1. Introduction
The aviation industry is increasingly exploring alternative fuels and fuel blends as a means to reduce its environmental impact and dependence on conventional fossil fuels. Recent scientific investigations have focused on assessing the feasibility and performance of aviation fuel mixtures containing biodiesel and alcohols. These studies have shed light on the physical-chemical properties, combustion characteristics, and environmental implications of these alternative fuel formulations.
Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) have emerged as a critical solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the aviation industry. From a physical-chemical properties perspective, SAF differ from conventional jet fuels primarily in terms of feedstock sources and production processes. This state-of-the-art review explores the key physical-chemical properties of SAF and their relevance in aviation, drawing upon recent research and developments.
Paper even though published in 1983, the handbook also provides a historical perspective on aviation fuel properties, reflecting the state of knowledge and industry standards at that time. While some details may have evolved since then, it remains a valuable reference for understanding the fundamentals of aviation fuels. It serves as a valuable reference document offering a comprehensive source of information on the properties of aviation fuels. Also, provide easy access to data pertaining to aviation fuel properties. This includes information on fuel composition, physical properties, combustion characteristics, and other relevant factors.
Recent research has evaluated the physical-chemical properties of aviation fuel blends with biodiesel and alcohols. For instance, studies have examined the density, viscosity, and thermal stability of these mixtures . These properties are essential for ensuring compatibility with existing aviation infrastructure and safe engine operation.
SAF can be derived from a variety of feedstocks, including biomass, waste oils, and synthetic processes like Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis and hydrotreatment of triglycerides. These diverse feedstocks result in a wide range of chemical compositions for SAF . The chemical composition impacts properties such as density, viscosity, and combustion characteristics, influencing engine performance .
The hydrocarbon structure of SAF influences its energy density and combustion behavior. Hydroprocessed SAF typically contain paraffinic hydrocarbons, which contribute to improved energy content and reduced emissions compared to conventional kerosene-based jet fuels. The absence of sulfur in most SAF contributes to lower sulfur dioxide emissions [
5,
6].
Density and viscosity, frrezing point, thermal stability areare critical physical properties affecting fuel handling and combustion. SAF generally exhibit higher densities and viscosities than conventional jet fuels due to their chemical composition, have higher freezing points than conventional fuels, which may necessitate the use of additives or blending with conventional jet fuel to ensure low-temperature operability and thermal stability of SAF can vary based on feedstock and production processes[
7,
8,
9,
10].
Conclusion: Sustainable aviation fuels are essential for mitigating the aviation industry's environmental impact. Their physical-chemical properties, shaped by feedstock and production methods, impact engine performance, emissions, and operational aspects. As research continues, understanding and optimizing these properties will be vital in integrating SAF into the aviation sector.
Assessments of the combustion characteristics of such fuel blends have been a central focus. Researchers have investigated parameters like ignition delay, flame stability, and emissions profiles during combustion . Understanding the combustion behavior is crucial for optimizing engine performance and reducing emissions. Also, environmental impact of aviation fuel mixtures involving biodiesel and alcohols has also been thoroughly studied. Emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2) have been quantified .These assessments contribute to our understanding of the potential reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and particulate matter, which are critical for air quality and climate change mitigation.
Paper explores the latest developments in sustainable alternative aviation fuels (SAF) with a focus on their impact on carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions. Additionally, the paper evaluates the potential of hydrogen as an alternative to SAF in the aviation industry. The paper discusses recent advancements in SAF, highlighting their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the aviation sector. These fuels have gained attention as a promising solution for mitigating the environmental impact of aviation.
The investigation the combustion characteristics of a blend consisting of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and hydrogen is studied within. The study is conducted within a constant volume combustion chamber to gain insights into the performance of this fuel mixture. The paper focuses on a mixture composed of traditional jet fuel (SAF) and hydrogen. This composition is analyzed for its combustion behavior to assess its potential as a sustainable alternative for aviation. The research evaluates the combustion performance of the SAF-hydrogen blend. This includes parameters such as combustion efficiency, emissions, and combustion stability, providing valuable data on the fuel's feasibility for use in aviation applications. The paper aids in the evaluation of alternative aviation fuels, advancing the industry's pursuit of more environmentally friendly options.
Paper delves into the modeling and assessment of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) with a focus on how their properties influence both aircraft engine performance and emissions. The study employs mathematical modeling to provide accurate estimations of fuel consumption and support the development and testing of alternative jet fuels. The study utilizes mathematical models to simulate the behavior of SAFs in aircraft jet engines. These models provide a means to predict fuel consumption and assess the overall impact of SAFs on engine performance and emissions, allowing for more informed decisions during fuel development and testing. The work supports the ongoing efforts to develop and assess alternative jet fuels with the goal of making aviation more environmentally sustainable.
In paper the authors provides a comprehensive examination of sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) with a particular emphasis on their environmental impact, focusing on both particulate matter and harmful gaseous exhaust gas compounds. The study explores various aspects of SAF, including their raw materials, emerging feedstock for production, and the stringent requirements for aviation bio fuels. The paper investigates the diverse range of raw materials used in the production of SAF. This encompasses traditional feedstock as well as innovative, sustainable sources that are crucial for reducing the carbon footprint of aviation fuels. A central focus of the paper is the assessment of emissions, including particulate matter and harmful gaseous compounds, associated with the use of SAF. This analysis sheds light on the environmental performance of SAF compared to conventional aviation fuels.
Paper presents an in-depth investigation into the experimental evaluation of a jet aviation fuel surrogate. This surrogate is carefully formulated based on actual fuel properties and is assessed through empirical measurements to validate its representational accuracy. The paper describes the formulation process of a surrogate fuel that closely mimics the characteristics of real jet aviation fuel. This surrogate is designed to possess similar chemical and physical properties, making it a suitable alternative for research and testing purposes. The primary focus of the study involves conducting a comprehensive experimental evaluation of the surrogate. Empirical measurements are performed to validate its ability to reproduce the critical properties and behaviors of real aviation fuel under varying conditions.
Paper presents a comprehensive review of the technical pathways associated with Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF). Sustainable aviation fuels are critical for reducing the aviation industry's carbon footprint and mitigating the environmental impacts of air travel. This review paper systematically assesses various SAF production methods, emphasizing their technical feasibility, environmental sustainability, and potential for integration into the existing aviation infrastructure. Furthermore, the paper addresses the challenges and opportunities associated with SAF production, including feedstock availability, economic viability, and regulatory frameworks.
Current paper is aiming to analyze how the most used jet fuel Jet A and different types of biodiesels: biodiesel obtained from used palm oil, pork fat and used sunflower oil and different alcohols: methanol, ethanol and butanol are influencing the burning process and gaseous pollution. All those 6 added liquids have been blended with Jet A in 3 different concentrations: 10, 20 and 30%. Also Aeroshell 500 oil has been added into the mixture (5% volume) due to the need of greasing the turbo engine.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blends Preparation
The blends have been prepared within the laboratory and have consisted of: Jet A fuel, 3 types of biodiesel (obtained from: used sunflower oil, pork fat and used palm oil) and 3 types of alcohols (methanol, ethanol and butanol). Also Aeroshell 500 oil have been added into the blends (5% vol.)
Jet A aviation fuel has been provided by OMV Petrom, Romania as jet fuel and is in accordance with STANAG 3747 standard.
Aeroshell 500 oil was provided by Shell Romania and is in accordance with the following standards: MIL-PRF-23699G Grade SDT, British DEF STAN 91-101 Grade OX-27, NATO code O-156.
The biodiesels have been provided by Bunge 200 Romania, and has been produced at Lehliu, Romania from domestic raw materials.
Alcohols have been provided by VWR Chemicals and have the following characteristics: Methanol 98.5% purity, Ethanol 99.8% purity and n-Butanol 99.8% purity.
In general, all the blends showed homogeny except for the blends with methanol who showed separation if the blend wasn't stirred constantly, as shown in
Figure 1.
2.2. Freezing Point Determination
Freezing point determination is a method for determining one d the most important parameters: the freezing point of a liquid. This parameter needs to be determined in order to assess the compatibility of the liquid to work as aviation fuel. The instrument used to determine the freezing point was provided by Ducom Instruments (Europe) B.V., Netherlands and has the following characteristics: temperature range +80 to -90°C, resolution: 0.01°C, accuracy: ±0.1°C, temperature measurement: PT100, class A.
