Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
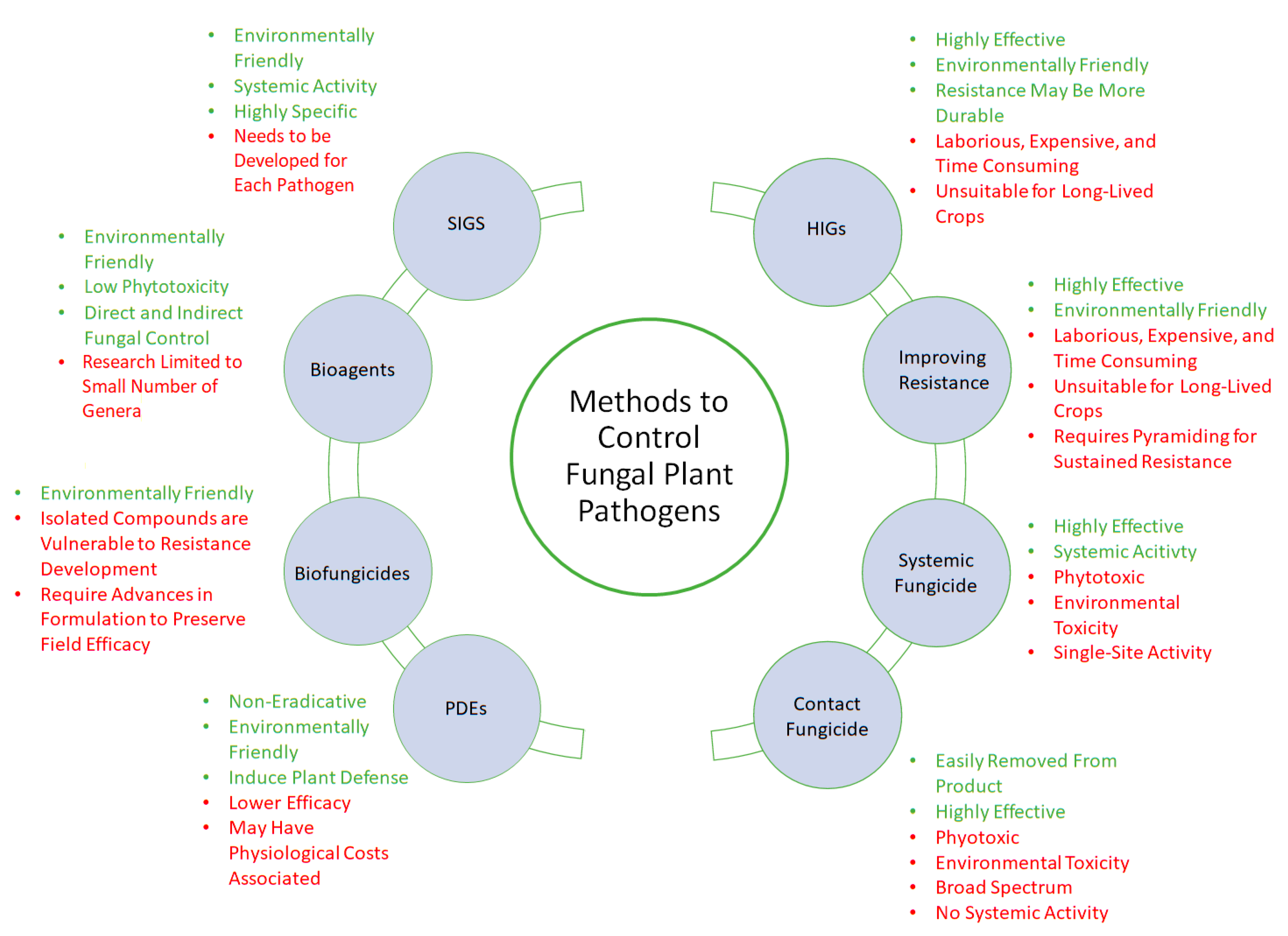
Introduction
Chemical Fungicides
Disadvantages of Chemical Fungicides: Environmental Toxicity and Resistance Development
Alternative Management of Fungal Diseases
Improving Plants’ Genetic Resistance Through the Use of R and S Genes
Use of Plant Defence Elicitors
Biological Control and Biofungicides
RNAi-Based Disease Management
Small RNA-Based Fungicides
i. Host-Induced Gene Silencing
ii. Using Spray-Induced Gene Silencing as the Basis for RNA-based Fungicides
Future Directions
Conclusion
Funding Information
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gullino, M.; Leroux, P.; Smith, C. Uses and challenges of novel compounds for plant disease control. Crop Protection 2000, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, A. Introduction: the importance of research on the control of postharvest diseases of perishable food crops. Phytopathology 1989, 79, 1374. [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale, N.N.; Sisler, H.D. Social and political implications of managing plant diseases with decreased availability of fungicides in the United States. Annu Rev Phytopathol 1994, 32, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, N.; Kulhanek, K.; Antúnez, K.; Human, H.; Chantawannakul, P.; Chauzat, M.P.; vanEngelsdorp, D. Drivers of colony losses. Curr Opin Insect Sci 2018, 26, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millardet, P.M.A. The Discovery of Bordeaux Mixture; The American Phytopathological Society: 2018; pp. –1.
