Submitted:
20 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Establishment and Solution of Seepage Model
- (1)
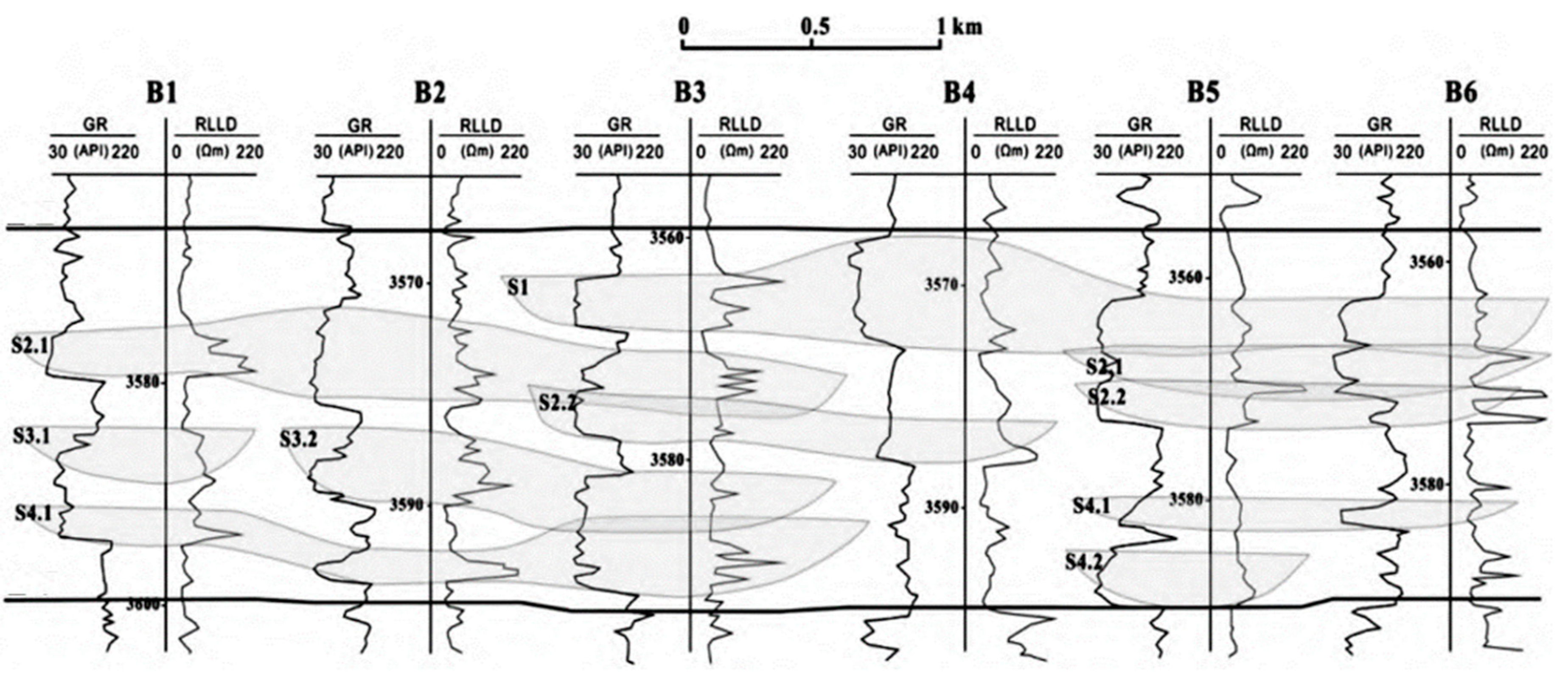
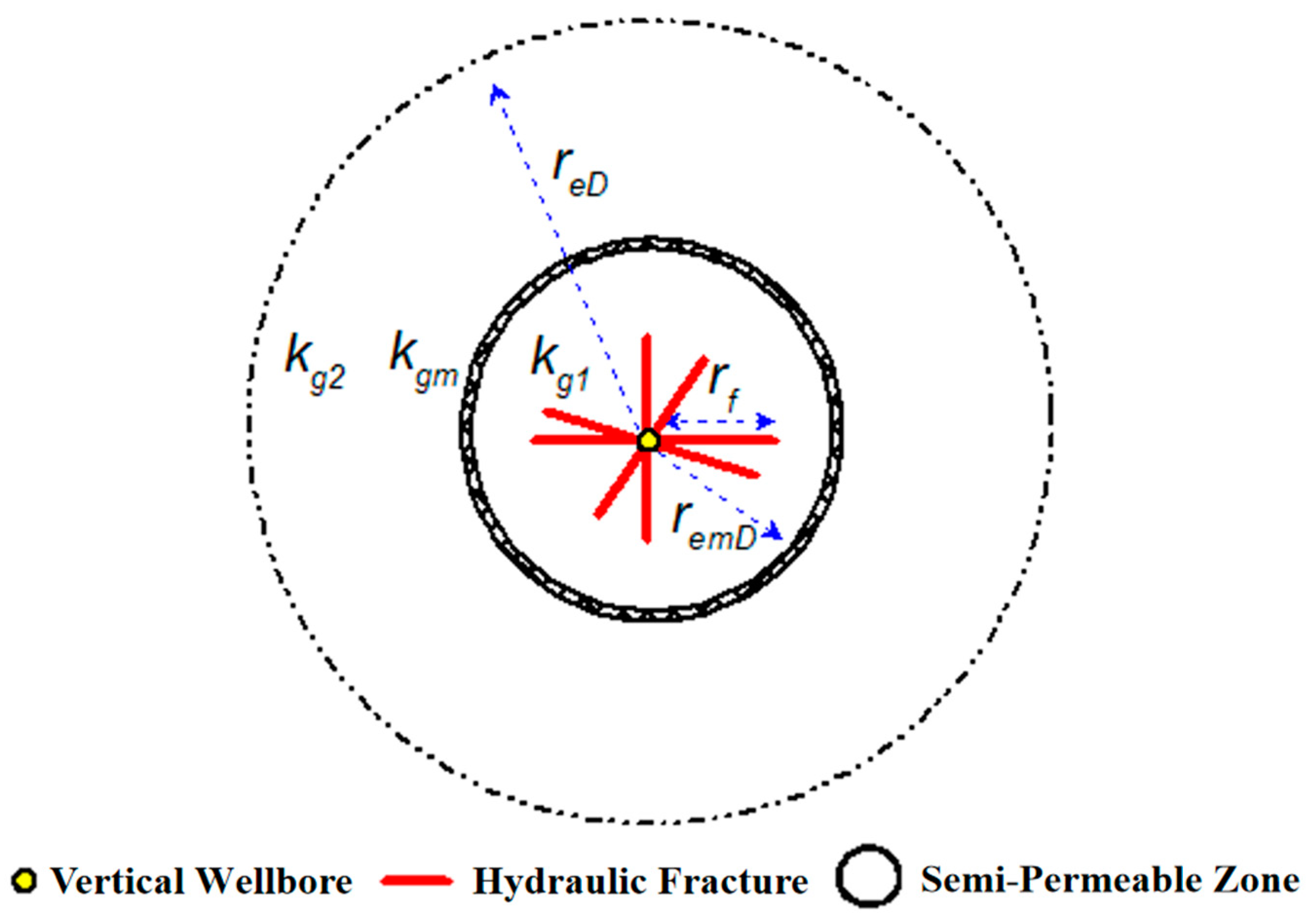
- The tight sandstone gas reservoir presents a circular distribution on the whole. The initial pressure in the whole area is pi, the thickness of the tight sandstone gas reservoir is h, and the porosity is φ;
- (2)
- The whole tight sandstone gas reservoir is homogeneous isotropy, in which the initial permeability of the inner zone