Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blackgrass populations, plant material, and genomic DNA extraction
2.2. EccDNA sequence enrichment, sequencing, and analysis
3. Results
3.1. EccDNA content and coding structure in multiple blackgrass populations
3.2. Coding content of eccDNAs in herbicide resistant and sensitive blackgrass populations
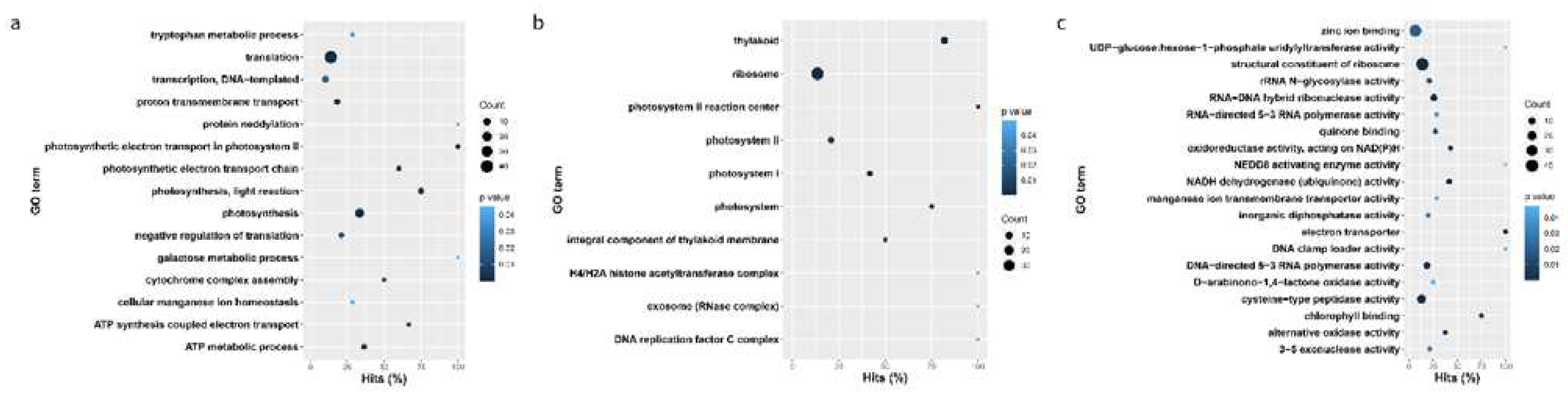
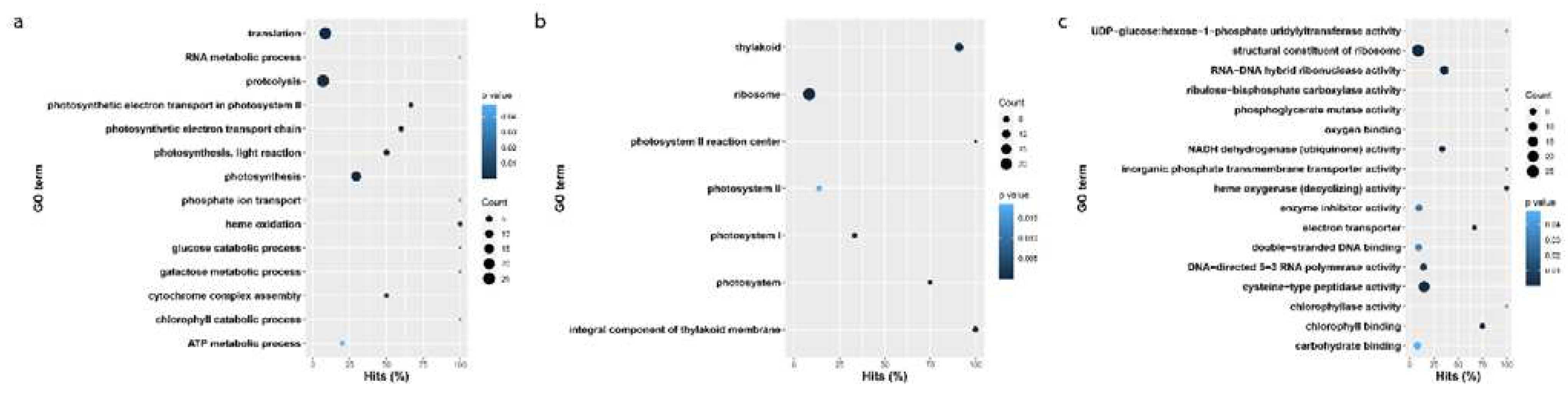
3.3. Gene ontology enrichment of blackgrass eccDNA
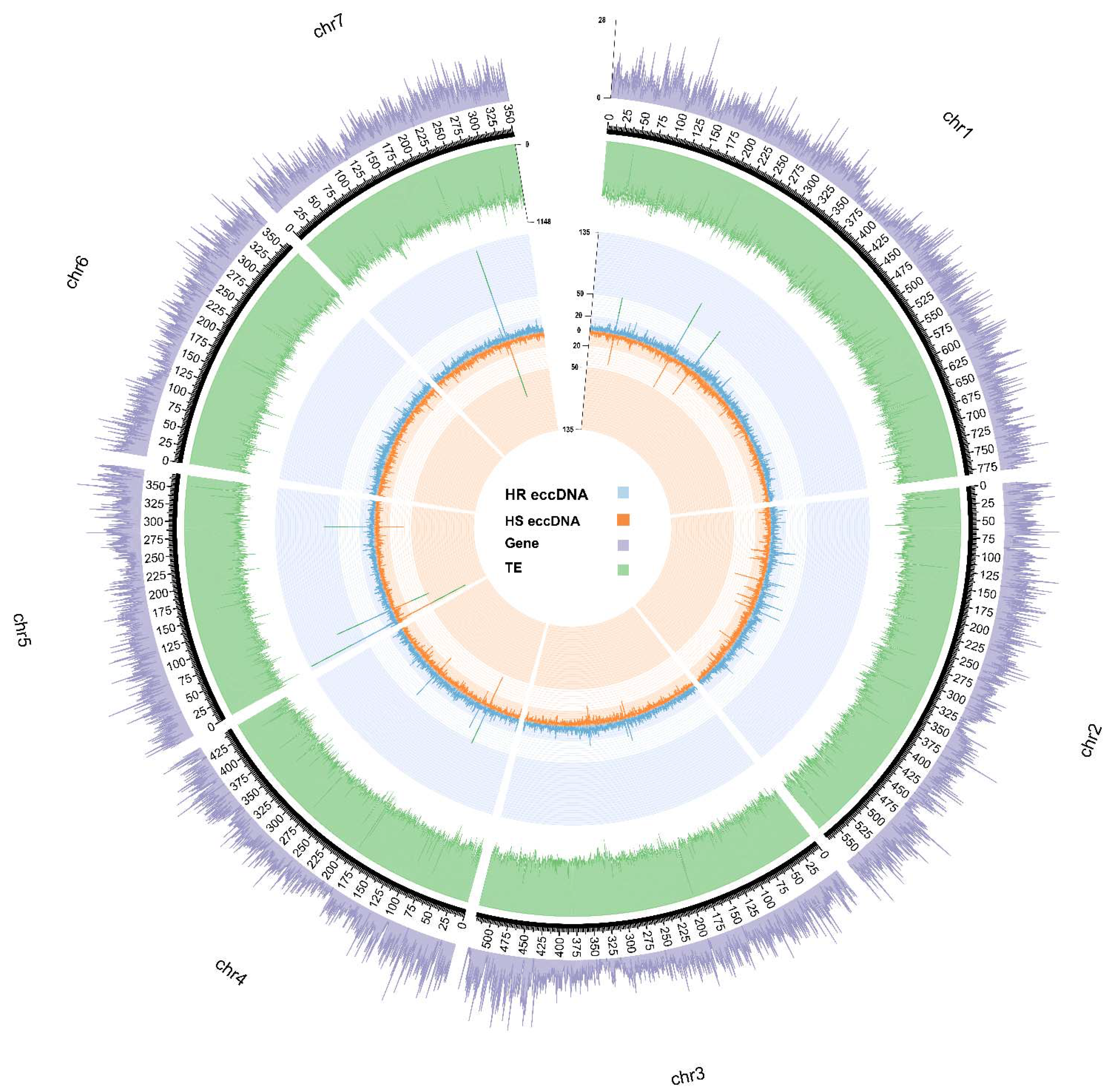
3.4. Genomic origins of blackgrass eccDNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spier Camposano H, Molin WT, Saski CA: Sequence characterization of eccDNA content in glyphosate sensitive and resistant Palmer amaranth from geographically distant populations. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0260906.
- Gaubatz JW: Extrachromosomal circular DNAs and genomic sequence plasticity in eukaryotic cells. Mutat Res 1990, 23, 271–292.
- Cohen S, Menut S, Mechali M: Regulated formation of extrachromosomal circular DNA molecules during development in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol 1999, 19, 6682–6689. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen S, Yacobi K, Segal D: Extrachromosomal circular DNA of tandemly repeated genomic sequences in Drosophila. Genome Res 2003, 13, 1133–1145. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller HD, Parsons L, Jorgensen TS, Botstein D, Regenberg B: Extrachromosomal circular DNA is common in yeast. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2015, 112, E3114–E3122.
- Peng HR, Mirouze M, Bucher E: Extrachromosomal circular DNA: A neglected nucleic acid molecule in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2022, 69.
- Hotta Y, Bassel A: Molecular Size and Circularity of DNA in Cells of Mammals and Higher Plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1965, 53, 356–362. [CrossRef]
- Mansisidor A, Molinar T, Srivastava P, Dartis DD, Delgado AP, Blitzblau HG, Klein H, Hochwagen A: Genomic Copy-Number Loss Is Rescued by Self-Limiting Production of DNA Circles. Mol Cell 2018, 72, 583–+. [CrossRef]
- Paulsen T, Kumar P, Koseoglu MM, Dutta A: Discoveries of Extrachromosomal Circles of DNA in Normal and Tumor Cells. Trends Genet 2018, 34, 270–278. [CrossRef]
