Submitted:
25 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Sperm Chromatin Status
2.1.1. Chromatin Maturation
2.1.2. Chromatin Compaction
2.1.3. Chromatin Stability
2.1.4. Protamine Deficiency
2.2. Analysis of DNA Fragmentation
2.3. Correlation between chromatin status and DNA fragmentation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Sperm collection
4.3. Aniline blue staining
4.4. Diff-Quik staining
4.5. Toluidine blue staining
4.6. Chromomycin A3 staining
4.7. DNA Fragmentation analysis
4.8. Statistical analyses
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andraszek, K.; Banaszewska, D.; Czubaszek, M.; Wójcik, E.; Szostek, M. Comparison of different chromatin staining techniques for bull sperm. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2014, 57, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, R. Protamines and male infertility. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 417-435. [CrossRef]
- Dogan, S.; Vargovic, P.; Oliveira, R.; Belser, L. E.; Kaya, A.; Moura, A.; Sutovsky, P.; Parrish, J.; Topper, E.; Memili, E. Sperm protamine-status correlates to the fertility of breeding bulls. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 92, 92-93. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T. R. D. S.; Assumpção M. E. O. D. Sperm DNA fragmentation: causes and identification. Zygote 2020, 28, 1-8.. [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Llavanera, M.; Mateo-Otero, Y.; Garcia-Bonavila, E.; Delgado-Bermúdez, A.; Yeste, M. Direct but not indirect methods correlate the percentages of sperm with altered chromatin to the intensity of chromatin damage. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 972. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T. R. D. S.; Siqueira, A. F. P.; De Castro, L. S.; Mendes, C. M.; Delgado, J. C.; de Assis, P. M.; Mesquita, L. P.; Maiorka, P. C.; Nichi, M.; Goissis, M. D.; Visintin, J. A.; Assumpção, M. E. O. D. Effect of heat stress on sperm DNA: protamine assessment in ram spermatozoa and testicle. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 5413056. [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Liu, L.; Murphy, K.; Ge, S.; Hotaling, J.; Aston, K. I.; Emery, B.; Carrell, D. T. Comparative analysis of three sperm DNA damage assays and sperm nuclear protein content in couples undergoing assisted reproduction treatment. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 904-917. [CrossRef]
- Virant-Klun, I.; Tomazevic, T.; Meden-Vrtovec, H. Sperm single-stranded DNA, detected by acridine orange staining, reduces fertilization and quality of ICSI-derived embryos. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2002, 19, 319. [CrossRef]
- Gosálvez, J.; López-Fernández, C.; Fernández, J. L.; Gouraud, A.; Holt, W. V. Relationships between the dynamics of iatrogenic DNA damage and genomic design in mammalian spermatozoa from eleven species. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2011, 78, 951-961. [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Garcia-Bonavila, E.; Bonet, S.; Catalán, J.; Salas-Huetos, A.; Yeste, M. The TUNEL assay underestimates the incidence of DNA damage in pig sperm due to chromatin condensation. Theriogenology 2021, 174, 94-101. [CrossRef]
- DelBarco-Trillo, J.; García-Álvarez, O.; Soler, A. J.; Tourmente, M.; Garde, J. J.; Roldan, E. R. S. A cost for high levels of sperm competition in rodents: increased sperm DNA fragmentation. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2016, 283, 20152708. [CrossRef]
- Balhorn, R. Sperm chromatin: an overview. In A Clinician’s Guide to Sperm DNA and Chromatin Damage; Zini, A., Agarwal, A., Eds.; Springer, 2018; pp. 3-30. [CrossRef]
- Annunziato, A. DNA packaging: nucleosomes and chromatin. In Nature Education; 2008; Volume 1, p. 26.