is kg1, the permeability of the semi-permeable zone is kgm, and the initial permeability of the outer zone is kg2;
- (3)
- It is assumed that any hydraulic fracture is distributed in the inner zone and each hydraulic fracture completely opens the reservoir vertically, and that the fracture is distributed in the inner zone laterally without passing through the semi-permeable zone. The half-length of the i fracture is marked as rfi, and the Angle between the i fracture and the x-axis is θi;
- (4)
- The hydraulic fracture is a finite conductivity fracture, and the flow in each fracture is independent of each other. The tip of the fracture can be regarded as an impermeable boundary, so the flow of tight sandstone gas into the wellbore through the tip of the fracture is negligible;
- (5)
- Flow patterns throughout the reservoir and in fractures are Darcy's law. Constant production in vertical Wells (qsc) is maintained.
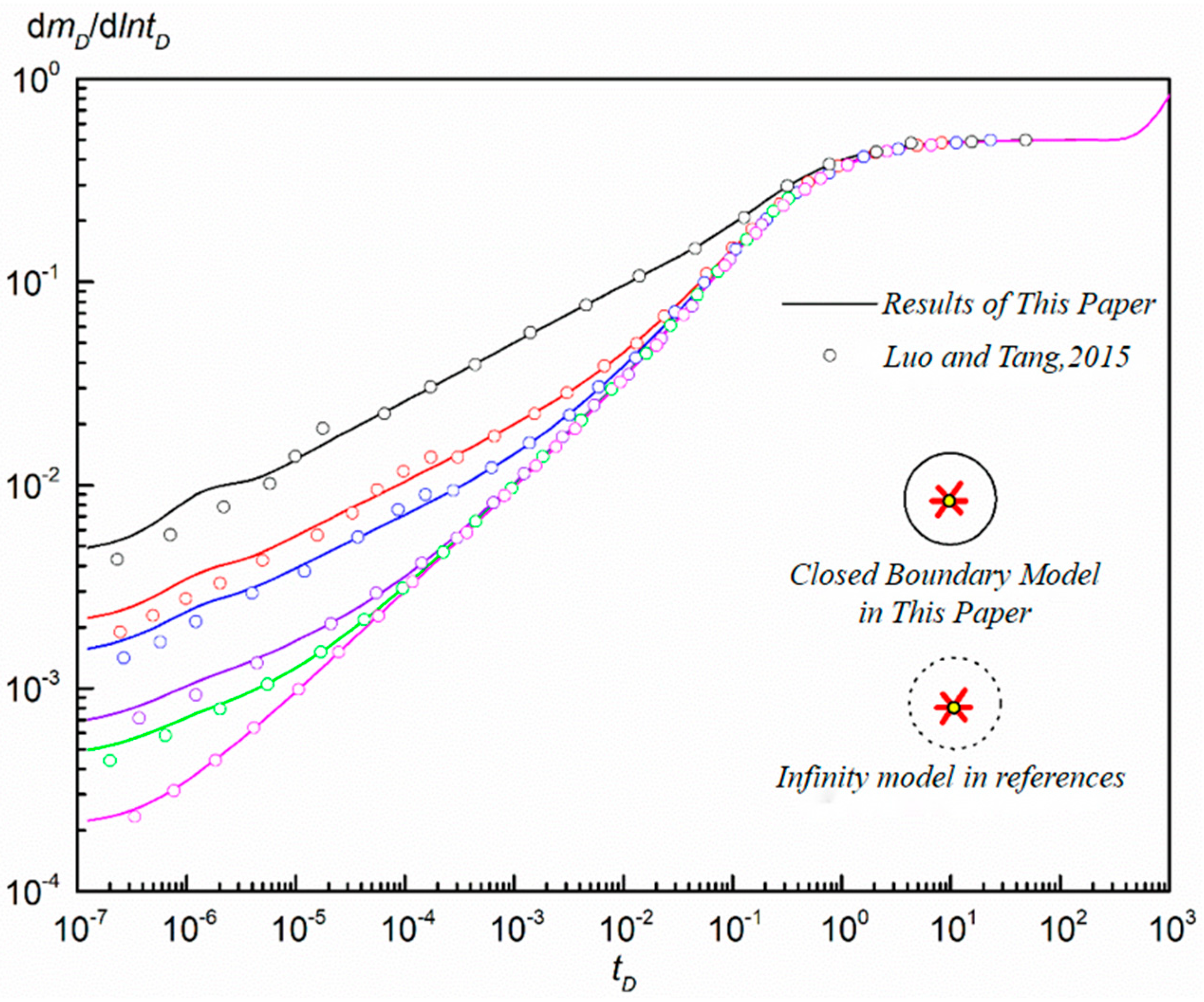
3. Model Verification and Analysis
4. Analysis of Pressure Response Curve and Influencing Factors
