1. Introduction
China is a major steel producer, and its crude steel production accounted for more than 50% of the global crude steel production. Steel production capacity is the embodiment of one country's industrial strength, but high output also means high energy consumption. The energy consumption of the steel industry accounted for about 15% of China’s total energy consumption. Blast furnace ironmaking and converter steelmaking require a large amount of oxygen gas, which is mainly produced by separating air in the air separation unit (ASU) using a cryogenic rectification method. Most of the iron and steel enterprises in China have captive oxygen plants, which are equipped with several large-scale ASUs. The oxygen system of iron and steel enterprises is mainly composed of ASUs, oxygen compressors, and high-pressure storage vessels.
The oxygen system is energy extensive and is a large power consumer in iron and steel production enterprises because the separation process of air and the pressure delivery process of oxygen consume a lot of electric energy. In China, the oxygen system often has an imbalance between supply and demand. On the oxygen supply side, the ASUs have the characteristics of stable production due to the characteristics of the equipment, and their output is relatively stable. However, on the oxygen demand side, affected by the production rhythm, the oxygen demand fluctuates greatly. At present, ASUs, blast furnaces, and converters tend to be super-large, and the number of equipment decreases when the steel output remains unchanged. This will further aggravate the imbalance between the supply and demand of the oxygen system, resulting in a waste of resources and energy.
To cope with the imbalance between supply and demand, the main scheduling means that can be adopted in the oxygen system are the gas storage by high-pressure spherical vessels and the load adjustment of ASUs. The high-pressure spherical vessels can passively buffer the fluctuation of oxygen demand, while the load adjustment of the ASUs can be used as an active means to alleviate the fluctuation of oxygen demand, but the oxygen demand needs to be forecasted in advance. Oxygen demand forecasting and ASU variable-load operation are relatively complex. In the absence of a decision-making support system, it is difficult to predict and schedule the oxygen system by human judgment. As a compromise, at present, on-site workers generally adopt the practice of oxygen supply exceeding demand to ensure production safety, but the price paid is that the pressure of the oxygen pipe pipeline is at a high level and oxygen is often emitted, which makes the energy consumption of oxygen delivery at a high level and causes release loss. The optimized production and reasonable transportation of oxygen can effectively reduce the total energy consumption of steel production, and play a positive role in promoting the early realization of carbon peak in the steel industry. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a demand forecasting and optimal scheduling model for the oxygen system.
There are few studies on oxygen balance. Han et al. [
1] proposed a two-stage predictive scheduling method, in which a predictive model based on granular computing (GrC) and a mixed integer optimization model were established in the prediction stage and the scheduling stage, respectively. The application results showed the accuracy and practicality of the method. Han et al.[
2] proposed an oxygen system scheduling model that considers power costs, using a particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve the model, and validated the model's effectiveness through actual field data. Zhang et al. [
3] studied oxygen balance and scheduling under blast furnace shutdown conditions, and established a scheduling model for air separation startup and shutdown based on mixed integer linear programming [
