Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study population
2.2. Gene expression analysis
2.3. BAP1, MTAP, p16 tests
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study population
3.2. Gene expression analysis
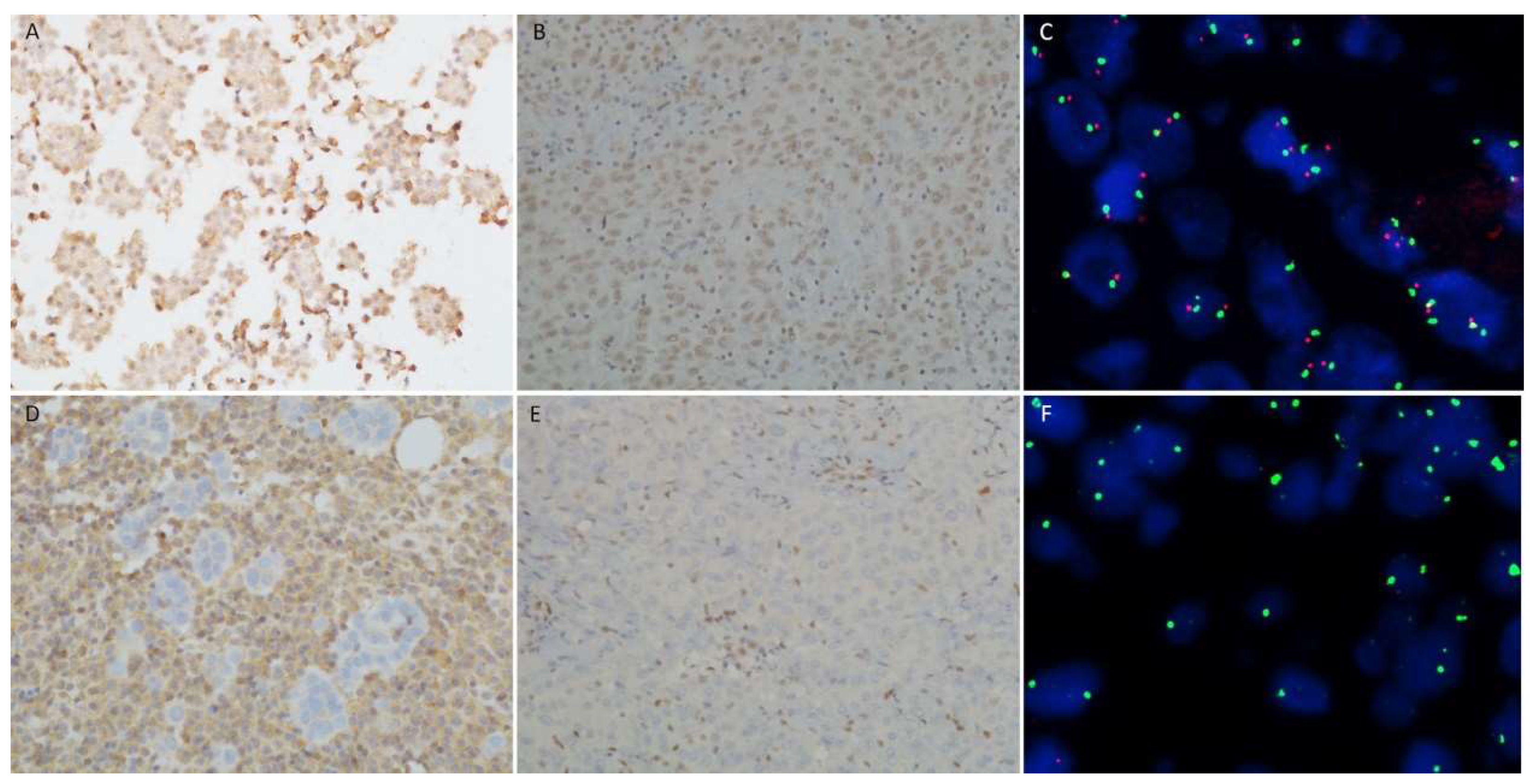
3.3. BAP1, MTAP, p16 tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson:, B.W.S.; Musk, A.W.; Lake, R.A. Malignant Mesothelioma. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2005, 366, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Baas, P.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Girard, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Nowak, A.K.; Opitz, I.; Scherpereel, A.; Reck, M. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up☆. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.W.S.; Lake, R.A. Advances in Malignant Mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, J.L.; Dacic, S.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Attanoos, R.L.; Butnor, K.J.; Churg, A.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Khoor, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances Since the 2015 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, K.; Hamasaki, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Sa-ngiamwibool, P. Update of Pathological Diagnosis of Pleural Mesothelioma Using Genomic-based Morphological Techniques, for Both Histological and Cytological Investigations. Pathol. Int. 2022, 72, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, I.; Myers, J. Update on Diagnosing and Reporting Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Acta Medica Acad. 2021, 50, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I. Management of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma-The European Experience. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6 Suppl 2, S238–252. [Google Scholar]
- Brcic, L.; Kern, I. Clinical Significance of Histologic Subtyping of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, M.B.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Dacic, S. Pleural Mesothelioma Classification Update. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacic, S. Pleural Mesothelioma Classification—Update and Challenges. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjerpe, A.; Ascoli, V.; Bedrossian, C.; Boon, M.; Creaney, J.; Davidson, B.; Dejmek, A.; Dobra, K.; Fassina, A.; Field, A.; et al. Guidelines for Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Epithelioid and Mixed Type Malignant Mesothelioma. Complementary Statement from the International Mesothelioma Interest Group, Also Endorsed by the International Academy of Cytology and the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology. CytoJournal 2015, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Nabeshima, K.; Ali, G.; Bruno, R.