2.3. Elemental Analysis Determination
Elemental analysis determination is a method for assessing the percentages of different atoms within a substance according to their molecular mass. Elemental analysis provide elemental composition of minerals, chemical compounds, soil and waste. Elemental analysis can be qualitative and quantitative and applied to bulk and surface analysis. Elemental analysis can be subdivided in two ways:
The elemental analyzer was provided by Horiba GmbH Tulln, Romania branch, and it is an EMIA-Pro device having the following characteristics: sample amount: 1 g ±0.1g, carrier gas: Oxygen 99.5% purity, operation gas: Nitrogen 99.5% purity, measurement range: Carbon: 1.6 ppm, Sulfur: 2.0 ppm.
2.4. Flash Point Determination
Flash point is the lowest temperature when the vapors ignite. The used instrument is an opened cup flash/fire point measurement apparatus provided by Scavini, Italy and it is used to determine the flash and/or fire temperature of a liquid. Its main characteristics are: working temperature: 400°C, number of cups: 1, working gas: propane for domestic use, sensor to correct the obtained results with the ambient temperature and relative humidity.
2.5. Cinematic Viscosity At 40° Determination
Cinematic viscosity was determined in order to assess the influence of the blending liquids compared to the usual aviation fuel. Thus, the measurement has been performed by using an instrument provided by Scavini, Italy that uses an ubelhode for measuring. The ubelhode is basically a glass capillary tube having a known constant. It is filled with the liquid to be measured and put in a thermal bath. Then the liquid is let freely through the capillary and the time is measured. Main characteristics of the apparatus are: working temperature: room to 100°C, number of simultaneous measurements: 6, thermostat precision: ±0.1°C.
2.6. FT-IR Spectrometry
FT_IR spectrometry is a very versatile method for determining the chemical transformations within a substance. The instrument used is a Spectrum Oil Express 100, from Perkin Elmer, USA. It draws spectra of a given oil based liquid and compare it to the already existing reference within its database. It show the modifications within the substance's chemical composition. Its main characteristics are: working wave length: 7800 - 370 cm-1, DTGS (deuterated tri-glycerin sulphate) detector, electronic signal processing system, CO2 laser, auto sampler, Borosilicate based working cell, used solvent: n-Heptane 99.5% purity.
2.7. Density at 22°C Measurement
The method used to determine the density of the liquids is thermo-density one. Basically the 1 liter of every liquid were kept at constant temperature of 22°C. Then the thermo-densimeter is immersed in the liquid. Due to the density of the liquid, it flows and showing the value on a marked scale. Thermo-densimeters were provided by Thermodensirom, Romania and are able to show density 0.6 and 1.2 g/cm3. There are 6 of them each one being able to show the density with an accuracy of ±0.01 g/cm3.
3. Results and Discussions
Within this section, the results obtained by analyzing the fuel blends are presented.
The results obtained in 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5 are shown in Table 1.
| Sample |
Flash Point
[°C]
|
Viscosity
[cSt]
|
Density
[g/cm3]
|
Calorific Power
[MJ/kg]
|
Elemental Analysis [%] |
| C |
H |
N |
O |
| Jet A |
40.1 |
1.27 |
0.808 |
45.59 |
84.71 |
15.29 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| Aeroshell 500 |
188.6 |
25.11 |
0.999 |
35.26 |
94.50 |
3.5 |
0 |
2 |
| Ke |
42.3 |
1.39 |
0.817 |
45.29 |
85.17 |
13.31 |
0.07 |
1.45 |
| A1
|
11.8 |
0.55 |
0.792 |
19.07 |
37.45 |
12.48 |
0 |
49.94 |
| A2
|
13 |
1.20 |
0.789 |
29.45 |
52.09 |
13.02 |
0 |
34.73 |
| A3
|
35 |
2.57 |
0.810 |
35.77 |
64.76 |
13.49 |
0 |
21.59 |
| Ke+10A1
|
23.7 |
1.31 |
0.815 |
42.67 |
80.40 |
13.23 |
0.06 |
6.30 |
| Ke+20A1
|
23.4 |
1.22 |
0.812 |
40.05 |
75.63 |
13.14 |
0.06 |
11.15 |
| Ke+30A1
|
23.3 |
1.14 |
0.810 |
37.42 |
70.85 |
13.06 |
0.05 |
16.00 |
| Ke+10A2
|
23.7 |
1.37 |
0.814 |
43.71 |
81.86 |
13.28 |
0.06 |
4.78 |
| Ke+20A2
|
23.6 |
1.35 |
0.811 |
42.12 |
78.55 |
13.25 |
0.06 |
8.11 |
| Ke+30A2
|
23.3 |
1.33 |
0.809 |
40.54 |
75.25 |
13.22 |
0.05 |
11.43 |
| Ke+10A3
|
33.9 |
1.51 |
0.816 |
44.34 |
83.13 |
13.33 |
0.06 |
3.46 |
| Ke+20A3
|
33.7 |
1.63 |
0.816 |
43.39 |
81.09 |
13.35 |
0.06 |
5.48 |
| Ke+30A3
|
33.1 |
1.74 |
0.815 |
42.43 |
79.05 |
13.36 |
0.05 |
7.49 |
| B1
|
86 |
5 |
0.884 |
39.42 |
77.28 |
12 |
0.07 |
10.65 |
| B2
|
164 |
9.47 |
0.882 |
40.89 |
78.65 |
12.61 |
0.07 |
8.67 |
| B3
|
161 |
5.08 |
0.875 |
39.32 |
77.43 |
12.38 |
0.06 |
10.13 |
| Ke+10B1
|
42.9 |
1.55 |
0.824 |
44.15 |
84.38 |
13.18 |
0.07 |
2.37 |
| Ke+20B1
|
46.2 |
1.73 |
0.832 |
43.93 |
83.59 |
13.05 |
0.07 |
3.29 |
| Ke+30B1
|
49.7 |
1.98 |
0.839 |
43.05 |
82.8 |
12.92 |
0.07 |
4.21 |
| Ke+10B2
|
45.6 |
1.75 |
0.832 |
44.69 |
84.52 |
13.24 |
0.07 |
2.17 |
| Ke+20B2
|
49.44 |
2.15 |
0.843 |
44.23 |
83.87 |
13.17 |
0.07 |
2.89 |
| Ke+30B2
|
53.5 |
2.54 |
0.854 |
43.68 |
83.21 |
13.1 |
0.07 |
3.62 |
| Ke+10B3
|
44.2 |
1.51 |
0.823 |
44.4 |
84.4 |
13.22 |
0.07 |
2.32 |
| Ke+20B3
|
50.2 |
1.82 |
0.83 |
43.3 |
83.62 |
13.12 |
0.07 |
3.19 |
| Ke+30B3
|
54.7 |
2.06 |
0.836 |
41.98 |
82.85 |
13.03 |
0.07 |
4.05 |
where:
- -
Ke is Jet A fuel +5% Aeroshell 500
- -
A1 - methanol
- -
A2 - ethanol
- -
A3 - n-butanol
- -
B1 - biodiesel obtained form used sunflower oil
- -
B2 - biodiesel obtained from pork fat
- -
B3 - biodiesel obtained from used palm oil
3.1. Variation of Flash Point of the Blends
The variation of the flash point of the blends made from Jet A and alcohols are shown in
Figure 2.
As it can be seen in
Figure 2 and assessed from Table 1, A
1 and A
2 have similar flash points, therefore the graphs are overlapping. A
3 having a flash point higher that the other two is well represented. As expected, the flash point decreases as alcohol concentration within the blend increases, but the decrease is rather insignificant. Nevertheless, a lower flash point means that the combustion of the blends starts at temperatures lower than regular aviation fuel.
In
Figure 3, the variation of the flash points of kerosene and biodiesels blends is shown.
All biodiesels used within the blends have flash point higher than regular aviation fuel, therefore, the flash point of the blends are higher that Jet A’s. As expected, the flash point value increases as the biodiesel concentration increases. If such blends consisting of regular aviation fuel and biodiesel are to be used as sustainable aviation fuels, these increased values of the flash point must be taken into consideration.