4]. With the rapid development of the industrial Internet and intelligent manufacturing technology, digital twins will gradually become popular in the industry. It has become possible to predict and analyze based on big data and machine learning and drive the physical world with optimal results. This study takes a large-scale iron and steel enterprise as a study case, develops an oxygen consumption prediction model and an oxygen optimization scheduling model according to the characteristics of the oxygen system of the iron and steel enterprise, and verifies the accuracy of the forecast model and the energy-saving effect of the scheduling model through field data.
2. Case Descriptions
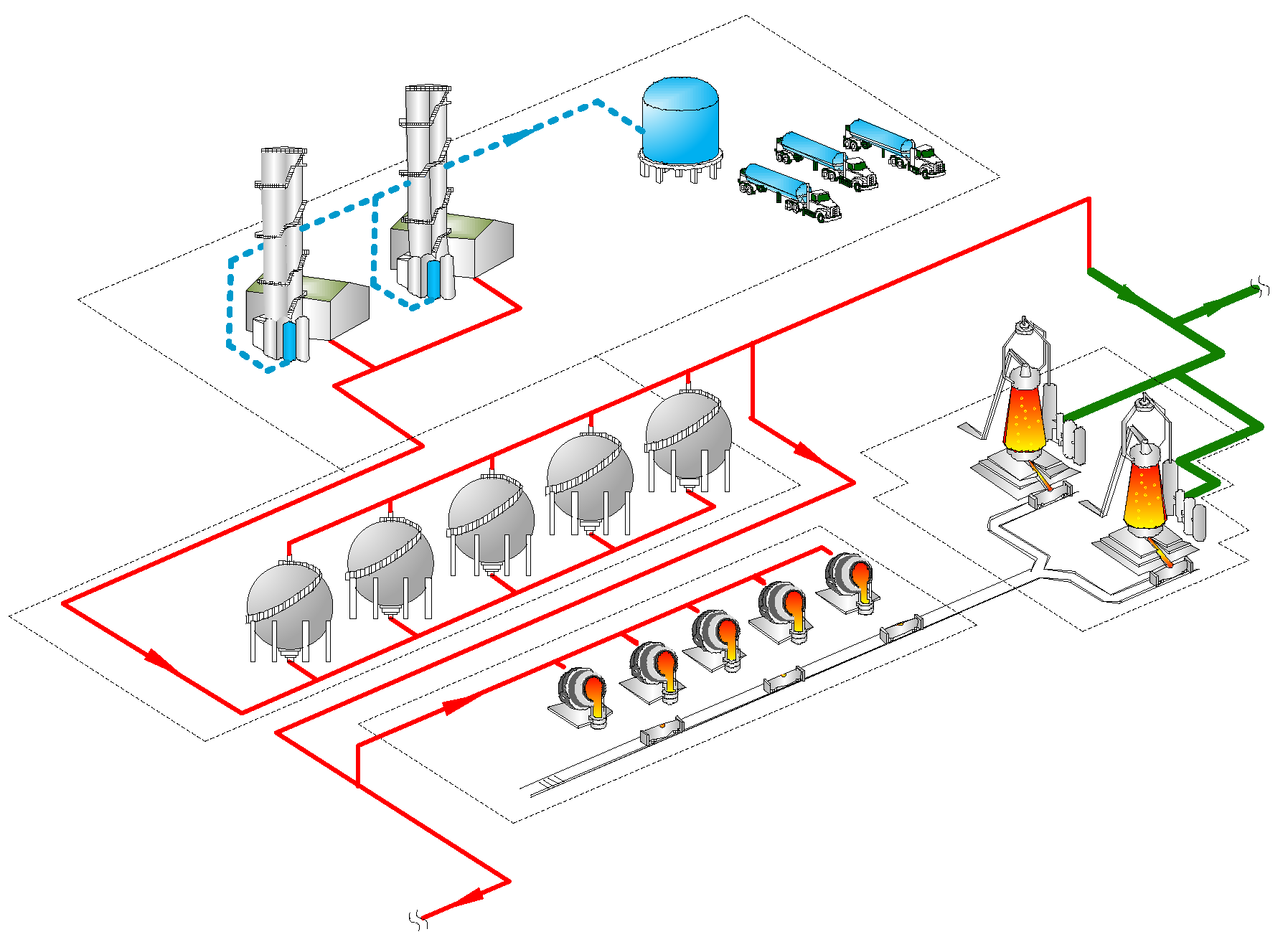
As shown in
Figure 1, the study case is the oxygen system of a large-scale iron and steel enterprise. In the oxygen system, the oxygen production equipment is two sets of large-scale load-variable ASUs with an internal compression process, and their relevant parameters are shown in
Table 1. The oxygen system is also equipped with five spherical vessels as buffer equipment, and its related parameters are shown in
Table 2. The main users of oxygen are five converters and two blast furnaces, among which the converters have the characteristics of batch smelting, and the time interval between two smelting cycles has great uncertainty, which is the main reason for the fluctuation of oxygen demand; the blast furnaces are in continuous production, the oxygen demand is relatively stable.
For research and analysis, a large amount of field data (collected every 2 minutes) has been collected. Then, the oxygen demands, ASU outputs, and pipeline pressures under normal production conditions (no blast furnace shutdown, converter maintenance, etc.) for four consecutive days were selected as the sample data to be analyzed.
3. Oxygen Demand Forecasting Model
The total amount of oxygen used in multi-converter steelmaking not only depends on linear factors that change over time but also is affected by nonlinear factors such as the randomness of manual operation and the random overlapping of oxygen consumption by multiple converters. The autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model [
5] can predict future data based on existing time series data and is suitable for processing time series data with strong linear correlation. The backpropagation (BP) neural network with genetic algorithm (GA) optimization (GABP) can learn historical data through neural network training. When the time series data has a strong nonlinear correlation, the GABP model has strong adaptability [
6]. Therefore, for comparison purposes, both the ARIMA and GABP models were selected to forecast oxygen demand.
3.1. The ARIMA model
For the non-stationary sequence analysis, the smoothing (difference) processing is performed first, and then the time series data after the stabilization (difference) are modeled and analyzed. For the
d-order difference, the expression is:
The general mathematical expression of the
model is:
where
d is the difference order,
p is the autoregressive order,
q is the moving average order,
L is the lag factor,
is the autoregressive factor corresponding to the
p-order,
L is the lag factor, and
is the observed value at the time
t during the random process,
is the moving average coefficient corresponding to
q-order,
is the term of random error.
3.2. The GABP model
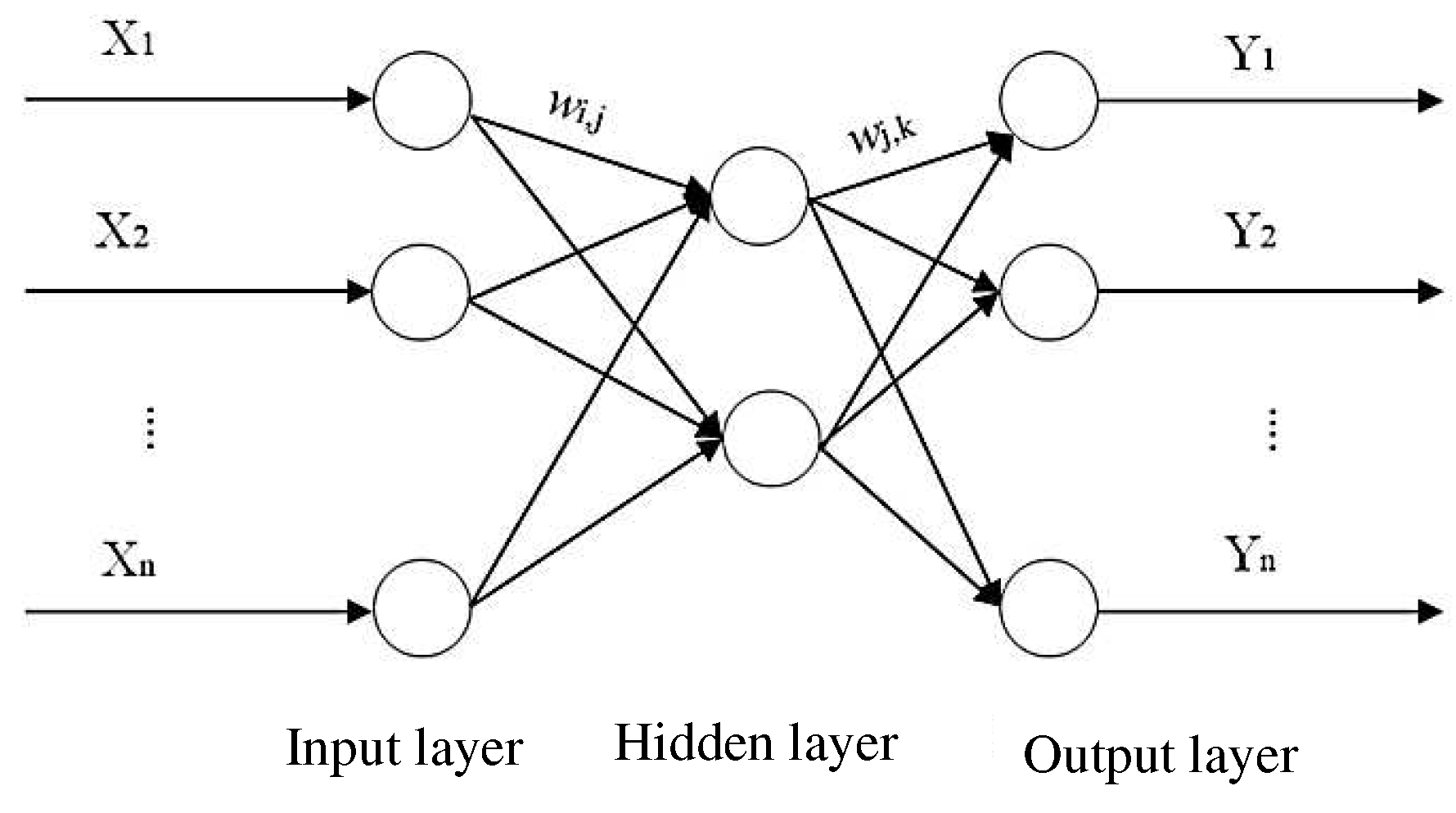
As shown in
Figure 2, the BP neural network is a kind of feed-forward network, and the network structure is composed of an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer. The neural network utilizes the network structure and parameters to perform nonlinear learning on the data samples, and stores the learning information in the network weights and thresholds, thereby memorizing the development law of the data sequence and realizing the forecast of the future data sequence. However, the randomness of parameter selection in the initial training of the neural network is strong, and the correction of weights and thresholds tends to fall into a local optimal solution, resulting in a forecast error greater than the expected error. This optimization defect can be made up by introducing a GA.
