1. Introduction
Until June 2023, more that seven hundred million people were infected with Coronavirus, and there were registered more than six million deaths worldwide(1). Although the virus affects primarily the respiratory tract, causing from mild to severe case of pneumonia, and ultimately severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), myocardial injury is frequently found in patients with COVID-19 (defined as increased levels of cardiac necrosis biomarkers, especially High-sensitive Troponin). One of the incriminated mechanisms is the fact that angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) worked as a receptor for coronavirus, and the fact that this enzyme is highly expressed in the heart and lungs(2). Studies showed that increase troponin levels in COVID patients were associated with higher mortality(3).
The myocardial injury can have different electrocardiographic expressions, from a normal EKG, to an ST-elevated acute myocardial infarction. In this review we studied the incidence, possible mechanism and specific challenges of acute myocardial infarction in patients with COVID-19. Previous studies reported that viral infections involving respiratory tract are potential risk factors for ACS (acute coronary syndromes). One of the possible mechanism of type 1 AMI (acute myocardial infarction) is the pro-inflammatory state, that could promote the destabilization of a coronary atherosclerotic plaque(5). Type 2 AMI (also known as MINOCA) could be promoted by hypoxia, tachycardia, hypotension, symptoms that appear in acute respiratory failure (5). In SARS-COV2 infection, there are particular pathways that can induce AMI, such as: endothelial and microvascular injuries, coronary vasospasm, thrombosis, increase platelet consumption, the cytokine storm (6). However, there is little information about the post-SARS-COV2 infection sequelae.
The present manuscript aims to evaluate the outcomes and long-term prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome and post-SARS-COV2 infection status, by performing a systematic review of available data.
2. Method
The authors used PubMedplatform for searchingarticles published from Feb 2020 to 2023, using the keywords “COVID” and ‘myocardial infarction”. Review articles, duplicate articles, opinion letters, animal studies, corrections and articles non-relevant for cardiology were excluded. The research was limited to articles published in English.
3. Results
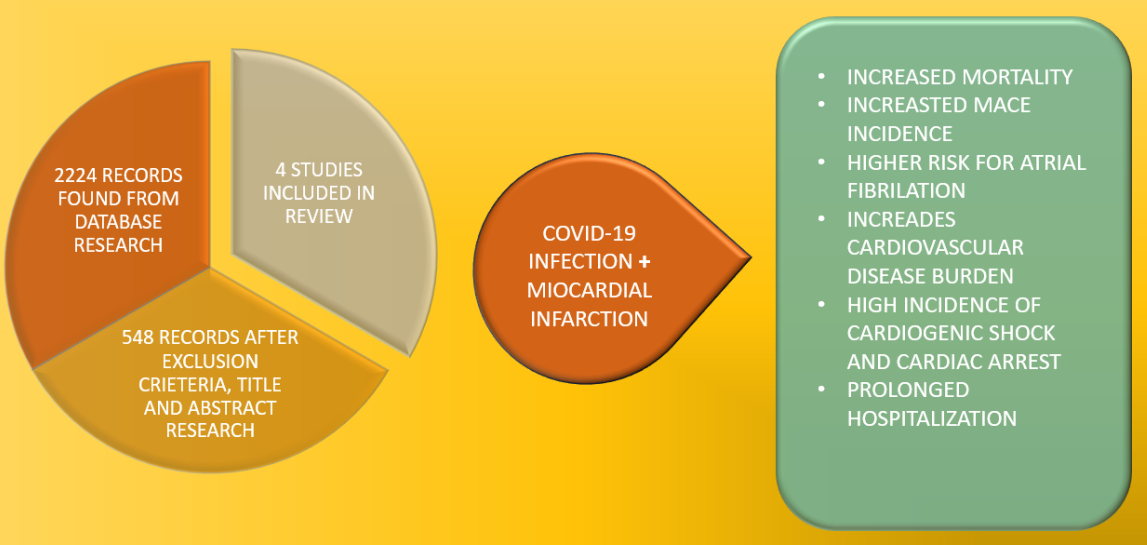
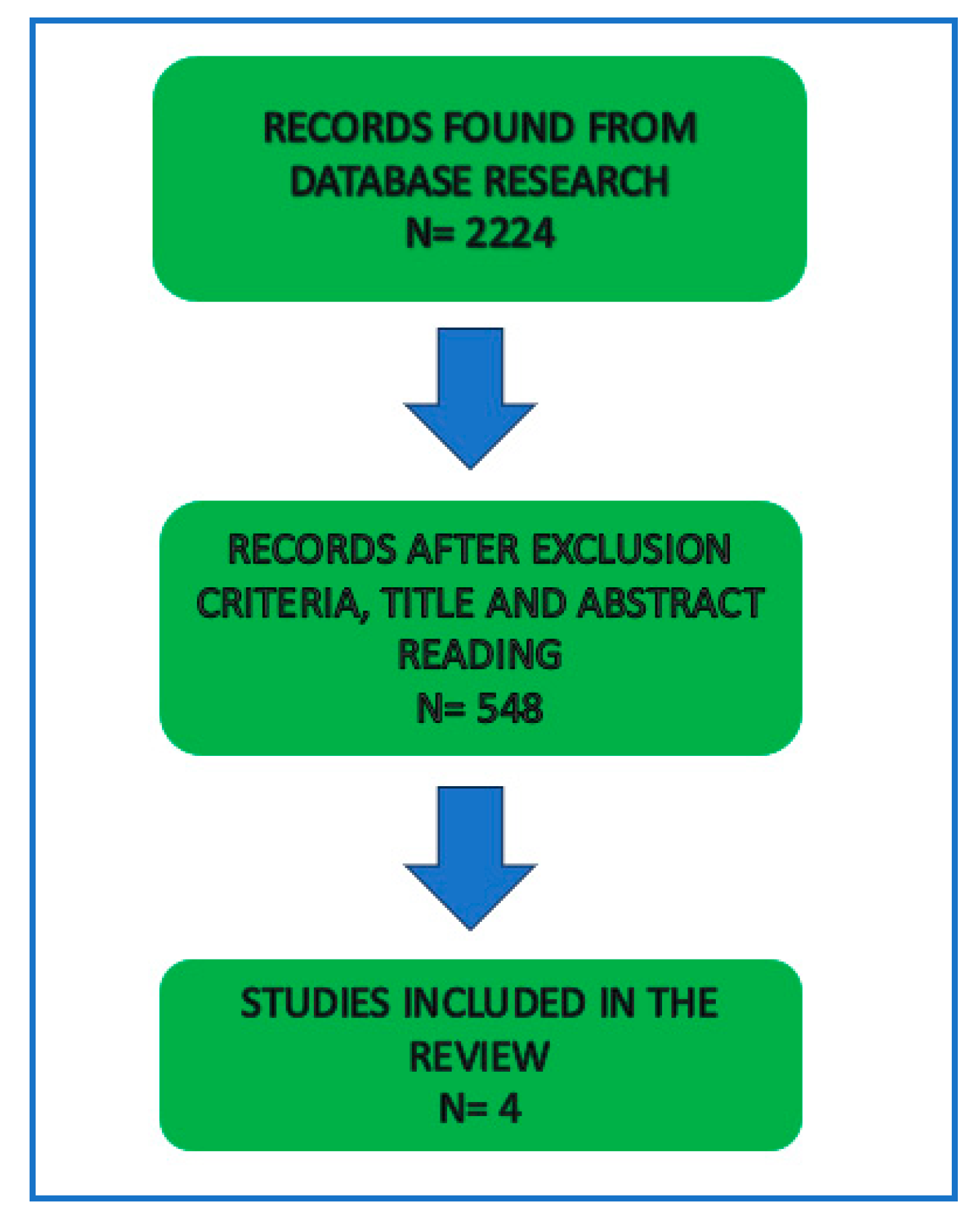
There were 2224 results that fit our initial search, after screening through our exclusion criteria, 548 articles remained. After full-text reading, 544 articles were excluded, leaving 4 studies that that treated our chosen subject and fulfill our intended research. Each study defined AMI according to the Forth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction(7).
Figure 1.
Research process.
Figure 1.
Research process.