- Baibakova, E.; Nefedjeva, E.; Suska-Malawska, M.; Wilk, M.; Sevriukova, G.; Zheltobriukhov, V. Modern Fungicides: Mechanisms of Action, Fungal Resistance and Phytotoxic Effects. Annual Research & Review in Biology 2019, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.; Thuerig, B.; Apostolov, S.; Blogg, H.; Borgo, E.; Corneo, P.E.; Fittje, S.; de Palma, M.; Donko, A.; Experton, C.; et al. Use of Copper-Based Fungicides in Organic Agriculture in Twelve European Countries. Agronomy 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Osdaghi, E.; Behlau, F.; Köhl, J.; Jones, J.B.; Aubertot, J.-N. Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppuchamy, P.; Venugopal, S. Chapter 21 - Integrated Pest Management. In Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security, Omkar, Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2016; pp. 651–684. [Google Scholar]
- Anna La, T.; Valeria, I.; Federica, C. Copper in plant protection: current situation and prospects. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 2018, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oziengbe; Osazee. Antifungal Activity of Copper Sulphate Against Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides. Journal of Asian Scientific Research 2012, 2, 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, R.; Hewitt, H.G. Fungicides in crop protection: Second edition. CABI Journal. CABI International 2014, 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M. Phytotoxicity: An Overview of the Physiological Responses of Plants Exposed to Fungicides. Journal of Botany 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, A.N.; Fontaine, F.; Vatsa, P.; Clément, C.; Vaillant-Gaveau, N. Fungicide impacts on photosynthesis in crop plants. Photosynth Res 2012, 111, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kromann, P.; Taipe, A.; Perez, W.; Forbes, G. Rainfall Thresholds as Support for Timing Fungicide Applications in the Control of Potato Late Blight in Ecuador and Peru. Plant Disease - PLANT DIS 2009, 93, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicent, A.; Armengol, J.; García-Jiménez, J. Rain Fastness and Persistence of Fungicides for Control of Alternaria Brown Spot of Citrus. Plant Disease - PLANT DIS 2007, 91, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Rivero, R.; Ruiz, J.; Romero, L. The Role of Fungicides in the Physiology of Higher Plants: Implications for Defense Responses. The Botanical Review 2003, 69, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klittich, C.J.R. Fungicide Mobility and the Influence of Physical Properties. In Retention, Uptake, and Translocation of Agrochemicals in Plants; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: 2014; Volume 1171, pp. 95–109.
- Klittich, C.J.; Ray, S.L. Effects of physical properties on the translaminar activity of fungicides. Pestic Biochem Physiol 2013, 107, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warneke, B.; Thiessen, L.; Mahaffee, W. Effect of Fungicide Mobility and Application Timing on the Management of Grape Powdery Mildew. Plant Disease 2019, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, M.S.; Suryanarayanan, T.S.; Nataraja, K.N.; Prasad, S.R.; Shaanker, R.U. Seed Treatment With Systemic Fungicides: Time for Review. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12, 654512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deising, H.; Reimann, S.; Pascholati, S. Mechanisms and significance of fungicide resistance†. Brazilian journal of microbiology : [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology] 2008, 39, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandoss, J.; Suryanarayanan, T. Effect of fungicide treatment on foliar fungal endophyte diversity in mango. Sydowia 2009, 61, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Leyronas, C.; Mériaux, B.; Raynal, G. Chemical Control of Neotyphodium spp. Endophytes in Perennial Ryegrass and Tall Fescue Seeds. Crop Science 2006, 46, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Gosal, S.K. Effect of pesticide application on soil microorganisms. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 2011, 57, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.R.; Doohan, F.M.; Hodkinson, T.R. A seed dressing combining fungal endophyte spores and fungicides improves seedling survival and early growth in barley and oat. Symbiosis 2017, 71, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.W.; Percival, D.; Yurgel, S.N. Effect of Fungicide Application on Lowbush Blueberries Soil Microbiome. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.W.; Percival, D.; Langille, M.G.I.; Yurgel, S.N. Changes to Soil Microbiome Resulting from Synergetic Effects of Fungistatic Compounds Pyrimethanil and Fluopyram in Lowbush Blueberry Agriculture, with Nine Fungicide Products Tested. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, M.; Buerge, I.J.; Hauser, A.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Azole Fungicides: Occurrence and Fate in Wastewater and Surface Waters. Environmental Science & Technology 2008, 42, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrod, J.P.; Bundschuh, M.; Arts, G.; Brühl, C.A.; Imfeld, G.; Knäbel, A.; Payraudeau, S.; Rasmussen, J.J.; Rohr, J.; Scharmüller, A.; et al. Fungicides: An Overlooked Pesticide Class? Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 3347–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaune, L.; Singhasemanon, N. Pesticidal copper (I) oxide: environmental fate and aquatic toxicity. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 2011, 213, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, J.; Joshi, N.K. Effects of Fungicide and Herbicide Chemical Exposure on Apis and Non-Apis Bees in Agricultural Landscape. Frontiers in Environmental Science 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisenburger, D.D. Human health effects of agrichemical use. Hum Pathol 1993, 24, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, M.; Lorrain, C.; Feurtey, A.; Komluski, J.; Stukenbrock, E.H. Epigenetic modifications affect the rate of spontaneous mutations in a pathogenic fungus. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, D.; Stenzel, K. FRAC Mode-of-action Classification and Resistance Risk of Fungicides. In Modern Crop Protection Compounds; 2019; pp. 589–608.
