Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Study Type: Peer-reviewed, original research studies, including randomized controlled trials (RCTs), clinical trials, observational studies, and cohort studies, were included. These studies should provide empirical data on the effects of mitochondrial-based interventions on clinical depression.
- Participants: Studies involving human participants of any age and gender, diagnosed with clinical depression according to recognized diagnostic criteria (e.g., DSM-5, ICD-10), were considered.
-
Intervention Categories: Studies investigating interventions falling within the following categories were included:
- Intermittent cold exposure
- Intermittent heat exposure
- Evolutionary-based foods
- Intermittent fasting
- Circadian-based interventions
- Fermented drinks
- Fermented foods
- Intermittent hypercapnia
- Intermittent hypoxia
- Intermittent exercise
- Outcome Measures: Studies that reported relevant clinical outcome measures for depression, such as scores on standardized depression rating scales (e.g., Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Beck Depression Inventory) or clinical diagnosis of depression by a qualified healthcare provider.
- Publication Type: Review articles, meta-analyses, conference abstracts, editorials, letters, commentaries, and non-peer-reviewed sources were excluded.
- Studies without relevant data: Studies that do not provide specific data or information related to the efficacy of mitochondrial-based interventions in the management of clinical depression will be excluded.
- Studies with irrelevant interventions: Studies investigating interventions not falling within the specified categories were excluded to maintain the review's focus on mitochondrial-based interventions.
- Studies without targeted outcomes: Studies that did not include clinical depression as an outcome measure will be excluded, as they did not align with the review's objective.
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
References
- Xu Y., Liu Z., Xu S., Li C., Li M., Cao S., et al. (2022). Scientific evidences of calorie restriction and intermittent fasting for neuroprotection in traumatic brain injury animal models: A review of the literature. Nutrients 14 (7), 1431. 10.3390/nu14071431.
- Yang Z., Zhao T., Zou Y., Zhang J. H., Feng H. (2014). Curcumin inhibits microglia inflammation and confers neuroprotection in intracerebral hemorrhage. Immunol. Lett. 160 (1), 89–95. 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.03.005.
- Wong C. O., Venkatachalam K. (2019). Motor neurons from ALS patients with mutations in C9ORF72 and SOD1 exhibit distinct transcriptional landscapes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 28 (16), 2799–2810. 10.1093/hmg/ddz104.
- Wang L., Yang Z., He X., Pu S., Yang C., Wu Q., et al. (2022). Mitochondrial protein dysfunction in pathogenesis of neurological diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15, 974480. 10.3389/fnmol.2022.974480.
- Vose A. K., Welch J. F., Nair J., Dale E. A., Fox E. J., Muir G. D., et al. (2022). Therapeutic acute intermittent hypoxia: A translational roadmap for spinal cord injury and neuromuscular disease. Exp. Neurol. 347, 113891. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113891.
- Tigchelaar C., van Zuylen M. L., Hulst A. H., Preckel B., van Beek A. P., Kema I. P., et al. (2022). Elevated cerebrospinal fluid glucose levels and diabetes mellitus are associated with activation of the neurotoxic polyol pathway. Diabetologia 65 (7), 1098–1107. 10.1007/s00125-022-05693-7.
- Seyfried T. N., Chinopoulos C. (2021). Can the mitochondrial metabolic theory explain better the origin and management of cancer than can the somatic mutation theory? Metabolites 11 (9), 572. 10.3390/metabo11090572.
- Shanmuganathan R., Tangavel C., Sva K. S., Muthurajan R., Nayagam S. M., Matchado M. S., et al. (2022). Comparative metagenomic analysis of human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus and cartilaginous end plates. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 9, 927652. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.927652.
- Sharma N., Pasala M. S., Prakash A. (2019). Mitochondrial DNA: Epigenetics and environment. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 60 (8), 668–682. 10.1002/em.22319.
- Shegay P. v., Zabolotneva A. A., Shatova O. P., Shestopalov A. v., Kaprin A. D. (2022). Evolutionary view on lactate-dependent mechanisms of maintaining cancer cell stemness and reprimitivization. Cancers (Basel) 14 (19), 4552. 10.3390/cancers14194552.
- Shen C., Rolls E., Cheng W., Kang J., Dong G., Xie C., et al. (2022). Associations of social isolation and loneliness with later dementia. Neurology 99, e164–e175. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200583.
- Shen K., Pender C. L., Bar-Ziv R., Zhang H., Wickham K., Willey E., et al. (2022). Mitochondria as cellular and organismal signaling hubs. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 38 (1), 179–218. 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-120420-015303.
- Shen Q., Wang R., Liu X., Song P., Zheng M., Ren X., et al. (2022). HSF1 stimulates glutamine transport by super-enhancer-driven lncRNA LINC00857 in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 14 (16), 3855. 10.3390/cancers14163855.