Together, the four studies had enrolled 8.733.687 patients, from which 74% were males, including 844.983 COVID-19 positive patients, with different severity of pulmonary infection. The characteristics of the selected studies are presented in
Table 1. The mean follow-up period was 21 mouths, raging between 1 and 60 mouths. The occurrence of AMI was screened by searching in the patient’s medical data by International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision (ICD-10) codes I21 and I22.
The North American COVID-19 Myocardial Infarction Registry (NACMI) (8) enrolled patients from January 2020 to December 2020 with ST- elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The study had as a primary end-point in-hospital death, stroke, recurrent myocardial infarction, unplanned revascularization. For comparison of reperfusion strategies, patients referring at a hospital within 60 miles of a PPCI hospital were excluded. As results the authors reveal a slightly longer door to balloon time in COVID-19 patients than control group. Primary endpoint occurred in 36% of COVID-19 positive patents and 5% of COVID-19 negative patients. This difference was made by increased in-hospital mortality of the first group. The mortality was higher for those who did not undergo coronary revascularization, and those patients stayed longer in intensive care unit.
Xie et al (9) aimed to asses the risk and one-year burdens of cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19 pneumonia recovery patients. The composite outcome was the burden of cardiovascular diseases such as: stroke, dysrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, inflammatory heart disease, thrombotic disorders, major acute cardiac events. The authors declared a high risk of cardiovascular disease, arrhythmias, stroke, thrombotic events at 12-months follow-up in patients with COVID-19 infection, even for those who were not hospitalized. The risk and associated burdens increase proportionally with the severity of COVID-19 pneumonia. The risk of cardiovascular disease extends beyond the acute phase of the infection.
The smaller study, leaded by Wei et al (10) showed that patients with acute myocardial injury were more likely to require admission to Intensive Care Unit (ICU), mechanical ventilation, vasoactive agents and death occurred more often. The authors found as predictors for severe disease older age, arterial hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, use of calcium canals blockers, lower glomerular filtration rate, elevated Troponin or C reacted protein (CRP).
Wang et al (11) analyzed the cardiovascular risk that COVID-19 survivors have at one year follow-up. For that purpose, the composite of cardiovascular outcome was defined as the first incidence of any complication. The outcomes followed were: stroke, arrhythmia, pericarditis, myocarditis, acute coronary disease, acute myocardial infarction, angina, heart failure, cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, thrombotic disease. The results of this study revealed that COVID-19 survivors have an increased risk of death in all the cardiovascular outcomes. The impact of this disease in cardio-related outcomes appeared to be more pronounced in hospitalized patients. The 12-mouths risk of incidental cardiovascular disease is higher in COVID-19 patients survivors than control group and they have higher risk of complications. Femaile survivors of COVID-19 pneumonia seemed to have more frequent arrhythmias than control group. Myocarditis and ischemic heart diseases were to of the most frequent diseases in younger survivors.
3.1. Long-Term Risk of Myocardial Infarction
In the studied population, we observe that the majority of patients were males, but even so, females develop more frequently arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, sinus tachycardia (9-11).
The NACMI only studied STEMI patients, and one of the main observation was that in the COVID-19 positive group, only 20% required coronary stent implantation, the rest didn’t present a culprit lesion at coronarography. In the Covid-19 negative group with STEMI, 93% needed stent implantation (8). The in-hospital cardiovascular death was twice as high among COVID-19 positive patients, with a poor short-term prognosis, 1out of 3 patients who survived the acute event, deceased at 30-days follow-up. More than one-third presented recurrent MI within 30-days.
(Table 2). More that 30% of COVID-19 patients met primary endpoint, compared to 5% of non-COVID-19 patients (8).
Wei et al (10) noted that increased Troponin I was a negative prognostic factor for COVID-19 patients, leading more often to the need on mechanical ventilation, the use of vasoactive agents and longer admission to ICU (Intensive Care Units).