3.2. Variation of Calorific Power
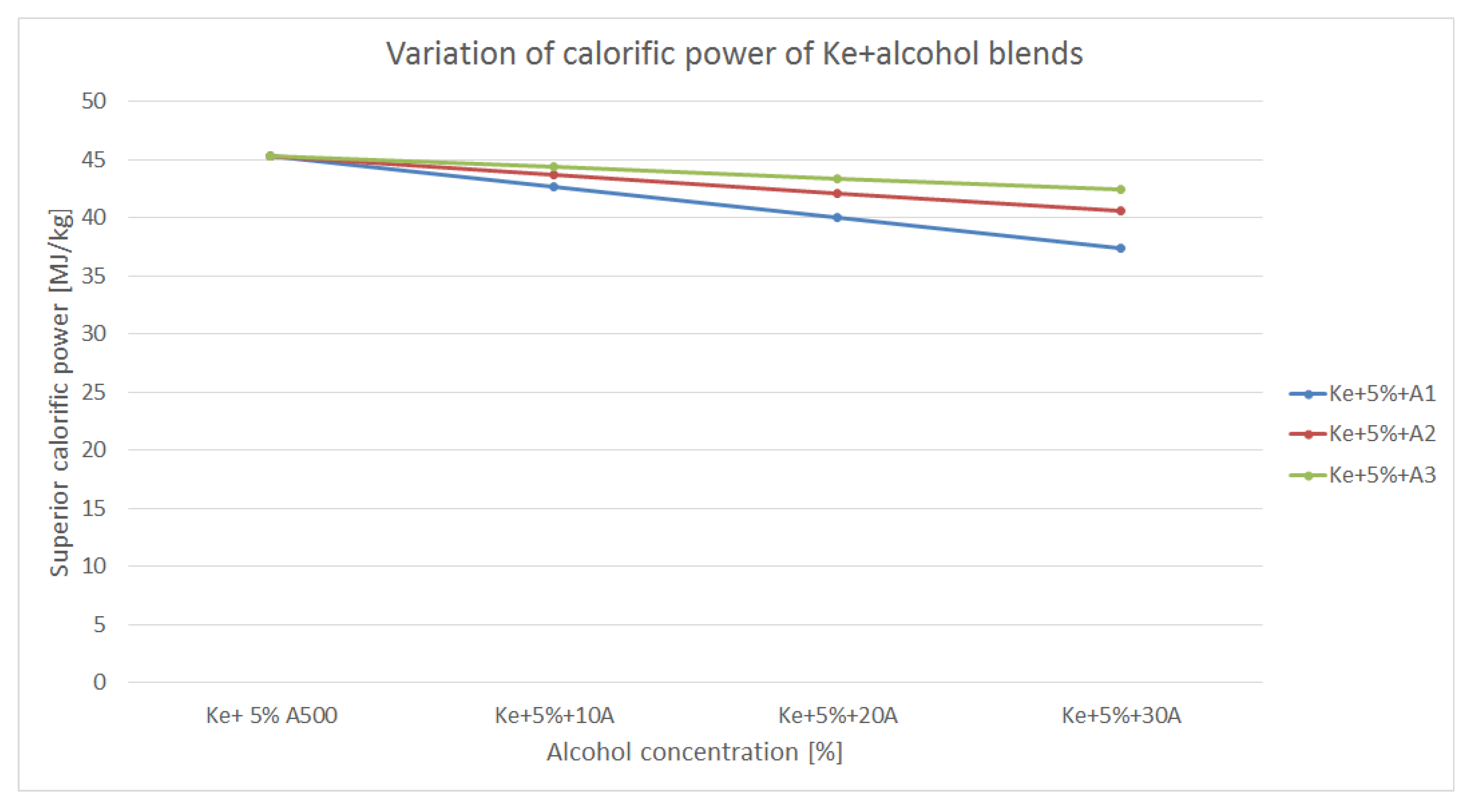
Calorific power of the blends differ from the calorific power of the regular aviation fuel. Thus, the variation of the calorific power of the blends made from kerosene and alcohols is shown in
Figure 4.
As it can be assessed from
Figure 4, all the blends’ calorific power decreases both as the concentration of the alcohols increases and as each alcohol’s calorific power is different. Thus, the blends made out of kerosene and A
1 shows the lowest calorific power and the blends made with A
3 shows the highest. This aspect can be observed also in table 1 since A
3’s calorific power is the highest. Nevertheless, all blends show an important decrease in calorific power. This aspect may influence the fuel consumption of an aviation engine while trying to maintain a specific power output. Low calorific power mean poorer combustion.
Figure 5 is representing the variation of calorific power of the blends made out of kerosene and biodiesel.
As it can be assessed both from
Figure 5 and Table 1, the calorific power of the blends also decreases but not as drastically as in the case of kerosene/alcohols blends due to the fact that, in fact Jet A is basically a diesel like liquid too. Therefore, the calorific power of the biodiesel is close to the one of the kerosene. Again, the calorific power decreases as the biodiesel concentration increases but the decrease is rather small, thus resulting in similar fuel consumption as regular aviation fuel. As compared to kerosene/alcohols blends, the kerosene/biodiesel blends seem more suitable to be used as aviation fuel.
3.3. Variation of Carbon Content
The percent of the Carbon atoms within gives an idea of how the combustion process unfolds. It is widely known that in an ideal combustion process, the end products will be H2O and CO2. Nevertheless, the combustion process in an aviation turbo engine is far from ideal, therefore secondary products such NOx CO, etc. will form.
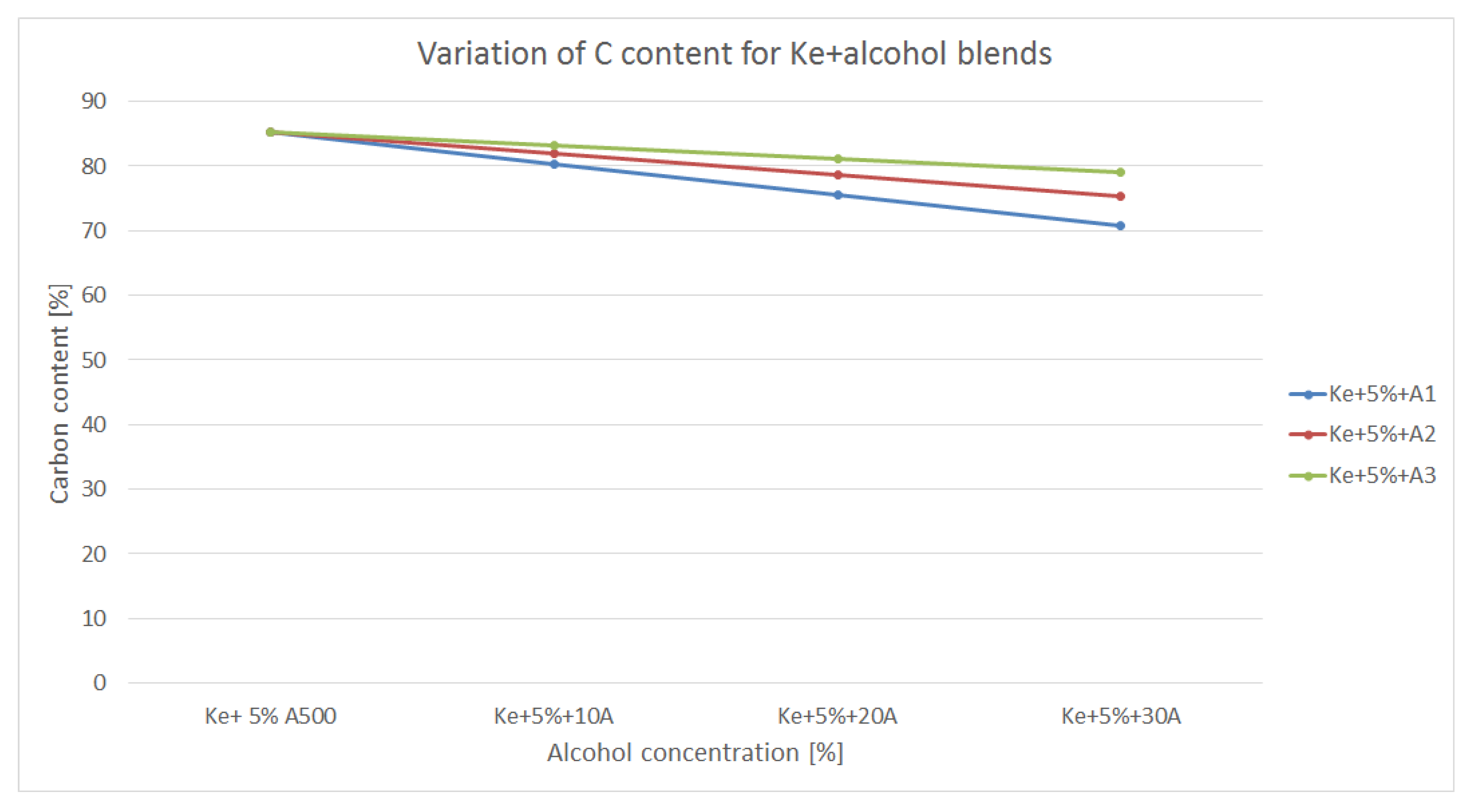
Figure 6 is showing the variation of Carbon content within the blends made out of kerosene and alcohol.
