Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. AGS-susceptibility test
2.3. Decapitation and brain dissection
2.4. Autoradiography
- For D1DR - 0.2nM [3H]SCH 23390 (specific activity 66.0 Ci/mmol, Amersham) for 90 min at room temperature.
- For D2DR - 0.4nM [3H]spiperone (specific activity 109.0 Ci/mmol, Amersham) for 60 min at room temperature.
- For D1DR - 0.2nM [3H]SCH 23390 and 10−7Mcis-flupenthixol.
- For D2DR - 0.4nM [3H]spiperone, 10−5M haloperidol and 10−5M ketanserin.
2.5. Measurements
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results
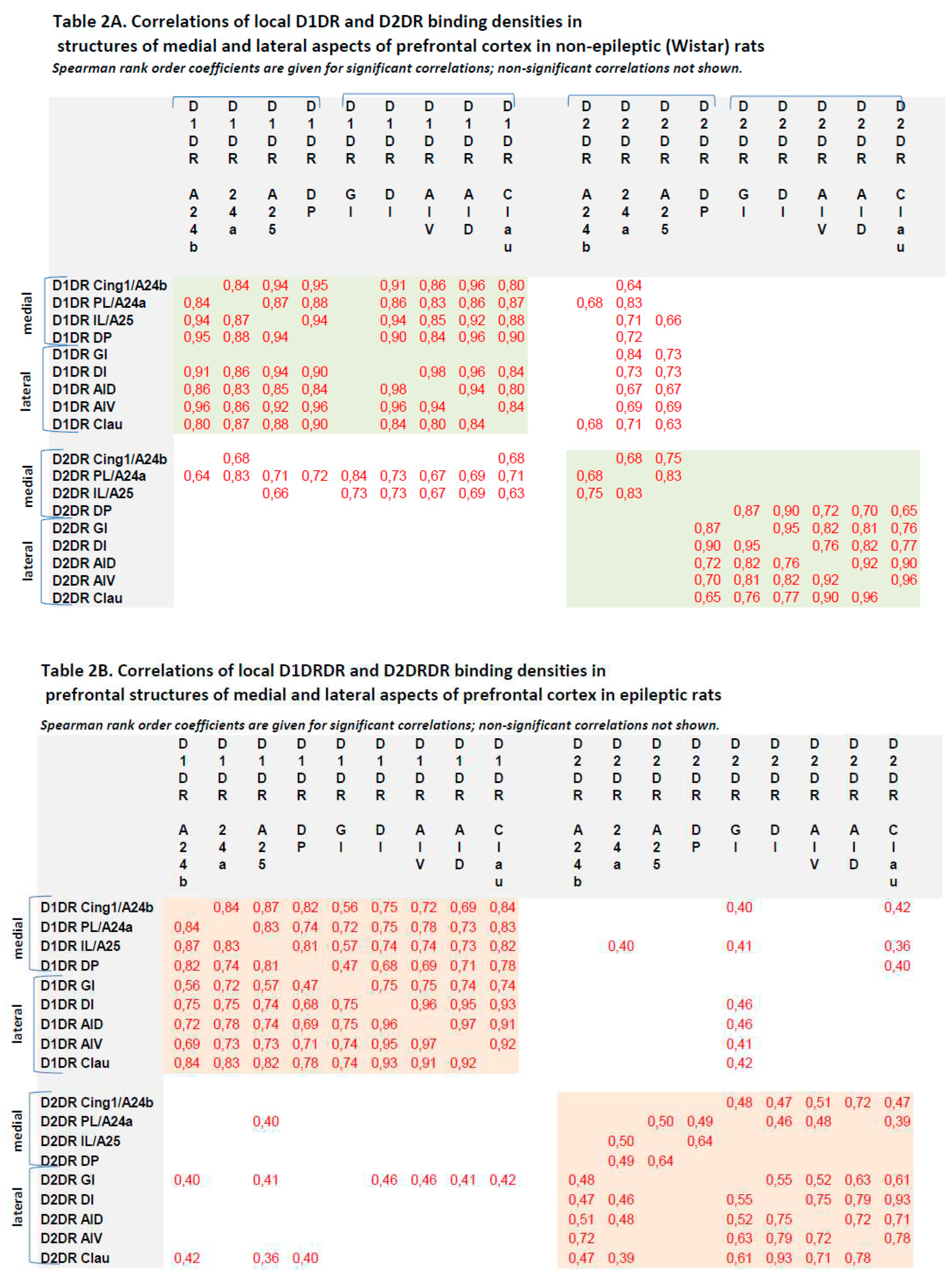
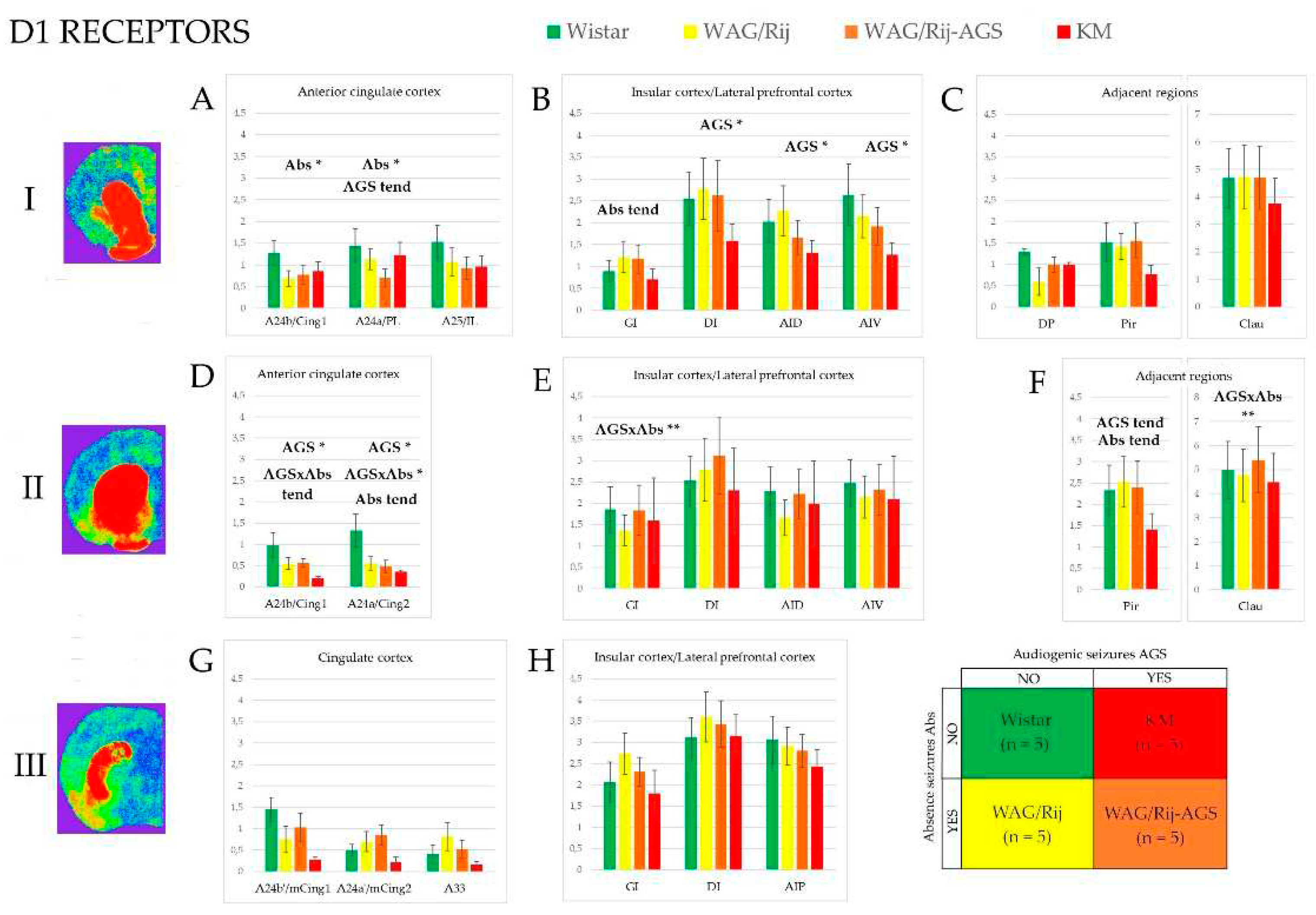
3.1. D1-DR binding density
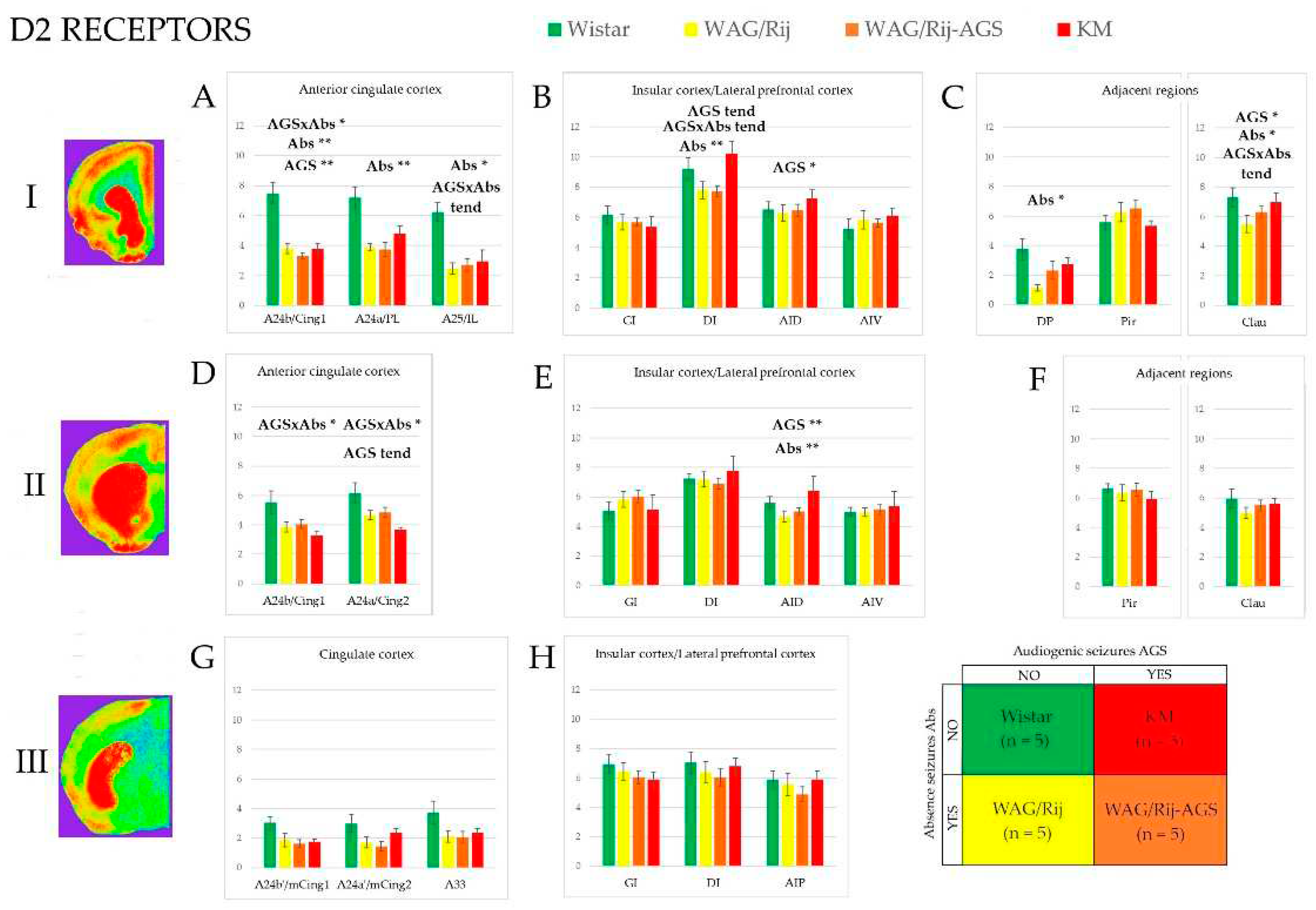
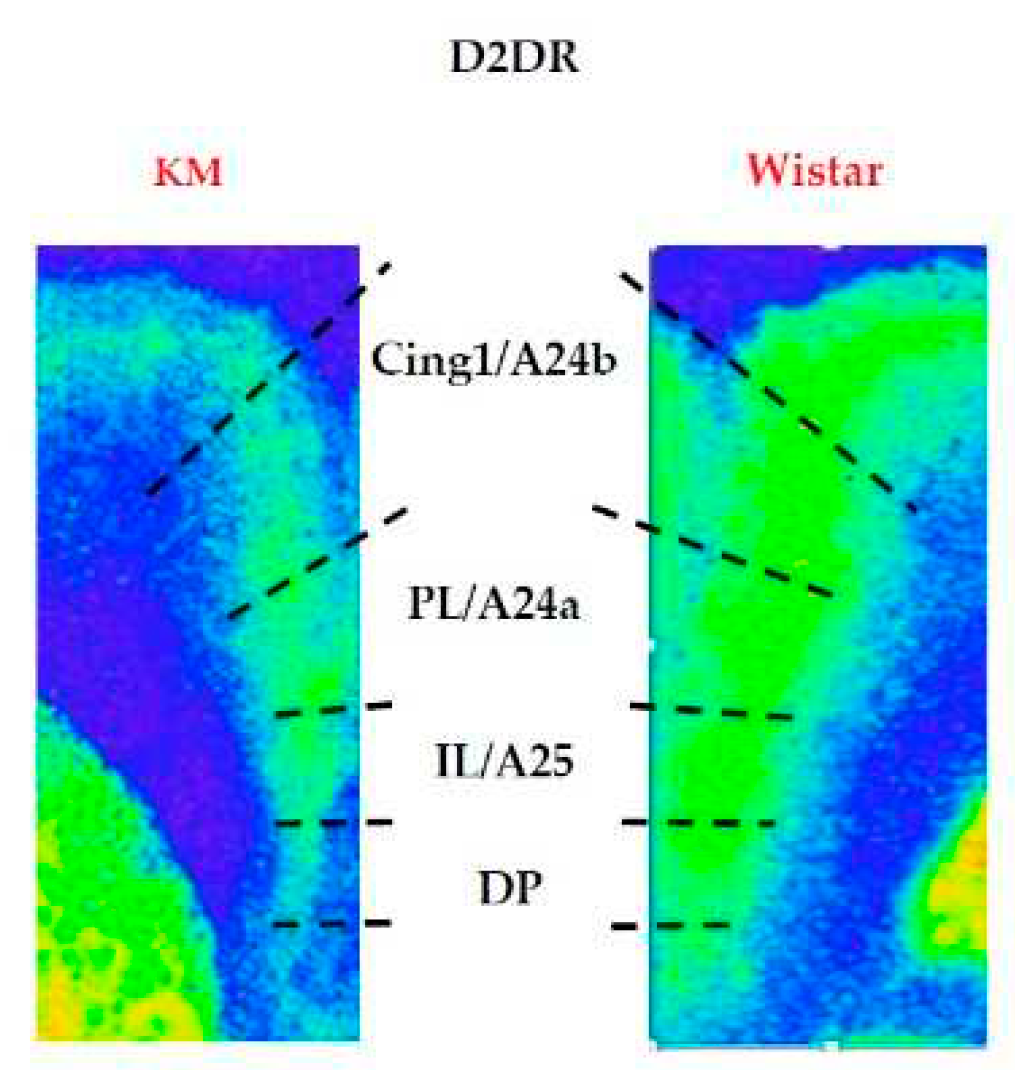
3.2. D2/3-DR binding density
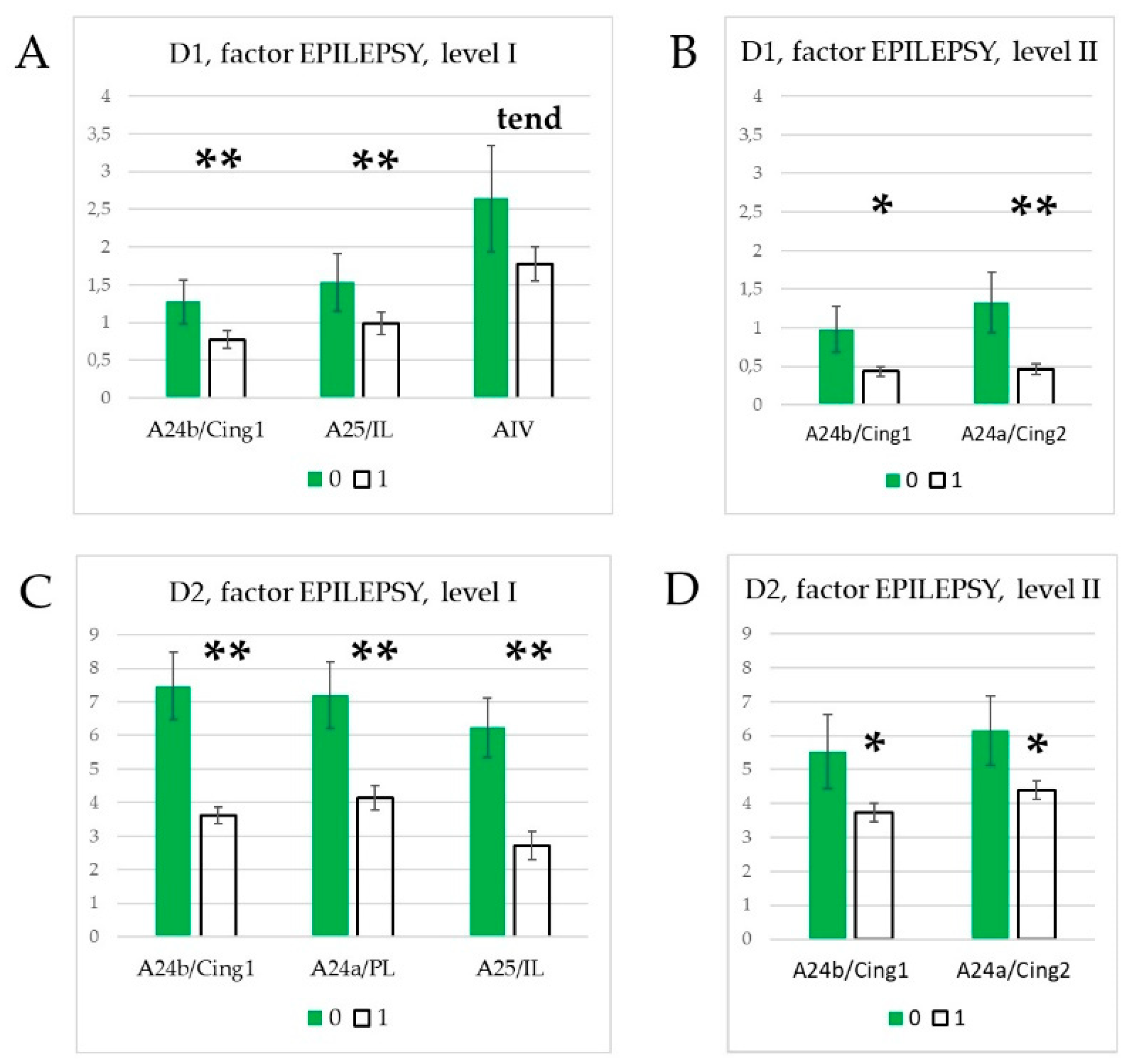
3.3. Effect of epilepsies
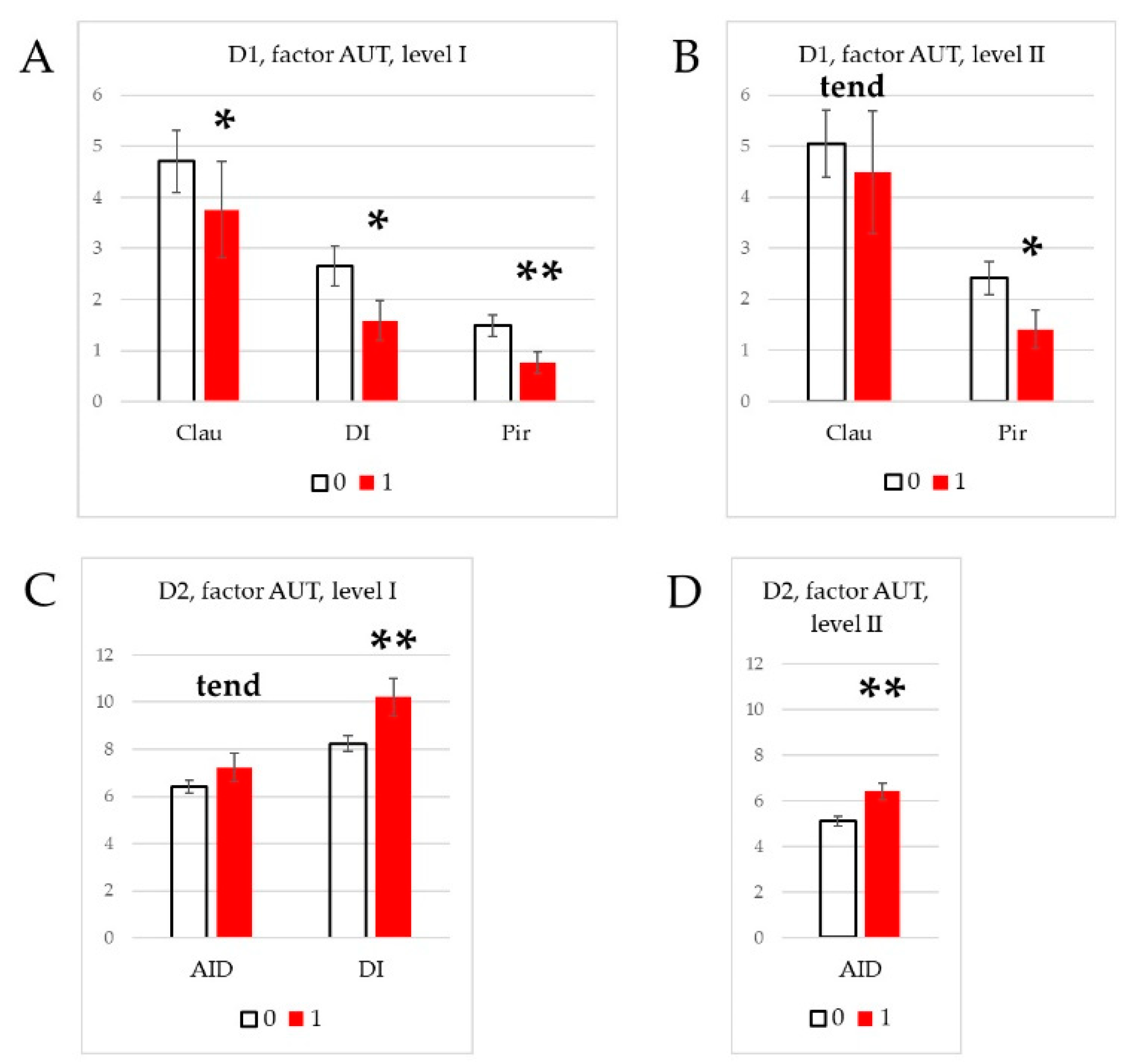
3.4. Effect of social phenotype.
3.3. Correlations between local binding densities to D1DR and D2DR within the prefrontal regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of specific epilepsy types.
4.2. Effects of generalized epilepsies
4.3. Effects of social phenotype
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holz, R.W.; Fisher, S.K. Chapter 12. Synaptic transmission and cellular signailng: An overview. In Basic neurochemistry: Principles of molecular, cellular and medical neurobiology, 8th ed.; Brady, S.T., Siegel G.J., Eds. Elsevier Academic Press, 2012, pp. 235-257. [CrossRef]
- Cumming, P. Imaging dopamine. Cambridge University Press, 2009.
- Dopamine receptor technologies. Tiberi, M. (Ed.) Dopamine receptor technologies. Tiberi, M., ed. Humana Press, Springer Science+Business Media New York, 2015.
