Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
27 September 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Disuse atrophy and the models that can be used to study it
2.1. Space flight
2.2. Bed rest
2.3. Hindlimb suspension
2.4. Unilateral Limb Suspension
2.5. Immobilization
2.6. Denervation
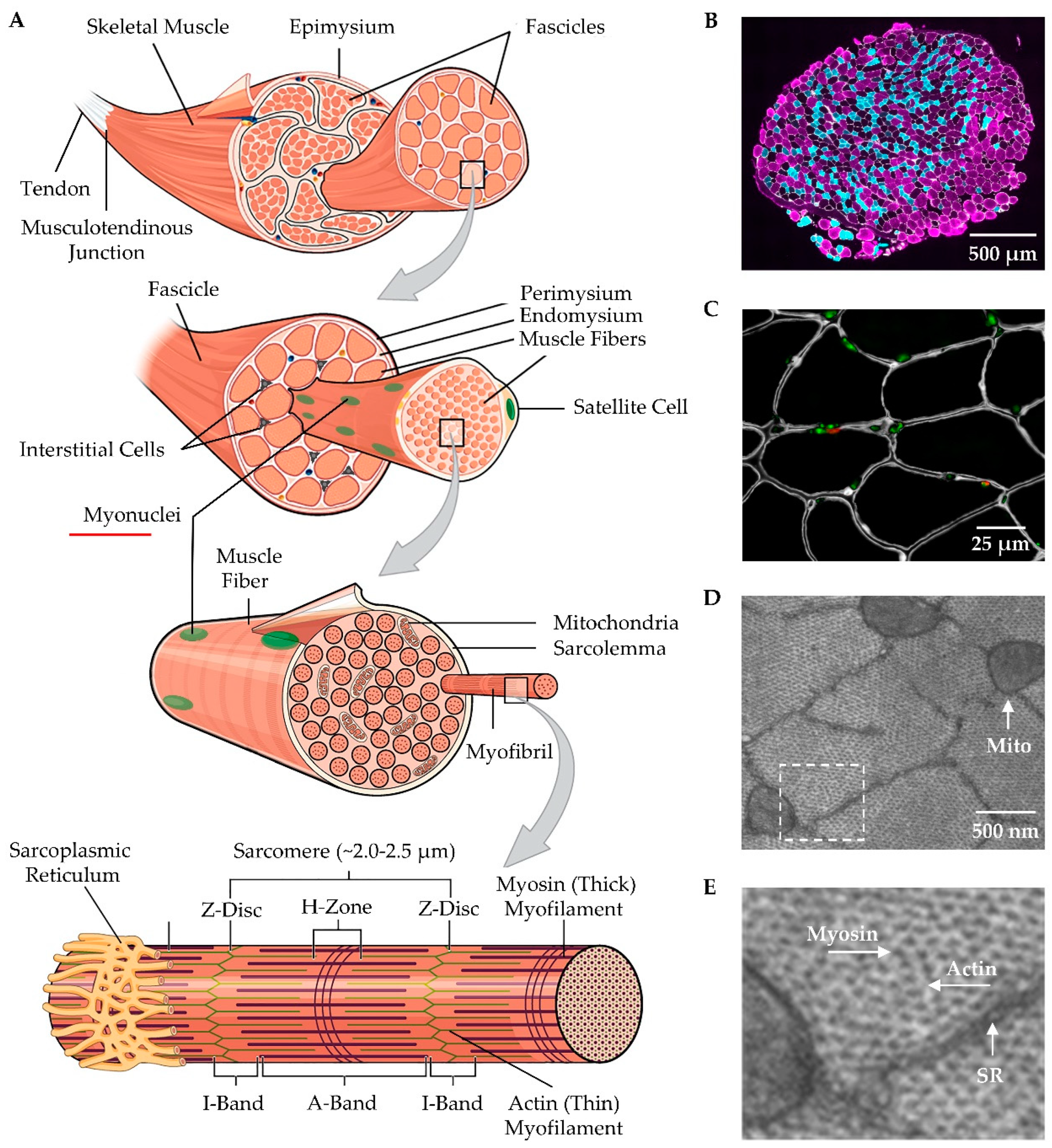
3. Overview of Skeletal Muscle Structure
4. Disuse-Induced Atrophy at the Macroscopic Level
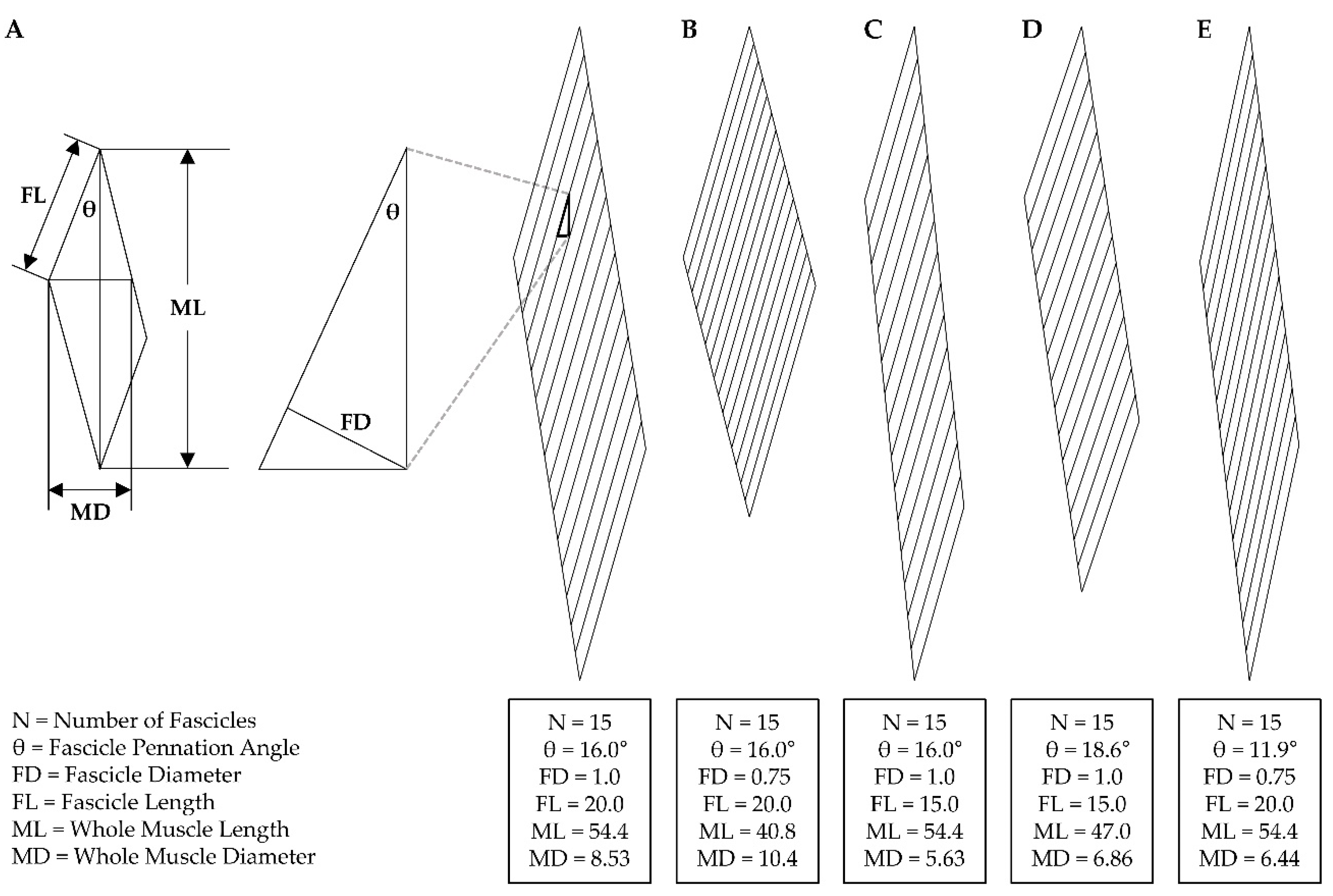
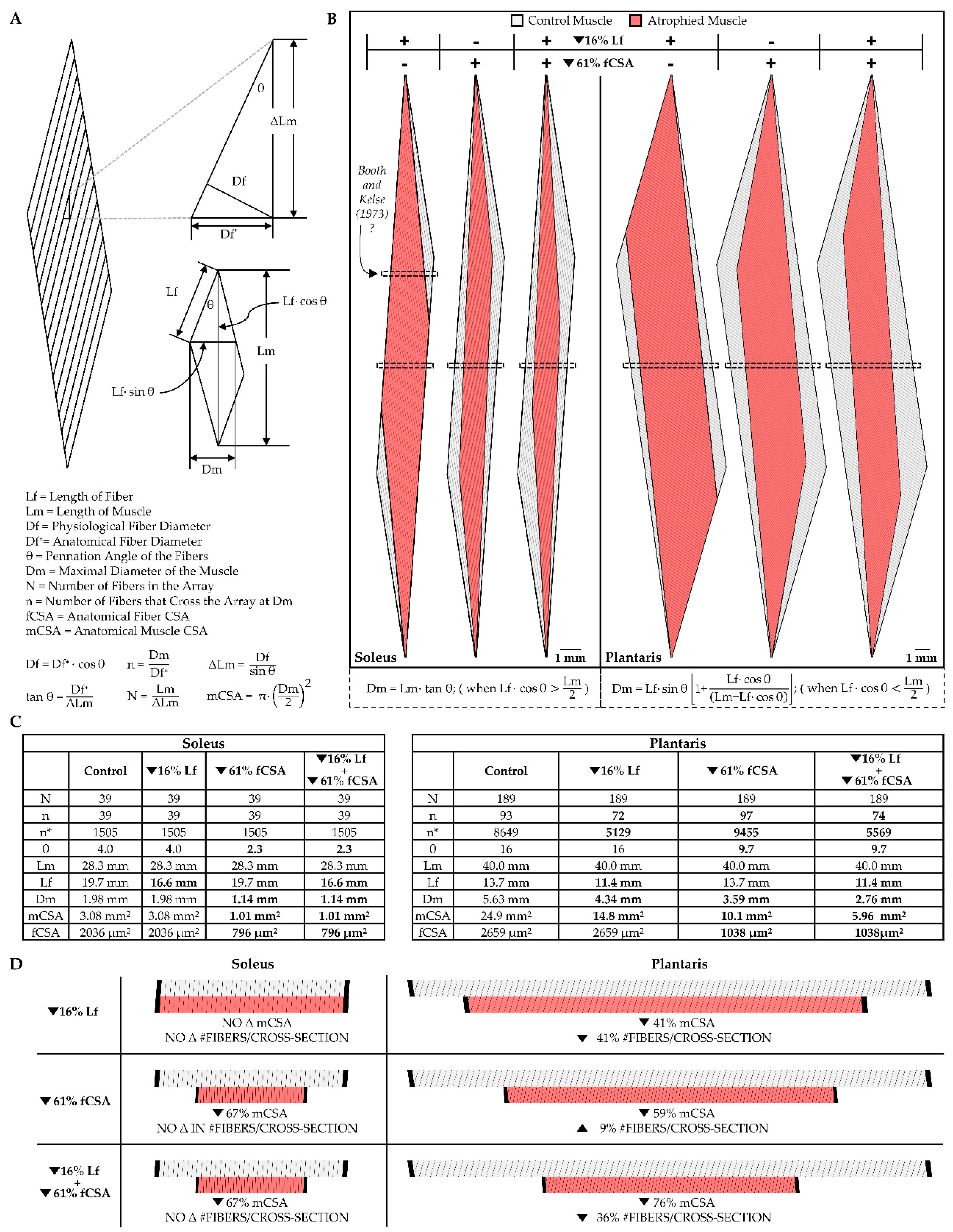
4.1. Whole muscle
4.2. Muscle fascicles
5. Disuse-Induced Atrophy at the Microscopic Level
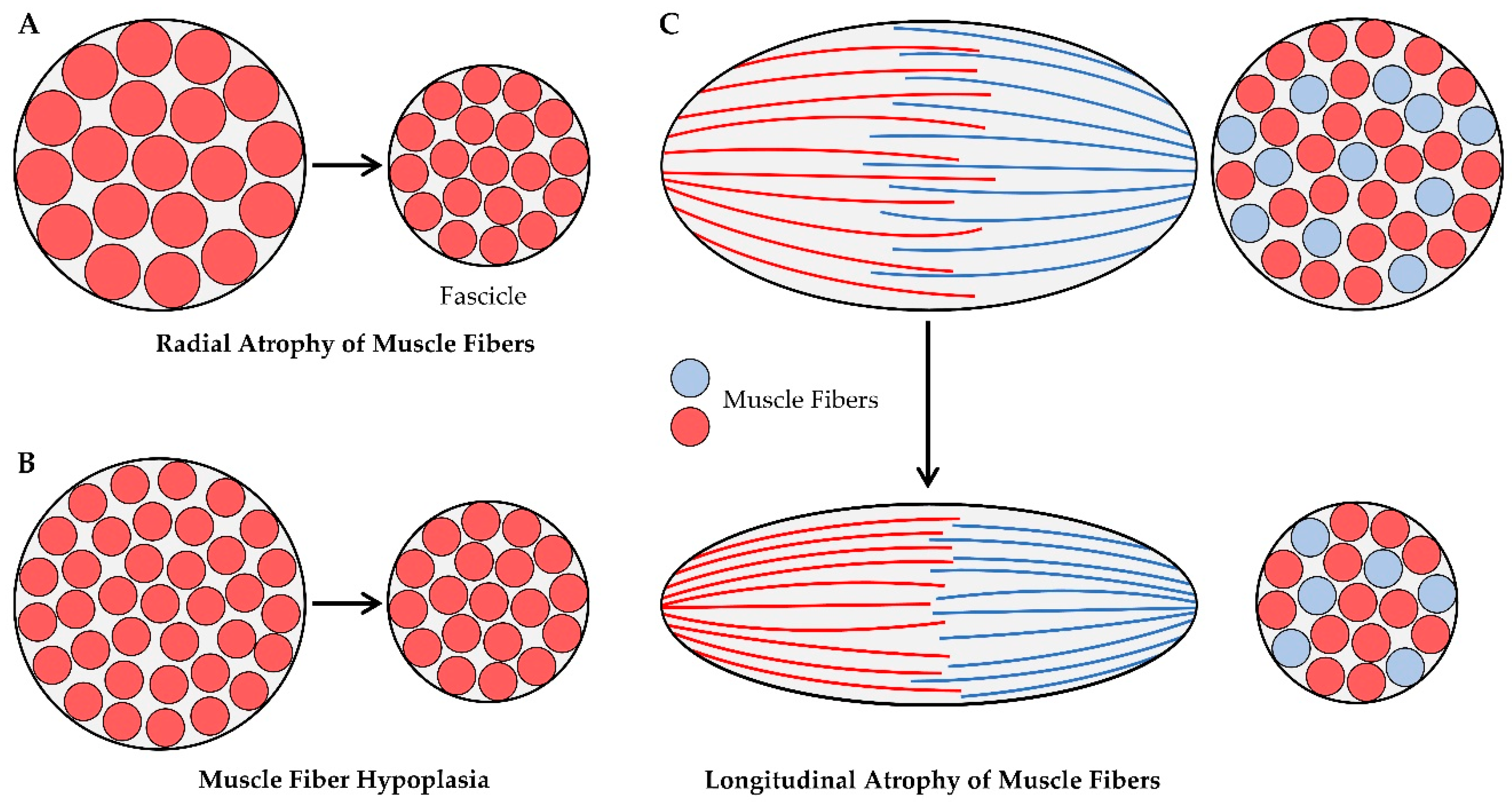
5.1. Longitudinal Atrophy of Fascicles
5.2. Radial Atrophy of Fascicles
5.2.1. Radial Atrophy of Muscle Fibers
5.2.2. Changes in the number of muscle fibers per cross-section
6. Disuse-Induced Atrophy at the Ultrastructural Level
6.1. Longitudinal Atrophy of Muscle Fibers
6.2. Radial Atrophy of Muscle Fibers
6.2.1. Radial Atrophy of Myofibrils
6.2.2. Myofibril Hypoplasia
6.2.3. Mechanisms that might promote the radial atrophy of myofibrils
7. Closing Remarks
Acknowledgements
References
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18-88 yr. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2000, 89, 81-88. [CrossRef]
- Rowland, L.A.; Bal, N.C.; Periasamy, M. The role of skeletal-muscle-based thermogenic mechanisms in vertebrate endothermy. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2015, 90, 1279-1297. [CrossRef]
- Thyfault, J.P.; Bergouignan, A. Exercise and metabolic health: beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1464-1474. [CrossRef]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab 2013, 17, 162-184. [CrossRef]
- Severinsen, M.C.K.; Pedersen, B.K. Muscle-Organ Crosstalk: The Emerging Roles of Myokines. Endocrine reviews 2020, 41, 594-609. [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.K.; Hall, C.B.; Amodu, A.; Sharma, D.; Androga, L.; Hawkins, M. Muscle mass, BMI, and mortality among adults in the United States: A population-based cohort study. PloS one 2018, 13, e0194697. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Dou, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X. Sarcopenia as a predictor of all-cause mortality among older nursing home residents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021252. [CrossRef]