As it can be observed in
Figure 6, the carbon content of the blends decreases due to the fact that alcohols have lower carbon percentage than biodiesel. Also, carbon content decreases, as expected, as the alcohol concentration increases. Lower carbon content means lower CO
2 formation as end product. But, correlated to the variation of calorific power, therefore with an increased fuel consumption, the actual CO
2 production of an aviation turbo engine might be higher than regular fuel. Also, alcohols having small structure (C1 – C3) are burning more efficiently than structures as jet A (having C9 – C11), therefore intermediate products such CO and NO
x are likely to be lower.
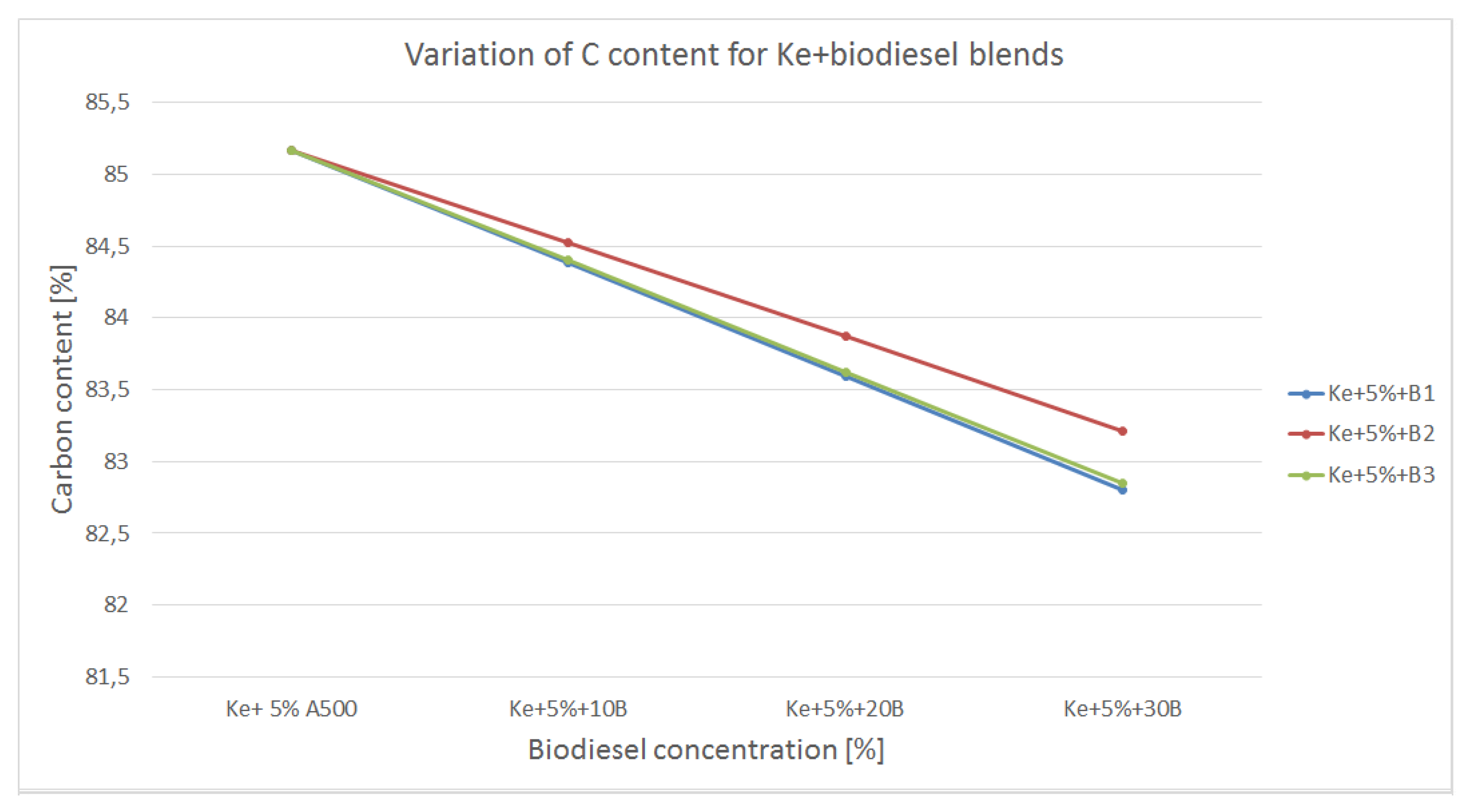
The variation of carbon content in the blends made out of kerosene and biodiesel is shown in
Figure 7.
All biodiesels used to form the blends shows similar carbon concentration as regular aviation fuel, only slightly lower. Therefore, even though the carbon concentrations decreases as compared to kerosene, the values are still high. This means that higher concentrations of CO2 is likely to be produced as combustion end-product but given the fact the calorific power of the blends is higher, fuel consumption should be lower. Also, given the fact that biodiesel as well as regular aviation fuel has long structure (C9 – C11) the combustion process might not be as efficient as in the case of alcohols, therefore intermediate products such CO and NOx are likely to be higher.
3.4. Variation of Oxygen Content
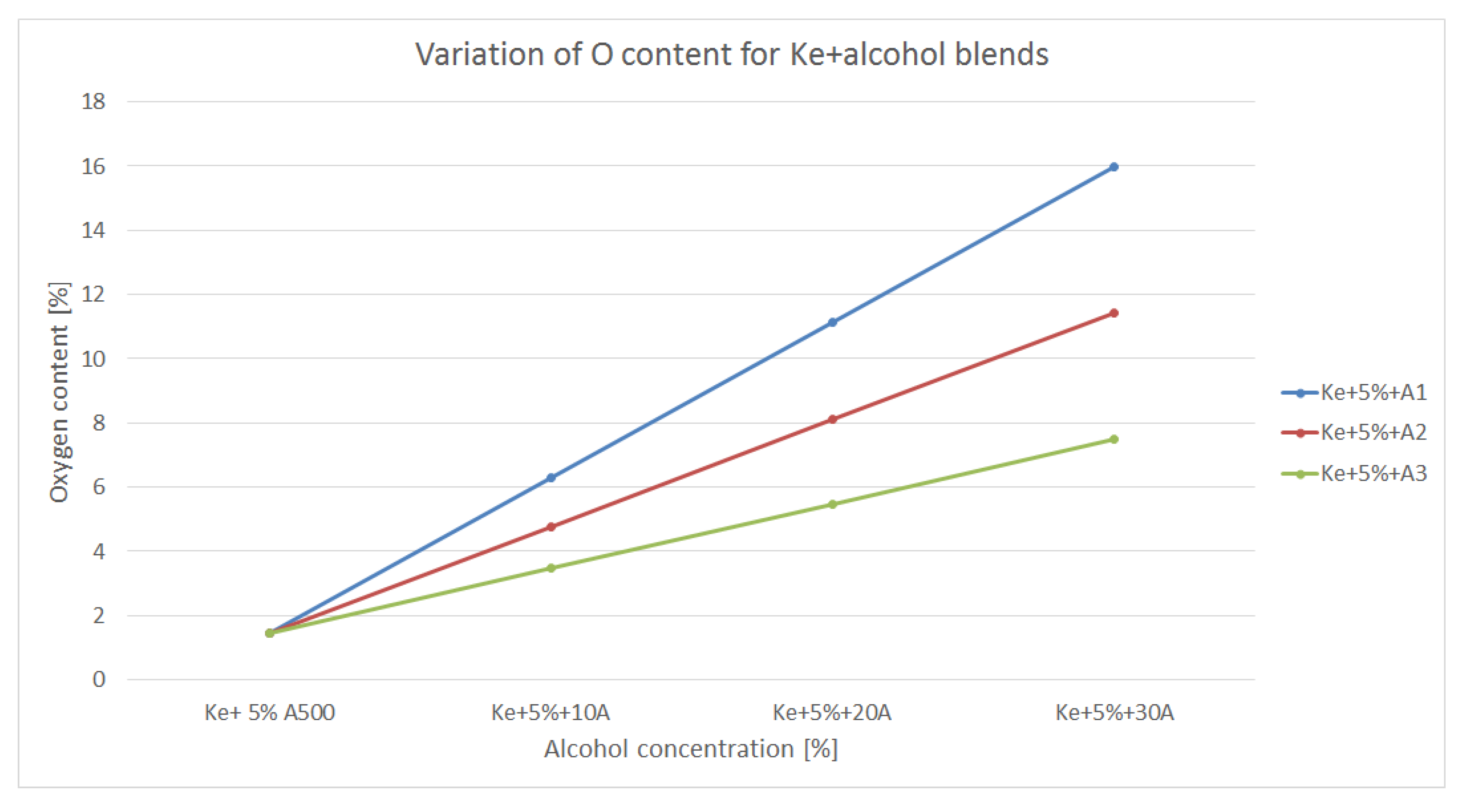
Oxygen content of a fuel is also an important aspect to be taken into consideration since higher O2 content means lower air intake for the combustion process.