- Shen X., Wang Y., Zhao R., Wan Q., Wu Y., Zhao L., et al. (2021). Metabolic syndrome and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 36 (10), 2215–2225. 10.1007/s00384-021-03974-y.
- Shetty A. K., Kodali M., Upadhya R., Madhu L. N. (2018). Emerging anti-aging strategies - scientific basis and efficacy. Aging Dis. 9 (6), 1165–1184. 10.14336/AD.2018.1026.
- Bar-Yosef, T., Hussein, W., Yitzhaki, O. et al. Mitochondrial function parameters as a tool for tailored drug treatment of an individual with psychosis: a proof of concept study. Sci Rep 10, 12258 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Berk M, Turner A, Malhi GS, Ng CH, Cotton SM, Dodd S, Samuni Y, Tanious M, McAulay C, Dowling N, Sarris J, Owen L, Waterdrinker A, Smith D, Dean OM. A randomised controlled trial of a mitochondrial therapeutic target for bipolar depression: mitochondrial agents, N-acetylcysteine, and placebo. BMC Med. 2019 Jan 25;17(1):18. Erratum in: BMC Med. 2019 Feb 17;17(1):35. PMID: 30678686; PMCID: PMC6346513. [CrossRef]
- Castora FJ, Kerns KA, Pflanzer HK, Hitefield NL, Gershon B, Shugoll J, Shelton M, Coleman RA. Expression Changes in Mitochondrial Genes Affecting Mitochondrial Morphology, Transmembrane Potential, Fragmentation, Amyloidosis, and Neuronal Cell Death Found in Brains of Alzheimer's Disease Patients. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;90(1):119-137. PMID: 36093691. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva T, Wu A, Laksono I, Prce I, Maheandiran M, Kiang M, Andreazza AC, Mizrahi R. Mitochondrial function in individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis. Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 18;8(1):6216. PMID: 29670128; PMCID: PMC5906614. [CrossRef]
- Deng H, Dodson MW, Huang H, Guo M. The Parkinson's disease genes pink1 and parkin promote mitochondrial fission and/or inhibit fusion in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 23;105(38):14503-8. Epub 2008 Sep 17. PMID: 18799731. [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi A, Takeda A, Onodera H, Kimpara T, Hisanaga K, Sato N, Nunomura A, Castellani RJ, Perry G, Smith MA, Itoyama Y. Systemic increase of oxidative nucleic acid damage in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. Neurobiol Dis. 2002 Mar;9(2):244-8. PMID: 11895375. [CrossRef]
- Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Fry D, Sesaki H, Reddy PH. Protective effects of reduced dynamin-related protein 1 against amyloid beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Dec 1;25(23):5148-5166. PMID: 27677309; PMCID: PMC6078633. [CrossRef]
- Wen L, Jin Y, Li L, Sun S, Cheng S, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Svenningsson P. Exercise prevents raphe nucleus mitochondrial overactivity in a rat depression model. Physiol Behav. 2014 Jun 10; 132:57-65. Epub 2014 May 8. PMID: 24813829. [CrossRef]
- Salehi B., Sharopov F., Fokou P. V. T., Kobylinska A., de Jonge L., Tadio K., et al. (2019). Melatonin in medicinal and food plants: Occurrence, bioavailability, and health potential for humans. MDPI 8, 681. [CrossRef]
- Salehi B., Sharopov F., Fokou P. V. T., Kobylinska A., Jonge L., Tadio K., et al. (2019). Melatonin in medicinal and food plants: Occurrence, bioavailability, and health potential for humans. Cells 8 (7), 681. [CrossRef]
- Salita T., Rustam Y. H., Mouradov D., Sieber O. M., Reid G. E. (2022). Reprogrammed lipid metabolism and the lipid-associated hallmarks of colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 14 (15), 3714. [CrossRef]
- Saltykova M. M. (2019). Cold adaptation as a means of increasing antioxidant protection. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 49 (3), 323–330. [CrossRef]
