1. Introduction
The use of supplementary cementitious materials in mortar and concrete production has been reported extensively with a view to getting our environment free of solid waste and air pollution. Besides, proliferation of carbondioxide due to disintegration of limestone in the process of manufacturing of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) has been an environmental concern owing to its effect on global warming. Supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) such as flyash, silica fume and other siliceous and pozzolanic materials have been considered to reduce the volume of OPC in construction industry. Silica fume is one of the pozzolanic materials that has shown potency in enhancing the strength and durability of concrete due to its fineness and ability to undergo secondary hydration characteristics [
1,
2,
3,
4].
It is very important to further improve the characteristics of silica fume (SF) blended concrete by investigating effect of other additives such as nano alumina (nA) on the setting time, workability, strength and thermal resistance. Alumina has been a very reactive oxide and could react with silica to produce a binder with good strength, and thermal and chemical resistant characteristics due to its refractory property [
5]. This is very essential to produce a concrete or retrofitting mortar that has far reaching application in kitchen, furnaces, and other heat resistant structures, more especially in the Middle East countries where the temperature during summer period could reach 49
C[
6], more especially in the countries like UAE, Iraq, Qatar and Saudi Arabia.
In the recent time, aluminium shaving at small quantity (< 3%) was used to achieve significant thermal resistance, reduction in apparent porosity and lightweight mortar due to effervescence of hydrogen gas [
7]. Hence, the use of nano-alumina as a construction material is supposed to be explored for numerous engineering applications [
8,
9]. The use of powdered additives and nano-scaled materials in synergy with OPC could improve the binder characteristics. This includes the use of SCMs such as a silica fume with the purpose of producing economic and durable concrete.
Silica fume blended concrete has lower early strength development and low consistency due to fineness of the material. The use of nano-alumina in OPC based binder has been reported, in contrast, to enhance early strength and reduction in porosity, more especially in the presence of lime (CaO) such as in GGBFS due to the possibility of formation of calcium aluminosilicate hydrate (CASH) and low composition of ettringite [Ca6Al(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O][
10]. Thus, the use of alumina could contribute to mechanical properties and durability of the binder [
11]. Furthermore, in the excess of CaO, monosulfate aluminate (MSA) and Al(OH)
3 (AH
3) dominate the products formed and not the expansive ettringite[
10]. The ettringite is formed by the reaction of MSA with excess sulfate (gypsum) thereby leading to expansion of microstructure. If such sample undergoes carbonation, ettringite shrinks thereby leading to reduction of compressive strength due to internal stresses that accompanies the formation of AH
3 [
11]. Moreover, the presence of AH
3 within the sample matrix has been reported to cause a potential danger due to its propensity to form late ettringite upon reacting with any possible ingress sulfate [
12,
13].
Shao et al. [
14] had established the possibility of alumina dissolution in pore solution to induce the formation of different aluminium dependent products such as ettringite, MSA (Ca4Al
2O6(SO4)·14H
2O]) and monocarbonaluminates (Ca4Al2O7(CO2)·11H2O]). The performance of alumina in binders depends on its level of crystallinity. Alpha-alumina has been reported to be more crystalline that
-alumina, which has more devastating effect in OPC placed in a sulfate environment [
11]. Zhan et al. [
15] reported that nano-alumina could enhance the reaction of silicate and alumina phase to form mullite thereby reducing the micropores. Shao et al. [
14] also reported the formation of carbon-based ettringite due to MSA interaction with atmospheric CO
2 [
14]. Shabbar et al. [
16] reported that incorporation of aluminium in OPC for aerated concrete with good sound and heat insulation, apart from its high-level fire resistance with the density in the range of 1000-2000 kg/m