Patients with COVID-19 infection, regarding respiratory disease severity, have and increased risk of developing acute myocardial infarction within 30 days after the primal infection (HR =2.32, burden 2.91/1000 patients). It was noted that the incidence increased with the severity of the viral pneumonia. The pathological mechanism is still unclear, several studies incriminated micro-thrombosis of small coronary arteries as part of the pro-coagulability status. Beside myocardial infarction, other forms of ischemic heart disease, such as acute coronary disease (ACD), ischemic cardiomyopathy and angina, are more frequent than in pre-COVID period and in control groups. The incidence of this diseases is twice higher in COVID-19 survivors.
The long-term burden of MI in COVID19 survivor remains high even at 12-mouths after de resolution of the infective disease, this group of patients have almost twice the risk of developing MI within a year (HR = 1.71, burden=7.59/1000patients)
Risk factors for acute myocardial infarction after COVID-19 infection: older age, diabetes mellitus, male gender, follow-up length (12).
3.2. Long-Term Outcomes of Post-COVID-19 Positive Patients
Atrial fibrillation was found twice as frequent in post-COVID-19 patients, although the incidence of other arrhythmias was increased as well, AF was the most common one (11).FemaleCOVID-19 survivors and younger patients have greater risk of developing myocarditis, ischemic heart disease and arrhythmias than male survivors. Older age survivors have increased risk of developing pulmonary embolism and ischemic heart disease (HR = 1.87).
Xie et al brought evidence that patients infected with Covid-19, beyond the first 30 days of infection, have increased risks of cardiovascular diseases, including cerebrovascular disorders, dysrhythmias, myocarditis, ischemic heart disease, heart failure and thromboembolic disease (10).
There was a significant increased incidence of myocarditis among non-hospitalized patients at 12-months follow-up according to Wang et all, possibly because of the lack of proper antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatment (11).
The NACVI study revealed that more than half of COVID-19 patients with STEMI developed several grades of hearth failure. Also, COVID-19 positive patients presented increased incidence of cardiac arrest and cardiogenic shock.
Patient with COVID-19 pneumonia develop twice as frequent major acute cardiovascular events (MACE), even at 12-month follow-up (HR = 1.87), with an HR of 1.64 regarding cardiovascular death. In the NACVI registry, 36% of STEMI patients with COVID-19 presented a further acute cardiovascular event. (
Table 3)
4. Discussios
For a long time, the risk of ACS during of after an acute infection was studied (13). Studies made during the COVID-19 pandemic showed that the risk of AMI returns to baseline after several months, and that patients with severe pneumonia were more likely to develop an acute coronary syndrome (14).
Potential cause of cardiovascular disease in Covid-19 include the damage from direct viral invasion of cardiomyocytes, causing cell death, endothelial cell infection, transcriptional alteration of multiple cell types, complement activation and complement-mediated coagulopathy and microangiopathy, downregulation of ACE2 and dysregulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, autonomic dysfunction, elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can induce fibrosis and scarring of cardiac tissue (15,16,17).When SARS-COV2 is binding with ACE2 receptors, it leads to the down-regulation of these receptors and thereby, increases the activity of angiotensin II. This mechanism leads to systemic vasoconstriction, apoptosis, inflammation, and endothelial proliferation, resulting in cardiomyocyte damage or worsening of previous ischemic condition (18). Another incriminated mechanism of acute myocardial infarction in COVID-19 patients is coronary embolism, found in 3% of AMI patients (19). A newer hypothesis claims that integration of the SARS-COV2 genome into the human DNA might express as chimeric transcripts fusing viral with cellular sequences (20).
COVID-19 survivors presented with an increased 30-days risk of stroke, increased risk o thrombotic events, inflammatory cardiac disease (mostly myocarditis), and higher risk of developing dysrhythmias (8,9,10,11). Patients that required hospitalization for COVID-19 pneumonia were more likely to present cardiovascular events such as heart failure, acute coronary syndromes, atrial fibrillation, stroke. The risk becomes ever higher for patients admitted in the ICU.
Survivors of COVID-19 have increased risk and burdens of cardiovascular diseases at 12-months follow-up. This increased risk was observed even in patients without history of cardiovascular disease and with low cardiovascular risk, proving that COVID-19 infection has a direct implication in the worsening of prognosis. The higher risk for cardiovascular events was greater even in COVID-19 non-hospitalized patients, than the general population, but there was a significant growth concurrently with the severity of the viral disease (9).