- Sampson T. R., Debelius J. W., Thron T., Janssen S., Shastri G. G., Ilhan Z. E., et al. (2016). Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167 (6), 1469–1480. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021 Mar 29;372:n71. PMID: 33782057; PMCID: PMC8005924. [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.KL., Mertz, D. & Loeb, M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol 14, 45 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Feng J.J., Li Y.H. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on depression and anxiety in the patients with incomplete spinal cord injury (a STROBE-compliant article) Medicine. 2017;96:e7334. [CrossRef]
- Rymaszewska J., Lion K.M., Pawlik-Sobecka L., Pawłowski T., Szcześniak D., Trypka E., Rymaszewska J.E., Zabłocka A., Stanczykiewicz B. Efficacy of the Whole-Body Cryotherapy as Add-on Therapy to Pharmacological Treatment of Depression-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Psychiatry. 2020;11:522. [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen T, Laukkanen JA, Kunutsor SK. Sauna Bathing and Risk of Psychotic Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study. Med Princ Pract. 2018;27(6):562-569. Epub 2018 Sep 2. PMID: 30173212; PMCID: PMC6422146. [CrossRef]
- Masuda A, Nakazato M, Kihara T, Minagoe S, Tei C. Repeated thermal therapy diminishes appetite loss and subjective complaints in mildly depressed patients. Psychosom Med. 2005 Jul-Aug;67(4):643-7. PMID: 16046381. [CrossRef]
- Behzad Zamani, Mobina Zeinalabedini, Ensieh Nasli Esfahani, Leila Azadbakht, "Can Following Paleolithic and Mediterranean Diets Reduce the Risk of Stress, Anxiety, and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Study on Iranian Women", Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, vol. 2023, Article ID 2226104, 10 pages, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Danan A, Westman EC, Saslow LR, Ede G. The Ketogenic Diet for Refractory Mental Illness: A Retrospective Analysis of 31 Inpatients. Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 6;13:951376. PMID: 35873236; PMCID: PMC9299263. [CrossRef]
- Berthelot E, Etchecopar-Etchart D, Thellier D, Lancon C, Boyer L, Fond G. Fasting Interventions for Stress, Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 5;13(11):3947. PMID: 34836202; PMCID: PMC8624477. [CrossRef]
- Stapel, B., Fraccarollo, D., Westhoff-Bleck, M. et al. Impact of fasting on stress systems and depressive symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 12, 7642 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Sit DK, McGowan J, Wiltrout C, Diler RS, Dills JJ, Luther J, Yang A, Ciolino JD, Seltman H, Wisniewski SR, Terman M, Wisner KL. Adjunctive Bright Light Therapy for Bipolar Depression: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 1;175(2):131-139. Epub 2017 Oct 3. PMID: 28969438. [CrossRef]
- Garbazza C, Cirignotta F, D'Agostino A, Cicolin A, Hackethal S, Wirz-Justice A, Cajochen C, Manconi M; “Life-ON” study group. Sustained remission from perinatal depression after bright light therapy: A pilot randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2022 Oct;146(4):350-356. . Epub 2022 Aug 3 PMID: 35876837; PMCID: PMC9804451. [CrossRef]
- Mohsenpour, M.A., Mohammadi, F., Razmjooei, N. et al. Milk kefir drink may not reduce depression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: secondary outcome analysis of a randomized, single-blinded, controlled clinical trial. BMC Nutr 9, 80 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kazemi A, Noorbala AA, Azam K, Eskandari MH, Djafarian K. Effect of probiotic and prebiotic vs placebo on psychological outcomes in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 2019 Apr;38(2):522-528. Epub 2018 Apr 24. PMID: 29731182. [CrossRef]
- Chahwan B, Kwan S, Isik A, van Hemert S, Burke C, Roberts L. Gut feelings: A randomised, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial of probiotics for depressive symptoms. J Affect Disord. 2019 Jun 15;253:317-326. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID: 31078831. [CrossRef]