- Bent, A.F.; Mackey, D. Elicitors, effectors, and R genes: the new paradigm and a lifetime supply of questions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 2007, 45, 399–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.; Vance, R.E.; Dangl, J.L. Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 2016, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.-Q.; Xue, J.-Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wu, Y.; Hang, Y.-Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.-Q. Large-Scale Analyses of Angiosperm Nucleotide-Binding Site-Leucine-Rich Repeat Genes Reveal Three Anciently Diverged Classes with Distinct Evolutionary Patterns. Plant physiology 2016, 170, 2095–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Golstein, C.; Ade, J.; Stoutemyer, M.; Dixon, J.E.; Innes, R.W. Cleavage of Arabidopsis PBS1 by a bacterial type III effector. Science 2003, 301, 1230–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-Microbe Interactions: Shaping the Evolution of the Plant Immune Response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur, L.A.J.; Kenton, P.; Lloyd, A.J.; Ougham, H.; Prats, E. The hypersensitive response; the centenary is upon us but how much do we know? Journal of Experimental Botany 2008, 59, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.-P.; Yang, Y.; Pichersky, E.; Klessig, D.F. Altering Expression of Benzoic Acid/Salicylic Acid Carboxyl Methyltransferase 1 Compromises Systemic Acquired Resistance and PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions® 2010, 23, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K.; Sato, M.; Stoddard, T.; Glazebrook, J.; Katagiri, F. Network properties of robust immunity in plants. PLoS Genet 2009, 5, e1000772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Bhatia, D.; Mavi, G.S. Eighty years of gene-for-gene relationship and its applications in identification and utilization of R genes. J Genet 2021, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, Y.P.; Kaul, S.; Wani, A.A.; Dhar, M.K. Genetics of resistance in apple against Venturia inaequalis (Wint.) Cke. Tree Genetics & Genomes 2018, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Wang, S. Broad-spectrum and durability: understanding of quantitative disease resistance. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2010, 13, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashfield, T.; Ong, L.E.; Nobuta, K.; Schneider, C.M.; Innes, R.W. Convergent evolution of disease resistance gene specificity in two flowering plant families. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.A.; Dwyer, G.; Mauricio, R.; Kreitman, M.; Bergelson, J. Dynamics of disease resistance polymorphism at the Rpm1 locus of Arabidopsis. Nature 1999, 400, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimbaud, L.; Papaïx, J.; Barrett, L.G.; Burdon, J.J.; Thrall, P.H. Mosaics, mixtures, rotations or pyramiding: What is the optimal strategy to deploy major gene resistance? Evolutionary Applications 2018, 11, 1791–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, C.C. Durable resistance: A key to sustainable management of pathogens and pests. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 2014, 27, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, V.; Neto, J.; da Silva, M.D.; Amorim, L.L.B.; Wanderley-Nogueira, A.C.; de Oliveira Silva, R.L.; Kido, E.A.; Crovella, S.; Iseppon, A.M.B. Resistance (R) Genes: Applications and Prospects for Plant Biotechnology and Breeding. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2017, 18, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundt, C. Pyramiding for Resistance Durability: Theory and Practice. Phytopathology 2018, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, W.; Salas, A.; Raymundo, R.; Huamán, Z.; Nelson, R.; Bonierbale, M. Evaluation of Wild Potato Species for Resistance to Late Blight. 2001.
