Submitted:
22 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soils, Biochars and Organic Amendments
2.2. Incubation Experiment
2.3. Activity of Enzymes
2.4. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
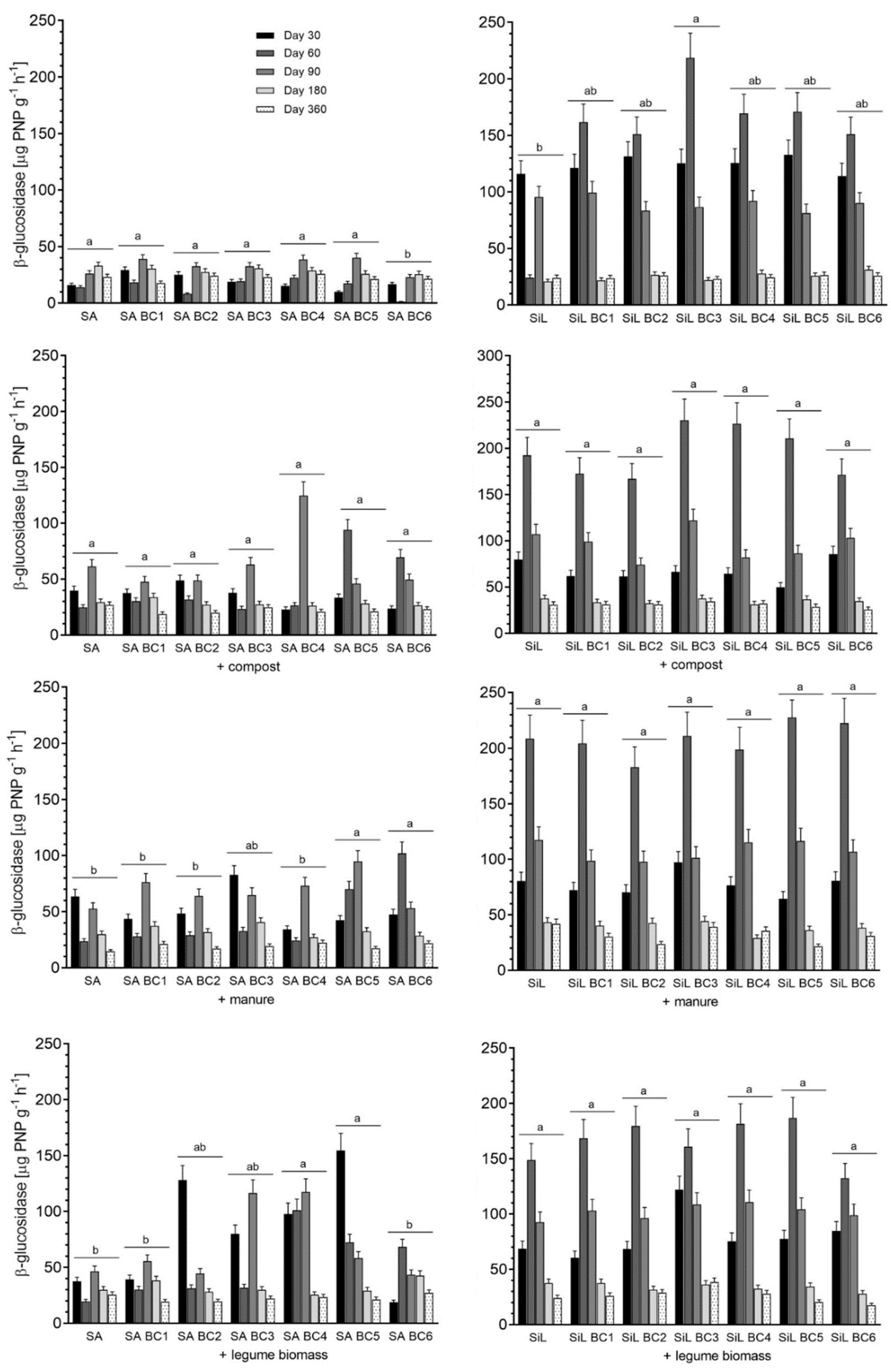
3.1. β-Glucosidase Activity
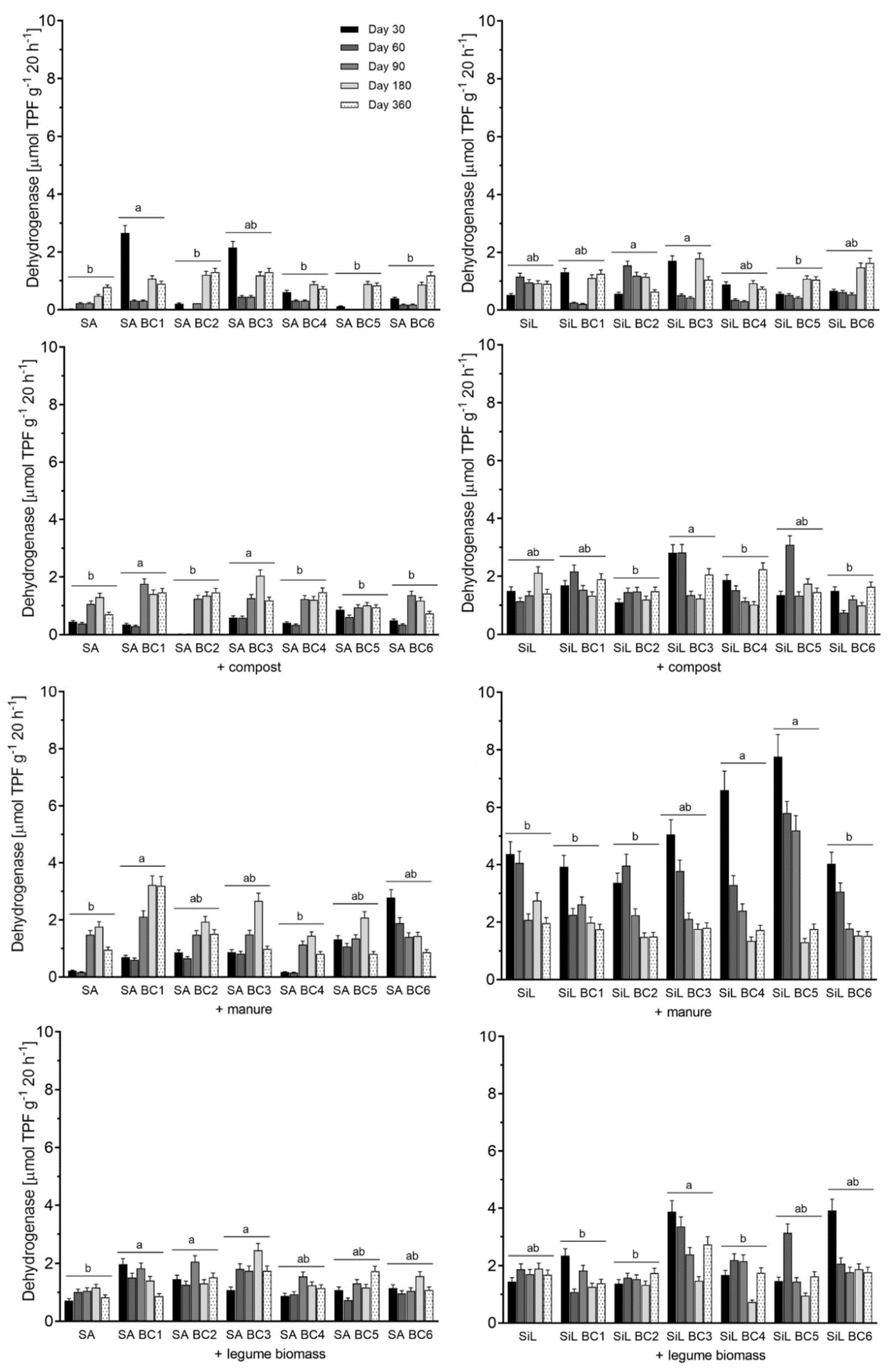
3.2. Dehydrogenase Activity
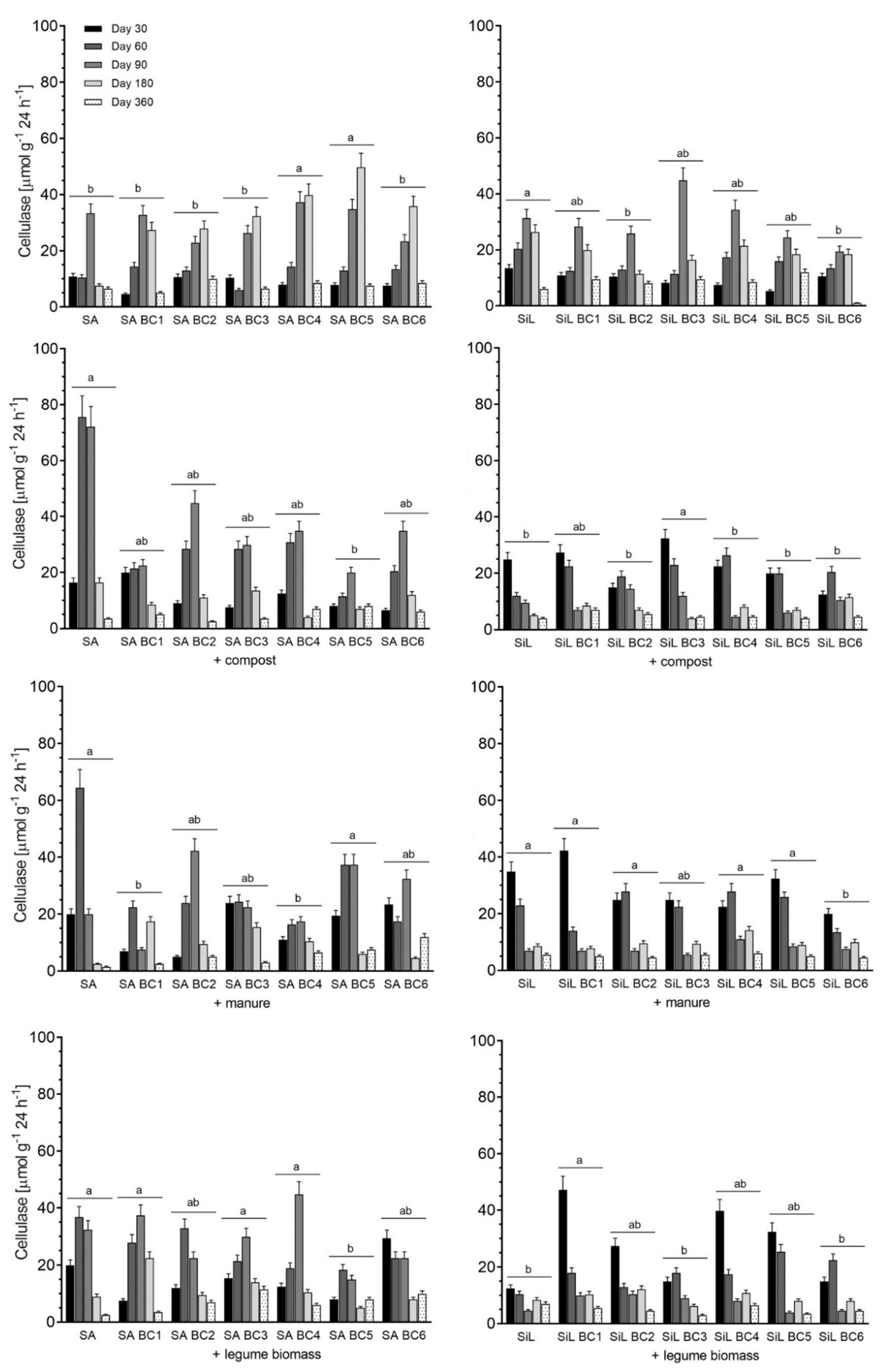
3.3. Cellulase Activity
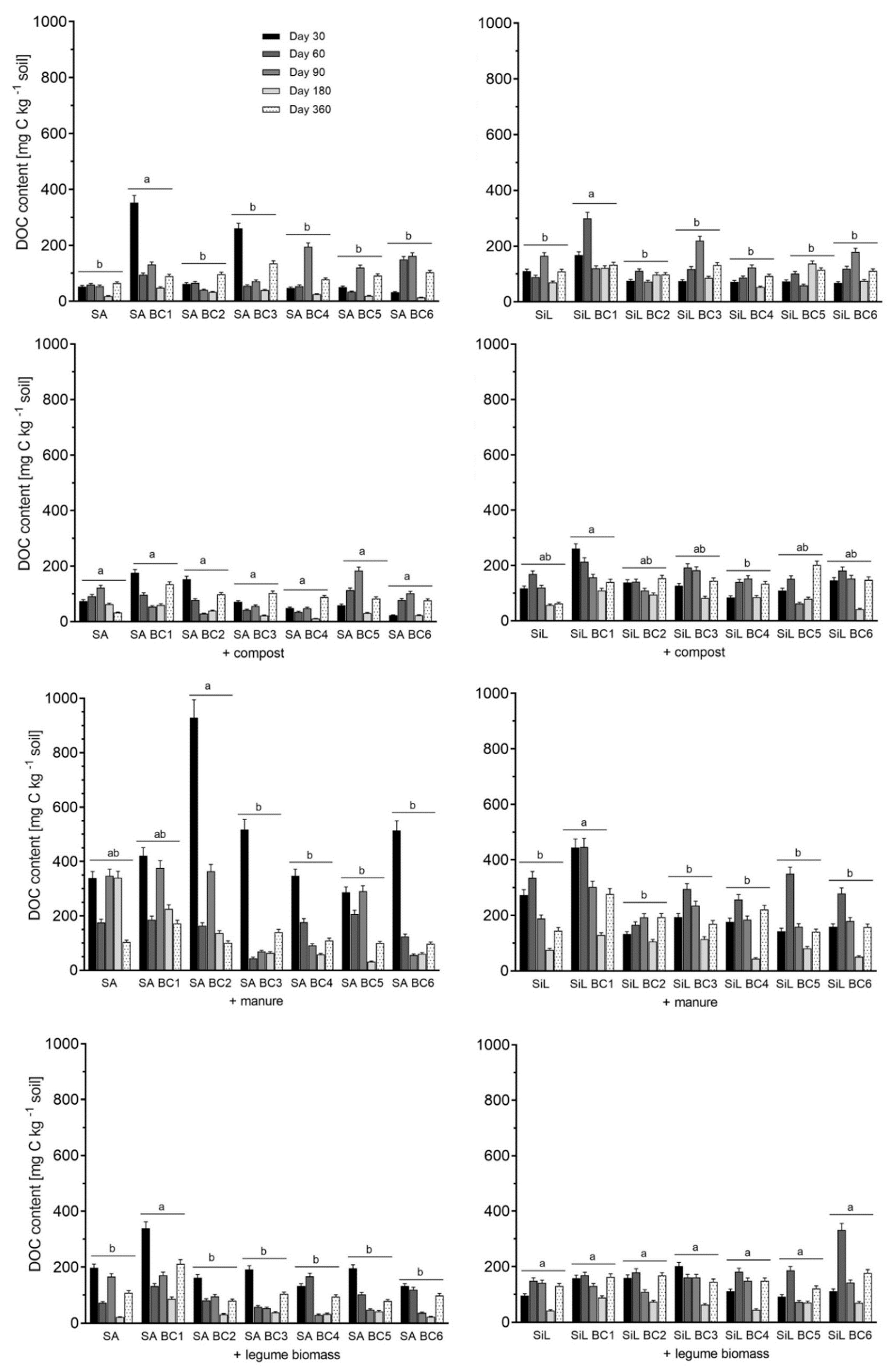
3.4. Dissolved Organic Carbon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mona, S.; Malyan, S.K.; Saini, N.; Deepak, B.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, S.S. Towards Sustainable Agriculture with Carbon Sequestration, and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Using Algal Biochar. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Hussain, S.; Guo, R.; Sarwar, M.; Ren, X.; Krstic, D.; Aslam, Z.; Zulifqar, U.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; et al. Carbon Sequestration to Avoid Soil Degradation: A Review on the Role of Conservation Tillage. Plants 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbeiss, S.; Gleixner, G.; Antonietti, M. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Soil Carbon Balance and Soil Microbial Activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2009, 41, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Bromm, T.; Glaser, B. Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration after Biochar Application: A Global Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Abiven, S.; Kleber, M.; Pan, G.; Singh, B.; Sohi, S.P.; Zimmerman, A.R. Persistence of Biochar in Soil. In Biochar for environmental management: science, technology and implementation; Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group: London ; New York, 2015; pp. 267–314 ISBN 978-0-415-70415-1.
