Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
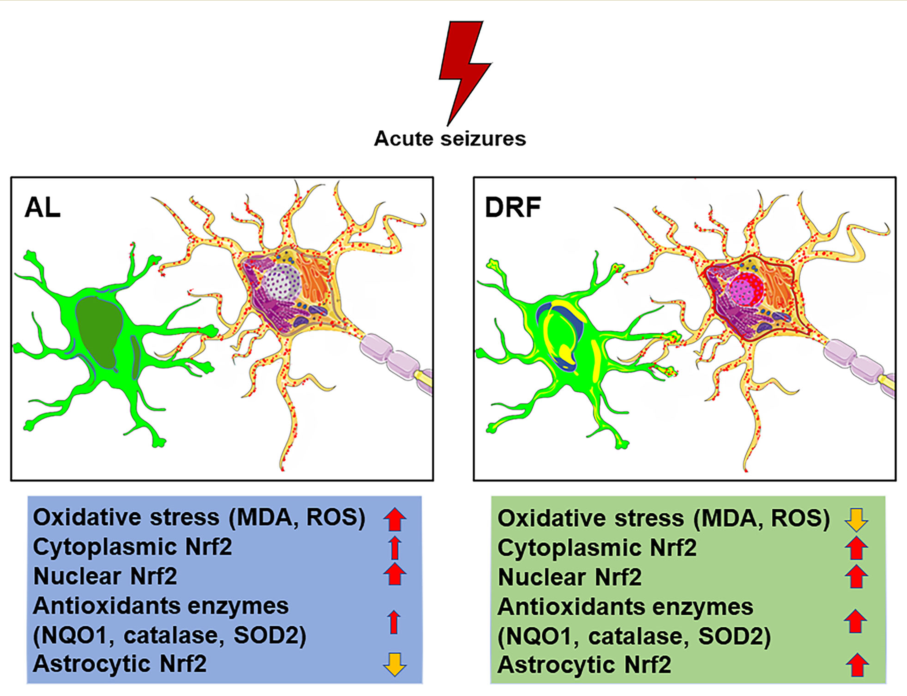
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental animals.
2.2. Daytime-restricted feeding and pilocarpine-induced seizure model.
2.3. Determination of lipid peroxidation.
2.4. Determination of reactive oxygen species in hippocampi.
2.5. Western blotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry
2.7. Confocal microscopy analysis
2.8. Statistical analysis
3. Results
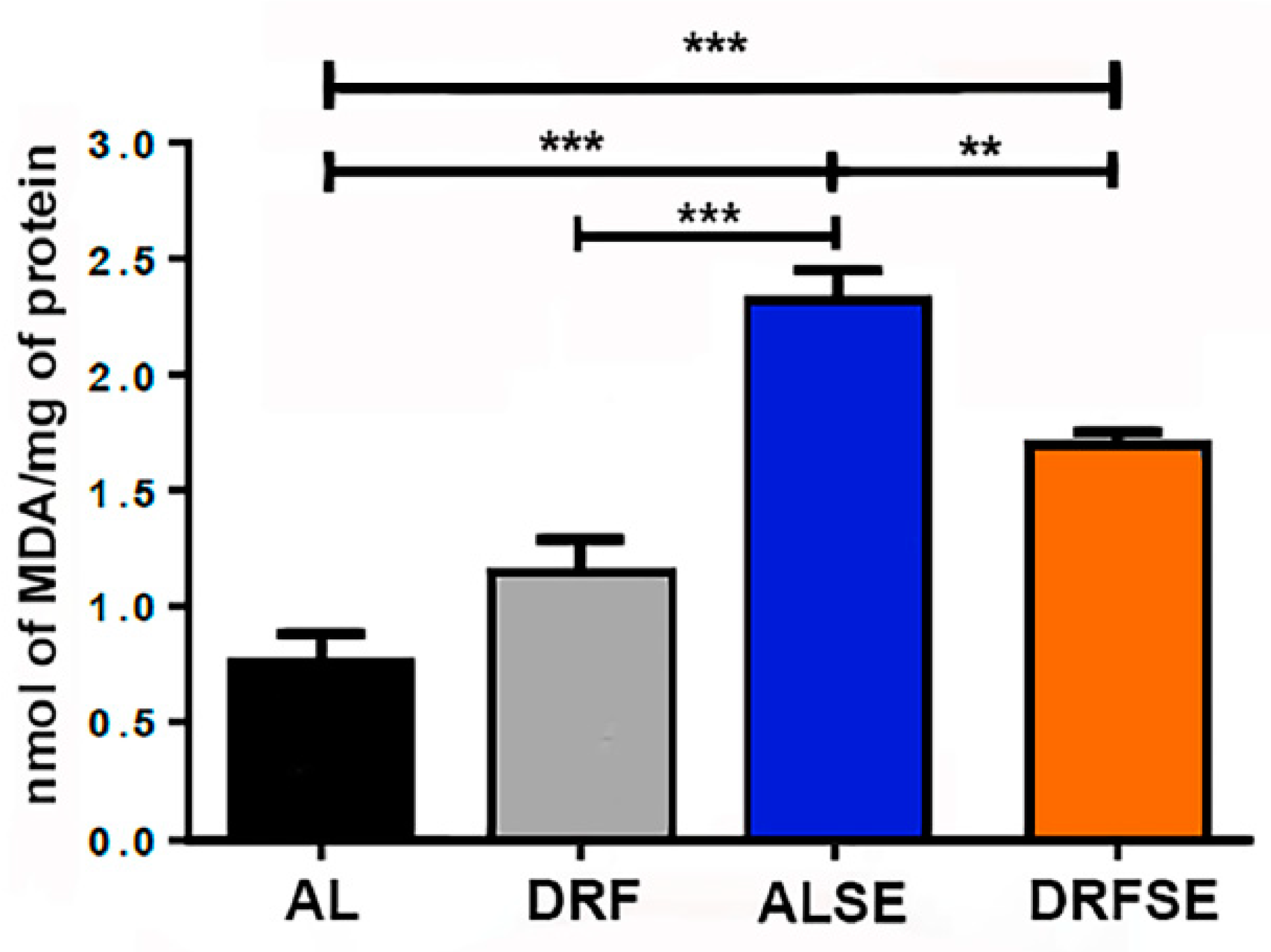
3.1. Dietary restriction reduces the levels of malondialdehyde in seizure-induced animals.
3.2. Daytime-restricted feeding reduces the levels of reactive oxygen species in seizure-induced animals in CA1 and CA3 hippocampal regions.
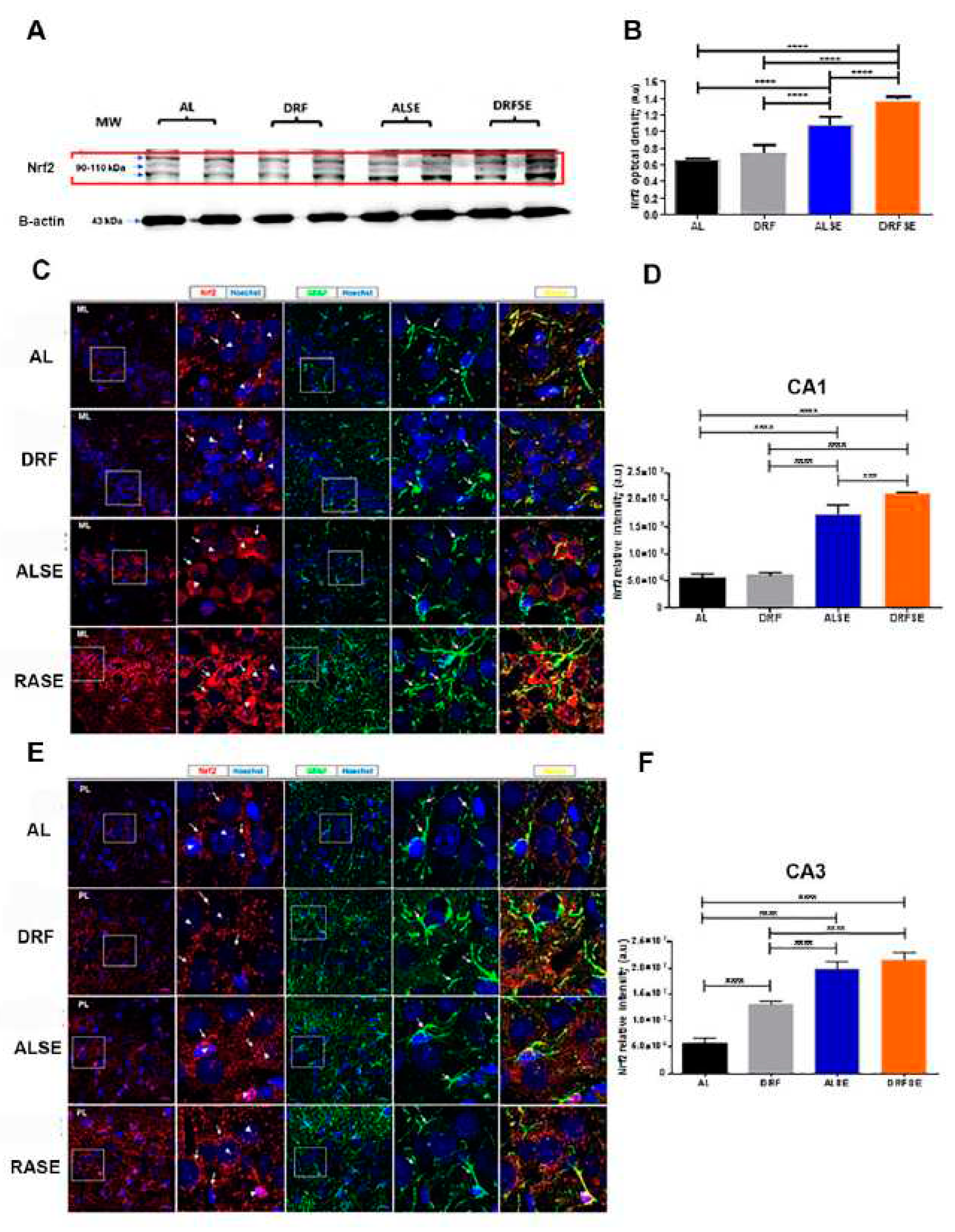
3.3. Daytime-restricted feeding modulates the content of the Nrf2 transcriptional factor in hippocampal homogenates and increases the Nrf2 immunostaining in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons in the SE model.
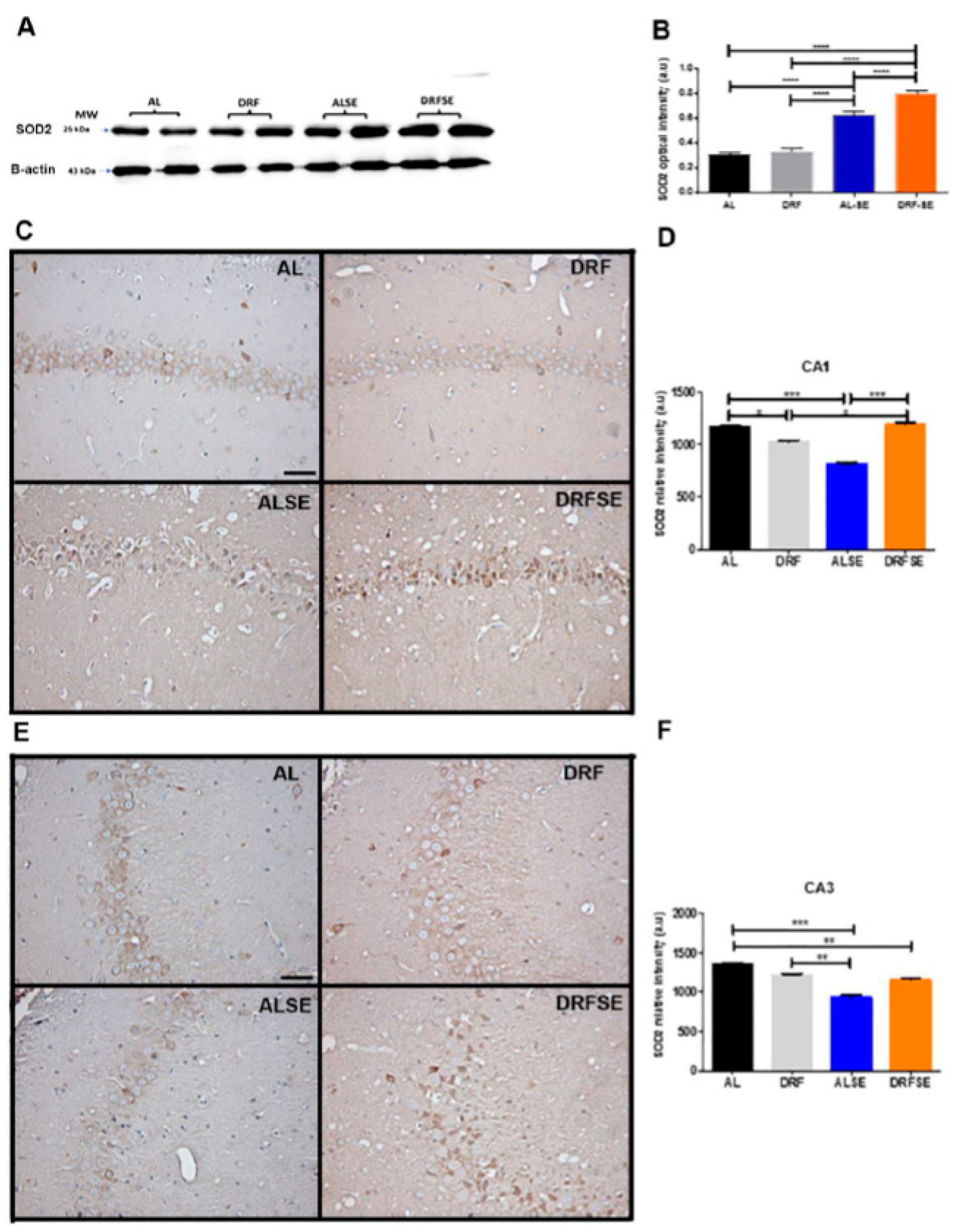
3.4. Daytime-restricted feeding increases the content of superoxide dismutase 2 in hippocampal homogenates and the immunostaining in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons after the acute seizure model.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data availability statement
Acknowledgments
Disclosure statement
References
- Thijs, R.D.; Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manford, M. Recent advances in epilepsy. J Neurol 2017, 264, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinka, E.; Höfler, J.; Leitinger, M.; Brigo, F. Pharmacotherapy for Status Epilepticus. Drugs 2015, 75, 1499–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, W.K.; Ko, K.H.; Bach, J.H.; Hong, J.S.; Yoneda, Y.; Kim, H.C. Role of oxidative stress in epileptic seizures. Neurochem Int. 2011, 59, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson-Smith, J.N.; Patel, M. Metabolic Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 18, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekh-Ahmad, T.; Kovac, S.; Abramov, A.Y.; Walker, M.C. Reactive