GA is an algorithm that simulates the natural evolution process of organisms to search for the optimal solution. It has the advantages of strong parallel computing ability and strong adaptability [
7]. The GA adopts the individual to express the value to be corrected and uses the error binary norm between the forecast output and the actual expected number as the population fitness value. The smaller fitness value is used as the candidate individual, and then a series of crossover and mutations are performed. After reaching the preset evolutionary algebra, the remaining individual is the optimal individual, and then the initial training parameters of the neural network are obtained.
4. Oxygen Scheduling Model
According to the actual situation of the oxygen system, the scheduling model adopts the following simplifications and assumptions: (1) the scheduling objects are gas spherical vessels and ASUs operated with variable loads; (2) in the load change process of ASU, both the nitrogen and argon products meet the demand, so the constraints for nitrogen and argon are not included; (3) during the scheduling process, no failures occurred in ASUs, blast furnace and converter.
4.1. Object Function
The production of oxygen by the ASU requires energy, so the oxygen emission will directly cause energy waste. Moreover, the higher the pressure of the oxygen pipeline, the greater the energy consumed to compress a unit of oxygen. Therefore, the scheduling object is to minimize both the oxygen emission and the pipeline pressure, and the objective function is as follows:
where
is the amount of oxygen emission at time
t,
is the pipeline pressure at time
t,
is the number of scheduling periods.
4.2. Constraint conditions
4.2.1. Constraints for the ASUs
In actual operation, the output of an ASU can be adjusted at a limited rate within a certain range, which is shown in
Table 1, and the constraint equation is as follows:
where
are the ASU output at time
and
, respectively,
is the maximum value of the load change rate of ASU,
is the step length of the period.
where
and
are the minimum and maximum oxygen output of ASU, respectively.
4.2.2. Constraints for the pipeline pressure
The pressure
of the gas storage vessels and the pipeline is restricted by the lower-pressure limit
and the upper-pressure limit
. The relevant parameters are shown in
Table 2, and the constraint equation is as follows:
4.2.3. Mass conservation constraints for the oxygen system
The oxygen system needs to satisfy mass conservation, that is, the sum of the total oxygen production of the ASUs minus the oxygen emission, and the oxygen demand is equal to the oxygen storage capacity of the buffer equipment. The constraint equation is as follows:
where
is the oxygen demand of the enterprise,
is the total volume of the gas storage vessels,
is the gas constant,
is the environmental temperature.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Analysis of forecasting results of oxygen demand
The collected field data is divided into 12 groups for forecasting and verification, each group of data contains 165 data points, of which the first 150 data points are used as input data for forecasting, and the last 15 data points are used as verification data for forecast results. Namely, it is equivalent to forecasting the oxygen demand for the next half hour based on 5 hours of historical data.
First, the ARIMA model forecast is performed on the data, and ARIMA (2,1,5) is obtained as the optimal model for time series prediction. Secondly, the GABP model forecast is performed on the data, in which the GA optimization algorithm was set as follows: the genetic algebra is 100, the population size is 50, the crossover probability is 0.4, the mutation probability is 0.3, the number of nodes in the hidden layer of the BP neural network is 18, and the activation function of the hidden layer is a tansig function, the excitation function of the output layer is a purelin function, the learning rate is 0.05, the target error precision is 0.01, and the number of network iteration steps is 5000.