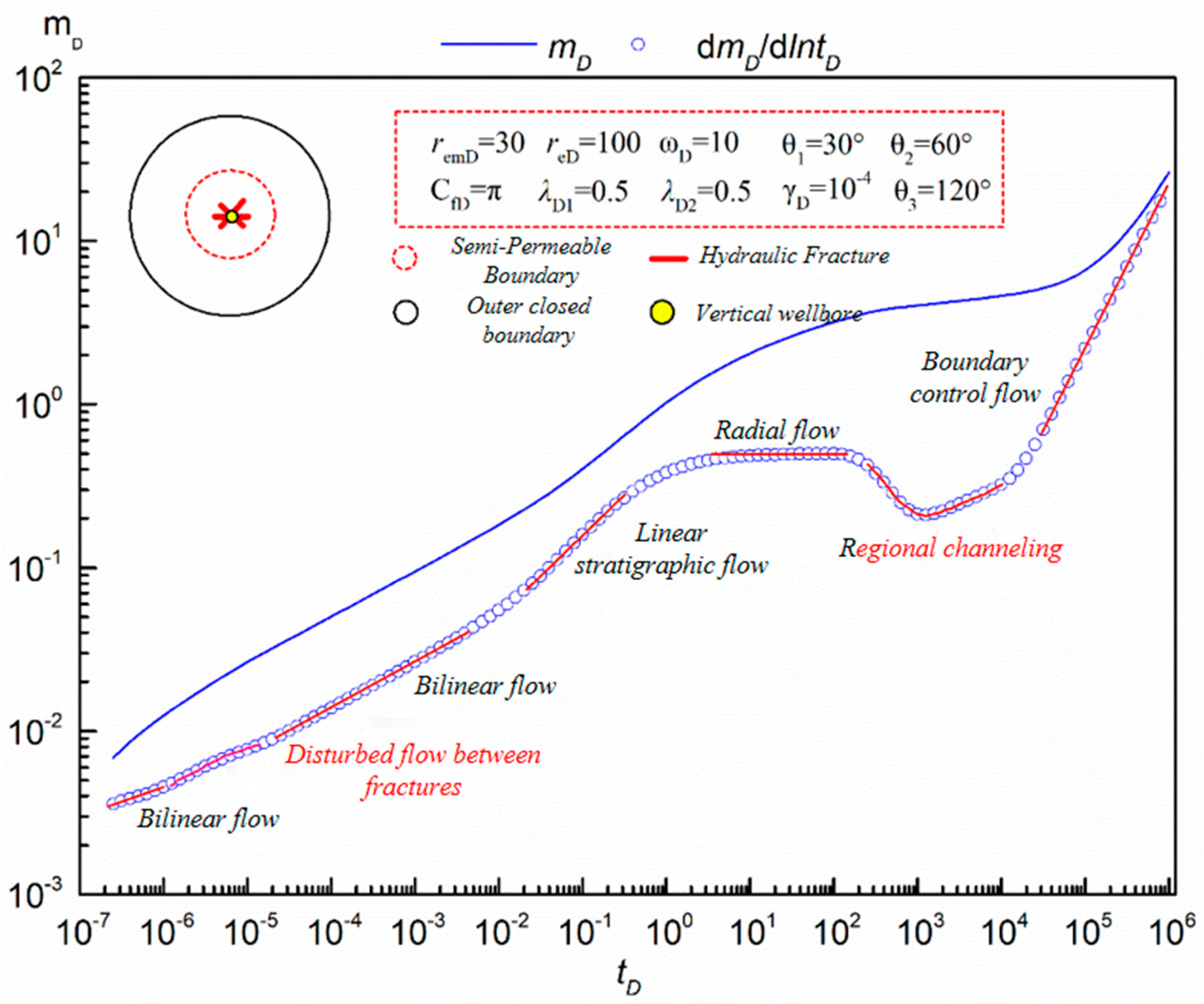
4.1. Pressure Response Characteristics
4.2. Influencing Factors of Pressure Response Curve of Multi-Fracture Vertical Well
- (1)
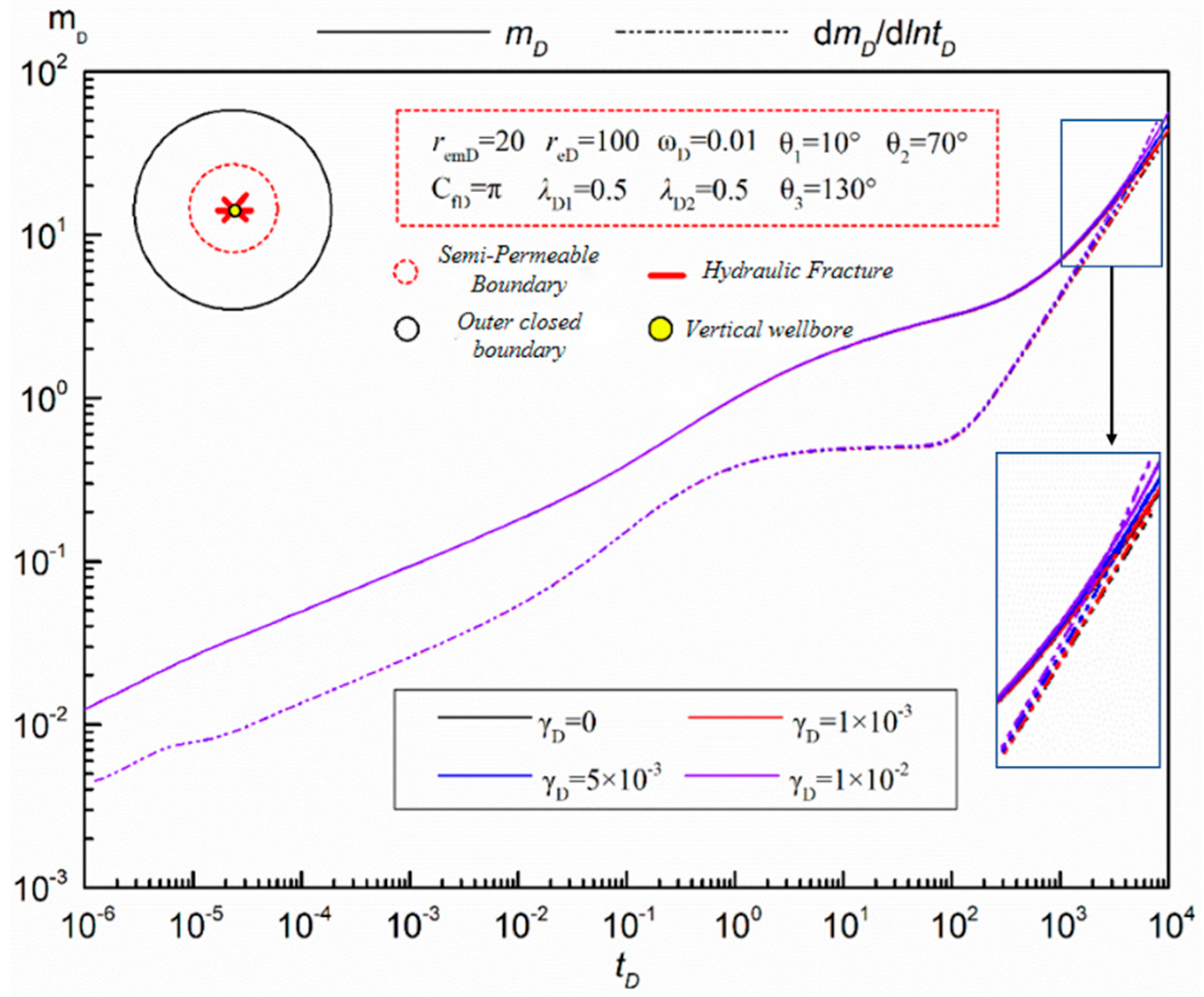
- Pressure sensitivity
- (2)
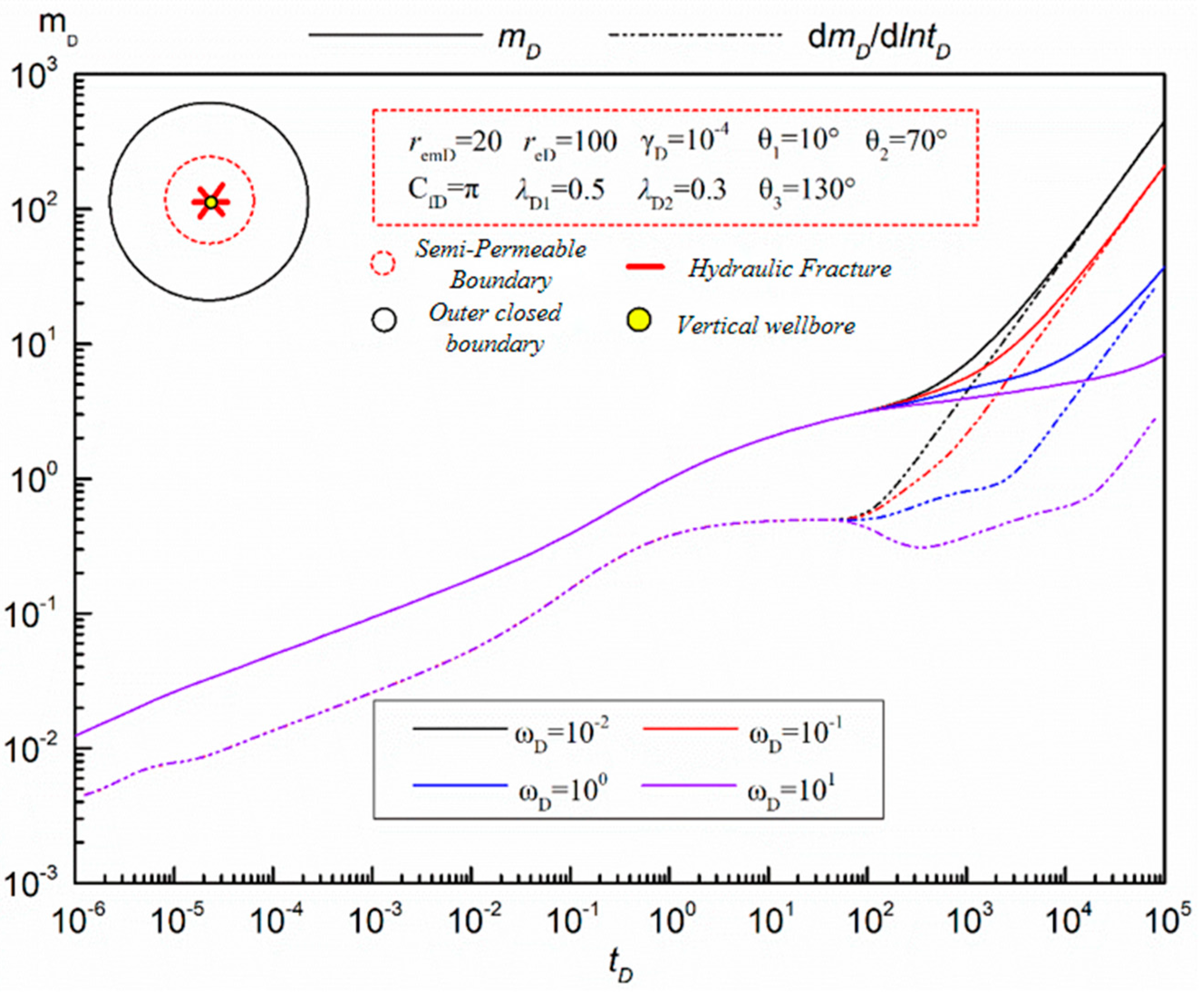
- Storage Capacity Ratio Of Inner And Outer Areas
- (3)
- Permeability Coefficient
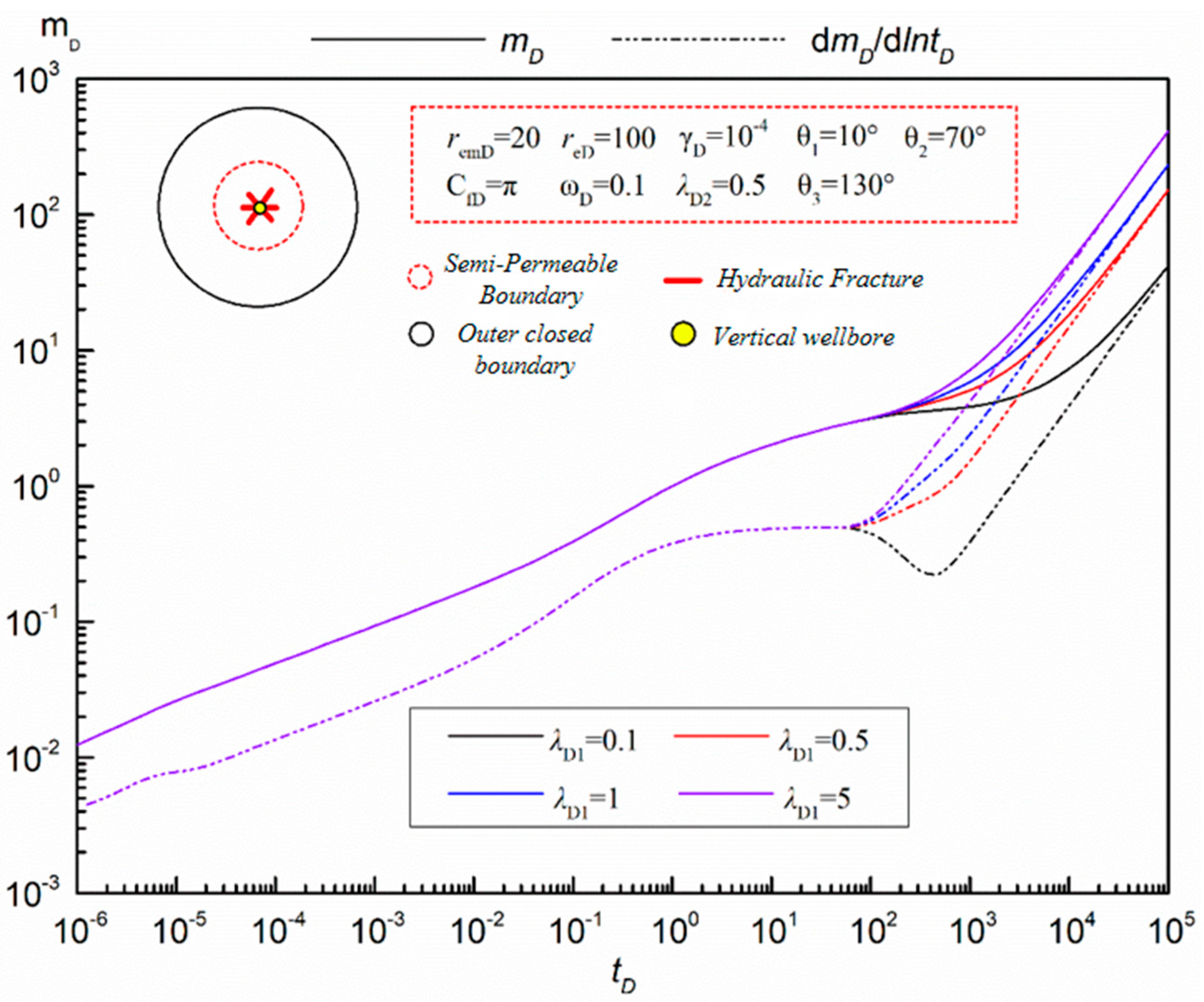
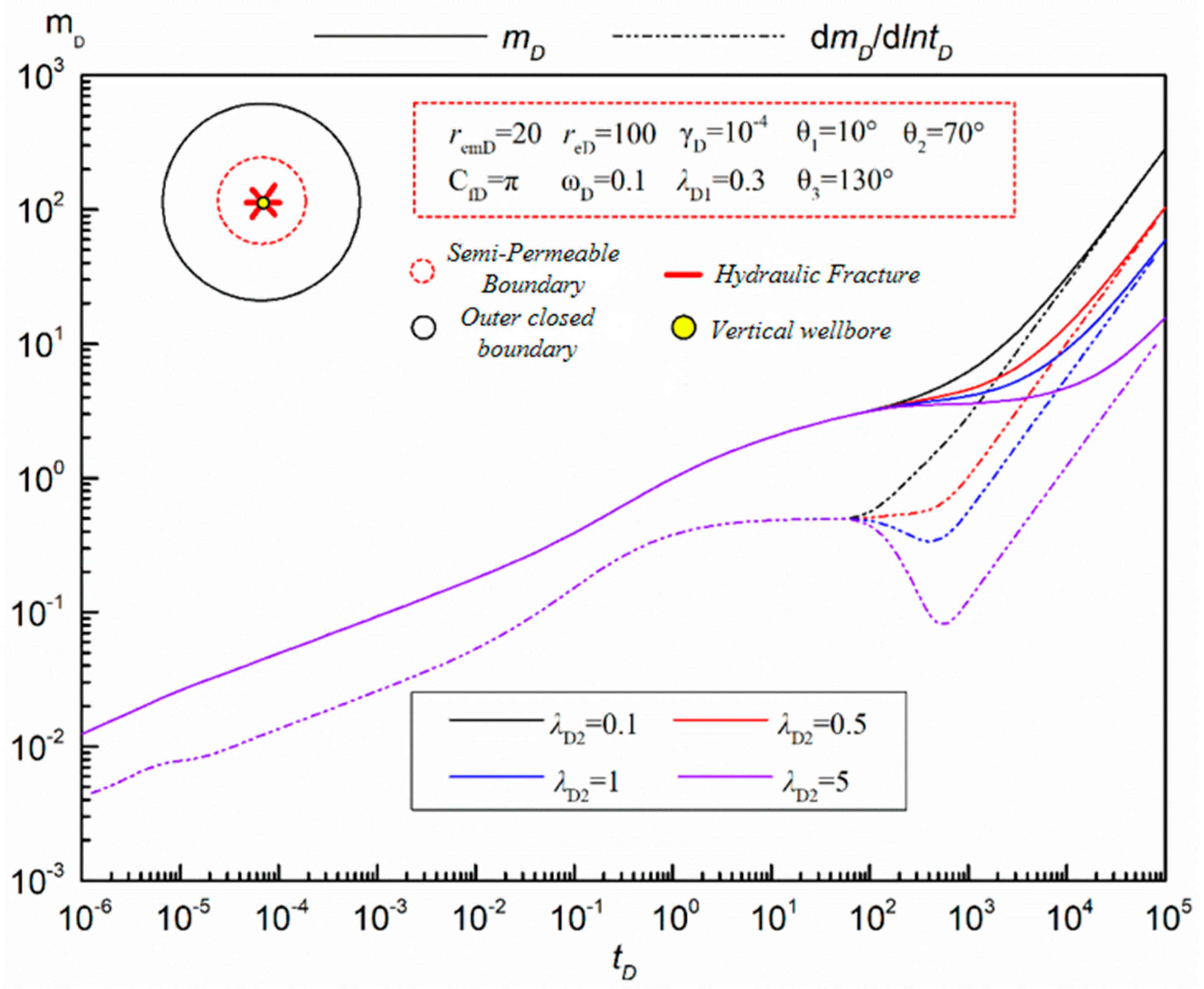
- (4)
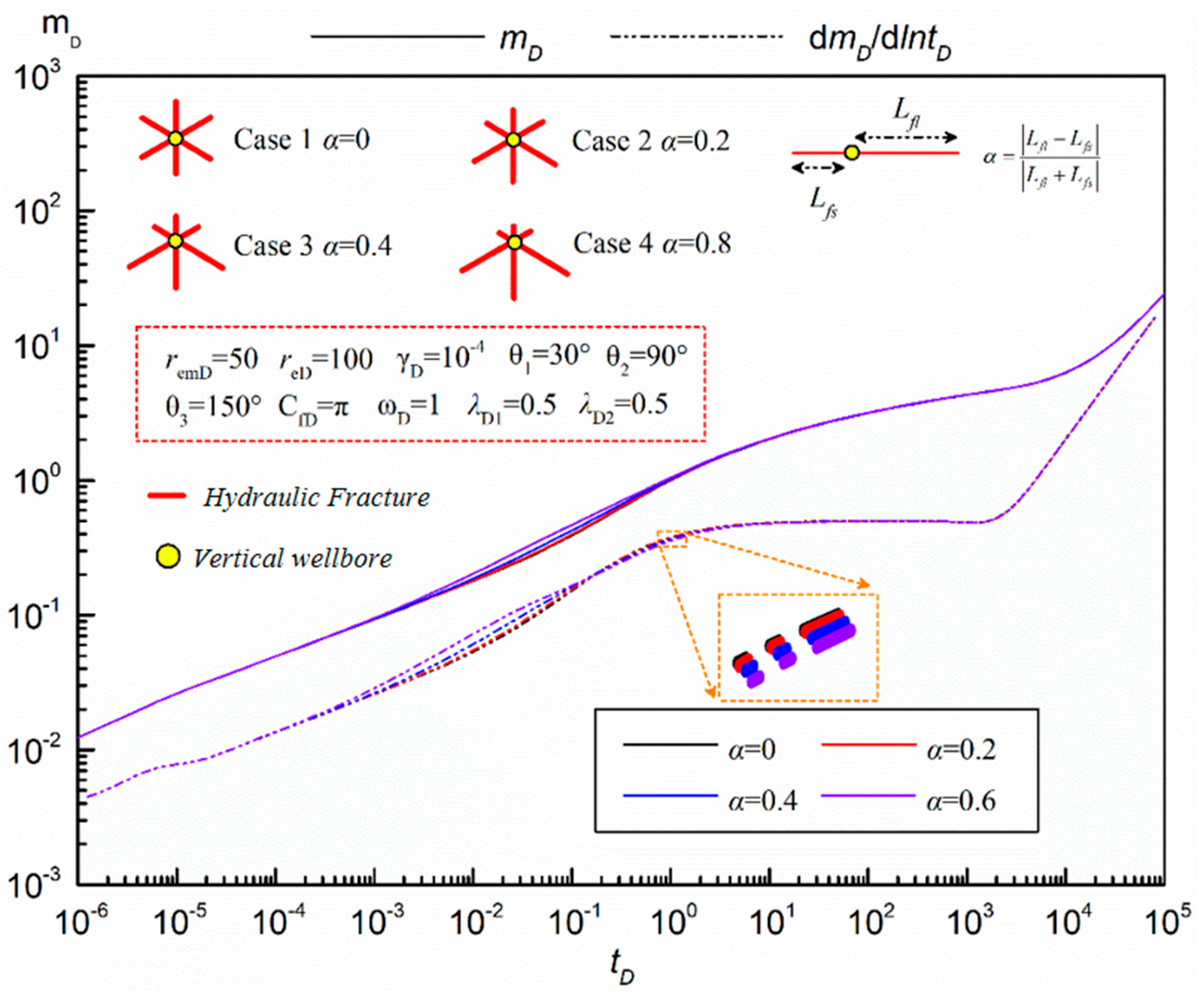
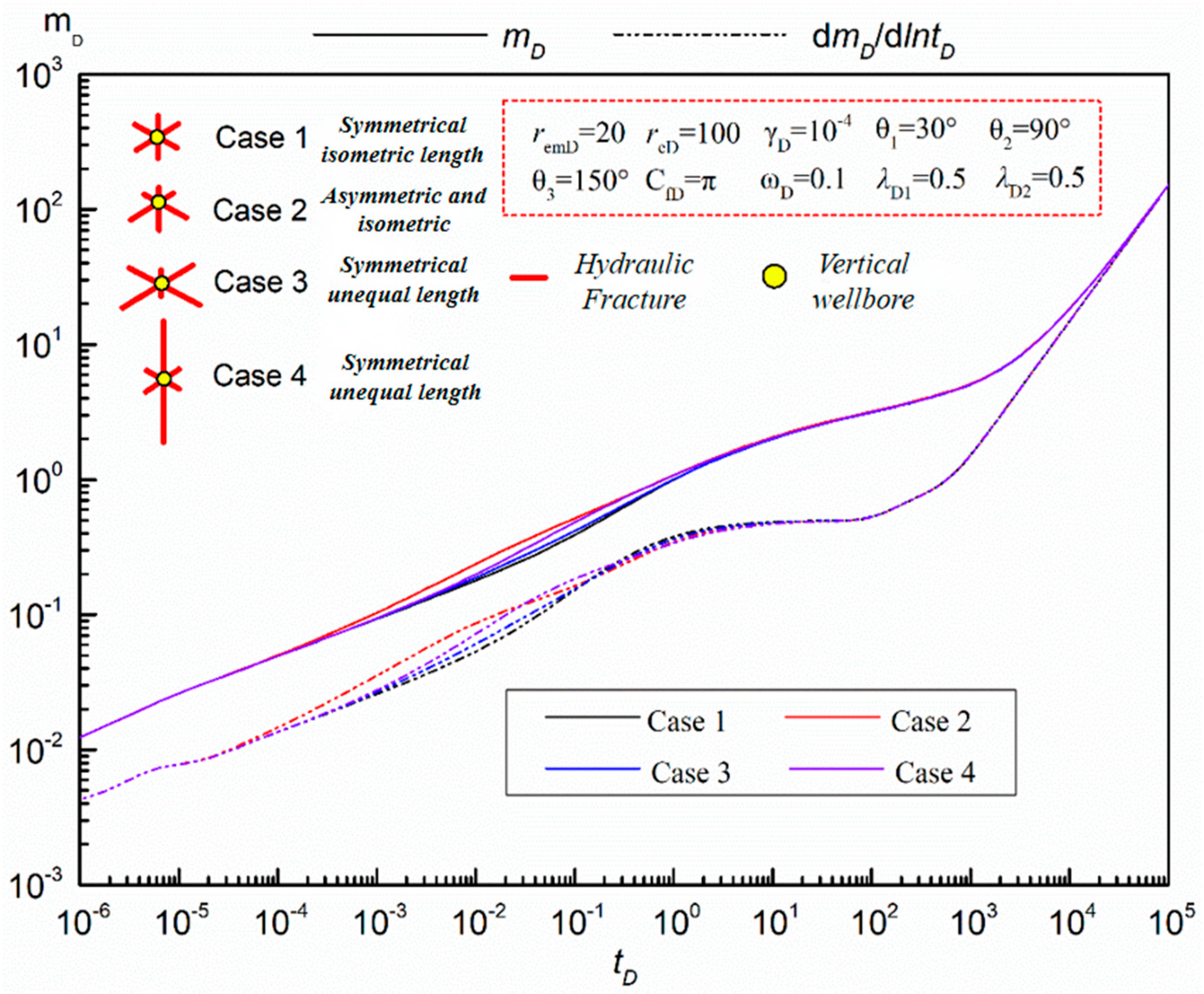