3. The compressive strength of the sample was noticeably reduced due to the formation of internal porosity that accompanied escape of hydrogen gas.
Despite these plethora studies on the use of alumina on OPC [
16,
17,
18], the impact of nA on SF binary blended mortar is still yet to be fully understood. It is also important to study the impact of alumina/silica interaction in ternary blended mortar to understand its workability, mechanical characteristics, and thermal resistance. It is expected that this study will provide insight and necessary information towards developing a new binder for structural retrofitting and construction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Nano aluminum oxide
Nano aluminum oxide comprises 99.87% alumina with other oxides in trace amount as shown in (
Table 1 and
Figure 1). The specific gravity (water) is 3.38 while the boiling and melting points are 2977
and 2072
, respectively. The X-ray diffractogram (XRD) of the aluminium (Fig 2) indicates that the crystalline phase present include
-alumina. Its surface area is greater than 100 m
2/g [
19] while the loss on ignition is 1.05%.
2.1.2. Cement
Type 1 ordinary Portland cement (OPC) in compliance with ASTM C 150 with specific gravity (by water) of 3.15 is shown in
Table 1. The oxides composition are mainly silica, alumina, lime iron oxide and potassium oxides while other oxides such as sodium, phosphorus, manganese and sulphite exist in trace quantities. Its surface area was 0.329 m
2/g while the loss on ignition (LOI) was 2.8. The combination of SiO
2+Al
2O
3+Fe
2O
3 was 28.9%. X-ray diffractogram (XRD) in
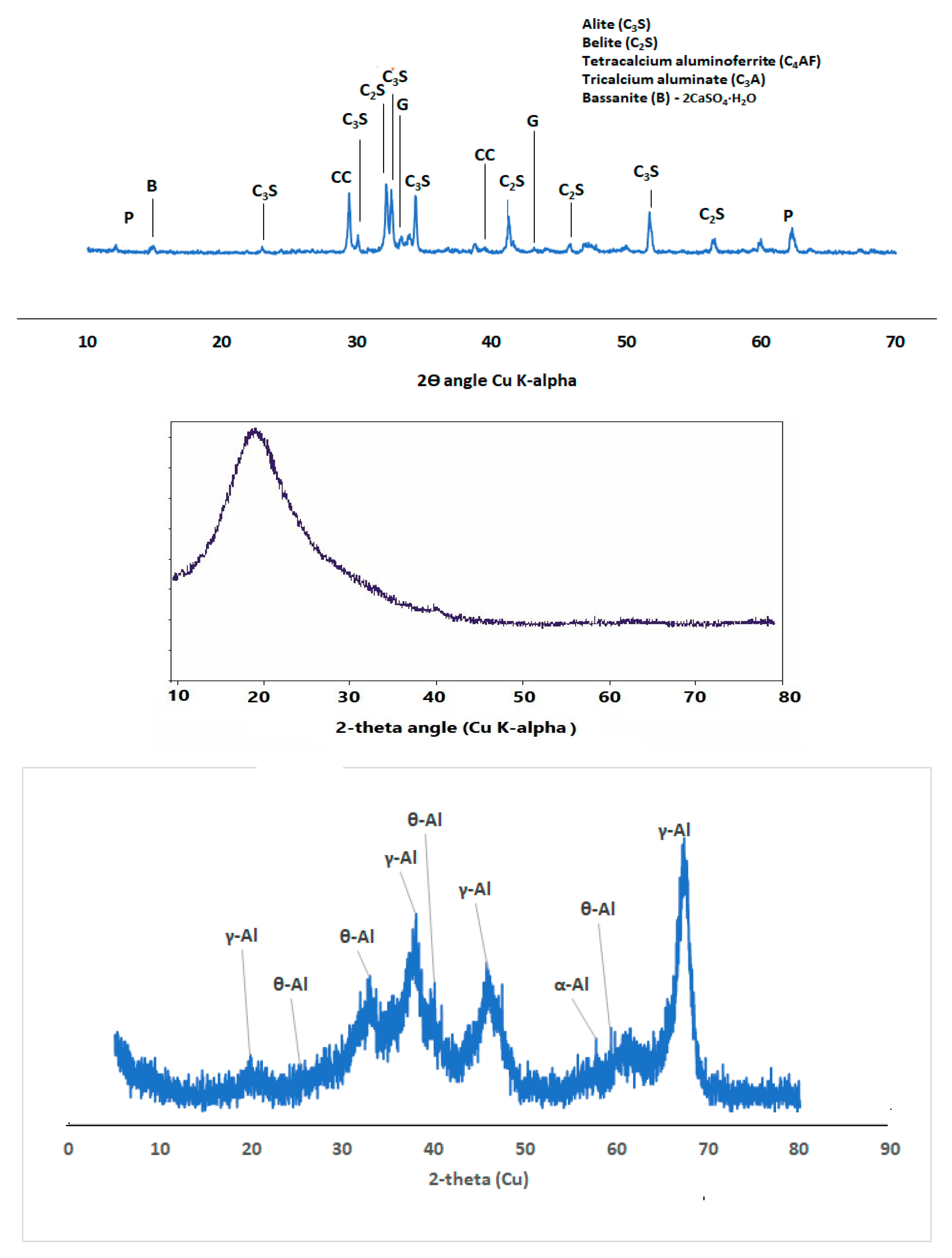
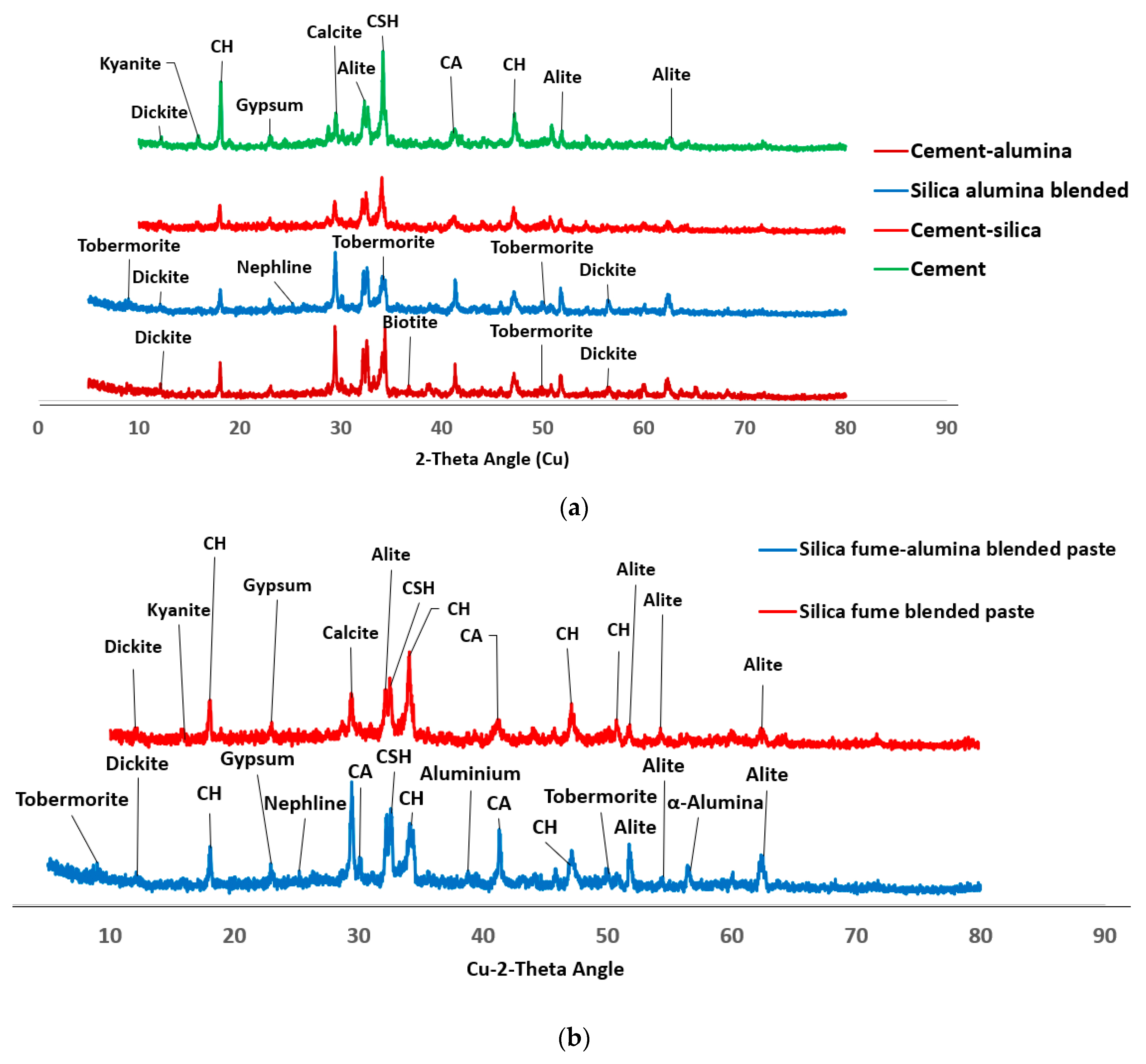
Figure 2 shows the phases of compounds present in the ordinary Portland cement (OPC) which include alite, belite, tetracalcium aluminoferrite and gypsum.
2.1.3. Silica fume
Silica fume (SF) is commercially obtained and has a relative density of 2.25, LOI of 2.48, and surface area of 22.8 m
2/g with SiO
2+Al
2O
3+Fe
2O
3 of 96.2% as shown in
Table 1. XRD diffractogram (
Figure 2) shows that the SF is mainly amorphous with diffractive halo shown at 2-theta angle of 20
.
2.1.4. Aggregates:
Fine aggregate that was used is natural sand in saturated surface dry (SSD) conditions. The absorption and moisture content were 6.14 and 3.43%, respectively. It passes through sieve no. 2.36 mm (No. 8) in accordance with ASTM C 157/C 157M – 08 [
20]. The fineness modulus of fine aggregate was 2.8 while its specific gravity was 2.75.
2.1.5. Superplasticizer:
High range water reducing superplasticizer (SP), namely, Glenium(R) was used in the proportion of 1% by the mass of the binders (OPC, SF and nano-alumina) to reduce the amount of water required for adequate flowability and adequate slump retention.
2.1.6. Water
Portable water with pH of 7.4 was used to prevent any contamination by deleterious substances. Water to binders’ ratios was kept at 0.45.
2.2. Experimental design
2.2.1. Mix design
Mix design of the sample shown in
Table 2 was prepared by considering the mass and specific gravity values of each material present in the mixture. The total binder mass was 350 kg in cubic meter (350 kg/m
3) of the mortar produced with water/binder ratio of 0.45. The nano alumina-binder (nA/b) ratio varied from 0 to 3% at the interval of 1% while the SF was kept constant as 10%.
2.2.2. Sample designation
The samples composed of OPC (88-100%), alumina (0, 1, 2 and 3%) and with constant percentage of SF (10%). For instance, the sample that contains 88% OPC, 10% SF and 1% nano-alumina (nA), will be designated as C89S10A1. The control samples were given as C100SF0A0 (OPC only).
2.2.3. Mixing procedure
Both OPC and SF were first mixed before adding nA after which 50% of the liquid (mixture of water and superplasticizers) was then added for about 3 mins. This was then followed with the addition of sand and 25% of the liquid for another 3 mins. The remaining water was finally added, and the mixture was in continuous mixing for additional 2 mins to achieve homogeneity. Flow table test was then conducted as a measure of workability before the samples were cast into the moulds. The samples were covered with polythene sheet and placed ASTM Cinside water tank at room temperature (25 oC) for curing.