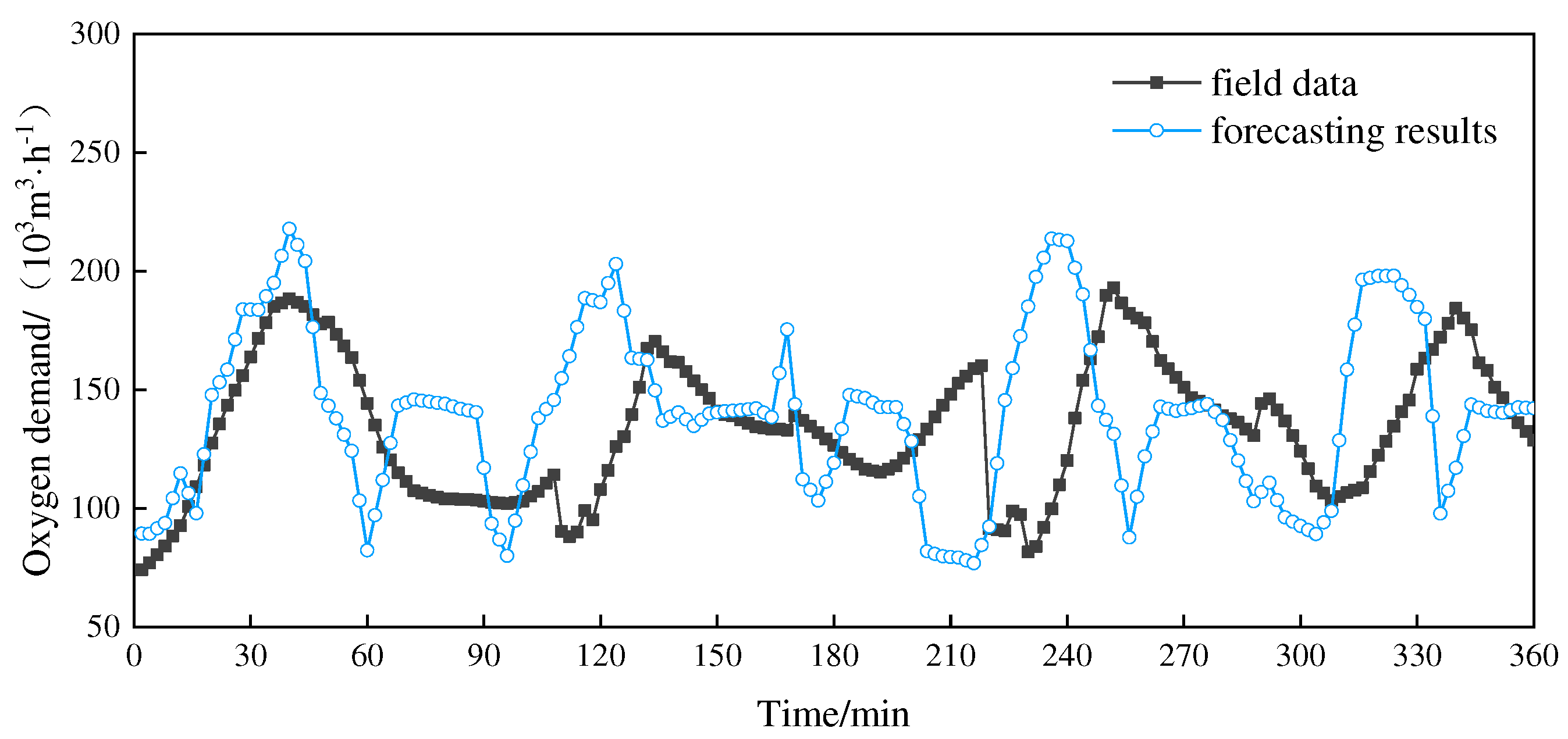
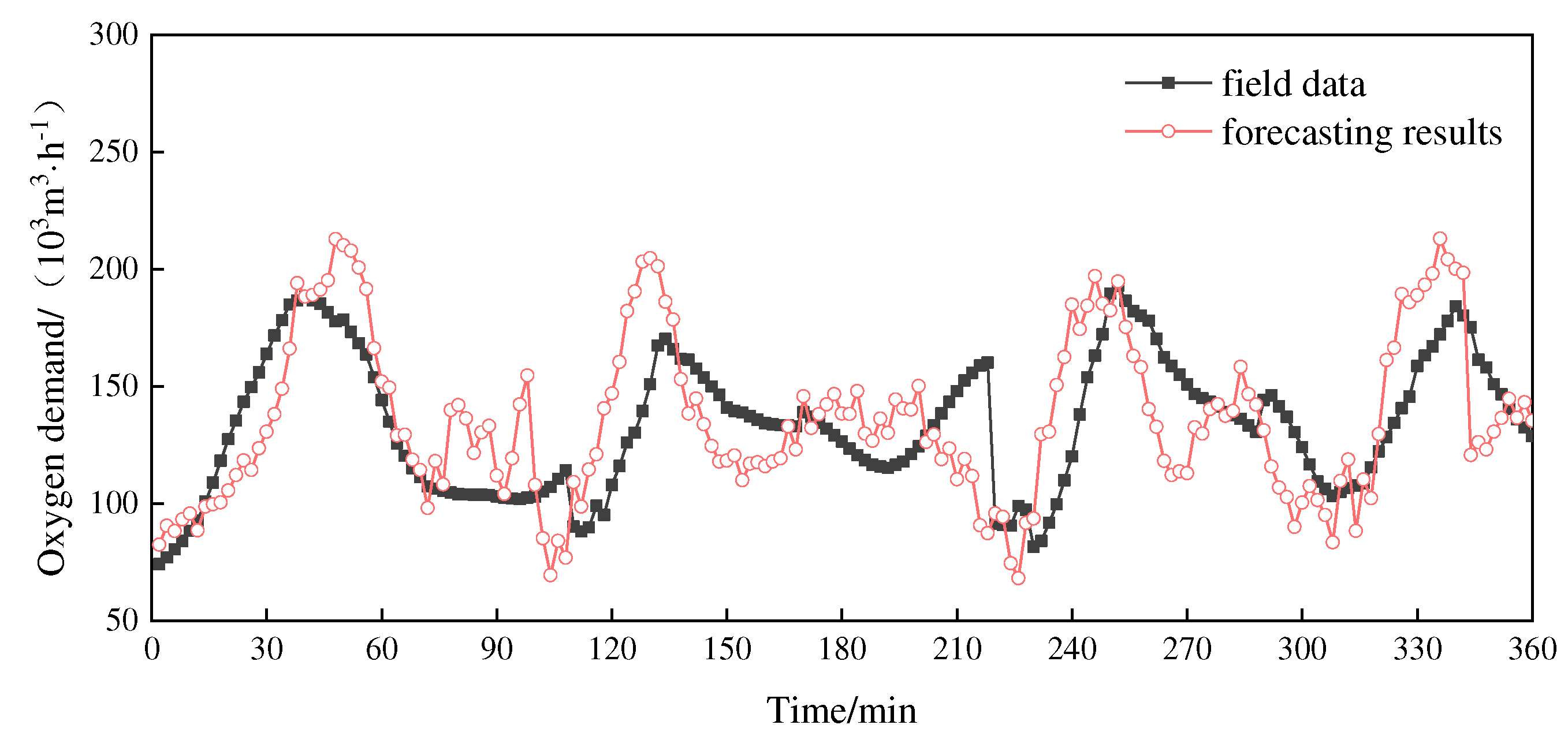
The forecasting results of the ARIMA model and GABP model are shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, respectively.
