Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The study region
2.2. Literature search strategy
2.3. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Papers selected for the review
3.2. Papers retained by country
3.3. The periodic trend in publication of epidemiological and entomological data by country
3.4. Occurrence of arboviruses in the Central African Region
i.Angola
DENV
YFV and CHIKV
ii.Cameroon
CHIKV
DENV
YFV
ZIKV
WNV
iii.Central African Republic
CHIKV
RVFV
YFV, DENV and ZIKV
iv.Chad
DENV
YFV
RVFV
v.Democratic Republic of Congo
YFV
CHIKV
DENV
ZIKV
RVFV
WNV
vi.Equatorial Guinea
CHIKV, DENV and YFV
vii.Gabon
CHIKV
DENV
RVFV, YFV, WNV, ZIKV
viii.Republic of the Congo
CHIKV
DENV
ZIKV
3.5. Distribution of arboviruses in the Central African subregion
| Country | Site (region, province, city) | arbovirus | Proportions (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gabon | Estuaire | CHIKV | 3-86 | [60,61,77] |
| DENV | 4-21.4 | [60,61,77] | ||
| Moyen Ogooue | CHIKV | 0.6-61.2 | [7,63,78] | |
| DENV | 12.3-88.24 | [7,63,65,66] | ||
| RVFV | 14.3 | [7] | ||
| YFV | 60.7 | [7] | ||
| WNV | 25.3 | [7] | ||
| ZIKV | 40.3 | [7] | ||
| Haut Ogooue | CHIKV | 45.2-62.3 | [62] | |
| DENV | 12.2 | [62] | ||
| Ogooue Lolo | CHIKV | 28.7 | [62] | |
| Woleu Ntem | CHIKV | 0.5 | [79] | |
| nationwide | CHIKV | 35.6-86 | [59,80] | |
| DENV | 0.2-94.8 | [59,64] | ||
| 212-220 villages | DENV | 0.5 | [81] | |
| RVFV | 3.3 | [82] | ||
| Cameroon | East | ZIKV | 7.6 | [30] |
| Littoral | CHIKV | 12.6-59.4 | [19,20] | |
| DENV | 3.9-68.3 | [20,22,23,24,25,26,28] | ||
| ZIKV | 10-26.2 | [20,30] | ||
| South | DENV | 0.5-14.28 | [79,83] | |
| North | YFV | 25.5 | [29] | |
| Far North | DENV | 6.7-14.36 | [25,26] | |
| ZIKV | 2-4.8 | [30] | ||
| Adamawa | DENV | 4.7-6.89 | [26,84] | |
| ZIKV | 2 | [30] | ||
| West | CHIKV | 15.7 | [60] | |
| DENV | 6.14-14.36 | [25,26,27,28] | ||
| Center | CHIKV | 3-59.4 | [19,20,85] | |
| DENV | 3-45.45 | [20,25,26,28,85] | ||
| ZIKV | 3.3 | [30] | ||
| North West | CHIKV | 51.4 | [86] | |
| South West | CHIKV | 4-63 | [6,21] | |
| ZIKV | 11.4 | [6] | ||
| DENV | 2.5-74 | [6,21] | ||
| YFV | 4-72 | [21] | ||
| WNV | 3-82 | [21] | ||
| Democratic Republic of Congo | Matadi | CHIKV | 83.2 | [47] |
| Kisangani | WNV | 66 | [46] | |
| CHIKV | 34 | [46] | ||
| DENV | 3 | [46] | ||
| RVFV | 4 | [46] | ||
| kinshasa | DENV | 0.4-8.1 | [39,45,48,49,51] | |
| YFV | 6.0-73 | [39,43] | ||
| CHIKV | 0.1-49.7 | [39,45,51,87,88,89] | ||
| Sud-Ubangi | ZIKV | 3.5% | [39] | |
| Republic of the Congo | Brazzaville | CHIKV | 11.7-71 | [90,91] |
| Pointe-Noire | - | [67,68] | ||
| - | ZIKV | 1.8 | [69] | |
| - | DENV | - | [13] | |
| Angola | Luanda | DENV | 11.1-94.4 | [17,92,93] |
| CHIKV | 7 | [17,94] | ||
| 13 provinces | YFV | 70 | [95] | |
| Equatorial Guinea | Bata | CHIKV | 1.1-33.3 | [58] |
| Chad | N’Djamena | YFV | 0.28 | [13,36] |
| RVFV | 4 | [38] | ||
| DENV | - | [13] | ||
| Central African Republic | Bangui | YFV | 6.5 | [96] |
| RVFV | 1.9-16.7 | [34] | ||
| CHIKV | - | [32] |
3.6. The mosquito fauna of the Central African Region from 1993 to 2023
| Species | Countries | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cameroon | RoC | Gabon | CAR | DRC | EG | Angola | Chad | ||
| Aedes aegypti | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [10,16,47,59,62,67,89,90,97,98,99,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149] |
| Aedes abnormalis | + | [150] | |||||||
| Aedes africanus | + | + | + | [62,86,101,103,104,105,106,116,118,123,150,151,152,153] | |||||
| Aedes albopictus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [10,47,59,86,89,90,97,98,99,101,103,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,114,115,116,117,118,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,134,135,136,137,138,140,142,145,146,148,151,154,155,156,157,158] |
| Aedes alternans | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes argenteopunctatus | + | + | [101,103,105,123,152] | ||||||
| Aedes australis | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes caspiua | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes centropunctatus | + | [103] | |||||||
| Aedes cinerus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes circum | + | + | [101,105,114,123] | ||||||
| Aedes circumluteocus | + | + | + | [101,123,152,153,159] | |||||
| Aedes contigus | + | [122,151] | |||||||
| Aedes cumminsii | + | + | [103,105] | ||||||
| Aedes dalzieli | + | + | + | [103,114,153] | |||||
| Aedes dendrophilus | [105] | ||||||||
| Aedes domesticus | + | [101,105] | |||||||
| Aedes dufouri | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes fraseri | + | [101,123,152] | |||||||
| Aedes flavifrons | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes fowleri | + | + | + | [103,114,140,150] | |||||
| Aedes furcifer | + | [153] | |||||||
| Aedes gibinsis | + | [101,152] | |||||||
| Aedes haworthi | + | [105] | |||||||
| Aedes ingrani | + | [105] | |||||||
| Aedes irritans | + | [132] | |||||||
| Aedes longipalpis | + | + | [105,153] | ||||||
| Aedes luteocephalus | + | [103,104,105] | |||||||
| Aedes mcintoshi | + | + | [103,114] | ||||||
| Aedes metallicus | + | [101,123] | |||||||
| Aedes minutus | + | [153] | |||||||
| Aedes mixtus | + | [103] | |||||||
| Aedes mucidus | + | [114] | |||||||
| Aedes multiplex | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes nigricephalus | + | [132] | |||||||
| Aedes notoscriptus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes ochraceus | + | [114] | |||||||
| Aedes opok | + | [105,150] | |||||||
| Aedes palpalis | + | [105,122,150] | |||||||
| Aedes polynesiensis | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes procax | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes simpsoni | + | + | + | [10,59,101,103,104,105,109,112,122,123,135,136,151] | |||||
| Aedes simulans | + | [160] | |||||||
| Aedes soleatus | + | [101,123] | |||||||
| Aedes stockesi | + | [105] | |||||||
| Aedes subargenteopunctatus | + | [105] | |||||||
| Aedes tarsalis | + | [101,105,123,125,150,152] | |||||||
| Aedes vexans | + | + | + | [117,128,140,153] | |||||
| Aedes vigilax | + | + | [140,153] | ||||||
| Aedes vittatus | + | + | + | + | [99,103,105,112,114,125,136,153] | ||||
| Aedes vittiger | + | [140] | |||||||
| Aedes wellmani | + | [101,123] | |||||||
| Anopheles annuliotus | + | [105,152] | |||||||
| Anopheles annulipes | + | [140] | |||||||
| Anopheles arabiensis | + | + | + | + | [140,161,162,163] | ||||
| Anopheles ardensis | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles argenteolobatus | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles austenii | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles azevedoi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles bambusae | + | [105] | |||||||
| Anopheles barberellus | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles berghei | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles bervoetsi | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles brohieri | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles brunnipe | + | + | + | + | + | [161,164] | |||
| Anopheles buxtoni | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles caliginosus | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles carnevalei | + | + | + | [161,165,166] | |||||
| Anopheles caroni | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles christyi | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles cinctus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,161] | |
| Anopheles cinerus | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles claviger | + | [140] | |||||||
| Anopheles coluzzii | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [117,128,140,161,163] |
| Anopheles confusus | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles cconcolor | + | + | + | [161,163] | |||||
| Anopheles coustani | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,105,140,161,162,163] | |
| Anopheles cydippis | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | |||
| Anopheles dureni | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles deemingi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles demeilloni | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||||
| Anopheles distinctus | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles dthali | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles domicolus | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles dualaensis | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles eouzani | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles faini | + | + | [160,161] | ||||||
| Anopheles flavicosta | + | + | + | [103,161] | |||||
| Anopheles freetownensis | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles fontenillei | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles fuscivenosus | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles funestus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,105,113,125,140,150,160,161,162,163,164,165,167] |
| Anopheles gambiae | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [10,59,97,99,101,103,105,107,108,110,112,113,115,118,125,128,131,132,136,140,142,150,151,161,162,163,164,165,167,168,169,[10,59,97,99,101,103,105,107,108,110,112,113,115,118,125,128,131,132,136,140,142,150,151,161–165,167–169,] |
| Anopheles garnhami | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles gabonensis | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles gibbinsi | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles hamoni | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles hancocki | + | + | + | + | [161,164] | ||||
| Anopheles hargreavesi | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | |||
| Anopheles charperi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles hyrcanus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Anopheles implexus | + | + | + | + | + | + | [105,161,166] | ||
| Anopheles jebudensis | + | + | + | + | + | [160,161] | |||
| Anopheles keniensis | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles kingi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles leesoni | + | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||
| Anopheles listeri | + | [161,163] | |||||||
| Anopheles lloreti | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles longipalpis | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||||
| Anopheles maculipalpis | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | |||
| Anopheles maculipennis | + | + | [140,152] | ||||||
| Anopheles marshallii | + | + | + | + | + | + | [159,160,161,166] | ||
| Anopheles melas | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [117,146,161,163,165,168] | |
| Anopheles meraukensis | + | [153] | |||||||
| Anopheles millecampsi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles mortiauxi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles moucheti | + | + | + | + | + | + | [115,117,151,161,164,165,166] | ||