- Kilzer JM, Stracker T, Beitzel B, Meek K, Weitzman M, Bushman FD: Roles of host cell factors in circularization of retroviral DNA. Virology 2003, 314, 460–467. [CrossRef]
- Molin WT, Yaguchi A, Blenner M, Saski CA: The EccDNA Replicon: A Heritable, Extranuclear Vehicle That Enables Gene Amplification and Glyphosate Resistance in Amaranthus palmeri. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2132–2140. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfinkel DJ, Stefanisko KM, Nyswaner KM, Moore SP, Oh J, Hughes SH: Retrotransposon suicide: Formation of Ty1 circles and autointegration via a central DNA flap. J Virol 2006, 80, 11920–11934. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande V, Luebeck J, Nguyen ND, Bakhtiari M, Turner KM, Schwab R, Carter H, Mischel PS, Bafna V: Exploring the landscape of focal amplifications in cancer using AmpliconArchitect. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 392. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta D, Cornet L, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Zaidi SS, Vanderschuren H: Full-length sequencing of circular DNA viruses and extrachromosomal circular DNA using CIDER-Seq. Nat Protoc 2020, 15, 1673–1689. [CrossRef]
- Moller HD: Circle-Seq: Isolation and Sequencing of Chromosome-Derived Circular DNA Elements in Cells. Methods Mol Biol 2020, 2119, 165–181.
- Turner KM, Deshpande V, Beyter D, Koga T, Rusert J, Lee C, Li B, Arden K, Ren B, Nathanson DA et al: Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification drives tumour evolution and genetic heterogeneity. Nature 2017, 543, 122–+. [CrossRef]
- Wu S, Turner KM, Nguyen N, Raviram R, Erb M, Santini J, Luebeck J, Rajkumar U, Diao Y, Li B et al: Circular ecDNA promotes accessible chromatin and high oncogene expression. Nature 2019, 575, 699–703. [CrossRef]
- Shibata Y, Kumar P, Layer R, Willcox S, Gagan JR, Griffith JD, Dutta A: Extrachromosomal microDNAs and chromosomal microdeletions in normal tissues. Science 2012, 336, 82–86. [CrossRef]
- Koo DH, Molin WT, Saski CA, Jiang J, Putta K, Jugulam M, Friebe B, Gill BS: Extrachromosomal circular DNA-based amplification and transmission of herbicide resistance in crop weed Amaranthus palmeri. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2018, 115, 3332–3337. [CrossRef]
- Molin WT, Yaguchi A, Blenner M, Saski CA: Autonomous replication sequences from the Amaranthus palmeri eccDNA replicon enable replication in yeast. BMC Res Notes 2020, 13, 330.
