CrossRef]
- Cherp, A.; Jewell, J. The concept of energy security: Beyond the four as. Energy Policy 2014, 75, 415–421. [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Muhd, M.Z. A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [CrossRef]
- Abdmouleh, Z.; Alammari, R.A.M.; Gastli, A. Recommendations on renewable energy policies for the GCC countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1181–1191. [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, G.; Tekbiyik-Ersoy, N. Development of renewable energy in china, usa, and brazil: A comparative study on renewable energy policies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9136. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.S.; Usman, M.; Hussain, S.; Jahanger, A.; Abrar, M. Determinants of renewable energy sources in Pakistan: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29183–29201 . [CrossRef]
- Mekhilef, S.; Barimani, M.; Safari, A.; Salam, Z. Malaysia’s renewable energy policies and programs with green aspects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 497–504. [CrossRef]
- Siksnelyte-Butkiene, I.; Karpavicius, T.; Streimikiene, D.; Balezentis, T. The Achievements of Climate Change and Energy Policy in the European Union. Energies 2022, 15, 5128. [CrossRef]
- Güney, T. Renewable energy, non-renewable energy and sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2019, 26, 389–397. [CrossRef]
- UN. Agenda 21-United Nations Conference on Environment and Development; UN: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1992. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/conferences/environment/rio1992 (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Horschig, T.; Thrän, D. Are decisions well supported for the energy transition? A review on modeling approaches for renewable energy policy evaluation. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2017, 7, 5. [CrossRef]
- Spyridaki, N.-A.; Flamos, A. A paper trail of evaluation approaches to energy and climate policy interactions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 1090–1107. [CrossRef]
- Waage, J.; Yap, C.; Bell, S.; Levy, C.; Mace, G.; Pegram, T.; Unterhalter, E.; Dasandi, N.; Hudson, D.; Kock, R.; et al. Governing the UN sustainable development goals: Interactions, infrastructures, and institutions. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e251–e252. [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD-Measuring-Distance-to-SDG-Targets (An Assessment of where OECD Countries Stand); OECD: Paris, France, 2017. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/wise/measuring-distance-to-the-sdg-targets-2019-a8caf3fa-en.htm. (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Kumba, H.; Akpan, J.; Twite, B.; Olanrewaju, O. Renewable energy adoption and integration in South Africa: An overview. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Clean and Green Energy (ICCGE 2023), Xiamen,China, 25-27 May 2023; Institution of Engineering and Technology: Stevenage, UK, 2023; pp. 74–87. [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Renewable energy and climate change. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 158, 112111. [CrossRef]
- Radpour, S.; Gemechu, E.; Ahiduzzaman; Kumar, A. Developing a framework to assess the long-term adoption of renewable energy technologies in the electric power sector: The effects of carbon price and economic incentives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111663. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.D.; Verma, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Gupta, M.; Chopra, R. Transitioning green finance from theory to practice for renewable energy development. Renew. Energy 2022, 195, 554–565. [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.-C.; McCarl, B. Sustainable energy development under climate change. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3269. [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Moubarak, M. Renewable energy consumption—Economic growth nexus for China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 111–117. [CrossRef]