- Brewer, L. R.; Corzett, M.; Balhorn, R. Protamine-induced condensation and decondensation of the same DNA molecule. Science 1999, 286, 120-123. [CrossRef]
- Wykes, S. M.; Krawetz, S. A. Conservation of the PRM1 → PRM2 → TNP2 domain. DNA Seq. 2003, 14, 359-367. [CrossRef]
- Manvelyan, M.; Hunstig, F.; Bhatt, S.; Mrasek, K.; Pellestor, F.; Weise, A.; Simonyan, I.; Aroutiounian, R.; Liehr, T. Chromosome distribution in human sperm – a 3D multicolor banding-study. Mol. Cytogenet. 2008, 1, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- De Yebra, L.; Ballesca, J. L.; Vanrell, J. A.; Bassas, L.; Oliva, R. Complete selective absence of protamine P2 in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10553-10557. [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Spiess, A. N.; Schuppe, H.C.; Steger, K. The impact of sperm protamine deficiency and sperm DNA damage on human male fertility: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology 2016, 4, 789-799. [CrossRef]
- Mengual, L.; Ballescà, J. L.; Ascaso, C.; Oliva, R. Marked differences in protamine content and P1/P2 ratios in sperm cells from percoll fractions between patients and controls. J. Androl. 2003, 24, 438-447. [CrossRef]
- Comizzoli, P.; Holt, W. V. Recent progress in spermatology contributing to the knowledge and conservation of rare and endangered species. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 10, 469–490. [CrossRef]
- Iranpour, F. G.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. H.; Valojerdi, M. R.; Taki Al-Taraihi, T. M. Chromomycin A3 staining as a useful tool for evaluation of male fertility. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2000, 17, 60-66. [CrossRef]
- Aitken, R. J.; De Iuliis, G. N., Mclachlan, R.I. Biological and clinical significance of DNA damage in the male germ line. Int. J. Androl. 2009, 32, 46-56. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Henkel, R.; Agarwal, A. Comparative analysis of tests used to assess sperm chromatin integrity and DNA fragmentation. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13718. [CrossRef]
- Dadoune, J. P.; Mayaux, M. J.; Guihard-Moscato, M. L. Correlation between defects in chromatin condensation of human spermatozoa stained by aniline blue and semen characteristics. Andrologia 1988, 20, 211-217. [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Chuan, S. S.; Patton, W. C.; Jacobson, J. D.; Corselli, J.; Chan, P. J. Addition of eosin to the aniline blue assay to enhance detection of immature sperm histones. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 90, 1999-2002. [CrossRef]
- Marchiani, S.; Tamburrino, L.; Benini, F.; Fanfani, L.; Dolce, R.; Rastrelli, G.; Maggi, M.; Pellegrini, S.; Baldi, E. Chromatin protamination and Catsper expression in spermatozoa predict clinical outcomes after assisted reproduction programs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Sellami, A.; Chakroun, N.; Ben Zarrouk, S.; Sellami, H.; Kebaili, S.; Rebai, T.; Keskes, L. Assessment of chromatin maturity in human spermatozoa: Useful aniline blue assay for routine diagnosis of male infertility. Adv. Urol. 2013, 2013, 578631. [CrossRef]
- Banaszewska, D.; Andraszek, K.; Biesiada-Drzazga, B. Evaluation of sperm chromatin structure in boar semen. Bull Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2015, 59, 271-277. [CrossRef]
- Pourmasumi, S.; Khoradmehr, A.; Rahiminia, T.; Sabeti, P.; Talebi, A. R.; Ghasemzadeh, J. Evaluation of sperm chromatin integrity using aniline blue and toluidine blue staining in infertile and normozoospermic men. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2019, 20, 95-101. PMID: 31058054; PMCID: PMC6486564.