By comparing
Figure 3 and
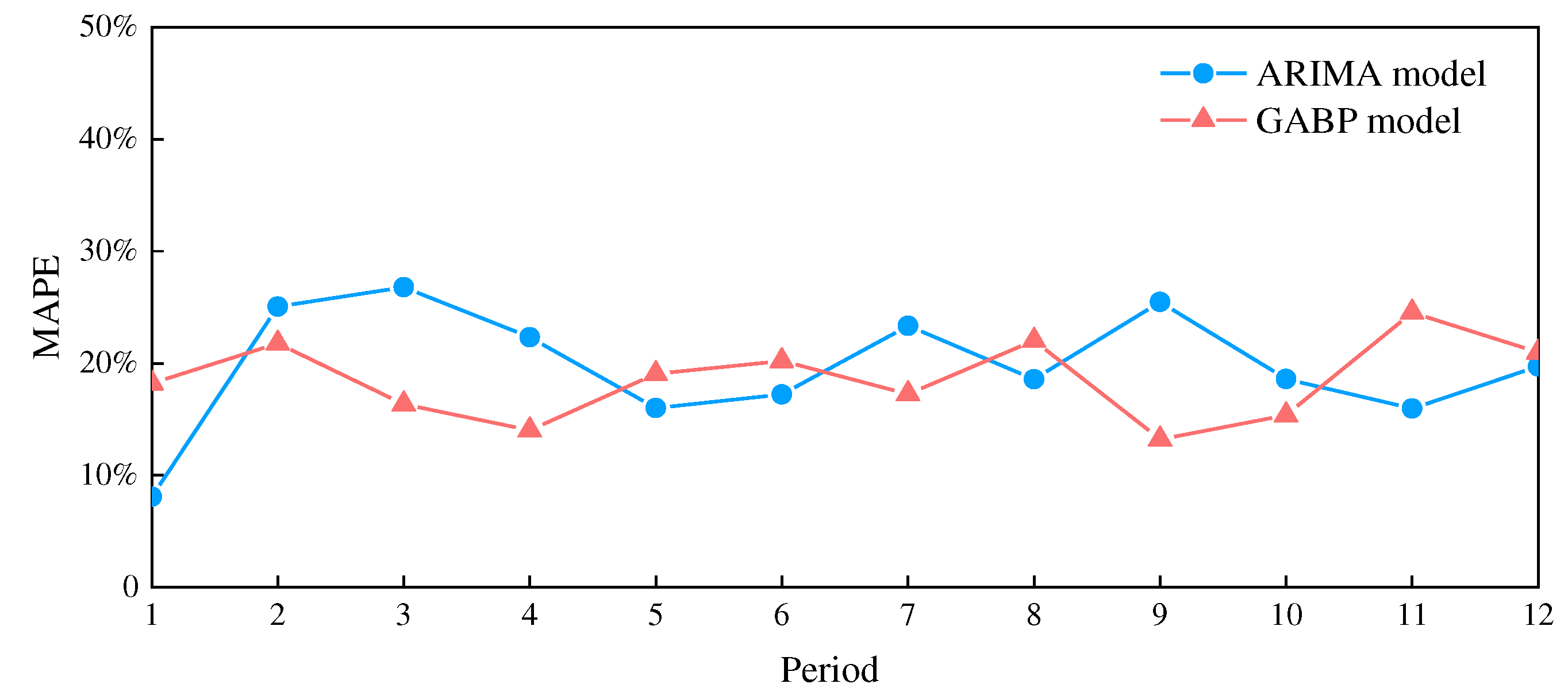
Figure 4, it can be seen that both the ARIMA and GABP models can forecast the changing trend of oxygen demand, but the GABP model is better than the ARIMA model in terms of coincidence with the field data. To quantificationally compare the forecast accuracy of the two models of ARIMA and GABP, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of each of the 12 sets of data is calculated and shown in
Figure 5. The calculation results show that the average values of MAPE of the 12 sets of data of the ARIMA and GABP models were 23.8% and 20.2%, respectively. Therefore, the prediction accuracy of the GABP model is better than that of the ARIMA model.
5.2. Analysis of scheduling results of the oxygen system
Substituting the forecast values of the GABP model in
Section 5.1 as
into the scheduling model, the scheduling of the oxygen system for a future period (fifteen data points, 30 min) can be realized. Through twelve times independent scheduling calculations (twelve periods), twelve sets of scheduling results are obtained, and the scheduling results are compared with the field data in Figs. 6 to 9.