- Minasny, B.; Malone, B.P.; McBratney, A.B.; Angers, D.A.; Arrouays, D.; Chambers, A.; Chaplot, V.; Chen, Z.-S.; Cheng, K.; Das, B.S.; et al. Soil Carbon 4 per Mille. Geoderma 2017, 292, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradette, O.; Marty, C.; Faubert, P.; Dessureault, P.-L.; Paré, M.; Bouchard, S.; Villeneuve, C. Additional Carbon Sequestration Potential of Abandoned Agricultural Land Afforestation in the Boreal Zone: A Modelling Approach. Forest Ecology and Management 2021, 499, 119565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, M.; Thiffault, E.; Bergeron, Y.; Ouimet, R.; Tremblay, S. Afforestation of Abandoned Agricultural Lands for Carbon Sequestration: How Does It Compare with Natural Succession? Plant Soil 2022, 475, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Nath, C.P.; Hazra, K.K.; Das, K.; Venkatesh, M.S.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, S.S.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, N.P. Impact of Zero-till Residue Management and Crop Diversification with Legumes on Soil Aggregation and Carbon Sequestration. Soil and Tillage Research 2019, 189, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, X. No Tillage Increases Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Decreases Carbon Dioxide Emission in the Crop Residue-Returned Farming System. Journal of Environmental Management 2020, 261, 1–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Gupta, C.K.; Dubey, R.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Sharma, G.; A., K.; Noor Mohamed, M.B.; Dev, R.; Shukla, A.K. Role of Biochar in Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation. In Biochar Applications in Agriculture and Environment Management; Singh, J.S., Singh, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 141–165 ISBN 978-3-030-40996-8.
- Smith, P. Soil Carbon Sequestration and Biochar as Negative Emission Technologies. Glob Change Biol 2016, 22, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B. Prehistorically Modified Soils of Central Amazonia: A Model for Sustainable Agriculture in the Twenty-First Century. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2007, 362, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Huang, J. Spectral Signatures of Soil Horizons and Soil Orders – An Exploratory Study of 270 Soil Profiles. Geoderma 2021, 389, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Bhat, S.; Kuriqi, A.; Dar, M.U.D.; Bhat, O.; Sammen, S.Sh.; Towfiqul Islam, A.R.Md.; Elbeltagi, A.; Shah, O.; AI-Ansari, N.; Ali, R.; et al. Application of Biochar for Improving Physical, Chemical, and Hydrological Soil Properties: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Lu, H.; Fu, S.; Méndez, A.; Gascó, G. Use of Phytoremediation and Biochar to Remediate Heavy Metal Polluted Soils: A Review. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Leavitt, S.W.; Kimball, B.A.; Pinter, P.J.; Ottman, M.J.; Matthias, A.; Wall, G.W.; Brooks, T.; Williams, D.G.; Thompson, T.L. Dynamics of Labile and Recalcitrant Soil Carbon Pools in a Sorghum Free-Air CO2 Enrichment (FACE) Agroecosystem. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2007, 39, 2250–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, M.; Ye, X.; Gao, H.; Chu, W.; Mao, J.; Thompson, M.L. Soil Labile Organic Carbon Fractions and Soil Enzyme Activities after 10 Years of Continuous Fertilization and Wheat Residue Incorporation. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, N.C.; Mrunalini, K.; Prasad, K.S.K.; Naresh, R.K.; Sirisha, L. Soil Quality Indicators, Building Soil Organic Matter and Microbial Derived Inputs to Soil Organic Matter under Conservation Agriculture Ecosystem: A Review. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci 2019, 8, 1859–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Chu, W.; Li, H.; Boyd, S.A.; Teppen, B.J.; Mao, J.; Lehmann, J.; Zhang, W. Quantification and Characterization of Dissolved Organic Carbon from Biochars. Geoderma 2019, 335, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino-Serrano, M.; Gielen, B.; Luyssaert, S.; Ciais, P.; Vicca, S.; Guenet, B.; Vos, B.D.; Cools, N.; Ahrens, B.; Altaf Arain, M.; et al. Linking Variability in Soil Solution Dissolved Organic Carbon to Climate, Soil Type, and Vegetation Type: Factors Controlling Soil Solution DOC. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.R. Dissolved Organic Carbon: Sources, Sinks, and Fluxes and Role in the Soil Carbon Cycle. In Soil Processes and the Carbon Cycle; Lal, R., Kimble, J.M., Follett, R.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; First Edition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2018 ISBN 978-0-203-73927-3.