- Srikanthan, P.; Karlamangla, A.S. Relative muscle mass is inversely associated with insulin resistance and prediabetes. Findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2011, 96, 2898-2903. [CrossRef]
- Sizoo, D.; Stam, S.P.; de Heide, L.J.M.; Emous, M.; van Zutphen, T.; van Dijk, P.R.; van Beek, A.P. The association of low muscle mass with prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes in different BMI classes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 195, 110197. [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.R. The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2006, 84, 475-482. [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, S.; Panagiotakos, D.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Haro, J.M.; Pitsavos, C. Skeletal muscle mass in relation to 10 year cardiovascular disease incidence among middle aged and older adults: the ATTICA study. J Epidemiol Community Health 2020, 74, 26-31. [CrossRef]
- Seguin, R.; Nelson, M.E. The benefits of strength training for older adults. American journal of preventive medicine 2003, 25, 141-149. [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.N.; Balagopal, P.; Nair, K.S. Age-related sarcopenia in humans is associated with reduced synthetic rates of specific muscle proteins. J Nutr 1998, 128, 351S-355S. [CrossRef]
- Pahor, M.; Kritchevsky, S. Research hypotheses on muscle wasting, aging, loss of function and disability. J Nutr Health Aging 1998, 2, 97-100.
- Goates, S.; Du, K.; Arensberg, M.B.; Gaillard, T.; Guralnik, J.; Pereira, S.L. Economic Impact of Hospitalizations in US Adults with Sarcopenia. J Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 93-99. [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C. Disuse-induced muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013, 45, 2200-2208. [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.R.; Bamman, M.M. Characterization and regulation of mechanical loading-induced compensatory muscle hypertrophy. Comprehensive Physiology 2012, 2, 2829-2870. [CrossRef]
- Hippocrates. The Genuine Works of Hippocrates; Dover New York, 1868.