- Zaidi, S.S.; Mukhtar, M.S.; Mansoor, S. Genome Editing: Targeting Susceptibility Genes for Plant Disease Resistance. Trends Biotechnol 2018, 36, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, C.C.; Takken, F.L. Susceptibility genes 101: how to be a good host. Annu Rev Phytopathol 2014, 52, 551–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, N.P.; Lenman, M.; Wang, E.S.; Petersen, B.L.; Andreasson, E. Mutations introduced in susceptibility genes through CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing confer increased late blight resistance in potatoes. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Bai, S.; Wang, N.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Dong, C. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Mutagenesis of MdCNGC2 in Apple Callus and VIGS-Mediated Silencing of MdCNGC2 in Fruits Improve Resistance to Botryosphaeria dothidea. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 575477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Qiu, J.L. Genome editing for plant disease resistance: applications and perspectives. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 2019, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticher, L.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Métraux, J.P. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 1997, 35, 235–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.Q.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2013, 64, 839–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektas, Y.; Eulgem, T. Synthetic plant defense elicitors. Frontiers in plant science 2015, 5, 804–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamy, J.; Carr, J.P.; Klessig, D.F.; Raskin, I. Salicylic Acid: a likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science 1990, 250, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, T.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Negrotto, D.; Nye, G.; Uknes, S.; Ward, E.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. Requirement of salicylic Acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 1993, 261, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gui, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J.; Niu, D. Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Plants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; Eggermont, K.; Penninckx, I.A.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Vogelsang, R.; Cammue, B.P.; Broekaert, W.F. Separate jasmonate-dependent and salicylate-dependent defense-response pathways in Arabidopsis are essential for resistance to distinct microbial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 15107–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koornneef, A.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Ritsema, T.; Verhage, A.; Den Otter, F.C.; Van Loon, L.C.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Kinetics of salicylate-mediated suppression of jasmonate signaling reveal a role for redox modulation. Plant physiology 2008, 147, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfte, M. Induced Resistance for Plant Defence. A Sustainable Approach to Crop Protection - Edited by Dale Walters, Adrian Newton and Gary Lyon. Plant Pathology 2007, 56, 1036–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.L. Plant Defense Activators: Application and Prospects in Cereal Crops. In 50 Years of Phytochemistry Research: Volume 43, Gang, D.R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2013; pp. 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.-S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.-S. Salicylic acid-induced differential resistance to the Tomato yellow leaf curl virus among resistant and susceptible tomato cultivars. BMC Plant Biology 2019, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deenamo, N.; Kuyyogsuy, A.; Khompatara, K.; Chanwun, T.; Ekchaweng, K.; Churngchow, N. Salicylic Acid Induces Resistance in Rubber Tree against Phytophthora palmivora. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, W.; Wang, C. Salicylic acid confers enhanced resistance to Glomerella leaf spot in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 2016, 106, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumayo, M.S.; Son, J.S.; Ghim, S.Y. Exogenous application of phenylacetic acid promotes root hair growth and induces the systemic resistance of tobacco against bacterial soft-rot pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Funct Plant Biol 2018, 45, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zeng, K.; Jiang, W. Enhancement of Postharvest Disease Resistance in Ya Li Pear ( Pyrus bretschneideri ) Fruit by Salicylic Acid Sprays on the Trees during Fruit Growth. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2006, 114, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadrami, A.; Adam, L.R.; El Hadrami, I.; Daayf, F. Chitosan in Plant Protection. Marine Drugs 2010, 8, 968–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Jiang, D.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, S.; Hou, X.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; et al. Paecilomyces variotii extracts (ZNC) enhance plant immunity and promote plant growth. Plant and Soil 2019, 441, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faugeron-Girard, C.; Gloaguen, V.; Koçi, R.; Célérier, J.; Raynaud, A.; Moine, C. Use of a Pleurotus ostreatus Complex Cell Wall Extract as Elicitor of Plant Defenses: From Greenhouse to Field Trial. Molecules 2020, 25, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritopoulou, T.; Toufexi, E.; Kizis, D.; Balayiannis, G.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Theocharis, A.; Rempelos, L.; Troyanos, Y.; Leifert, C.; Markellou, E. Reynoutria sachalinensis extract elicits SA-dependent defense responses in courgette genotypes against powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, J.; Wan, A.; Rahman, M.; Punja, Z. Application of seaweed extract reduces foliar fungal diseases on carrot. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology 2009, 31, 137–138. [Google Scholar]
- Esserti, S.; Smaili, A.; Rifai, L.A.; Koussa, T.; Makroum, K.; Belfaiza, M.; Kabil, E.M.; Faize, L.; Burgos, L.; Alburquerque, N.; et al. Protective effect of three brown seaweed extracts against fungal and bacterial diseases of tomato. Journal of Applied Phycology 2016, 29, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, C.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Xu, B.; Jin, Z. Activation of salicylic acid metabolism and signal transduction can enhance resistance to Fusarium wilt in banana (Musa acuminata L. AAA group, cv. Cavendish). Funct Integr Genomics 2015, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidel, A.J.; Clarke, J.D.; Antonovics, J.; Dong, X. Fitness costs of mutations affecting the systemic acquired resistance pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2004, 168, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, M. The Ecological Concept of Costs of Induced Systemic Resistance (ISR). European Journal of Plant Pathology 2001, 107, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngullie, C.R.; Tank, R.; Bhanderi, D. Effect of salicylic acid and humic acid on flowering, fruiting, yield and quality of mango (Mangifera indica L.) cv. KESAR. ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT 2014, 5, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. Biostimulant Properties of Seaweed Extracts in Plants: Implications towards Sustainable Crop Production. Plants 2021, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMondia, J.A. Actigard Increases Fungicide Efficacy Against Tobacco Blue Mold. Plant Disease 2008, 92, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosamia, T.C.; Barbadikar, K.M.; Modi, A. 9 - Genomic insights of plant endophyte interaction: prospective and impact on plant fitness. In Microbial Endophytes, Kumar, A., E.K, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: 2020; pp. 227–249.