- Akkasheh G, Kashani-Poor Z, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Jafari P, Akbari H, Taghizadeh M, Memarzadeh MR, Asemi Z, Esmaillzadeh A. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition. 2016 Mar;32(3):315-20. Epub 2015 Sep 28. PMID: 26706022. [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova EA, Samoilov MO, Mironova VI, Tyul'kova EI, Pivina SG, Vataeva LA, Ordyan NE, Abritalin EY, Kolchev AI. The possible use of hypoxic preconditioning for the prophylaxis of post-stress depressive episodes. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2008 Sep;38(7):721-6. PMID: 18709460. [CrossRef]
- Lim SW, Sung KC, Shiue YL, Wang CC, Chio CC, Kuo JR. Hyperbaric Oxygen Effects on Depression-Like Behavior and Neuroinflammation in Traumatic Brain Injury Rats. World Neurosurg. 2017 Apr;100:128-137. Epub 2017 Jan 6. PMID: 28065873. [CrossRef]
- Rymaszewska, J., Ramsey, D. & Chładzińska-Kiejna, S. Whole-body cryotherapy as adjunct treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 56, 63–68 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Eliacik K, Bolat N, Kanik A, Sargin E, Selkie E, Korkmaz N, Baydan F, Akar E, Sarioglu B. Parental attitude, depression, anxiety in mothers, family functioning and breath-holding spells: A case control study. J Paediatr Child Health. 2016 May;52(5):561-5. Epub 2016 Apr 18. PMID: 27089451. [CrossRef]
- Mattie-Luksic M, Javornisky G, DiMario FJ. Assessment of stress in mothers of children with severe breath-holding spells. Pediatrics. 2000 Jul;106(1 Pt 1):1-5. PMID: 10878140. [CrossRef]
- Paolucci EM, Loukov D, Bowdish DME, Heisz JJ. Exercise reduces depression and inflammation but intensity matters. Biol Psychol. 2018 Mar;133:79-84. Epub 2018 Feb 3. PMID: 29408464. [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Fernández D, Fernández-Rodríguez R, Taboada-Iglesias Y, Gutiérrez-Sánchez Á. Impact of High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition and Depressive Symptoms in Adults under Home Confinement. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 18;19(10):6145. PMID: 35627681; PMCID: PMC9140689. [CrossRef]
- Sandhir R., Halder A., Sunkaria A. (2017). Mitochondria as a centrally positioned hub in the innate immune response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1863 (5), 1090–1097. [CrossRef]
- Saner N. J., Lee M. J. C., Kuang J., Pitchford N. W., Roach G. D., Garnham A., et al. (2021). Exercise mitigates sleep-loss-induced changes in glucose tolerance, mitochondrial function, sarcoplasmic protein synthesis, and diurnal rhythms. Mol. Metab. 43, 101110. [CrossRef]
- Santín-Márquez R., Alarcón-Aguilar A., López-Diazguerrero N. E., Chondrogianni N., Königsberg M. (2019). Sulforaphane - role in aging and neurodegeneration. Geroscience 41 (5), 655–670. [CrossRef]
- Sardon Puig L., Valera-Alberni M., Cantó C., Pillon N. J. (2018). Circadian rhythms and mitochondria: Connecting the dots. Front. Genet. 9, 452. [CrossRef]
- Sato T., Higuchi Y., Shibagaki Y., Hattori S. (2017). Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies signaling pathways regulated by curcumin in human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37 (9), 4789–4798. [CrossRef]
- Savencu C. E., Linţa A., Farcaş G., Bînă A. M., Creţu O. M., Maliţa D. C., et al. (2021). Impact of dietary restriction regimens on mitochondria, heart, and endothelial function: A brief overview. Front. Media S.A. 12, 768383. [CrossRef]
- Scalise M., Console L., Rovella F., Galluccio M., Pochini L., Indiveri C. (2020). Membrane transporters for amino acids as players of cancer metabolic rewiring. Cells 9, 2028. [CrossRef]
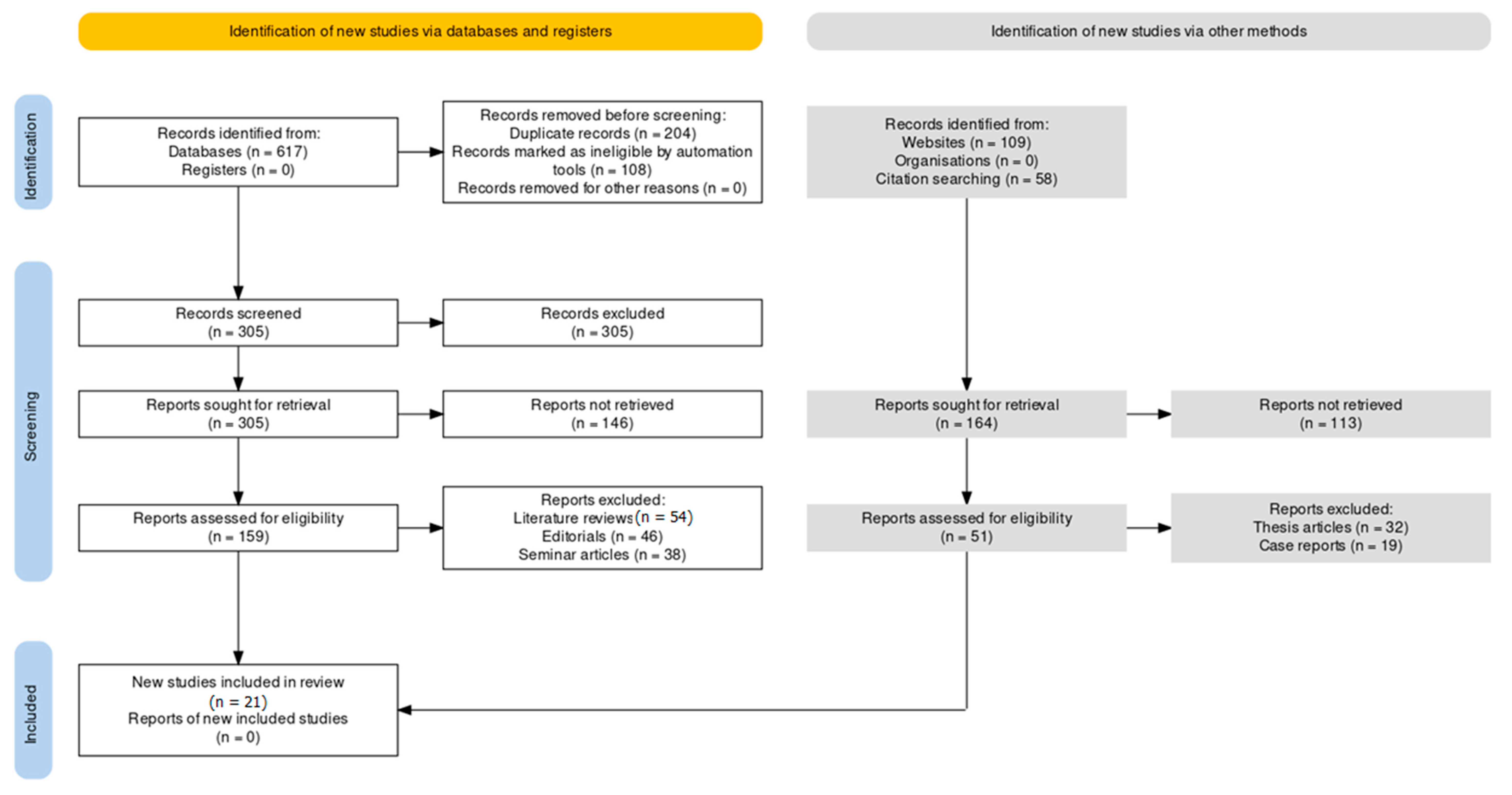
| Database | Intermittent Cold Exposure | Intermittent Heat Exposure | Evolutionary Based Foods | Intermittent Fasting | Circadian-Based Interventions | Fermented Drinks | Fermented Foods | Intermittent Hypercapnia | Intermittent Hypoxia | Intermittent Exercise |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| ScienceDirect | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| IEEE Xplore | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| PsycINFO | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| Web of Science | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| Embase | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| CINAHL | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| Scopus | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
