Introduction
Histone modifications play an indispensable role in epigenetic regulation, governing the intricate dance of gene expression and cellular homeostasis. These post-translational modifications, particularly lysine (K) methylation, are executed and reversed by a range of enzymes termed as histone writers and erasers, respectively2. Beyond these enzymes, a set of adaptor proteins, termed histone readers, discern these histone marks, connecting them to myriad cellular processes such as transcription, DNA-damage response, and proliferation3. Among the myriad of histone modifications, H3 Lysine 27 (K27) and Lysine 36 (K36) methylation stand out, having been associated with a spectrum of human pathologies, especially cancer and developmental disorders2,3. Despite their recognized significance, a thorough pancancer examination of genomic variations in these key histone modulators has been absent. This study addresses this gap, elucidating the genomic landscape of H3K27 and H3K36 modifiers across a spectrum of cancers.
Results
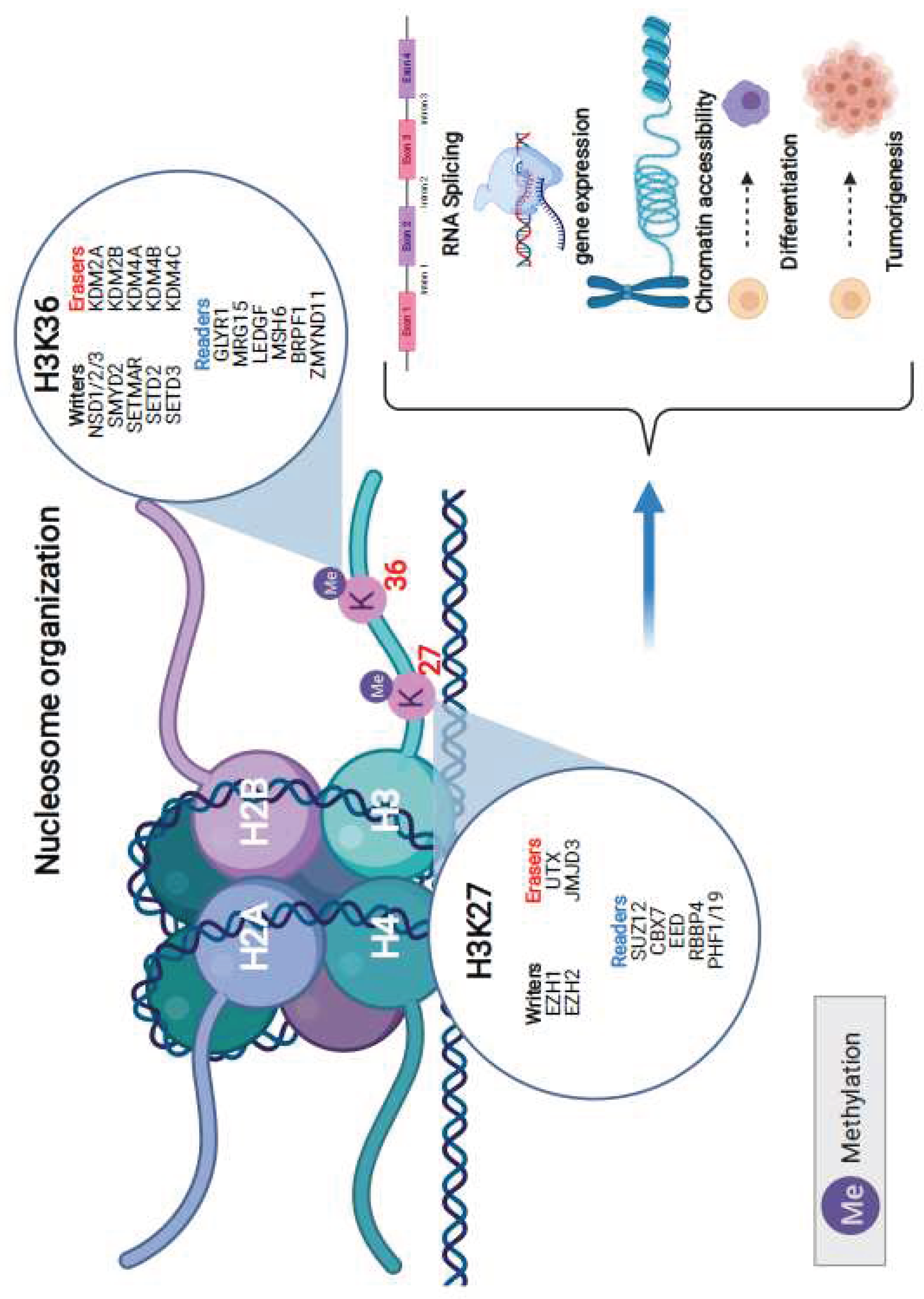
In our endeavor to unravel the role of specific proteins in H3K36 and H3K27 methylation dynamics, we analyzed their genomic alteration profiles. For H3K36 methylation, the writers involved are NSD1/2/3, SMYD2, SETMAR, SETD2, and SETD3. Erasers for this methylation include KDM2A, KDM2B, KDM4A, KDM4B, and KDM4C. The readers of this methylation process encompass GLYR1, MRG15, LEDGF, MSH6, BRPF1, and ZMYND11. On the other hand, for H3K27 methylation, the writers are represented by EZH1 and EZH2, while the erasers include UTX and JMJD3. The readers for this methylation feature SUZ12, CBX7, EED, RBBP4, and PHF1/19. These proteins have been identified as paramount in a myriad of cellular mechanisms, such as RNA splicing, gene expression, chromatin accessibility, cell differentiation, and even tumorigenesis (
Figure 1).