- Cohen S, Segal D: Extrachromosomal circular DNA in eukaryotes: possible involvement in the plasticity of tandem repeats. Cytogenet Genome Res 2009, 124, 327–338. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker SP, Grant PA: The SAGA continues: expanding the cellular role of a transcriptional co-activator complex. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5329–5340. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrup K, Yang Y: Cell cycle regulation in the postmitotic neuron: oxymoron or new biology? Nat Rev Neurosci 2007, 8, 368–378. [CrossRef]
- Molin WT, Wright AA, Lawton-Rauh A, Saski CA: The unique genomic landscape surrounding the EPSPS gene in glyphosate resistant Amaranthus palmeri: a repetitive path to resistance. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 91.
- Moller HD, Mohiyuddin M, Prada-Luengo I, Sailani MR, Halling JF, Plomgaard P, Maretty L, Hansen AJ, Snyder MP, Pilegaard H et al: Circular DNA elements of chromosomal origin are common in healthy human somatic tissue. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1069. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ain Q, Schmeer C, Wengerodt D, Witte OW, Kretz A: Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: Current Knowledge and Implications for CNS Aging and Neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21.
- Tomaska L, Nosek J, Kramara J, Griffith JD: Telomeric circles: universal players in telomere maintenance? Nat Struct Mol Biol 2009, 16, 1010–1015. [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco G, Huda A, Galli M, Piccini D, Giannattasio M, Pessina F, Doksani Y: Telomere damage induces internal loops that generate telomeric circles. Nature Communications 2020, 11.
- Hull RM, King M, Pizza G, Krueger F, Vergara X, Houseley J: Transcription-induced formation of extrachromosomal DNA during yeast ageing. Plos Biol 2019, 17.
- Gresham D, Usaite R, Germann SM, Lisby M, Botstein D, Regenberg B: Adaptation to diverse nitrogen-limited environments by deletion or extrachromosomal element formation of the GAP1 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 18551–18556. [CrossRef]
- Moss SR, Perryman SAM, Tatnell LV: Managing herbicide-resistant blackgrass (Alopecurus myosuroides): Theory and practice. Weed Technol 2007, 21, 300–309. [CrossRef]
- Hicks HL, Comont D, Coutts SR, Crook L, Hull R, Norris K, Neve P, Childs DZ, Freckleton RP: The factors driving evolved herbicide resistance at a national scale. Nat Ecol Evol 2018, 2, 529–536. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heap I: The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. 2023.
- Varah A, Ahodo K, Coutts SR, Hicks HL, Comont D, Crook L, Hull R, Neve P, Childs DZ, Freckleton RP et al: The costs of human-induced evolution in an agricultural system. Nat Sustain 2020, 3, 63–71.
- Comont D, Lowe C, Hull R, Crook L, Hicks HL, Onkokesung N, Beffa R, Childs DZ, Edwards R, Freckleton RP et al: Evolution of generalist resistance to herbicide mixtures reveals a trade-off in resistance management. Nature Communications 2020, 11.
- Cai L, Comont D, MacGregor D, Lowe C, Beffa R, Neve P, Saski C: The blackgrass genome reveals patterns of non-parallel evolution of polygenic herbicide resistance. New Phytologist 2023, 237, 1891–1907. [CrossRef]
- Mellado-Sánchez M, McDiarmid F, Cardoso V, Kanyuka K, MacGregor DR: Virus-mediated transient expression techniques enable gene function studies in black-grass. Plant Physiology 2020, 183, 455–459. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li W, Godzik A: Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RepeatMasker Open-4.0. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org.
- Cantarel BL, Korf I, Robb SM, Parra G, Ross E, Moore B, Holt C, Sanchez Alvarado A, Yandell M: MAKER: an easy-to-use annotation pipeline designed for emerging model organism genomes. Genome Res 2008, 18, 188–196. [CrossRef]
- Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A: Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 2010, 11.
- Villanueva RAM, Chen ZJ: ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd edition. Meas-Interdiscip Res 2019, 17, 160–167.
- Chan PP, Lowe TM: GtRNAdb: a database of transfer RNA genes detected in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, D93–D97. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li H: Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 45. Quinlan AR: BEDTools: The Swiss-Army Tool for Genome Feature Analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2014, 11, 11–34.
- Tetard-Jones C, Sabbadin F, Moss S, Hull R, Neve P, Edwards R: Changes in the proteome of the problem weed blackgrass correlating with multiple-herbicide resistance. Plant J 2018, 94, 709–720. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins I, Cole DJ, Edwards R: A role for glutathione transferases functioning as glutathione peroxidases in resistance to multiple herbicides in black-grass. The Plant Journal 1999, 18, 285–292. [CrossRef]
- Cai L, Comont D, MacGregor D, Lowe C, Beffa R, Neve P, Saski C: The blackgrass genome reveals patterns of non-parallel evolution of polygenic herbicide resistance. New Phytol 2022.
- Li R, Wang Y, Li J, Zhou X: Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA): an emerging star in cancer. Biomark Res 2022, 10, 53.
- Fan W, Wang L, Chu J, Li H, Kim EY, Cho J: Tracing Mobile DNAs: From Molecular to Population Scales. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 837378. [CrossRef]
- Conde A, Chaves MM, Geros H: Membrane transport, sensing and signaling in plant adaptation to environmental stress. Plant Cell Physiol 2011, 52, 1583–1602. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Wang B, Yuan F: The Role of Transmembrane Proteins in Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Responses. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23.
- Pu XJ, Lv X, Tan TH, Fu FQ, Qin GW, Lin HH: Roles of mitochondrial energy dissipation systems in plant development and acclimation to stress. Ann Bot-London 2015, 116, 583–600. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto P, Koltun A, Nonato J, Yassitepe J, Maia IG, Arruda P: Metabolism and Signaling of Plant Mitochondria in Adaptation to Environmental Stresses. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23.
- Phukan UJ, Jeena GS, Shukla RK: WRKY Transcription Factors: Molecular Regulation and Stress Responses in Plants. Front Plant Sci 2016, 7, 760.