- George, S.R.; Kern, A.; Smith, R.G.; Franco, R. Dopamine receptor heteromeric complexes and their emerging functions. Prog. Brain Res. 2014, 211, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, E.; Polat, A.K.; Eroglu, E.; Kullu, I.; Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N. Revisiting the role of neurotransmitters in epilepsy: An updated review. Life Sci. 2020, 265, 118826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, A.M.L.; van Luijtelaar, E.L.J.M. Genetic Animal Models for Absence Epilepsy: A Review of the WAG/Rij Strain of Rats. Behav. Genet. 2003, 33, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijtelaar, G.; Zobeiri, M. Progress and Outlooks in a Genetic Absence Epilepsy Model (WAG/Rij). Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Luijtelaar, G.; van Oijen, G. Establishing Drug Effects on Electrocorticographic Activity in a Genetic Absence Epilepsy Model: Advances and Pitfalls. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, G.D. [Audiogenic seizures in rats of different genetic strains]. . 1998, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Kuznetsova, G.D.; Vinogradova, L.V.; Shatskova, A.B.; Coenen, A.M.; van Luijtelaar, G. Mixed forms of epilepsy in a subpopulation of WAG/Rij rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2004, 5, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletaeva, I.; Surina, N.; Kostina, Z.; Perepelkina, O.; Fedotova, I. The Krushinsky-Molodkina rat strain: The study of audiogenic epilepsy for 65 years. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 71, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, I.B.; Surina, N.M.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Revishchin, A.V.; Poletaeva, I.I. Rodent Brain Pathology, Audiogenic Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuz, D.G.; Davletshin, A.A.; Litvinova, S.A.; Fedotova, I.B.; Surina, N.M.; Poletaeva, I.I. Rodent Models of Audiogenic Epilepsy: Genetic Aspects, Advantages, Current Problems and Perspectives. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.; Shatskova, A.; Sarkisova, K.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Tuomisto, L.; Kuznetsova, G. Convulsive and nonconvulsive epilepsy in rats: Effects on behavioral response to novelty stress. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 6, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.; Kuznetsova, G.; van Luijtelaar, E.; van Rijn, C.; Tuomisto, L.; MacDonald, E. The brain 5HTergic response to an acute sound stress in rats with generalized (absence and audiogenic) epilepsy. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Birioukova, L.M.; Shatskova, A.B.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Tuomisto, L.M. H1 histamine receptor densities are increased in brain regions of rats with genetically generalized epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 127, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.; Petrenko, T.; Birioukova, L.; Tuomisto, L. Reduced H3 histamine receptor binding densities in the upper layers of motor cortex in rats prone to audiogenic convulsive seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 170, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Birioukova, L.M.; Storvik, M.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Tuomisto, L.M. The prefrontal cortex shows widespread decrease in H3 histamine receptor binding densities in rats with genetic generalized epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 182, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyba, E.T.; Midzyanovskaya, I.S.; Birioukova, L.M.; Tuomisto, L.M.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Abbasova, K.R. Striatal Patchwork of D1-like and D2-like Receptors Binding Densities in Rats with Genetic Audiogenic and Absence Epilepsies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebik, A.A.; Riga, V.D.; Smirnov, K.S.; Sysoeva, O.V.; Midzyanovskaya, I.S. Social Behavioral Deficits in Krushinsky-Molodkina Rats, an Animal Model of Audiogenic Epilepsy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebik, A.A.; Broshevitskaya, N.; Kuzhuget, S.; Aleksandrov, P.; Abbasova, K.; Zaichenko, M.; Mi-dzyanovskaya, I.S. Audiogenic Seizures and Social Deficits: No Aggravation Found in KM Rats. Biomedi-cines, 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Besag, F. Epilepsy in patients with autism: links, risks and treatment challenges. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, ume 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Kayal, A. Epilepsy and autism spectrum disorders: Are there common developmental mechanisms? Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, Y.; Provenzano, G.; Casarosa, S. Neurobiological bases of autism-epilepsy comorbidity: A focus on excita-tion/inhibition imbalance. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.L.; Thurm, A.; Ethridge, S.B.; Soller, M.M.; Petkova, S.P.; Abel, T.; Bauman, M.D.; Brodkin, E.S.; Harony-Nicolas, H. ; Wöhr, M.; et al. Reconsidering animal models used to study autism spectrum disorder: Current state and optimizing future. Genes, Brain Behav. 2022, 21, e12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Arregui, T.; Llorente, J.; Minguez, P.G.; Tønnesen, J.; Peñagarikano, O. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Epilepsy, Insights from Animal Models. Neuroscience 2020, 445, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratizadeh, S.; Parvan, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Shabani, M.; Nozari, M. An overview of modeling and behavioral assessment of autism in the rodent. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2021, 81, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, J.M. The prefrontal cortex, 5th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press, 2015.
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780123919496. [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780123919496. [Google Scholar]
- Zilles, K. The cortex of the rat: A stereotaxic atlas. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985.
- Vogt, B.A.; Paxinos, G. Cytoarchitecture of mouse and rat cingulate cortex with human homologies. Anat. Embryol. 2012, 219, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, L.W. Brain maps 4. 0 – Structure of the rat brain: An open access atlas with global nervous system nomenclature ontology and flatmaps. J Comp Neurol 2018, 526, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Kassem, M.S.; Kirkcaldie, M.; Carrive, P. Chemoarchitectonic atlas of the rat brain, 3rd ed. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, B.A. Cingulate cortex and pain architecture. In The rat nervous system, 4th ed. Paxinos, G., ed. Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, 2015; pp. 575-600. [CrossRef]
- Laubach, M.; Amarante, L.M.; Swanson, K.; White, S.R. What, If Anything, Is Rodent Prefrontal Cortex? eneuro 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, T.M.; Wise, S.P. Evolution of prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 47, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoyama, K.; Devinsky, O. Chapter 19 - Cingulate seizures and recent treatment strategies. In Cingulate Cortex, 1st ed.; Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol.166. Vogt, B.A., Ed. Elsevier, 2019, pp. 341-353. [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. 