- Bellar, A.; Welch, N.; Dasarathy, S. Exercise and physical activity in cirrhosis: opportunities or perils. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2020, 128, 1547-1567. [CrossRef]
- Pina, I.L.; Apstein, C.S.; Balady, G.J.; Belardinelli, R.; Chaitman, B.R.; Duscha, B.D.; Fletcher, B.J.; Fleg, J.L.; Myers, J.N.; Sullivan, M.J.; et al. Exercise and heart failure: A statement from the American Heart Association Committee on exercise, rehabilitation, and prevention. Circulation 2003, 107, 1210-1225. [CrossRef]
- Rausch, V.; Sala, V.; Penna, F.; Porporato, P.E.; Ghigo, A. Understanding the common mechanisms of heart and skeletal muscle wasting in cancer cachexia. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 1. [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S. Cause and management of muscle wasting in chronic liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2016, 32, 159-165. [CrossRef]
- Lavine, K.J.; Sierra, O.L. Skeletal muscle inflammation and atrophy in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 2017, 22, 179-189. [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.P.; Marks, D.L. The regulation of muscle mass by endogenous glucocorticoids. Front Physiol 2015, 6, 12. [CrossRef]
- Vandenburgh, H.; Chromiak, J.; Shansky, J.; Del Tatto, M.; Lemaire, J. Space travel directly induces skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J 1999, 13, 1031-1038. [CrossRef]
- National Research, C.; Division on, E.; Physical, S.; Aeronautics; Space Engineering, B.; Space Studies, B.; Committee for the Decadal Survey on, B.; Physical Sciences in, S. Recapturing a Future for Space Exploration : Life and Physical Sciences Research for a New Era; National Academies Press: Washington, D.C., UNITED STATES, 2012.
- Lee, P.H.U.; Chung, M.; Ren, Z.; Mair, D.B.; Kim, D.H. Factors mediating spaceflight-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2022, 322, C567-C580. [CrossRef]
- Fitts, R.H.; Riley, D.R.; Widrick, J.J. Functional and structural adaptations of skeletal muscle to microgravity. The Journal of experimental biology 2001, 204, 3201-3208. [CrossRef]
- Clement, G.; Lestienne, F. Adaptive modifications of postural attitude in conditions of weightlessness. Exp Brain Res 1988, 72, 381-389. [CrossRef]
- Thornton, W.E., Hoffler, G.W. Rummel, J.A. Anthropometric changes and fluid shifts. Proc. of the Skylab Life Sci. Symp. 1974, Vol. 2.
- Wisdom, K.M.; Delp, S.L.; Kuhl, E. Use it or lose it: multiscale skeletal muscle adaptation to mechanical stimuli. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2015, 14, 195-215. [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, K.W.; Phillips, S.M.; Hornberger, T.A. Identifying the Structural Adaptations that Drive the Mechanical Load-Induced Growth of Skeletal Muscle: A Scoping Review. Cells 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Rivares, C.; Weide, G.; Tilp, M.; Jaspers, R.T. Stimuli for Adaptations in Muscle Length and the Length Range of Active Force Exertion-A Narrative Review. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 742034. [CrossRef]
- Zollner, A.M.; Abilez, O.J.; Bol, M.; Kuhl, E. Stretching skeletal muscle: chronic muscle lengthening through sarcomerogenesis. PloS one 2012, 7, e45661. [CrossRef]
- Hilton, J. On the influence of Mechanical and Physiological Rest in the Treatment of Accidents and Surgical Diseases, and the Diagnostic Value of Pain. Br Foreign Med Chir Rev 1864, 34, 53-58.
- Deitrick, J.E.; Whedon, G.D.; Shorr, E. Effects of immobilization upon various metabolic and physiologic functions of normal men. The American journal of medicine 1948, 4, 3-36. [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.D.; Schneider, V.S.; Evans, H.J.; Pientok, C.; Rowe, R.; Spector, E. Regional changes in muscle mass following 17 weeks of bed rest. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992, 73, 2172-2178. [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.R.; Horstman, A.M.; Stegeman, D.F.; de Haan, A.; Belavy, D.L.; Miokovic, T.; Armbrecht, G.; Felsenberg, D.; Gerrits, K.H. Influence of vibration resistance training on knee extensor and plantar flexor size, strength, and contractile speed characteristics after 60 days of bed rest. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2009, 107, 1789-1798. [CrossRef]
- Hides, J.A.; Belavy, D.L.; Stanton, W.; Wilson, S.J.; Rittweger, J.; Felsenberg, D.; Richardson, C.A. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of trunk muscles during prolonged bed rest. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007, 32, 1687-1692. [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.; Gogia, P.; Schneider, V.; Krebs, J.; Schonfeld, E.; Evans, H. Calf muscle area and strength changes after five weeks of horizontal bed rest. Am J Sports Med 1988, 16, 624-629. [CrossRef]
- Kawano, F.; Ishihara, A.; Stevens, J.L.; Wang, X.D.; Ohshima, S.; Horisaka, M.; Maeda, Y.; Nonaka, I.; Ohira, Y. Tension- and afferent input-associated responses of neuromuscular system of rats to hindlimb unloading and/or tenotomy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004, 287, R76-86. [CrossRef]
- Anzil, A.P.; Sancesario, G.; Massa, R.; Bernardi, G. Myofibrillar disruption in the rabbit soleus muscle after one-week hindlimb suspension. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 358-369. [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.A.; Slocum, G.R.; Bain, J.L.; Sedlak, F.R.; Sowa, T.E.; Mellender, J.W. Rat hindlimb unloading: soleus histochemistry, ultrastructure, and electromyography. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990, 69, 58-66. [CrossRef]
- Morey-Holton, E.R.; Globus, R.K. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: technical aspects. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2002, 92, 1367-1377. [CrossRef]
- Hargens, A.R.; Vico, L. Long-duration bed rest as an analog to microgravity. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2016, 120, 891-903. [CrossRef]
- Ohira, Y. Effects of hindlimb suspension with stretched or shortened muscle length on contractile properties of rat soleus; 2000; Vol. 16, pp. S. 80-87.
- Fujita, N.; Arakawa, T.; Matsubara, T.; Ando, H.; Miki, A. Influence of fixed muscle length and contractile properties on atrophy and subsequent recovery in the rat soleus and plantaris muscles. Archives of Histology and Cytology 2009, 72, 151-163.
- Tesch, P.A.; Lundberg, T.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalo, R. Unilateral lower limb suspension: From subject selection to "omic" responses. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2016, 120, 1207-1214. [CrossRef]
- Hackney, K.J.; Ploutz-Snyder, L.L. Unilateral lower limb suspension: integrative physiological knowledge from the past 20 years (1991-2011). Eur J Appl Physiol 2012, 112, 9-22. [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, N.; Glover, E.I.; Phillips, S.M.; Isfort, R.J.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Sex-based differences in skeletal muscle function and morphology with short-term limb immobilization. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2005, 99, 1085-1092. [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, A.; Jespersen, J.G.; Pingel, J.; Christensen, B.; Sroczynski, N.; Langberg, H.; Kjaer, M.; Schjerling, P. Effects of 2 weeks lower limb immobilization and two separate rehabilitation regimens on gastrocnemius muscle protein turnover signaling and normalization genes. BMC Res Notes 2012, 5, 166. [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.Z.; Drouin, G.; Desrosiers, J.; Trensz, F.; Grenier, G. A novel hindlimb immobilization procedure for studying skeletal muscle atrophy and recovery in mouse. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2009, 106, 2049-2059. [CrossRef]
- You, J.S.; Anderson, G.B.; Dooley, M.S.; Hornberger, T.A. The role of mTOR signaling in the regulation of protein synthesis and muscle mass during immobilization in mice. Disease models & mechanisms 2015, 8, 1059-1069. [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Gregorios, J.; Chou, S.M. Core myofibers and related alterations induced in rats' soleus muscle by immobilization in shortened position. J Neurol Sci 1984, 63, 267-275. [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.; Luco, J.V. CHANGES OF WEIGHT AND NEUROMUSCULAR TRANSMISSION IN MUSCLES OF IMMOBILIZED JOINTS. Journal of Neurophysiology 1944, 7, 245-251. [CrossRef]
- Carraro, U.; Gargiulo, P.; Kern, H. Induced Muscle Fiber Regeneration in Permanent Skeletal Muscle Denervation: Implication for Functional Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Degenerated Muscles in Spinal Cord Injury. J Transl Sci Res 2017, 1.