- Sousa, A. P. M.; Tavares, R. S.; Velez De La Calle, J. F.; Figueiredo, H.; Almeida, V.; Almeida-Santos, T.; Ramalho-Santos, J. Dual use of Diff-Quik-like stains for the simultaneous evaluation of human sperm morphology and chromatin status. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 28-36. [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R. S.; Silva, A. F.; Lourenço, B.; Almeida-Santos, T.; Sousa A. P.; Ramalho-Santos, J. Evaluation of human sperm chromatin status after selection using a modified Diff-Quik stain indicates embryo quality and pregnancy outcomes following in vitro fertilization. Andrology 2013, 1, 830-837. [CrossRef]
- Windt, M. L.; de Beer, P. M.; Franken, D. R.; Rhemrev, J.; Menkveld, R.; Lombard, C.; Kruger, T. F. Sperm decondensation and semen parameters: utilization of a simple staining technique for the evaluation of human sperm decondensation. Andrologia 2009, 26, 67-72. [CrossRef]
- Pourmasumi, S.; Nazari, A.; Fagheirelahee, N.; Sabeti, P. Cytochemical tests to investigate sperm DNA damage: Assessment and review. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1533-1539. [CrossRef]
- Castro, L. S.; Siqueira, A. F. P.; Hamilton, T. R. S.; Mendes, C. M.; Visintin, J. A.; Assumpção, M. E. O. D. Effect of bovine sperm chromatin integrity evaluated using three different methods on in vitro fertility. Theriogenology 2018, 107, 142-148. [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, D.; Manicardi, G. C.; Bianchi, P. G.; Bianchi, U.; Mariethoz, E.; Sakkas, D. In-situ competition between protamine and fluorochromes for sperm DNA. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 127-132. [CrossRef]
- Lolis, D.; Georgiou, I.; Syrrou, M.; Zikopoulos, K.; Konstantelli, M.; Messinis, I. Chromomycin A3-staining as an indicator of protamine deficiency and fertilization. Int. J. Androl. 1996, 19, 23-27. [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M. H.; Razavi, S.; Mardani, M. Relation between different human sperm nuclear maturity tests and in vitro fertilization. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2001, 18, 219-225. [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, P.; Amidi, F.; Kalantar, S. M.; Sedighi Gilani, M. A.; Pourmasumi, S.; Najafi, A.; Talebi, A. R. Evaluation of intracellular anion superoxide level, heat shock protein A2 and protamine positive spermatozoa percentages in teratoasthenozoospermia. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2017, 15, 279-286. [CrossRef]
- Czubaszek, M.; Andraszek, K.; Banaszewska, D. Influence of the age of the individual on the stability of boar sperm genetic material. Theriogenology 2020, 147, 176-182. [CrossRef]
- Kazerooni, T.; Asadi, N.; Jadid, L.; Kazerooni, M.; Ghanadi, A.; Ghaffarpasand, F.; Kazerooni, Y.; Zolghadr, J. Evaluation of sperm’s chromatin quality with acridine orange test, chromomycin A3 and aniline blue staining in couples with unexplained recurrent abortion. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2009, 26, 591-596. [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Murphy, K.; Shamsi, M. B.; Liu, L.; Emery, B.; Aston, K. I.; Hotaling, J.; Carrell, D. T. Paternal influence of sperm DNA integrity on early embryonic development. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 2402-2412. [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M. R. S.; Satake, N.; Corbet, D. H.; Corbet, N. J.; Burns, B. M.; Moore, S. S.; Boe-Hansen, G. B. Sperm protamine deficiency correlates with sperm DNA damage in Bos indicus bulls. Andrology 2014, 2, 370-378. [CrossRef]
- Kipper, B. H.; Trevizan, J. T.; Carreira, J. T.; Carvalho, I. R.; Mingoti, G. Z.; Beletti, M. E.; Perri, S. H. V.; Franciscato, D. A.; Pierucci, J. C.; Koivisto, M. B. Sperm morphometry and chromatin condensation in Nelore bulls of different ages and their effects on IVF. Theriogenology 2017, 87, 154-160. [CrossRef]
- Simoes, R.; Feitosa, W. B.; Mendes, C. M.; Marques, M.G.; Nicacio, A. C.; de Barros, F. R. O.; Visintin, J. A.; Assumpção, M. E. O. D. Use of chromomycin A3 staining in bovine sperm cells for detection of protamine deficiency. Biotech. Histochem. 2009, 84, 79-83. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Talebi, A. R.; Shahedi, A.; Moein, M. R.; Abbasi-Sarcheshmeh, A. Effects of tamoxifen on DNA integrity in mice. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2019, 20, 10-15. PMID: 30859077; PMCID: PMC6386794.