- Karanfil, F.; Li, Y. Electricity consumption and economic growth: Exploring panel-specific differences. Energy Policy 2015, 82, 264–277. [CrossRef]
- Török, L. Effects of Energy Economic Variables on the Economic Growth of the European Union (2010–2019). Energies 2023, 16, 6094. [CrossRef]
- Pao, H.-T.; Fu, H.-C. Renewable energy, non-renewable energy and economic growth in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 381–392. [CrossRef]
- Koçak, E.; Şarkgüneşi, A. The renewable energy and economic growth nexus in Black Sea and Balkan countries. Energy Policy 2016, 100, 51–57. [CrossRef]
- Ito, K. CO2 emissions, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, and economic growth: Evidence from panel data for developing countries. Int. Econ. 2017, 151, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A. Renewable energy consumption and economic growth in newly industrialized countries: Evidence from asymmetric causality test. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 478–484. [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Aslan, A. Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth in emerging economies: Evidence from bootstrap panel causality. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 757–763. [CrossRef]
- Elum, Z.; Momodu, A. Climate change mitigation and renewable energy for sustainable development in Nigeria: A discourse approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 72–80. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Khan, S.; Ozturk, I.; Murshed, M. The role of renewable energy investment in tackling climate change concerns: Environmental policies for achieving SDG-13. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 1888–1901. [CrossRef]
- Halsnæs, K.; Shukla, P.R.; Garg, A. Sustainable development and climate change: Lessons from country studies. Clim. Policy 2008, 8, 202–219. [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, D. Sustainable energy development and climate change in China. Clim. Policy 2005, 5, 185–198. [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, S.S.; Quitzow, R.; Steckel, J.C. Tackling energy, climate and development challenges in Africa. Economics 2018, 12, 20180061. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.; Kuramochi, T.; Höhne, N. The G20 emission projections to 2030 improved since the Paris Agreement, but only slightly. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2022, 27, 39. [CrossRef]
- Tosam, M.J.; Mbih, R.A. Climate change, health, and sustainable development in Africa. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2014, 17, 787–800. [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Baležentis, T.; Kriščiukaitienė, I. Promoting interactions between local climate change mitigation, sustainable energy development, and rural development policies in Lithuania. Energy Policy 2012, 50, 699–710. [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Solangi, Y.A. Fostering a Sustainable Energy Future to Combat Climate Change: EESG Impacts of Green Economy Transitions. Processes 2023, 11, 1548. [CrossRef]
- al Irsyad, M.I.; Halog, A.; Nepal, R. Renewable energy projections for climate change mitigation: An analysis of uncertainty and errors. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 536–546. [CrossRef]
- Beg, N.; Morlot, J.C.; Davidson, O.; Afrane-Okesse, Y.; Tyani, L.; Denton, F.; Sokona, Y.; Thomas, J.P.; La Rovere, E.L.; Parikh, J.K.; et al. Linkages between Climate Change and Sustainable Development. Climate Policy, 2002, 2, 129–144. [CrossRef]
- Weldu, Y.W.; Assefa, G. The search for most cost-effective way of achieving environmental sustainability status in electricity generation: Environmental life cycle cost analysis of energy scenarios. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2296–2304. [CrossRef]
- Biel, K.; Glock, C.H. Systematic literature review of decision support models for energy-efficient production planning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 243–259. [CrossRef]