STEMI in COVID-19 positive patients occurs mostly in patients with diabetes mellitus (46%) and they have a high risk of cardiogenic shock (8). The association between COVID-19 infection and STEMI confers a poor prognosis, with the death of 1 of 3 patients. 20% of COVI-19 positive patients did not have a culprit vessel, therefore did not need PCI.
The fact that cardiovascular risk expands even at 12 months after the acute phase of COVID-19 imposes the need for a better primary prevention of COVID-19 infection and a thorough screening for cardiovascular disease and follow-up for post-COVID-19 patients.
Excepting the NACVI registry (that didn’t yet published the 5-years follow-up results), there were few data regarding the type of acute myocardial infarction (STEMI/NSTEMI), AMI-related mortality, chosen therapy used, the post-procedural complication, recurrent MI, the in the studied population.
Earlier studies showed that COVID infection could lead to irreversible damage to cardiovascular and respiratory system, such as congestive heart disease or chronic cell hypoxia, increasing the risk of arrhythmias, cardiogenic shock, ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke (21).
A more recent Turkish study compared outcomes of patients with acute coronary syndrome in pre-COVID-19 era, with COVID-19 era. Although the two groups were similar when it came to previous statin or antiplatelet treatment, history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, tobacco use and previous coronary artery disease, it was observed that pre-COVID-19 era patients had more frequent coronary thrombosis and the need of glycoproteins IIb/IIIa usage. There were no differences in obtaining post-procedural TIMI flow grade 3 in the two groups, but COVID-19 patients had higher mortality and stent thrombosis (23).
Mortality rates in AMI patients increase proportionally with total ischemic time, and COID-19 patients had prolonged first medical contact and door-to-balloon time, this may be one of the reasons of poorly prognosis (24).
A recently published study runed by Phua et al showed no significant differences between COVID-19 positive and negative patients regarding all-cause mortality, recurrent coronary event, cardiac-related readmission (25).
Data for the Danish registry reveal that the incidence of acute myocardial infarction 14 days after a positive test for COVID-19 was approximately five times higher that in pre-COVID-19 era (27). COVID-19 positive patients seem to have increased enzymatic infarct size, assessed by the peak of troponin or creatinekinase levels, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, higher intracoronary thrombotic burden (28).
5. Conclusions
Because of the increased cardiovascular risk and increased CV disease burden, we need to divide our attention in primary prevention of viral diseases, especially SARS-COV2 infection, in the presence of solid evidence of direct involvement of COVID19 infection and their increased incidence.
Screening for cardiovascular illnesses is mandatory in all COVID-19 survivors, disregarding the severity of the respiratory affectation in the acute phase.
Cardiovascular complications are frequent in COVID-19 patients and leads to higher risk of myocardial infarction, especially type 2, and therefore, to an adverse prognosis.
The short-term and long-term risk of cardiovascular events is substantial higher in COVID-19 survivors, even for those who were not hospitalized.
Author Contributions
GCF: MR: concept and design. GCF: draftingthe manuscript. MR: review supervision.GCF: data curation, statisticanalysis. All authors contributed equally to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- https://covid19.who.int/.
- Turner AJ, Hiscox JA, Hooper NM. Ace2: from vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004;25:291–4. [CrossRef]
- Majure DT, Gruberg L, Saba SG, Kvasnovsky C, Hirsch JS, Jauhar R. Northwell Health COVID-19 Research Consortium. Usefulness of elevated troponin to predict death in patients with COVID-19 and myocardial injury. Am J Cardiol 2021; 138: 100-106. [CrossRef]
- Bonow RO, O’Gara PT, Yancy CW. Cardiology and COVID-19. JAMA. (2020) 324:1131–2. [CrossRef]
- Schiavone M, Gobbi C, Biondi-Zoccai G, D’Ascenzo F, Palazzuoli A, Gasperetti A, et al. Acute coronary syndromes and Covid-19: exploring the uncertainties. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:1683. [CrossRef]
- Canzano P, Brambilla M, Porro B, Cosentino N, Tortorici E, Vicini S, et al. Platelet and endothelial activation as potential mechanisms behind the thrombotic complications of COVID-19 patients. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2021) 6:202–18. [CrossRef]
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS. et al. Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol 2018; 72 (18) 2231-2264.