- Mohammadzadeh, M.; Pourentezari, M.; Zare-Zardini, H.; Nabi, A.; Esmailabad, S. G.; Khodadadian, A.; Talebi, A. R. The effects of sesame oil and different doses of estradiol on testicular structure, sperm parameters, and chromatin integrity in old mice. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2021, 48, 34-42. [CrossRef]
- Ozkosem, B.; Feinstein, S. I.; Fisher, A. B.; O’Flaherty, C. Advancing age increases sperm chromatin damage and impairs fertility in peroxiredoxin 6 null mice. Redox Biol. 2015, 5, 15-23. [CrossRef]
- Merges, G. E.; Meier, J.; Schneider, S.; Kruse, A.; Fröbius, A. C.; Kirfel, G.; Steger, K.; Arévalo, L.; Schorle, H. Loss of Prm1 leads to defective chromatin protamination, impaired PRM2 processing, reduced sperm motility and subfertility in male mice. Development 2022, 149, dev200330. [CrossRef]
- Agudo-Rios, C.; Rogers, A.; King I.; Bhagat, V.; Nguyen, L. M. T.; Córdova-Fletes, C.; Krapf, D.; Strauss III, J. F.; Arévalo, L.; Merges, G. E.; Schorle, H.; Roldan, E. R. S.; Teves, M. E. SPAG17 mediates nuclear translocation of protamines during spermiogenesis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2023, (in press).
- Suarez, S. S. Mammalian sperm interactions with the female reproductive tract. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 185-194. [CrossRef]
- Kölle, S. Sperm-oviduct interactions: Key factors for sperm survival and maintenance of sperm fertilizing capacity. Andrology 2022, 10, 837-843. [CrossRef]
- Mahé, C.; Zlotkowska, A. M.; Reynaud, K.; Tsikis, G.; Mermillod, P.; Druart, X.; Schoen, J.; Saint-Dizier, M. Sperm migration, selection, survival, and fertilizing ability in the mammalian oviduct†. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 317-331. [CrossRef]
- Tourmente, M.; Villar-Moya, P.; Varea-Sanchez, M.; Luque-Larena, J.J.; Rial, E.; Roldan, E.R.S. Performance of rodent spermatozoa over time is enhanced by increased ATP concentrations: The role of sperm competition. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 64. [CrossRef]