- Busby, P.E.; Ridout, M.; Newcombe, G. Fungal endophytes: modifiers of plant disease. Plant Mol Biol 2016, 90, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, P.; Sikora, R. Endophytes: An emerging tool for biological control. Biological Control - BIOL CONTROL 2008, 46, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.J.; White Jr, J.F.; Arnold, A.E.; Redman, R.S. Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytologist 2009, 182, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, R.S.; Freeman, S.; Clifton, D.R.; Morrel, J.; Brown, G.; Rodriguez, R.J. Biochemical Analysis of Plant Protection Afforded by a Nonpathogenic Endophytic Mutant of Colletotrichum magna1. Plant Physiology 1999, 119, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilaka, A.A. Natural products from plant-associated microorganisms: distribution, structural diversity, bioactivity, and implications of their occurrence. J Nat Prod 2006, 69, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusari, S.; Hertweck, C.; Spiteller, M. Chemical Ecology of Endophytic Fungi: Origins of Secondary Metabolites. Chemistry & Biology 2012, 19, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig-Müller, J. Plants and endophytes: equal partners in secondary metabolite production? Biotechnology letters 2015, 37, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-L.; Sun, S.-Z.; Miao, C.-P.; Wu, K.; Chen, Y.-W.; Xu, L.-H.; Guan, H.-L.; Zhao, L.-X. Endophytic Trichoderma gamsii YIM PH30019: a promising biocontrol agent with hyperosmolar, mycoparasitism, and antagonistic activities of induced volatile organic compounds on root-rot pathogenic fungi of Panax notoginseng. Journal of Ginseng Research 2016, 40, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualhato, T.F.; Lopes, F.A.; Steindorff, A.S.; Brandão, R.S.; Jesuino, R.S.; Ulhoa, C.J. Mycoparasitism studies of Trichoderma species against three phytopathogenic fungi: evaluation of antagonism and hydrolytic enzyme production. Biotechnol Lett 2013, 35, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimby, P.C.; King, L.R.; Grey, W.E. Biological control as a means of enhancing the sustainability of crop/land management systems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2002, 88, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.R. Biocontrol and bioremediation: two areas of endophytic research which hold great promise. Advances in Endophytic Research 2014, 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-González, U.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Fuentes-Aragón, D.; Hernández-Castrejón, J.; Romero-Bautista, A.; Rebollar-Alviter, A. Comparative Performance of Fungicides and Biocontrol Products in the Management of Fusarium Wilt of Blackberry. Plant Disease 2022, 106, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, M.; Tronsmo, A.; Edel-Hermann, V.; Hjeljord, L.G.; Héraud, C.; Steinberg, C. Characterization of field isolates of Trichoderma antagonistic against Rhizoctonia solani. Fungal Biol 2010, 114, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, L.; Zaidi, R.K. Seed Priming Through Fungicides, Biocontrol Agents and Botanicals as Effective Method for Controlling Spot Blotch Pathogen, Bipolaris sorokiniana in Barley. Gesunde Pflanzen 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosa, R.; Cardoza, R.E.; Rubio, M.B.; Gutiérrez, S.; Monte, E. Secondary metabolism and antimicrobial metabolites of Trichoderma. In Biotechnology and biology of Trichoderma; Elsevier: 2014; pp. 125–137.