- Wang H, Chen W, Xu Z, Chen M, Yu D: Functions of WRKYs in plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci 2023, 28, 630–645. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li J, Han G, Sun C, Sui N: Research advances of MYB transcription factors in plant stress resistance and breeding. Plant Signal Behav 2019, 14, 1613131. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang LD, Jia RB, Ge TX, Ge SF, Zhuang A, Chai PW, Fan XQ: Extrachromosomal circular DNA: biogenesis, structure, functions and diseases. Signal Transduct Tar 2022, 7.
- Cao X, Wang S, Ge L, Zhang W, Huang J, Sun W: Corrigendum: Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: Category, Biogenesis, Recognition, and Functions. Front Vet Sci 2021, 8, 784611. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Chen X, Yu F, Ding H, Zhang Y, Wang K: Extrachromosomal Circular DNAs: Origin, formation and emerging function in Cancer. Int J Biol Sci 2021, 17, 1010–1025. [CrossRef]
- Chitwood DG, Wang Q, Klaubert SR, Green K, Wu CH, Harcum SW, Saski CA: Microevolutionary dynamics of eccDNA in Chinese hamster ovary cells grown in fed-batch cultures under control and lactate-stressed conditions. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 1200. [CrossRef]
- Chitwood DG, Uy L, Fu W, Klaubert SR, Harcum SW, Saski CA: Dynamics of Amino Acid Metabolism, Gene Expression, and Circulomics in a Recombinant Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Line Adapted to Moderate and High Levels of Extracellular Lactate. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14.