- Beletti, M. E.; Mello, M. L. S. Comparison between the toluidine blue stain and the Feulgen reaction for evaluation of rabbit sperm chromatin condensation and their relationship with sperm morphology. Theriogenology 2004, 62, 398-402. [CrossRef]
- Flores, R. B.; Angrimani, D. S. R.; Rui, B. R.; Brito, M. M.; Abreu, R. A.; Vannucchi, C. I. The influence of benign prostatic hyperplasia on sperm morphological features and sperm DNA integrity in dogs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 310-315. [CrossRef]
- Krzanowska, H. Toluidine blue staining reveals changes in chromatin stabilization of mouse spermatozoa during epididymal maturation and penetration of ova. J. Reprod Fertil. 1982, 64, 97-101. [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Talebi, A. R.; Mangoli, E.; Shahedi, A.; Ghasemi, M. R.; Pourentezari, M. Effects of acrylamide in the presence of vitamin E on sperm parameters, chromatin quality, and testosterone levels in mice. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2020, 47, 101-107. [CrossRef]
- Danafar, A.; Khoradmehr, A.; Hosseini Bondarabadi, M.; Mazaheri, F.; Tamadon, A.; Pourmasoumi, S.; Gholizadeh, L.; Moshrefi, M.; Halvaei, I.; Hosseini, A.; Golzadeh, J.; Rahiminia, T.; Anvari, M. Impairment of sperm efficiency in mice following short-term nano-titanium dioxide exposure: An experimental study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2021, 19, 1045-1058. [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Mojaverrostami, S.; Khadivi, F.; Rastegar, T.; Abbasi, Y.; Bashiri, Z. Protective effects of human amniotic membrane derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) secreted factors on mouse spermatogenesis and sperm chromatin condensation following unilateral testicular torsion. Ann. Anat. 2023, 249, 152084. [CrossRef]