- Borisov, A.B.; Carlson, B.M. Cell death in denervated skeletal muscle is distinct from classical apoptosis. Anat Rec 2000, 258, 305-318. [CrossRef]
- Dedkov, E.I.; Kostrominova, T.Y.; Borisov, A.B.; Carlson, B.M. Reparative myogenesis in long-term denervated skeletal muscles of adult rats results in a reduction of the satellite cell population. Anat Rec 2001, 263, 139-154. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Harii, K. A regenerative change during muscle adaptation to denervation in rats. J Surg Res 1999, 81, 139-146. [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int 2015, 96, 183-195. [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.A.; Gomez, C.G.; Novak, S.M.; Mi-Mi, L.; Gregorio, C.C. Overview of the Muscle Cytoskeleton. Compr Physiol 2017, 7, 891-944. [CrossRef]
- Lieber, R.L. Skeletal muscle adaptability. I: Review of basic properties. Dev Med Child Neurol 1986, 28, 390-397. [CrossRef]
- Narici, M.; Franchi, M.; Maganaris, C. Muscle structural assembly and functional consequences. J Exp Biol 2016, 219, 276-284. [CrossRef]
- Friederich, J.A.; Brand, R.A. Muscle fiber architecture in the human lower limb. J Biomech 1990, 23, 91-95. [CrossRef]
- Lieber, R.L.; Friden, J. Functional and clinical significance of skeletal muscle architecture. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1647-1666. [CrossRef]
- Biferali, B.; Proietti, D.; Mozzetta, C.; Madaro, L. Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitors Cross-Talk in Skeletal Muscle: The Social Network. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 1074. [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.R.; Baily, J.E.; Chen, W.C.W.; Dar, A.; Gonzalez, Z.N.; Jensen, A.R.; Petrigliano, F.A.; Deb, A.; Henderson, N.C. Skeletal and cardiac muscle pericytes: Functions and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 2017, 171, 65-74. [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, F.S.; Moyle, L.A.; Perdiguero, E. Muscle Interstitial Cells: A Brief Field Guide to Non-satellite Cell Populations in Skeletal Muscle. Methods Mol Biol 2017, 1556, 129-147. [CrossRef]
- Murach, K.A.; Fry, C.S.; Kirby, T.J.; Jackson, J.R.; Lee, J.D.; White, S.H.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E.; McCarthy, J.J.; Peterson, C.A. Starring or Supporting Role? Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Fiber Size Regulation. Physiology (Bethesda) 2018, 33, 26-38. [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, J.D.; Sale, D.G.; Elder, G.C.; Sutton, J.R. Muscle ultrastructural characteristics of elite powerlifters and bodybuilders. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 1982, 48, 117-126. [CrossRef]
- Seiden, D. Quantitative analysis of muscle cell changes in compensatory hypertrophy and work-induced hypertrophy. Am J Anat 1976, 145, 459-465. [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, T.J.; Lieber, R.L. Sarcomere length operating range of vertebrate muscles during movement. J Exp Biol 2001, 204, 1529-1536. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.; Huxley, A.F.; Julian, F. The variation in isometric tension with sarcomere length in vertebrate muscle fibres. The Journal of physiology 1966, 184, 170-192. [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, T.J.; Fingado, B.; Baron, S.; Lieber, R.L. Relationship between muscle fiber types and sizes and muscle architectural properties in the mouse hindlimb. Journal of morphology 1994, 221, 177-190. [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.; Huxley, H.E. Structural basis of the cross-striations in muscle. Nature 1953, 172, 530-532. [CrossRef]
- Huxley, A.F.; Niedergerke, R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature 1954, 173, 971-973. [CrossRef]
- Huxley, H.; Hanson, J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature 1954, 173, 973-976. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Green, W.T. Lengths of the femur and the tibia; norms derived from orthoroentgenograms of children from 5 years of age until epiphysial closure. Am J Dis Child (1911) 1948, 75, 279-290. [CrossRef]
- Beaucage, K.L.; Pollmann, S.I.; Sims, S.M.; Dixon, S.J.; Holdsworth, D.W. Quantitative in vivo micro-computed tomography for assessment of age-dependent changes in murine whole-body composition. Bone Rep 2016, 5, 70-80. [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.N.; Harmison, C.R. Growth, disease, and aging in the rat. J Gerontol 1957, 12, 370-377. [CrossRef]
- Spector, S.; Simard, C.; Fournier, M.; Sternlicht, E.; Edgerton, V. Architectural alterations of rat hind-limb skeletal muscles immobilized at different lengths. Experimental neurology 1982, 76, 94-110. [CrossRef]
- Witzmann, F.A.; Kim, D.; Fitts, R.H. Hindlimb immobilization: length-tension and contractile properties of skeletal muscle. Journal of applied physiology 1982, 53, 335-345. [CrossRef]
- Gossman, M.R.; Rose, S.J.; Sahrmann, S.A.; Katholi, C.R. Length and circumference measurements in one-joint and multijoint muscles in rabbits after immobilization. Physical therapy 1986, 66, 516-520. [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, E.; Gomes, A.; França, C.; Oishi, J.; Salvini, T. Effect of passive stretching on the immobilized soleus muscle fiber morphology. Brazilian journal of medical and biological research 2004, 37, 1853-1861. [CrossRef]
- Tesch, P.A.; Berg, H.E.; Bring, D.; Evans, H.J.; LeBlanc, A.D. Effects of 17-day spaceflight on knee extensor muscle function and size. European journal of applied physiology 2005, 93, 463-468. [CrossRef]
- Sandonà, D.; Desaphy, J.-F.; Camerino, G.M.; Bianchini, E.; Ciciliot, S.; Danieli-Betto, D.; Dobrowolny, G.; Furlan, S.; Germinario, E.; Goto, K. Adaptation of mouse skeletal muscle to long-term microgravity in the MDS mission. PloS one 2012, 7, e33232. [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.; Berry, I.; Manelfe, C. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lower limb muscles during bed rest--a microgravity simulation model. Aviation, space, and environmental medicine 1993, 64, 212-218.
- Ferretti, G.; Antonutto, G.; Denis, C.; Hoppeler, H.; Minetti, A.E.; Narici, M.V.; Desplanches, D. The interplay of central and peripheral factors in limiting maximal O2 consumption in man after prolonged bed rest. The Journal of physiology 1997, 501, 677. [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.R.; Stegeman, D.F.; Gerrits, K.; Paalman, M.; Rittweger, J.; Felsenberg, D.; De Haan, A. Strength, size and activation of knee extensors followed during 8 weeks of horizontal bed rest and the influence of a countermeasure. European journal of applied physiology 2006, 97, 706-715. [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.E.; Eiken, O.; Miklavcic, L.; Mekjavic, I.B. Hip, thigh and calf muscle atrophy and bone loss after 5-week bedrest inactivity. European journal of applied physiology 2007, 99, 283-289. [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.R.; Horstman, A.M.; Stegeman, D.F.; De Haan, A.; Belavý, D.L.; Miokovic, T.; Armbrecht, G.; Felsenberg, D.; Gerrits, K.H. Influence of vibration resistance training on knee extensor and plantar flexor size, strength, and contractile speed characteristics after 60 days of bed rest. Journal of applied physiology 2009, 107, 1789-1798. [CrossRef]
- Miokovic, T.; Armbrecht, G.; Felsenberg, D.; Belavý, D.L. Heterogeneous atrophy occurs within individual lower limb muscles during 60 days of bed rest. Journal of Applied Physiology 2012, 113, 1545-1559. [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.; Clément, G.; Linnarsson, D.; Paloski, W.; Wuyts, F.; Zange, J.; Frings-Meuthen, P.; Johannes, B.; Shushakov, V.; Grunewald, M. Musculoskeletal effects of 5 days of bed rest with and without locomotion replacement training. European journal of applied physiology 2015, 115, 727-738. [CrossRef]
- Dirks, M.L.; Wall, B.T.; van de Valk, B.; Holloway, T.M.; Holloway, G.P.; Chabowski, A.; Goossens, G.H.; van Loon, L.J. One week of bed rest leads to substantial muscle atrophy and induces whole-body insulin resistance in the absence of skeletal muscle lipid accumulation. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2862-2875. [CrossRef]
- Liphardt, A.M.; Bolte, V.; Eckstein, F.; Wirth, W.; Brüggemann, G.P.; Niehoff, A. Response of thigh muscle cross-sectional area to 21-days of bed rest with exercise and nutrition countermeasures. Translational Sports Medicine 2020, 3, 93-106. [CrossRef]
- Smeuninx, B.; Elhassan, Y.S.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Sapey, E.; Rushton, A.B.; Edwards, S.J.; Morgan, P.T.; Philp, A.; Brook, M.S.; Gharahdaghi, N. The effect of short-term exercise prehabilitation on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and atrophy during bed rest in older men. Journal of cachexia, sarcopenia and muscle 2021, 12, 52-69. [CrossRef]
- Franchi, M.V.; Sarto, F.; Simunič, B.; Pišot, R.; Narici, M.V. Early Changes of Hamstrings Morphology and Contractile Properties During 10 Days of Complete Inactivity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2022.
- Hather, B.M.; Adams, G.R.; Tesch, P.A.; Dudley, G.A. Skeletal muscle responses to lower limb suspension in humans. Journal of applied physiology 1992, 72, 1493-1498. [CrossRef]
- De Boer, M.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Seynnes, O.R.; Rennie, M.J.; Narici, M.V. Time course of muscular, neural and tendinous adaptations to 23 day unilateral lower-limb suspension in young men. The Journal of physiology 2007, 583, 1079-1091.
- Abadi, A.; Glover, E.I.; Isfort, R.J.; Raha, S.; Safdar, A.; Yasuda, N.; Kaczor, J.J.; Melov, S.; Hubbard, A.; Qu, X. Limb immobilization induces a coordinate down-regulation of mitochondrial and other metabolic pathways in men and women. PloS one 2009, 4, e6518. [CrossRef]
- Vandenborne, K.; Elliott, M.A.; Walter, G.A.; Abdus, S.; Okereke, E.; Shaffer, M.; Tahernia, D.; Esterhai, J.L. Longitudinal study of skeletal muscle adaptations during immobilization and rehabilitation. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 1998, 21, 1006-1012.