- Joubert PM, Krasileva KV: The extrachromosomal circular DNAs of the rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae contain a wide variety of LTR retrotransposons, genes, and effectors. BMC Biol 2022, 20, 260.
- Sen MK, Hamouzova K, Kosnarova P, Roy A, Soukup J: Herbicide resistance in grass weeds: Epigenetic regulation matters too. Frontiers in Plant Science 2022, 13.
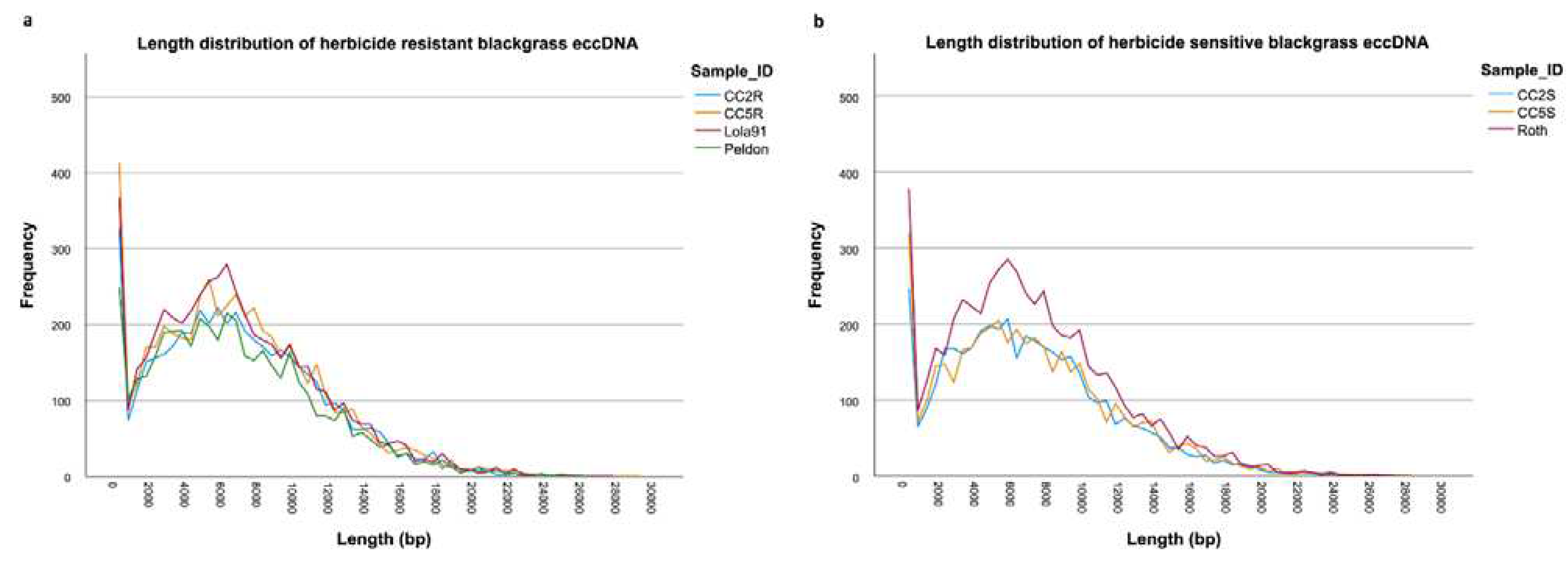
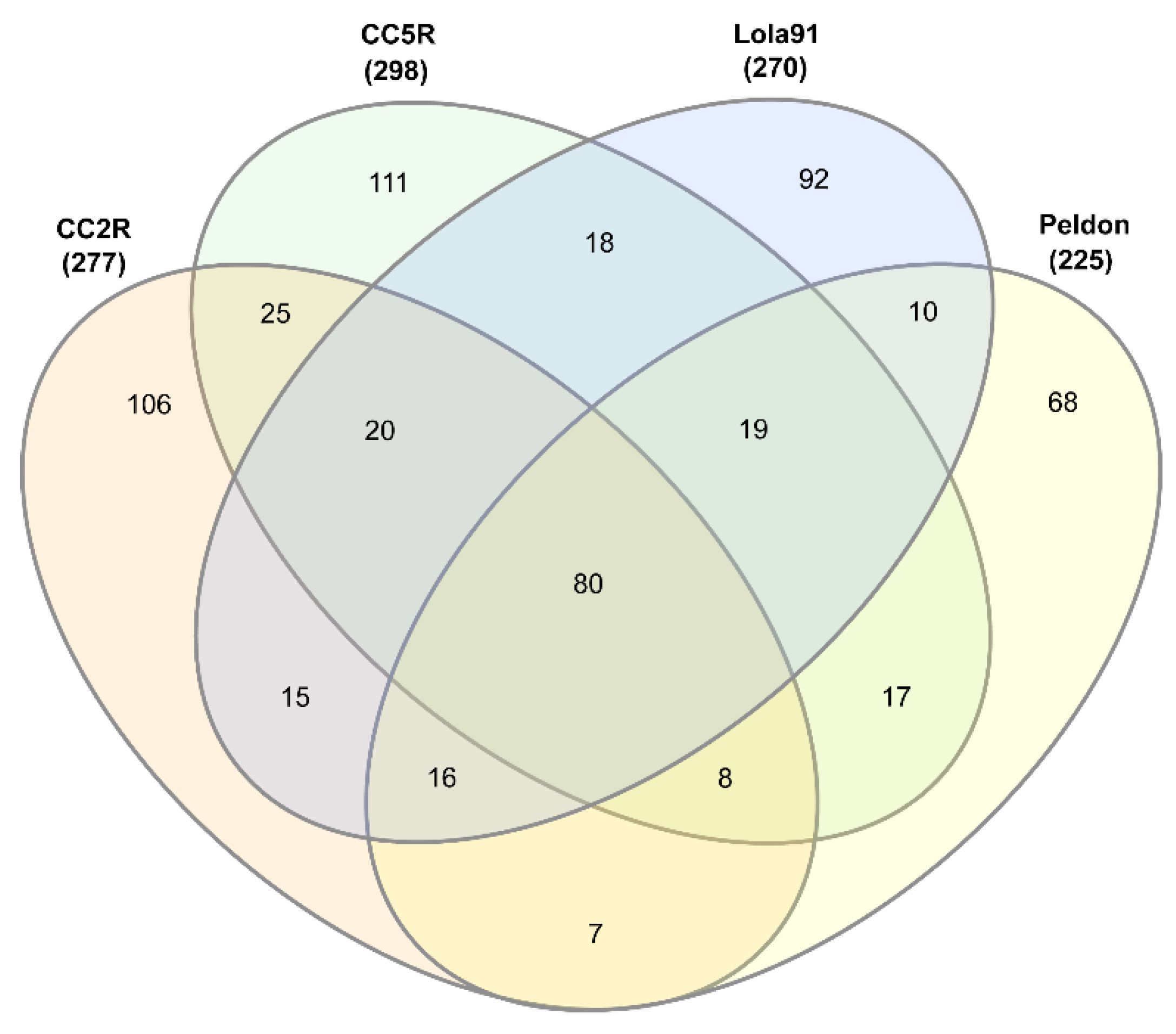
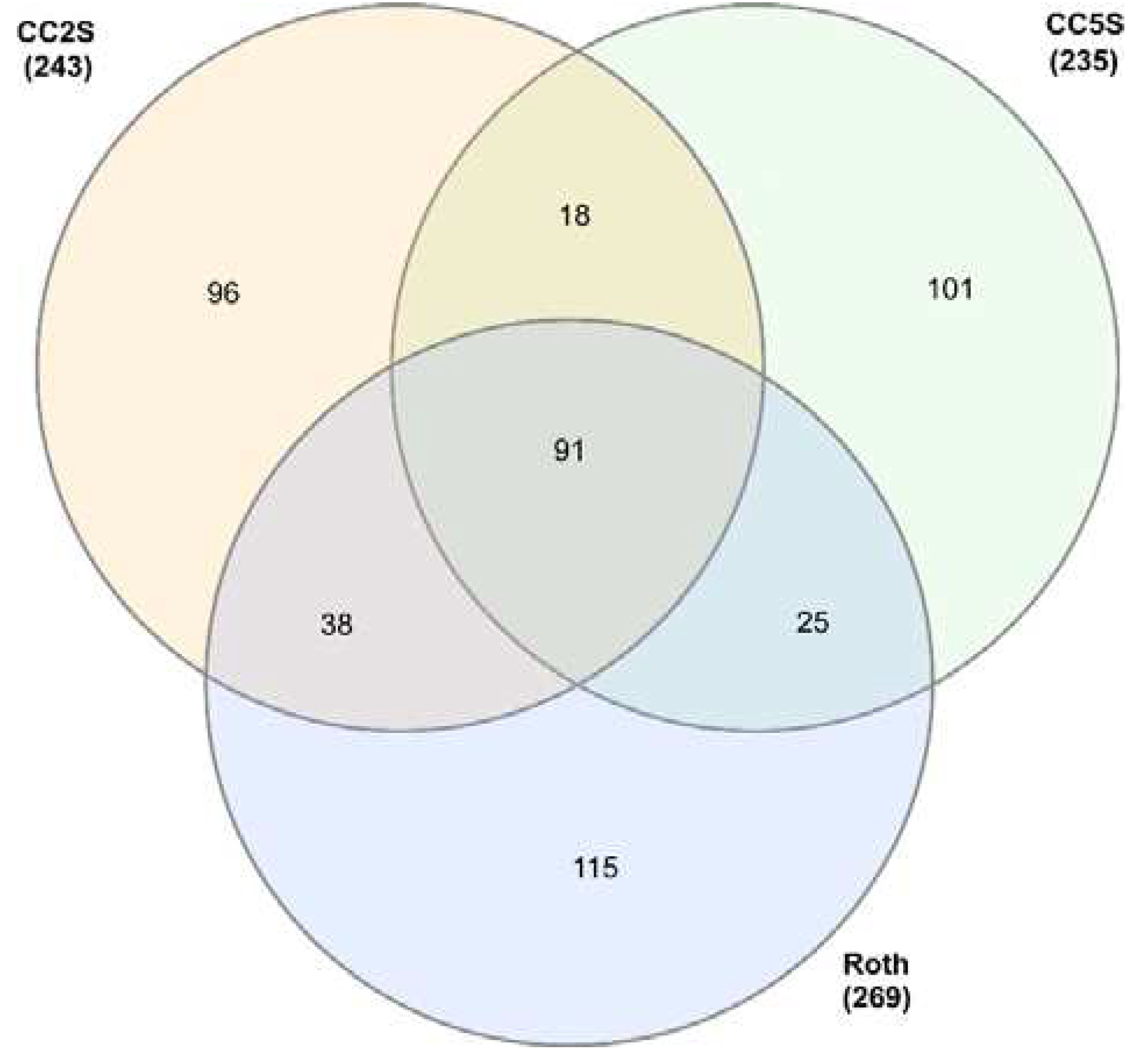
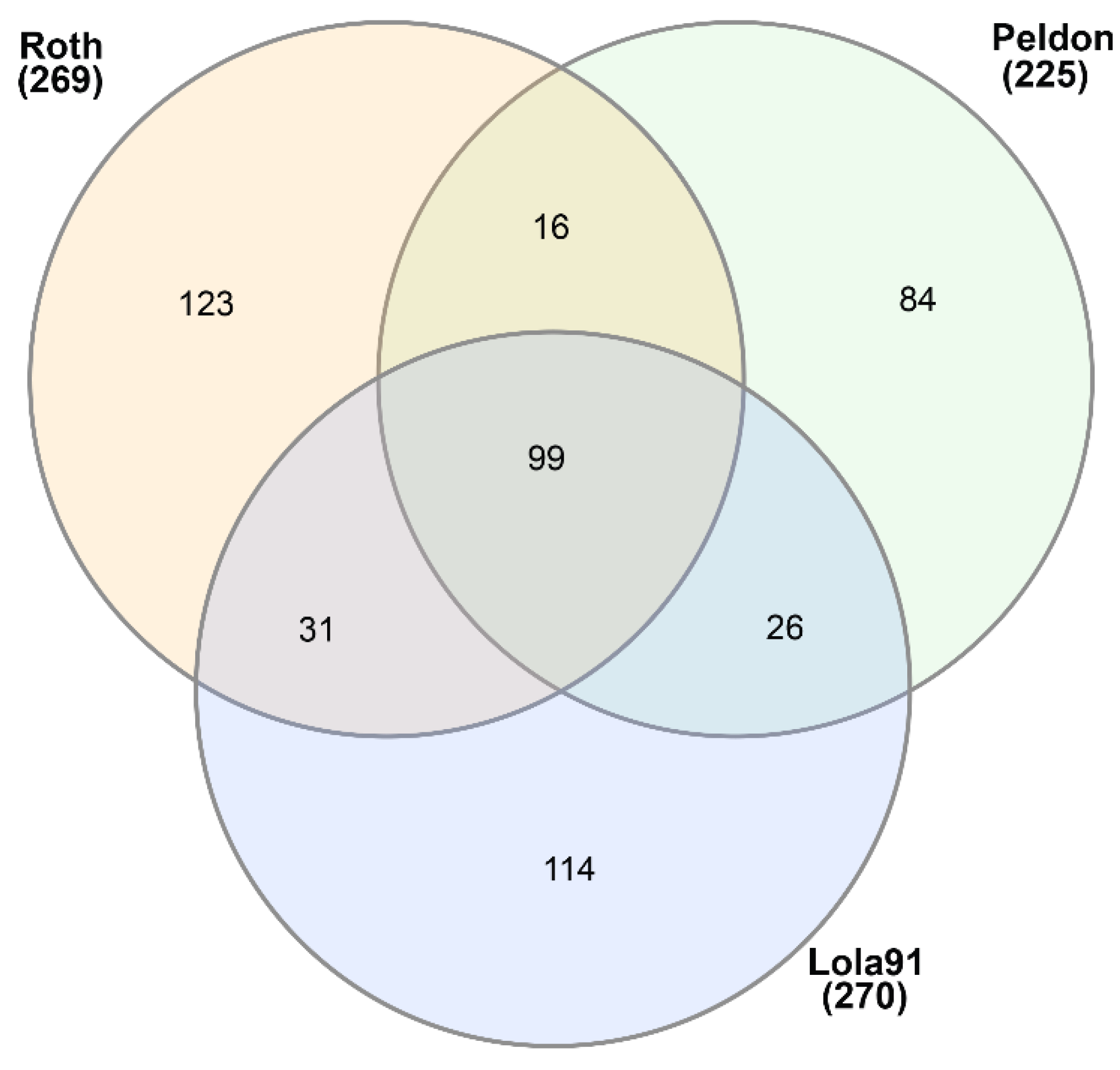
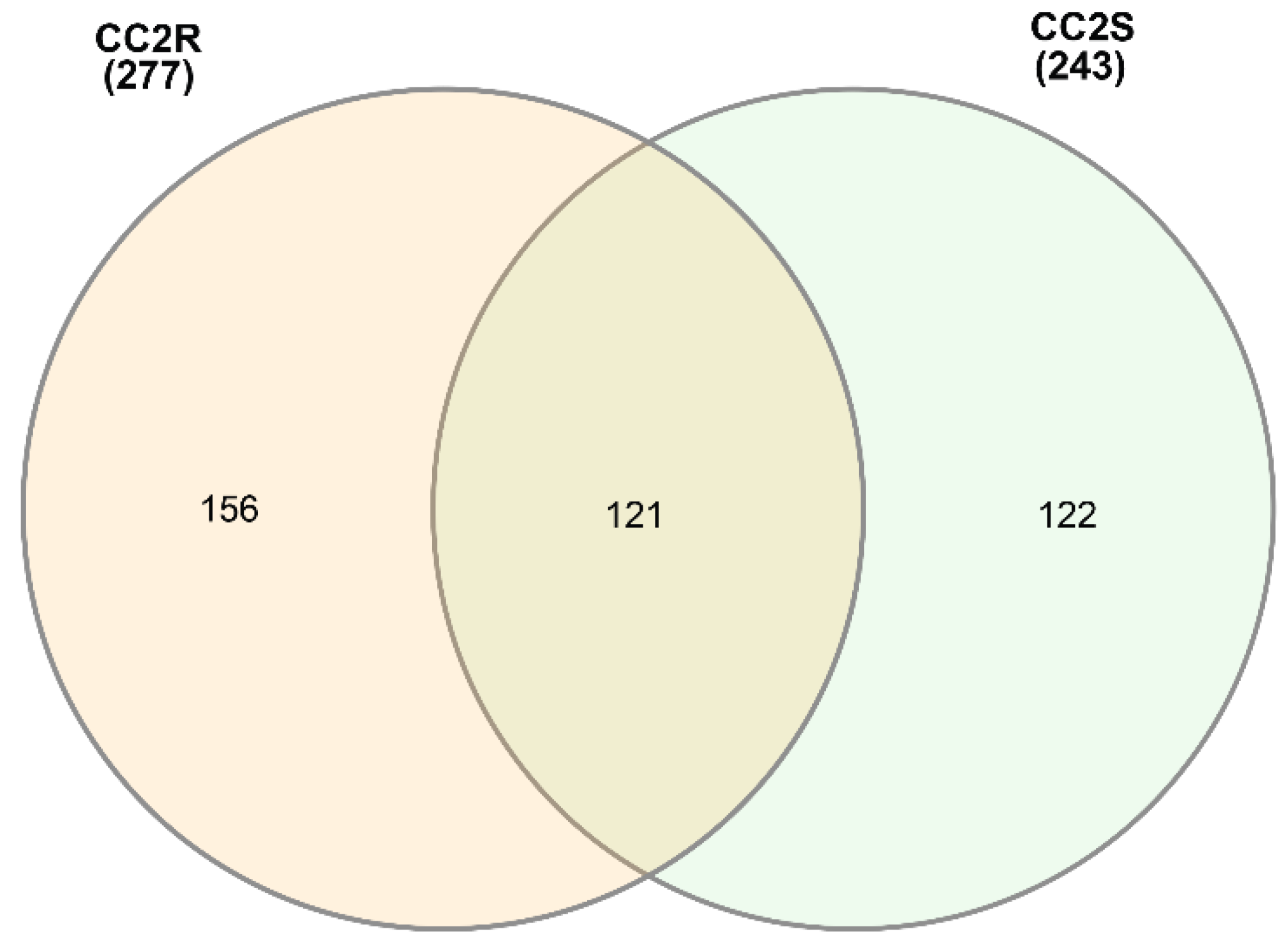
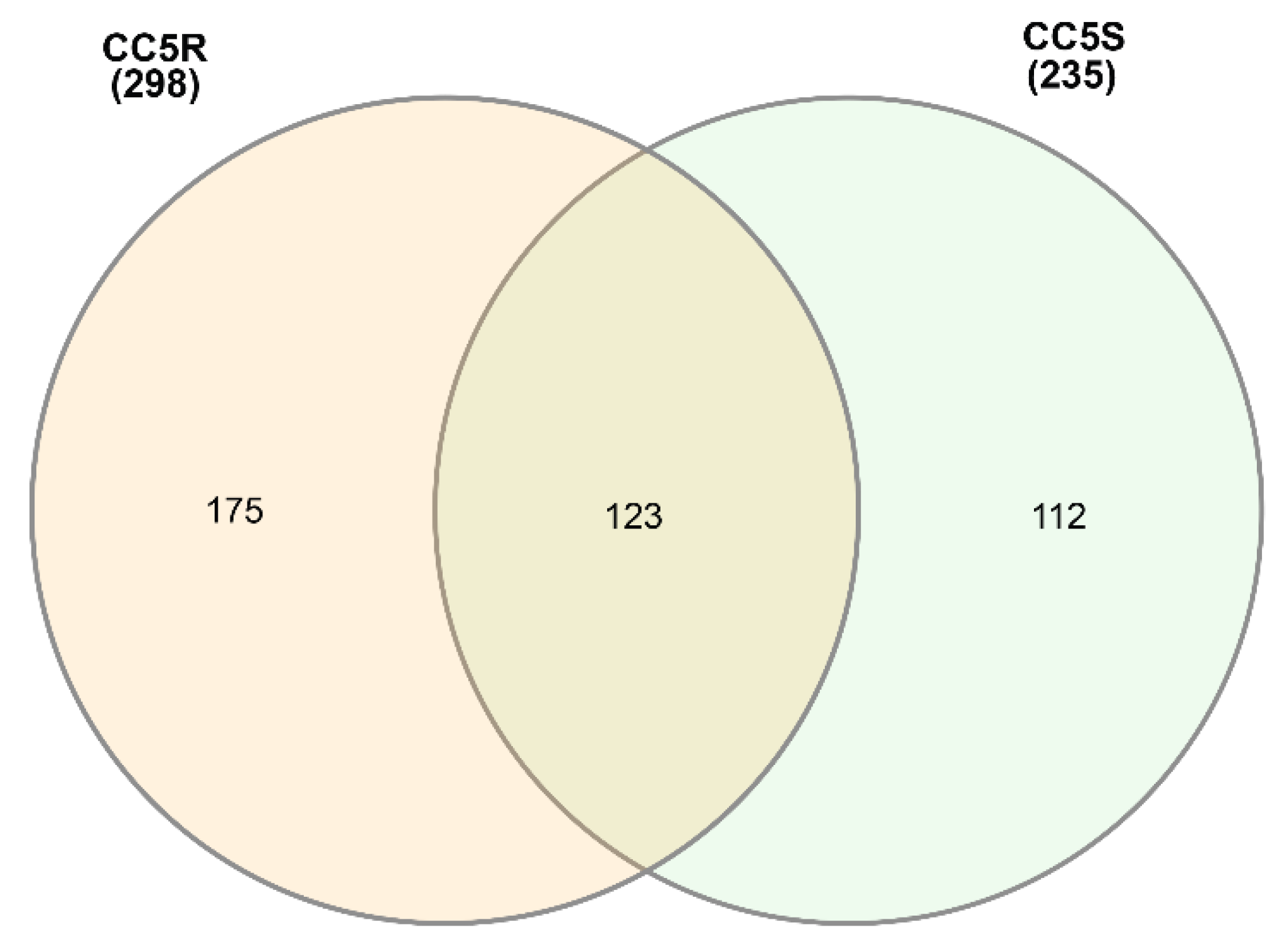
| Sample ID | # eccDNA | Mean length | Length range | # eccDNA with gene | # eccDNA with tRNA | % eccDNA with CDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC2R | 4812 | 7058 | 31-28980 | 1031 | 53 | 21.43 |
| CC2S | 4233 | 6994 | 60-25087 | 1010 | 77 | 23.86 |
| CC5R | 5288 | 6946 | 51-29081 | 1145 | 74 | 21.65 |
| CC5S | 4332 | 7002 | 54-28260 | 958 | 45 | 22.11 |
| Peldon | 4443 | 6868 | 36-26368 | 962 | 59 | 21.65 |
| Lola91 | 5426 | 6918 | 49-27814 | 1153 | 70 | 21.25 |
| Roth | 5663 | 7040 | 51-27090 | 1291 | 70 | 22.8 |
| Pfam Accession | Annotation | # eccDNA |
|---|---|---|
| PF04195 | Putative gypsy type transposon | 416 |
| PF00361 | Proton-conducting membrane transporter | 348 |
| PF00146 | NADH dehydrogenase | 148 |
| PF00223 | Photosystem I psaA/psaB protein | 139 |
| PF00499 | NADH-ubiquinone/plastoquinone oxidoreductase chain 6 | 133 |
| PF00420 | NADH-ubiquinone/plastoquinone oxidoreductase chain 4L | 112 |
| PF13237 | 4Fe-4S dicluster domain | 103 |
| PF00124 | Photosynthetic reaction centre protein | 93 |
| PF01578 | Cytochrome C assembly protein | 91 |