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Galateau-Salle, F. Highlights of the 14th International Mesothelioma Interest Group Meeting: Pathologic Separation of Benign from Malignant Mesothelial Proliferations and Histologic/Molecular Analysis of Malignant Mesothelioma Subtypes. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebe, S.; Galateau Salle, F.; Bruno, R.; Brcic, L.; I. Chen-Yost, H.; Jaurand, M.-C. The Highlights of the 15th International Conference of the International Mesothelioma Interest Group – Do Molecular Concepts Challenge the Traditional Approach to Pathological Mesothelioma Diagnosis? Lung Cancer 2022, 163, 1–6.
- Monaco, S.E.; Brcic, L.; Dacic, S. State-of-the-Art Cytology of Pleural Fluid, Focusing on the Diagnosis of Mesothelioma. Cytopathol. Off. J. Br. Soc. Clin. Cytol. 2022, 33, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, M.; Monaco, S.E.; Jerome, J.A.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Churg, A.; Dacic, S. Testing for BAP1 Loss and CDKN2A/P16 Homozygous Deletion Improves the Accurate Diagnosis of Mesothelial Proliferations in Effusion Cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.C.; Sheffield, B.S.; Rodriguez, S.; Thompson, K.; Tse, C.H.; Gown, A.M.; Churg, A. Utility of BAP1 Immunohistochemistry and P16 (CDKN2A) FISH in the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusion Cytology Specimens. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walts, A.E.; Hiroshima, K.; McGregor, S.M.; Wu, D.; Husain, A.N.; Marchevsky, A.M. BAP1 Immunostain and CDKN2A (P16) FISH Analysis: Clinical Applicability for the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2016, 44, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.B.; Dacic, S.; Miller, C.; Cheung, S.; Churg, A. Utility of Methylthioadenosine Phosphorylase Compared With BAP1 Immunohistochemistry, and CDKN2A and NF2 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Separating Reactive Mesothelial Proliferations From Epithelioid Malignant Mesotheliomas. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Kamei, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Nabeshima, K. Cytoplasmic MTAP Expression Loss Detected by Immunohistochemistry Correlates with 9p21 Homozygous Deletion Detected by FISH in Pleural Effusion Cytology of Mesothelioma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynggård, L.A.; Panou, V.; Szejniuk, W.; Røe, O.D.; Meristoudis, C. Diagnostic Capacity of BAP1 and MTAP in Cytology from Effusions and Biopsy in Mesothelioma. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2022, 11, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Alì, G.; Giannini, R.; Proietti, A.; Lucchi, M.; Chella, A.; Melfi, F.; Mussi, A.; Fontanini, G. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Mesothelial Hyperplasia: A New Molecular Tool for the Differential Diagnosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2758–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alì, G.; Bruno, R.; Poma, A.; Proietti, A.; Ricci, S.; Chella, A.; Melfi, F.; Ambrogi, M.; Lucchi, M.; Fontanini, G. A Gene-expression-based Test Can Outperform Bap1 and P16 Analyses in the Differential Diagnosis of Pleural Mesothelial Proliferations. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 19, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, R.; Alì, G.; Poma, A.M.; Proietti, A.; Libener, R.; Mariani, N.; Niccoli, C.; Chella, A.; Ribechini, A.; Grosso, F.; et al. Differential Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma on Cytology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, R.; Poma, A.M.; Alì, G.; Distefano, C.; Proietti, A.; Chella, A.; Lucchi, M.; Melfi, F.; Franco, R.; Fontanini, G. Gene Expression Analysis of Biphasic Pleural Mesothelioma: New Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrici, J.; Sheen, A.; Sioson, L.; Wardell, K.; Clarkson, A.; Watson, N.; Ahadi, M.S.; Farzin, M.; Toon, C.W.; Gill, A.J. Loss of Expression of BAP1 Is a Useful Adjunct, Which Strongly Supports the Diagnosis of Mesothelioma in Effusion Cytology. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, I.; Oprescu, F.A.; Rullo, E.; Ascoli, V. Loss of BRCA1-Associated Protein 1 (BAP1) Expression Is Useful in Diagnostic Cytopathology of Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2018, 46, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, T.; Hamasaki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Okamoto, T.; Oda, Y.; Honda, H.; et al. Immunohistochemical Detection of MTAP and BAP1 Protein Loss for Mesothelioma Diagnosis: Comparison with 9p21 FISH and BAP1 Immunohistochemistry. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2017, 104, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, G.K.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Birditt, B.; Dahl, T.; Dowidar, N.; Dunaway, D.L.; Fell, H.P.; Ferree, S.; George, R.D.; Grogan, T.; et al. Direct Multiplexed Measurement of Gene Expression with Color-Coded Probe Pairs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H.-F.; Xue, V.W.; Koh, S.-P.; Chiu, Y.-M.; Ng, L.P.-W.; Wong, S.-C.C. NanoString, a Novel Digital Color-Coded Barcode Technology: Current and Future Applications in Molecular Diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.