- Hespel, P.; Op't Eijnde, B.; Leemputte, M.V.; Ursø, B.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Labarque, V.; Dymarkowski, S.; Hecke, P.V.; Richter, E.A. Oral creatine supplementation facilitates the rehabilitation of disuse atrophy and alters the expression of muscle myogenic factors in humans. The Journal of physiology 2001, 536, 625-633. [CrossRef]
- Thom, J.; Thompson, M.; Ruell, P.; Bryant, G.; Fonda, J.; Harmer, A.; De Jonge, X.J.; Hunter, S. Effect of 10-day cast immobilization on sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium regulation in humans. Acta physiologica scandinavica 2001, 172, 141-147. [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, N.; Glover, E.I.; Phillips, S.M.; Isfort, R.J.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Sex-based differences in skeletal muscle function and morphology with short-term limb immobilization. Journal of applied physiology 2005, 99, 1085-1092. [CrossRef]
- Psatha, M.; Wu, Z.; Gammie, F.M.; Ratkevicius, A.; Wackerhage, H.; Lee, J.H.; Redpath, T.W.; Gilbert, F.J.; Ashcroft, G.P.; Meakin, J.R. A longitudinal MRI study of muscle atrophy during lower leg immobilization following ankle fracture. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2012, 35, 686-695. [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.T.; Dirks, M.L.; Snijders, T.; Senden, J.M.; Dolmans, J.; Van Loon, L.J. Substantial skeletal muscle loss occurs during only 5 days of disuse. Acta physiologica 2014, 210, 600-611. [CrossRef]
- Kilroe, S.P.; Fulford, J.; Jackman, S.R.; Van Loon, L.J.; Wall, B.T. Temporal muscle-specific disuse atrophy during one week of leg immobilization. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, L.C.; Faulkner, J.A.; Hyatt, G.J. Estimation of number of fibers in guinea pig skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol 1974, 37, 259-264. [CrossRef]
- Reeves, N.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Ferretti, G.; Narici, M.V. Influence of simulated microgravity on human skeletal muscle architecture and function. In Proceedings of Life in Space for Life on Earth; pp. 373-374.
- De Boer, M.D.; Seynnes, O.R.; Di Prampero, P.E.; Pišot, R.; Mekjavić, I.B.; Biolo, G.; Narici, M.V. Effect of 5 weeks horizontal bed rest on human muscle thickness and architecture of weight bearing and non-weight bearing muscles. European journal of applied physiology 2008, 104, 401-407.
- Koryak, Y.A. Architectural and functional specifics of the human triceps surae muscle in vivo and its adaptation to microgravity. Journal of applied physiology 2019, 126, 880-893. [CrossRef]
- Sarto, F.; Monti, E.; Šimunič, B.; Pišot, R.; Narici, M.V.; Franchi, M.V. Changes in Biceps Femoris Long Head Fascicle Length after 10-d Bed Rest Assessed with Different Ultrasound Methods. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2021, 53, 1529-1536.
- Campbell, E.-L.; Seynnes, O.R.; Bottinelli, R.; McPhee, J.S.; Atherton, P.; Jones, D.; Butler-Browne, G.; Narici, M.V. Skeletal muscle adaptations to physical inactivity and subsequent retraining in young men. Biogerontology 2013, 14, 247-259. [CrossRef]
- Seynnes, O.R.; Maganaris, C.N.; De Boer, M.D.; Di Prampero, P.E.; Narici, M.V. Early structural adaptations to unloading in the human calf muscles. Acta physiologica 2008, 193, 265-274. [CrossRef]
- Narici, M.; Cerretelli, P. Changes in human muscle architecture in disuse-atrophy evaluated by ultrasound imaging. Journal of gravitational physiology: a journal of the International Society for Gravitational Physiology 1998, 5, P73-74.
- Cary, D.; Jacques, A.; Briffa, K. Examining relationships between sleep posture, waking spinal symptoms and quality of sleep: A cross sectional study. PloS one 2021, 16, e0260582. [CrossRef]
- Tetley, M. Instinctive sleeping and resting postures: an anthropological and zoological approach to treatment of low back and joint pain. BMJ 2000, 321, 1616-1618. [CrossRef]
- Skarpsno, E.S.; Mork, P.J.; Nilsen, T.I.L.; Holtermann, A. Sleep positions and nocturnal body movements based on free-living accelerometer recordings: association with demographics, lifestyle, and insomnia symptoms. Nat Sci Sleep 2017, 9, 267-275. [CrossRef]
- Cary, D.; Collinson, R.; Sterling, M.; Briffa, K. Examining the validity and reliability of a portable sleep posture assessment protocol, using infrared cameras, under a variety of light and bed cover situations in the home environment. Work 2019, 63, 291-298. [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.C. Muscle length affects the architecture and pattern of innervation differently in leg muscles of mouse, guinea pig, and rabbit compared to those of human and monkey muscles. The Anatomical Record: An Official Publication of the American Association of Anatomists 2001, 262, 301-309.
- Paul, A.C.; Rosenthal, N. Different modes of hypertrophy in skeletal muscle fibers. The Journal of cell biology 2002, 156, 751-760. [CrossRef]
- Loeb, G.; Pratt, C.; Chanaud, C.; Richmond, F. Distribution and innervation of short, interdigitated muscle fibers in parallel-fibered muscles of the cat hindlimb. journal of Morphology 1987, 191, 1-15.
- Gans, C.; Loeb, G.E.; De Vree, F. Architecture and consequent physiological properties of the semitendinosus muscle in domestic goats. journal of Morphology 1989, 199, 287-297. [CrossRef]
- Heron, M.I.; Richmond, F.J. In-series fiber architecture in long human muscles. Journal of Morphology 1993, 216, 35-45. [CrossRef]
- Richmond, F.; MacGillis, D.; Scott, D. Muscle-fiber compartmentalization in cat splenius muscles. Journal of Neurophysiology 1985, 53, 868-885. [CrossRef]
- Tabary, J.; Tabary, C.; Tardieu, C.; Tardieu, G.; Goldspink, G. Physiological and structural changes in the cat's soleus muscle due to immobilization at different lengths by plaster casts. The Journal of physiology 1972, 224, 231-244.
- Wang, X.; Kawano, F.; Matsuoka, Y.; Fukunaga, K.; Terada, M.; Sudoh, M.; Ishihara, A.; Ohira, Y. Mechanical load-dependent regulation of satellite cell and fiber size in rat soleus muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2006, 290, C981-C989. [CrossRef]
- Widrick, J.J.; Maddalozzo, G.F.; Hu, H.; Herron, J.C.; Iwaniec, U.T.; Turner, R.T. Detrimental effects of reloading recovery on force, shortening velocity, and power of soleus muscles from hindlimb-unloaded rats. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 2008, 295, R1585-R1592. [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.B.; Peters, D.; Jordan, K.A.; Milner, D.J.; Fridén, J.; Capetanaki, Y.; Lieber, R.L. Sarcomere number regulation maintained after immobilization in desmin-null mouse skeletal muscle. Journal of Experimental Biology 2001, 204, 1703-1710. [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.S.; Passadore, M.D.; Gasparetti, A.L.; Bibancos, T.; Prada, P.O.; Furukawa, L.L.; Furukawa, L.N.; Fukui, R.T.; Casarini, D.E.; Saad, M.J.; et al. High- or low-salt diet from weaning to adulthood: effect on body weight, food intake and energy balance in rats. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2006, 16, 148-155. [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.A.; Bariteau, J.T.; Loomis, R.M.; Strauss, J.A.; Damron, T.A. Ontogeny of skeletal maturation in the juvenile rat. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2008, 291, 283-292. [CrossRef]
- Wickiewicz, T.L.; Roy, R.R.; Powell, P.L.; Edgerton, V.R. Muscle architecture of the human lower limb. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® 1983, 179, 275-283.
- Ward, S.R.; Eng, C.M.; Smallwood, L.H.; Lieber, R.L. Are current measurements of lower extremity muscle architecture accurate? Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2009, 467, 1074-1082. [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, V.; Zhou, M.; Ohira, Y.; Klitgaard, H.; Jiang, B.; Bell, G.; Harris, B.; Saltin, B.; Gollnick, P.; Roy, R. Human fiber size and enzymatic properties after 5 and 11 days of spaceflight. Journal of Applied Physiology 1995, 78, 1733-1739. [CrossRef]
- Widrick, J.J.; Knuth, S.T.; Norenberg, K.M.; Romatowski, J.; Bain, J.L.; Riley, D.A.; Karhanek, M.; Trappe, S.; Trappe, T.A.; Costill, D. Effect of a 17 day spaceflight on contractile properties of human soleus muscle fibres. Journal of Physiology 1999. [CrossRef]
- Belozerova, I.; Nemirovskaya, T.; Shenkman, B.; Kozlovskaya, I. Characteristic of changes in the structure and metabolism of the vastus lateralis muscles in monkeys after space flight. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2003, 33, 735-740. [CrossRef]
- Fitts, R.; Trappe, S.; Costill, D.; Gallagher, P.M.; Creer, A.C.; Colloton, P.; Peters, J.R.; Romatowski, J.; Bain, J.; Riley, D.A. Prolonged space flight-induced alterations in the structure and function of human skeletal muscle fibres. The Journal of physiology 2010, 588, 3567-3592. [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Li, J.; Spieker, A.; Spatz, J.; Ellman, R.; Ferguson, V.; Bateman, T.; Rosen, G.; Bouxsein, M.; Rutkove, S. Spaceflight and hind limb unloading induce similar changes in electrical impedance characteristics of mouse gastrocnemius muscle. Journal of musculoskeletal & neuronal interactions 2013, 13, 405.