| PF00346 | Respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase, 49 Kd subunit | 87 |
| PF00662 | NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I), chain 5 N-terminus | 81 |
| PF01010 | NADH-dehyrogenase subunit F, TMs, (complex I) C-terminus | 78 |
| PF00421 | Photosystem II protein | 48 |
| PF00623 | RNA polymerase Rpb1, domain 2 | 42 |
| PF01535 | PPR repeat | 41 |
| PF00006 | ATP synthase alpha/beta family, nucleotide-binding domain | 38 |
| PF13456 | Reverse transcriptase-like | 36 |
| PF00276 | Ribosomal protein L23 | 32 |
| PF13041 | PPR repeat family | 31 |
| PF01824 | MatK/TrnK amino terminal region | 30 |
| Pfam Accession | Annotation | # eccDNA |
|---|---|---|
| PF04195 | Putative gypsy type transposon | 361 |
| PF00361 | Proton-conducting membrane transporter | 208 |
| PF00223 | Photosystem I psaA/psaB protein | 107 |
| PF00146 | NADH dehydrogenase | 91 |
| PF00499 | NADH-ubiquinone/plastoquinone oxidoreductase chain 6 | 81 |
| PF13237 | 4Fe-4S dicluster domain | 65 |
| PF00124 | Photosynthetic reaction centre protein | 63 |
| PF00346 | Respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase, 49 Kd subunit | 62 |
| PF00662 | NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I), chain 5 N-terminus | 56 |
| PF01578 | Cytochrome C assembly protein | 55 |
| PF01010 | NADH-dehyrogenase subunit F, TMs, (complex I) C-terminus | 51 |
| PF00420 | NADH-ubiquinone/plastoquinone oxidoreductase chain 4L | 43 |
| PF13456 | Reverse transcriptase-like | 36 |
| PF00421 | Photosystem II protein | 35 |
| PF01535 | PPR repeat | 35 |
| PF00006 | ATP synthase alpha/beta family, nucleotide-binding domain | 34 |