- Fleiter, T.; Worrell, E.; Eichhammer, W. Barriers to energy efficiency in industrial bottom-up energy demand models—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3099–3111. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I., Han, L., BiBi, R.; Khan, H. The role of technological innovations and renewable energy consumption in reducing environmental degradation: Evidence from the belt and road initiative countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73085–73099. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, R.; Guo, J. Climate change and sustainable development for cities. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1995–2001. [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, K.; Sano, F.; Hayashi, A.; Homma, T.; Oda, J.; Wada, K.; Nagashima, M.; Tokushige, K.; Tomoda, T. Consistent assessments of pathways toward sustainable development and climate stabilization. Nat. Resour. Forum 2012, 36, 231–244. [CrossRef]
- Meyar-Naimi, H.; Vaez-Zadeh, S. Sustainable development based energy policy making frameworks, a critical review. Energy Policy 2012, 43, 351–361. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Saboohi, Y.; Vakili, A. Frameworks, quantitative indicators, characters, and modeling approaches to analysis of energy system resilience: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110988. [CrossRef]
- Knox, S.; Hannon, M.; Stewart, F.; Ford, R. The (in)justices of smart local energy systems: A systematic review, integrated framework, and future research agenda. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 83, 102333. [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, R.C.; Fragkos, P.; Dobbins, A.H.; Schmid, D.; Pye, S.; Fahl, U. Beyond the Energy System: Modeling Frameworks Depicting Distributional Impacts for Interdisciplinary Policy Analysis. Energy Technol. 2020, 9, 2000668. [CrossRef]
- Candas, S.; Muschner, C.; Buchholz, S.; Bramstoft, R.; van Ouwerkerk, J.; Hainsch, K.; Löffler, K.; Günther, S.; Berendes, S.; Nguyen, S.; et al. Code exposed: Review of five open-source frameworks for modeling renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112272. [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Šivickas, G. The EU sustainable energy policy indicators framework. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1227–1240. [CrossRef]
- Luty, L.; Zioło, M.; Knapik, W.; Bąk, I.; Kukuła, K. Energy Security in Light of Sustainable Development Goals. Energies 2023, 16, 1390. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, W.; Xiao, H.; Ren, J. Measuring and improving regional energy security: A methodological framework based on both quantitative and qualitative analysis. Energy 2021, 227, 120534. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, K. A framework for evaluating global national energy security. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 19–31. [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Sovacool, B.K. Quantifying, measuring, and strategizing energy security: Determining the most meaningful dimensions and metrics. Energy 2014, 76, 838–849. [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.-S.; Kim, S.-S.; Moon, K.-H.; Lim, C.-Y.; Yun, S.-W. A conceptual framework for energy security evaluation of power sources in South Korea. Energy 2017, 137, 1066–1074. [CrossRef]
- Martchamadol, J.; Kumar, S. The Aggregated Energy Security Performance Indicator (AESPI) at national and provincial level. Appl. Energy 2014, 127, 219–238. [CrossRef]
- Sharifuddin, S. Methodology for quantitatively assessing the energy security of Malaysia and other southeast Asian countries. Energy Policy 2014, 65, 574–582. [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.; Choong, W.L.; Ng, T.S. A framework for evaluating Singapore’s energy security. Appl. Energy 2015, 148, 314–325. [CrossRef]
- Böhringer, C.; Bortolamedi, M. Sense and no(n)-sense of energy security indicators. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 359–371. [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Saunders, H. Competing policy packages and the complexity of energy security. Energy 2014, 67, 641–651. [CrossRef]
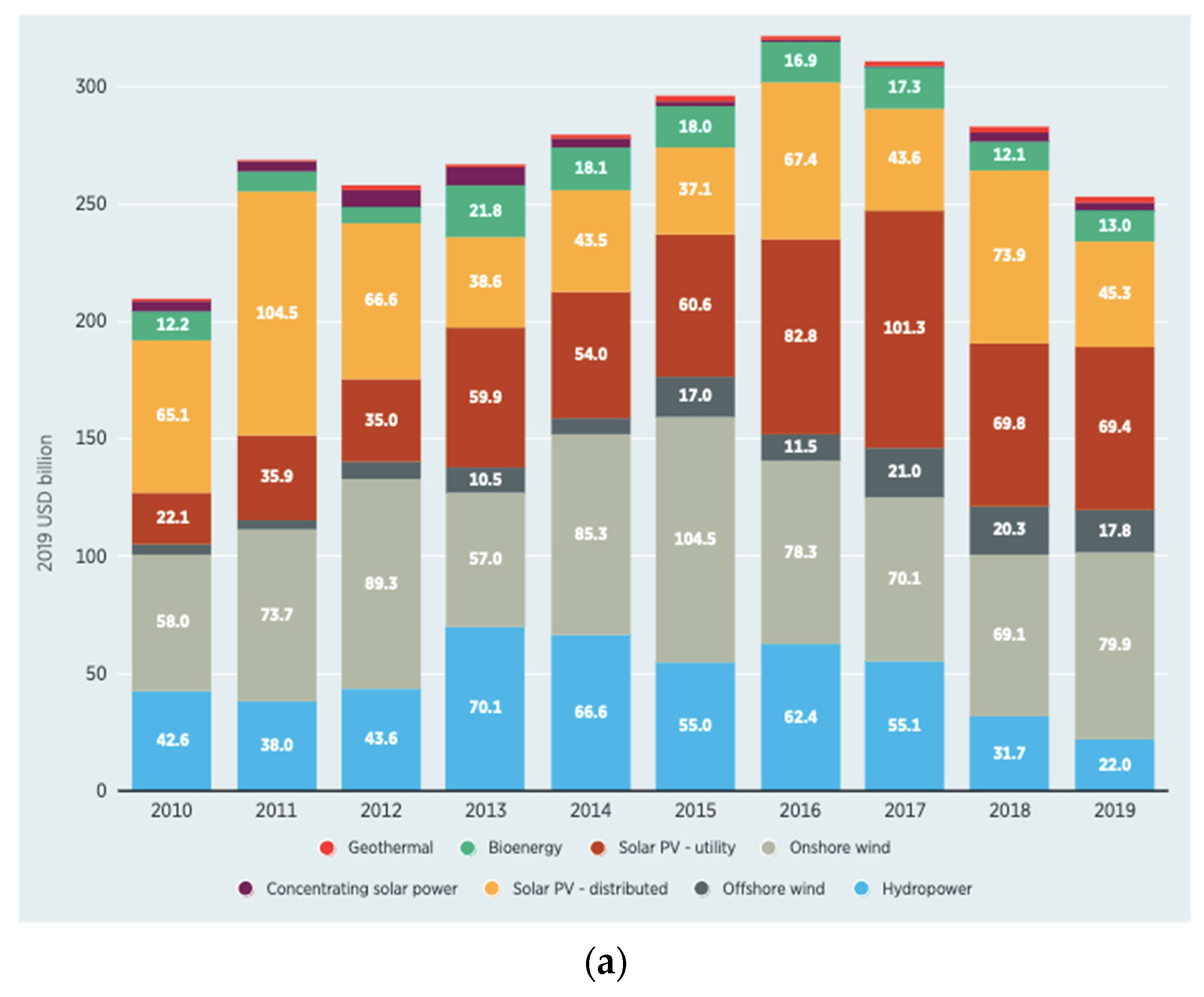