2.3. Experimental tests
2.3.1. Setting time
Initial and final setting times for all the samples were tested by using paste specimens according to ASTMC 191 [
21] by Vicat’s apparatus with the percentage nano alumina (nA) varied from 0 to 3% at interval of 1% while SF was maintained at 10%. The OPC only paste was also prepared as the control.
2.3.2. Workability
The consistency of the mortar was tested by using flow table in accordance with ASTM C 1437-20 [
22]. The diameter of the flow was recorded in each mix was then recorded.
2.3.3. Compressive strength
The compressive strengths of the samples were determined using cubic samples of 50 mm size in accordance with ASTM C 109 [
23]. The testing was conducted using a universal testing machine at different ages 7, 14, 21 and 28 days under the loading rate of 2.4 kN/s while the average of triplicate samples was recorded.
2.3.4. Residual compressive strength after thermal exposure
The residual compressive strengths were determined by exposing the 28-day samples to 300 C for 1 h, and thereafter determining the residual strength of nA-SF ternary blended mortar in comparison with SF binary blended samples, and the control.
2.3.5. Characterization and morphology of the specimens
The crystallinity of the sample was determined by using XRD Bruker apparatus model d2-Phaser with Cu Ka radiation (40 kV, 30 mA). It was also used to determine the compounds present in the OPC, SF binary blended and SF-nA ternary blended mortar by using a scan speed of 2.5°/min and continuous scanning with 2-theta angle range of 5-80°. The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of the paste samples were conducted by using Perkin Elmer 880 spectrometer [
24]. The morphology and elemental compositions of the powder materials were determined with scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM + EDS) instrument that was manufactured by JEOL model 5800 LV at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV.
3. Discussion of results
3.1. Workability of nano-alumina/silica fume ternary blended mortar
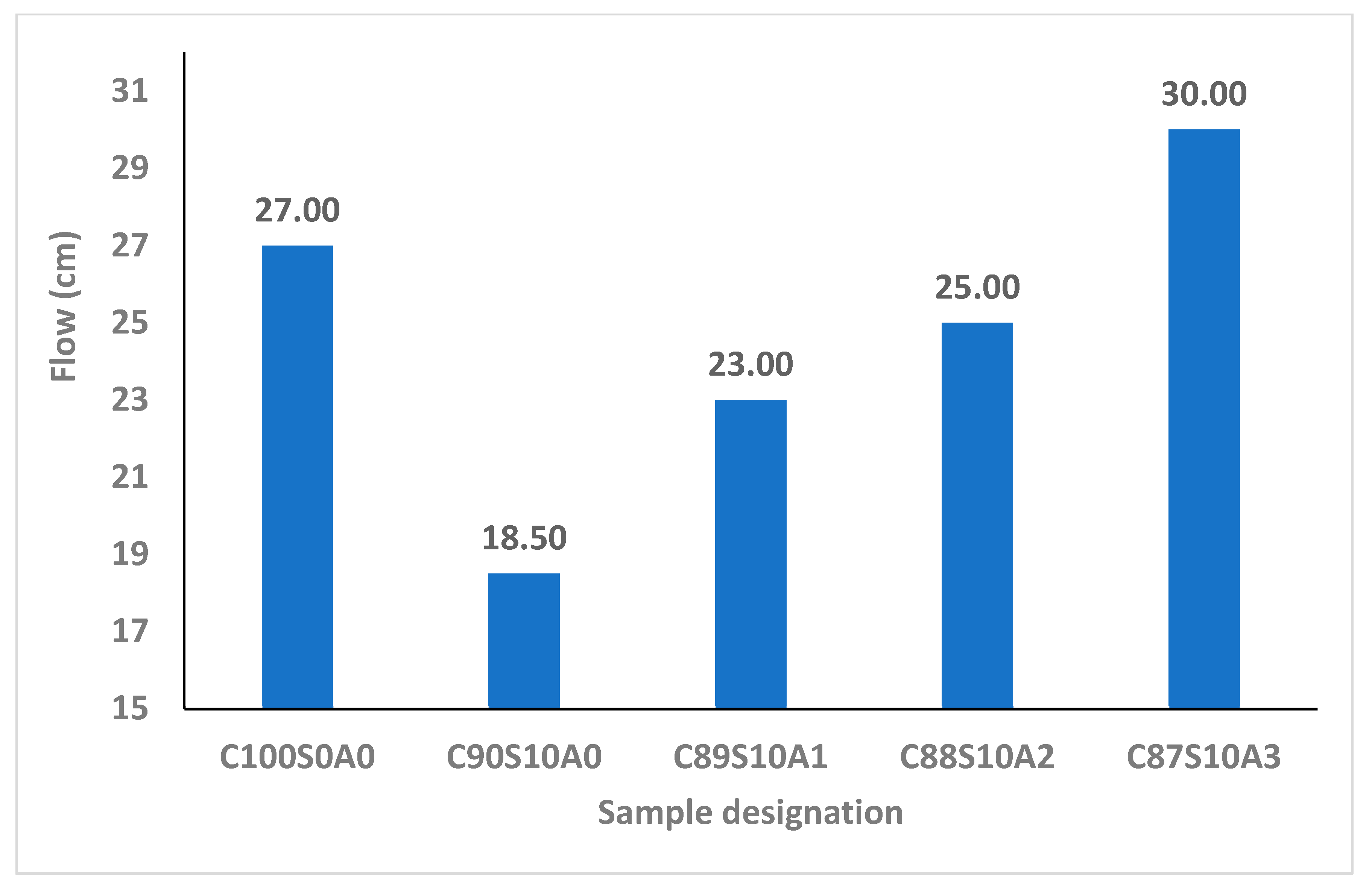
From
Figure 3, it is apparent that introducing SF into OPC mortar reduced its workability due to its fineness and interparticle frictional resistance that negatively affected the consistency. It has been reported that the binder with SF loses fluidity in comparison with that where it is absent. The flow of OPC binder (C
100S
0A
0) was 270 mm but reduced by 31.5, 14.8, 7.4 and 11.1%, upon adding 0, 1, 2 and 3% nA with 10%SF (C
90S
10A
0, C
89S
10A
1, C
88S
10A
2, and C
87S
10A
3), respectively. The consistency of SF blended mortar (C
90S
10A
0) upon adding 1, 2 and 3% nA increased by 24.3, 35.1 and 62.2%, respectively. This implies that nA could improve the interparticle lubrication and workability of SF blended mortar significantly. This means that the challenge of loss of fluidity in SF blended binder could be improved by incorporating nA.