| PF00069 | Protein kinase domain | 32 |
| PF00646 | F-box domain | 24 |
| PF02874 | ATP synthase alpha/beta family, beta-barrel domain | 24 |
| PF03040 | CemA family | 24 |
| Category | eccDNA gene ID | Homologous candidate gene | Identity (%) | E-value | Bit score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | CC2R_00001032 | GSTF1 | 95.434 | 4.95E-162 | 436 |
| CC5R_00001033 | GSTF1 | 31.25 | 1.07E-14 | 64.7 | |
| CC5R_00001372 | GSTF1 | 55 | 2.22E-91 | 257 | |
| Lola91_00001333 | GSTU2 | 61.364 | 1.70E-42 | 128 | |
| Lola91_00001340 | GSTU2 | 38.009 | 1.69E-42 | 133 | |
| Peldon_00000910 | OPR1 | 59.6 | 7.35E-108 | 306 | |
| Peldon_00000911 | OPR1 | 64.646 | 6.10E-44 | 137 | |
| Sensitive | CC2S_00001307 | GSTU2 | 65.741 | 8.99E-53 | 157 |
| CC5S_00001012 | GSTF2 | 61.176 | 1.37E-33 | 105 | |
| Roth_00001016 | GSTU2 | 31.429 | 2.42E-24 | 85.1 |
| Chr | Start (Mb) | End(Mb) | # Herbicide resistant eccDNA | # Herbicide sensitive eccDNA | Genes located | Functional annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 251.0 | 251.5 | 83 | 48 | ALOMY1G03512 | ||
| ALOMY1G03513 | PF00646 | F-box domain | |||||
| ALOMY1G03514 | PF02485 | Core-2/I-Branching enzyme | |||||
| ALOMY1G03515 | |||||||
| ALOMY1G03516 | PF01288 | 7,8-dihydro-6-hydroxymethylpterin-pyrophosphokinase (HPPK) | |||||
| ALOMY1G03517 | PF00809 | Pterin binding enzyme | |||||
| 5 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 133 | 104 | ALOMY5G31542 | PF01015 | Ribosomal S3Ae family |
| ALOMY5G31543 | PF03641 | Possible lysine decarboxylase | |||||