oxygen species in status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 101, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Chen, T.Y.; Hsu, K.S.; Wu, H.M. NADPH oxidases as potential pharmacological targets against increased seizure susceptibility after systemic inflammation. J Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in seizure-induced neuronal cell death. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2010, 19, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Guan, Q.W.; Chen, F.H.; Xia, Q.X.; Yin, X.X.; Zhou, H.H.; Mao, X.Y. Antioxidants targeting mitochondrial oxidative stress: promising neuroprotectants for epilepsy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020, 6687185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unoki, T.; Akiyama, M.; Kumagai, Y. Nrf2 Activation and its coordination with the protective defense systems in response to electrophilic stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Kobori, N.; Aronowski, J.; Dash, P.K. Sulforaphane reduces infarct volume following focal cerebral ischemia in rodents. Neurosci Lett. 2006, 393, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, A.L. Neuroprotection in metabolism-based therapy. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 100, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgrave-Gómez, J.; Mercado-Gómez, O.F.; Vázquez-García, M.; Rodríguez-Molina, V.; Córdova-Dávalos, L.; Arriaga-Ávila, V.; Miranda-Martínez, A.; Guevara-Guzmán, R. Anticonvulsant effect of time-restricted feeding in a pilocarpine-induced seizure model: Metabolic and epigenetic implications. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán-Cigales, J.J.; Mercado-Gómez, O.F.; Arriaga-Ávila, V.; Landgrave-Gómez, J.; Guevara-Guzmán, R. Daytime-restricted feeding modulates the expression of inflammatory mediators and diminishes reactive astrogliosis and microgliosis following status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2020, 1734, 146724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, R.J.; Gartner, J.G.; Burnham, W.M. Epileptiform