Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
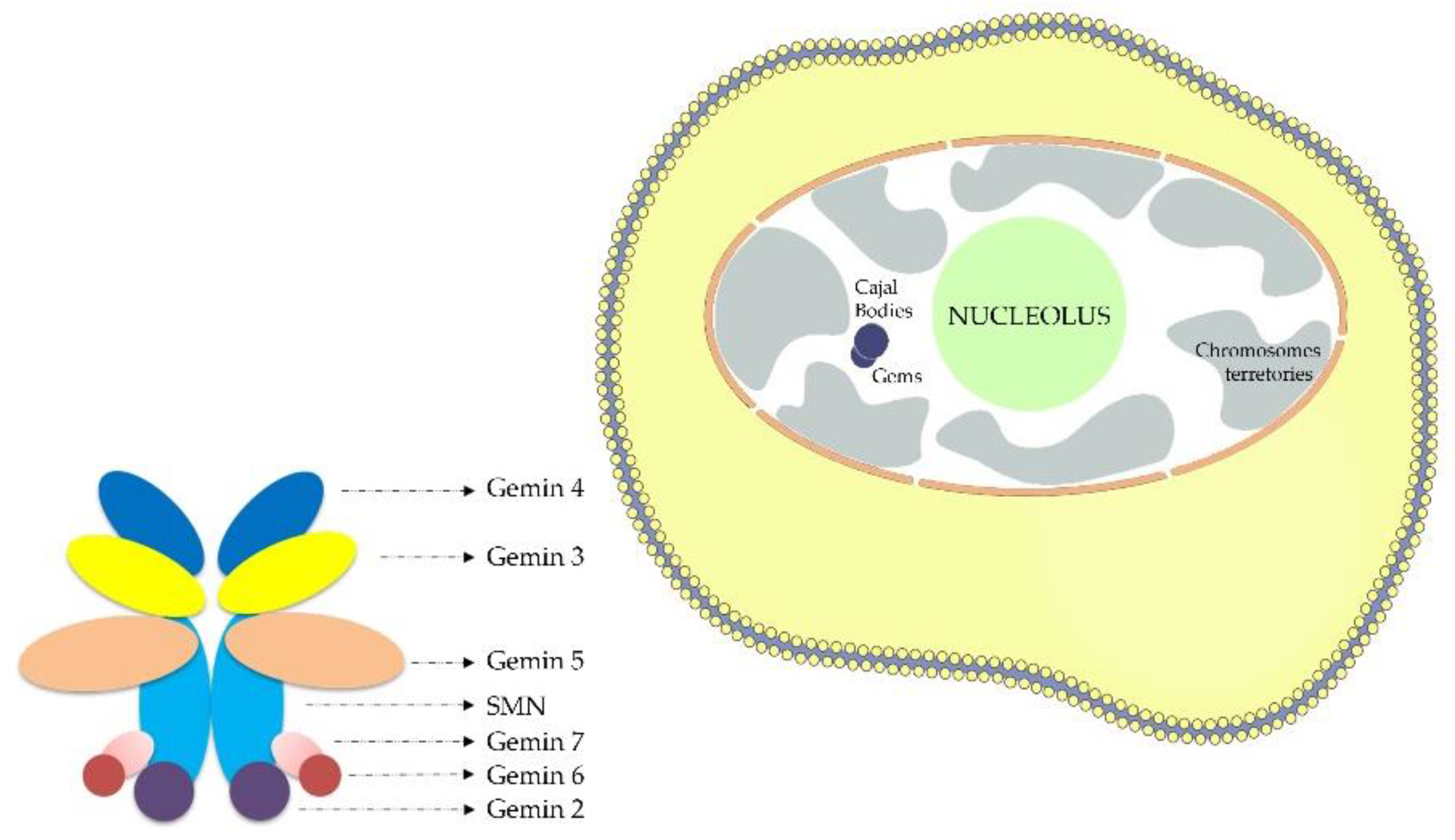
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials:
2.2. Methods:
2.2.1. Fibroblast transfection:
2.2.2. Immunocytochemical staining:
- Fixation, permeabilization and blocking:
- Antibody Incubation:
- Mounting and Imaging:
2.2.3. RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis:
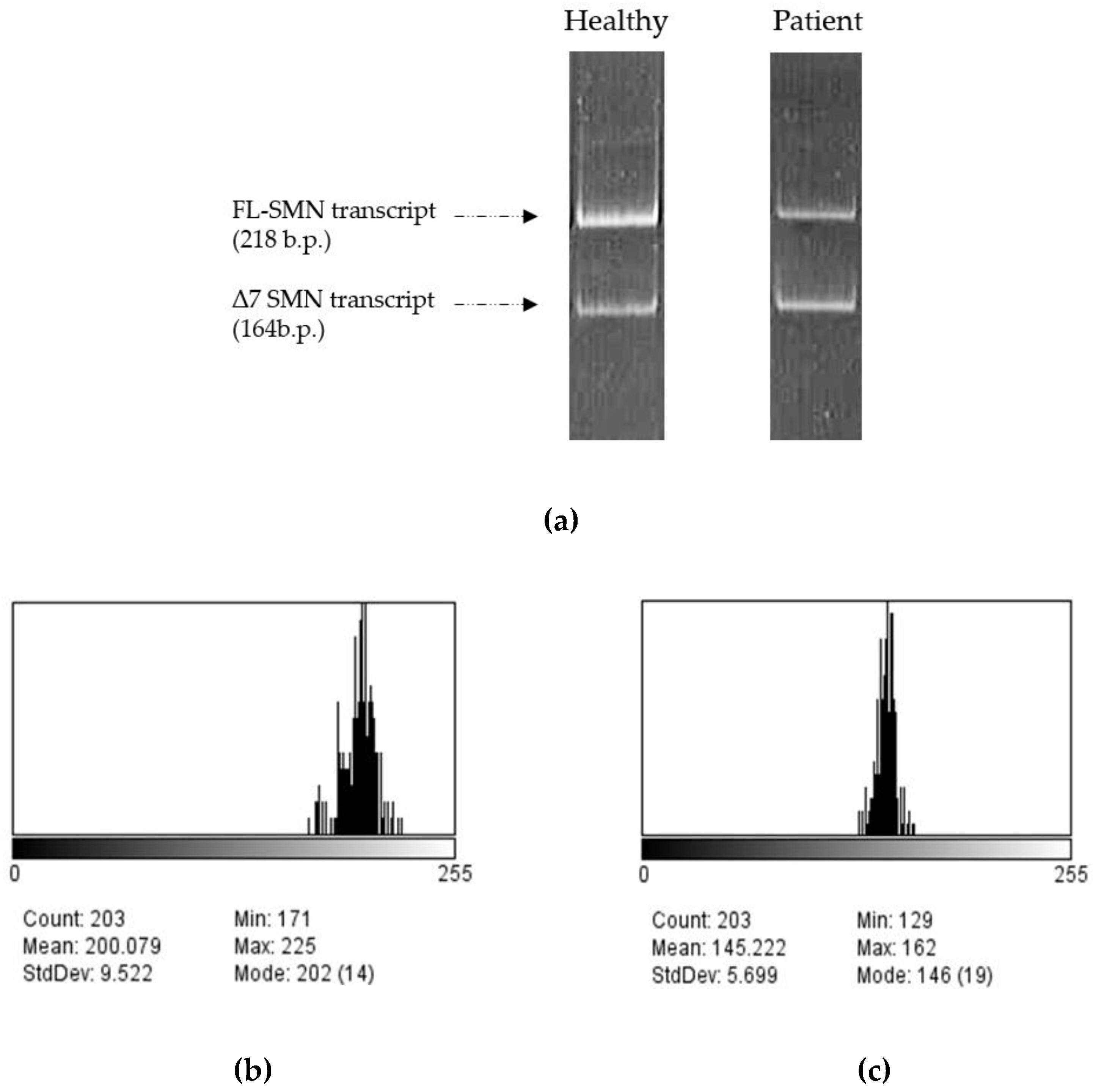
2.2.4. Semiquantitative RT-PCR:
2.2.5. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis:
2.2.6. Statistical analysis:
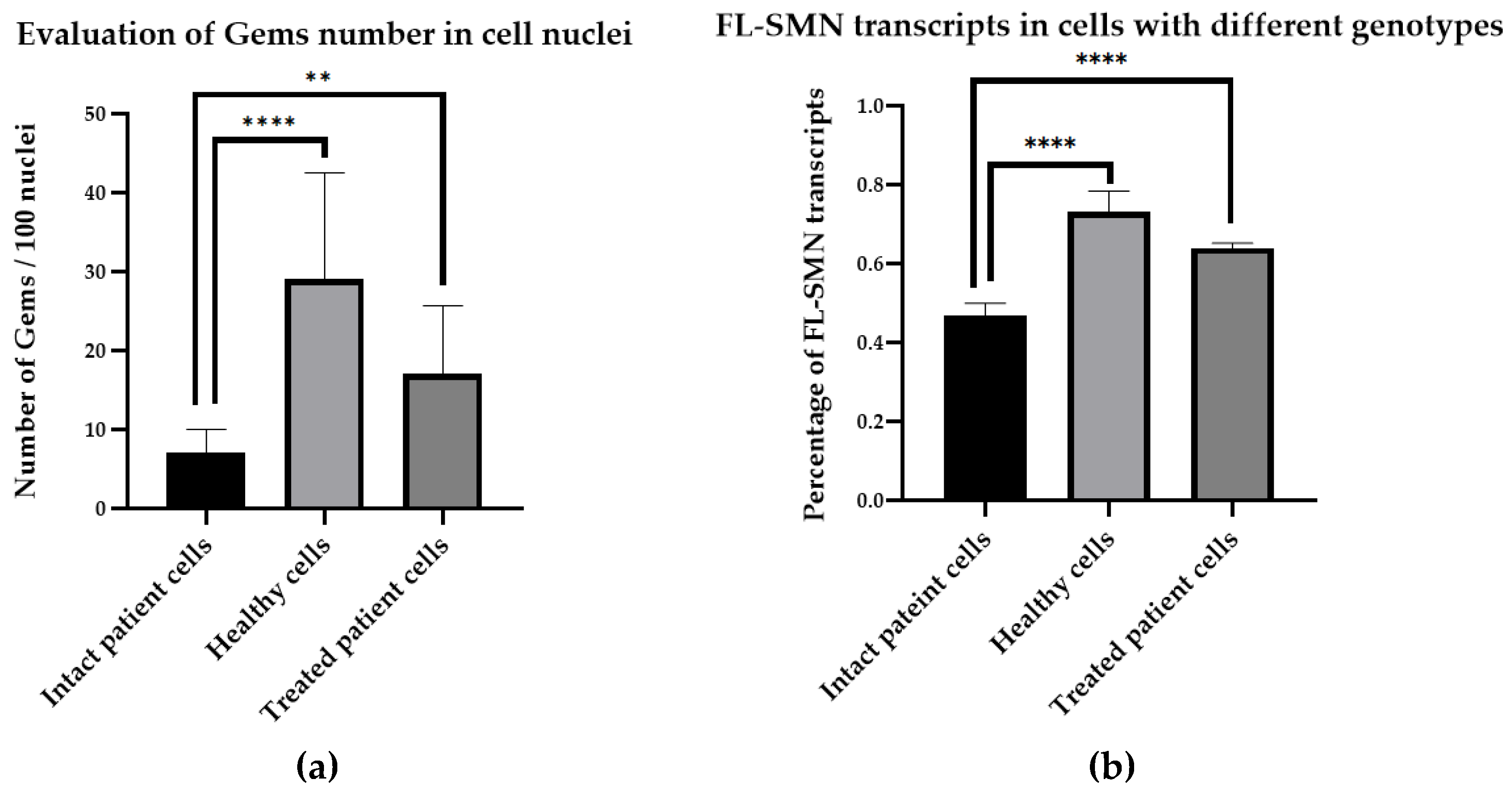
3. Results
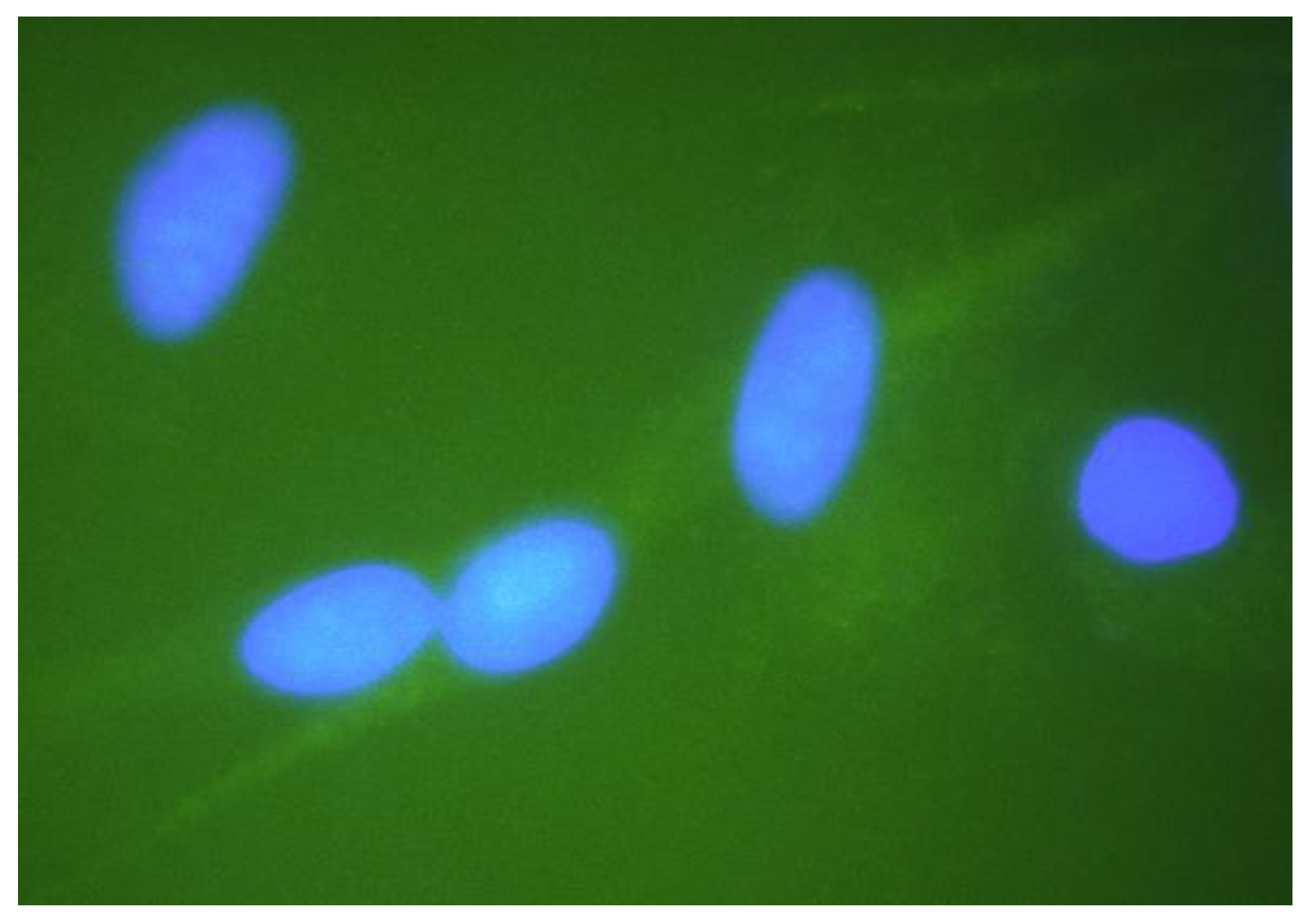
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Amico, A.; Mercuri, E.; Tiziano, F.D.; Bertini, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2011, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, B.; Brichta, L.; Hahnen, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: From Gene to Therapy. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2006, 13, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Sumner, C.J.; Muntoni, F.; Darras, B.T.; Finkel, R.S. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2022, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Bürglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Benichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, P.; Zeviani, M. Identification and Characterization of a Spinal Muscular Atrophy-Determining Gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellizzoni, L.; Yong, J.; Dreyfuss, G. Essential Role for the SMN Complex in the Specificity of snRNP Assembly. Science 2002, 298, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monani, U.R.; Lorson, C.L.; Parsons, D.W.; Prior, T.W.; Androphy, E.J.; Burghes, A.H.; McPherson, J.D. A