3.2. Setting time of the SF blended and nano-alumina silica fume blended mortar.
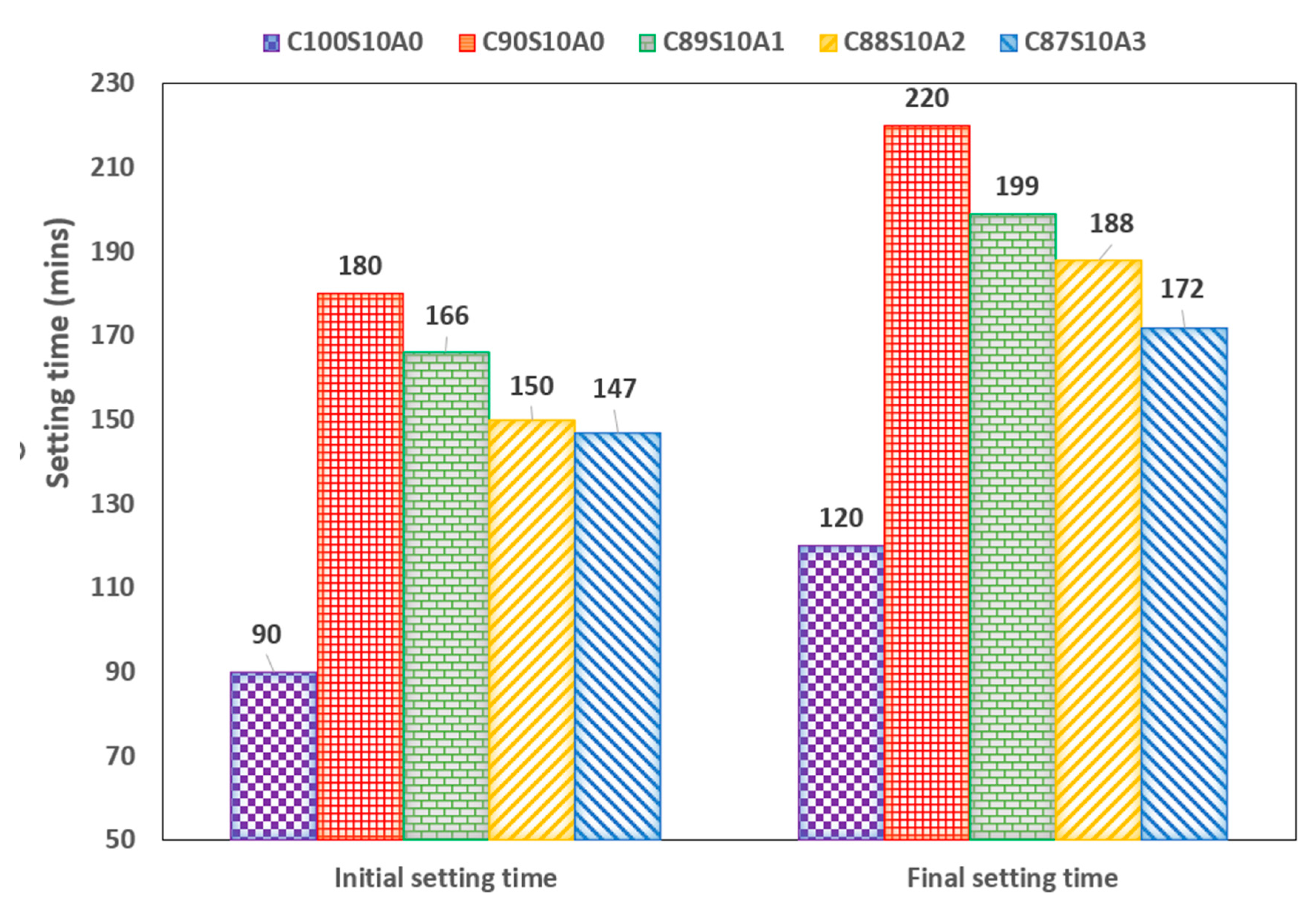
Figure 4 shows the setting time of SF blended mortar in which the control sample (OPC only: C
100S
0A
0) which has initial setting time of 90 mins. Upon adding 10%SF, the setting time of OPC binder was doubled while SF-nA ternary blended paste increased by 84, 67 and 63% in C
89S
10A
1, C
88S
10A
2, C
87S
10A
3, respectively compared to the value obtained in C
100S
0A
0. The SF blended (C
90S
10A
0) had initial setting time of 180 mins and but reduced by 8, 17 and 18% upon adding varied percentage of nA as in C
89S
10A
1, C
88S
10A
2, and C
87S
10A
3, respectively. The final setting time of OPC binder (C
100S
0A
0) was 120 mins which increased by 83% upon adding 10%SF (C
90S
10A
0). The synergy of 10% SF and 1-3% nA paste increased the setting time of OPC by 66, 57, 43%, respectively. However, in SF blended paste (C
90S
10A
0), adding 1-3wt.%nA reduced the setting time by 10, 15 and 22%, respectively. There is insignificant difference in the initial setting recorded in C
88S
10A
2 and C
87S
10A
3 while the trend of decrease in setting is relatively linear in both initial and final setting period (
Figure 4). This implies that nA can be used in ternary blending to accelerate the delayed setting of SF blended binder.
3.4. Compressive strength of SF-nA ternary blended mortar
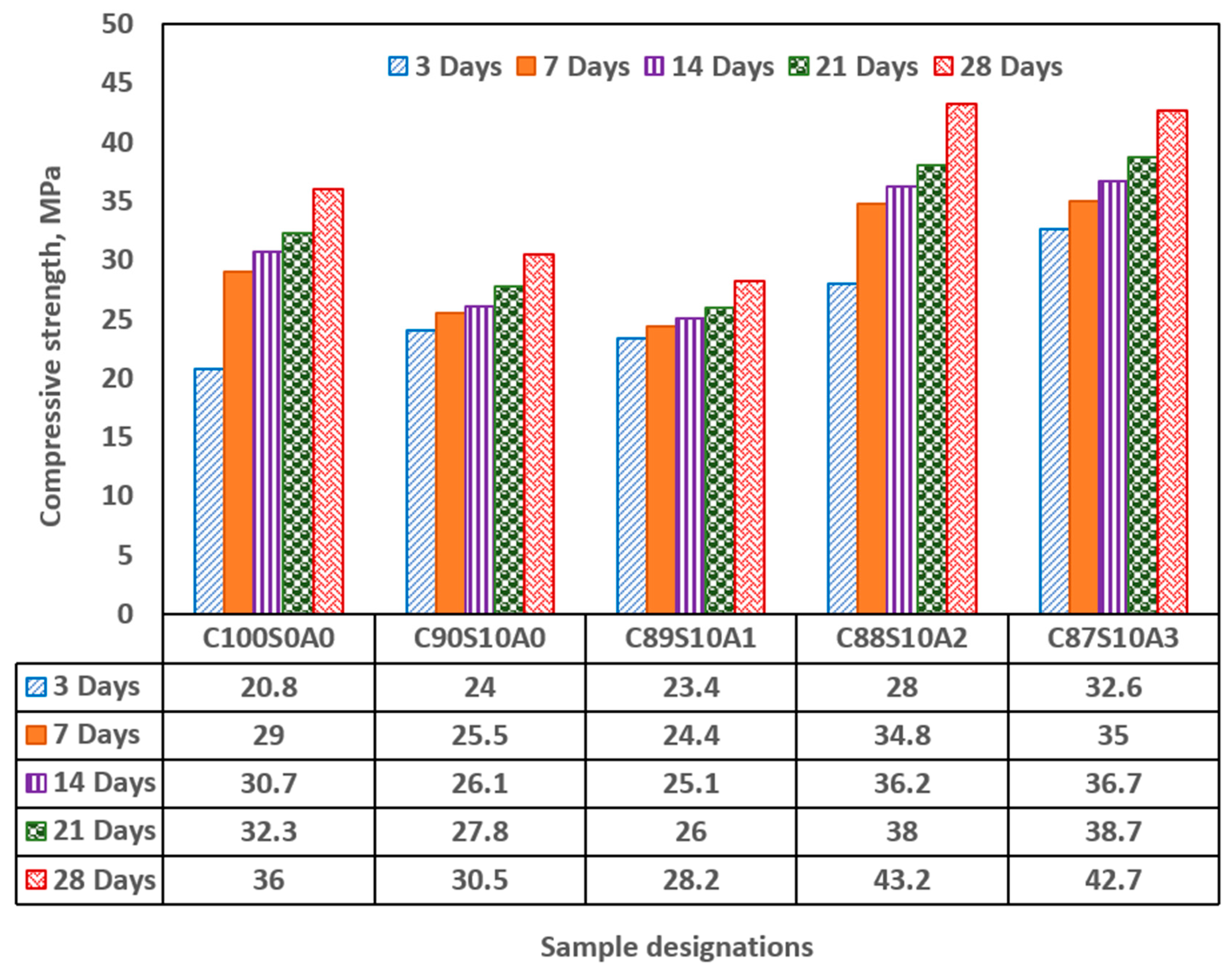
Figure 5 shows strength development in OPC, SF blended and SF-nA ternary blended mortar. Incorporation of 10% SF diminished the early compressive strength of the mortar by significant amount while infusing nA in synergistic ternary blending increases it. The early (3-d) strength of 20 MPa was recorded in OPC and increased by 20% in SF binary (C
90S
10A
0), and 38.1% and 59% ternary blended mortar for 2 and 3%nA, (C
87/88S
10A
2-3) respectively. There was a significant strength development between 3 and 7 days for OPC mortar whereas there was no concomitant strength development in SF blended mortar. This indicated that there was no spontaneous pozzolanic reaction within this period as secondary hydration begin after the production of portlandite as an aftermath of primary hydration. The absence of calcium aluminate or mayenite (COD: 2102957, Al4Ca
12O
33) in the compound formed in SF-blended mortar could be responsible for the observable low early strength.