activity and neural plasticity in limbic structures. Brain Res. 1972, 47, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.G.; Trabesinger, A.H.; Boesiger, P.; Wieser, H.G. Brain glutathione levels in patients with epilepsy measured by in vivo (1) H-MRS. Neurology 2001, 57, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N.; Coballase-Urrutia, E.; Pérez-Cruz, C.; Montesinos-Correa, H.; Rivera-Espinosa, L.; Sampieri, A., 3rd; Carmona-Aparicio, L. Relevance of the glutathione system in temporal lobe epilepsy: evidence in human and experimental models. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014, 759293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E. The dentate gyrus and temporal lobe epilepsy: An “exciting” era. Epilepsy Curr. 2019, 19, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. CDDO-Me attenuates astroglial autophagy via Nrf2-, ERK1/2-SP1- and Src-CK2-PTEN-PI3K/AKT-mediated signaling pathways in the hippocampus of chronic epilepsy rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonsêca, D.V.; da Silva Maia Bezerra Filho, C.; Lima, T.C.; de Almeida, R.N.; de Sousa, D.P. Anticonvulsant essential oils and their relationship with oxidative stress in epilepsy. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.R.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Hagenn, M.; Siqueira, I.R.; Araújo, E.; Torres, I.L.; Gottfried, C.; Netto, C.A.; Gonçalves, C.A. Ketogenic diet increases glutathione peroxidase activity in rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 2003, 28, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalouf, M.; Sullivan, P.G.; Davis, L.; Kim, D.Y.; Rho, J.M. Ketones inhibit mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species production following glutamate excitotoxicity by increasing NADH oxidation. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzuferi, M.; Kumar, G.; van Eyll, J.; Danis, B.; Foerch, P.; Kaminski, R.M. Nrf2 defense pathway: Experimental evidence for its protective role in epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 2013, 74, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.P.; Zhang, G.