Figure 8 is showing the variation of O
2 content within the blends made of kerosene and alcohols.
By assessing the graphs shown in
Figure 8, it can be observed that the oxygen content increases as the alcohol concentration increases and the oxygen content of the alcohol is higher. Therefore, A
1 shows the highest O
2 concentration, thus it is likely for the blend consisting of kerosene and A
1 to have the highest efficiency in terms of combustion. Nevertheless, one can take into consideration the fact that A
1 has the lowest calorific power and separates as shown in
Figure 1. In theory those blends should have improved combustion behavior.
Nevertheless, alcohol are bringing huge amount of oxygen within the structure of the newly formed blends, resulting, in theory, in a more efficient combustion process. This can be translated into lover CO, NOx and CO2 concentrations.
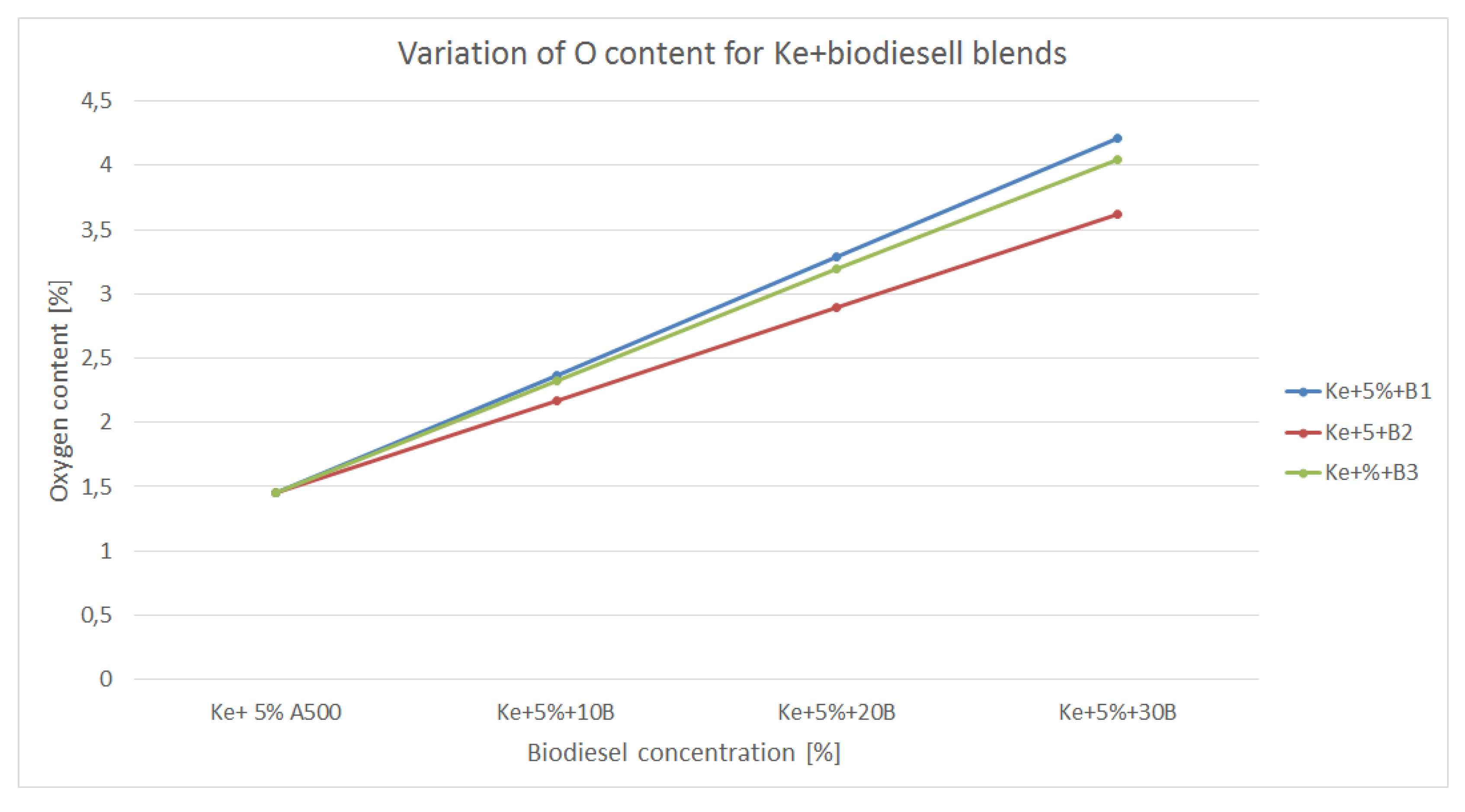