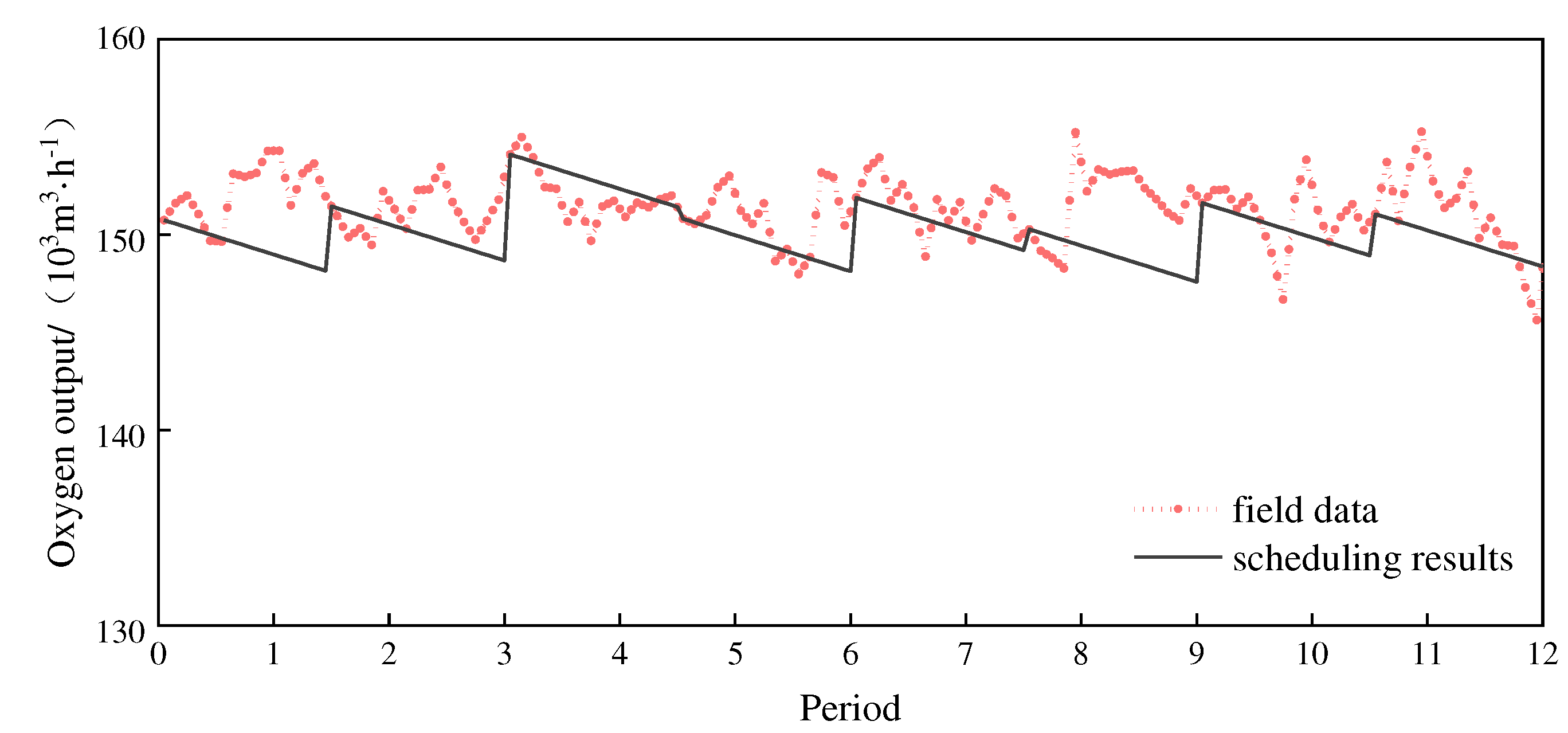
As shown in
Figure 6, the scheduling results of oxygen output of ASUs in each scheduling period are declining, and the slope of the decline is the load change rate of ASU, which shows that under the current case conditions, oxygen is in a state of oversupply. The scheduling results of oxygen output in
Figure 6 are mostly lower than the field data. If the on-site works can perform the load adjustment of ASUs according to the scheduling results, the oxygen output can be reduced. According to the calculation results, the oxygen output of ASUs after scheduling is about 1.38% lower than the field data.
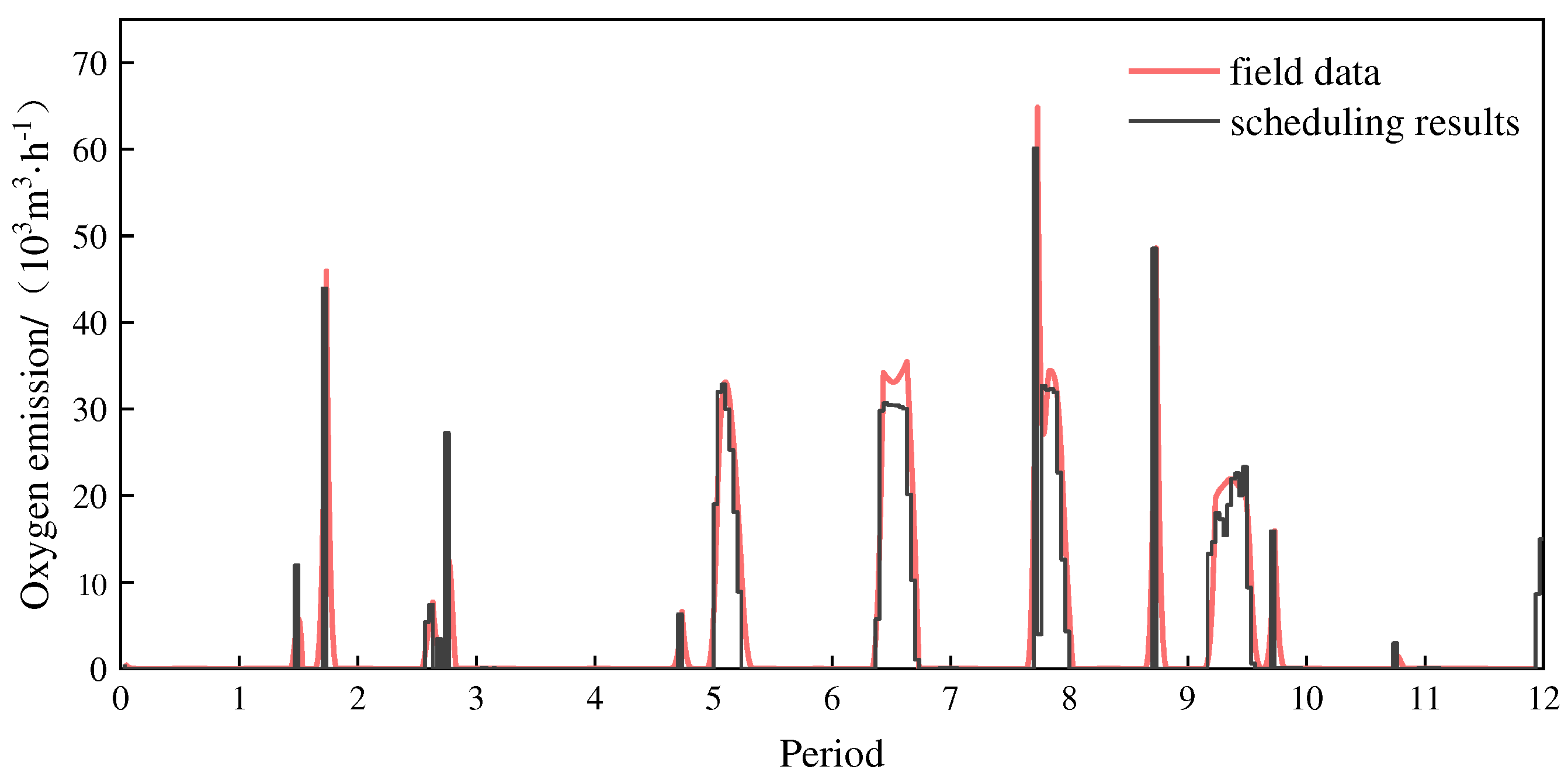
Figure 7 compares the field data and the scheduling results in terms of oxygen emission, which shows that the oxygen emission decreases after scheduling. Calculations show that within the time frame of the case study, the oxygen emission can be reduced by about 6.32% through scheduling.