With the incorporation of 1% nA (C
89S
10A
1), there was no significance increase in the compressive strength. However, when nA increased to 2 to 3% (C
87/88S
10A
2-3), the strength increased by 36.5 and 37.2%, respectively in comparison with SF binary blended mortar ((C
90S
10A
0). The reaction between nA and silica could lead to the formation of aluminosilicate (Al2O5Si or NaAlO4Si) in crystalline phases of dickite (COD #10111062) and nepheline (COD#1008755), respectively as shown in
Figure 6.
There is also possibility of formation of calcium aluminate hydrate (CAH) or calcium aluminosilicate hydrate (CASH) as shown in Eqn. 1. In addition, the formation of calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) (COD ID #1519934: CSH-Ca
3.22H
2O
8Si
2) or tobermorite (COD ID: 9013974: Ca
5Si
6(O,OH)
18.5H
2O) could occur in parallel as shown in Eqn.2 due to the presence of silica, lime and nano-alumina in alkaline medium of pore solution. Unlike other sources of alumina where hydrogen gas is liberated and then resulted to loss of sample weight, no noticeable hydrogen gas effervescence was noticed in the use of 1-3wt.% range of nA in the synthesis of the mortar.
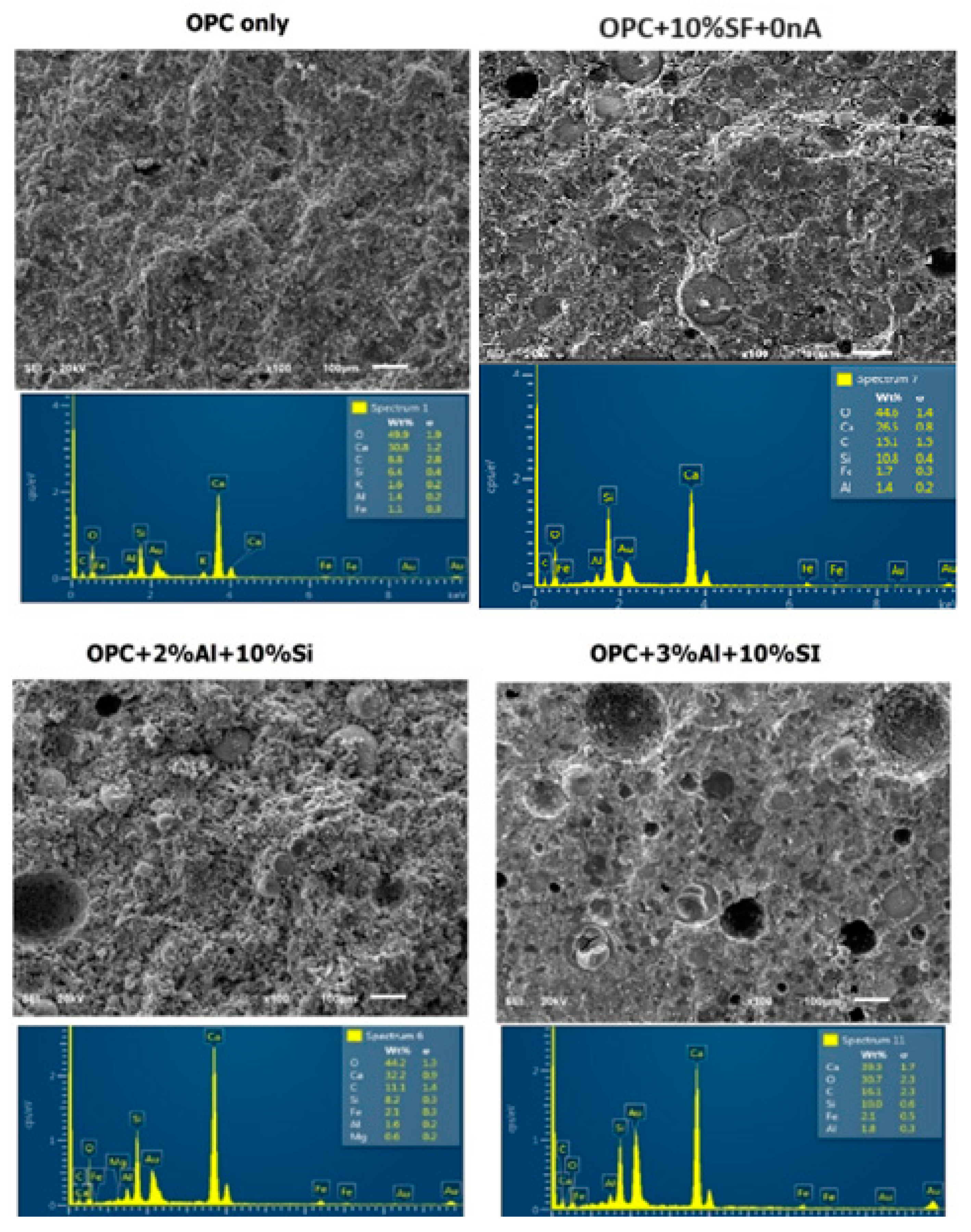
The dual presence of CSH and tobermorite in addition to calcium aluminate hydrate could significantly contribute to the compressive strength of the ternary (SF-nA) blended mortar. This assertion is corroborated by the presence of calcium aluminate in the XRD diffractogram shown in Fig 6. Therefore, the compounds like tobermorite, nepheline, calcium aluminate hydrate and dickite that could be said to be responsible for additional strength recorded. The reason is that portlandite is readily available to react with alumina to make free calcium aluminate and in the presence of SF could form additional calcium silicate hydrate. The 28-d compressive strength of 43.2 MPa with the presence 2%nA. The presence of more nA relative to SF beyond the optimum percentage could result in the reduction of the strength. Since the quantity of nA that gave the maximum value was 2%, that could be taken as the optimum value as incorporating 3% led to slight reduction in the strength of the mortar (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8).
The strength development could also be due to microfilling or micro reinforcement of nA and SF thereby blocking the micropores (capillary pores) that exist within the nucleation site during hydration process. SF is seen to be embedded within the micropores leaving behind other tiny pores. However, upon adding 2%nA, the microstructure becomes denser which culminates into more compressive strength recorded in SF binary blended mortar in comparison with SF-nA ternary blended mortar (
Figure 7).
XRD diffractogram also shows that SF fume blended binder could be less susceptible to carbonation through observation of calcite peak (COD ID: #1010962, CaCO
3) but this peak was very conspicuous in SF-nA blended sample as shown in
Figure 6. This is possibly due to the possibility of excess nA reaction with portlandite in the presence of CO
2 to produce calcium carbonate and aluminium hydroxide with liberation of hydrogen gas as shown in Eqn.3.