- Khordad, E.; Nikravesh, M. R.; Jalali, M.; Fazel, A.; Sankian, M.; Alipour, F. Evaluation of sperm chromatin/DNA integrity, morphology, and Catsper expression on diabetic C57BL/6 mice. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 8-18. [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, D.; Manicardi, G.; Bianchi, P. G.; Bizzaro, D.; Bianchi, U. Relationship between the presence of endogenous nicks and sperm chromatin packaging in maturing and fertilizing mouse spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 52, 1149-1155. [CrossRef]
- Mota, P. C.; Ramalho-Santos, J. Comparison between different markers for sperm quality in the cat: Diff-Quik as a simple optical technique to assess changes in the DNA of feline epididymal sperm. Theriogenology 2006, 65, 1360-1375. [CrossRef]
- Boe-Hansen, G. B.; Fortes, M. R. S.; Satake, N. Morphological defects, sperm DNA integrity, and protamination of bovine spermatozoa. Andrology 2018, 6, 627-633. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P. J.; Orzylowska, E. M.; Corselli, J. U.; Jacobson, J. D.; Wei, A. K. A simple sperm DNA toroid integrity test and risk of miscarriage. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 780983. [CrossRef]
- Nur Karakus, F.; Bulgurcuoglu Kuran, S.; Solakoglu, S. Effect of curcumin on sperm parameters after the cryopreservation. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 267, 161-166. [CrossRef]
- Belloc, S.; Benkhalifa, M.; Junca, A. M.; Dumont, M.; Bacrie, P. C.; Ménézo, Y. Paternal age and sperm DNA decay: discrepancy between chromomycin and aniline blue staining. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2009, 19, 264-269. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cerezales, S.; Miranda, A.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A. Comparison of four methods to evaluate sperm DNA integrity between mouse caput and cauda epididymidis. Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 335-337. [CrossRef]
- Sansegundo, E.; Tourmente, M.; Roldan, E. R. S. Energy metabolism and hyperactivation of spermatozoa from three mouse species under capacitating conditions. Cells 2022, 11, 220. [CrossRef]