- Demisie, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. Effect of Biochar on Carbon Fractions and Enzyme Activity of Red Soil. CATENA 2014, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBC, 2012-2022. European Biochar Certificate - Guidelines for a Sustainable Production of Biochar.’ Carbon Standards International (CSI), Frick, Switzerland. (http://european-biochar.org). Version 10.2 from 8th Dec 2022 (acessed 10 March 2023). 10 March.
- Munera-Echeverri, J.L.; Martinsen, V.; Strand, L.T.; Zivanovic, V.; Cornelissen, G.; Mulder, J. Cation Exchange Capacity of Biochar: An Urgent Method Modification. Science of The Total Environment 2018, 642, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogsteen, M.J.J.; Lantinga, E.A.; Bakker, E.J.; Groot, J.C.J.; Tittonell, P.A. Estimating Soil Organic Carbon through Loss on Ignition: Effects of Ignition Conditions and Structural Water Loss: Refining the Loss on Ignition Method. Eur J Soil Sci 2015, 66, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günal, E.; Erdem, H.; Demirbaş, A. Effects of Three Biochar Types on Activity of β-Glucosidase Enzyme in Two Agricultural Soils of Different Textures. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 2018, 64, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Alef, K.; Wilke, B.; Mai, M.; Li, P. Assessment of Microbial Respiratory Activity of a Manufactured Gas Plant Soil after Remediation Using Sunflower Oil. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2005, 124, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, M.; Włodarczyk, T. Enzymy wewnątrzkomórkowych przemian redoks (okydoreduktazy). Acta Agrophysica 2005, 3, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Maiti, S.K. Soil Dehydrogenase Enzyme Activity in Natural and Mine Soil - A Review. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 2013, 13, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.; Varma, A. Soil Enzyme: The State-of-Art. In Soil Enzymology; Shukla, G., Varma, A., Eds.; Soil Biology; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010; Volume 22, pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-3-642-14224-6. [Google Scholar]
- Safari Sinegani, A.A.; Safari Sinegani, M. The Effects of Carbonates Removal on Adsorption, Immobilization and Activity of Cellulase in a Calcareous Soil. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Willett, V. Experimental Evaluation of Methods to Quantify Dissolved Organic Nitrogen (DON) and Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) in Soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The Contentious Nature of Soil Organic Matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednik, M.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I. Effect of Six Different Feedstocks on Biochar’s Properties and Expected Stability. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Townsend, A.R. Increases in Soil Respiration Following Labile Carbon Additions Linked to Rapid Shifts in Soil Microbial Community Composition. Biogeochemistry 2007, 82, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuz, S.; Mackay, A.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; DeVantier, B.; Minor, M. Biochar Increases Soil Enzyme Activities in Two Contrasting Pastoral Soils under Different Grazing Management. Crop & Pasture Science 2022, 74, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; De Neve, S.; Jegajeevagan, K.; Yildiz, G.; Buchan, D.; Funkuin, Y.N.; Prins, W.; Bouckaert, L.; Sleutel, S. Short-Term CO2 and N2O Emissions and Microbial Properties of Biochar Amended Sandy Loam Soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2013, 57, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojewódzki, P.; Lemanowicz, J.; Debska, B.; Haddad, S.A. Soil Enzyme Activity Response under the Amendment of Different Types of Biochar. Agronomy 2022, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Harris, W.G.; Migliaccio, K.W. Physicochemical and Sorptive Properties of Biochars Derived from Woody and Herbaceous Biomass. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Influence of Biochar on Potential Enzyme Activities in Two Calcareous Soils of Contrasting Texture. Geoderma 2017, 308, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammirato, C.; Miltner, A.; Kaestner, M. Effects of Wood Char and Activated Carbon on the Hydrolysis of Cellobiose by β-Glucosidase from Aspergillus Niger. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2011, 43, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; Sleutel, S.; Case, S.D.C.; Alberti, G.; McNamara, N.P.; Zavalloni, C.; Vervisch, B.; Vedove, G.D.; De Neve, S. C Mineralization and Microbial Activity in Four Biochar Field Experiments Several Years after Incorporation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2014, 78, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Fang, Y.; Van Zwieten, L.; Xuan, Y.; Tavakkoli, E.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Priming, Stabilization and Temperature Sensitivity of Native SOC Is Controlled by Microbial Responses and Physicochemical Properties of Biochar. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2021, 154, 108139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of Amendment of Different Biochars on Soil Carbon Mineralisation and Sequestration. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Singh, B.; Singh, B.P. Effect of Temperature on Biochar Priming Effects and Its Stability in Soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2015, 80, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Sekaran, U.; Ozlu, E.; Hoilett, N.O.; Kumar, S. Short-Term Impacts of Biochar and Manure Application on Soil Labile Carbon Fractions, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Community Structure. Biochar 2019, 1, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.-S.; Hur, J. Biochar-Induced Priming Effects in Soil via Modifying the Status of Soil Organic Matter and Microflora: A Review. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 805, 150304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar Effects on Soil Biota – A Review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Sanaullah, M.; Heitkamp, F.; Zelenev, V.; Kumar, A.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial Decomposition of Soil Organic Matter Is Mediated by Quality and Quantity of Crop Residues: Mechanisms and Thresholds. Biol Fertil Soils 2017, 53, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Cheng, K.; Jinwei, Z. Biochar Decreased Microbial Metabolic Quotient and Shifted Community Composition Four Years after a Single Incorporation in a Slightly Acid Rice Paddy from Southwest China. Science of The Total Environment 2016, 571, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Wolny-Koładka, K.; Gondek, K.; Gałązka, A.; Gawryjołek, K. Effect of Coapplication of Biochar and Nutrients on Microbiocenotic Composition, Dehydrogenase Activity Index and Chemical Properties of Sandy Soil. Waste Biomass Valor 2020, 11, 3911–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, V.L.; Fansler, S.J.; Smith, J.L.; Bolton, H. Reconciling Apparent Variability in Effects of Biochar Amendment on Soil Enzyme Activities by Assay Optimization. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2011, 43, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, D.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Moorhead, D.L.; Andersen, M.N.; Smith, P.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. Trade-offs in Carbon-degrading Enzyme Activities Limit Long-term Soil Carbon Sequestration with Biochar Addition. Biological Reviews 2023, 98, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Simpson, A.J.; Soong, R.; Simpson, M.J. Biochar Amendment Altered the Molecular-Level Composition of Native Soil Organic Matter in a Temperate Forest Soil. Environ. Chem. 2016, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Chang, S.X.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. Biochar Increases Soil Microbial Biomass but Has Variable Effects on Microbial Diversity: A Meta-Analysis. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 749, 141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margida, M.G.; Lashermes, G.; Moorhead, D.L. Estimating Relative Cellulolytic and Ligninolytic Enzyme Activities as Functions of Lignin and Cellulose Content in Decomposing Plant Litter. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2020, 141, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.; Lehmann, J. Modelling the Long-Term Response to Positive and Negative Priming of Soil Organic Carbon by Black Carbon. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Zang, H.; Ugurlar, F.; Aydemir, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Blagodatskaya, E. Effect of Biochar Origin and Soil pH on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Sandy and Clay Soils. Applied Soil Ecology 2018, 129, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Hopkins, D.W.; Haygarth, P.M.; Ostle, N. β-Glucosidase Activity in Pasture Soils. Applied Soil Ecology 2002, 20, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of Long-Term Nitrogen Addition on Microbial Enzyme Activity in Eight Forested and Grassland Sites: Implications for Litter and Soil Organic Matter Decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Lin, X.; Fujii, T.; Morimoto, S.; Yagi, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J. Soil Microbial Biomass, Dehydrogenase Activity, Bacterial Community Structure in Response to Long-Term Fertilizer Management. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2007, 39, 2971–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Moezzi, A.; Chorom, M.; Enayatizamir, N. Application of Biochar Changed the Status of Nutrients and Biological Activity in a Calcareous Soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 2020, 20, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Razavi, B.S.; Ludwig, B.; Zamanian, K.; Zang, H.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Dippold, M.A.; Gunina, A. Combined Biochar and Nitrogen Application Stimulates Enzyme Activity and Root Plasticity. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 735, 139393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biochar: A Guide to Analytical Methods; Singh, B., Arbestain, M.C., Lehmann, J., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton South, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4987-6553-4.
- Lehmann, J.; Cowie, A.; Masiello, C.A.; Kammann, C.; Woolf, D.; Amonette, J.E.; Cayuela, M.L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Whitman, T. Biochar in Climate Change Mitigation. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Abbr. in paper |
Substrate | pH (H2O) |
CEC 1 [cmol (+) kg−1] |
TOC [g 100 g−1] |
TN [g 100 g−1] |
Ash [%] |
|
| Soils | SA | Loamy sand | 4.62 | 1.62 | 0.72 | 0.04 | n/a |
| SiL | Silt loam | 6.40 | 11.70 | 0.99 | 0.07 | n/a | |
| Biochars | BC1 | Food wastes | 9.41 ± 0.05 | 228 | 53.0 ± 1.10 | 2.05 ± 0.16 | 10.1 ± 1.00 |
| BC2 | Cut green grass | 10.43 ± 0.04 | 228 | 52.0 ± 1.00 | 2.37 ± 0.01 | 31.3 ± 3.10 | |
| BC3 | Coffee grounds | 6.91 ± 0.07 | 35.0 | 68.0 ± 1.40 | 3.16 ± 0.37 | 3.70 ± 0.40 | |
| BC4 | Wheat straw | 7.20 ± 0.13 | 7.41 | 76.0 ± 1.50 | 0.32 ± 0.26 | 1.30 ± 0.1 | |
| BC5 | Sunflower husk | 10.29 ± 0.02 | 35.3 | 78.0 ± 1.60 | 0.80 ± 0.06 | 5.60 ± 0.60 | |
| BC6 | Wood chips | 6.96 ± 0.07 | 22.7 | 70.0 ± 1.40 | 1.23 ± 0.07 | 9.80 ± 1.00 | |
| Organic matter | CO | Compost | 5.66 | 10.8 | 17.6 | 2.01 | n/a |
| MA | Manure | 7.00 | n/a | 28.0 | 1.90 | n/a | |
| LE | Legume plants | n/a | n/a | 51.8 | n/a | 12.20 | |
| Description | Abbreviation |
| Loamy sand without amendments | SA |
| Loamy sand + 6 types of biochar | SA BC1 - SA BC6 1 |
| Loamy sand + 6 types of biochar + 3 types of organic matter | SA BC1- BC6 + CO for compostSA BC1- BC6 + MA for manureSA BC1- BC6 + LE for legumes |
| Silt loam soil without amendments | SiL |
| Silt loam soil + 6 types of biochar | SiL BC1 - SiL BC6 |
| Silt loam + 6 types of biochar + 3 types of organic matter | SiL BC1- BC6 + CO for compostSiL BC1- BC6 + MA for manureSiL BC1- BC6 + LE for legumes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