The presence of pores in the morphology of OPC-SF-3% alumina sample in Fig 8 in comparison with OPC-SF-2% alumina corroborated this fact. From Eqn.3, Al(OH)
3 could react with hydroxy ions to form 2[Al(OH)
6]
3− [
25] which in turn reacted with capillary water and calcium ion to produce calcium aluminate hydroxide (Eqn. 4).
The product could also react with silica to produce calcium aluminosilicate hydrate or react with other cations present in the matrix to produce biotite-like mineral (COD: #1000038, AlFeH
2KMg
2O
12Si
3) as shown in
Figure 6. There are other peaks of unreacted particle like alite (COD: #1540704, Ca
3SiO
5) and gypsum (COD: #1010981, CaH
4O
6S) among the prominent peaks in
Figure 6.
3.5. Morphology of SF blended binary and SF-nA ternary blended pastes
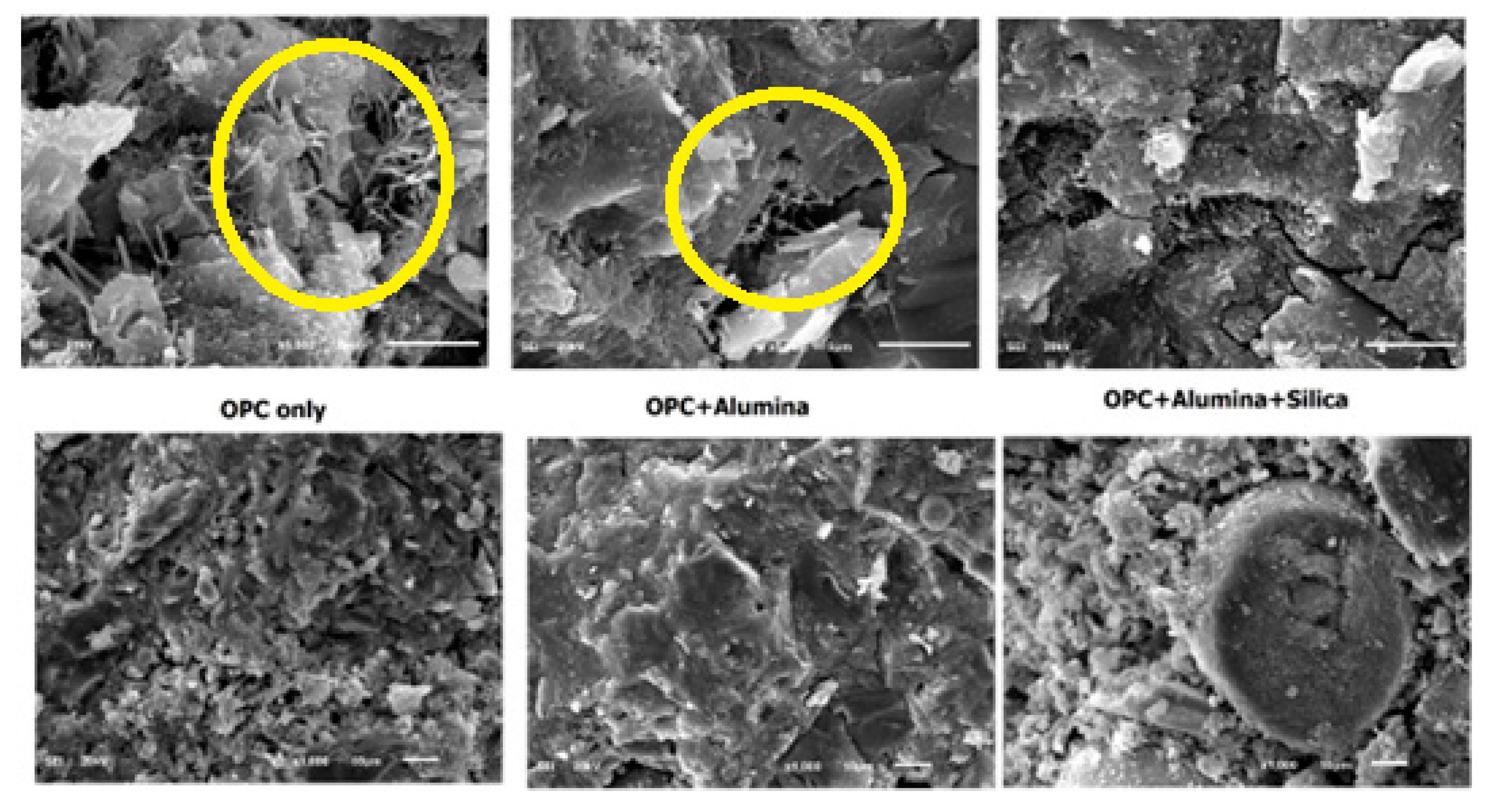
Fig 8 shows different morphology of nA treated binders. The morphology of OPC (OPC only) is seen to be very weak with excess of needle-like ettringite formation. The presence of nA apparently shows the blockage of the pores with a denser texture with visible ettringite formation (Aft). Upon adding both SF and nA together in ternary blending with OPC, the microstructural density was more pronounced with complete disappearance of Aft while the zone of transition interface of silica fume particle and cement matrix could have been possibly filled with nA.
It is very apparent that this microstructural density contributed significantly to the compressive strength of the ternary blended (SF and nA) mortar. Upon addition of silica fume, it appears the hydrogen gas is entrapped thereby leading to denser microstructure. Increasing the content of nA beyond 2% could lead to the formation of more micropores as shown by the micropore present in the SF-3%Al (
Figure 7). This could lead to slight reduction in the compressive strength as shown in
Figure 6 when the nA was 3%.
From the EDS results shown in
Table 3 for OPC (C
100S
0A
0), SF+OPC (C
90S
10A
0), SF+2%nA+OPC (C
88S
10A
2), and OPC+nA, it is apparent that introducing nA in SF blended binder increases the Ca/Al and Ca/Si ratios but reduces the Si/Al ratio whereas it reduces all these parameters in OPC binder. The presence of SF however, reduces Ca/Si and Ca/Al ratios in OPC binder but increases its Si/Al ratio. Therefore, the formation of tobermorite in SF-nA ternary binder in
Figure 6 is connected to the reduction in Ca/Si and Si/Al ratios compared to what is available in OPC binder.