2010. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Morimoto, K.; Fahnestock, M.; Racine, R.J. Kindling and status epilepticus models of epilepsy: rewiring the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V. Audiogenic kindling and secondary subcortico-cortical epileptogenesis: Behavioral correlates and electrographic features. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, S.B.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Autoradiographic study of striatal D1- and D2-like dopamine re-ceptors in 6-OHDA lesioned rats receiving foetal ventral mesencephalic grafts and chronic treatment with L-DOPA and carbidopa. Brain Res. 1992, 582, (2), 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birioukova, L.; Midzyanovskaya, I.; Lensu, S.; Tuomisto, L.; van Luijtelaar, G. Distribution of D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors in the brain of genetic epileptic WAG/Rij rats. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 63, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, N.; Artigas, F. Laminar and Cellular Distribution of Monoamine Receptors in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 87–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, M.S.; LaLumiere, R.T. Still a “hidden island”? The rodent insular cortex in drug seeking, reward, and risk. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 153, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flik, G.; Folgering, J.H.A.; Cremers, T.I.H.F.; Westerink, B.H.C.; Dremencov, E. Interaction Between Brain Histamine and Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and Dopamine Systems: In Vivo Microdialysis and Electrophysiology Study. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisova, K.; Midzianovskaia, I.; Kulikov, M. Depressive-like behavioral alterations and c-fos expression in the dopaminergic brain regions in WAG/Rij rats with genetic absence epilepsy. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 144, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, N.H.; Bechara, A. The hidden island of addiction: the insula. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krushinsky, L. V. , Molodkina, L. N., Fless, D. A., Dobrokhotova, L. P., Steshenko, A. P., Semiokhina, A. F.,... & Romanova, held in Boston, Massachusetts, December 28–30, 1969, in conjunction with the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (pp. 159-183). Springer US., L. G. (1970). The functional state of the brain during sonic stimulation. In Physiological Effects of Noise: Based upon papers presented at an international symposium on the Extra-Auditory Physiological Effects of Audible Sound. [Google Scholar]
- Fadyukova, O.E.; Storozhevykh, T.P.; Pinelis, V.G.; Koshelev, V.B. Ischemic and hemorrhagic disturbances in cerebral circulation alter contractile responses of the rat middle cerebral artery. Brain Res. 2004, 995, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, D.A.; Mraovitch, S.; Granata, A.R.; Anwar, M.; Reis, D.J. A role of insular cortex in cardiovascular function. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 257, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.V. , Saper, C.B., Hurley, K.M., Cechetto, D.F., 1991. Organization of visceral and limbic connec-tions in the insular cortex of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 311 (1), 1–16. [CrossRef]