- Barykin, S.E.; Sergeev, S.M.; Mottaeva, A.B.; Plaza, E.D.L.P.; Baydukova, N.V.; Gubenko, A.V. Evaluating energy financing considerations and sustainable energy innovation with the role of financial development and energy development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 6849–6863. [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhu, M.N.; Yu, H. Is green finance really a blessing for green technology and carbon efficiency? Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106272. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Saydaliev, H.B.; Ma, X. Does green finance investment and technological innovation improve renewable energy efficiency and sustainable development goals. Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 991–1000. [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2022; IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2023. Available online: https://www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Aug/Renewable-power-generation-costs-in-2022 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Sharif, A.; Mehmood, U.; Tiwari, S. A step towards sustainable development: Role of green energy and environmental innovation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Li, X.; Yu, C.-H.; Zhao, J. The contribution of climate finance toward environmental sustainability: New global evidence. Energy Econ. 2022, 111, 106072. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Tang, Z.; Qiao, S. Green Finance, Innovation and the Energy-Environment-Climate Nexus. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 879681. [CrossRef]
- Elzen, M.G.J.D.; Dafnomilis, I.; Forsell, N.; Fragkos, P.; Fragkiadakis, K.; Höhne, N.; Kuramochi, T.; Nascimento, L.; Roelfsema, M.; van Soest, H.; et al. Updated nationally determined contributions collectively raise ambition levels but need strengthening further to keep Paris goals within reach. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2022, 27, 33. [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, O.; Buenestado, P.; Escribano, B.; Sureda, B.; Turon, A.; Xercavins, J. The global carbon budget and the Paris agreement. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strat. Manag. 2019, 11, 310–325. [CrossRef]
- Iacobuţă, G.I.; Brandi, C.; Dzebo, A.; Duron, S.D.E. Aligning climate and sustainable development finance through an SDG lens. The role of development assistance in implementing the Paris Agreement. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 74, 102509. [CrossRef]
- Karakosta, C.; Doukas, H.; Psarras, J. Technology transfer through climate change: Setting a sustainable energy pattern. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1546–1557. [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.D.; Landry, J.-S.; Partanen, A.-I.; Allen, M.; Eby, M.; Forster, P.M.; Friedlingstein, P.; Zickfeld, K. Estimating Carbon Budgets for Ambitious Climate Targets. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2017, 3, 69–77. [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, J.; Gasser, T.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.; Tao, S.; Shen, G.; Lai, Y.; Han, L.; Li, B. Climate Warming Mitigation from Nationally Determined Contributions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1217–1228. [CrossRef]
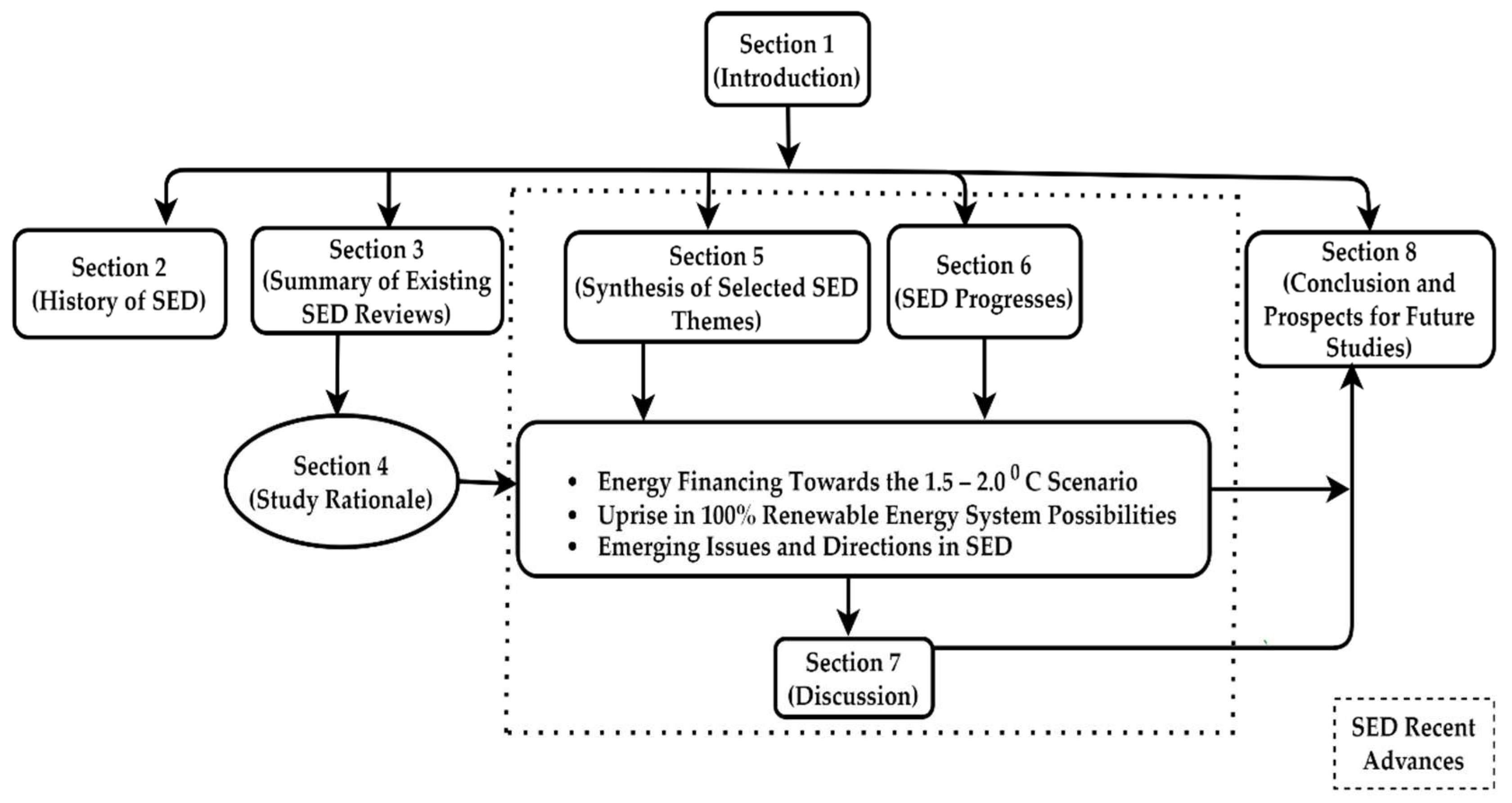
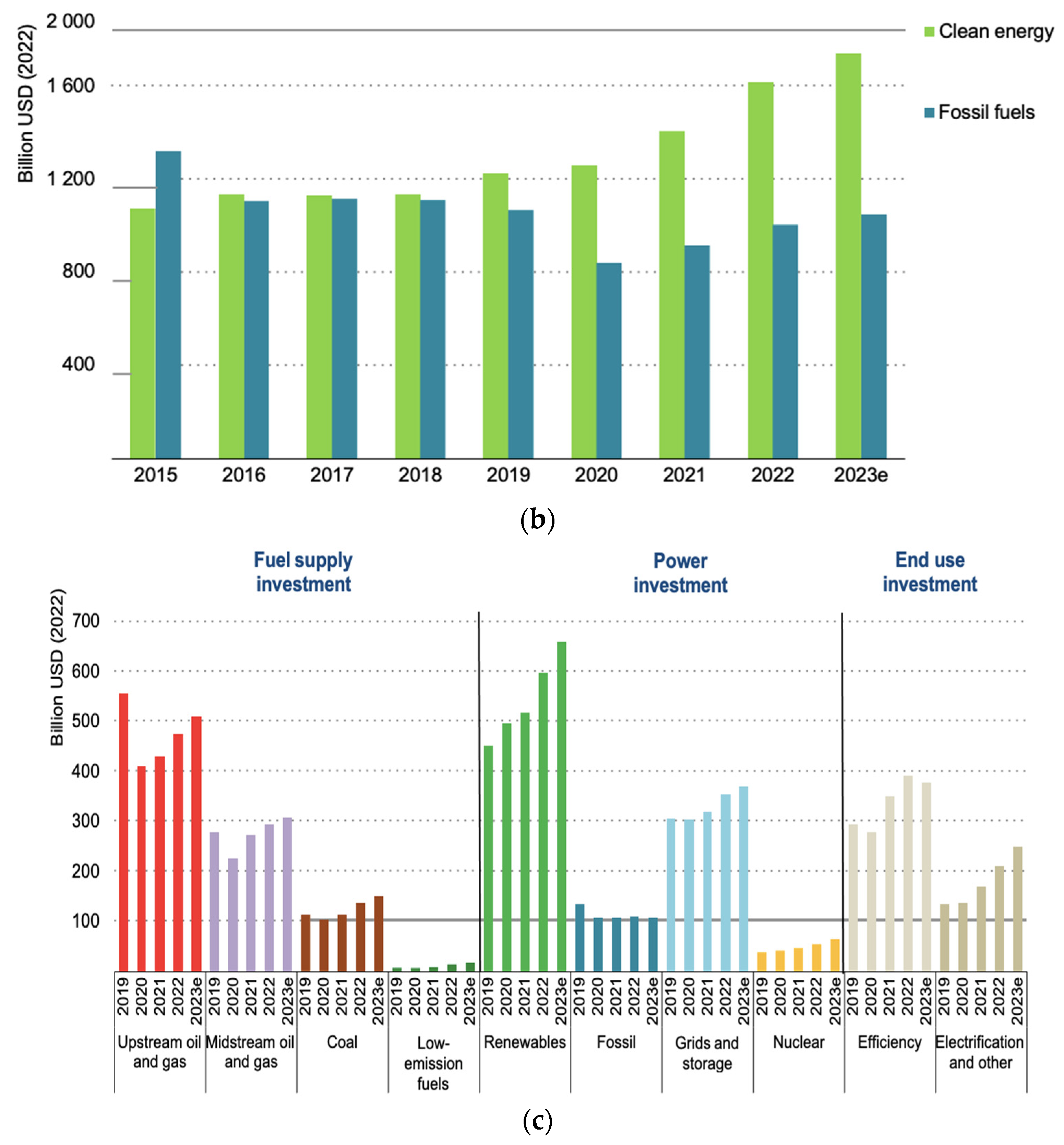
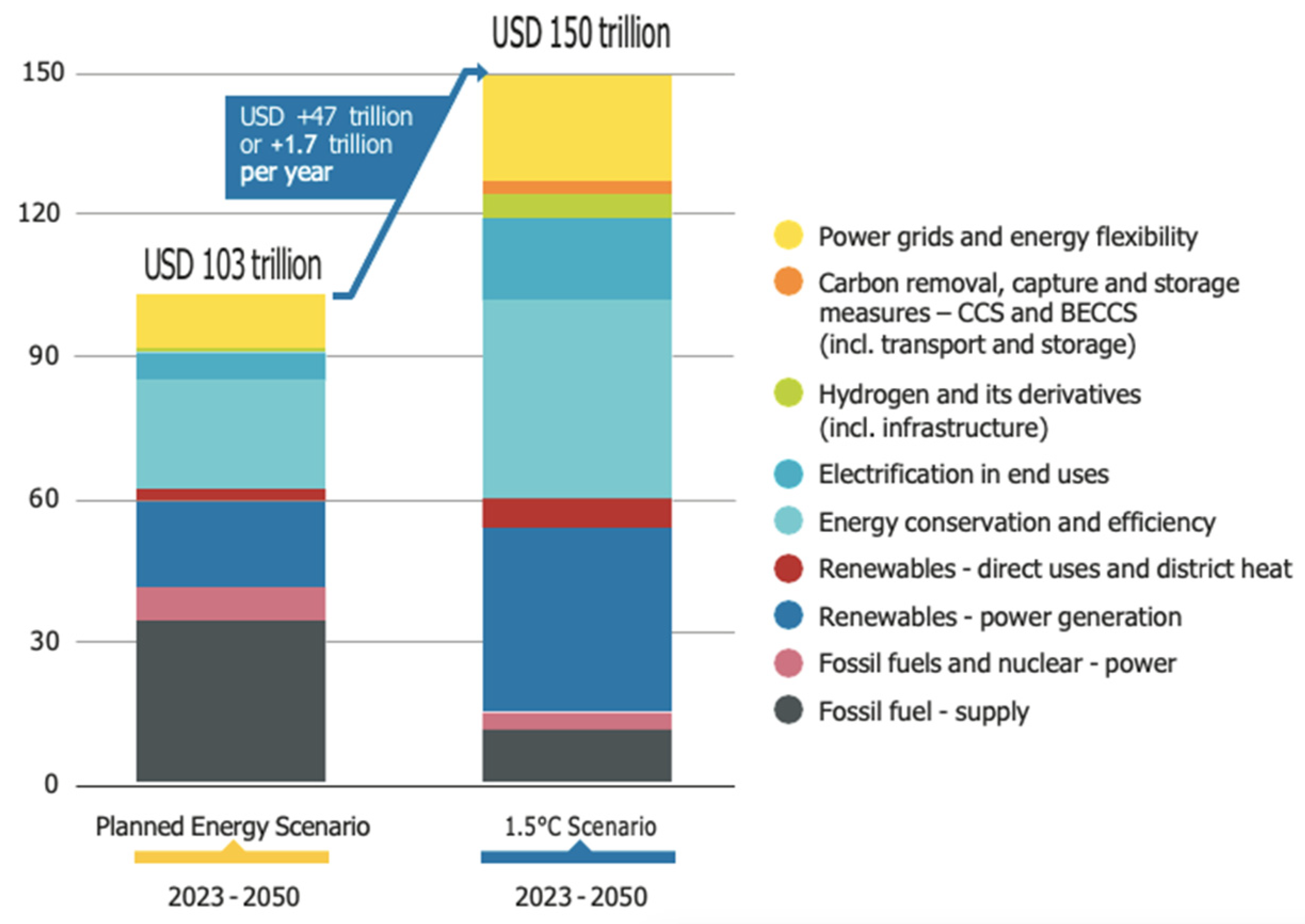
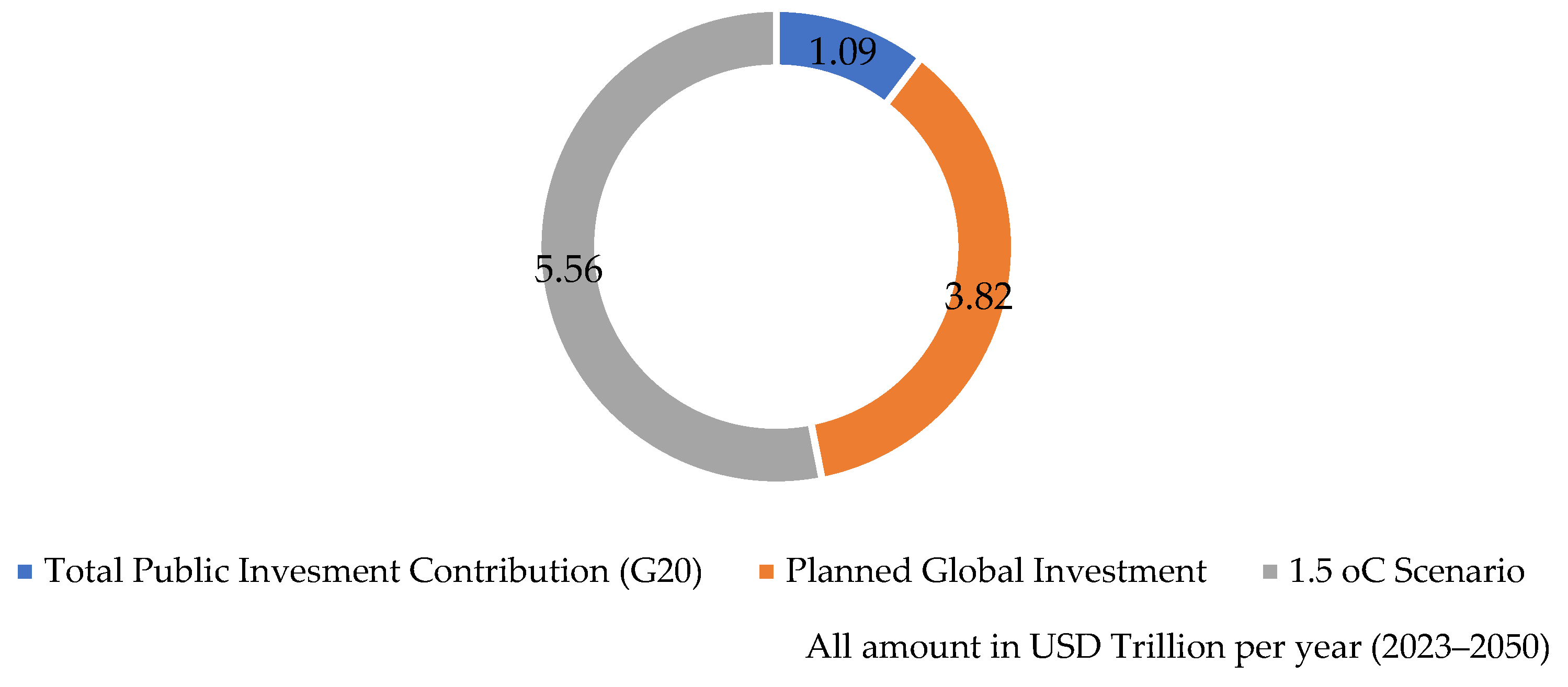
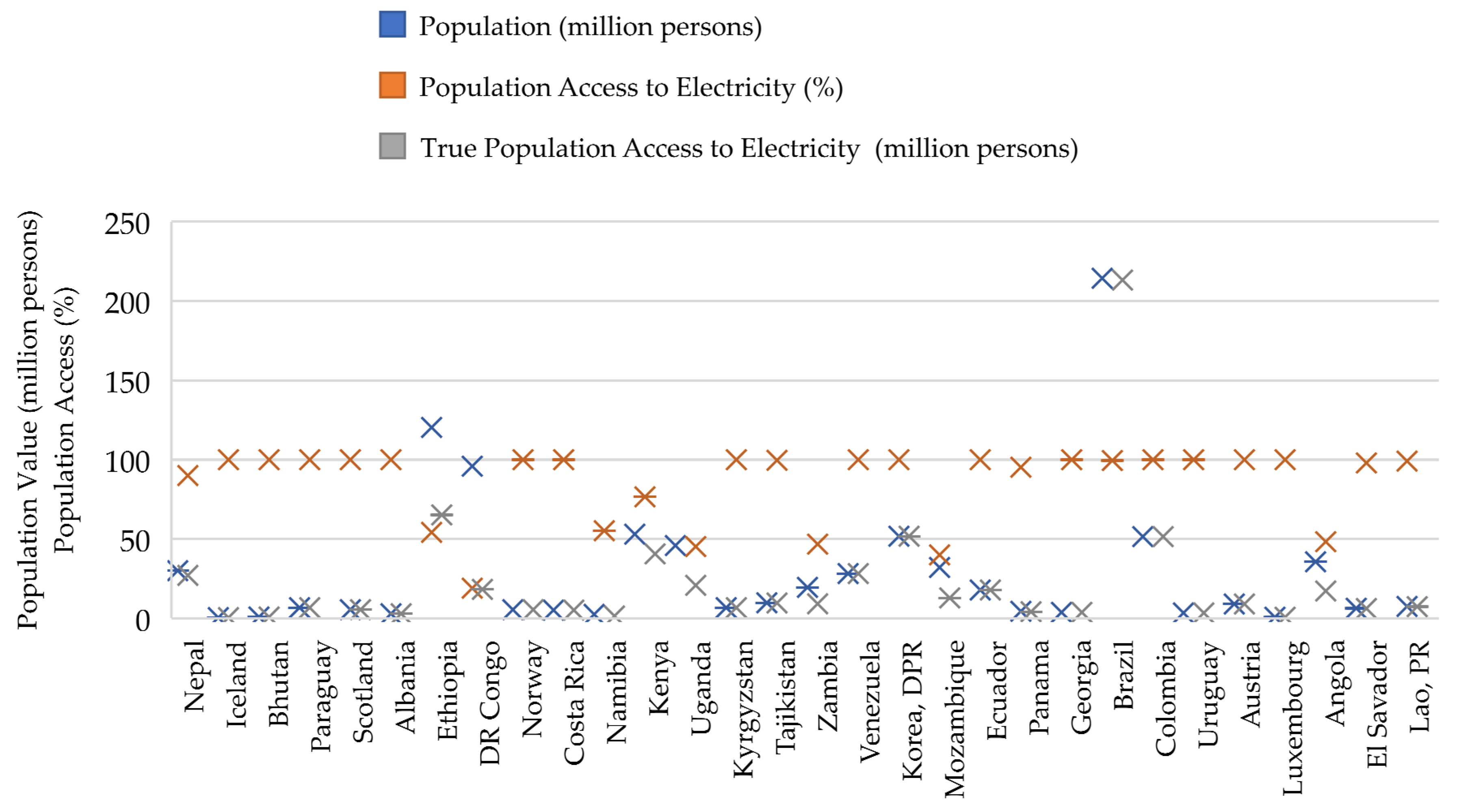

| Year | Protocol and Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 1972 | Stockholm Meeting The first international meeting devoted to global environmental issues, which led to the formation of the Brundtland Commission. |
[10] |
| 1974 | International Energy Agency (IEA) A year after the Stockholm meeting, a global oil crisis occurred in 1973. In response to the global physical disruption in oil supplies, IEA, under the framework of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), was formed to compile data on the international oil market with the aim of promoting energy efficiency and conservation and fostering international technological cooperation for research and development. Subsequently, there have been relevant energy reports and world energy outlooks from the IEA.