3.6. FTIR of SF binary and SF-nA ternary binder
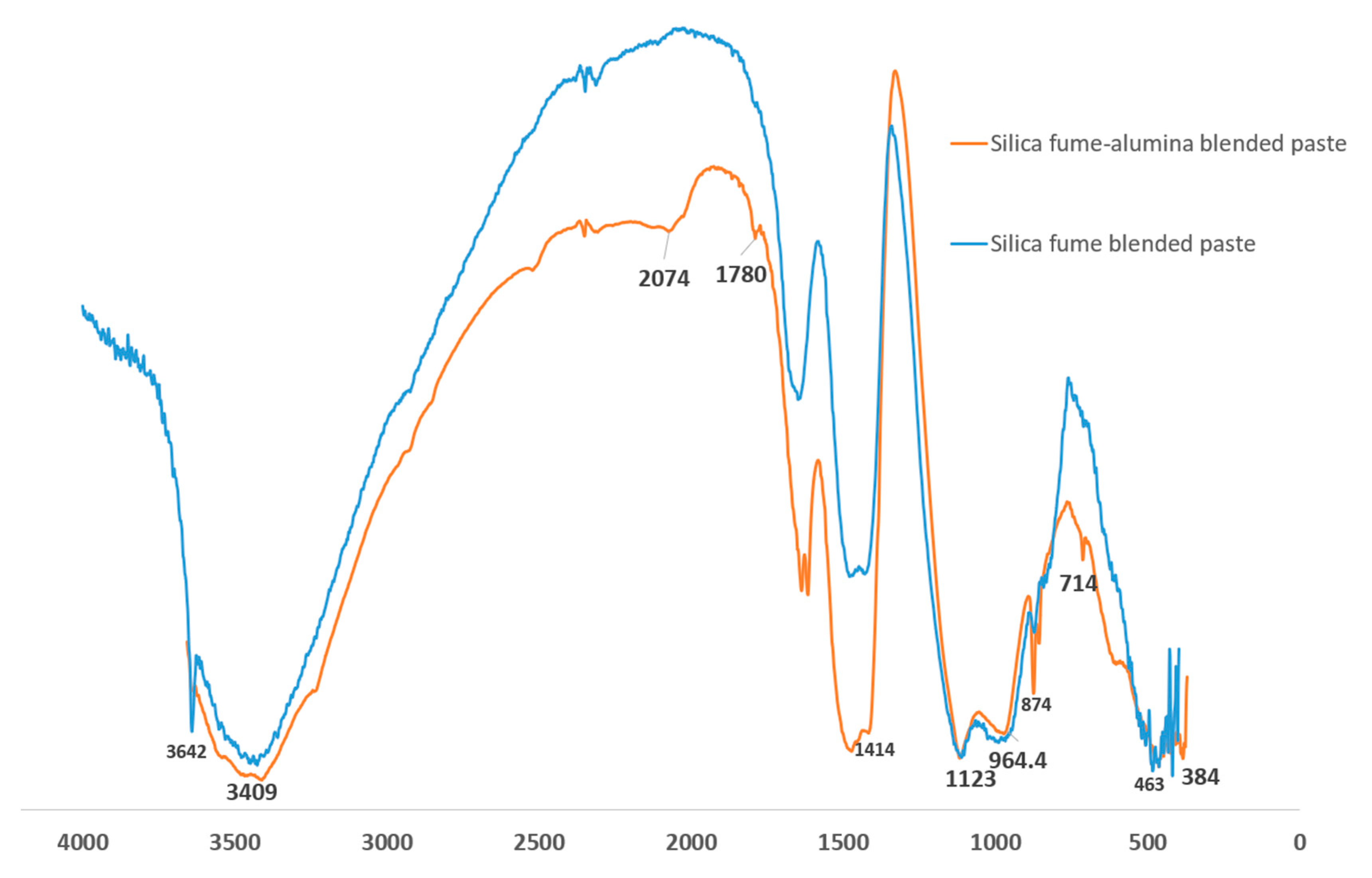
Figure 9 shows the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of SF blended and SF-nA blended binders. The prominent peaks that distinguish SF blended and SF-nA blended binder include 3642, 2074, 1780, 874, and 714 cm
-1. The octahedral stretching of O-A-O band is indicated by 463 cm
-1. Si-O-T (T: Si or Al) vibration from C/NASH source [
24] appears identical due to overlapping of the spectra in the range of 1100-1150 cm
-1 likewise, -OH vibration band at 3409 cm
-1. The asymmetric stretching of CO - from calcite source - had a stronger peak in SF-nA blended binder at 1414 cm
-1 and 1780 cm
-1 while CO out-of-plane and in-plane bending vibrations were indicated by 874 cm
-1 and 714 cm
-1, respectively. This further supports the strong calcite peak noted in XRD diffractogram in
Figure 6. It also indicates that ternary blended binder involving alumina additive could be more prone to carbonation. The HOH vibration is indicated by the peak 3642 cm
-1 in SF blended binder which was found to be absent in SF-nA blended mortar possibly due to penetration of nano particle into gel and capillary pores as a result of interaction of portlandite with both SF and alumina during the primary and secondary hydration reactions. This assertion need further verification through advanced microstructural analysis that is beyond the scope of this study.
3.7. Thermal performance of SF binary and SF-nA ternary blended mortar
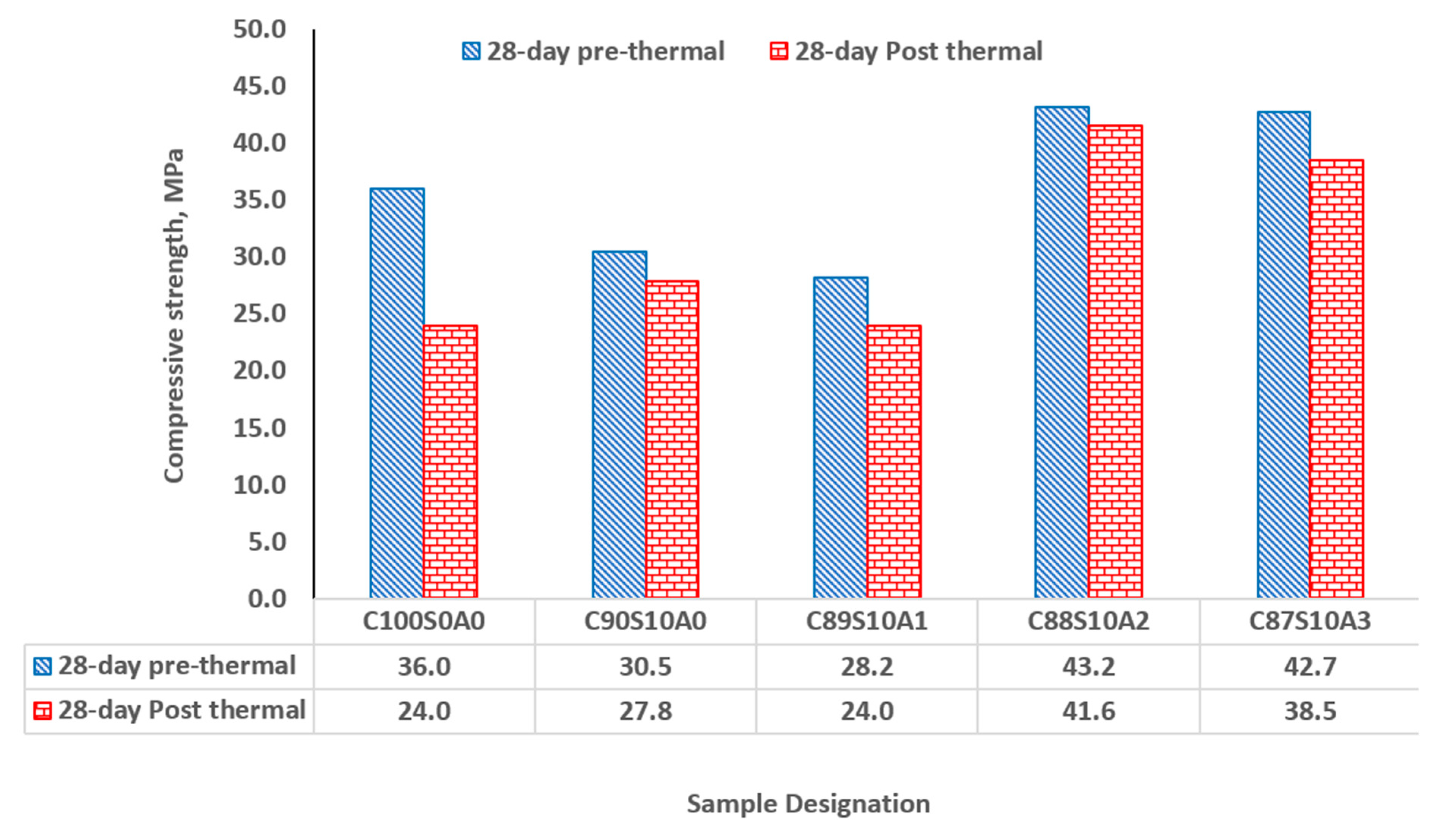
In all samples that were exposed to the temperature of 300
for 1 h, SF-nA ternary mortar showed significant thermal stability and resistance in comparison with SF binary and OPC binders. Upon exposure of the binders to thermal condition, OPC loss 33.33% of its 28-d compressive strength while SF binary binder (C
90S
10A
0) loss about 8.85% (
Figure 10). The incorporation of 1, 2 and 3% nA in SF-nA ternary binder results in the loss of 14.9, 3.70 and 9.84% of strength respectively. This implies that there is significant thermal resistance for the mortar synthesized using the 10% SF and 2% nA (C
88S
10A
2) which was due to refractory properties of alumina. The samples also showed no physical deterioration upon visual examination. For structures such as kitchen, furnace, and other facilities where fire resistance is very important could be repaired or constructed by using this SF-nA ternary mortar or concrete. Using SF-nA binder for concrete production could reduce the thickness of cover required to meet the minimum fire requirement in reinforced concrete design.