| Anopheles mousinhoi | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles multicinctus | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles namibiensis | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles natalensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | [105,160,161] | ||
| Anopheles nili | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,105,151,160,161,162,163,164,165] |
| Anopheles njombiensis | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles obscurus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [159,161] | |
| Anopheles okuensis | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles ovengensis | + | + | [161,165] | ||||||
| Anopheles paludis | + | + | + | + | + | + | [105,151,153,159,161,164] | ||
| Anopheles pharaoensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,131,140,161,162,163] | ||
| Anopheles pretoriensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||
| Anopheles rageaui | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles rhodesiensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||
| Anopheles rodhaini | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles rivulorum | + | + | + | + | [161] | ||||
| Anopheles rivulorum-like | + | [161] | |||||||
| nopheles ruarinus | + | [161,163] | |||||||
| Anopheles rufipes | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,140,161,162,163] | |
| Anopheles schwetzi | + | + | + | [160,161] | |||||
| Anopheles seydeli | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles smithii | + | + | + | + | [160,161] | ||||
| Anopheles somalicus | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles squamosus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [114,161,162,163,[114,161–163,] | |
| Anopheles symesi | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles tchekedii | + | [161] | |||||||
| Anopheles tenebrosus | + | + | + | + | + | + | [115,117,128,159,161] | ||
| Anopheles theileri | + | + | + | [161] | |||||
| Anopheles vanhoofi | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles versus | + | [170] | |||||||
| Anopheles vinckei | + | [161,166] | |||||||
| Anopheles walravensi | + | + | [161] | ||||||
| Anopheles wellecomei | + | + | + | + | + | + | [140,161,162] | ||
| Anopheles ziemmani | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [103,115,140,161,162,163] | |
| Anopheles zombaensi | + | [160] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia spp. | + | + | [103,105,151] | ||||||
| Coquelettidia annettii | + | [101] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia aurites | + | [159,160] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia cristata | + | [105] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia fraseri | + | [105] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia maculipennis | + | [101,123] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia microannulata | + | [160] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia pseudoconopas | + | + | [105,160] | ||||||
| Coquelettidia richiardii | + | [140] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia versicor | + | [160] | |||||||
| Coquelettidia xanthogaster | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex albiventis | + | + | [123,171] | ||||||
| Culex annulioris | + | + | + | [103,105,123,153,160,161] | |||||
| Culex annulirostries | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex antenatus | + | + | [112,114,118,123,132,171] | ||||||
| Culex andersoni | + | [160] | |||||||
| Culex argenteopunctatus | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex australicus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex cinerus | + | + | + | [103,107,132,159,160,171] | |||||
| Culex cinerellus | + | + | + | [97,132,160,171] | |||||
| Cx.duttoni | + | + | + | [97,101,106,112,115,117,118,122,123,125,128,150,151,152,153,171,172] | |||||
| Cx.decens | + | + | [97,106,107,112,117,118,128,131,132,150,159] | ||||||
| Culex eouzani | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex fatigans | + | [125] | |||||||
| Culex guiarti | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex horridus | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex individiosus | + | [101] | |||||||
| Culex insignis | + | + | [140,171] | ||||||
| Culex macfie | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex muspratti | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex musarum | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex simpliciforceps | + | [171] | |||||||
| Cx.moucheti | + | [101,122,123,151,152,171] | |||||||
| Culex modestus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex molestus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex neavei | + | + | + | [140,153,171] | |||||
| Culex nebulosus | + | + | + | [103,132,160,171] | |||||
| Culex orbostiensis | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex ornothoracic | + | [101,152,171] | |||||||
| Culex perexiguus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex perfuscus | + | [101,112,125,151,171] | |||||||
| Culex perfidiosus | + | + | [103,105,107,125,150,151,171] | ||||||
| Cx.pipiens | + | + | [101,118,140,172] | ||||||
| Culex phillipi | + | [123,171] | |||||||
| Culex poicilipes | + | + | [105,115,118,128,140] | ||||||
| Culex poecilipes | + | + | [117] | ||||||
| Culex pruina | + | [123,151,171] | |||||||
| Culex quasiguiarti | + | [160] | |||||||
| Culex quinquefasciatus | + | + | + | + | + | + | [10,59,97,103,105,106,107,108,110,112,113,114,115,117,122,123,128,131,132,136,140,142,146,151,153] | ||
| Culex rubinotus | + | + | [159,160] | ||||||
| Culex rima | + | + | + | [132,140,160,171] | |||||
| Culex sitiens | + | [140] | |||||||
| Culex schwetzi | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex semibrunneus | + | [160,171] | |||||||
| Culex simpsoni | + | + | [117,118,160] | ||||||
| Culex sunyaniensis | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex subaequali | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex tigripes | + | + | + | + | [99,103,105,106,107,112,113,118,122,123,125,131,132,152] | ||||
| Culex trifilatus | + | + | [101,160] | ||||||
| Culex univittatus | + | + | [101,118,123,151,152,160] | ||||||
| Culex watti | + | + | [140,160] | ||||||
| Culex wiggleworthi | + | [101,123,151,152,171] | |||||||
| Culex taufliebi | + | [97] | |||||||
| Culex thalassius | + | [171] | |||||||
| Culex theileri | + | [160] | |||||||
| Culex trifoliatus | + | + | [97,101,171,[97,101,171,] | ||||||
| Culex umbripes | + | [97,161] | |||||||
| Eretmapodites spp. | + | + | + | + | [101,122,123] | ||||
| Eretmapodites quinquevittatus | + | + | + | [10,106,112] | |||||
| Eretmapodites chrysogaster | + | + | [101,105,123,152,160,[101,105,123,152,160,] | ||||||
| Eretmapodites grahami | + | [160] | |||||||
| Eretmapodites inornatus | + | + | [97,105,153] | ||||||
| Eretmapodites plioleucus | + | [101] | |||||||
| Ficolbia spp | + | [123] | |||||||
| Ficalbia Flavopicta | + | [101] | |||||||
| Ficalbia malfeyi | + | [159] | |||||||
| Ficalbia mediolineata | + | [132] | |||||||
| Ficalbia uniformis | + | [160] | |||||||
| Finlayas spp. | + | [160] | |||||||
| Lutzia tigripes | + | + | + | + | [97,101,107,123,140,150,151,160,172] | ||||
| Mansona africana | + | + | + | + | [10,59,103,105,106,108,114,132,151,153,159] | ||||
| Mansona uniformis | + | + | + | + | [10,59,103,105,108,110,114,131,132,140,151] | ||||
| Mimmonyia.spp | + | [123] | |||||||
| Mimmonyia flavopicta | + | [101] | |||||||
| Mimmonyia plumosa | + | [160] | |||||||
| Ochlerothatus rusticus | + | [140] | |||||||
| Ochlerothatus excrucians | + | [140] | |||||||
| Orthopodomyia reunionensis | + | [140] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia spp. | + | + | + | [123] | |||||
| Uranotaenia bilineata | + | + | [101,152,159,160] | ||||||
| Uranotaenia cavernicola | + | [159,160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia nigromaculata | + | [159,160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia nigripes | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia caliginosa | + | [159] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia caeruleocephala | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia machadoi | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia pallidocephala | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia balfoui | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia chorleyi | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia alboabdominalis | + | [160] | |||||||
| Uranotaenia mashonaensis | + | + | [101,132,159,160] | ||||||
| Verralina funerea | + | [140] | |||||||
| Toxorhinchites.spp | + | [122,123] | |||||||
3.7. Arboviruses and associated mosquito vectors in the Central African Region from 1993 to 2023
| Species | Virus | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ae.aegypti | Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, Yellow Fever, Rift Valley fever virus, Ross River, Murray Vallée, Wesselsbron, Encephalitis, Dugbe, Orungo, Bakanki, O’nyong Nyong | [101,108,114,116,138,173,174,175,182,183] |
| Ae.abnormalis | n.a | / |
| Ae.africanus | Bouboui, Chikungunya, Orungo, Wesselsbron, West Nile, Yellow fever, Zika, Bozo, Wamba, Uganda, Bouboui, Bozo, Middelburg, Orungo, Saboya, Semliki Forest, Yaoundé, ArB 28215 | [116,150,153,173,175,184,185] |
| Ae.albopictus | Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, Yellow fever, Usutu, Weeselsbron, Ross River, Rif Valley fever, West Nile virusl, Murray Vallée, Japonese encephalitis, St-Louis encephalitis, sindbis virus | [108,114,116,138,174,176] |
| Ae.alternans | n.a | / |
| Ae.argenteopunctatus | Middelburg, Semliki Forest, Ndumu, Kedougou, Wesselsbron, Bunyamuera, Shokwe, Simbu, Pongola, Zinga, Zika, Yellow Fever, Sindbis, Chikungunya, Nkolbisson, Ngari, Pongola | [101,153,175,179] |
| Ae.australis | n.a | / |
| Ae.bromelia | Yellow Fever | [186] |
| Ae.caballus | Wesselsbron, Rift Valley fever, Midelburg | [175,187] |
| Ae. cordeleri | Chikungunya | [175] |
| Ae.caspiua | Usutu | [175] |
| Ae.centropunctatus | n.a | / |
| Ae.cinerus | n.a | / |
| Ae.circumluteocus | Wesselsbron, Pongola, Bunyamwera, Rift Valley Fever, Ndumu, Spondweni, Simbu, Middelburg, Shokwe, West Nile | [101,114,153,175,187] |
| Ae.contigus | n.a | / |
| Ae.cumminsii | Middelburg, Nkolbisson, Rift Valley fever, Shokwe, Sindbis, Spondweni | [175,188] |
| Ae.dalzieli | Zika, Yellow Fever, Rift Valley Fever, Sindbis, Middelburg, Semeliki forest, Ndumu, Kedougou, Chikungunya, Wesselsbron, Bunyawera, Shokwe, Simbu, Pongola, Zinga | [114,153,179,189] |
| Ae.dendrophillus | n.a | / |
| Ae.dentatus | Yellow Fever, Rift Valley Fever, Wesselsbron | [173,175] |
| Ae.domesticus | Wesselsbron, Bunyamwera | [101] |
| Ae.dufouri | n.a | / |
| Ae.fraseri | n.a | / |
| Ae.flavifrons | n.a | / |
| Ae.fowleri | n.a | / |
| Ae.furcifer | Yellow Fever, Bouboui, Chikungunya, Bunyawera, Bouboui, Dengue, Rift Valley Fever, Zika, Bwamba | [153,173,175,190] |