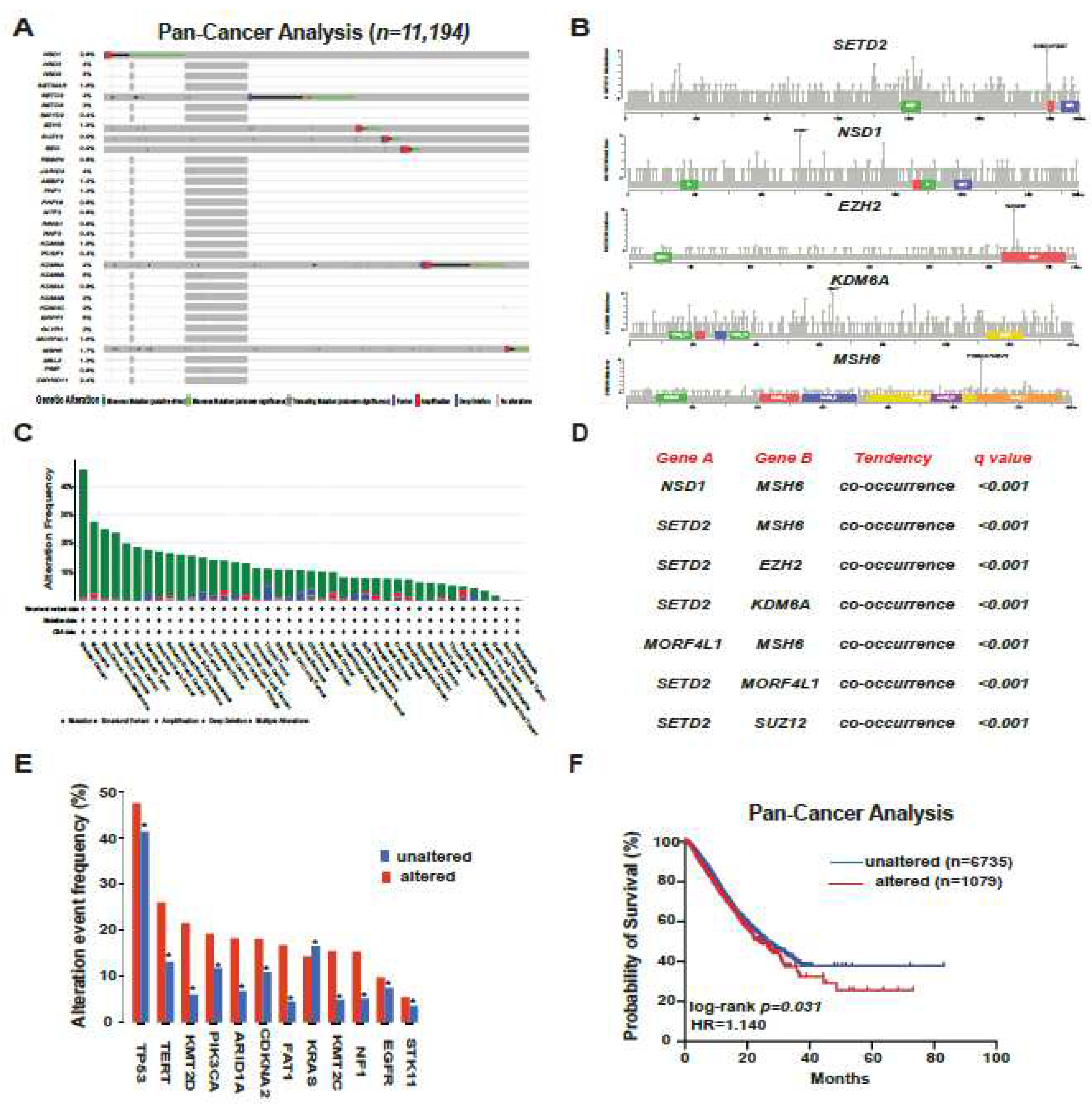
Our analysis, built on the extensive dataset of TCGA encompassing a cohort of 11,194 patients from the cbioportal atlas of cancer genomics, brought forth enlightening results. Notably, bladder cancer, melanoma, and renal cancer stood out as the cancer types bearing the highest frequency of altered modifiers (
Figure 2A–C). As we delved deeper, the mutation rates of these proteins became evident. The likes of KDM6B, BRPF1, KDM6A, SETD2, and NSD1 surfaced as the most frequently altered. In addition, a significant pattern of co-occurrence among these alterations was unearthed, where atients with these alterations also frequently exhibited mutations in genes like
TP53 and
PIK3CA. These findings are hinting at potential synergistic or interactive roles these proteins may adopt in the process of carcinogenesis (
Figure 2D,E). Rounding up our analysis with a clinical perspective, the Kaplan-Meier curves painted a somber picture. When comparing the overall survival rates across the spectrum, patients with genomic alterations in these pivotal modifiers fared worse (HR = 1.14, p=0.031). This observation, reaffirms the oncogenic and prognostic gravity these mutations carry in human cancers (
Figure 2F).