-M.; Arnau, G.M.; Ryland, G.L.; Huang, S.; Lira, M.E.; Emmanuel, Y.; Perez, O.D.; Irwin, D.; Fellowes, A.P.; Wong, S.Q.; et al. Multiplexed Transcriptome Analysis to Detect ALK, ROS1 and RET Rearrangements in Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galateau Salle, F.; Le Stang, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Pissaloux, D.; Churg, A.; Klebe, S.; Roggli, V.L.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Vignaud, J.M.; Attanoos, R.; et al. New Insights on Diagnostic Reproducibility of Biphasic Mesotheliomas: A Multi-Institutional Evaluation by the International Mesothelioma Panel From the MESOPATH Reference Center. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brčić, L.; Jakopović, M.; Brčić, I.; Klarić, V.; Milošević, M.; Šepac, A.; Samaržija, M.; Seiwerth, S. Reproducibility of Histological Subtyping of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, N.; Mangiante, L.; Le-Stang, N.; Gustafson, C.E.; Boyault, S.; Damiola, F.; Alcala, K.; Brevet, M.; Thivolet-Bejui, F.; Blanc-Fournier, C.; et al. Redefining Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Types as a Continuum Uncovers Immune-Vascular Interactions. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, R.; Stawiski, E.W.; Goldstein, L.D.; Durinck, S.; De Rienzo, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Gnad, F.; Nguyen, T.T.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Identifies Recurrent Mutations, Gene Fusions and Splicing Alterations. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

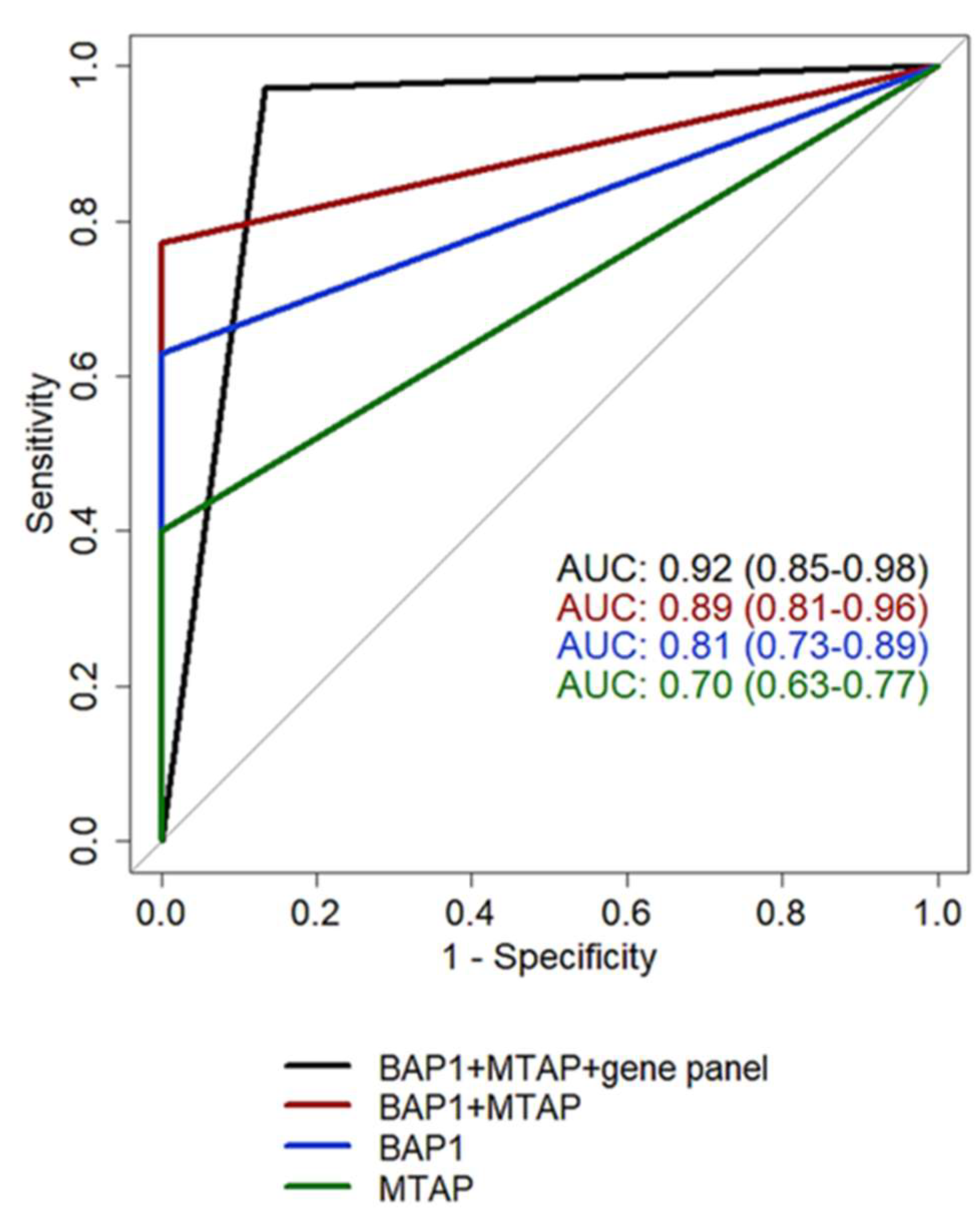
| BAP1 | p16 | MTAP | BAP1+MTAP | 117 gene panel | BAP1+MTAP+117 gene panel* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95%CI) | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| (0.73-0.89) | (0.61-0.77) | (0.63-0.77) | (0.81-0.96) | (0.76-0.96) | (0.85-0.98) | |
| Sensitivity (95%CI) | 0.63 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| (0.46-0.77) | (0.21-0.52) | (0.23-0.57) | (0.63-0.89) | (0.69-0.94) | (0.91-1) | |
| Specificity (95%CI) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.87 |
| (1-1) | (1-1) | (1-1) | (1-1) | (0.93-1) | (0.73-0.97) | |
| Accuracy | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.92 |
| (95%CI) | (0.71-0.88) | (0.59-0.75) | (0.58-0.77) | (0.80-0.94) | (0.83-0.95) | (0.86-0.98) |
| PPV | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.90 |
| (95%CI) | (1-1) | (1-1) | (1-1) | (1-1) | (0.94-1) | (0.81-0.97) |
| NPV (95%CI) | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| (0.61-0.79) | (0.54-0.65) | (0.53-0.67) | (0.70-0.88) | (0.73-0.94) | (0.89-1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