The variation of oxygen content of the blends made of kerosene and biodiesel is shown in
Figure 9.
As in the case of alcohols, biodiesel bring more oxygen into the newly blended fuel, therefore the combustion process should be more efficient. It is to be noticed the amount of oxygen is significantly lower than in the case of alcohols, thus the combustion might be less efficient leading to increased amounts of CO, NOx and CO2. Nevertheless, those concentration should be, theoretically, lower that in the case of combustion of regular aviation fuel.
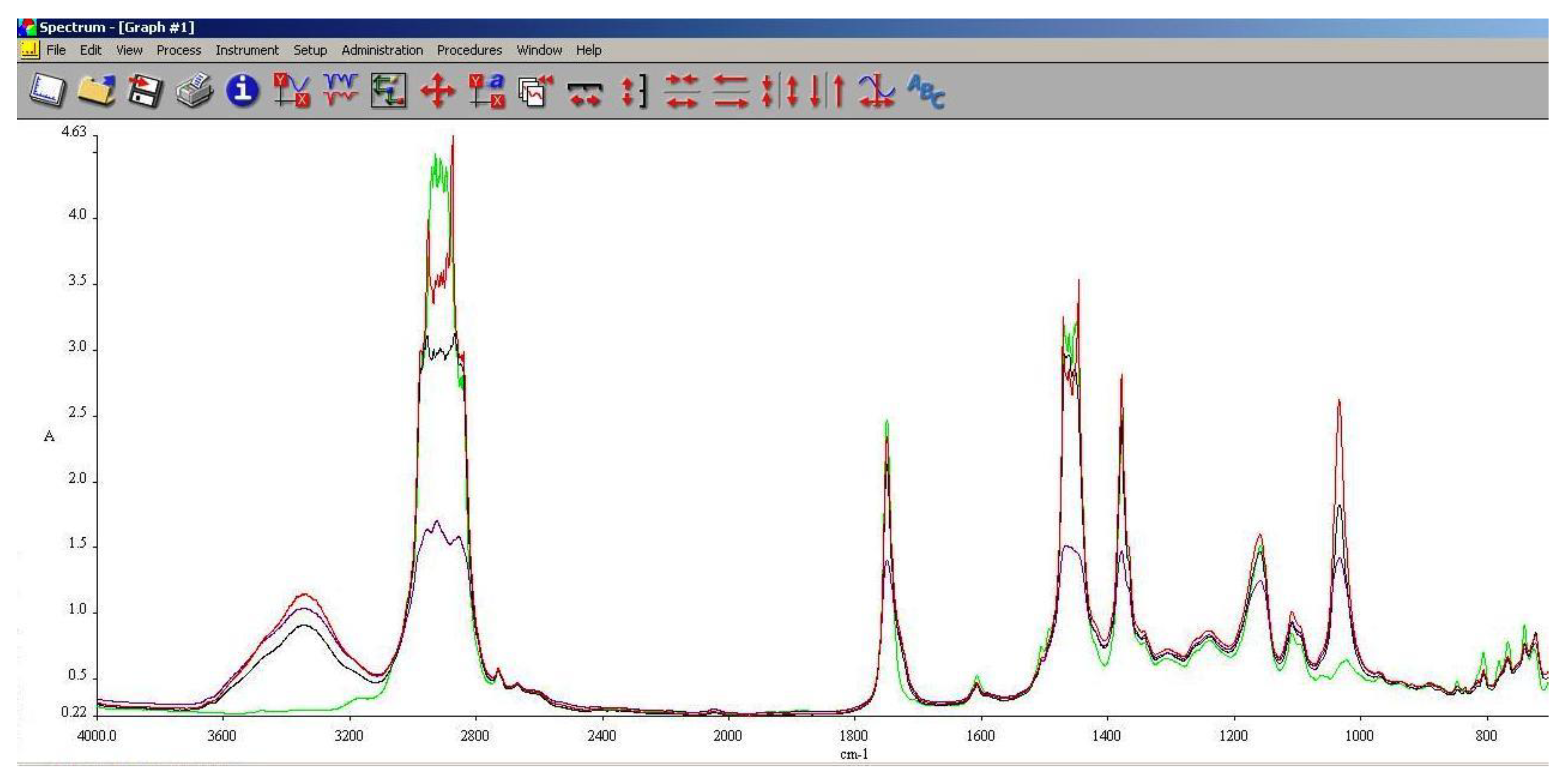
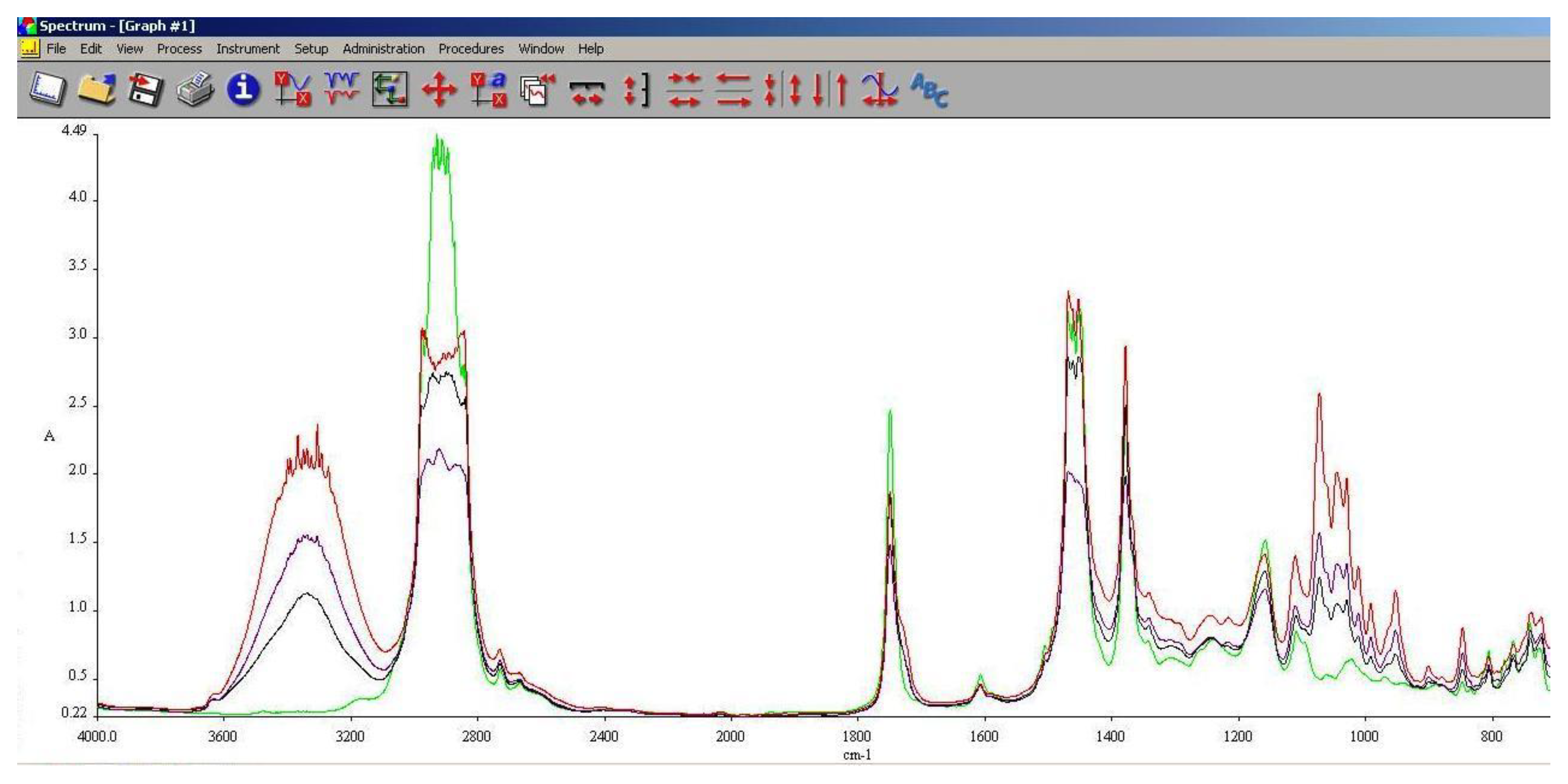
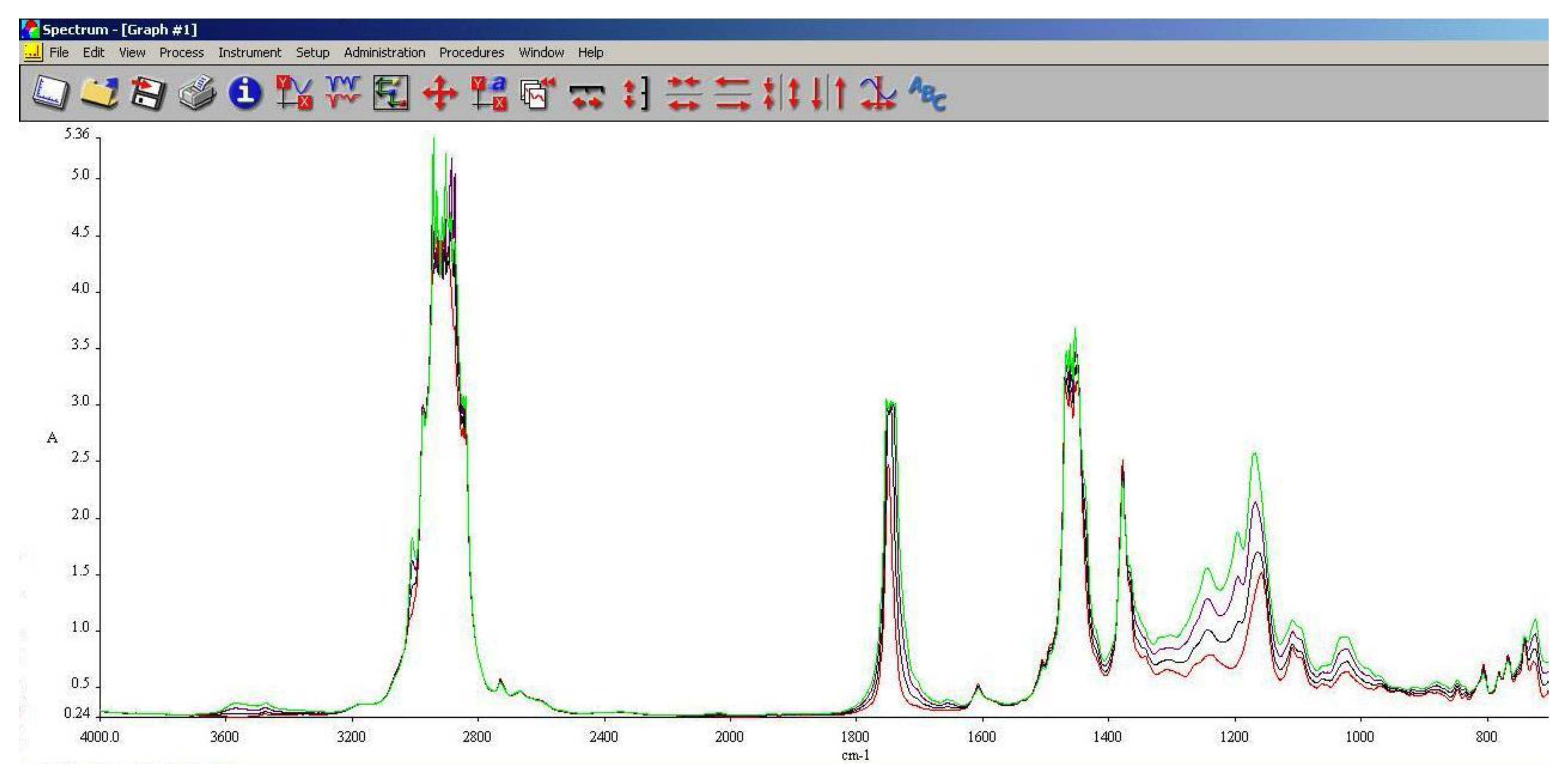
3.5. FT-IR Analysis
FT-IR spectroscopy is a very useful tool in assessing the chemical modifications within a substance. By adding alcohols or biodiesel within regular aviation fuel its chemical composition modifies as assessed within 3.3 and 3.4.