In summary, Our exhaustive pancancer analysis has illuminated the critical role of histone H3K27 and H3K36 modifiers and erasers in the oncogenic narrative. Their genomic perturbations not only emerge as potent drivers of various malignancies but also pave the way for promising therapeutic investigations and translational avenues.
Discussion
The results underscore the vital role of H3K27 and H3K36 modifiers and readers in cancer pathogenesis. The high prevalence of genomic alterations in key modifiers like KDM6B and KDM6A, coupled with their co-occurrence with other oncogenic mutations, accentuates their significance in the complex molecular tapestry of cancer. Additionally, the observed poorer survival outcomes among patients with these genomic alterations cement their potential as prognostic factors.
This comprehensive mapping of histone modifications across multiple cancer types reiterates their importance not only as biological markers of disease but also as potential therapeutic targets, as reported previously in the literature4. Given the crucial nature of these modifications in cellular processes, further investigations are warranted to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting these modifiers in cancer therapy. Moreover, understanding the intricate interplay between these modifiers and other oncogenic pathways may open up new avenues for combinatorial therapeutic approaches5. In conclusion, the identified genomic landscape of histone H3K27 and H3K36 modifiers lays a robust foundation for subsequent translational research, holding promise for novel therapeutic strategies in oncology.
Methods
For our study, we utilized data exclusively from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), which provided an extensive repository of patient samples for our pancancer analysis. All data extraction and subsequent analyses were carried out using the tools available on cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics
6,7 (
https://www.cbioportal.org/). cBioPortal, with its comprehensive suite of visualization and analysis tools, facilitated the detailed exploration of the genomic alteration profiles of the specified histone modifiers. The platform enabled the identification of prevalent mutations, co-occurrence patterns, and the association of these genomic alterations with clinical outcomes. The integrated tools within cBioPortal ensured robustness and reproducibility in our analysis, aligning with the standards for genomic data examination.
Conflicting interests
G.L has options to own or owns stock from Natera, Inc., acts as scientific advisor in docus.ai and as consultant for Tegus.
References
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Y. and Han, J., 2023. The Role of Histone Modification in DNA Replication-Coupled Nucleosome Assembly and Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), p.4939.
- Bannister, A.J. and Kouzarides, T., 2011. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell research, 21(3), pp.381-395. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. and Shilatifard, A., 2019. Epigenetic modifications of histones in cancer. Genome biology, 20, pp.1-16. [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M., Daujat, S. and Schneider, R., 2016. Lateral thinking: how histone modifications regulate gene expression. Trends in Genetics, 32(1), pp.42-56. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I., Poręba, E., Kamieniarz, K. and Schneider, R., 2011. Histone modifiers in cancer: friends or foes?. Genes & cancer, 2(6), pp.631-647. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J., Aksoy, B.A., Dogrusoz, U., Dresdner, G., Gross, B., Sumer, S.O., Sun, Y., Jacobsen, A., Sinha, R., Larsson, E. and Cerami, E., 2013. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Science signaling, 6(269), pp.pl1-pl1. [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E., Gao, J., Dogrusoz, U., Gross, B.E., Sumer, S.O., Aksoy, B.A., Jacobsen, A., Byrne, C.J., Heuer, M.L., Larsson, E. and Antipin, Y., 2012. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer discovery, 2(5), pp.401-404. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).