| Ae.gibinsis | n.a | / |
| Ae.haworth | n.a | / |
| Ae.ingrani | n.a | / |
| Ae.irritans | n.a | / |
| Ae.lili | Yellow Fever | [8] |
| Ae.longipalpis | Uganda | [153] |
| Ae.luteocephalus | Yellow Fever, Chikungunya, Bouboui, Bweyawera, Zika | [173,175,179] |
| Ae.mcintoshi | Pongola, Ndumu, Chikungunya | [175] |
| Ae.metallicus | Yellow Fever, Zika, Bagaza | [173,175,185] |
| Ae.minutus | Zika, Yellow Fever, Sindbis, Middelburg, Semeliki Forest, Ndumu, Kedougou, Chikv, Wesselsbron, Bunyawera, Shokwe, Simbu, Pongola, Zinga | [153,175,179] |
| Ae.mixtus | n.a | / |
| Ae.mucidus | n.a | / |
| Ae.multiplex | n.a | / |
| Ae.neoafricanus | Yellow Fever | [8] |
| Ae.nigricephalus | n.a | / |
| Ae.notoscriptus | n.a | / |
| Ae.ochraceus | Ndumu, Rift Valley Fever | [175,189] |
| Ae.opok | Yellow Fever, Chinkungunya, Bouboui, Orungo, Wesselbron, Zika, Bozo, Wamba, Uganda, Bouboui, Bozo, Middelburg, Orungo, Saboya, Semeniki Forest, Yaoundé | [116,150,173,175,185] |
| Ae.palpalis | Rift Valley Fever, Simbu, Uganda | [150] |
| Ae.polynesiensis | n.a | / |
| Ae.procax | n.a | / |
| Ae.simpsoni | Yellow Fever, Chinkungunya, Babanki, Ngari, Bwamba, Uganda, Bouboui, Bozo, Middelburg, Orungo, Saboya, Semeniki Forest, Yaoundé | [101,173,175,185,186] |
| Ae.simulans | n.a | / |
| Ae.soleatus | n.a | / |
| Ae.stockesi | n.a | / |
| Ae.subargenteopunctatus | n.a | / |
| Ae.tarsalis | Pata, Pangola, Kedougou, Wesselbron, Zika | [150,175] |
| Ae.tricholabic | Ndumu | [175] |
| Ae.vexans | Eastern Equine Encephalitis, Batai, Banna, Japonese Encephalitis, West Nile, Zika, Semiliki Forest, Trivittatus, wesselsbron | [153,191] |
| Ae.vigilax | Edge | [153] |
| Ae.vittatus | Yellow Fever, Chikungunya, Sindbis. Middelburg, Semliki Forest, Ndumu, Kedougou, Wesselsbron, Bunyamuera, Shokwe, Simbu, Pongola, Zinga, Zika, Usutu | [153,173,175,179,184] |
| Ae.vittiger | n.a | / |
| Ae.wellemani | n.a | / |
| An. annuliotus | n.a | / |
| An.annulipes | n.a | / |
| An.arabiensis | n.a | / |
| An.ardensis | n.a | / |
| An.argenteolobatus | n.a | / |
| An.austenii | n.a | / |
| An.azevedoi | n.a | / |
| An.bambusae | n.a | / |
| An.barberellus | n.a | / |
| An.berghei | n.a | / |
| An.bervoetsi | n.a | / |
| An.brohieri | Sindbis | [179] |
| An.brunnipe | n.a | / |
| An.buxtoni | n.a | / |
| An.caliginosus | n.a | / |
| An.carnevalei | n.a | / |
| An.caroni | n.a | / |
| An.christyi | n.a | / |
| An.cinctus | n.a | / |
| An.cinerus | n.a | / |
| An.claviger | n.a | / |
| An.coluzzii | n.a | / |
| An.confusus | n.a | / |
| An.concolor | n.a | / |
| An.coustani | Bwanba, Chikungunya | [175,179] |
| An.cydippis | n.a | / |
| An.dureni | n.a | / |
| An.deemingi | n.a | / |
| An.demeilloni | n.a | / |
| An.distinctus | n.a | / |
| An.dthali | n.a | / |
| An.domicolus | n.a | / |
| An.dualaensis | n.a | / |
| An.eouzani | n.a | / |
| An.faini | n.a | / |
| An.flavicosta | n.a | / |
| An.freetownensis | n.a | / |
| An.fontenillei | n.a | / |
| An.fuscivenosus | n.a | / |
| An.funestus | Ckikungunya, Nyonda, Bwamba, Bunyamwera, O’nyong Nyong, Pongola | [175,179] |
| An.gambiae | Yellow Fever, Ilesha, Bwamba, O’nyong Nyong, Yaoundé, Tataguine, Bangui, Nyando | [101,173,175] |
| An.garnhami | n.a | / |
| An.gabonensis | n.a | / |
| An.gibbinsi | n.a | / |
| An.hamoni | n.a | / |
| An.hancocki | n.a | / |
| An.hargreavesi | n.a | / |
| An.harperi | n.a | / |
| An.hyrcanus | n.a | / |
| An.implexus | n.a | / |
| An.jebudensis | n.a | / |
| An.keniensis | n.a | / |
| An.kingi | n.a | / |
| An.leesoni | n.a | / |
| An.listeri | n.a | / |
| An.lloreti | n.a | / |
| An.longipalpis | n.a | / |
| An.maculipalpis | n.a | / |
| An.maculipennis | n.a | / |
| An.marshallii | n.a | / |
| An.melas | n.a | / |
| Ae.mercaukensis | Edge | [153] |
| An.millecampsi | n.a | / |
| An.mortiauxi | n.a | / |
| An.moucheti | Bwanba, Tataguine, Zika | [179] |
| An.mousinhoi | n.a | / |
| An.multicinctus | n.a | / |
| An.namibiensis | n.a | / |
| An.natalensis | n.a | / |
| An.nili | Bwanba, Tataguine | [179] |
| An.njombiensis | n.a | / |
| An.obscurus | n.a | / |
| An.okuensis | n.a | / |
| An.ovengensis | Tataguine | [179] |
| An.paludis | Bouboui | [153,175] |
| An.pharaoensis | n.a | / |
| An.pretoriensis | n.a | / |
| An.rageaui | n.a | / |
| An.rhodesiensis | n.a | / |
| An.rodhaini | n.a | / |
| An.rivulorum | n.a | / |
| An.rivulorum-like | n.a | / |
| An.ruarinus | n.a | / |
| An.rufipes | n.a | / |
| An.schwetzi | n.a | / |
| An.seydeli | n.a | / |
| An.smithii | n.a | / |
| An.somalicus | n.a | / |
| An.squamosus | n.a | / |
| An.symesi | n.a | / |
| An.tchekedii | n.a | / |
| An.tenebrosus | n.a | / |
| An.theileri | n.a | / |
| An.vanhoofi | n.a | / |
| An.versus | n.a | / |
| An.vinckei | n.a | / |
| An.walravensi | n.a | / |
| An.wellecomei | n.a | / |
| An.ziemmani | n.a | / |
| An.zombaensis | n.a | / |
| Coquelettidia.spp | Yellow Fever, Rift Valley, Sindbis, Usutu | [173,175,177] |
| Co.annettii | n.a | / |
| Co.aurites | n.a | / |
| Co.cristata | n.a | / |
| Co.fraseri | n.a | / |
| Co.fuscopennata | Sindbis | [175] |
| Co.maculipennis | n.a | / |
| Co.microannulata | n.a | / |
| Co.pseudoconopas | n.a | / |
| Co.richiardii | n.a | / |
| Co.versicor | n.a | / |
| Co.xanthogaster | n.a | / |
| Cx.albiventis | Arumowot | [175] |
| Cx.annulioris | Kamese, Edge | [153,175] |
| Cx.annulirostries | n.a | / |
| Cx.antenatus | Rift Valley Fever, Arumowot | [175,177] |
| Cx.andersoni | n.a | / |
| Cx.argenteopunctatus | n.a | / |
| Cx.australicus | n.a | / |
| Cx.cinerus | M’Poko, Sindbis | [159] |
| Cx.cinerellus | n.a | / |
| Cx.duttoni | Usutu, Bagaza, wesselsbron | [150,153,175] |
| Cx.decens | Sindbis, Usutu, Kamese, M’Poko, West Nile | [150,159,179] |
| Cx.eouzani | n.a | / |
| Cx.fatigans | n.a | / |
| Cx.guiarti | n.a | / |
| Cx.horridus | n.a | / |
| Cx.individiosus | Sindbis, Usutu | [179] |
| Cx.ingrani | Bagaza | [175] |
| Cx.insignis | n.a | / |
| Cx.macfiei | n.a | / |
| Cx.muspratti | n.a | / |
| Cx.musarum | n.a | / |
| Cx.simpliciforceps | n.a | / |
| Cx.moucheti | Ntaya | [101] |
| Cx.modestus | West Nile | [9] |
| Cx.molestus | n.a | / |
| Cx.neavei | Spondweni, Bagaza, West Nile | [175,189] |
| Cx.nebulosus | n.a | / |
| Cx.orbostiensis | n.a | / |
| Cx.ornothoracic | n.a | / |
| Cx.perexiguus | n.a | / |
| Cx.perfuscus | Sindbis, Usutu, Bagaza, M’Poko, Tataguine, West Nile | [150,179] |
| Cx.perfidiosus | n.a | / |
| Cx.pipiens | Chikungunya, Rift Valley Fever, West Nile | [9,177,179,180] |
| Cx.phillipi | n.a | / |
| Cx.poicilipes | West Nile, Bagaza | [189] |
| Cx.poecilipes | n.a | / |
| Cx.pruina | Kamese, Bozo | [150,175] |
| Cx.quasiguiarti | n.a | / |
| Cx.quinquefasciatus | West Nile, Wesselsbron | [175] |
| Cx.rubinotus | Banzi, Yaoundé, Ndumu | [175] |
| Cx.rima | n.a | / |
| Cx.sitiens | n.a | / |
| Cx.schwetzi | n.a | / |
| Cx.semibrunerus | n.a | / |
| Cx.simpsoni | Sondbis, West Nile, Usutu, Wanowri | [101,175] |
| Cx.sunyaniensis | n.a | / |
| Cx.subaequalis | n.a | / |
| Cx.tigripes | n.a | / |
| Cx.trifilatus | Sinbis, Usutu | [179] |
| Cx.univittatus | Sindbis, West Nile, Wesselsbron, Usutu, Spondweni, Bagaza, Japanese Encephalitis, Eastern Equine Encephalitis, Murray Valley | [101,175] |
| Cx.watti | n.a | / |
| Cx.wiggleworthi | n.a | / |
| Cx.taufliebi | n.a | / |
| Cx.tarsalis | West Nile | [180] |
| Cx.telesilila | Sindbis, Usutu | [179] |
| Cx.thalassius | n.a | / |
| Cx.theileri | Rift Valley Fever, Shuni | [175,178] |
| Cx. trifoliatus | n.a | / |
| Cx.umbripes | n.a | / |
| Eretmapodites.spp | Zika Virus, Spondweni, Simbu | [101,175] |
| Er.quinquevittatus | Zika, Arumorwot | [175] |
| Er.chrysogaste | Semliki forest, Middelburg, Ntaya, Simbu, Nkolbisson, Rift valley | [101] |
| Er.grahami | n.a | / |
| Er.inornatus | Zika, Bouboui | [153,175] |
| Er.pliol | n.a | / |
| Ficolbia.spp | n.a | / |
| Fi.Flavopicta | n.a | / |
| Fi.malfeyi | n.a | / |
| Fi.mediolineata | n.a | / |
| Fi.uniformis | n.a | / |
| Finlayas.spp | n.a | / |
| Lu.tiggipes | Yellow Fever, Dengue, Japanese Encephalitis, West Nile, Kamese, Mossuril, Sindbis, Babanki | [101,159,175] |
| Ma.africana | Middelburg, Wesselsbron, Spondweni, Banzi | [153,175] |
| Ma.uniformis | Pongla, Bwamba, O’nyong Nyong, Ndumu, Zika, Spondweni | [175,179] |
| Mimmonyia.spp | n.a | / |
| Mi.flavopicta | n.a | / |
| Mi. plumosa | n.a | / |
| Oc.rusticus | n.a | / |
| Oc.excrucians | n.a | / |
| Or.reunionensis | n.a | / |
| Uranotaenia.spp | n.a | / |
| Ur.bilineata | n.a | / |
| Ur.cavernicola | n.a | / |
| Ur.cavernicola | n.a | / |
| Ur.nigripes | n.a | / |
| Ur.caliginosa | n.a | / |
| Ur.caeruleocephala | n.a | / |
| Ur.machadoi | Yellow fever, Dengue, Japanese Encephalitis, West nile, Wesselsbron | [101,159] |
| Ur.pallidocephala | n.a | / |
| Ur.balfoui | n.a | / |
| Ur.chorleyi | n.a | / |
| Ur.alboabdominali | n.a | / |
| Ur.mashonaensis | n.a | / |
| Ve.funerea | n.a | / |
| Toxorhinchite.spp | Mosuril, Kamese | [150] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morin-Rivat, J.; Fayolle, A.; Favier, C.; Bremond, L.; Gourlet-Fleury, S.; Bayol, N.; Lejeune, P.; Beeckman, H.; Doucet, J.-L. Present-day central African forest is a legacy of the 19th century human history. eLife. 2017, 6, e20343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, J. Comparative Virology, Arboviruses: Incorporation in a General System of Virus classification. Academic press. 1979, 307–333. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Surveillance and control of arboviral diseases in the WHO African RegionWorld Health Organization on behalf of the UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. 2022, 148.
- Bourgarel, M.; Wauquier, N.; Gonzalez, J.P. Emerging viral threats in Gabon: health capacities and response to the risk of emerging zoonotic diseases in Central Africa. Emerg Hlth Threats J. 2010, 3, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madewell, Z.J. Arboviruses and Their Vectors. South. Med. J. 2020, 113, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokam, E.B.; Levai, L.D.; Guzman, H.; Amelia, P.A.; Titanji, V.P.K.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Silent circulation of arboviruses in Cameroon. East. Afr. Med. J. 2010, 87, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushijima, Y.; Abe, H.; Ngema-Ondo, G.; Bikangui, R.; Massinga, L.M.; Zadeh, V.R.; Essimengane, J.G.E.; Mbouna, A.V.N.; Bache, E.B.; Agnandji, S.T.; Lell, B.; et al. Surveillance of the major pathogenic arboviruses of public health concern in Gabon, Central Africa: increased risk of West Nile virus and dengue virus infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahouli, J.B.Z.; Koudou, B.G.; Müller, P.; Malone, D.; Tano, Y.; Utzinger, J. Urbanization is a main driver for the larval ecology of Aedes mosquitoes in arbovirus endemic settings in south-eastern Côte d’Ivoire. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriet, F. Des moustiques et des hommes. Chronique d’une pullulation annonée. coll. Didactiques. 2014, ed. IRD, Marseille.