As it can be seen in
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12, the main differences between the spectra of the regular aviation fuel (Ke) and the blends are at 3200-3600 cm
-1, meaning that hydroxyl (-O-H) has been brought into the structure. As expected, the higher the alcohol concentration, the higher the peak. Another important modification appear at 1750 cm
-1 representing the presence oxygen bonded by a C atom (C-O). At 1450 cm
-1 the presence of methylene groups (-CH
2) are shoving a slight decrease compared with Ke. The radiation absorbed at 1350 cm
-1 is showing in increase of methyl groups (–CH
3). Another large difference is shown at 1000 cm
-1 representing C-OH bond. As in the case oh –OH, as the concentration of the alcohol increases, C-OH increases.
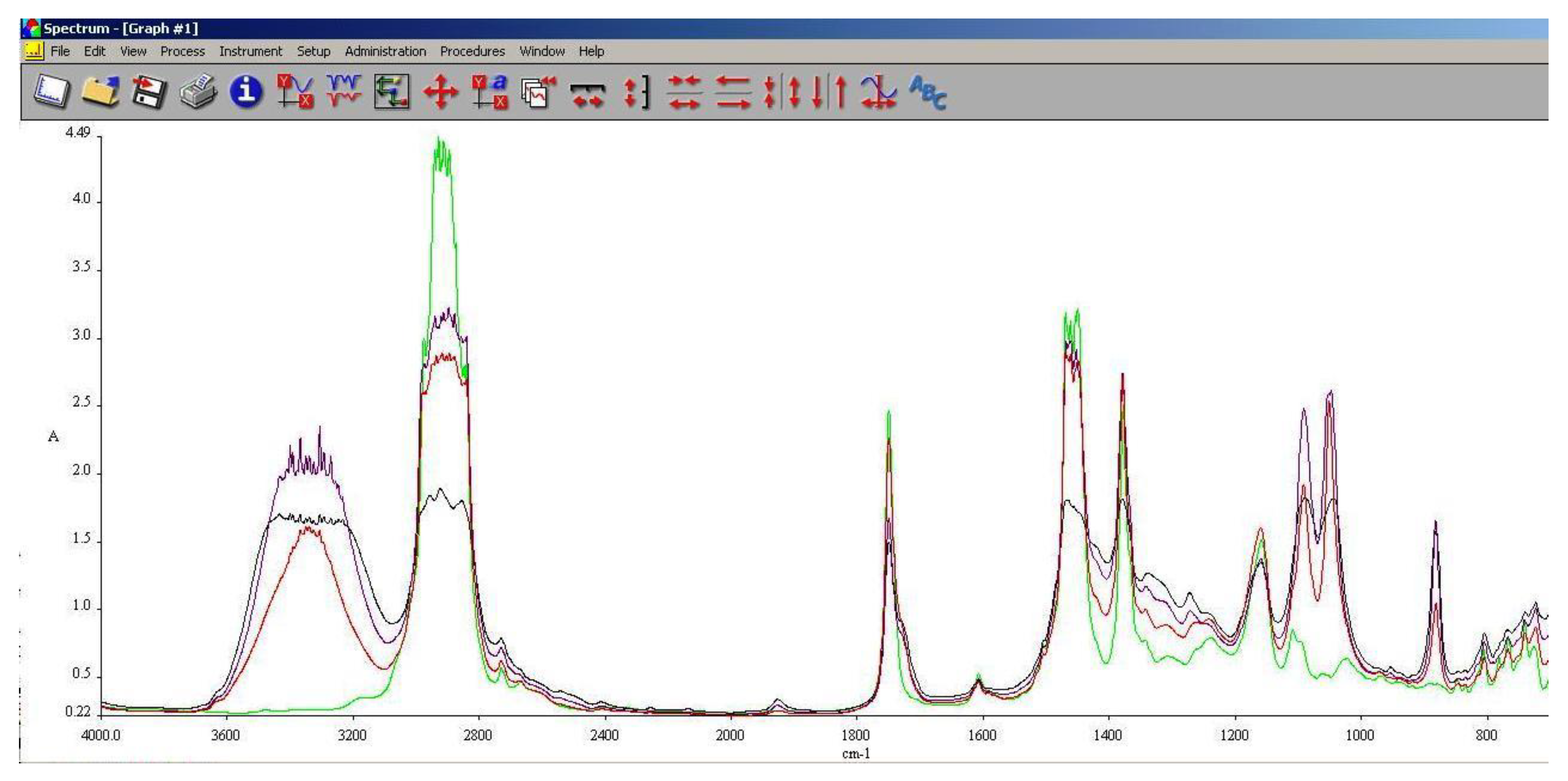
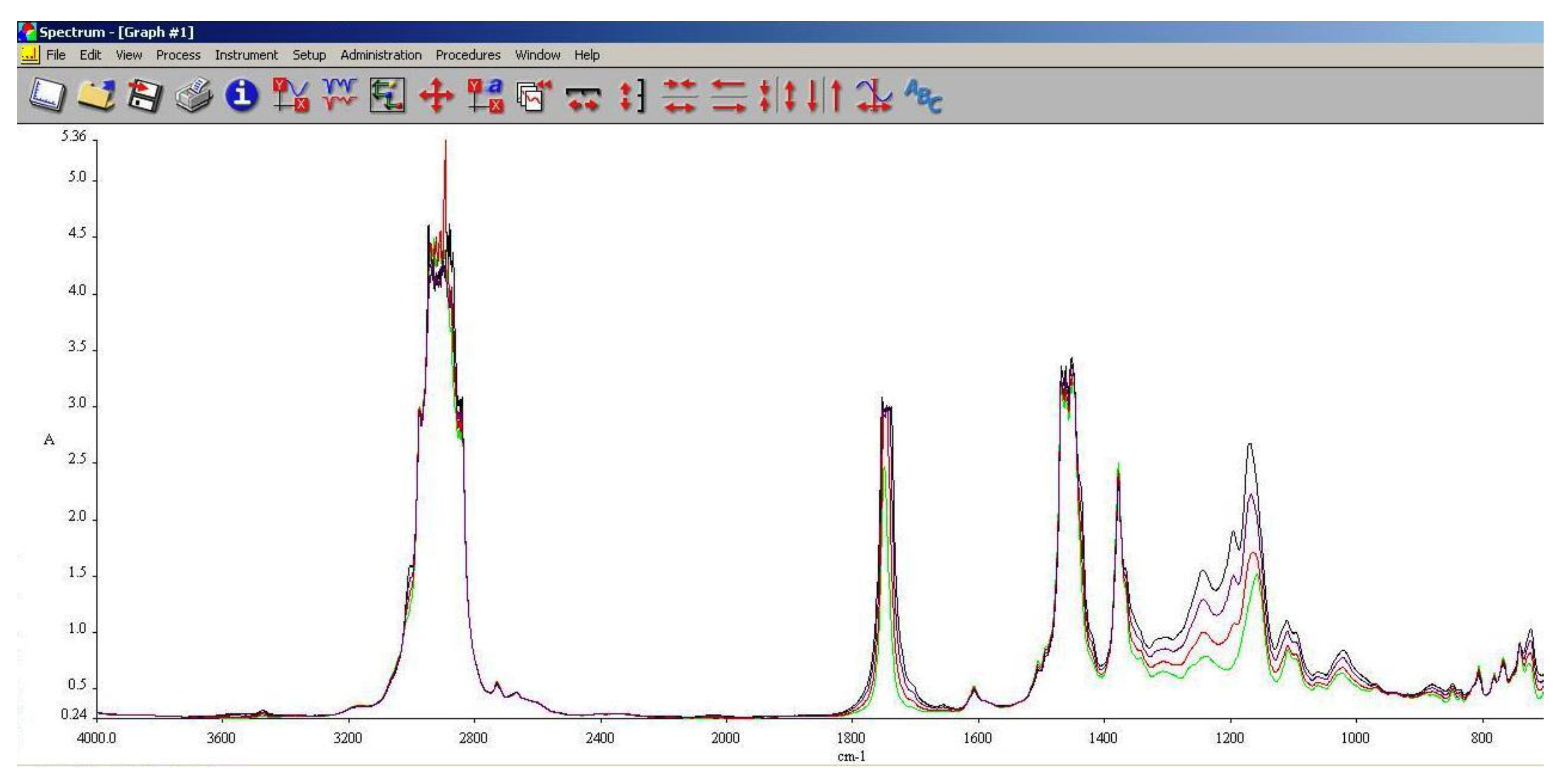
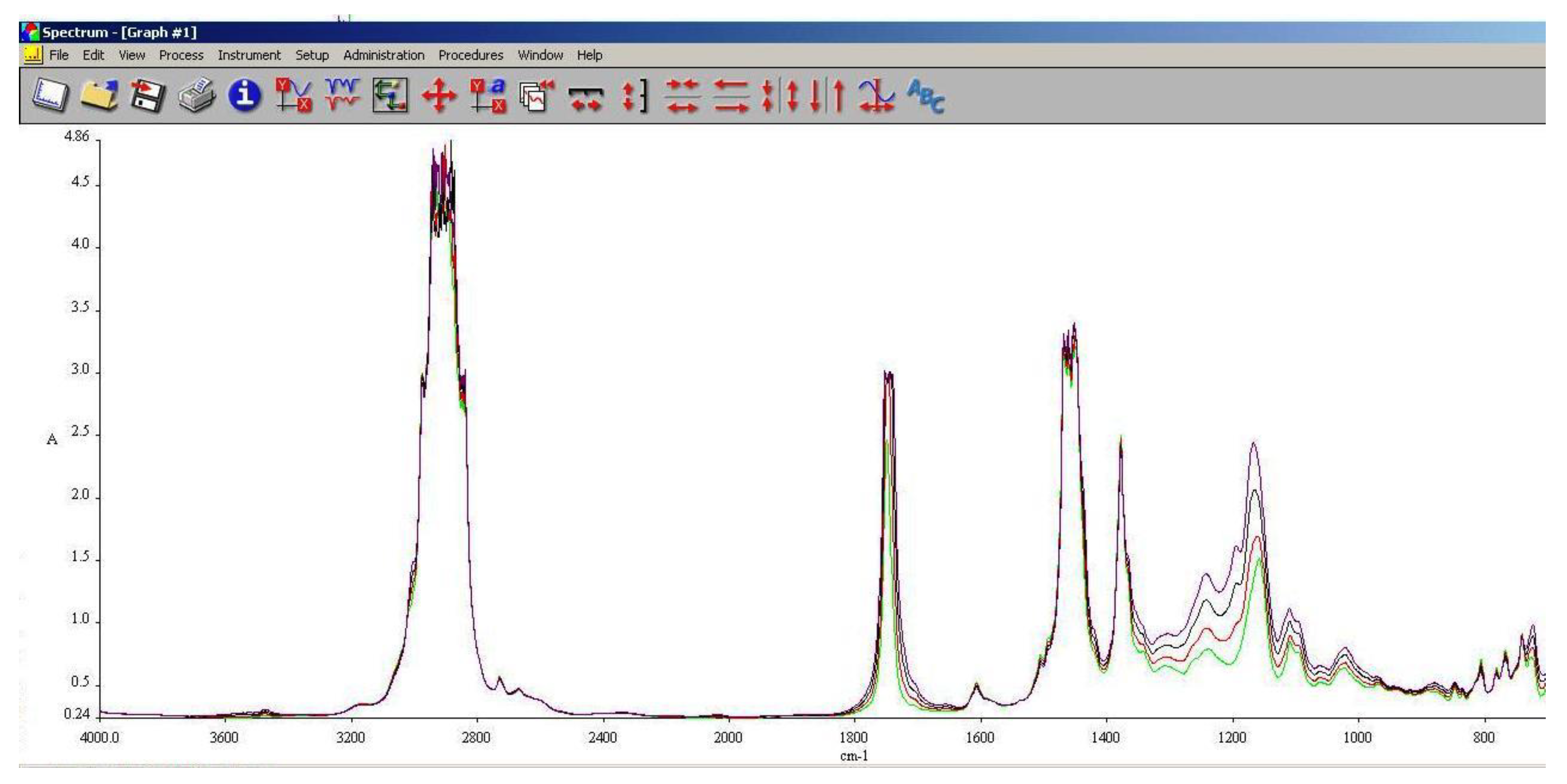
As it can be observed in
Figure 13,
Figure 14 and
Figure 15, the main differences between the spectra of the regular aviation fuel (Ke) and the blends are at 1280 cm
-1 representing the presence of ethers (C-O-C) and esters (C=O) groups. The obtaining of biodiesel is a succession of etherification followed by esterification reactions, therefore ether and ester groups are present within the structure. Those groups are bringing oxygen into the structure, resulting in a more efficient combustion process. Also, large differences can be observed at 2850 cm
-1 representing asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of (-CH2) groups.
4. Conclusions
Biodiesel and alcohols are two suitable substances to be used in blends with regular aviation fuel with the aim of decreasing the gaseous pollutants resulted from the combustion in an aviation turbo engine.
Engine’s performances and fuel consumption must be taken into consideration when fuel blends are formed.
Alcohols are bringing more oxygen into the structure, but have lower calorific power, therefore fuel consumption should increase
Biodiesel also brings oxygen into the structure, but in lower amount. However, their calorific power similar to the regular aviation fuel should keep fuel consumption constant.
Carbon content is decreasing for both alcohol and biodiesel, meaning that CO and CO2 should, in theory decrease
The flash point of the blends are lower for alcohol ones and higher for biodiesel ones.
Combustion tests must be performed on an aviation turbo engine in order to assess the fuel consumption, gaseous pollution and engine’s performances in order to experimentally assess the most suitable blend for the transition towards sustainable aviation fuels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, GC and RM.; methodology, G.C.; software, GC.; validation, RM and GC.; formal analysis, RM.; investigation, GC and RM.; resources, RM.; writing—original draft preparation, RM.; writing—review and editing, RM. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Nucleu program within National Research, Development and Innovation Plan 2022-2027 of Romanian Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitalization, grant number PN 23.12.02.02”
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge INCDT COMOTI-Bucharest and Polytechnic University of Bucharest for administrative and technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Coordinating research Coincil Inc. Handbook of aviation fuel properties. 1983.