| Google Scholar | ("ice bath" OR "cold plunge" OR "whole body cryotherapy" OR "cryochamber") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("sauna" OR "infrared sauna") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("paleo diet" OR "paleolithic diet" OR "ketogenic diet" OR "carnivore diet") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("intermittent fasting" OR "caloric restriction" OR "fasting") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("bluelight therapy" OR "melatonin" OR "bright light therapy" OR "light therapy" OR "blue light blocker") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("probiotic drinks" OR "kefir" OR "kombucha" OR "ayran" OR "buttermilk") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("fermented foods" OR "miso" OR "natto" OR "Tempeh" OR "skyr" OR "strained yoghurt" OR "greek yoghurt") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("breath holding" OR "hypercapnia") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("ihht" OR "altitude training" OR "breath holding") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") | ("hiit" OR "high intensity interval training" OR "tabata" OR "interval training") AND ("depression" OR "clinical depression") |
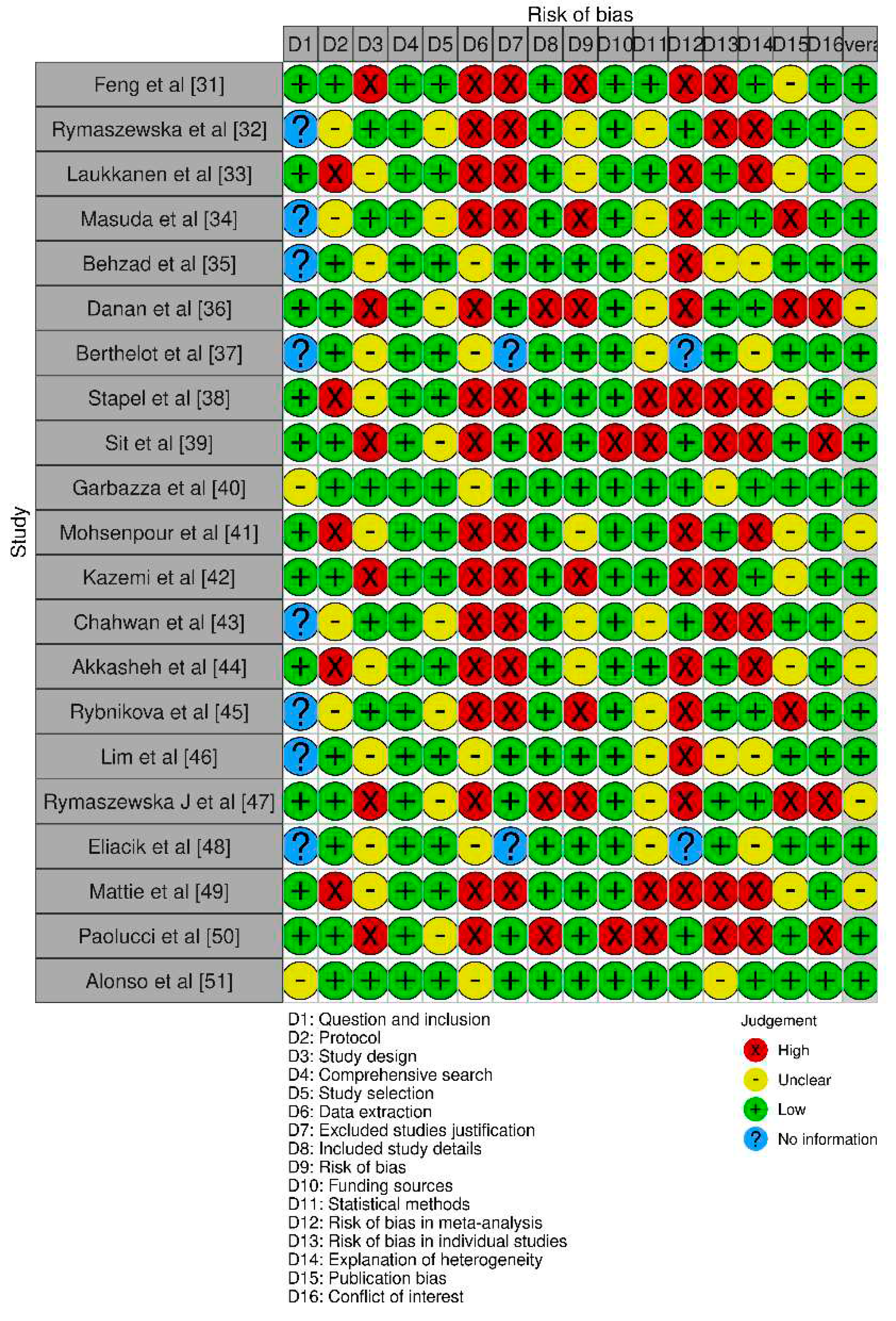
| Study | Aims | Study Design | Methodology Assessed | Type of Mitochondrial Intervention Assessed |
| Feng et al [31] | To investigate the effects of HBO on psychological problems and nerve function, especially on depression and anxiety in patients. | RCT | Hamilton Depression (HAMD) scale, | Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy |
| Rymaszewska et al [32] | To assess the efficacy of repetitive short exposure to extremely low temperatures on mood, quality of life, and biochemical measures in people diagnosed with depressive episodes undergoing pharmacological treatment. | Prospective RCT | Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II), | Whole-body cryotherapy (WBC) |
| Laukkanen et al [33] | To assess the association between frequency of sauna bathing and the risk of depressive symptoms in a population-based study. | Prospective cohort study | Sauna bathing frequency | Sauna bathing |
| Masuda et al [34] | To clarify the effects of repeated thermal therapy in mildly depressed patients with appetite loss and subjective complaints. | RCT | Scores (hunger, relaxation, etc.) | Thermal therapy (far-infrared ray dry sauna) |
| Behzad et al [35] | To investigate the association of Paleolithic and Mediterranean diets with psychological disorders in a sample of adult women. | Cross-sectional study | Diet scores (Paleolithic, Mediterranean) | Dietary patterns (Paleolithic, Mediterranean) |
| Danan et al [36] | To assess the effects of a ketogenic diet on adults with severe, persistent mental illness whose symptoms were poorly controlled despite intensive psychiatric management. | Retrospective analysis | Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, | Ketogenic diet (maximum 20g carb/day) |
| Berthelot et al [37] | To determine the effectiveness of fasting interventions on stress, anxiety, depression, and their association with fatigue/energy. | Meta-analysis of 11 studies | Stress, Anxiety, Depression levels | Fasting interventions |
| Stapel et al [38] | To assess the impact of fasting on metabolic parameters, stress hormones, and mood in depressed inpatients. | Prospective study | Metabolic parameters, Stress systems | 72-hour fasting |
| Sit et al [39] | To determine remission rate, depression symptom level, mood polarity switch rate, and explore sleep quality in bipolar depression. | Randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Depression symptoms, Sleep quality | Bright white light therapy |
| Garbazza et al [40] | To investigate the efficacy and safety of Bright Light Therapy (BLT) for postnatal depression (PND) during the perinatal period. | Single-blind RCT | Depression levels (EPDS) | Bright Light Therapy (BLT) |