- Berg, H.; Larsson, L.; Tesch, P. Lower limb skeletal muscle function after 6 wk of bed rest. Journal of applied physiology 1997.
- Yamashita-Goto, K.; Okuyama, R.; Honda, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Yamada, T.; Nonaka, I.; Ohira, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Maximal and submaximal forces of slow fibers in human soleus after bed rest. Journal of Applied Physiology 2001, 91, 417-424. [CrossRef]
- Arentson-Lantz, E.J.; English, K.L.; Paddon-Jones, D.; Fry, C.S. Fourteen days of bed rest induces a decline in satellite cell content and robust atrophy of skeletal muscle fibers in middle-aged adults. Journal of applied physiology 2016, 120, 965-975. [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Longa, E.; Cannavino, J.; Seynnes, O.; de Vito, G.; McPhee, J.; Narici, M.; Pellegrino, M.A.; Bottinelli, R. Human skeletal muscle fibre contractile properties and proteomic profile: adaptations to 3 weeks of unilateral lower limb suspension and active recovery. The Journal of Physiology 2015, 593, 5361-5385. [CrossRef]
- Desplanches, D.; Kayar, S.; Sempore, B.; Flandrois, R.; Hoppeler, H. Rat soleus muscle ultrastructure after hindlimb suspension. Journal of Applied Physiology 1990, 69, 504-508. [CrossRef]
- Mortreux, M.; Rosa-Caldwell, M.E.; Stiehl, I.D.; Sung, D.M.; Thomas, N.T.; Fry, C.S.; Rutkove, S.B. Hindlimb suspension in Wistar rats: Sex-based differences in muscle response. Physiological Reports 2021, 9, e15042. [CrossRef]
- Haida, N.; Fowler Jr, W.M.; Abresch, R.T.; Larson, D.B.; Sharman, R.B.; Taylor, R.G.; Entrikin, R.K. Effect of hind-limb suspension on young and adult skeletal muscle: I. normal mice. Experimental neurology 1989, 103, 68-76.
- Murakami, T.; Hijikata, T.; Yorifuji, H. Staging of disuse atrophy of skeletal muscles on immunofluorescence microscopy. Anatomical science international 2008, 83, 68-76. [CrossRef]
- Nicks, D.K.; Beneke, W.M.; Key, R.M.; Timson, B.F. Muscle fibre size and number following immobilisation atrophy. Journal of anatomy 1989, 163, 1.
- Gomes, A.; Coutinho, E.; França, C.; Polonio, J.; Salvini, T. Effect of one stretch a week applied to the immobilized soleus muscle on rat muscle fiber morphology. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 2004, 37, 1473-1480. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.; Cornachione, A.; Salvini, T.F.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Morphological effects of two protocols of passive stretch over the immobilized rat soleus muscle. Journal of Anatomy 2007, 210, 328-335. [CrossRef]
- Booth, F.; Kelso, J. Effect of hind-limb immobilization on contractile and histochemical properties of skeletal muscle. Pfluegers Archiv 1973, 342, 231-238. [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, D.; Stolov, W.; Hardy, R. Muscle fiber number in immobilization atrophy. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation 1977, 58, 423-426.
- Boyes, G.; Johnston, I. Muscle fibre composition of rat vastus intermedius following immobilisation at different muscle lengths. Pfluegers Archiv 1979, 381, 195-200.
- Templeton, G.; Sweeney, H.; Timson, B.F.; Padalino, M.; Dudenhoeffer, G. Changes in fiber composition of soleus muscle during rat hindlimb suspension. Journal of applied physiology 1988, 65, 1191-1195. [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.M.; Smallwood, L.H.; Rainiero, M.P.; Lahey, M.; Ward, S.R.; Lieber, R.L. Scaling of muscle architecture and fiber types in the rat hindlimb. Journal of Experimental Biology 2008, 211, 2336-2345. [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Muller-Delp, J.M.; Majors, A.K.; Scalise, D.; Delp, M.D. Hindlimb unloading induces a collagen isoform shift in the soleus muscle of the rat. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 2001, 281, R1710-R1717. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarraf, H.; Mouihate, A. Muscle Hypertrophy in a Newly Developed Resistance Exercise Model for Rats. Frontiers in Physiology 2022, 962. [CrossRef]
- Winters, T.M.; Takahashi, M.; Lieber, R.L.; Ward, S.R. Whole muscle length-tension relationships are accurately modeled as scaled sarcomeres in rabbit hindlimb muscles. Journal of biomechanics 2011, 44, 109-115. [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.E.; Goldspink, G. The effect of immobilization on the longitudinal growth of striated muscle fibres. Journal of Anatomy 1973, 116, 45.
- Williams, P.E.; Goldspink, G. Changes in sarcomere length and physiological properties in immobilized muscle. Journal of anatomy 1978, 127, 459.
- Hikida, R.S.; Gollnick, P.D.; Dudley, G.A.; Convertino, V.A.; Buchanan, P. Structural and metabolic characteristics of human skeletal muscle following 30 days of simulated microgravity. Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine 1989, 60, 664-670.
- Sakakima, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Sakae, K.; Morimoto, N. Different frequency treadmill running in immobilization-induced muscle atrophy and ankle joint contracture of rats. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2004, 14, 186-192. [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.; Ilyina-Kakueva, E.; Ellis, S.; Bain, J.; Slocum, G.; Sedlak, F. Skeletal muscle fiber, nerve, and blood vessel breakdown in space-flown rats. The FASEB Journal 1990, 4, 84-91.
- Nonaka, I.; Miyazawa, M.; Sukegawa, T.; Yonemoto, K.; Kato, T. Muscle fiber atrophy and degeneration induced by experimental immobility and hindlimb suspension. International journal of sports medicine 1997, 18, S292-S294. [CrossRef]
- Baewer, D.V.; Hoffman, M.; Romatowski, J.G.; Bain, J.; Fitts, R.H.; Riley, D.A. Passive stretch inhibits central corelike lesion formation in the soleus muscles of hindlimb-suspended unloaded rats. Journal of Applied Physiology 2004, 97, 930-934. [CrossRef]
- Cornachione, A.; Cação-Benedini, L.; Shimano, M.; Volpon, J.B.; Martinez, E.Z.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Morphological comparison of different protocols of skeletal muscle remobilization in rats after hindlimb suspension. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 2008, 18, 453-461.
- Baker, J.H.; Matsumoto, D.E. Adaptation of skeletal muscle to immobilization in a shortened position. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 1988, 11, 231-244.
- Murakami, T.; Hijikata, T.; Yorifuji, H. Staging of disuse atrophy of skeletal muscles on immunofluorescence microscopy. Anat Sci Int 2008, 83, 68-76. [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.H. Segmental necrosis in tenotomized muscle fibers. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 1983, 6, 29-39.
- Appell, H.-J. Morphology of immobilized skeletal muscle and the effects of a pre-and postimmobilization training program. International journal of sports medicine 1986, 7, 6-12. [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Vizziello, E.; Tidball, J.; Falcieri, E.; Curzi, D. Plantaris muscle adaptation to atrophy generated by disuse: an ultrastructural study. Microscopie 2014, 22, 31-36.
- Widrick, J.J.; Romatowski, J.; Bain, J.L.; Trappe, S.W.; Trappe, T.A.; Thompson, J.L.; Costill, D.L.; Riley, D.A.; Fitts, R.H. Effect of 17 days of bed rest on peak isometric force and unloaded shortening velocity of human soleus fibers. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 1997, 273, C1690-C1699. [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.A.; Bain, J.L.; Thompson, J.L.; Fitts, R.H.; Widrick, J.J.; Trappe, S.W.; Trappe, T.A.; Costill, D.L. Decreased thin filament density and length in human atrophic soleus muscle fibers after spaceflight. Journal of applied physiology 2000, 88, 567-572. [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.A.; Ellis, S.; Slocom, G.R.; Satyanarayana, T.; Bain, J.L.; Sedlak, F.R. Hypogravity-induced atrophy of rat soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 1987, 10, 560-568.
- Riley, D.A.; Bain, J.L.; Thompson, J.L.; Fitts, R.H.; Widrick, J.J.; Trappe, S.W.; Trappe, T.A.; Costill, D.L. Disproportionate loss of thin filaments in human soleus muscle after 17-day bed rest. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 1998, 21, 1280-1289.
- Jakubiec-Puka, A.; Szczepanowska, J.; Wieczorek, U. Myosin heavy chains in striated muscle immobilized in a shortened position. Basic Appl Myol 1995, 5, 147-153.
- Goldspink, D. The influence of immobilization and stretch on protein turnover of rat skeletal muscle. The Journal of physiology 1977, 264, 267-282. [CrossRef]
- Booth, F.; Seider, M. Early change in skeletal muscle protein synthesis after limb immobilization of rats. Journal of Applied Physiology 1979, 47, 974-977. [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, S.R.; Tischler, M.E. Atrophy and growth failure of rat hindlimb muscles in tail-cast suspension. Journal of Applied Physiology 1984, 57, 1472-1479. [CrossRef]
- Loughna, P.; Goldspink, G.; Goldspink, D. Effect of inactivity and passive stretch on protein turnover in phasic and postural rat muscles. Journal of applied physiology 1986, 61, 173-179. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Halliday, D.; Morrison, W.; Stoward, P.; Hornsby, G.; Watt, P.; Murdoch, G.; Rennie, M. Decrease in human quadriceps muscle protein turnover consequent upon leg immobilization. Clinical science 1987, 72, 503-509. [CrossRef]
- Thomason, D.B.; Biggs, R.B.; Booth, F.W. Protein metabolism and beta-myosin heavy-chain mRNA in unweighted soleus muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 1989, 257, R300-R305. [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, A.A.; Lane, H.W.; Stuart, C.A.; Davis-Street, J.; Wolfe, R.R. Prolonged bed rest decreases skeletal muscle and whole body protein synthesis. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 1996, 270, E627-E633.