- Sarathy, S. M., Hanson, R. K., & Westbrook, C. K. (2020). Detailed chemical kinetic modeling of aviation fuels. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 76, 100777.
- Kumar, A. , Chandel, A. K., & Singh, S. P. (2018). Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass: biochemical and molecular perspectives. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 45(5), 343-361.
- De Laurentiis, V. , Blasi, A. D., Daniele, P., & Pernice, M. (2019). Sustainable aviation fuels: a process chain analysis for hydrogen production from biomass. Sustainability, 11(14), 3964.
- Dahmen, N. , Hallmann, S., & Sauer, J. (2020). Impact of aviation fuels on particulate matter emissions from aircraft engines: a review. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 86, 102409.
- Ma, Y. , Chen, C., & Yang, Y. (2020). Characteristics and impacts of biomass burning emissions in the atmosphere: A review. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115176.
- Liu, Y. , Fang, S., Xu, X., & Lai, X. (2020). Development of alternative aviation fuels from algal oils: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 133, 110303.
- Strzelecki, K. , Marques, J. C., & Gomes, J. (2021). Sustainable aviation fuel: A systematic review of feedstocks, technologies, and regulations. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 135, 110240.
- Larson, D. F. , Pitz, W. J., & West, B. H. (2019). Synthetic aviation turbine fuels from renewable sources: Combustion properties and emissions. Fuel, 254, 115667.
- Mukherjee, J. J. , Esterle, A., & Pitsch, H. (2020). Thermal stability of alternative aviation fuels: A review. Fuel, 278, 118308.
- Li, Y. , Huang, J., Li, T., & Ji, H. (2021). Combustion characteristics of biodiesel and its blends: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 139, 110675.
- Myhrvold, N. P. , Randall, L. S., & Wood, R. (2019). Particulate matter emissions from aviation: A summary of major factors and impacts. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(8), 3727-3737.
- Undavalli, V. , Olatunde O.B.G., Boylu R., Wei C., Haeker J., Hamilton J., Khandelwal B., Recent advances is sustainable aviation fuels, Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yelugoti, S.R. , Wang W.C., The combustion performance of sustainable aviation fuel with hydrogen addition, Intl. Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kroyan, Y. , Wojcieszik M., Kaario O., Larmi M., Modeling the impact of sustainable aviation fuel peoperties on end-use performance and emissions in aircraft jet engines, Energy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kurzawska, P. , Overview of sustainable aviation fuels including emissions of paarticlate matters and harmful gaseous exhaus gas compounds, Transportation research procedia, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Dooley, S. , Won S.H., Chaos M., Heyne J., Ju Y., Dryer F.L., Kumar K., Sung C. J., Wang H., Oehlschlaeger M. A., Santoro R. J., Litzinger T. A., A jet fuel surrogate formulated by real fuel properties, Combustion and flame, 2010. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Energy, Sustainable aviation fuel: review of technical pathways. 2020.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).