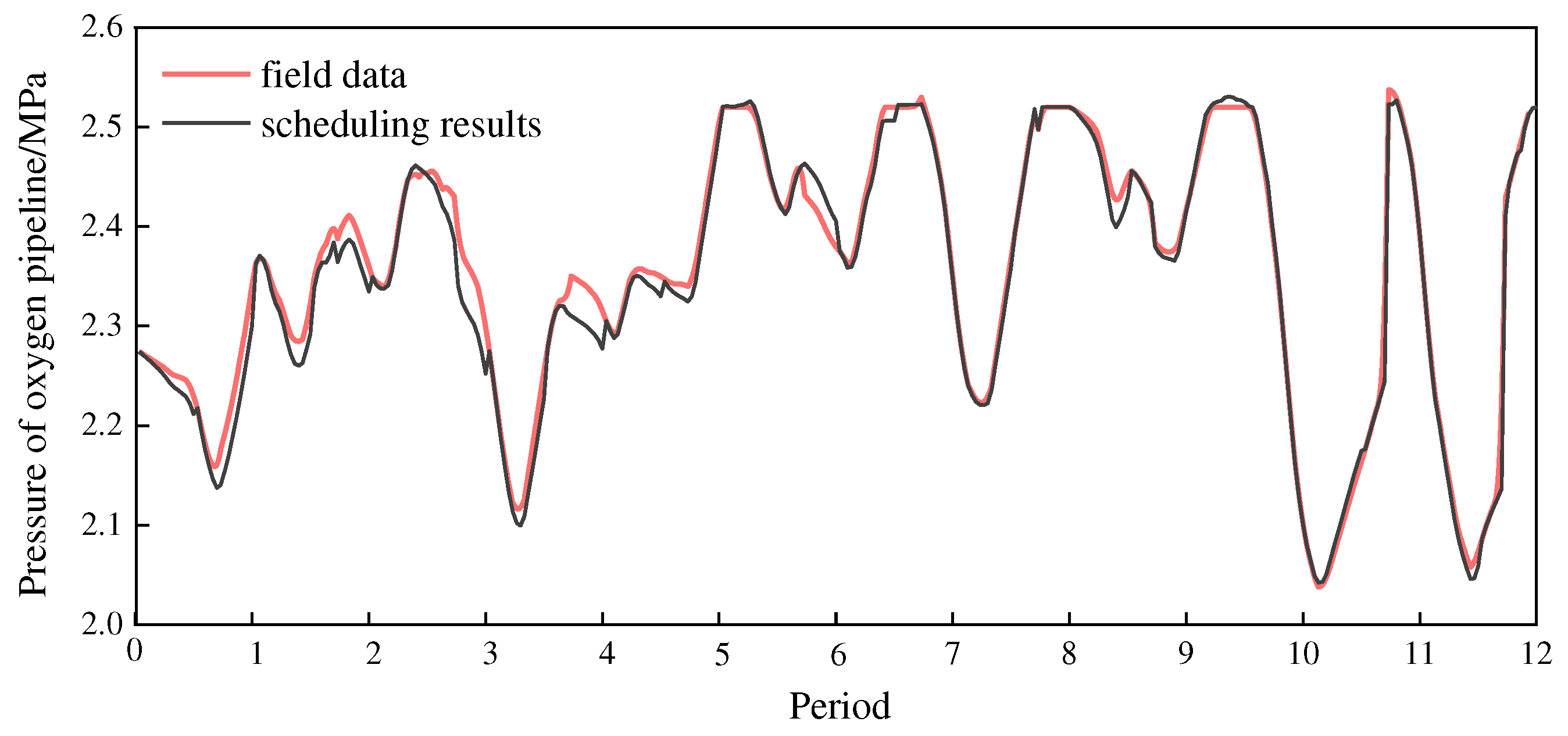
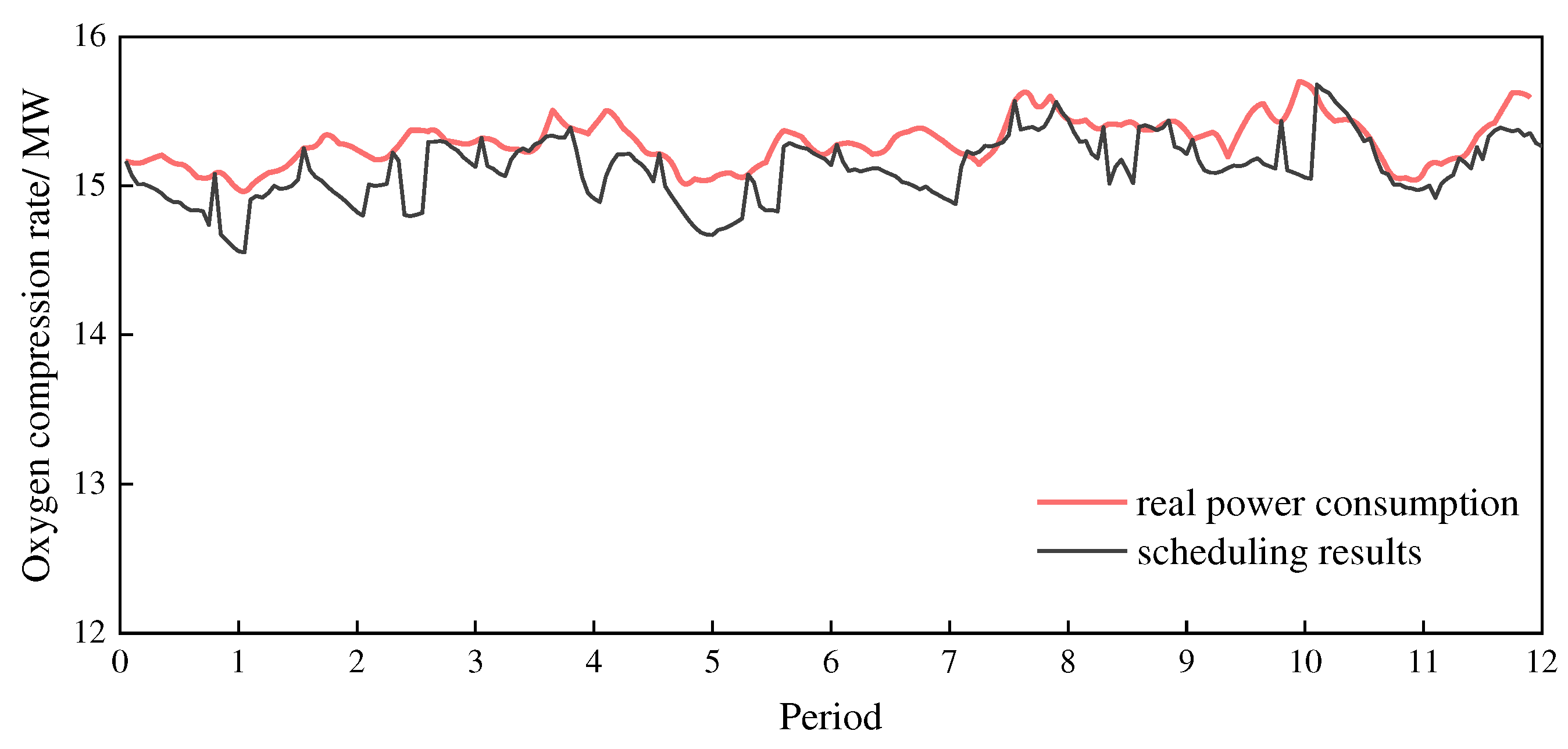
Figure 8 shows the comparison between the scheduling results and the field data in terms of pipeline pressures. The calculation results show that, within the time range of the case study, the pipeline pressure after scheduling is about 0.61% lower than the field data.
The high-pressure oxygen in the pipeline has pressure energy, and the energy consumption required by the system is not only the energy consumption of oxygen separation (the oxygen separation energy consumption of the ASU is usually 0.4 kWh·m
-³) but also the energy consumption of oxygen compression. The compression energy input by the system for the produced oxygen per unit of time is the compression power of oxygen, which is related to the pipeline pressure as well as the oxygen output. For the convenience of comparison, the compression power can be quantified according to the energy consumption equation of multi-stage adiabatic compression, namely:
where
is the compression power of oxygen,
m is the number of compression stages (in this paper, m=3),
n is the adiabatic coefficient,
is the single-stage pressure ratio,
is the ambient pressure,
is the conversion coefficient (
= 0.0000124008).
According to the pressure shown in
Figure 8, the calculated oxygen compression power is shown in
Figure 9. Since the compression power is affected by both the oxygen output and the pipeline pressure, the scheduled compression power has a significant decrease compared with the unscheduled field data. The calculation results show that, within the time range of the case study, the energy consumption of the oxygen compression after the schedule has decreased by about 1.60% compared with the filed data.
Considering the loss of oxygen emission as well as compression energy consumption, the total power consumption of the oxygen system after scheduling is reduced by about 1.38% compared with the filed data. The total annual power consumption of the oxygen system of the case enterprise is about 120 million kWh, so about 16.42 million kWh/year of electricity consumption can be saved through scheduling. Converted according to the electricity price of 0.55 RMB/kWh, optimal scheduling can bring economic benefits of 9.03 million RMB/year to the enterprise.
6. Conclusions
This study researches the optimal scheduling of the oxygen system of a large-scale iron and steel enterprise, an oxygen consumption forecast model for oxygen demand prediction was developed, and an optimal scheduling model for oxygen system scheduling based on the oxygen demand forecast was established. Based on the case study, the following conclusions are obtained:
- (1)
For the forecast of oxygen demand, the prediction accuracy of the GABP model is better than that of the ARIMA model. The case analysis shows that the average values of MAPE for the 12 sets of data of the ARIMA and GABP models are 23.8% and 20.2%, respectively.
- (2)
By comparing the scheduling results and the field data, it was found that after scheduling, the amount of oxygen emission decreased by 6.32%, the pipeline pressure decreased by 0.61%, and the energy consumption of oxygen compression decreased by 1.6%. Considering the loss of oxygen emission and the compression energy consumption, the total power consumption of the oxygen system is reduced by 1.38%, which means an annual saving of about 9.03 million RMB in electricity costs.
This study shows that if the oxygen demand forecast based on the GABP model and the optimal scheduling is carried out, the oxygen emission and the pipeline pressure of the oxygen system in iron and steel enterprises can be significantly reduced, and considerable energy saving and economic benefits can be achieved.
References
- Han Z: Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; et al. A two-stage method for predicting and scheduling energy in an oxygen/nitrogen system of the steel industry[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2016, 52, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W. An optimized oxygen system scheduling with electricity cost consideration in steel industry[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2017, 4(5), 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L. Optimal Shut-Down Policy for Air Separation Units in Integrated Steel Enterprises during a Blast Furnace Blow-Down[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2017, 56(8), 2140–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Tong, L. MILP-based optimization of oxygen distribution system in integrated steel mills[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2016, 93, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; et al. Time series analysis: forecasting and control[M]; John Wiley & Sons, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Su, C.; Yu, J. An optimizing BP neural network algorithm based on genetic algorithm[J]. Artificial intelligence review 2011, 36(2), 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Su, H.; Jing, K. Dam safety monitoring model based on ARIMA-ANN[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University/ Wuhan Daxue Xuebao 2010, 45(5), 585–588. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).