|
[11,12,13] |
| 1987 | Our Common Future—Brundtland Report At the Brundtland Commission meeting, sustainable development was introduced, with energy being an integral part of the concept, because of concerns about the global oil crisis. |
[3] |
| 1988 | International Climate Negotiations—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) The United Nations Environmental Protection (UNEP) Agency sought an international convention to provide direction for restricting greenhouse gas emissions while improving energy and industrial processes and driving sustainable development. Then, the IPCC was formed, which has, since its establishment, made public findings from the scientific community and summarized them in the following reports, which were more specific to energy and sustainable development. These include the following:
|
[14] |
| 1992 | UN Agenda 21 Following the Brundtland report Our Common Future, the IPCC’s formation, and the identification of the importance of energy, an action plan was developed that was discussed in more detail in the UN Kyoto Protocol of 1997. |
[7] |
| 1992 | UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) As a result of the action plan developed by the UN Agenda 21, countries made a global commitment to work together to develop solutions to limit rising global average temperatures, and the UNFCC was founded. |
[15] |
| 1995 | Conference of Parties (COP) The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the highest decision-making body for the UNFCC, which first held its meetings in Berlin every year (with this year’s known as COP28, to be held in Dubai, UAE), involving delegates from all parties’ countries, meeting to assess the convention’s effectiveness through evaluating national communications and emission inventories of countries working towards sustainable societies. |
[16] |
| 1997 | UN General Assembly The 1997 UN General Assembly emphasized sustainable energy production, distribution, and use for improved sustainable development. The UN Commission on Sustainable Development focused on atmosphere, energy, and transport in 2001. |
[17] |
| 1997 | UNDP Kyoto Protocol A protocol was developed to ensure financial assistance for clean energy projects under the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), which emphasizes that organizations must engage in sustainability practices to be able to receive funding for energy programs and projects. |
[18] |
| 2000 | UN Millennium Declaration In September of 2000, world leaders signed the United Nations Millennium Declaration, committing to work together to end extreme poverty, hunger, disease, illiteracy, environmental degradation, and gender discrimination. However, sustainable energy targets were not included in the declaration. |
[19] |
| 2000 | UNDP World Energy Assessment Report The first proposal for sustainable energy development was introduced in this assessment report. |
[7] |
| 2001 | UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD-9) The UN Commission on Sustainable Development was birthed from the UN 1997 General Assembly, which proposed CSD-9 to focus on atmosphere, energy, and transport. |
[20] |
| 2002 | UN World Summit on Sustainable Development Following the establishment of UN CSD-9, the world’s first summit on sustainable development was held in Johannesburg, where the concept of a sustainable energy development initiative was discussed and adopted, alongside another set of activities that considered respect for the environment, with ten-year regional and national sustainable production and consumption programs being proposed. |
[21] |
| 2003 | UN World Summit on Sustainable Development report A report on the UN World Summit on Sustainable Development discussion was released. |
[21] |
| 2004 | UN-Energy Following the UN World Summit on Sustainable Development, the UN Energy inter-agency mechanism was established to aid countries in transitioning to sustainable energy by accelerating roadmap implementation, especially through the activities listed in the resolution of the UN World Summit on Sustainable Development report. Consequently, this initiative called for existing and newly created energy organizations at the national, regional, and international levels to come together to work towards sustainable development. |