Single Nucleotide Difference That Alters Splicing Patterns Distinguishes the SMA Gene SMN1 from the Copy Gene SMN2. Hum Mol Genet 1999, 8, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchbach, M.E.R. Genomic Variability in the Survival Motor Neuron Genes (SMN1 and SMN2): Implications for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Phenotype and Therapeutics Development. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B.; Karakaya, M.; Kye, M.J.; Mendoza-Ferreira, N. Twenty-Five Years of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Research: From Phenotype to Genotype to Therapy, and What Comes Next. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2020, 21, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.K.; Ferner, R.E. Biomarkers-A General Review. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 2017, 76, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, M.G.; Rich, K.A.; Kolb, S.J. Update on Biomarkers in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Biomark Insights 2021, 16, 11772719211035643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maretina, M.; Egorova, A.; Lanko, K.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Evaluation of Mean Percentage of Full-Length SMN Transcripts as a Molecular Biomarker of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Dreyfuss, G. A Novel Nuclear Structure Containing the Survival of Motor Neurons Protein. EMBO J 1996, 15, 3555–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, D.; Neugebauer, K.M. The Cajal Body: A Meeting Place for Spliceosomal snRNPs in the Nuclear Maze. Chromosoma 2006, 115, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciottolo, R.; Ciantar, J.; Lanfranco, M.; Borg, R.M.; Vassallo, N.; Bordonné, R.; Cauchi, R.J. SMN Complex Member Gemin3 Self-Interacts and Has a Functional Relationship with ALS-Linked Proteins TDP-43, FUS and Sod1. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 18666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Chiang, P.-M.; Price, D.L.; Wong, P.C. Altered Distributions of Gemini of Coiled Bodies and Mitochondria in Motor Neurons of TDP-43 Transgenic Mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 16325–16330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coovert, D.D.; Le, T.T.; McAndrew, P.E.; Strasswimmer, J.; Crawford, T.O.; Mendell, J.R.; Coulson, S.E.; Androphy, E.J.; Prior, T.W.; Burghes, A.H. The Survival Motor Neuron Protein in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 1997, 6, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Burlet, P.; Liu, Q.; Bertrandy, S.; Clermont, O.; Munnich, A.; Dreyfuss, G.; Melki, J. Correlation between Severity and SMN Protein Level in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nat Genet 1997, 16, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, A.D.; Yu, J.; Rose, F.F.; Mattis, V.B.; Lorson, C.L.; Thomson, J.A.; Svendsen, C.N. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from a Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patient. Nature 2009, 457, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrizi, A.L.; Tiziano, F.; Zappata, S.; Donati, M.A.; Neri, G.; Brahe, C. SMN Protein Analysis in Fibroblast, Amniocyte and CVS Cultures from Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patients and Its Relevance for Diagnosis. Eur J