| ALOMY5G31544 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31545 | PF00294 | pfkB family carbohydrate kinase | |||||
| ALOMY5G31546 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31547 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31548 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31549 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31550 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31551 | PF00069 | Protein kinase domain | |||||
| ALOMY5G31552 | PF00069 | Protein kinase domain | |||||
| ALOMY5G31553 | PF00069 | Protein kinase domain | |||||
| ALOMY5G31554 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G31555 | |||||||
| 5 | 45.0 | 45.5 | 82 | 55 | ALOMY5G32133 | PF06747 | CHCH domain |
| ALOMY5G32134 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G32135 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G32136 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G32137 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G32138 | PF00179 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme | |||||
| ALOMY5G32139 | PF00829 | Ribosomal prokaryotic L21 protein | |||||
| ALOMY5G32140 | |||||||
| ALOMY5G32141 | |||||||
| 7 | 243.5 | 244.0 | 130 | 80 | ALOMY7G40250 | PF02493 | MORN repeat |
| ALOMY7G40251 | |||||||
| ALOMY7G40252 | |||||||
| ALOMY7G40253 | PF00023 | Ankyrin repeat | |||||
| ALOMY7G40254 | PF01694 | Rhomboid family | |||||
| ALOMY7G40255 | |||||||
| ALOMY7G40256 | PF12937 | F-box-like | |||||
| ALOMY7G40257 | PF00194 | Eukaryotic-type carbonic anhydrase | |||||
| ALOMY7G40258 | |||||||
| ALOMY7G40259 | PF00153 | Mitochondrial carrier protein | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