- Grard, G.; Caron, M.; Mombo, I.M.; Nkoghe, D.; Ondo, S.M.; Jiolle, D.; Fontenille, D.; Paupy, C.; Leroy, E.M. Zika Virus in Gabon (Central Africa) – 2007: A New Threat from Aedes albopictus? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Mckenzi, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BJM. 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Cook, D.J.; Eastwood, S.; Olkin, I.; Rennie, D.; Stroup, D.F. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. QUOROM Group. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.; Jassoy, C. Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnostics of Dengue, Yellow Fever, Zika, and Chikungunya Virus Infections in Africa. Pathogens. 2021, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, R.C.; Veenstra, J.; Dingemans-Dumas, A.M.; Wetsteyn, C.F.M.; Kager, P.A. Imported Dengue in the Netherlands. J. Travel Med. 1996, 3, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.; Meltzer, E.; Mendelson, M.; Tooke, A.; Steiner, F.; Gautret, P.; Friedrich-Jaenicke, B.; Libman, M.; Bin, H.; Wilder-Smith, A.; et al. Detection on four continents of dengue fever cases related to an ongoing outbreak in Luanda, Angola, March to May 2013. Euro. Surveill. 2003, 18. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20488 Euro Surveill. 2011;16 (22):pii=19883. [CrossRef]
- Sharp, T.M.; Moreira, R.; Soares, M.J.; da Costa, L.M.; Mann, J.; DeLorey, M.; Hunsperger, E.; Muñoz-Jordán, J.L.; Colón, C.; Margolis, H.S.; de Caravalho, A.; Tomashek, K.M. Underrecognition of Dengue during 2013 Epidemic in Luanda, Angola. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 27, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, Z.; Martinez, P.A.; HillI, S.C.; Jandondo, D.; Theze, J.; Mirandela, M.; Aguiar, R.S.; Xavier, J.; Sebastião, C.D.S.; Candido, A.M.; et al. Molecular and genomic investigation of an urban outbreak of dengue virus serotype 2 in Angola, 2017–2019; PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, A.R.; Pinto, M.R. Arbovirus studies in Luanda, Angola; Virological and serological studies during an outbreak of dengue -like disease caused by the Chikungunya virus. Bull. Wld.Hlth. Org. 1973, 49, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Demanou, M.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Ngapana, E.; Kouagang, E.; Nfor, C.; Ndiforchu, V.; Vola, L.S.; Tchendjou, P.; Rousset, D.; Manuguerra, J.C.; et al. Retrospective Investigation of a Dengue-Like Syndrome in a Rural Area in Western Cameroon. 13th International Congress on Infectious Diseases Abstracts (Oral Presentations) 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana-Ndjangwo, S.M.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Mony, R.; Demanou, M.; Keumezeu-Tsafack, J.; Bamou, R.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Bilong, B.C.F.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C. Assessment of Dengue and Chikungunya Infections among Febrile Patients Visiting Four Healthcare Centres in Yaoundé and Dizangué, Cameroon. Viruses. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndip, L.M.; Bouyer, D.H.; Da Rosa, A.P.A.T.; Titanji, V.P.K.; Tesh, R.B.; Walker, D.H. Acute Spotted Fever Rickettsiosis among Febrile Patients, Cameroon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, F.B.Y.; Simo, F.B.N.; Ngouanet, S.A.; Mekanda, F.M.O.; Demanou, M. Detection and serotyping of dengue viruses in febrile patients consulting at the New-Bell District Hospital in Douala, Cameroon. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Tchetgna, H.D.S.; Yousseu, F.B.S.; Kamgang, B.; Tedjou, A.; Mccall, P.J.; Wondj, C.S. Concurrent circulation of Dengue Serotype 1, 2, and 3 among acute febrile patients in cameroon. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techetgna, H.S.; Descorps-Declere, S.; Selekon, B.; Garba-Ouangole, S.; Konamna, X.; Berthet, N. Continuous Circulation of Yellow Fever among Rural Populations in the Central African Republic. Viruses. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Tchuandom, S.B.; Tchouangueu, T.F.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Lissom, A.; Djang, J.O.N.; Atabonkeng, E.P.; Assompta, K.; Nchinda, G.; Kuiate, J-R. Seroprevalence of dengue virus among children presenting with febrile illness in some public health facilities in Cameroon. PAMJ. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchuandom, S.B.; Tchadji, J.C.; Tchouangueu, T.F.; Biloa, M.Z.; Atabonkeng, E.P.; Fumba, M.I.M.; Massom, E.S.; Nchinda, G.G.; Kuiate, J.R. A cross-sectional study of acute dengue infection in paediatric clinics in Cameroon. BMC Pub. Hlth. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.M.; Tchuenkam, V.P.K.; Colton, M.; Stittleburg, V.; Mitchell, C.; Gaither, C.; Thwai, K.; Espinoza, D.O.; Zhu, Y.; Jamal, H.; et al. Arboviruses as an unappreciated cause of non-malarial acute febrile illness in the Dschang Health District of western Cameroon. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monamele, G.C.; Demanou, M. First documented evidence of dengue and malaria co-infection in children attending two health centers in Yaoundé, Cameroon. PAMJ. 2018, 29, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demanou, M.; Ratsitoharana, R.; Seukap, E.; Abassora, M.; Nimpa, M.; Onambay, C.; Gake, B.; Tabonfack, A.; Faye, O.; Sall, A.; Njouom, R. Yellow fever outbreak in North Cameroon, 2011. Conference Paper. January 2011. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331089142.
- Gake, B.; Vernet, M.A.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Drexler, J.F.; Goulda, E.A.; Galliana, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Low seroprevalence of Zika virus in Cameroonian blood donors. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiot, C.C.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Georges, A.J. Current problems of arboviruses in central Africa. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1988, 81, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Tricou, V.; Desdouits, M.; Nakouné, E.; Gessain, A.; Kazanji, M.; Berthet, N. Complete genome sequences of two chikungunya viruses isolated in the Central African Republic in the 1970s and 1980s. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00003–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluzzo, J.F.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Hervé, J.P.; Georges, A.J. Serological survey for the prevalence of certain arboviruses in the human population of the south-east area of Central African Republic. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1981, 490–499. [Google Scholar]
- Nakouné, E.; Kamgang, B.; Berthet, N.; Manirakiza, A.; Kazanji, M. Rift Valley Fever Virus Circulating among Ruminants, Mosquitoes and Humans in the Central African Republic. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherm, J.M.; Gonella-Legall, C.; Legall, F.; Nanouke, E.; Vincent, J. Seroprevalence of five arboviruses in Zebu cattle in the Central African Republic. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 90, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessimbaye, N.; Mbanga, D.; Moussa, A.M.; Ferdinand, D.Y.; Maxime, N.D.; Barro, N.; Tidjani, A.; Ouchemi, C. Evaluation of yellow fever surveillance in Chad, 2015-2020. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 15, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Maurice, Y. Premières constatations sérologiques sur l’incidence de la maladie de Wesselsbron et de la Fièvre de la Vallée du Rift chez les ovins et les ruminants sauvages du Tchad et du Cameroun. Rev. Elev. Méd. Vét. Pays Trop. 1967, 20, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, J.P.; Bouloy, M.; Richecoeur, L.; Peyrefitte, C.N.; Tolou, H. Rift Valley Fever Virus Infection among French Troops in Chad. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, A.C.; Matthew, H.; Collins, M.H.; Jadi, R.; Keeler, C.; Parr, J.B.; Mumba, D.; Kashamuka, M.; Tshefu, A.; de Silva, A.M.; et al. Seroepidemiology of Dengue, Zika, and Yellow Fever Viruses among Children in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuCDC. Assessing the yellow fever outbreak in Angola – European Medical Corps mission undertaken in the framework of the European Union Civil Protection Mechanism. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control ,10–20 May 2016. Stockholm: ECDC 2016,7.
- WHO. Winning the war against yellow fever, angola. 2016. Available from: www.who.int.org.
- Mbanzulu, M.K.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Luzolo, F.K.; Wumba, R.; Misinzo, G.; Sharadhuli, I.K. Mosquito-borne viral diseases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: a review. Parasit. Vectors. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelbeen, B.; Weregemere, N.A.; Noel, H.; Tshapenda, G.P.; Mossoko, M.; Nsio, J.; Ronsse, A.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Cohuet, S.; Kebela, B. Urban yellow fever outbreak—Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2016: Towards more rapid case detection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0007029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatte, H.; Paupy, C.; Dehecq, J.S.; Thiria, J.; Failloux, A.B.; Fontenille, D. Aedes albopictus, vecteur des virus du Chikungunya et de la dengue à La Réunion: Biologie et contrôle. Parasite. 2008, 15, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekani, M.J.; McCollum, A.; Monroe, B.P.; Malekani, V.D.; Mulumba, M.L.; Tshilenge, C.G.; Kondas, A.; Doty, J.B.; Okitolonda, E.W.; Muyembe, J.J.T.; et al. Cas de dengue chez les patients suspects de chikungunya à Kinshasa. Ann. Afr. Med. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Nur, Y.A.; Groen, J.; Heuvelmans, H.; Tuynman, W.; Copra, C.; Osterhaus, A.D. An outbreak of West Nile fever among migrants in Kisangani, Democratic Republic of Congo. Am. J. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weggheleire, A.; Nkuba-Ndaye, A.; Mbala-Kingebeni, P.; Mariën, J.; Kindombe-Luzolo, E.; Ilombe, G.; Mangala-Sonzi, D.; Binene-Mbuka, G.; De Smet, B.; Vogt, F.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Investigation of the First Chikungunya Virus Outbreak in Matadi in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Viruses. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.P.; Kasamatsu, Y.; Kanbayashi, D.; Kaida, A.; Shirano, M.; Kubo, H.; Goto, T.; Iritani, N. Dengue Virus in Traveler Returning to Japan from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2015. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 72, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proesmans, S.; Katshongo, F.; Milambu, J.; Fungula, B.; Mavoko, H.M.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; da Luz, R.I.; Esbroeck, M.V.; Arien, K.K.; Cnops, L.; et al. Dengue and chikungunya among outpatients with acute undifferentiated fever in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo: A crosssectional study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasinghe, A.; Kuritsky, J.N.; Letson, W.G.; Margolis, S.H. Dengue virus infection in Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiala-Mandanda, S.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Abbate, J.L.; Pukuta-Simbu, E.; Nsio-Mbeta, J.; Berthet, N.; Leroy, E.M.; Becquart, P.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J. Identification of dengue and chikungunya cases among suspected cases of yellow fever in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavita, F.; Vairo, F.; Carletti, F.; Boccardo, C.; Ferraro, F.; Iaiani, G.; Moghazia, S.A.; Galardo, G.; Lalle, E.; Selvaggi, C.; et al. Full-length genome sequence of a dengue serotype 1 virus isolate from a traveler returning from Democratic Republic of Congo to Italy, July 2019. IJID. 2020, 9, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshilenge, G. Immunogeno: protective mechanism for Rift valley fever in the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, T.M.; Justin, M.; Victor, M.; Marie, K.J.; Mark, R.; Léopold, M.M.K. Seroprevalence and virus activity of Rift valley fever in cattle in eastern region of Democratic Republic of the Congo. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 4956378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanzulu, K.M.; Wumba, R.; Mukendi, J.K.; Zanga, J.K.; Shija, F.; Bobanga, T.L.; Aloni, M.N.; Misinzo, G. Mosquito-borne viruses circulating in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 57, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterrieth, P.; Deleplanque-Liegeois, P. Présence d’anticorps vis-à-vis de virus transmis par les arthropodes chez le chimpanzé (Pan tronglodites), comparaison de leur état immunitaire à celui de l’homme. Ann. Soc. Belge Méd. Trop. 1961, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-seco, M.P.; Negredo, A.I.; Puente, S.; Pinazo, M.J.; Shufffenecker, I.; Tenorio, A.; Fedele, C.G.; Domingo, C.; Rubio, J.M.; de Ory, F. Diagnóstico microbiológico del virus chikungunya importado en España (2006-2007): deteccion de casos en viajeros. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2009, 27, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collao, X.; Negredo, A.I.; Cano, J.; Tenorio, A.; de Ory, F.; Benito, A.; Masia, M.; Sánchez-Seco, M.-P. Different Lineages of Chikungunya Virus in Equatorial Guinea in 2002 and 2006. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Nkoghe, D.; Ollomo, B.; Nze-Nkogue, C.; Becquart, P.; Grard, G.; Pourrut, X.; Charrel, R.; Moureau, G.; Ndjoyi-Mbiguino, A.; De Lamballerie, X. Concurrent Chikungunya and Dengue Virus Infections during Simultaneous Outbreaks, Gabon, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoghe, D.; Kassa Kassa, R.F.; Bisvigou, U.; Caron, M.; Grard, G.; Leroy, E.M. No clinical or biological difference between Chikungunya and Dengue Fever during the 2010 Gabonese outbreak. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2012, 4, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazeille, M.; Moutailler, S.; Pages, F.; Jarjaval, F.; Failloux, A.B. Introduction of Aedes albopictus in Gabon: what consequences for dengue and chikungunya transmission? Trop. Med. Int. Health. 2008, 13, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoghe, D.; Kassa, R.F.; Caron, M.; Grard, G.; Mombo, I.; Bikie, B.; Paupy, C.; Becquart, P.; Bisvigou, U.; Leroy, E.M. Clinical Forms of Chikungunya in Gabon, 2010. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, J.J.; Schwarz, N.G.; Esen, M.; Kremsner, P.G.; Grobusch, M.P. Dengue and chikungunya seroprevalence in Gabonese infants prior to major outbreaks in 2007 and 2010: A sero-epidemiological study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Grard, G.; Paupy, C.; Mombo, I.M.; Bikie, B.N.B.; Kassa Kassa, F.R.; Nkoghe, D.; Leroy, E.M. First Evidence of Simultaneous Circulation of Three Different Dengue Virus Serotypes in Africa. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Ushijima, Y.; Massinga, L.M.; Bikangui, R.; Nguema-Ondo, G.; Mpingabo, P.; Zadeh, R.V.; Pemba, C.M.; Kurosaki, Y.; Igasaki, Y. Re-emergence of dengue virus serotype 3 infections in Gabon in 2016-2017, and evidence for the risk of repeated dengue virus infections. IJID. 2020, 91, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.k.; Fernandes, J.F.; Yoon, I.-K.; Lee, I.J.; Mba, R.O.; Lee, K.S.; Namkung, S.; Yang, J.S.; Bae, S.H.; Lim, S.-K.; et al. Epidemiology of dengue fever in Gabon: Results from a health facility-based fever surveillance in Lambaréné and its surroundings. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritza, M.; Taty, R.T.; Portella, C.; Guimbi, C.; Mankou, M.; Leroy, E.M.; Becquart, P. Re-emergence of chikungunya in the Republic of the Congo in 2019 associated with a possible vector-host switch. IJID. 2019, 84, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vairo, F.; Coussoud-Mavoungou, M.P.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Castilletti, C.; Kitembo, L.; Haider, N.; Carletti, F.; Colavita, F.; Gruber, C.E.M.; Iannetta, M.; et al. Chikungunya Outbreak in the Republic of the Congo, 2019-Epidemiological, Virological and Entomological Findings of a South-North Multidisciplinary Taskforce Investigation. Viruses. 2020, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurtop, E.; Moyen, N.; Dzia-Lepfoundzou, A.; Dimi, Y.; Ninove, L.; Drexler, J.F.; Gallian, P.; de Lamballerie, X.; Priet, S. A Report of Zika Virus Seroprevalence in Republic of the Congo. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.G.; Halstead, S.B.; Artsob, H.; Buchy, P.; Farrar, J.; Gubler, D.J.; Hunsperger, E.; Kroeger, A.; Margolis, H.S.; Martinez, E. Dengue: A continuing global threat. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2010, 8, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature. 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, F.Y.; Tchetgna, H.S.; Kamgang, B.; Djonabaye, D.; Nakouné, E. Seroprevalence of Rift Valley fever virus in domestic ruminants of various origins in two markets of Yaoundé, Cameroon. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebogo-Belobo, J.T.; Sadeuh-Mba, S.A.; Mveng-Sanding, G.M.A.; Chavely, G.M.; Groschup, M.H.; Mbacham, W.F.; Njouom, R. Serological evidence of the circulation of the Rift Valley fever virus in sheep and goats slaughtered in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Gao, X.; Gould, E.A. Factors responsible for the emergence of arboviruses; strategies, challenges and limitations for their control. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2015, 4, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Faria, N.R.; Reiner Jr, R.C.; Golding, N.; Nikolay, B.; Stasse, S.; Johansson, M.A.; Salje, H.; Faye, O.; Wint, G.R.W.; et al. Spread of yellow fever virus outbreak in Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo 2015–16: a modelling study. The lancet infectious dis. 2016, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajudeen, Y.A.; Oladipo, H.J.; Oladunjoye, I.O.; Yusuf, R.O.; Sodiq, H.; Omotosho, A.O.; Adesuyi, D.S.; Yusuff, S.I.; El-Sherbini, M.S. Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Concern in Africa: Priorities for Future Research and Control Strategies. Challenges. 2022, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrefitte, C.N.; Bessaud, M.; Pastorino, B.A.M.; Gravier, P.; Plumet, S.; Merle, O.L.; Moltini, I.; Coppin, E.; Tock, F.; Daries, W.; et al. Circulation of Chikungunya Virus in Gabon, 2006-2007. JMV. 2008, 80, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.K.; Ridde, V.; Agnandji, S.T.; Lell, B.; Yaro, S.; Yang, J.S.; Hoinard, D.; Weaver, S.C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Salje, H.; et al. Seroepidemiological Reconstruction of Long-term Chikungunya Virus Circulation in Burkina Faso and Gabon. JID. 2023, 227, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongho, G.B.D.; Venturi, G.; Fortuna, C.; Paganotti, G.M.; Severini, C.L.; Episcopia, M.; Tsapi, A.T.; Benedetti, E.; Marsili, G.; Amendola, A.; et al. Dengue and Chikungunya virus circulation in Cameroon and Gabon: molecular evidence among symptomatic individuals Access. Microbiology. 2022, 2, 000340. [Google Scholar]
- Tchetgna, H.S.; Ouilibona, R.S.; Nkili-Meyong, A.A.; Caron, M.; Labouba, I.; Selekon, B.; Njouom, R.; Leroy, E.M.; Nakoune, E.; Berthet, N. Viral Exploration of Negative Acute Febrile Cases Observed during Chikungunya Outbreaks in Gabon. Intervirology. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrut, X.; Nkoghé, D.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Leroy, E.M. No Evidence of Dengue Virus Circulation in Rural Gabon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1568–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, X.; NKogué, D.; Souris, M.; Paupy, C.; Pawweska, J.; Padilla, C.; Moussavou, G.; Leroy, E.M. Rift Valley Fever Virus Seroprevalence in Human Rural Populations of Gabon. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010, 4, e763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, F.B.N.; Sado, F.B.Y.; Mbarga, A.E.; Bigna, J.J.; Melong, A.; Ntoude, A.; Kamgang, B.; Bouyne, R.; Fewou, P.M.; Demanoua, M. Investigation of an Outbreak of Dengue Virus Serotype 1 in a Rural Area of Kribi, South Cameroon: A Cross-Sectional Study. Intervirology. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Galani, B.R.T.; Mapouokam, D.W.; Simo, F.B.N.; Mohamadou, H.; Chuisseu, P.D.D.; Njintang, N.Y.; Moundipa, P.F. ; Investigation of dengue-malaria coinfection among febrile patients consulting at Ngaoundere Regional Hospital, Cameroon. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrefitte, C.N.; Rousset, D.; Pastorino, B.A.M.; Pouillot, R.; Bessaud, M.; Tock, F.; Mansaray, H.; Merle, O.L.; Pascual, A.M.; Paupy, C.; et al. Chikungunya Virus, Cameroon, 2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demanou, M.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Ngapana, E.; Rousset, D.; Paupy, C.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; Zeller, H. Chikungunya outbreak in a rural area of Western Cameroon in 2006: A retrospective serological and entomological survey. BMC Res. Notes. 2010, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, B. , Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Bessaud, M.; Tock, F.; Tolou, H.; Durand, J.P.; Peyrefitte, C.N. Epidemic Resurgence of Chikungunya Virus in Democratic Republic of the Congo: Identification of a New Central African Strain. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ido, E.; Ahuka, S.; Karhemere, S.; Shibata, K.; Kameoka, M.; Muyembe, J.J. Infection du virus de la dengue survenue lors d’une épidémie du virus chikungunya en République démocratique du Congo. Ann. Afr. Med. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Selhorst, P.; Makiala-Mandanda, S.; De Smet, B.; Mariën, J.; Anthony, C.; Binene-Mbuka, G.; De Weggheleire, A.; Ilombe, G.; Kinganda-Lusamaki, E.; Pukuta-Simbu, E.; et al. Molecular characterization of chikungunya virus during the 2019 outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020, 9, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyen, N.; Thiberville, S.-D.; Pastorino, B.; Nougairede, A.; Thirion, L.; Mombouli, J.-V.; Dimi, Y.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Lepfoundzou, A.D.; et al. First Reported Chikungunya Fever Outbreak in the Republic of Congo, 2011. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biboussi, B. Epidémie de fièvre virale Chikungunya au Congo. Bulletin d’information du Bureau de la Représentation de l’OMS au Congo. 2011, N° 098 5 Juillet 2011.
- Sebastião, C.S.; Gaston, C.; Paixão, J.P.; Sacomboio, E.N.M.; Neto, Z.; de Vasconcelos, J.N.; Morais, J. Coinfection between SARS-CoV-2 and vector-borne diseases in Luanda, Angola. J Med Virol. 2021, 94, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiãoa, C.S.; Neto, Z.; Jandondo, D.; Mirandela, M.; Morais, J.; Britoa, M. Dengue virus among HIV-infected pregnant women attending antenatal care in Luanda, Angola: An emerging public health Concern. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, S.; Kutsuna, S.; Nakayama, E.; Taniguchi, S.; Tajima, S.; Katanami, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeshita, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Kato, Y.; et al. Chikungunya Fever in Traveler from Angola to Japan, 2016. Emerg.Infect.Dis. 2017, 23, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, P.F.C.; Monath, T.P. Yellow fever remains a potential threat to public health. Vector-borne and zoonotic Diseases 2016, xx, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakouné, E.; Selekon, B.; Morvan, J. Summary: Microbiological surveillance:viral haemorrhagic fevers in the Central African Republic. Santé publique. 2000, 2035. [Google Scholar]
- Obame-Nkoghe, J.; Makanga, B.K.; Zongo, S.B.; Koumba, A.A.; Komba, P.; Longo-Pendy, N.-M.; Mounioko, F.; Akone-Ella, R.; Nkoghe-Nkoge, L.-C.; Ngangue-Salamba, M.-F.; et al. Urban Green Spaces and Vector-Borne Disease Risk in Africa: Case of the Sibang Forested Park in Libreville (Gabon, CenTral Africa). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5774. [Google Scholar]
- Kamgang, B.; Happi, J.Y.; Boisier, P.; Njiokou, F.; Hervé, J.P.; Simard, F.; Paupy, C. Geographic and ecological distribution of the dengue and chikungunya virus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in three major Cameroonian towns. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Kamgang, B.; Lenga, A.; Wondji, C.S. Larval ecology and infestation indices of two major arbovirus vectors, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidea), in Brazzille, the capital city of the Republic of the Congo. Parasits Vectors, 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianney, B.J.M.; Diakaridia, F.; Yahaya, S.; Koné, A.B.; Lambert, K.K.; Sevidzem, S.L.; Acapovi -Yao, G.L. Molecular detection of arboviruses in culicidae in some sites of Côte d’Ivoire. International Journal Biology 2021, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mayi, M.P.A.; Bamou, R.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Fontaine, A.; Jeffries, C.L.; Walker, T.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Cornel, A.J.; Tchuinkam, T. Habitat and Seasonality Affect Mosquito Community Composition in the West Region of Cameroon. Insects. 2020, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Neto, J.A.; Powell, J.R.; Bonizzoni, M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infection, genetics and evolution 2019, 67, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, M.; Laganier, R.; Nangouma, A. First record of Ae. albopictus (Skuse 1894), in Central African Republic. Trop. Med. Int.Hlth. 2010, 15, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, J.E.; Diallo, M.; Janusz, K.B.; Manengu, C.; Lewis, R.F.; Perea, W.; Yactayo, S.; Sallb, A.A.; on behal of the RCA Risk Assessment Team. Yellow fever risk assessment in the Central African Republic. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 108, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoagouni, C.; Kamgang, B.; Manirakiza, A.; Nangouma, A.; Paupy, C.; Nakoune, E.; Kazanji, M. Entomological profile of yellow fever epidemics in the Central African Republic, 2006-2010. Parasit. Vector. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toto, J.-C.; Abaga, S.; Carnevaley, P.; Simard, F. First report of the oriental mosquito Aedes albopictus on the West African island of Bioko, Equatorial Guinea. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2003, 17, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Ngoagouni, C.; Manirakiza, A.; Nakoune, E.; Paupy, C.; Kazanji, M. Temporal Patterns of Abundance of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Mitochondrial DNA Analysis of Ae. albopictus in the Central African Republic. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paupy, C.; Delatte, H.; Bagny, L.; Corbel, V.; Fontenille, D. Aedes albopictus, an arbovirus vector: From the darkness to the light. Microb. Infect. 2009, 11, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paupy, C.; Kassa Kassa, F.; Caron, M.; Nkoghé, D.; Leroy, E.M. A Chikungunya Outbreak Associated with the Vector Aedes albopictus in Remote Villages of Gabon. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Dis 2012, 12, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages, F.; Peyrefitte, C.N.; Mve, M.T.; Jarjaval, F.; Brisse, S.; Iteman, I.; Gravier, P.; Nkoghe, D.; Grandadam, M. Aedes albopictus Mosquito: The Main Vector of the 2007 Chikungunya Outbreak in Gabon. PLoS ONE. 2009, 4, e4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Vazeille, M.; Tedjou, A.N.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Yougang, A.P.; Mousson, L.; Wondji, C.S.; Failloux, A.B. Risk of dengue in Central Africa: Vector competence studies with Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) populations and dengue 2 virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, F.; Nchoutpouen, E.; Toto, JC.; Fontenille, D. Geographic Distribution and Breeding Site Preference of Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in Cameroon, Central Africa. Entomological Society of America. 2005, 42, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saotoing, P.; Tchuenguem, F.N.F.; Nlôga, A.M.N. Entomological Survey on Culicidae fauna in the City of Maroua, Far North Region Cameroon. Int. J. Innovation. 2014, 9, 438–448. [Google Scholar]
- Namegni, R.S.P.; Njan-Nloga, A.M.; Wade, A.; Eisenbarth, A.; Groschup, M.H.; Stoek, F. Diversity and Abundance of Potential Vectors of Rift Valley Fever Virus in the North Region of Cameroon. Insects. 2020, 11, 814. [Google Scholar]
- Akono-Ntonga, P.; Peka-Nsangou, M.F.; Kekeunou, S.; Kojom-Fozie-Kamga, R.; Tonga, C.; Ngo-Hondt, E.; Mbida, J.A. Diversité et agressivité de la culicidofaune dans la ville de Douala, Cameroun. Faun. Entomol. 2020, 73, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kamgang, B.; Vazeille, M.; Tedjou, A.; Yougang, A.P.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Mousson, L.; Wondji, C.S.; Failloux, A.-B. Different populations of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Central Africa are susceptible to Zika virus infection. PLoS Negl. Trop 2020, 14, e0008163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talipouo, A.; Akono, P.N.; Tagne, D.; Mbida, A.M.; Etang, J.; Fobasso, R.T.; Ekoko, W.; Binyang, J.; Dongmo, A. Comparative study of Culicidae biodiversity of Manoka island and Youpwe mainland area, Littoral Cameroon. Int. J. Biosci. 2017, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ntoumba, A.A.; Foko, L.P.K.; Ekoko, W.E.; Ndongo, J.M.; Bunda, G.W.; Meva, F.E.; Lehman, L.G. Entomological characteristics of mosquitoes breeding sites in two areas of the town of Douala, Cameroon. J. Trop. Insect. Scie. Sci. 2020.