- Kritaniya, D.; Yadav, S.; Swain, D. K.; Reddy, A. V.; Dhariya, R.; Yadav, B.; Anand, M.; Nigam, R. Freezing-thawing induces deprotamination, cryocapacitation-associated changes; DNA fragmentation; and reduced progesterone sensitivity in buck spermatozoa. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 223, 106628. [CrossRef]
- Tavalaee, M.; Razavi, S.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. H. Influence of sperm chromatin anomalies on assisted reproductive technology outcome. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 1119-1126. [CrossRef]
- Khezri, A.; Narud, B.; Stenseth, E. B.; Johannisson, A.; Myromslien, F. D.; Gaustad, A. H.; Wilson, R. C.; Lyle, R.; Morrell, J. M.; Kommisrud, E.; Ahmad, R. DNA methylation patterns vary in boar sperm cells with different levels of DNA fragmentation. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 897. [CrossRef]
- Franken, D. R.; Franken, C. J.; De La Guerre, H.; De Villiers, A. Normal sperm morphology and chromatin packaging: comparison between aniline blue and chromomycin A3 staining. Andrologia 1999, 31, 361-366. [CrossRef]
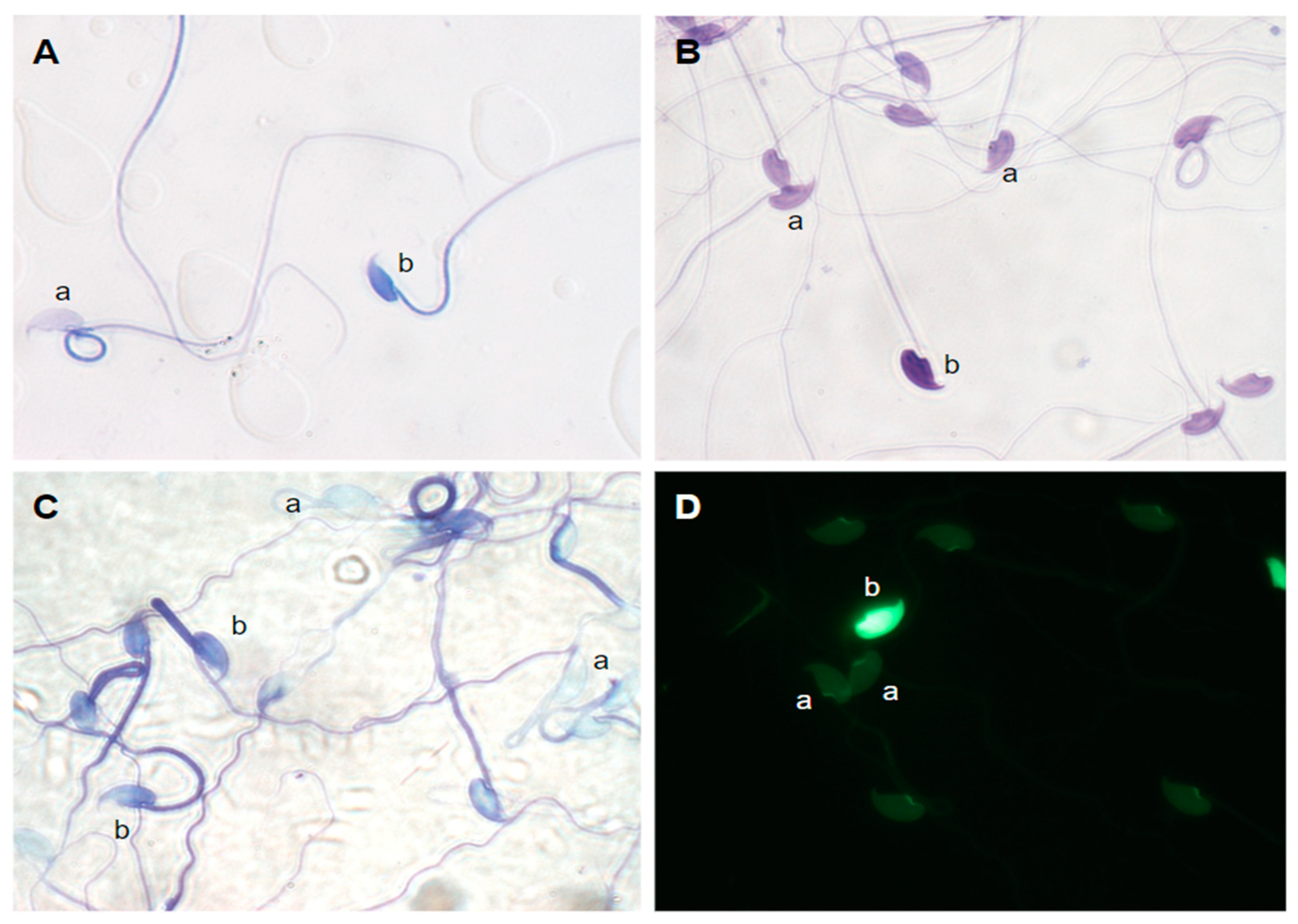
| Species | Percentage of stained cells at | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h | |
| M. musculus | 0.55±0.23 | 1.45±0.42 | 0.90±0.39 |
| M. spretus | 0.55±0.36 | 0.90±0.32 | 0.35±0.52 |
| M. spicilegus | 0.00±0.00 | 0.65±0.26 | 0.65±0.26 |
| Species | Percentage of stained cells at | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h | |
| M. musculus | 1.15±0.06a | 2.25±0.14a | 1.10±0.19 |
| M. spretus | 0.70±0.20a | 1.95±0.59a | 1.25±0.50 |
| M. spicilegus | 0.50±0.16a | 1.75±0.47a | 1.25±0.36 |
| Completely stained (%) |
Partially stained (%) |
Total staining (%) |
Total staining |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 0 h | 3 h | 0 h | 3 h | 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h |
| M. musculus | 0.95±0.20 | 1.40±0.47 | 0.10±0.06 | 0.40±0.29 | 1.05±0.18 | 1.80±0.70 | 0.75±0.68 |
| M. spretus | 1.15±0.36 | 1.80±0.24 | 0.05±0.05 | 0.25±0.19 | 1.20±0.40 | 2.05±0.34 | 0.85±0.56 |