- Fracture Symmetry
- (5)
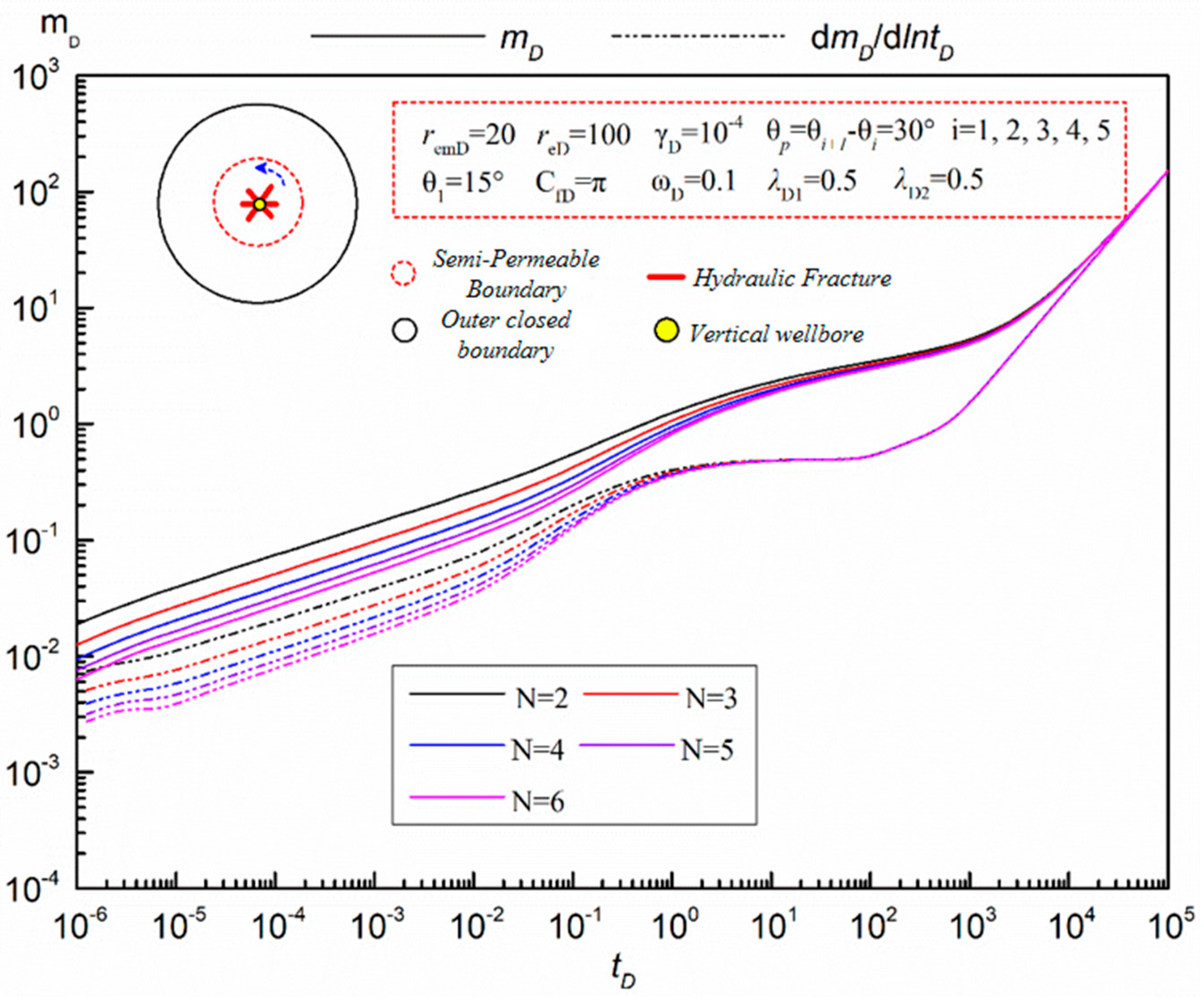
- The Number Of Fractures
- (6)
- Fracture Network
5. Discussion
- (1)
- For tight sandstone gas reservoirs, cross-fracture networks are formed in the fracturing process. However, the fracture network in this paper only considers non-coplanar fractures, and does not study the complex seepage of cross-fracture networks. Therefore, further studies are needed for the unstable seepage of such complex fracture networks.
- (2)
- In the development process of tight sandstone gas reservoir, the occurrence of gas-water two-phase seepage may lead to the temporary closure and opening of artificial fractures. However, this paper only considers the artificial fractures with constant conductivity and ignores the temporary closure and opening of fractures. Therefore, further studies on the temporary closure and opening of fractures in the gas-water two-phase seepage process of tight sandstone gas reservoir need to be strengthened.
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The phenomenon of superimposed sand body deposition in tight gas reservoirs is common, and the well test curve warps up and then falls down. This phenomenon is often analyzed based on the constant pressure boundary or radial composite reservoir model, and the inversion results are prone to be misleading. In this paper, a mathematical model of unsteady seepage flow in fractured vertical Wells in tight sandstone gas reservoirs is established, which takes into account factors such as stress sensitivity, fracture density and fracture symmetry.