- Paupy, C.; Brengues, C.; Kamgang, B.; Herve, J.P.; Fontenille, D.; Simard, F. Gene Flow Between Domestic and Sylvan Populations of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in North Cameroon. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenille, D.; Toto, J.C. Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse), vecteur potentiel du virus de la dengue, a envahi les villes du sud du Cameroun; Maladies à transmission vectorielle en milieu urbain. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001, 7, 1066–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondt, O.E.N.; Ntonga, P.A.; Hiol, J.V.N.; Edou, D.N.; Tonga, C.; Dadji, G.A.F.; Kekeunou, S. Adaptation compétitive d’Aedes albopictus Skuse, 1894 en présence d’Aedes aegypti Linné, 1862 dans quelques gîtes larvaires temporaires de la ville de Douala (Cameroun) dans un contexte de résistance aux pyréthrinoïdes. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2020, 113, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Nana-Ndjangwo, M.S.; Nchoutpouen, E.; Makoudjou, I.; Ngangue-Siewe, I.N.; Talipouo, A.; Mayi, M.P.A.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Wondji, C.; Tchuinkam, T.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C. Aedes Mosquito Surveillance Using Ovitraps, Sweep Nets, and Biogent Traps in the City of Yaoundé, Cameroon. Insects. 2022, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayi, M.P.A.; Bamou, R.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Djojo-Tachegoum, C.; Fontaine, A.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Tchuinkam, T. A mosquito survey along a transect of urbanization in Dschang, West Region of Cameroon, reveals potential risk of arbovirus. Spillovers 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Brengues, C.; Fontenille, D.; Njiokou, F.; Simard, F.; Paupy, C. Genetic Structure of the Tiger Mosquito, Aedes albopictus, in Cameroon (Central Africa). PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e20257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakwo-Fils, E.M.; Ntonga-Akono, P.; Belong, P.; Messi, J. Impact des aménagements piscicoles sur le pullulement culicidien à Yaoundé, Cameroun. Faun. Entomol. 2009, 62, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tedjou, A.N.; Kamgang, B.; Yougang, A.P.; Njiokou, F.; Wondji, C.S. Update on the geographical distribution and prevalence of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae), two major arbovirus vectors in Cameroon. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Vazeille, M.; Youganga, A.P.; Tedjoua, A.N.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Mousson, L.; Wondji, C.S.; Failloux, A.B. Potential of Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) to transmit yellow fever virus in urban areas in Central Africa. Emerg. Microb.Infect. 2019, 8, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbida, M.A.; Etang, J.; Ntonga, A.P.; Talipouo, A.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Oke-Agbo, F.; Eboumbou, C.; Akogbéto, M.; Osse, R.; Lehman, G.; Ekoko, W.; et al. Preliminary investigation on aggressive culicidae fauna and malaria transmission in two wetlands of the Wouri river estuary, Littoral-Cameroon. J. Entomol. Zoo Stud. 2016, 4, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tedjou, A.N.; Kamgang, B.; Yougang, A.P.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Njiokou, F.; Wondji, C.S. Patterns of Ecological Adaptation of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus and Stegomyia Indices Highlight the Potential Risk of Arbovirus Transmission in Yaoundé, the Capital City of Cameroon. Pathogens. 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamgang, B.; Nchoutpouen, E.; Simard, F.; Paupy, C. Notes on the blood-feeding behavior of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Cameroon. Parasit. Vectors. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamba, R.; Koumba, A.A.; Zinga-Koumba, C.R.; Sevidzem, S.L.; Mbouloungou, A.; Yacka, L.L.; Djogbenou, L.S.; Mavoungou, J.F.; M’Batchi, B. Typology of Breeding Sites and Species Diversity of Culicids (Diptera: Culicidae) in Akanda and its Environs (North West, Gabon). European J. Biology Biotech. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, A.; Hagen, R.M. First record of Aedes albopictus in Gabon, Central Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Hlth. 2007, 12, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Dweck, H.K.M.; Lutomiah, J.; Sang, R.; McBride, C.S.; Rose, N.H.; Ayala, D.; Powell, J.R. Larval sites of the mosquito Aedes aegypti formosus in forest and domestic habitats in Africa and the potential association with oviposition evolution. Ecology and Evol. 2021, 11, 16327–16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Irving, H.; Kusimo, M.O.; Lenga, A.; Wondji, C.S. Geographical distribution of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and genetic diversity of invading population of Ae. albopictus in the Republic of the Congo. Wellcome Open Research. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kamgang, B.; Wilson-Bahun, T.A.; Yougang, A.P.; Lenga, A.; Wondji, C.S. Contrasting resistance patterns to type I and II pyrethroids in two major arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in the Republic of the Congo, Central Africa. Infect. Dis. Poverty, 2020, 9, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsindou, P.; Bantsimba-Ndziona, M.J.; Lenga, A. Distribution actuelle et caractérisations bioécologiques d’Aedes aegypti et d’Aedes albopictus dans deux arrondissements de Brazzaville. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2018, 111, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombouli, J.V.; Bitsindou, P.; Elion, D.O.A.; Grolla, A.; Feldmann, H.; Niama, F.R.; Parra, H.-J.; Vincent, J.; Munster, V.J. Chikungunya Virus Infection, Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2011. Emerg.Infect.Dis. 2018, 19, 1542–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, R.; Centeno-Lima, S.; Lopes, A.; Portugal-Calisto, D.; Constantino, A.; Nina, J. Dengue virus serotype 4 and chikungunya virus coinfection in a traveller returning from Luanda, Angola. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20730.
- Fernández, M.C.M.; Arletty, T.; Cani, P.; Flores, Y.H. Longitudinal spatial distribution of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) during the yellow fever epidemic in Angola, 2016. Glob. J. Zool. 2018, 4, 001–006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, A.Z.; Laroche, M.; Berger, F.; Parola, P. Use of MALDI-TOF MS for the Identification of Chad Mosquitoes and the Origin of Their Blood Meal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yougang, A.P.; Kamgang, B.; Wilson Bahun, T.A.; Tedjou, A.N.; Nguiffo-Nguete, D.; Njiokou, F.; Wondji, C.S. First detection of F1534C Knockdown resistance mutation in Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) from Cameroun. Infect. Dis. Poverty. 2020, 9, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Nana-Ndjangwo, M.S.; Mavridis, K.; Talipouo, A.; Nchoutpouen, E.; Makoudjou, I.; Bamou, R.; Mayi, A.M.P.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Tchuinkam, T.; Vontas, J.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C. Analyses of Insecticide Resistance Genes in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus Mosquito Populations from Cameroon. Genes. 2021, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazeille, M.; Failloux, A.N.; Mousson, L.; Elissa, N.; Roudhain, F. Receptivité orale d’Aedes aegypti formosus de Franceville (Gabon, Afrique centrale) pour le virus de la dengue de typtes 2. Bull. Soc. Path. exot. 1999, 92, 341–342. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, L.B.; Sarah, H.; Merkling, S.H.; Gautier, M.; Ghozlane, A.; Jiolle, D.; Paupy, C.; Ayala, D.; Moltini-Conclois, I.; Fontaine, A.; Lambrechts, L. Exomewide association study reveals largely distinct gene sets underlying specific resistance to dengue virus types 1 and 3 in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiolle, D.; Moltini-Conclois, I.; Obame-Nkoghe, J.; Yangari, P.; Porciani, A.; Scheid, B.; Kengne, P.; Ayala, D.; Failloux, A.B.; Paupy, C. Experimental infections with Zika virus strains reveal high vector competence of Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti populations from Gabon (Central Africa) for the African virus lineage Emerging. Microb. Infect. 2021, 10, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffinet, T.; Mourou, J.R.; Pradines, B.; Toto, J.C.; Jarjaval, F.; Amalvict, R.; Kombila, M.; Carnevale, P.; Pages, F. First record of Aedes albopictus in Gabon. journal of the American Mosquito Control Association. 2007, 23, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Cosme, L.V.; Lutomiah, J.; Sang, R.; Ngangue, M.F.; Rahola, N.; Ayala, D.; Powell, J.R. Genetic structure of the mosquito Aedes aegypti in local forest and domestic habitats in Gabon and Kenya. Parasit. Vectors. 2020, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobanga, T.; Moyo, M.; Vulu, F.; Irish, S.R. First report of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Afr. Entomol. 2018, 26, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgang, B.; Marcombe, S.; Chandre, F.; Nchoutpouen, E.; Nwane, P.; Etang, J.; Corbel, V.; Paupy, C. Insecticide susceptibility of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Central Africa. Parasit. Vectors. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saluzzo, J.F.; Vincent, T.; Miller, J.; Veas, F.; Gonzalez, J.P. Arbovirus Discovery in Central African Republic (1973- 1993): Zika, Bozo, Bouboui, and More. Annals Infect. Dis. Epidemiol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bamou, R.; Diarra, A.; Mayi, M.P.A.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Parola, P. Wolbachia Detection in Field-Collected Mosquitoes from Cameroon. Insects. 2021, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, A.M.; Gidley, A.; Mayi, M.P.A.; Bamou, R.; Dhokiya, V.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Jeffries, C.L.; Walker, T. Diverse novel Wolbachia bacteria strains and widespread co-infections with Asaia in Culicine mosquitoes from ecologically diverse regions of Cameroom. Wellcome Open Res. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar]
- Grard, G.; Moureau, G.; Charrel, R.N.; Holmes, E.C.; Gould, E.A.; de Lamballerie, X. Genomics and evolution of Aedes-borne flaviviruses. J. General Virology. 2023, 91, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariën, J.; Laurent, N.; Gombeer, S.N. First observation of Aedes albopictus in the Tshuapa province (Boende) of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. preprint. 2021.