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Xie, T.; Kan, M.C.; Fang, H.B.; Wang, H.C. Activation of Nrf2-ARE signal pathway in hippocampus of amygdala kindling rats. Neurosci Lett. 2013, 543, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, A.M.; Al Kury, L.T.; Alattar, A.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, A.J.; Alshaman, R.; Shah, F.A.; Khan, A.U.; Feng, J.; Li, S. Carveol Attenuates seizure severity and neuroinflammation in pentylenetetrazole-kindled epileptic rats by regulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021, 9966663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fang, H.; Wang, H.; Zang, H.; Xie, T.; Wang, W. Activation of Nrf2-ARE signal pathway protects the brain from damage induced by epileptic seizure. Brain Res. 2014, 1544, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Lv, C.; Cao, P. Neuroprotection of edaravone on the hippocampus of kainate-induced epilepsy rats through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Neurochem Int. 2018, 112, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Vijayanti, S.; Saha, L.; Bhatia, A.; Banerjee, D.; Chakrabarti, A. Neuroprotective effect of Nrf2 activator dimethyl fumarate, on the hippocampal neurons in chemical kindling model in rat. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 143, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguía-Martínez, M.F.; Nava-Ruíz, C.; Ruíz-Díaz, A.; Díaz-Ruíz, A.; Yescas-Gómez, P.; Méndez-Armenta, M. Immunohistochemical study of antioxidant enzymes regulated by Nrf2 in the models of epileptic seizures (KA and PTZ). Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019, 1327986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Steinhäuser, C. Role of astrocytes in epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015, 5, a022434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Steinhäuser, C. Astrocytes and Epilepsy. Neurochem Res. 2021, 46, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.E.; Kwak, S.E.