Hum Genet 1999, 7, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassi, C.; Angelozzi, C.; Tiziano, F.D.; Vitali, T.; De Vincenzi, E.; Boninsegna, A.; Villanova, M.; Bertini, E.; Pini, A.; Neri, G.; et al. Phenylbutyrate Increases SMN Expression in Vitro: Relevance for Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Eur J Hum Genet 2004, 12, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstencroft, E.C.; Mattis, V.; Bajer, A.A.; Young, P.J.; Lorson, C.L. A Non-Sequence-Specific Requirement for SMN Protein Activity: The Role of Aminoglycosides in Inducing Elevated SMN Protein Levels. Hum Mol Genet 2005, 14, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riessland, M.; Brichta, L.; Hahnen, E.; Wirth, B. The Benzamide M344, a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Significantly Increases SMN2 RNA/Protein Levels in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Cells. Hum Genet 2006, 120, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattis, V.B.; Rai, R.; Wang, J.; Chang, C.-W.T.; Coady, T.; Lorson, C.L. Novel Aminoglycosides Increase SMN Levels in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Fibroblasts. Hum Genet 2006, 120, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumpkin, C.; Harris, A.; Connell, A.; Kirk, R.; Whiting, J.; Saieva, L.; Pellizzoni, L.; Burghes, A.; Butchbach, M. Evaluation of the Orally Bioavailable 4-Phenylbutyrate-Tethered Trichostatin A Analogue AR42 in Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Scientific Reports 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coady, T.H.; Baughan, T.D.; Shababi, M.; Passini, M.A.; Lorson, C.L. Development of a Single Vector System That Enhances Trans-Splicing of SMN2 Transcripts. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’eva, E.; Valetdinova, K.; Ustyantseva, E.; Shevchenko, A.; Medvedev, S.; Mazurok, N.; Maretina, M.; Kuranova, M.; Kiselev, A.; Baranov, V.; et al. Neural Differentiation of Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Patients with a Hereditary Form of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Genes Cells 2016, 11, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.N.; Shishimorova, M.; Cao, L.C.; Gangwani, L.; Singh, R.N. A Short Antisense Oligonucleotide Masking a Unique Intronic Motif Prevents Skipping of a Critical Exon in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. RNA Biol 2009, 6, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, S.; Marcuzzo, S.; Malacarne, C.; Giagnorio, E.; Masson, R.; Zanin, R.; Arnoldi, M.T.; Andreetta, F.; Simoncini, O.; Venerando, A.; et al. Circulating MyomiRs as Potential Biomarkers to Monitor Response to Nusinersen in Pediatric SMA Patients. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneri, M.; Abati, E.; Gagliardi, D.; Faravelli, I.; Parente, V.; Ratti, A.; Verde, F.; Ticozzi, N.; Comi, G.P.; Ottoboni, L.; et al. Identification of Novel Biomarkers of Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Therapeutic Response by Proteomic and Metabolomic Profiling of Human Biological Fluid Samples. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glascock, J.; Darras, B.T.; Crawford, T.O.; Sumner, C.J.; Kolb, S.J.; DiDonato, C.; Elsheikh, B.; Howell, K.; Farwell, W.; Valente, M.; et al. Identifying Biomarkers of Spinal Muscular Atrophy for Further Development. J Neuromuscul Dis 2023, 10, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