- Canelas, T.; Thomsen, E.; Kamgang, B.; Kelly-Hope, L.A. Demographic and environmental factors associated with the distribution of Aedes albopictus in Cameroon. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2023, 37, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbodzi, B.; Sado, F.B.Y.; Simo, F.B.N.; Kumordjie, S.; Yeboah, C.; Mosore, M.-T.; Bentil, R.E.; Prieto, K.; Colston, S.M.; Attram, N.; et al. Chikungunya viruses containing the A226V mutation detected retrospectively in Cameroon form a new geographical subclade. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 113, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolovschi, C.; Pagés, F.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia felis in Aedes albopictus Mosquitoes, Libreville, Gabon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1687–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoagouni, C.; Kamgang, B.; Brengues, C.; Yahouedo, G.; Paupy, C.; Nakouné, E.; Kazanji, M.; Fabrice, C.F. Susceptibility profile and metabolic mechanisms involved in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus resistant to DDT and deltamethrin in the Central African Republic. Parasit. Vectors. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makanga, B.K.; Koumba, A.A.; Makouloutou, P.; Mougoubi, J.W.; Koumba, C.R.Z.; Mavoungou, J.F. Diversité de la culicidofaune et risques potentiels de maladies dans le Parc National de Loango au Gabon. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2022, 37, 368–377. [Google Scholar]
- Obame-Nkoghe, J.; Rahola, N.; Ayala, D.; Yangari, P.; Jiolle, D.; Allene, X.; Bourgarel, M.; Maganga, G.D.; Berthet, N.; Leroy, E.M.; Paupy, C. Exploring the diversity of bloodsucking Diptera in caves of Central Africa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irish, S.R.; Kyalo, D.; Snow, R.W.; Coetzee, M. Updated list of Anopheles species (Diptera: Culicidae) by country in the Afrotropical Region and associated islands. Zootaxa 2020, 4747, 401–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerah-Hinzoumbé, C.; Péka, M.; Nkondjio, C.A.; Donan-Gouni, I.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Samè-Ekobo, A.; Simard, F. Malaria vectors and transmission dynamics in Goulmoun, a rural city in south-western Chad. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.; Morais, J.; Martins, J.F.; Scalsky, R.J.; Stabler, T.C.; Medeiros, M.M.; Fortes, F.J.; Arez, A.P.; Silva, J.C. Malaria in Angola: recent progress, challenges and future opportunities using parasite demography studies. Malar. J. 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trape, J.F.; Zoulani, A. Malaria and urbanization in Central Africa: the example of Brazzaville: Part II: Results of entomological surveys and epidemiological analysis. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medecine and Hygiene. 1987, 81, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridl, F.C.; Bass, C.; Torrez, M.; Govender, D.; Ramdeen, V.; Yellot, L.; Edu, A.E.; Schwabe, C.; Mohloai, P.; Maharaj, R.; Kleinschmidt, I. A pre-intervention study of malaria vector abundance in Rio Muni, Equatorial Guinea: Their role in malaria transmission and the incidence of insecticide resistance alleles. Malar. J. 2008, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanga, B.; Yangari, P.; Rahola, N.; Rougeron, V.; Elguero, E.; Boudenga, L.; Moukodoum, N.D.; Okouga, A.P.; Arnathau, C.; Durand, P.; et al. Malaria transmission and potential for Ape to human transfers in Africa. PNAS (proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) Early Edittion 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuamba, N.; Choi, K.S.; Townson, H. Malaria vectors in Angola: Distribution of species and molecular forms of the Anopheles gambiae complex, their pyrethroid insecticide knockdown resistance (kdr) status and Plasmodium. Malar. J. 2006, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, H.J.; Sæbo, S.; Reddy, M.R.; Reddy, V.P.; Abaga, S.; Matias, A.; Slotman, M.A. Light traps fail to estimate reliable malaria mosquitobiting rates on Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea. Malar. J. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Koumba, A.A.; Koumba, C.R.Z.; Nguema, R.M.; Zahouli, B.J.Z.; Ovono, A.M.; Souza, A.; Ketoh, G.K.; Djogbenou, L.S.; M’batchi, B.; Mavoungou, J.F. Preliminary evaluation of the insecticide susceptibility in the Culicid Fauna, particularity Malaria plasmodium and Arbovirus vectors in the region of Mouila, South-West GABON. Indian J. Med. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Tezzo, F.W.; Fasine, S.; Zola, E.M.; Marquetti, M.C.; Mbuka, G.B.; Ilombe, G.; Takasongo, R.M.; Smitz, N.; Bisset, J.A.; Bortel, W.V.; Vanlerberghe, V. Parasites High Aedes spp. larval indices in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo. Vectors. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Mayi, M.P.A.; Foncha, D.F.; Kowo, C.; Tchuinkam, T.; Brisco, K.; Anong, D.N.; Ravinder, S.; Cornel, A.J. Impact of deforestation on the abundance, diversity, and richness of Culex mosquitoes in a southwest Cameroon tropical rainforest. J. Vector Ecology. 2019, 44, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoufounna, J.; Mayi, M.P.A.; Bamou, R.; Ningahi, L.G.; Magatsing, F.O.; Djiappi-Tchamen, B.; Djamouko-Djonkam, L.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Tchuinkam, T. Larval habitats characterization and population dynamics of Culex mosquitoes in two localities of the Menoua Division, Dschang and Santchou, West Cameroon. The J. Basic and Appl. Zoo. 2022, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordelier, R.; Geoffroy, B. Contribution à l’étude des Culicides de la République Centrafricaine Rythmes d’activités en Secteur Préforestier. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M., Em. méd. et Parasitol. 1974, 12, 19–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bouree, P.; Ensaf, A. Aedes albopictus: A multifunctional mosquito. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Braack, L.; d’Almeida, A.P.G.; Cornel, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; de Jage, C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: review of key viruses and vectors. Parasit. Vectors. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, P. Fièvre à virus Chikungunya: Progrès en Pédiatrie, France. Ed.Pédiatrie tropicale et des voyages. 2012, Chapitre 25, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Turell, M.; Linthicum, K.J.; Patrican, L.A.; Davies, F.G.; Kairo, A.; Bailey, C.L. Vector Competence of Selected African Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) Species for Rift Valley Fever Virus. Vect.Path.Host.Int.Trans 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, C.C. Etude Bibliographique des zoonoses en côte d’ivoire. Ecole National de vétérinaire Toulouse 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cornet, M.; Robin, Y.; Château, R.; Heme, G.; Adam, C.; Valade, M.; Le Gonidec, G.; Jan, C.; Renaudet, J.; Dieng, P.L.; et al. Isolements d’arbovirus au Sénégal Oriental h partir de moustiques (19724977) et notes sur l’épidémiologie des virus transmis par les Aedes, en particulier du virus amaril. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M., sér. Ent. méd. et Parasitol. 1979, 17, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, T.C.; Lemenager, D.A.; Kluh, S.; Carrol, B.D.; Lothrop, H.D.; Keisen, W.K. Spatial Variation in Host Feeding Patterns of Culex tarsalis and the Culex pipiens complex (Diptera: Culicidae) in California. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Cordelier, R.; Geoffroy, B. Observqtions sur les vecteurs potentiels de la fievre jaune en Républiaque Centrafricaine. Cah. ORSTM., Sér. Ent. Méd. Et Parasitol. 1972, x, 127–144, acces autorisé via le site https://horizon.documentation.ird.fr. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Vector-borne diseases. 2020 Available online from www.who.int.
- Armindo, R.F.; Manuel, R.P. Arbovirus studies in Luanda, Angola. Bull. Wld Hith Org. 1973, 49, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, M.; Robin, Y.; Geoffrey, B.; Cornet, M.; Vauchez, M.F. Isolements du virus de la fièvre jaune à partir d’Aedes du groupe A. africanus (Theobald) en République Centrafricaine. Importance des savanes humides et semi-humides en tant que zone d’émergence du virus amaril. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M., sér. Ent. méd. et Parasitol. 1976, XIV, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Obame-Nkoghe, J.; Roiz, D.; Ngangue, M.F.; Costantini, C.; Rahola, N.; Jiolle, D.; Lehmann, D.; Makaga, L.; Ayala, D.; Kengne, P.; et al. Invasion of forested areas in Gabon (Central Africa) by the Asian tiger mosquito and the potential consequences from the One Health perspective. 2022.
- Huang, Y.-M. The subgenus Stegomyia of Aedes in the Afrotropical Region with keys to the species (Diptera: Culicidae). Zootaxa 2019, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokernot, R.H.; Paterso, H.E.; De Meillon, B. Studies on the transmission of wesselsbron virus by Aedes (Oclherotatus) Caballus (Theo). Medical J. 1958. [Google Scholar]
- White, G.B. Notes on a Catalogue of Culicidae of the Ethiopian Region. Mosquito Systematics. 1975, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, M. Dynamique comparée des populations de Culicidae à Kédougou (zone soudano-guinéenne) et à Barkédji (zone de savane sahélienne): conséquences dans la transmission des arbovirus. Université Cheikh Anta Diop de Dakar Faculté des Sciences et Techniques. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.M.; Rueda, L. A pictorial key to the sections, groups, and species of the Aedes (Diceromyia) in the Afrotropical Region (Diptera: Culicidae). Zootaxa. 2016, 4079, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, R. Les moustiques: Histoire Naturelle et Médicale. Paris SFR de Rudeval, 1905, Imprimeur -éditeur 4.