4. Conclusions
The study investigates the fresh and hardened properties of silica fume-nano alumina (SF-nA) ternary blended mortar such that the percentage of nA was kept with 1-3% while the SF was kept at 10%. These characteristics include workability, initial and final setting time, compressive strength, and thermal resistance to 300 C for 1h. The following are the conclusions:
SF-nA ternary blended binder (C90-xS10Ax) had a better consistency than SF only binary blended paste. nA improved the interparticle lubrication and the workability of silica fume blended mortar significantly. The mortar developed with 3% nA and 10%SFv(C87S10A3) could attain equal consistency with ordinary Portland cement (OPC) binder (C100S0A0).
SF delays the setting time of OPC due to dilution effect, however, the more the quantity of nA in C90-xS10Ax, the shorter the setting time. This implies that nA can be used to accelerate the delayed setting of SF blended binder (C90S10A0).
Early compressive strength of SF blended mortar (C90S10A0) was lower than that of OPC (C100S0A0) but incorporation of nA significantly enhanced the 28-d compressive strength while CSH, CASH, tobermorite (CSH of lower Ca/Si ratio), calcite and mayenite dominated the phases present in the SF-nA ternary binder as noticed in the x-ray diffractograms (XRD).
Introduction of nA in SF blended binder caused reduction in Ca/Al and Si/Al ratios compared to what is available in OPC binder.
The calcite peak and CO vibration peaks in x-ray diffractogram and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicate that SF-nA ternary blended binder is more prone to carbonation compared to SF blended concrete.
The optimum and maximum 28-day compressive strength of 43.2 MPa was achieved in the mixture with 10%SF and 2%nA (C88S10A2) whereas 36 and 30.5 MPa were recorded in OPC (C100S0A0) and 10%SF blended mortar (C90S10A0), respectively. The optimum mixture produced the densest microstructure.
The SF-nA ternary blended binder (C88S10A2) had a better thermal resistance - with 3.7% loss in its 28-day strength - than SF binary blended binder (C90S10A0) and OPC binders (C100S0A0), that lost 8.85 and 33.3%, respectively.
References
- M. O. Yusuf, “Synergistic-effect of iron-filing and silica-fume on the absorption and shrinkage of cement paste,” Magazine of Civil Engineering, vol. 91, no. 7, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Memphis, “Fly ash, Slag, silica fume, and natural Pozzolans,” Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures, no. 54048, pp. 57–72, 1996.
- P. C. A. K.H. Khayat, “Silica fume: a unique supplementary cementitious material, in: S.N. Ghosh (Ed.), Miner. Admixtures Cem. Concr.,” in ABI Books Private Limited, 1993, pp. 227–265.
- M. S. Fallah, Nematzadeh, “Mechanical properties and durability of high-strength concrete containing macro-polymeric and polypropylene fibers with nano-silica and silica fume.,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 132, 2017.
- C. Sadik, I. El Amrani, and A. Albizane, “Recent advances in silica-alumina refractory: A review,” Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies , vol. 2, pp. 83–96, 2014. [CrossRef]
- http://climateandweather.com/, “Weather in the Middle East,” http://climateandweather.com/weather-in-middle-east accessed Sept 11, 2023, Sep. 2023.
- Moruf O. Yusuf, “Performance of Aluminium Shaving Waste and Silica fume Blended Mortar,” Magazine of Civil Engineering, vol. 06, no. 22, 2023.
- C. A. ; D. S. K. ; J. I. S. Ungureanu, “Life-cycle cost analysis: aluminum versus steel in passenger cars.,” In aluminum alloys for transportation, packaging, aerospace, and other applications, 1st ed.; Das, K.S., Yin, W., Eds.; TMS: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, pp. 11–24, 2007.
- S. Capuzzi and G. Timelli, “Preparation and melting of scrap in aluminum recycling: A review,” Metals, vol. 8, no. 4. MDPI AG, Apr. 01, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. , Yu et al., “Influence of the degree of crystallinity of added nano-alumina on strength and reaction products of the CaO-activated GGBFS system.,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. ,296, no. 123647, 2021.
- J. , Yu et al., “Examination of sulfate resistance of nano-alumina added ordinary Portland cement paste, focusing on the two different crystallinity of nano-aluminas,” Int J Concr Struct Mater, vol. 17, no. 1, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. Dyer, Concrete durability. . Boca Raton: Crc Press., 2014.
- P. K. Mehta and A. Klein, “Formation of ettringite in pastes containing calcium aluminoferrites and gypsum,” National Science Foundation Committee on basic research partaining to Portland cement and concrete, vol. Grant No 6, pp. 36–45, 1965.
- Q. , Shao, K. , Zheng, X. , Zhou, J. , Zhou, and X. Zeng, “Enhancement of nano-alumina on long-term strength of portland cement and the relation to its influences on compositional and microstructural aspects. ,” Cem Concr Compos, vol. 98, pp. 39–48, 2019.
- B. J. , Zhan, D. X. , Xuan, and C. S. Poon, “The effect of nanoalumina on early hydration and mechanical properties of cement pastes. ,” Construction and Building Materials,202, 169–176., vol. 202, pp. 169–176, 2019.
- R. Shabbar, P. Nedwell, and Z. Wu, “Mechanical properties of lightweight aerated concrete with different aluminium powder content,” 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Shabbar, P. Nedwell, and Z. Wu, “Mechanical properties of lightweight aerated concrete with different aluminium powder content,” in MATEC Web of Conferences, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Shabbar, P. Nedwell, M. Al-Taee, and Z. Wu, “Effect of Different Aluminium Powder Content on the Behaviour of Aerated Concrete: Experimental and Finite Element Validation,” International Journal of Materials, Mechanics and Manufacturing, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 155–158, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia, “Aluminium oxide nano particle,” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminium_oxide_nanoparticle, Sep. 16, 2023.
- ASTM C157, “Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hardened Hydraulic-Cement Mortar and Concrete,” 2008.
- ASTM, “ASTM C191-21 Standard Test Methods for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle,” America Standard Method of Testing, Nov. 2021.
- ASTM C1437-20, “Standard Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar.” ASTM International, 2020.
- ASTM C109/C109M-20, “Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens).” ASTM International, 2020.
- M. O. Yusuf, “Bond Characterization in Cementitious Material Binders Using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy,” Applied Sciences, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 3353, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Zahedi and S. J. Mirmohammadi, “Sulfate removal from chemical industries’ wastewater using ettringite precipitation process with recovery of Al(OH)3,” Appl Water Sci, vol. 12, no. 9, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).