| Mohsenpour et al [41] | To investigate the effect of milk kefir drinks on depression status in individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). | Randomized controlled trial (RCT) | Depression status (BDI-II-Persian) | Milk kefir drinks |
| Kazemi et al [42] | To compare the effect of probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on depression scores and metabolic parameters in patients with MDD. | Double-blind RCT | Depression score (BDI) | Probiotic (Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum), Prebiotic (galactooligosaccharide) |
| Chahwan et al [43] | To determine the effect of probiotic supplements (Winclove's Ecologic® Barrier) on depressive symptoms in participants with mild to severe depression. | Clinical trial (RCT) | Symptoms, vulnerability markers | Probiotic supplements (Winclove's Ecologic® Barrier) |
| Akkasheh et al [44] | To determine the effects of probiotic intake on symptoms of depression and metabolic status in patients with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). | Randomized, double-blind RCT | Symptoms, metabolic status | Probiotic supplements |
| Rybnikova et al [45] | To study the protective effects of hypoxic preconditioning on the development of depressive states in rat models. | Experimental study | Depressive behavioral reactions | Hypoxic preconditioning (Intermittent hypobaric hypoxia) |
| Lim et al [46] | To determine the effect of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy on TBI-induced depression-like behavior and neuroinflammation in rats. | Experimental (Rat Model) | Behavior, neuroinflammation | Hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO) Therapy |
| Rymaszewska J et al [47] | To assess the efficacy of whole-body cryotherapy (WBCT) as an adjunctive treatment for depressive and anxiety disorders. | Clinical Trial (Control vs Study Group) | Psychopharmacotherapy, WBCT | Whole-Body Cryotherapy (WBCT) |
| Eliacik et al [48] | To identify differences in antenatal stressful life events, parenting style, family functioning, depression, and anxiety of mothers of children with breath-holding spells (BHS). | Case-Control Study | Antenatal events, family functioning | BHS (hypercapnia induction) |
| Mattie et al [49] | To examine maternal stress in parenting children with breath-holding spells (BHS) and depressive symptoms (DS) compared to control children. | Observational (Comparative) | Parenting Stress, Coping Mechanisms | BHS (hypercapnia induction) |
| Paolucci et al [50] | To measure changes in depression, anxiety, and perceived stress along with pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to exercise. | Experimental (Exercise Intervention) | Mental Health, Pro-inflammatory Cytokines | High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) |
| Alonso et al [51] | To observe the impact of an 8-week HIIT protocol on body composition and depressive symptoms during home confinement. | Experimental (Exercise Intervention) | Body Composition, Depressive Symptoms | High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) |
| Study | Parameters Assessed | Inferences Observed | Results Observed |
| Feng et al [31] | Depression (HAMD), Anxiety (HAMA), Nerve function (ASIA score), Activities of daily living (FIM score) | HBO and psychotherapy both significantly reduced HAMD scores compared to the control group. HBO group had lower HAMA scores than the control group. HBO improved ASIA and FIM scores more than psychotherapy. HBO is similar to psychotherapy in reducing depression and anxiety but superior in improving nerve function and daily living activities depressive patients. | - HAMD scores significantly lower in HBO and psychotherapy groups vs. control.- HAMA scores significantly lower in HBO group vs. control.- ASIA and FIM scores significantly higher in HBO and psychotherapy groups vs. control. |