[21] |
| 2005 | Energy Indicators for Sustainable Development Five international agencies and organizations (United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA), International Energy Agency (IEA), International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), European Environment Agency (EEA), and Eurostat), recognized worldwide as leaders in energy and environmental statistics and analysis, presented a set of indicators for sustainable energy development. |
[22] |
| 2009 | International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) IRENA, an international organization promoting renewable energy adoption and sustainable use, was formed to ensure that both industrialized and developing countries’ needs are addressed.
|
[23] |
| 2010 | UN Millennium Development Goals follow-up resolution As a follow-up to the outcome of the Millennium summit and the declaration of 2000, energy was recognized and stressed as necessary to achieving the MDGs and sustainable development. |
[19,24] |
| 2011 | UN Sustainable Energy for All (SE4ALL) UN initiative focused on advancing sustainable energy development. Presently, the SE4ALL has become an international organization that works with the UN and leaders in government, the private sector, financial institutions, civil society, and philanthropies to accelerate Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG7)—access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all by 2030—in line with the Paris Agreement on climate change |
[25] |
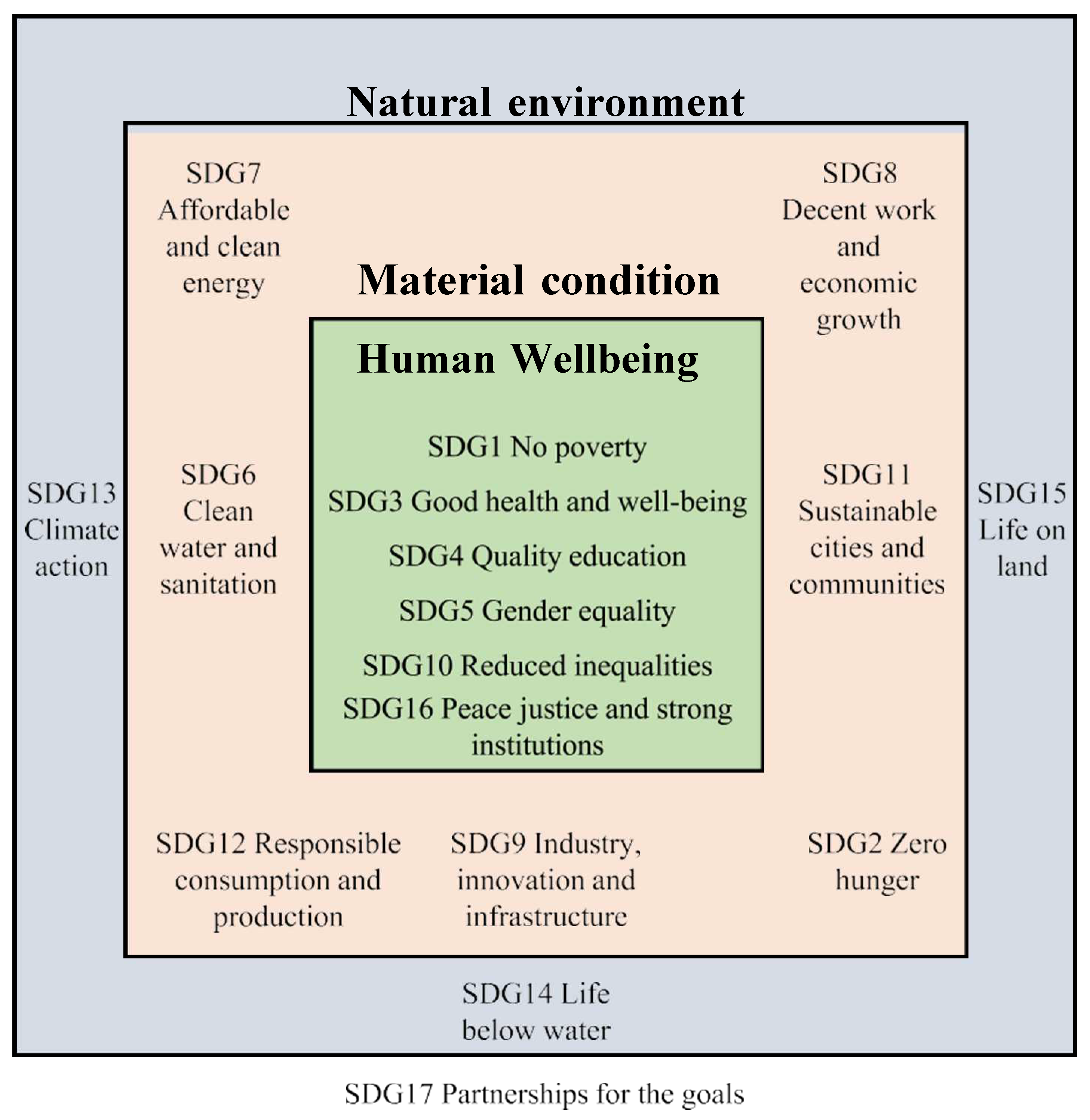
| 2015 | UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development The SDGs were first introduced, with energy and climate change established as an integral part of sustainable development, with SDG 7 for energy and SDG 13 for climate change actions. |
[26] |
| 2015–present | Development of SDG Trackers As a result of the responsibilities for stocktaking and progress measurement of implementation towards sustainable development achievements, different organizations have used the targets and indicators from the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development to build platforms to assess the progress levels of countries. 2015 and later years to present—Research on SDG indicators’ assessment and composition. 2019—SDG tracker systems and platforms. |
[27,28] |
| 2016 | National Determined Contribution (NDC) The Lima COP agreed to cut emissions using collective and collaborative efforts under the concepts of NDC referenced in Article 4(2) of the Paris Agreement. |
[29,30] |
| 2018–present | Stocktaking for National Determined Contribution (NDC) Following the Paris Agreement’s framework, mandates were created for countries to submit revised and enhanced nationally determined contributions (NDCs) in 2020 and every five years after that. In addition, beginning in 2023, signatories to the agreement are enjoined in a global stocktaking of progress towards reducing global CO2 emissions every five years. |
[31] |
| 2019–present | Emerging New Global Energy System Many discussions revolve around emerging global energy systems because of the several issues governing energy, such as the following:
|
Authors’ elaboration |
| 2023 | IEA World Energy Investment Alongside the issues mentioned regarding the need for a new emerging energy system, IEA’s support of the Paris Agreement’s first global stocktake has resulted in a need for a world energy investment path. The upcoming UN Climate Change Conference, COP28 UAE, is expected to be held at Dubai Expo City from 30 November to 12 December 2023. The conference represents the culmination of the first global stocktake of the Paris Agreement. |
|
| 2023 | 1st African Climate Summit The first-ever Africa Climate Summit on 4–6 September 2023, in Kenya, focused on clean energy and industrial financing and Africa’s negotiating their stance in the global discourse ahead of COP 28 for mitigating climate change consequences, being the most affected continent. |
