Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cardiac Ischemia and Reperfusion (CIR) Induction
2.3. Assessment of Cardiac Activity during CIR
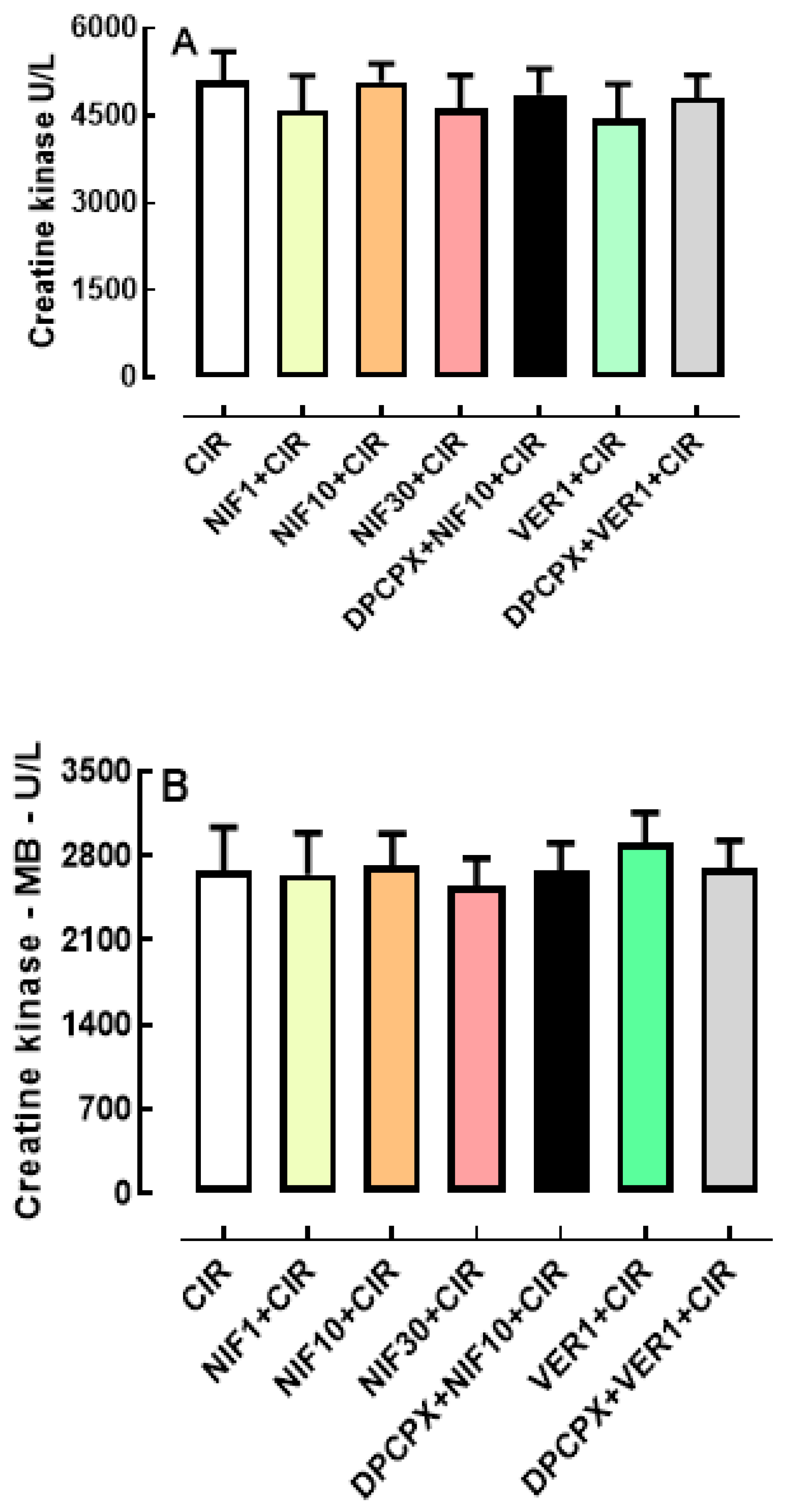
2.4. Biochemical Assessment of Heart Lesions' Biomarkers
2.5. Pharmacological Treatments
- (1)
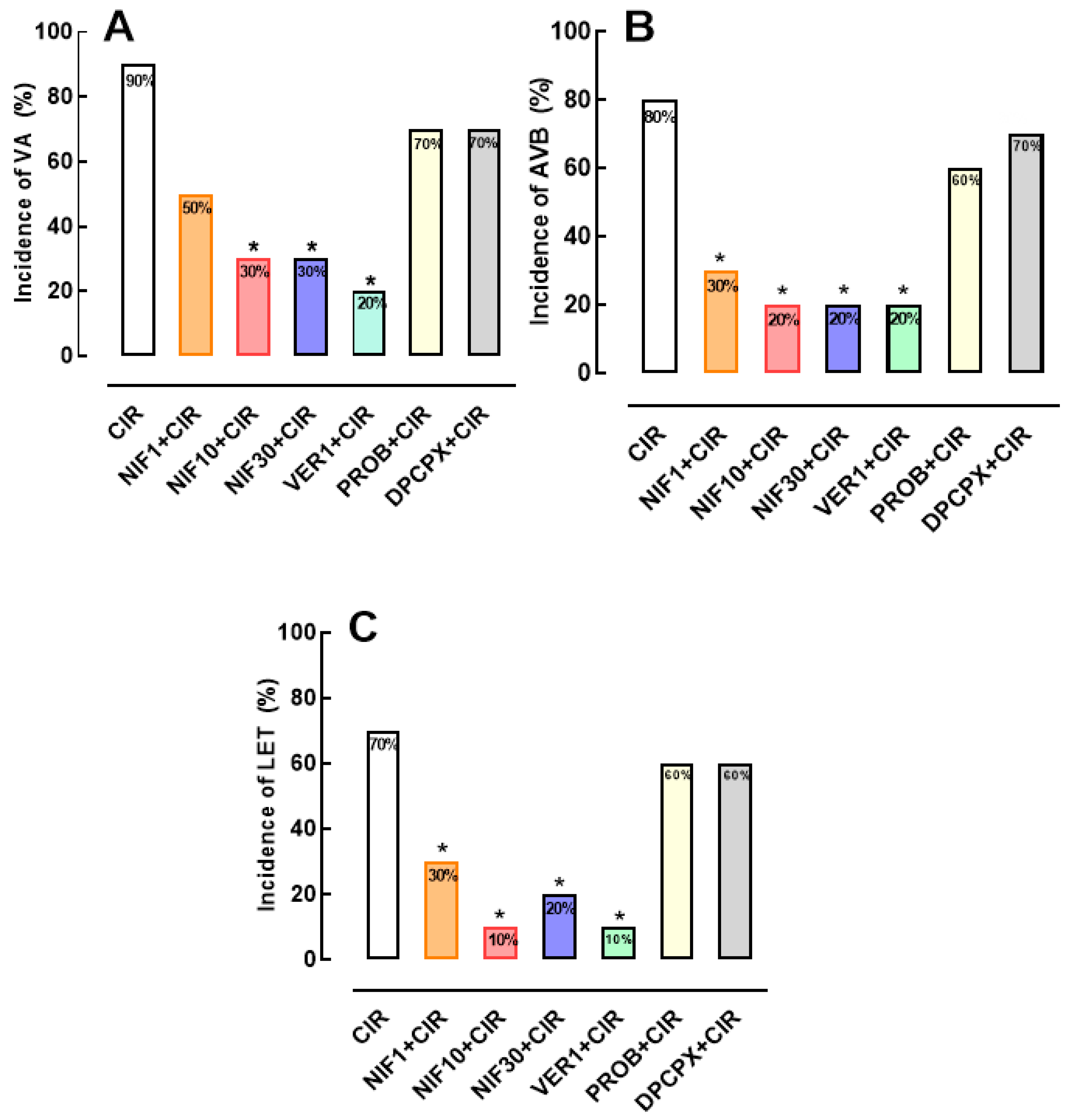
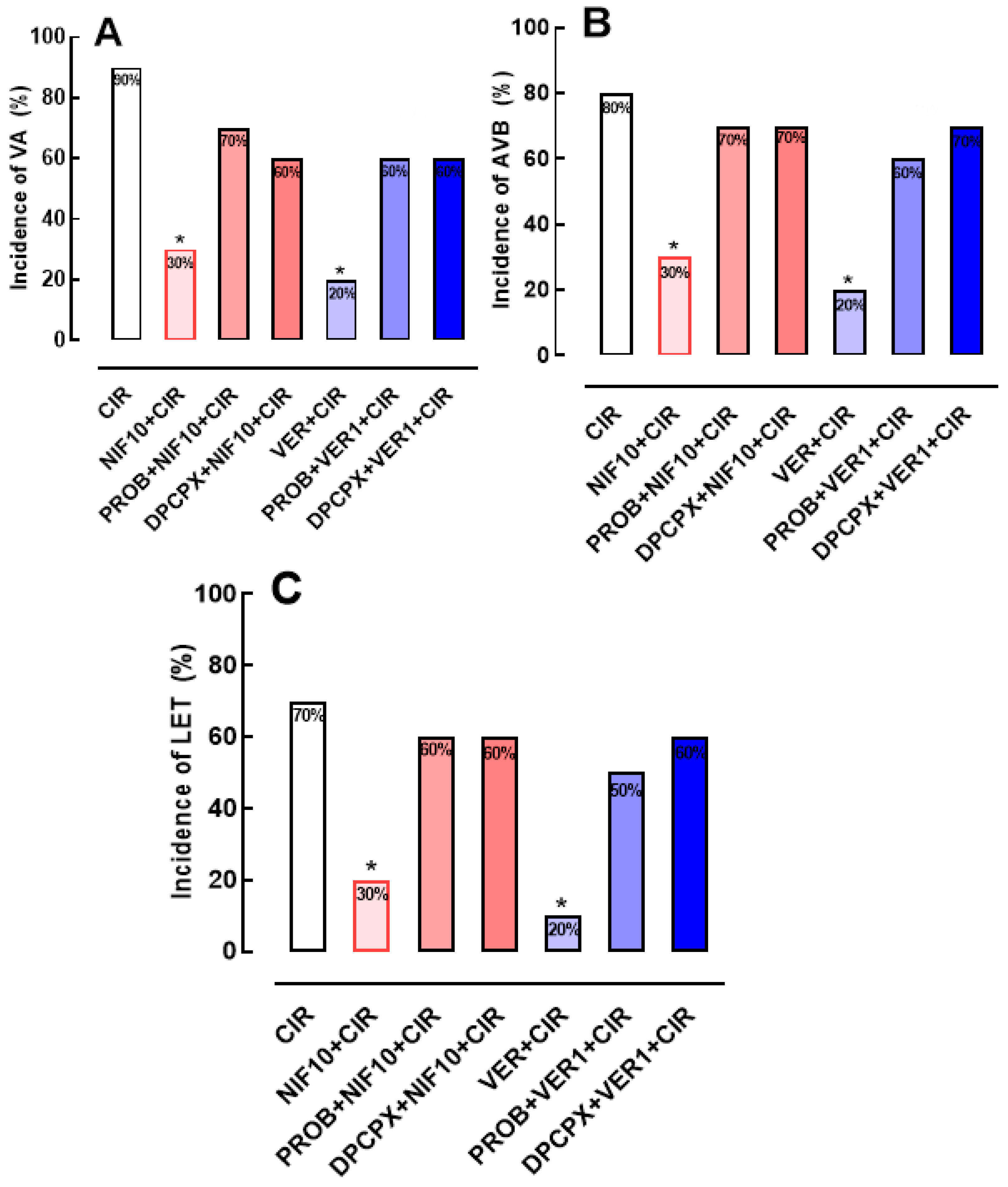
- CIR group (n = 40): animals treated with 0.9% SS vehicle (IV) one minute before were subjected to a surgical procedure to induce cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring (100 min) for determination of VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (2)
- PROB+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with blocker ABC transporter-mediated cAMP efflux from cardiac cells probenecid (PROB, 100 mg/kg, IV) five minutes before were subjected to a surgical procedure to induce cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring (100 min) for determination of VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (3)
- NIF1+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with NIF (1mg/kg, IV) one minute before were subjected to a surgical procedure to induce cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring (100 min) for determination of VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (4)