| Rymaszewska et al [32] | Depressive symptoms (BDI-II, HAM-D 17), Quality of life, Mood, Vitality, Sleep quality, Disease acceptance | WBC showed statistically significant improvements in depressive symptoms (HAM-D 17, BDI-II) and quality of life. No significant changes in sexual satisfaction, vitality, or sleep. WBC is a useful addition to pharmacological treatment for depression. | - Statistically significant improvements in HAM-D 17, BDI-II, and quality of life in the WBC group.- No significant changes in sexual satisfaction, vitality, or sleep. |
| Laukkanen et al [33] | Risk of depressive symptoms | Frequent sauna bathing (4–7 times per week) was inversely associated with the risk of depressive symptoms in a male population. | - Frequent sauna bathing (4–7 times per week) associated with a significantly lower risk of depressive symptoms in males.- The association remained significant after adjusting for various factors. |
| Masuda et al [34] | Somatic and mental complaints, hunger, relaxation, plasma ghrelin concentrations, daily caloric intake | Repeated thermal therapy improved somatic complaints, hunger, relaxation, and increased plasma ghrelin concentrations and daily caloric intake. | - Somatic complaints, hunger, relaxation scores significantly improved. - Mental complaints slightly improved. - Increased plasma ghrelin concentrations and daily caloric intake in the thermal therapy group. |
| Behzad et al [35] | Psychological disorders (depression, anxiety, stress) | Greater adherence to Paleolithic and Mediterranean diets was associated with a decreased risk of psychological disorders such as depression, anxiety, and stress. | - Higher Paleolithic diet tertile associated with lower odds of depression, anxiety, and stress. - Higher Mediterranean diet tertile associated with lower odds of depression, anxiety, and stress. |
| Danan et al [36] | Depression (Hamilton Depression Rating Scale), Psychosis (Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale), Metabolic health measures | Ketogenic diet was associated with substantial improvements in depression and psychosis symptoms and multiple markers of metabolic health. | - Significant improvements in Hamilton Depression Rating Scale scores. - Significant improvements in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale scores.- Improvements in metabolic health measures (weight, blood pressure, blood glucose, triglycerides). |
| Berthelot et al [37] | Anxiety, Depression levels, Body mass index | Fasting interventions were associated with lower anxiety and depression levels and lower body mass index without increased fatigue. These interventions were found to be safe, even in patients with type 2 diabetes. | - Fasting groups had lower anxiety and depression levels. - Lower body mass index without increased fatigue. - Safe for patients with type 2 diabetes. |
| Stapel et al [38] | Metabolic parameters, Stress systems, Depression symptoms (BDI-2), BDNF levels | Fasting impacted metabolic parameters and stress systems similarly in both groups. In depressed patients, fasting improved cognitive-affective symptoms, especially in those with moderate/severe symptoms. | - Fasting improved cognitive-affective symptoms in depressed patients with moderate/severe symptoms. - No mood polarity switches observed. |
| Sit et al [39] | Remission rate, Depression scores, Mood polarity switch rate, Sleep quality | Bright white light therapy was associated with a significantly higher remission rate and lower depression scores compared to placebo light therapy in bipolar depression. Sleep quality improved in both groups. | - Bright white light therapy had a higher remission rate and lower depression scores. - No mood polarity switches observed. - Improved sleep quality. |
| Garbazza et al [40] | Depression levels (EPDS) | Morning BLT induced significant remission from PND compared to dim red light (DRL) therapy. The effect was maintained across the perinatal period. | - 73% remission rate with BLT vs. 27% with DRL. - Significant reduction in EPDS scores in the BLT group. - No major side effects reported. |