- Garcia S, Dehghani P, Grines C, Davidson L, et al. Initial Findings From the North American COVID-19 Myocardial Infarction Registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021; vol 77 (16) 1994-2003. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y, Xu E, Bowe B, Al-Aly Z. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19. Nature Medicine 2022; vol 28, 583–590. [CrossRef]
- Wei JF, Huang FY, Xiong TY, Liu Q et al. Acute myocardial injury is common in patients with COVID-19 and impairs their prognosis. Heart 2020; 106(15): 1154–1159. [CrossRef]
- Wang W, Wang CY, Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in COVID-19 survivors among non-vaccinated population: A retrospective cohort study from the TriNetX US collaborative networks. eClinicalMedicine. 2022 Nov; 53: 101619. [CrossRef]
- Zuin Ma, Rigatelli G, Battisti V, Costola G, Roncon L, Bilatoa C. Increased risk of acute myocardial infarction after COVID-19 recovery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2023 Feb 1; 372: 138–143. [CrossRef]
- Corrales-Medina V.F., Madjid M., Musher D.M. Role of acute infection in triggering acute coronary syndromes. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010;10:83–92. [CrossRef]
- Sutherland N., Dayawansa N.H., Filipopoulos B., Vasanthakumar S., Narayan O., Ponnuthurai F.A., van Gaal W. Acute coronary syndrome in the COVID-19 pandemic: reduced cases and increased ischaemic time. Heart Lung Circ. 2022 Jan; 31(1): 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Delorey, T. M. et al. COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature 595, 107–113 (2021).
- Varga, Z. et al. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 395, 1417–1418 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Song, W.-C. & FitzGerald, G. A. COVID-19, microangiopathy, hemostatic activation, and complement. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 3950–3953 (2020).
- Lasica R, Djukanovic L, Mrdovic I, Savic L, Ristic A, Zdravkovic M, Simic D, Krljanac G, Popovic D, Simeunovic D, Rajic D, Asanin M. Acute Coronary Syndrome in the COVID-19 Era - Differences and Dilemmas Compared to the Pre-COVID-19 Era. Clin. Med. 2022, 11(11), 3024. [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Kawakami, S.; Noguchi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Asaumi, Y.; Kanaya, T.; Nagai, T.; Nakao, K.; Fujino, M.; Nagatsuka, K.; et al. Prevalence, Clinical Features, and Prognosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction Attributable to Coronary Artery Embolism. Circulation 2015, 132, 241–250. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. et al. Reverse-transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA can integrate into the genome of cultured human cells and can be expressed in patient-derived tissues. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2105968118 (2021).
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506.
- Toscano O, Cosentino N, Campodonico J, Bartorelli AL, Marenzi G. Acute Myocardial Infarction During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Update on Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med., 23 December 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kiris T, Avci E, Ekin T, Akgun DE, et al. Comparison of long-term outcome of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction between pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 era. Eur J Clin Invest, 2022 Vol 52, Issue 10, e13834.
- Garcia S, Albaghdadi MS, Meraj PM, et al. Reduction in ST segment elevation cardiac catheterization laboratory activations in the United States during COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 75(22): 2871-2872. [CrossRef]
- Phua K, Chew NWS, Sim V, et al. One-year outcomes of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2022; 53(2): 335-345. [CrossRef]
- Lopes RD, Macedo AVS, de Barros E Silva PGM. et al. BRACE CORONA Investigators. Effect of discontinuing vs continuing angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin ii receptor blockers on days alive and out of the hospital in patients admitted with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2021; 325 (03) 254-264.
- Modin D, Claggett B, Sindet-Pedersen C. et al. Acute COVID-19 and the incidence of ischemic stroke and acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2020; 142 (21) 2080-2082. [CrossRef]
- Primessnig U, Pieske BM, Sherif M. Increased mortality and worse cardiac outcome of acute myocardial infarction during the early COVID-19 pandemic. ESC Heart Fail. (2021) 8:333–43. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).