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Kumar, D. Trichoderma: a beneficial antifungal agent and insights into its mechanism of biocontrol potential. Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control 2020, 30, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Jützeler, M.; França, S.C.; Wäckers, F.; Andreasson, E.; Stenberg, J.A. Bee-Vectored Aureobasidium pullulans for Biological Control of Gray Mold in Strawberry. Phytopathology® 2022, 112, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.; Custódio, V.; Nunes, M.; Songy, A.; Rabenoelina, F.; Courteaux, B.; Clément, C.; Gomes, A.C.; Fontaine, F. Understand the potential role of Aureobasidium pullulans, a resident microorganism from grapevine, to prevent the infection caused by Diplodia seriata. Frontiers in microbiology 2018, 9, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencheqroun, S.; Bajji, M.; Sebastien, M.; Bentata, F.; Labhilili, M.; el hassan, A.; el Jaafari, S.; Jijakli, M. Biocontrol of blue mold on apple fruits by Aureobasidium pullulans (strain Ach 1-1): in vitro and in situ evidence for the possible involvement of competition for nutrients. Communications in agricultural and applied biological sciences 2006, 71, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Schena, L.; Nigro, F.; Pentimone, I.; Ligorio, A.; Ippolito, A. Control of postharvest rots of sweet cherries and table grapes with endophytic isolates of Aureobasidium pullulans. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2003, 30, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirman, B.; Erten, H. Biocontrol ability and action mechanisms of Aureobasidium pullulans GE17 and Meyerozyma guilliermondii KL3 against Penicillium digitatum DSM2750 and Penicillium expansum DSM62841 causing postharvest diseases. Yeast 2020, 37, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di francesco, A.; Ugolini, L.; Lazzeri, L.; Mari, M. Production of volatile organic compounds by Aureobasidium pullulans as a potential mechanism of action against postharvest fruit pathogens. Biological Control 2015, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoudi, D.; Tsaltas, D. The Multiple and Versatile Roles of Aureobasidium pullulans in the Vitivinicultural Sector. Fermentation 2018, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, M.; Badosa, E.; Cabrefiga, J.; Montesinos, E. Development of a strain-specific quantitative method for monitoring Pseudomonas fluorescens EPS62e, a novel biocontrol agent of fire blight. FEMS Microbiology Letters 2005, 249, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.d.C.; Govindappa, M. Mechanisms of biocontrol and plant growth-promoting activity in soil bacterial species of Bacillus and Pseudomonas: a review. Biocontrol Science and Technology 2012, 22, 855–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicedo, B.; Peñalver, R.; Asins, M.J.; López, M.M. Biological Control of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Colonization, and pAgK84 Transfer with Agrobacterium radiobacter K84 and the Tra Mutant Strain K1026. Appl Environ Microbiol 1993, 59, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, D.B.; Jensen, D.F.; Rabiey, M.; Sarrocco, S.; Shaw, M.W.; Shaw, R.H. Biological control of plant diseases – What has been achieved and what is the direction? Plant Pathology 2022, 71, 1024–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, M.; Ajouz, S.; Comby, M.; Lopez-Ferber, M.; Graillot, B.; Siegwart, M.; Nicot, P.C. Is the efficacy of biological control against plant diseases likely to be more durable than that of chemical pesticides? Front Plant Sci 2015, 6, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, M.; Ajouz, S.; Comby, M.; Lopez-Ferber, M.; Graillot, B.; Siegwart, M.; Nicot, P.C. Is the efficacy of biological control against plant diseases likely to be more durable than that of chemical pesticides? Frontiers in Plant Science 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guetsky, R.; Shtienberg, D.; Elad, Y.; Dinoor, A. Combining biocontrol agents to reduce the variability of biological control. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pedrajas, M.D.; Cañizares, M.C.; Sarmiento-Villamil, J.L.; Jacquat, A.G.; Dambolena, J.S. Mycoviruses in Biological Control: From Basic Research to Field Implementation. Phytopathology® 2019, 109, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnon, P.-L. Ecological and evolutionary implications of hyphal anastomosis in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS microbiology ecology 2014, 88, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jiang, D. New insights into mycoviruses and exploration for the biological control of crop fungal diseases. Annual Review of Phytopathology 2014, 52, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.N.; Beever, R.E.; Boine, B.; Arthur, K. Mycoviruses of filamentous fungi and their relevance to plant pathology. Molecular Plant Pathology 2009, 10, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bian, R.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Pang, T.; Salaipeth, L.; Andika, I.B.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Identification of a Novel Hypovirulence-Inducing Hypovirus From Alternaria alternata. Frontiers in microbiology 2019, 10, 1076–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, M.; He, G.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, G. A Novel Partitivirus in the Hypovirulent Isolate QT5-19 of the Plant Pathogenic Fungus Botrytis cinerea. Viruses 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttimer, C.; McAuliffe, O.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; O'Mahony, J.; Coffey, A. Bacteriophages and Bacterial Plant Diseases. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, Y.; Fieseler, L.; Klumpp, J.; Eugster, M.R.; Zurfluh, K.; Duffy, B.; Loessner, M.J. The tail-associated depolymerase of Erwinia amylovora phage L1 mediates host cell adsorption and enzymatic capsule removal, which can enhance infection by other phage. Environ Microbiol 2014, 16, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Bhowmick, T.S.; Ahern, S.J.; Young, R.; Gonzalez, C.F. Control of Pierce's Disease by Phage. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0128902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos Gomes, A.C.; da Silva, R.R.; Moreira, S.I.; Vicentini, S.N.C.; Ceresini, P.C. Biofungicides: An Eco-Friendly Approach for Plant Disease Management. In Encyclopedia of Mycology, Zaragoza, Ó., Casadevall, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2021; pp. 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Trejo-Raya, A.B.; Rodríguez-Romero, V.M.; Bautista-Baños, S.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Villanueva-Arce, R.; Durán-Páramo, E. Effective in vitro control of two phytopathogens of agricultural interest using cell-free extracts of pseudomonas fluorescens and chitosan. Molecules 2021, 26, 6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Kaur, A.; Sharma, V.; Manhas, R.K. Purification and Characterization of a New Antifungal Compound 10-(2, 2-dimethyl-cyclohexyl)-6, 9-dihydroxy-4, 9-dimethyl-dec-2-enoic Acid Methyl Ester from Streptomyces hydrogenans Strain DH16. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 7, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, K.J.J.; Campos, H.L.M.; Olivera, C.C.; Nakayo, J.L.J.; Flores, J.W.V. Biofungicide for the Control of Botrytis Cinerea and Fusarium Oxysporum: a Laboratory Study. Chemical Engineering Transactions 2021, 87, 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, E.; Zida, E.; Torp, J.; Lund, O. Yucca schidigera extract: a potential biofungicide against seedborne pathogens of sorghum. Plant Pathology 2012, 61, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraka, M.; Fatma; Shaban, M. ; H, A. Efficiency of Some Plant Extracts, Natural Oils, Biofungicides and Fungicides Against Root Rot of Date Palm. J. Biol. Chem. Environ. Sci. 2011, 6, 405–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Han, Z.; Yao, L. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial efficacy of essential oils and individual compounds against Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2013, 115, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Géza, N.; Hochbaum, T.; Sarosi, S.; Ladanyi, M. In vitro and in planta activity of some essential oils against Venturia inaequalis (Cooke) G. Winter. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 2014, 42, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Tarafdar, A.; Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishanan, S. Biological Control as a Tool for Eco-friendly Management of Plant Pathogens. 2017; pp. 153–188.
- Al-Samarrai, G.; Singh, H.; Syarhabil, M. Evaluating eco-friendly botanicals (natural plant extracts) as alternatives to synthetic fungicides. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2012, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Verdel, A.; Jia, S.; Gerber, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Gygi, S.; Grewal, S.I.; Moazed, D. RNAi-mediated targeting of heterochromatin by the RITS complex. Science 2004, 303, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A.J.; MacRae, I.J. The RNA-induced silencing complex: a versatile gene-silencing machine. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 17897–17901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yan, X.; Gu, C.; Yuan, X. Biogenesis, Trafficking, and Function of Small RNAs in Plants. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 825477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yi, R.; Cullen, B.R. MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 9779–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Dolz, L.; Spada, M.; Daròs, J.A.; Carbonell, A. Fine-tune control of targeted RNAi efficacy by plant artificial small RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 6234–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugas, D.V.; Bartel, B. Sucrose induction of Arabidopsis miR398 represses two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutases. Plant Mol Biol 2008, 67, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Axtell, M.J. Analysis of complementarity requirements for plant microRNA targeting using a Nicotiana benthamiana quantitative transient assay. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbard, D.J.; Gordon, K.H.; Buck, A.H.; Jiggins, F.M. The evolution of RNAi as a defence against viruses and transposable elements. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2009, 364, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.J.W.; Lewsey, M.G.; Patel, K.; Westwood, J.; Heimstädt, S.; Carr, J.P.; Baulcombe, D.C. An Antiviral Defense Role of AGO2 in Plants. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Biedenkopf, D.; Furch, A.; Weber, L.; Rossbach, O.; Abdellatef, E.; Linicus, L.; Johannsmeier, J.; Jelonek, L.; Goesmann, A.; et al. An RNAi-Based Control of Fusarium graminearum Infections Through Spraying of Long dsRNAs Involves a Plant Passage and Is Controlled by the Fungal Silencing Machinery. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12, e1005901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.C.; Dean, R.A. Host-induced gene silencing: a tool for understanding fungal host interaction and for developing novel disease control strategies. Mol Plant Pathol 2012, 13, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, V.M.; Kumar, A. Nematode resistance in plants: the battle underground. Trends Genet 2006, 22, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Allen, R.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J.; Hussey, R.S. Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 14302–14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowara, D.; Gay, A.; Lacomme, C.; Shaw, J.; Ridout, C.; Douchkov, D.; Hensel, G.; Kumlehn, J.; Schweizer, P. HIGS: Host-Induced Gene Silencing in the Obligate Biotrophic Fungal Pathogen Blumeria graminis Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3130–3141. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Thomma, B. Host-induced gene silencing compromises Verticillium wilt in tomato and Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Pathol 2018, 19, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Xiong, H.; Xu, F.X.; Shi, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Cao, X.L.; et al. Host-Induced Gene Silencing of MoAP1 Confers Broad-Spectrum Resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Weiberg, A.; Lin, F.M.; Thomma, B.P.; Huang, H.D.; Jin, H. Bidirectional cross-kingdom RNAi and fungal uptake of external RNAs confer plant protection. Nat Plants 2016, 2, 16151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, A.G.; Wytinck, N.; Walker, P.L.; Girard, I.J.; Rashid, K.Y.; de Kievit, T.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Whyard, S.; Belmonte, M.F. Identification and application of exogenous dsRNA confers plant protection against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedenkopf, D.; Will, T.; Knauer, T.; Jelonek, L.; Furch, A.C.U.; Busche, T.; Koch, A. Systemic spreading of exogenous applied RNA biopesticides in the crop plant Hordeum vulgare. ExRNA 2020, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfle, L.; Biedenkopf, D.; Werner, B.T.; Shrestha, A.; Jelonek, L.; Koch, A. Study on the efficiency of dsRNAs with increasing length in RNA-based silencing of the Fusarium CYP51 genes. RNA Biol 2020, 17, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitter, N.; Worrall, E.A.; Robinson, K.E.; Li, P.; Jain, R.G.; Taochy, C.; Fletcher, S.J.; Carroll, B.J.; Lu, G.Q.; Xu, Z.P. Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat Plants 2017, 3, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wei, J.; Huff Hartz, K.E.; Lydy, M.J.; Moon, T.S.; Sander, M.; Parker, K.M. Analysis of RNA Interference (RNAi) Biopesticides: Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA) Extraction from Agricultural Soils and Quantification by RT-qPCR. Environ Sci Technol 2020, 54, 4893–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S.; Schena, L. Spatial and compositional variation in the fungal communities of organic and conventionally grown apple fruit at the consumer point-of-purchase. Hortic Res 2016, 3, 16047–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Bartz, S.R.; Schelter, J.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Burchard, J.; Mao, M.; Li, B.; Cavet, G.; Linsley, P.S. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat Biotechnol 2003, 21, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, J.; Meister, G. siRNA Specificity: RNAi Mechanisms and Strategies to Reduce Off-Target Effects. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 526455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, G.; Noviss, K.; Haynes, I. Field evaluation of systemic inducing resistance chemicals at different growth stages for the control of apple (Venturia inaequalis) and pear (Venturia pirina) scab. Crop Protection 2009, 28, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaker, M. Natural Plant Products as Eco-friendly Fungicides for Plant Diseases Control- A Review. The Agriculturists 2016, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balba, H. Review of strobilurin fungicide chemicals. Journal of environmental science and health. Part. B, Pesticides, food contaminants, and agricultural wastes 2007, 42, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveau, R.; Fontaine, J.; Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, A. Essential Oils as Potential Alternative Biocontrol Products against Plant Pathogens and Weeds: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.D.; Cantó-Tejero, M.; Pascual-Villalobos, M.J. New Insights into biopesticides: Solid and liquid formulations of essential oils and derivatives. Frontiers in Agronomy 2021, 3, 763530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, I.; Vilardell, P.; Bugiani, R.; Gherardi, I.; Montesinos, E. Evaluation of BSPcast Disease Warning System in Reduced Fungicide Use Programs for Management of Brown Spot of Pear. Plant Disease 2000, 84, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holb, I.J. Timing of first and final sprays against apple scab combined with leaf removal and pruning in organic apple production. Crop Protection 2008, 27, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kraker, J.; van den Ende, J.E.; Rossing, W.A.H. Control strategies with reduced fungicide input for Botrytis leaf blight in lily—a simulation analysis. Crop Protection 2005, 24, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertely, J.C.; MacKenzie, S.J.; Legard, D.E. Timing of Fungicide Applications for Botrytis cinerea Based on Development Stage of Strawberry Flowers and Fruit. Plant Disease 2002, 86, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, L.; Pennypacker, S.; MacNab, A. FAST, a forecast system for Alternaria solani on tomato. Phytopathology 1978, 68, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, N.; Mamo, B.E.; Subbarao, K.V.; Koike, S.T.; Fox, A.; Anchieta, A.; Klosterman, S.J. Measurements of Aerial Spore Load by qPCR Facilitates Lettuce Downy Mildew Risk Advisement. Plant Disease 2020, 104, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, L.D.; Keune, J.A.; Neill, T.M.; Turechek, W.W.; Grove, G.G.; Mahaffee, W.F. Development of a grower-conducted inoculum detection assay for management of grape powdery mildew. Plant Pathology 2016, 65, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, K.R.; Pushparajah, I.P.S.; Timudo, O.E.; Ah Chee, A.; Scheper, R.W.A.; Shaw, P.W.; Spiers, T.M.; Taylor, J.T.; Wallis, D.R.; Wood, P.N. Infection criteria, inoculum sources and splash dispersal pattern of Colletotrichum acutatum causing bitter rot of apple in New Zealand. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2018, 152, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ons, L.; Bylemans, D.; Thevissen, K.; Cammue, B.P.A. Combining Biocontrol Agents with Chemical Fungicides for Integrated Plant Fungal Disease Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