- (2)
- There are great differences in the seepage mechanism at different stages of complex fracture Wells with superposition sand bodies. In the early linear flow stage, interwing interference plays a dominant role, which lasts to the middle and late production stage. In the middle seepage stage, the interfracture interference plays a dominant role until the boundary control flow appears. Finally, the interference between the wings is reflected in the curve as a "bulge" in the pseudo pressure derivative, and the interference between the slots will affect the duration of the first radial flow.
- (3)
- For tight sandstone gas reservoirs, cross-fracture networks are formed in the fracturing process. However, the fracture network in this paper only considers non-coplanar fractures, and does not study the complex seepage of cross-fracture networks. Therefore, the unstable seepage of such complex fracture networks needs further study.
References
- Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; He, D.; et al. Theory, technology and prospect of conventional and unconventional natural gas. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; et al. Significant progress of continental petroleum geology theory in the basins of central and western China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q et al. Advances and challenges in shale oil development: A critical review. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4, 406–418.
- Sun, L.; Zou, C.; Jia, A.; et al. Development characteristics and direction of tight oil and gas in China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Pang, X.; Li, F.; et al. Reservoir-forming mechanism and type division of tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Geological Society of China, 2013, 267-268.
- Wang, X. Numerical simulation of low permeability tight sandstone gas reservoir considering stress sensitivity. Petrochemical Applications, 2020, 39, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhu, R. Development status, challenges and concerns of unconventional oil and gas in PetroChina. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. Well testing and productivity prediction of tight oil and gas reservoirs. University of Science and Technology of China, 2019.
- Zhang, F.; Zou, L.; Rui, Z.; et al. A two-phase type-curve method with multiscale fluid transport mechanisms in hydraulically fractured shale reservoirs. Petroleum Science. 2023, 20, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Leng, S.; Deng, J.; et al. Sand body architecture characteristics of lower Member of Hehe 8 in Western Sulige Gas Field. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2022, 48, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchuk, F.; Biryukov, D.; Fitzpatrick, T.; et al. Pressure transient behavior of horizontal wells intersecting multiple hydraulic and natural fractures in conventional and unconventional unfractured and naturally fractured reservoirs. Paper SPE 175037 presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, Texas, USA, 28-30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Qin, C.; Feng, Q.; et al. A framework for predicting the production performance of unconventional resources using deep learning. Applied Energy, 2021, 295, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Research on Dynamic Analysis of fractured horizontal well. Doctoral Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2005.
- Wan, J.; Aziz, K. Semi-analytical well model of horizontal wells with multiple hydraulic fractures. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 2002, 7, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Interpretation of well testing of fractured horizontal Wells based on different dip angles. Research and Progress in Hydrodynamics, 2009, 24, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zerar, Z.; Bettam, Y. Interpretation of multiple hydraulically fractured horizontal wells in closed systems. Paper presented at the Canadian International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, Alberta, 8-10 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M, et al. A well-testing method for parameter evaluation of multiple fractured horizontal wells with non-uniform fractures in shale oil reservoirs. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4, 187–198.
- Cui, G.; Rui, Z.; Pei, S.; et al. Whole process analysis of geothermal exploitation and power generation from a depleted high-temperature gas reservoir by recycling CO2. Energy, 2021, 217, 119340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kou, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Performance analysis for a model of a multi-wing hydraulically fractured vertical well in a coalbed methane gas reservoir. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 166, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. C. Z. A semi-analytical model for the transient pressure behaviors of a multiple fractured well in a coal seam gas reservoir. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2021, 198, 108159. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.; Yu, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Fractal well test model for multi-wing fractured vertical well with finite conductivity in the coal bed methane reservoir. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2021, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao K, Du P. Performance of horizontal wells in composite tight gas reservoirs considering stress sensitivity. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2019, 3, 287–303.
- Yao, J.; Yin, X.; Fan, D.; et al. Three-linear flow test model for fractured horizontal Wells in low permeability reservoir. Oil & Gas Well Testing, 2011, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Luo, W.; Hou, X.; et al. Unsteady pressure analysis of multi-stage fractured horizontal well in rectangular reservoir. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S. Development and application of the method of distributed volumetric sources to the problem of unsteady-state fluid flow in reservoirs. Ph.D Thesis, Texas A&M University, 2007.
- Bear, J.; Braester, C.; Menier, P. C. Effective and relative permeabilities of anisotropie porous media. Transport in Porous Media, 1987, 2, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantush, M. N. Non-steady Green's functions for an infinite strip of leaky aquifer. Trans, AGU, 1955, 36, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Boussila, A. K.; Tiab, D.; Owayed, J. Pressure Behavior of Well Near a leaky Boundary in Heterogeneous Reservoirs. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 2003, 27, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N. M.; Miller, M. D.; Mattar, L. Analytical Solution to the Transient-Flow Problems for a Well Located near a Finite-Conductivity Fault in Composite Reservoirs. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2003, 96, 120–139. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar, F.; Fahes, M.; Gonzalez, R.; et al. Determination of Reservoir Drainage Area for Constant-Pressure Systems by Conventional Transient Pressure Analysis. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2015, 10, 5193–5199. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaziz, Bensadok & Tiab, Djebbar. (2004). Pressure Behaviour of a Well Between Two Intersecting Leaky Faults. Paper PETSOC-2004-209 presented at the Canadian International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, Alberta, 8-10 June 2004.
- Jongkittinarukorn, K.; Tiab, D.; Escobar, F. H. Interpretation of Horizontal Well Performance in Complicated Systems by the Boundary Element Method. Paper SPE 50437 presented at the SPE International Conference on Horizontal Well Technology, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 1-4 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ayala, L. F. Explicit Determination of Reserves for Variable-Bottomhole-Pressure Conditions in Gas Rate-Transient Analysis. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2020, 25, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, X. Action mechanism of water on the gas seepage capacity in tight gas reservoir. Spec. Oil Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Experimental Study on Mechanism of Water Sensitivity and Water Lock Damage in Tight Gas Reservoir. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2019, 154, 654–611. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L. B.; Petalas, N.; Arbabi, S.; et al. An experimental study of single-phase and two-phase fluid flow in horizontal wells. Paper SPE 46221 presented at the SPE Western Regional Meeting, Bakersfield, California, 10-13 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