| Year of Study | Review Method | Sub-Themes | Main Themes Nomenclature | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Citation analysis of most cited energy development studies |
|
1, 2, 3, 4 | [8] |
| 2022 | Two-decade overview of studies from SED conferences and special issues |
|
5, 2, 6, 7, 8 | [32] |
| 2022 | Critical review of sustainable energy transition strategies |
|
6, 1, 8, 3 | [33] |
| 2022 | Analysis of studies from selected energy journals |
|
7, 8, 6 | [35] |
| 2023 | Bibliometric |
|
8, 9, 2 | [37] |
| 2023 | Editorial |
|
2, 3, 7, 9, 10 | [36] |
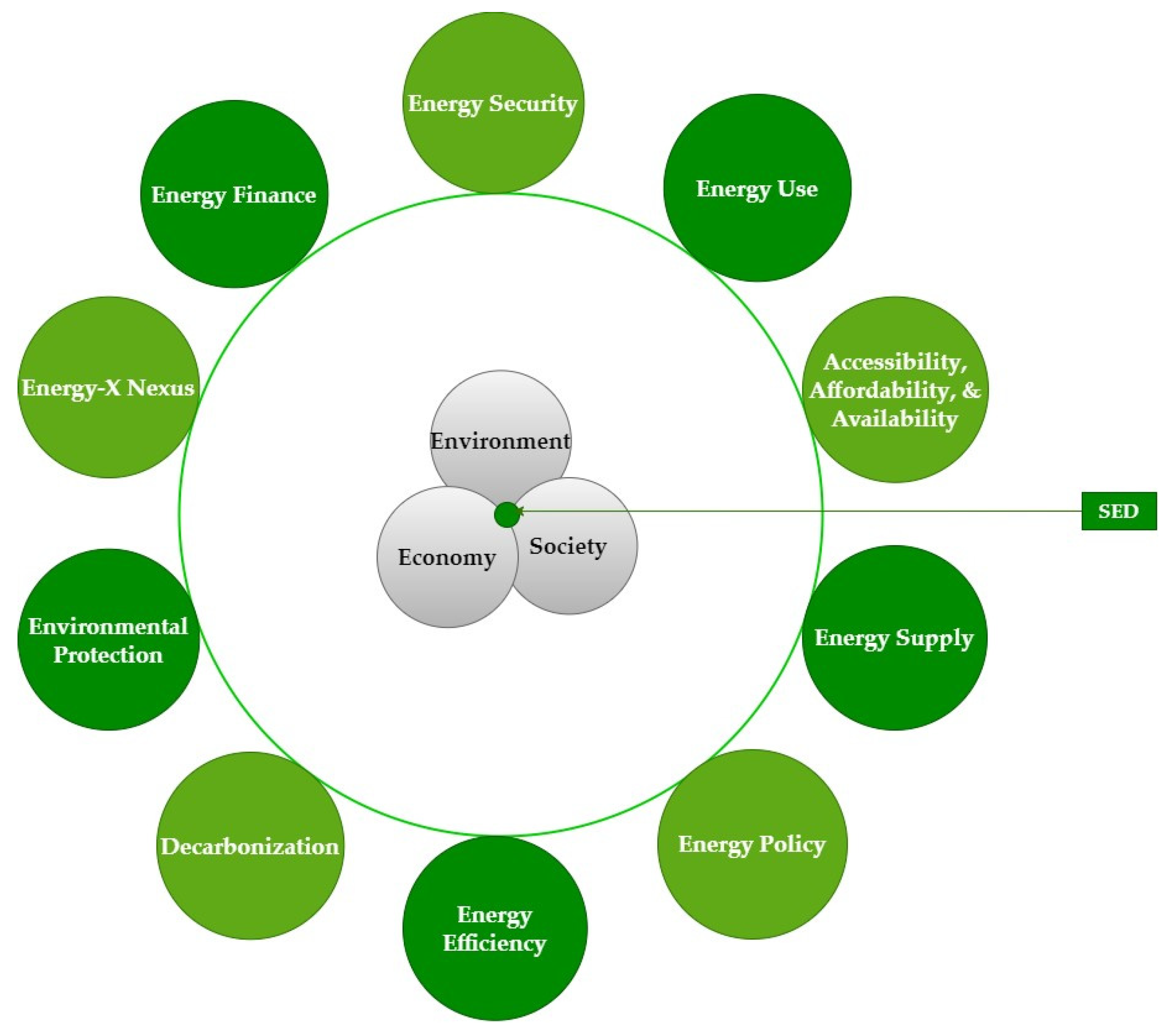
| Theme No. | Sub-Themes | Main Themes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
Energy security |
| 2 |
|
Energy use |
| 3 |
|
Accessibility, affordability, and availability |
| 4 |
|
Energy supply |
| 5 |
|
Energy policy |
| 6 |
|
Energy efficiency |
| 7 |
|
Decarbonization |
| 8 |
|
Environmental protection |
| 9 |
|
Energy-X nexus |
| 10 |
|
Energy finance |
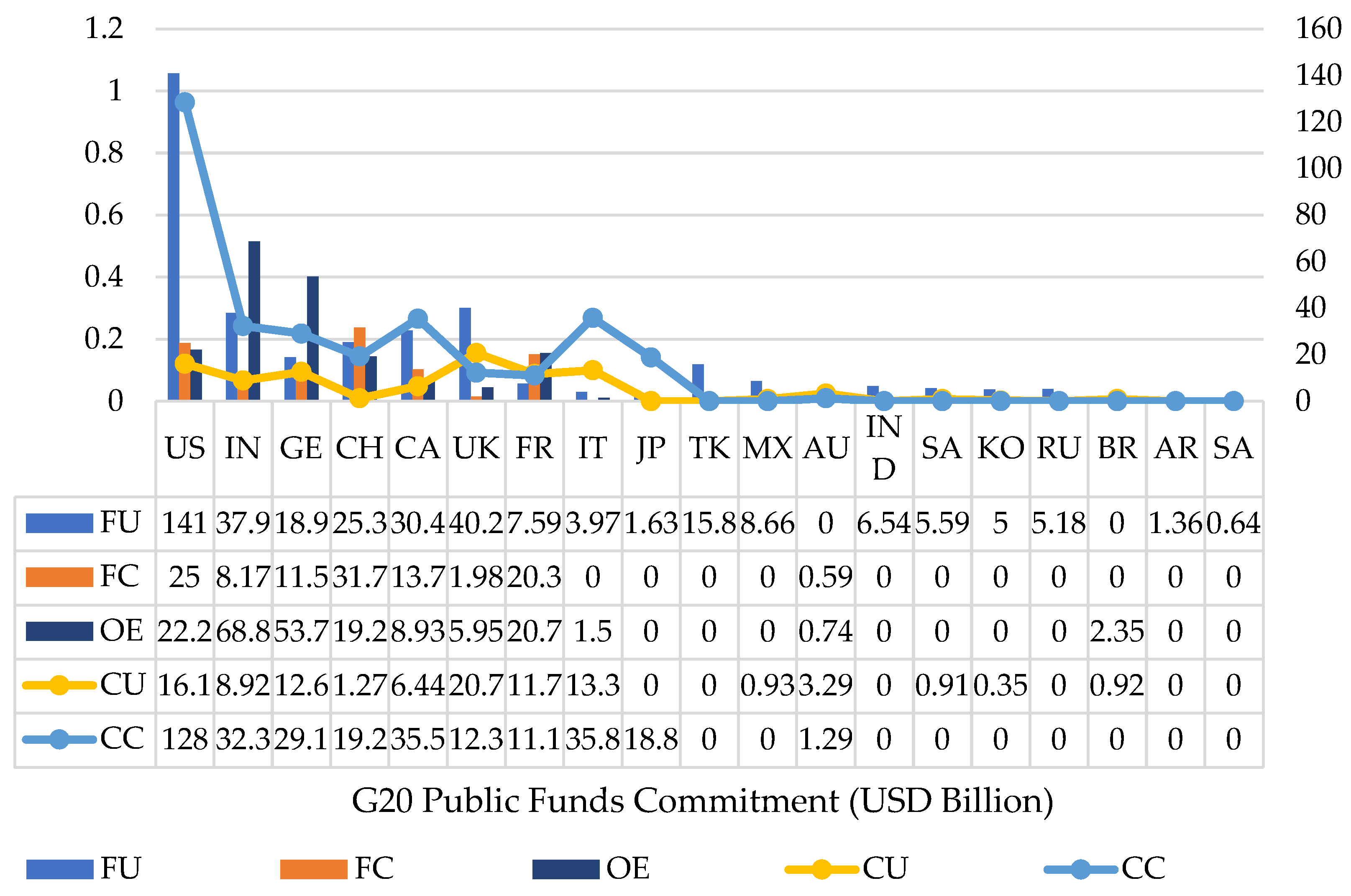
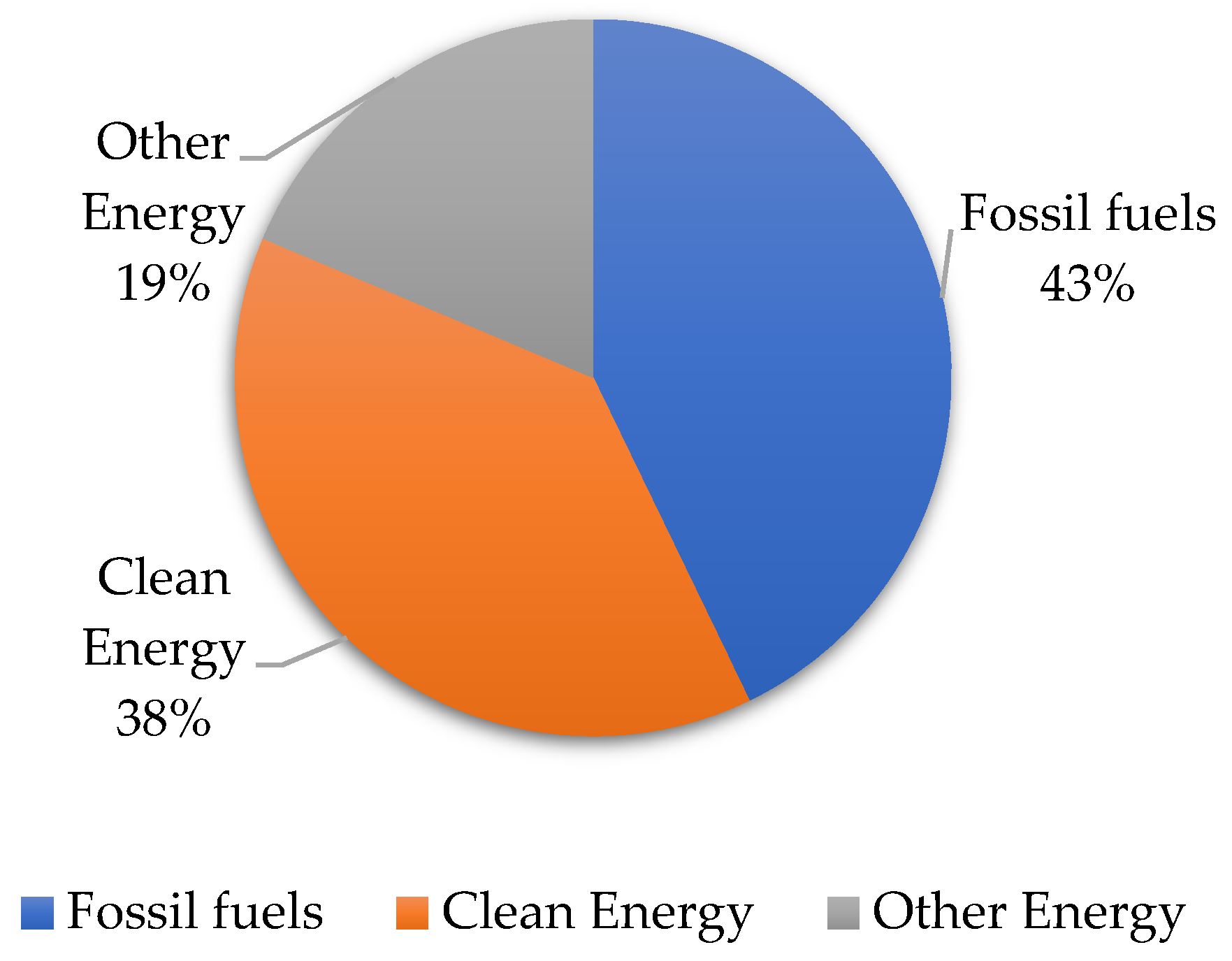
| S/N | Energy Type | Description | Public Funds Commitment (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fossil conditional (FC) |
|
113.19 |
| 2 | Fossil unconditional (FU) |
|
357.78 |
| 3 | Clean conditional (CC) |
|
326.13 |
| 4 | Clean unconditional (CU) |
|
98.46 |
| 5 | Other energy type (OT) |
|
204.11 |
| Country/Region | Summary of Energy-Related Policies for Climate Commitments | Addressing 1.5 °C Scenario Issues | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Increased RE Target in the National Grid
|
Partial | [40,43] |
| USA | Approval of the Inflation Reduction Act
|
Partial | [40,44] |
| India | Expansion of the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
|
Partial | [40,45] |
| Europe | Commitment to Increasing Offshore Wind Capacity
|
Partial | [40,46] |
| Japan |
|
Partial | [40] |
| Iran | - | None | |
| Canada |
|
Partial | [47] |
| South Korea | Planned Production Capacity Reduction of Coal-fired Plants and Expansion of Nuclear Power Plants
|
Partial | [40] |
| Indonesia and Southeast Asia | Indonesia-Introduction of Just Energy Transition Investment Plan (JETIP)
|
Partial | [40] |
| Saudi Arabia | - | None | |
| South Africa | Introduction of Just Energy Transition Investment Plan (JETIP)
|
Partial | [48] |
| Egypt |
|
Partial | [49] |
| Algeria | - | None | |
| Nigeria | Introduction of Energy Transition Plan (ETP)
|
Partial | [50] |
| Libya | - | None | |
| Morocco |
|
Partial | [51] |
| S/N | Country (G20) | Emission (CO2) in 2018 Mt | Emission (CO2) in 2019 Mt | Emission (CO2) in 2020 Mt | Emission (CO2) in 2021 Mt | Emission (CO2) in 2022 Mt | RE in National Mix (%) in 2018 |
RE in National Mix (%) in 2019 |
RE in National Mix (%) in 2020 |
RE in National Mix (%) in 2021 |
RE in National Mix (%) in 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 5380 | 5260 | 4720 | 4903 | 4970 | 17.45 | 18.29 | 20.32 | 20.74 | 22.52 |
| 2 | India | 2600 | 2630 | 2450 | 2701 | - | 16.69 | 18.69 | 20.21 | 19.38 | 20.48 |
| 3 | Germany | 754.41 | 707.15 | 639.38 | 674.75 | 655.5 | 35.1 | 40.09 | 44.33 | 39.7 | 42.95 |
| 4 | China | 10350 | 10,740 | 10,960 | 11,470 | 11447 | 25.77 | 27 | 28.25 | 28.91 | 30.67 |
| 5 | Canada | 584.37 | 584.71 | 534.86 | 545.63 | - | 67.37 | 67.17 | 68.78 | 68.17 | 69.74 |
| 6 | United Kingdom | 379.73 | 364.75 | 326.26 | 346.77 | 331.5 | 33.29 | 37.46 | 42.86 | 39.78 | 41.45 |
| 7 | France | 322.53 | 316.39 | 280.03 | 274.4 | 269.7 | 19.73 | 20.01 | 23.76 | 22.23 | 24.54 |
| 8 | Italy | 349.01 | 339.23 | 302.28 | 328.69 | 317.7 | 39.81 | 39.76 | 42.04 | 40.62 | 36.44 |
| 9 | Japan | 1140 | 1110 | 1040 | 1170 | - | 18.14 | 19.42 | 21.32 | 22.61 | 23.63 |
| 10 | Turkey | 422.57 | 401.72 | 413.43 | 446.2 | - | 32.18 | 43.68 | 42.02 | 35.56 | 41.97 |
| 11 | Mexico | 475.27 | 472.19 | 391.71 | 407.21 | - | 17.7 | 18.55 | 21.26 | 23.94 | 22.94 |
| 12 | Australia | 416.28 | 416.36 | 399.92 | 391.19 | - | 17.15 | 21.38 | 25.05 | 29.13 | 32.3 |
| 13 | Indonesia | 603.66 | 659.44 | 609.79 | 619.28 | - | 17.05 | 16.26 | 18.13 | 18.17 | 19.62 |