- Gamrin, L.; Berg, H.; Essen, P.; Tesch, P.; Hultman, E.; Garlick, P.; McNurlan, M.; Wernerman. The effect of unloading on protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. Acta physiologica scandinavica 1998, 163, 369-377.
- Fluckey, J.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.; Montague, D.; Knox, M.; Tesch, P.; Peterson, C.; Gaddy-Kurten, D. A rat resistance exercise regimen attenuates losses of musculoskeletal mass during hindlimb suspension. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 2002, 176, 293-300.
- Paddon-Jones, D.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Cree, M.G.; Hewlings, S.J.; Aarsland, A.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. Atrophy and impaired muscle protein synthesis during prolonged inactivity and stress. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2006, 91, 4836-4841.
- De Boer, M.D.; Selby, A.; Atherton, P.; Smith, K.; Seynnes, O.R.; Maganaris, C.N.; Maffulli, N.; Movin, T.; Narici, M.V.; Rennie, M.J. The temporal responses of protein synthesis, gene expression and cell signalling in human quadriceps muscle and patellar tendon to disuse. The Journal of physiology 2007, 585, 241-251.
- Kortebein, P.; Ferrando, A.; Lombeida, J.; Wolfe, R.; Evans, W.J. Effect of 10 days of bed rest on skeletal muscle in healthy older adults. Jama 2007, 297, 1769-1774.
- Glover, E.I.; Phillips, S.M.; Oates, B.R.; Tang, J.E.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Selby, A.; Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. Immobilization induces anabolic resistance in human myofibrillar protein synthesis with low and high dose amino acid infusion. The Journal of physiology 2008, 586, 6049-6061.
- Symons, T.B.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Chinkes, D.L.; Ferrando, A.A.; Paddon-Jones, D. Artificial gravity maintains skeletal muscle protein synthesis during 21 days of simulated microgravity. Journal of applied physiology 2009, 107, 34-38.
- Lang, S.M.; Kazi, A.A.; Hong-Brown, L.; Lang, C.H. Delayed recovery of skeletal muscle mass following hindlimb immobilization in mTOR heterozygous mice. PloS one 2012, 7, e38910.
- Phillips, S.M.; McGlory, C. CrossTalk proposal: The dominant mechanism causing disuse muscle atrophy is decreased protein synthesis. The Journal of physiology 2014, 592, 5341.
- Wall, B.T.; Dirks, M.L.; Snijders, T.; van Dijk, J.-W.; Fritsch, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. Short-term muscle disuse lowers myofibrillar protein synthesis rates and induces anabolic resistance to protein ingestion. American journal of physiology-endocrinology and metabolism 2016.
- Mirzoev, T.; Tyganov, S.; Vilchinskaya, N.; Lomonosova, Y.; Shenkman, B. Key markers of mTORC1-dependent and mTORC1-independent signaling pathways regulating protein synthesis in rat soleus muscle during early stages of hindlimb unloading. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2016, 39, 1011-1020.
- Tyganov, S.A.; Mochalova, E.P.; Belova, S.P.; Sharlo, K.A.; Rozhkov, S.V.; Vilchinskaya, N.A.; Paramonova, I.I.; Mirzoev, T.M.; Shenkman, B.S. Effects of plantar mechanical stimulation on anabolic and catabolic signaling in rat postural muscle under short-term simulated gravitational unloading. Frontiers in Physiology 2019, 10, 1252.
- Rozhkov, S.V.; Sharlo, K.A.; Mirzoev, T.M.; Shenkman, B.S. Temporal changes in the markers of ribosome biogenesis in rat soleus muscle under simulated microgravity. Acta Astronautica 2021, 186, 252-258.
- Lin, K.H.; Wilson, G.M.; Blanco, R.; Steinert, N.D.; Zhu, W.G.; Coon, J.J.; Hornberger, T.A. A deep analysis of the proteomic and phosphoproteomic alterations that occur in skeletal muscle after the onset of immobilization. J Physiol 2021, 599, 2887-2906. [CrossRef]
- Tesch, P.A.; von Walden, F.; Gustafsson, T.; Linnehan, R.M.; Trappe, T.A. Skeletal muscle proteolysis in response to short-term unloading in humans. Journal of applied physiology 2008, 105, 902-906.
- Steffen, J.M.; Musacchia, X. Spaceflight effects on adult rat muscle protein, nucleic acids, and amino acids. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 1986, 251, R1059-R1063.
- Bodine, S.C.; Latres, E.; Baumhueter, S.; Lai, V.K.-M.; Nunez, L.; Clarke, B.A.; Poueymirou, W.T.; Panaro, F.J.; Na, E.; Dharmarajan, K. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 2001, 294, 1704-1708.
- Nikawa, T.; Ishidoh, K.; Hirasaka, K.; Ishihara, I.; Ikemoto, M.; Kano, M.; Kominami, E.; Nonaka, I.; Ogawa, T.; Adams, G.R. Skeletal muscle gene expression in space-flown rats. The FASEB journal 2004, 18, 522-524.
- Hussain, S.N.; Mofarrahi, M.; Sigala, I.; Kim, H.C.; Vassilakopoulos, T.; Maltais, F.; Bellenis, I.; Chaturvedi, R.; Gottfried, S.B.; Metrakos, P. Mechanical ventilation–induced diaphragm disuse in humans triggers autophagy. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2010, 182, 1377-1386.
- Reich, K.A.; Chen, Y.-W.; Thompson, P.D.; Hoffman, E.P.; Clarkson, P.M. Forty-eight hours of unloading and 24 h of reloading lead to changes in global gene expression patterns related to ubiquitination and oxidative stress in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 2010, 109, 1404-1415.
- Andrianjafiniony, T.; Dupré-Aucouturier, S.; Letexier, D.; Couchoux, H.; Desplanches, D. Oxidative stress, apoptosis, and proteolysis in skeletal muscle repair after unloading. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2010, 299, C307-C315.
- Nandi, D.; Tahiliani, P.; Kumar, A.; Chandu, D. The ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Biosci 2006, 31, 137-155. [CrossRef]
- Stuart, C.A.; Shangraw, R.E.; Peters, E.J.; Wolfe, R.R. Effect of dietary protein on bed-rest-related changes in whole-body-protein synthesis. The American journal of clinical nutrition 1990, 52, 509-514.
- Stein, T.; Schluter, M. Human skeletal muscle protein breakdown during spaceflight. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 1997, 272, E688-E695.
- Reid, M.B.; Judge, A.R.; Bodine, S.C. CrossTalk opposing view: The dominant mechanism causing disuse muscle atrophy is proteolysis. J Physiol 2014, 592, 5345-5347. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M.; McGlory, C. CrossTalk proposal: The dominant mechanism causing disuse muscle atrophy is decreased protein synthesis. J Physiol 2014, 592, 5341-5343. [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.A.; Hornberger, T.A.; al., e. Comments on the CrossTalk proposal and opposing view: The dominant mechanism causing disuse muscle atrophy is decreased protein synthesis/proteolysis. Journal of Physiology 2015, 1-10.
- Galavazi, G. Identification of helical polyribosomes in sections of mature skeletal muscle fibers. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie 1971, 121, 531-547.
- Galavazi, G.; Szirmai, J.A. The influence of age and testosterone on the ribosomal population in the m. levator ani and a thigh muscle of the rat. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie 1971, 121, 548-560.
- Horne, Z.; Hesketh, J. Immunological localization of ribosomes in striated rat muscle. Evidence for myofibrillar association and ontological changes in the subsarcolemmal: myofibrillar distribution. Biochemical Journal 1990, 268, 231-236.
- Morkin, E. Postnatal muscle fiber assembly: localization of newly synthesized myofibrillar proteins. Science 1970, 167, 1499-1501.
- Kannus, P.; Jozsa, L.; Jarvinen, T.L.; Kvist, M.; Vieno, T.; Jarvinen, T.A.; Natri, A.; Jarvinen, M. Free mobilization and low-to high-intensity exercise in immobilization-induced muscle atrophy. Journal of Applied Physiology 1998, 84, 1418-1424.
- Järvinen, T.A.; Józsa, L.; Kannus, P.; Järvinen, T.L.; Hurme, T.; Kvist, M.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Kalimo, H.; Järvinen, M. Mechanical loading regulates the expression of tenascin-C in the myotendinous junction and tendon but does not induce de novo synthesis in the skeletal muscle. Journal of cell science 2003, 116, 857-866.
- Etlinger, J.; Zak, R.; Fischman, D.; Rabinowitz, M. Isolation of newly synthesised myosin filaments from skeletal muscle homogenates and myofibrils. Nature 1975, 255, 259-261.
- Etlinger, J.; Zak, R.; Fischman, D. Compositional studies of myofibrils from rabbit striated muscle. The Journal of cell biology 1976, 68, 123-141.
- Van der Westhuyzen, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Etlinger, J. Easily releasable myofilaments from skeletal and cardiac muscles maintained in vitro. Role in myofibrillar assembly and turnover. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1981, 256, 11791-11797.
- Belcastro, A.N.; Scrubb, J.; Gilchrist, J.S. Regulation of ATP-stimulated releasable myofilaments from cardiac and skeletal muscle myofibrils. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 1991, 103, 113-120.