| M. spicilegus | 0.35±0.17 | 1.35±0.33 | 0.05±0.05 | 0.60±0.15 | 0.40±0.19a | 1.95±0.40a | 1.55±0.35 |
| Species | Parameter | 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. musculus | %tDFI | 1.38±0.14a,1,2 | 1.89±0.19a,1,2 | 0.51±0.22 |
| %HDS | 3.77±0.51 | 6.98±1.45 | 3.21±1.24 | |
| M. spretus | %tDFI | 0.56±0.061 | 0.76±0.171 | 0.19±0.12 |
| %HDS | 2.60±0.25 | 7.84±2.14 | 5.24±2.07 | |
| M. spicilegus | %tDFI | 0.35±0.032 | 0.41±0.052 | 0.06±0.05 |
| %HDS | 2.76±0.48 | 6.86±2.58 | 4.11±2.24 |
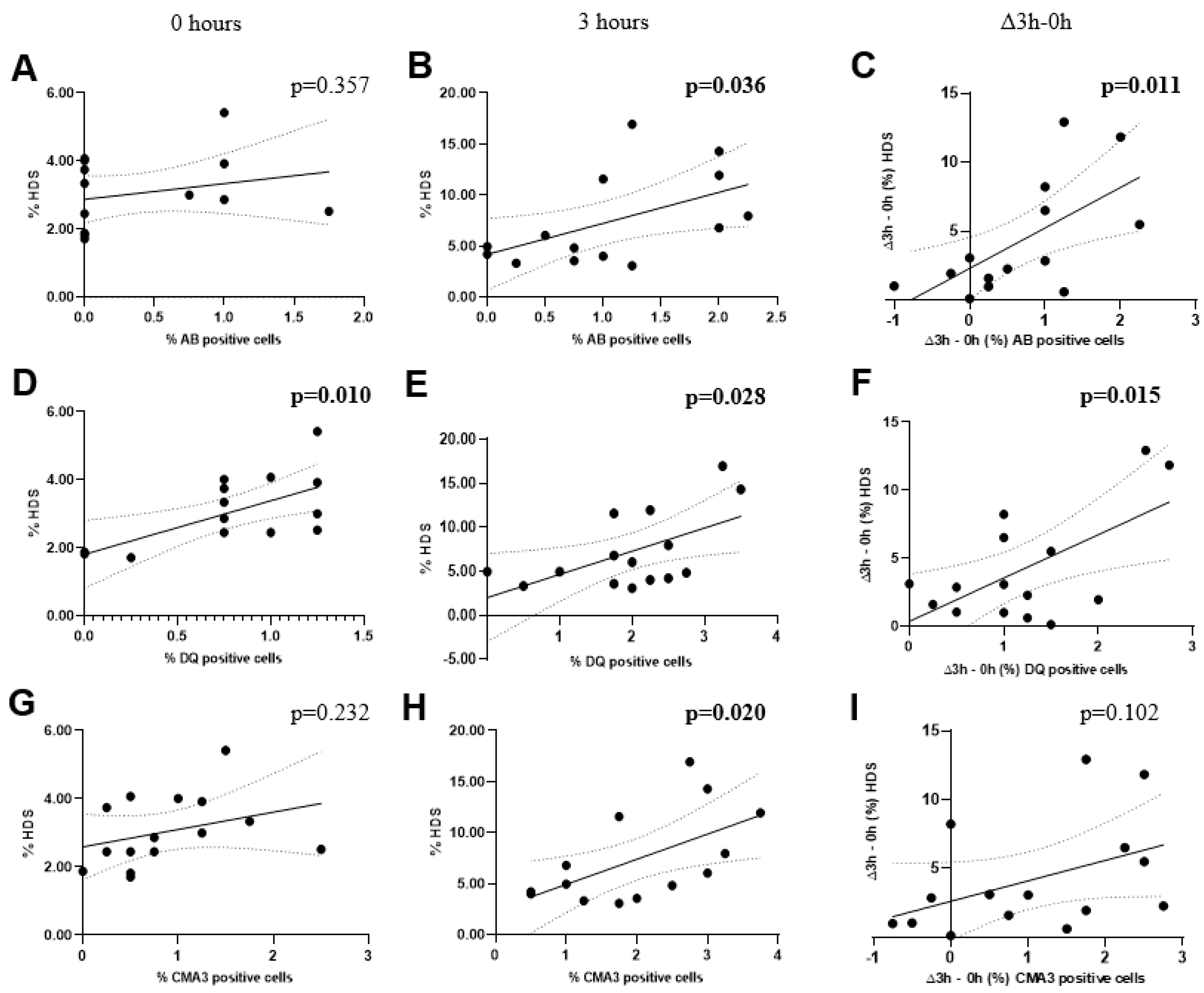
| Species | Parameter | tDFI | HDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h | 0 h | 3 h | Δ3h–0h | ||
| All species | AB | 0.2925 (0.290) |
0.3679 (0.177) | 0.1002 (0.722) |
0.2562 (0.357) |
0.5450 (0.036) |
0.6345 (0.011) |
| DQ |
0.6163 (0.014) |
0.2625 (0.345) | 0.0486 (0.864) |
0.6412 (0.010) |
0.5670 (0.028) |
0.6132 (0.015) |
|
| CMA3 | 0.2918 (0.291) |
0.0382 (0.892) | -0.0833 (0.768) |
0.3284 (0.232) |
0.5927 (0.020) |
0.4381 (0.102) |
|
| M. musculus | AB | 0.2858 (0.641) |
-0.2360 (0.702) |
-0.0253 (0.968) |
0.5228 (0.366) |
0.7169 (0.173) |
0.7819 (0.118) |
| DQ | 0.4016 (0.503) |
0.6120 (0.273) |
0.4455 (0.452) |
0.4116 (0.491) |
-0.0899 (0.886) |
-0.0478 (0.939) |
|
| CMA3 | 0.5115 (0.378) |
0.4793 (0.412) |
0.3814 (0.526) |
0.4551 (0.441) |
0.9148 (0.030) |
0.8926 (0.042) |
|
| M. spretus | AB | -0.3486 (0.565) |
0.1641 (0.792) |
-0.0292 (0.963) |
0.0717 (0.909) |
0.8115 (0.095) |
0.9833 (0.003) |
| DQ | 0.0602 (0.923) |
0.2023 (0.744) | -0.0995 (0.874) |
0.5443 (0.343) |
0.5308 (0.357) |
0.6044 (0.280) |
|
| CMA3 | -0.0890 (0.887) |
0.0645 (0.918) | -0.5108 (0.379) |
0.4174 (0.485) |
0.4768 (0.417) |
0.5130 (0.377) |
|
| M. spicilegus | AB | - | -0.1220 (0.845) | 0.4029 (0.501) |
- | 0.4940 (0.398) |
0.4454 (0.452) |
| DQ | -0.8715 (0.054) |
-0.2552 (0.679) | 0.3730 (0.536) |
0.7893 (0.112) |
0.8107 (0.096) |
0.8480 (0.070) |
|
| CMA3 | -0.5783 (0.307) |
-0.3926 (0.513) | -0.3614 (0.550) |
0.5568 (0.330) |
0.5962 (0.289) |
0.1483 (0.812) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