| 14 | Saudi Arabia | 626.19 | 656.48 | 661.19 | 672.38 | - | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.21 |
| 15 | Korea, DPR | 670.17 | 646.1 | 597.63 | 616.08 | - | 5.23 | 5.76 | 6.13 | 7.77 | 9.21 |
| 16 | Russia | 1700 | 1690 | 1620 | 1760 | - | 18.42 | 18.55 | 20.74 | 19.96 | 18.36 |
| 17 | Brazil | 477.1 | 475.1 | 442.31 | 488.88 | - | 82.92 | 82.85 | 84.64 | 76.77 | 86.94 |
| 18 | Argentina | 180.6 | 178.51 | 169.26 | 186.45 | - | 25.02 | 26.01 | 26.71 | 25.35 | 31.43 |
| 19 | South Africa | 435.24 | 466.92 | 435.83 | 435.93 | - | 5.16 | 5.36 | 5.78 | 7.56 | 9.09 |
| 20 | European Union | 3050 | 2910 | 2620 | 2740 | 2730 | 32.29 | 34 | 38.45 | 37.34 | 38.36 |
| Impact | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Positive |
|
| Negative |
|
| Performance Indices | Chemical | Thermal | Electromagnetic | Mechanical | Peak Cutting and Trough Filling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life span | 1.14 years 4 | 30 years 2 | 30 years 2 | 30–60 years 1 | 2 years 3 |
| Storage cycle | 365 days 1 | 7–28 days 3 | 1–6 days 4 | 7–30 days 2 | 1–6 days 4 |
| Response time | Minutes 3 | Weeks to hours 4 | Days long 5 | Seconds to minutes 2 | Hundred milliseconds1 |
| Storage capacity | MW–GW 1 | MW 2 | kW–MW 2 | GW 1 | kW–MW 2 |
| Storage efficiency (range) | 0.3–0.8 5 | 0.5–0.9 3 | 0.8–0.98 1 | 0.7–0.85 4 | 0.6–0.95 2 |
| Cost | USD (2801–7002)/kW 3 | USD (280–420)/kW 2 | - 4 or 5 | USD (140–840)/kW 1 | USD (281–420)/kW 2 |
| Energy density | Very high 1 | Moderate 3 | Low 4 | Low 4 | High 2 |
| Environmental Impact | |||||
| Resources for generation | Existing energy resources (both fossil and RE), depending on the production method 1 | Heat 2 | Electromagnetic field 2 | Mechanical work 2 | Cutting and trough filling 2 |
| Technology/ Pathway |
Storage Application | Applicable Scenarios | Merits | Demerits | Maturity of Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Hydrogen Natural gas |
Large-scale, long-cycle energy storage | Long storage cycle High storage energy volume |
High infrastructure requirements Sluggish response Low efficiency but high cost |
Low |
| Thermal | Molten salt | 7–28 days | High thermal storage volume | Limited applicable scenarios | Moderate |
| Electromagnetic | Supercapacitor Superconducting |
Peak load regulation, direct use of thermal energy | Long life span Fast response |
Seconds to minutes | Low |
| Mechanical | Flywheel Compressed air Hydro-pump |
Large-scale energy storage by peak cutting and trough filling | Very high technological maturity Longer life span Low cost of operation Large energy and power capacity |
High infrastructure requirements Sluggish response |
Very high |
| Peak cutting and trough filling | Battery | Peak load and frequency regulation | High technological maturity High flexibility in construction/installation Fast response |
Intermittent problem of heating High infrastructure cost requirements |
High |
| Category | Issues and Constraints | Related SED Themes (from Table 2 and Table 3) |
|---|---|---|
| Institution and Politics |
|
5, 7, 10, 1 |
| Technology Systems |
|
6, 1, 8, 10, 7 |
| Climate Change Concerns |
|
8, 10, 2, 4 |
| Public Opinion |
|
3, 5, 10, 9 |
| Sector | Emerging Energy-Related Decarbonization Strategies | Merits | Demerits | Technology Maturity Level | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power |
|
|
|
low | [67,74,75,76,77] |
| Industrial processes |
|
|
|
low | [78,79] |
| Transport |
|
|
|
low | [80,81] |
| Building |
Innovative Active Cooling/Heating
|
|
|
low | [82,83] |
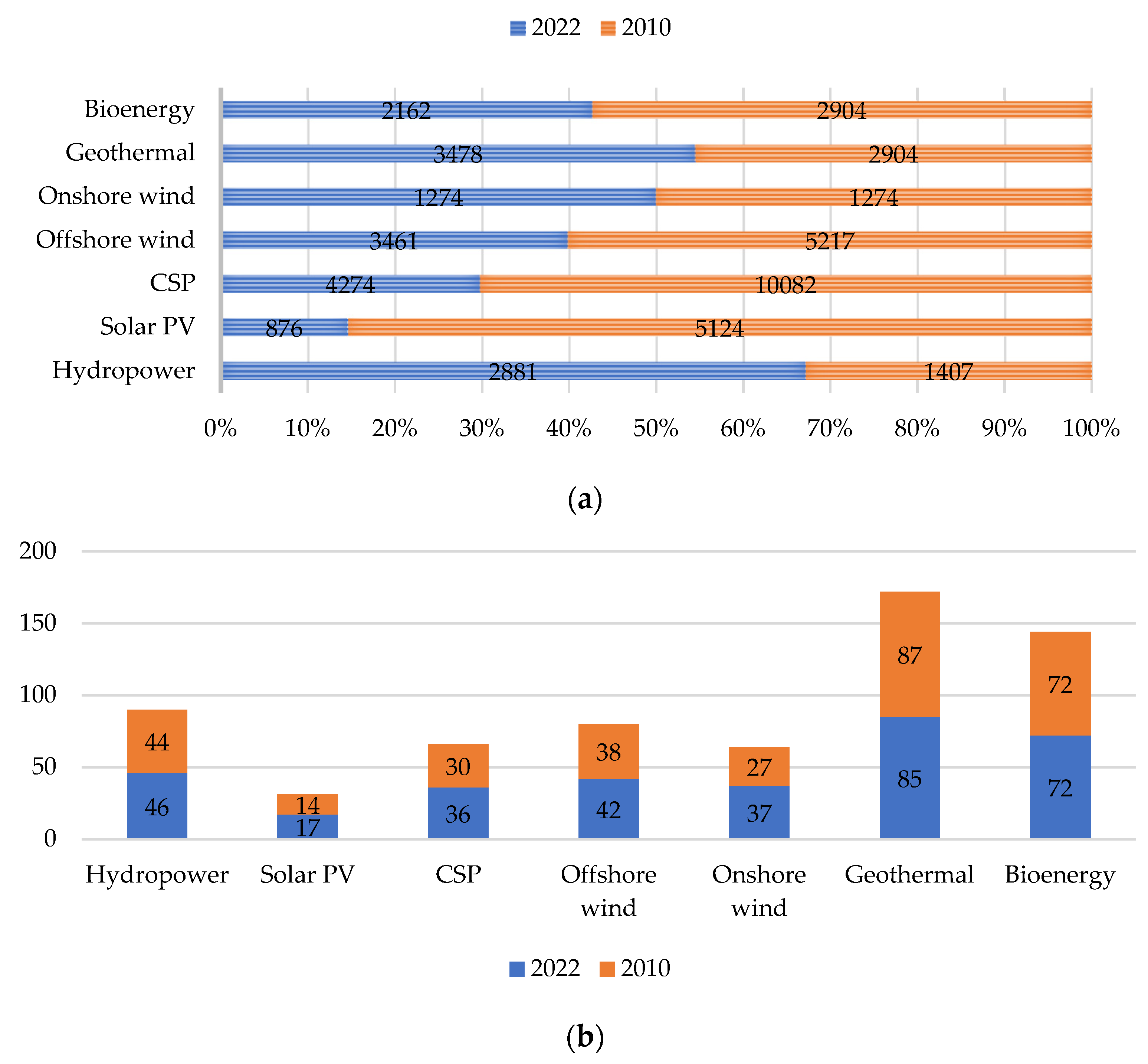
| Energy Technology | LCOE (USD/kWh) | LCOE (USD/kWh) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 2010 | % Change | |
| Hydropower | 0.061 | 0.082 | 25.61 decrease |
| Solar PV | 0.049 | 0.445 | 88.98% decrease |
| CSP | 0.118 | 0.380 | 68.95% decrease |
| Offshore wind | 0.081 | 0.197 | 58.88% decrease |
| Onshore wind | 0.033 | 0.107 | 69.16% decrease |
| Geothermal | 0.056 | 0.053 | 5.666% increase |
| Bioenergy | 0.061 | 0.082 | 25.61% decrease |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