- Neti, G.; Novak, S.M.; Thompson, V.F.; Goll, D.E. Properties of easily releasable myofilaments: are they the first step in myofibrillar protein turnover? American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2009, 296, C1383-C1390.
- Williams, A.B.; Decourten-Myers, G.M.; Fischer, J.E.; Luo, G.; Sun, X.; Hasselgren, P.O. Sepsis stimulates release of myofilaments in skeletal muscle by a calcium-dependent mechanism. The FASEB Journal 1999, 13, 1435-1443.
- Dahlmann, B.; Rutschmann, M.; Reinauer, H. Effect of starvation or treatment with corticosterone on the amount of easily releasable myofilaments in rat skeletal muscles. Biochemical Journal 1986, 234, 659-664.
- Smuder, A.J.; Nelson, W.B.; Hudson, M.B.; Kavazis, A.N.; Powers, S.K. Inhibition of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway does not protect against ventilator-induced accelerated proteolysis or atrophy in the diaphragm. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 115-126.
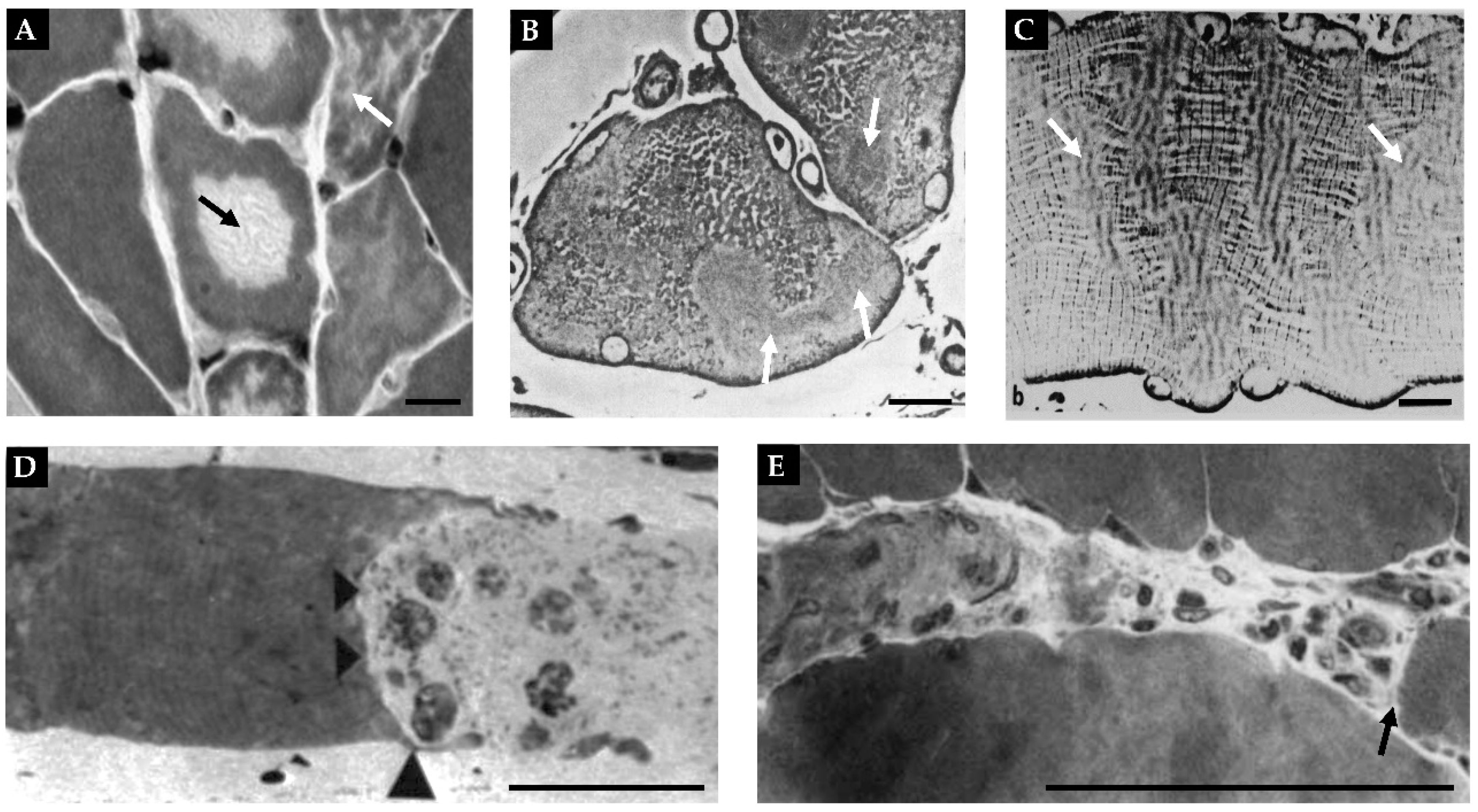
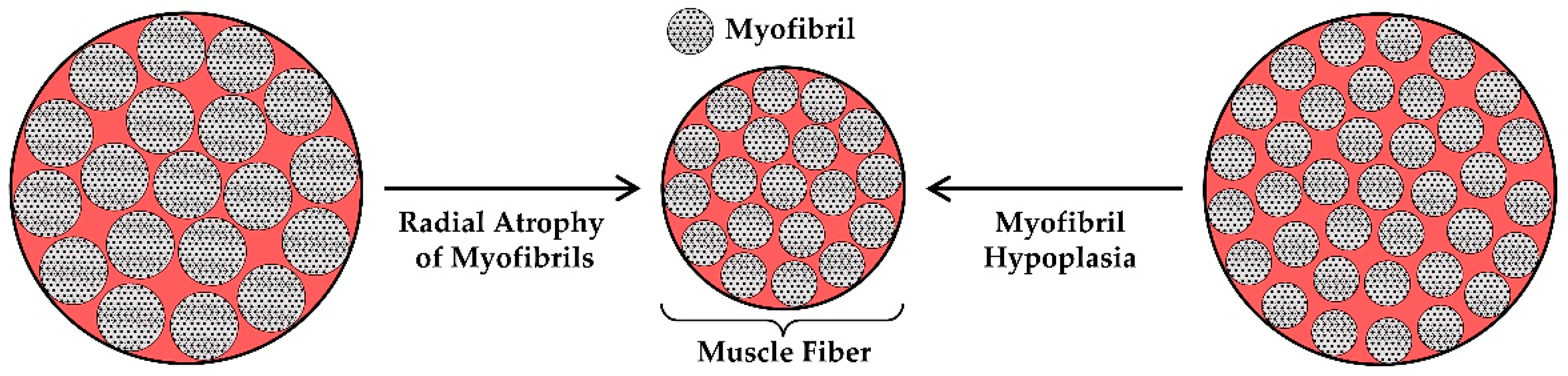
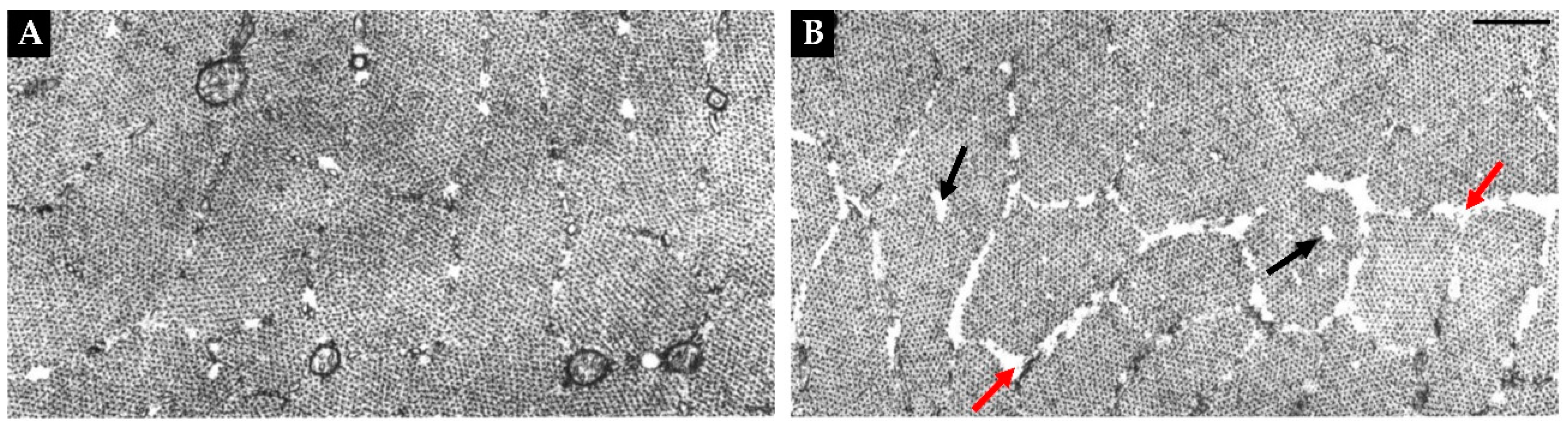
| Adaptation | Evidence | Major Gaps in Knowledge |
|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal Atrophy of Fascicles | High (for disuse in a shortened position) |
|
| Radial Atrophy of Fascicles | High |
|
| Longitudinal Atrophy of Muscle Fibers | High (for disuse in a shortened position) |
|
| Radial Atrophy of Muscle Fibers | Extremely High |
|
| Radial Atrophy of Myofibrils | Moderate |
|
| Myofibril Hypoplasia | Very Low |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