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, D.W.; Kwon, O.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, T.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of astroglial death in the rat hippocampo-entorhinal complex following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Comp Neurol. 2008, 511, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, S.; Patel, M. Mitochondrial involvement and oxidative stress in temporal lobe epilepsy. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013, 62, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluck, M.R.; Jayatilleke, E.; Shaw, S.; Rowan, A.J.; Haroutunian, V. CNS oxidative stress associated with the kainic acid rodent model of experimental epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 39, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantseva, M.V.; Perez-Velazquez, J.L.; Tsoraklidis, G.; Mendonca, A.J.; Adamchik, Y.; Mills, L.R.; Carlen, P.L.; Burnham, M.W. Oxidative stress is involved in seizure-induced neurodegeneration in the kindling model of epilepsy. Neuroscience. 2000, 97, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, F.R.; He, C.; Danes, J.M.; Paviani, V.; Coelho, D.R.; Gantner, B.N.; Bonini, M.G. Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase: What the established, the intriguing, and the novel reveal about a key cellular redox switch. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.P.; Waldbaum, S.; Rowley, S.; Huang, T.T.; Day, B.J.; Patel, M. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and epilepsy in SOD2 deficient mice: attenuation by a lipophilic metalloporphyrin. Neurobiol Dis. 2012, 45, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.E.; Pearson-Smith, J.N.; Huynh, C.Q.; Fabisiak, T.; Liang, L.P.; Aivazidis, S.; High, B.A.; Buscaglia, G.; Corrigan, T.; Valdez, R.; Shimizu, T.; Patel, M.N. Neuron-specific mitochondrial oxidative stress results in epilepsy, glucose dysregulation and a striking astrocyte response. Neurobiol Dis. 2021, 158, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