- A Gehrlach, D.; Weiand, C.; Gaitanos, T.N.; Cho, E.; Klein, A.S.; A Hennrich, A.; Conzelmann, K.-K.; Gogolla, N. A whole-brain connectivity map of mouse insular cortex. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, Y.; Andermann, M.L. Cellular activity in insular cortex across seconds to hours: Sensations and predictions of bodily states. Neuron 2021, 109, 3576–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, D.; Ameis, S.H.; Lai, M.; Casanova, M.F.; Desarkar, P. Interoception in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A review. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2016, 52, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskens, J.B.; Velders, F.P.; Staal, W.G. Medical comorbidities in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders: a systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
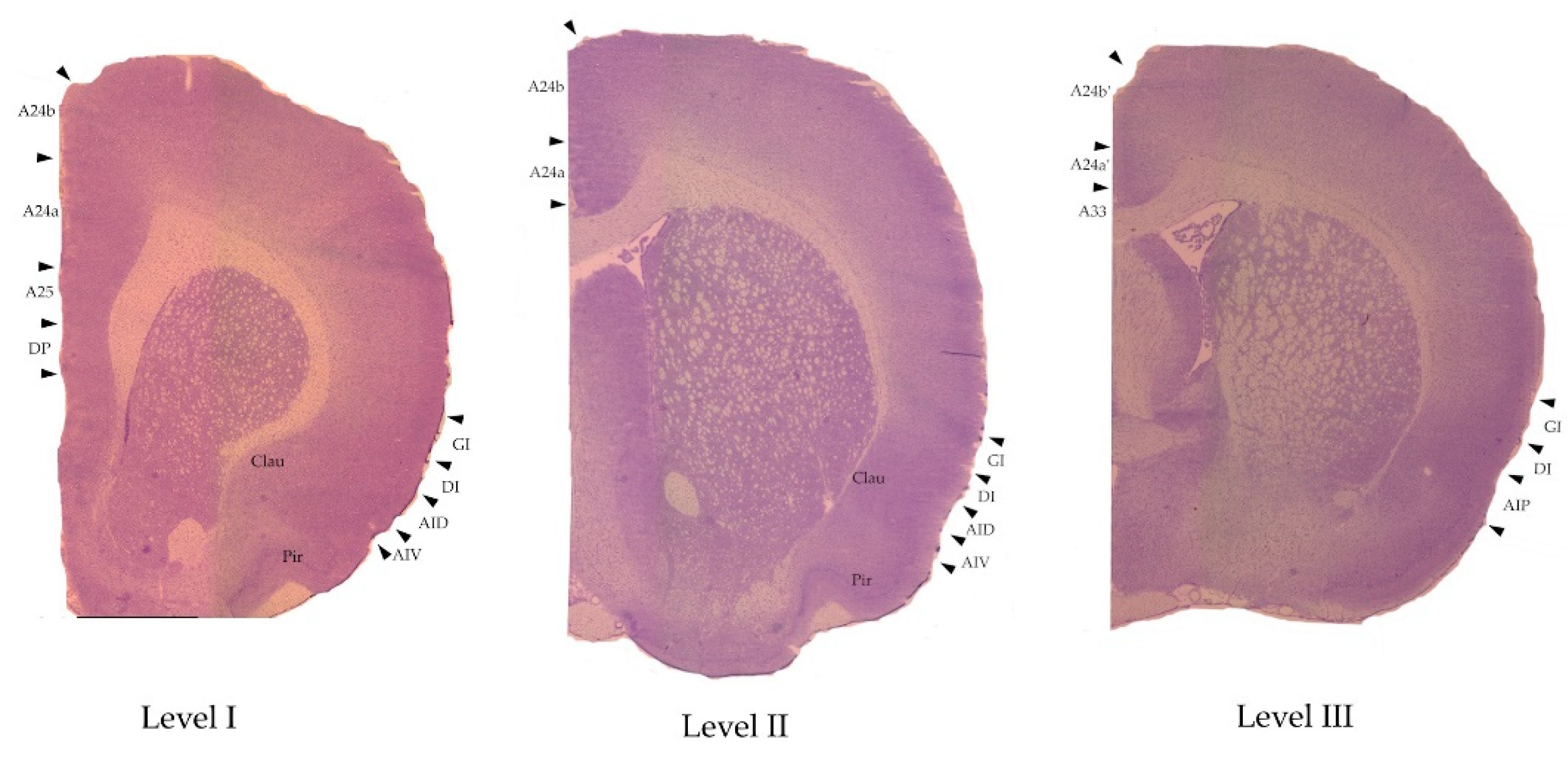
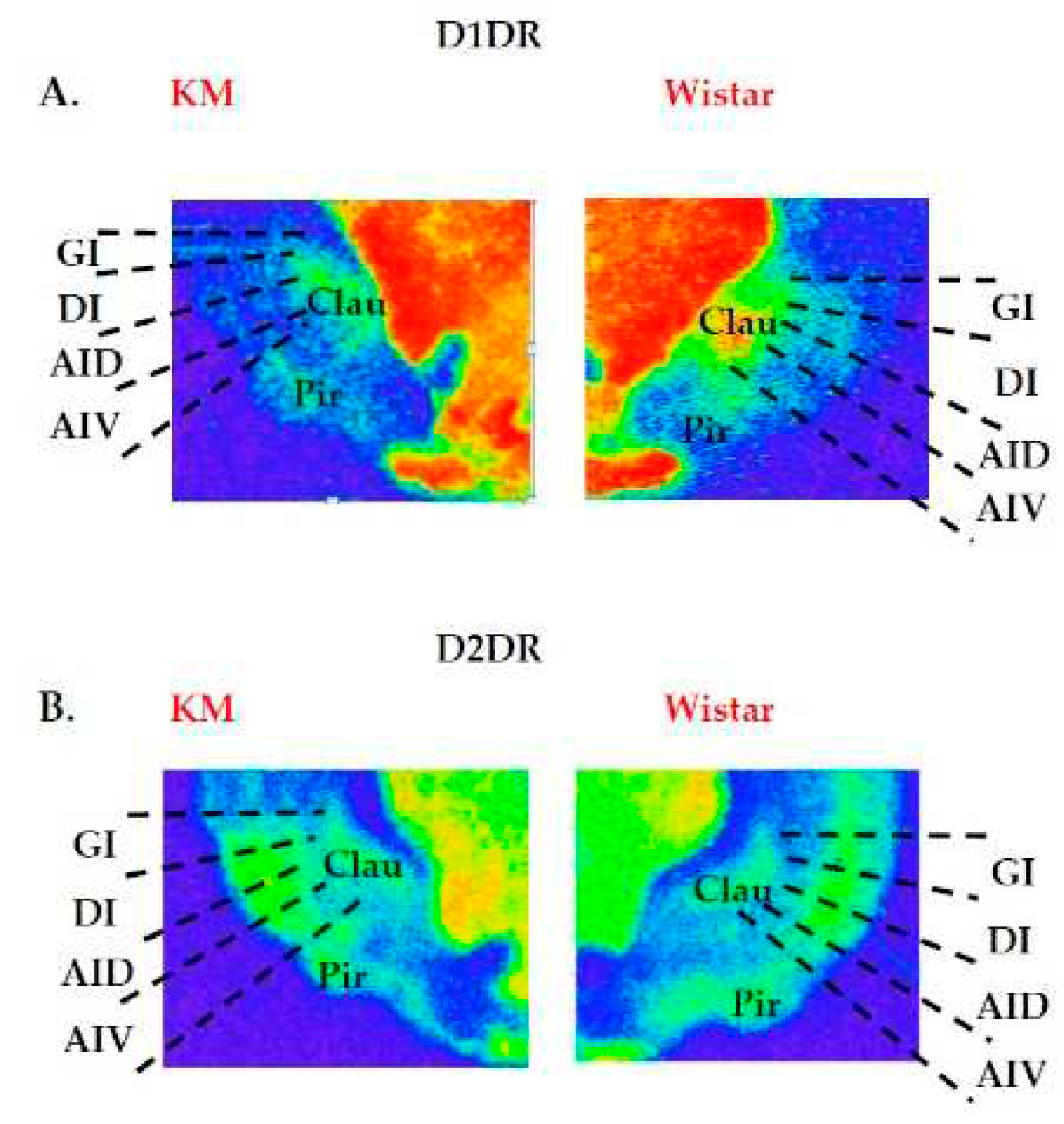
| 6th edition, 2007[30] | 7th edition, 2014[29] |
|---|---|
| Medial prefrontal cortex | Medial frontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) |
| Infralimbic cortex IL | A25 |
| Prelimbic cortex PL | A24a |
| Primary cingulate cortex Cing1 | A24b |
| Secondary cingulate cortex Cing2 | A24a |
| Homologue of area 33 A33 | |
| Midcingulate cortex (MCC) | |
| Primary midcingulate cortex mCing1 | A24b’ |
| Secondary midcingulate cortex mCing2 | A24a’ |
| Lateral prefrontal cortex | Insular cortex |
| Granular insular cortex GI | Granular insular cortex GI |
| Dysgranular insular cortex DI | Dysgranular insular cortex DI |
| Dorsal agranular insular cortex AID | Dorsal agranular insular cortex AID |
| Ventral agranular insular cortex AIV | Ventral agranular insular cortex AIV |
| Posterior agranular insular cortex AIP | Posterior agranular insular cortex AIP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