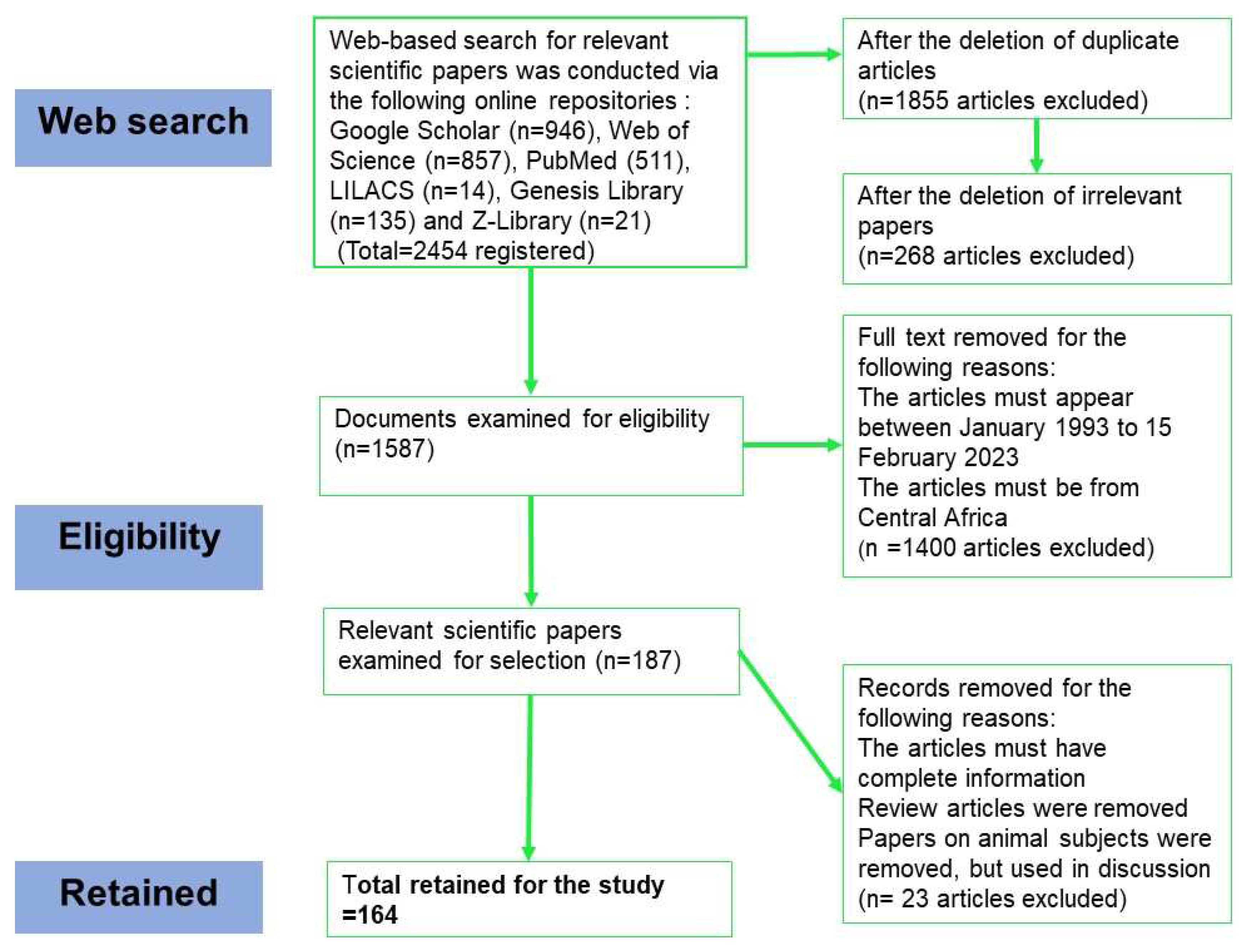
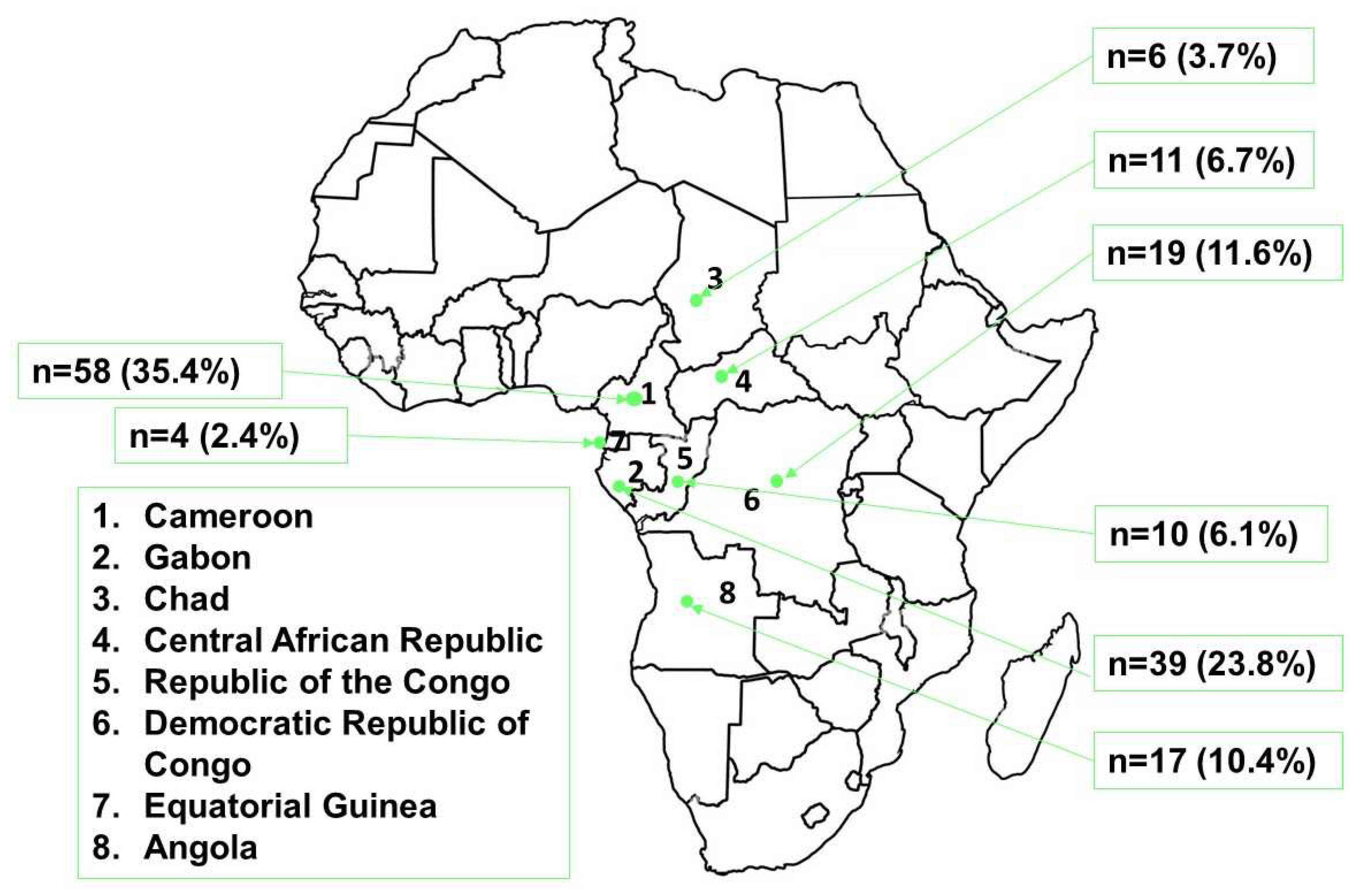
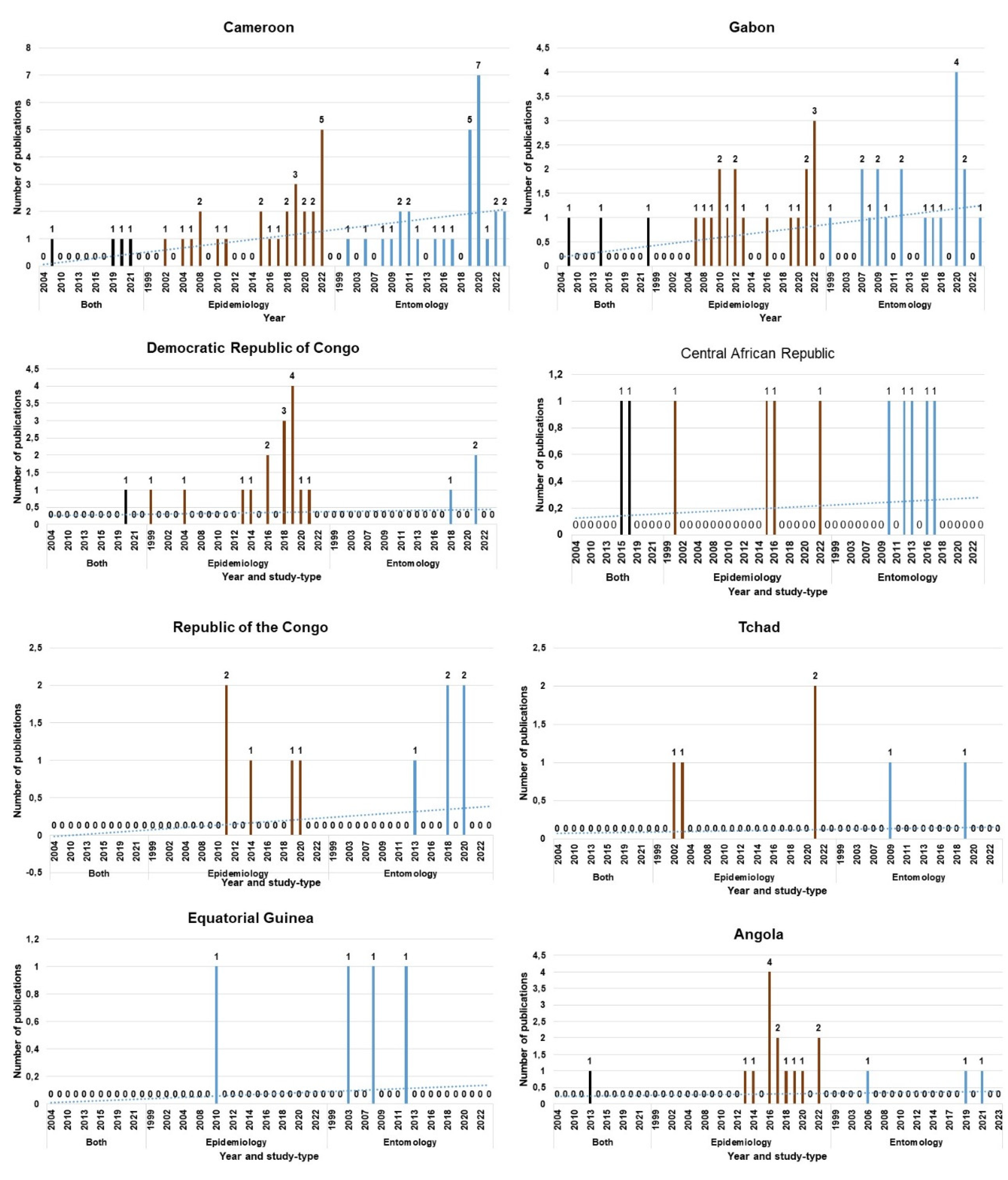
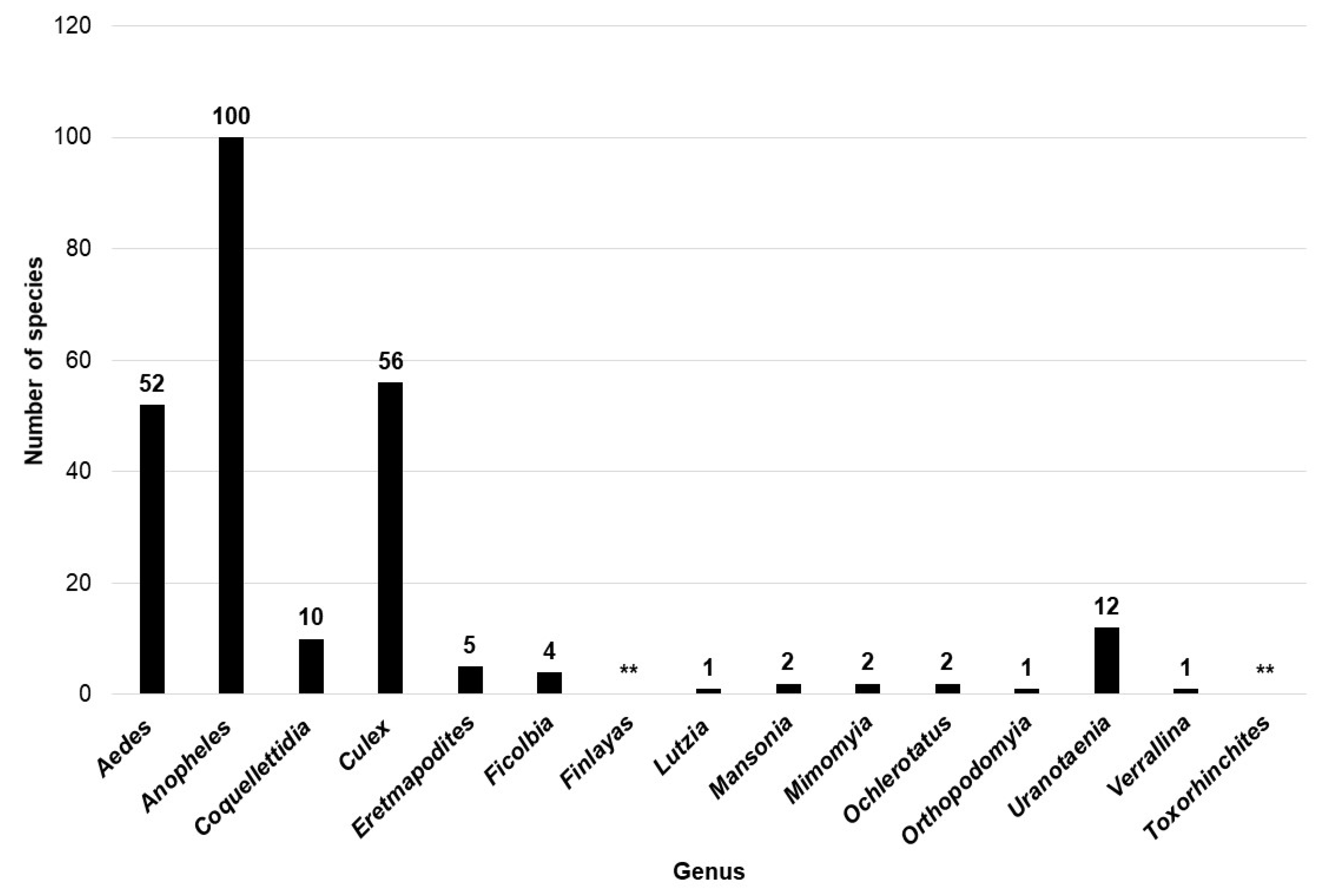
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