| Mohsenpour et al [41] | Depression status (BDI-II-Persian) | Diet + Kefir group showed a significant reduction in depression compared to the Diet group. No significant between-group differences. | - Diet + Kefir group had a significant reduction in depression. - No reduction in depression in the Diet group. |
| Kazemi et al [42] | Depression score (BDI), Kynurenine/Tryptophan ratio, Tryptophan/BCAAs ratio | Probiotic supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in depression score compared to placebo. No significant inter-group differences in metabolic parameters. | - Probiotic group had a significant decrease in depression score. - No significant differences in metabolic parameters among groups. |
| Chahwan et al [43] | Symptoms, gut microbiota composition | Probiotic group showed a significantly greater reduction in cognitive reactivity. Probiotics did not significantly alter the gut microbiota. | - Improvement in symptoms in all clinical trial participants. - Greater reduction in cognitive reactivity in probiotic group. - No significant gut microbiota changes. |
| Akkasheh et al [44] | Symptoms, metabolic markers | Probiotic group had significantly decreased Beck Depression Inventory scores. Significant decreases in serum insulin levels, insulin resistance, and hs-CRP concentrations. | - Significant improvement in depression scores in probiotic group. - Improvement in metabolic markers in probiotic group. |
| Rybnikova et al [45] | Depressive behavioral reactions, hormonal markers | Hypoxic preconditioning prevented the onset of depressive reactions and hormonal changes. Anxiolytic and antidepressant effects were observed. | - Hypoxic preconditioning prevented depressive reactions in rat models. - Anxiolytic and antidepressant effects observed. |
| Lim et al [46] | Depression-like behavior, motor function, infarction volume, neuronal apoptosis, microglial activation, TNF-α expression | HBO therapy attenuated TBI-induced depression-like behavior and neuroinflammation. | - Improvement in depression-like behavior with HBO therapy. - Reduced neuroinflammation with HBO therapy. |
| Rymaszewska J et al [47] | Hamilton's Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), Hamilton's Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS) | WBCT as an adjunctive treatment led to significant reductions in depression and anxiety in the study group. | - Significant reduction in HDRS and HARS scores in the study group after WBCT. |
| Eliacik et al [48] | Stressful life events, depression traits, state-trait anxiety, parenting style, family functioning | Mothers of children with BHS had higher exposure to stressful events, anxiety, depression, and poor family functioning. | - Significant differences in stressful events, anxiety, depression, and family functioning between groups. |
| Mattie et al [49] | Overall stress, attachment, child's behavior, sense of competence, self-identity, positive reinforcement, maternal health, depression/isolation, spousal support, child's mood, life stresses | Parenting children with BHS or DS is more stressful, impacting mothers' sense of competence and self-identity. | - Mothers of BHS and DS children perceive more stress and child's behavior issues. - Significant disruption in mothers' sense of competence for BHS group. |
| Paolucci et al [50] | Depression, anxiety, perceived stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, CRP) | Moderate-intensity exercise decreases depression and TNF-α levels, while high-intensity exercise increases perceived stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines. | - Depression increased in the control group. - MCT and HIT decreased depression. - HIT increased perceived stress, TNF-α, and IL-6. |
| Alonso et al [51] | Body fat mass (percentage and kg), body fat mass index (BFMI), depressive symptoms | HIIT during home confinement reduces body fat mass and depressive symptoms. | - Significant reductions in body fat mass and BFMI. - Reduction in depressive symptoms with HIIT. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