- NIF10+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with NIF (10 mg/kg, IV) one minute before were subjected to a surgical procedure to induce cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring (100 min) for determination of VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (5)
- NIF30+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with NIF (30 mg/kg, IV) one minute before were subjected to a surgical procedure to induce cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring (100 min) for determination of VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (6)
- PROB+NIF+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with block ABC transporter-mediated cAMP efflux from cardiac cells probenecid (PROB; 100 mg/kg, IV), 5 min before administration of NIF (10 mg/kg, IV) for 1 min before induction of cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by cardiac reperfusion, and subsequent ECG monitoring for 100 min for determination of the VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (7)
- DPCPX+NIF+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with A1R antagonist 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX; 100 µg/kg, IV), 5 min before administration of NIF (10 mg/kg, IV) for 1 min before induction of cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by cardiac reperfusion, and subsequent ECG monitoring for 100 min for determination of the VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (8)
- VER1+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with verapamil (VER, 1 mg/kg, IV) for 1 min before induction of cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by coronary reperfusion (75 min), and subsequent ECG monitoring (100 min) for determination of the VA, AVB and LET incidence.
- (9)
- PROB+VER+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with blocker ABC transporter-mediated cAMP efflux from cardiac cells probenecid (PROB; 100 mg/kg, IV), 5 min before administration of VER (1 mg/kg, IV) for 1 min before induction of cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by cardiac reperfusion, and subsequent ECG monitoring for 100 min for determination of the VA, AVB and LET incidence;
- (10)
- DPCPX+VER+CIR group (n = 20): animals treated with A1R antagonist 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX; 100 µg/kg, IV), 5 min before administration of VER (1 mg/kg, IV) for 1 min before induction of cardiac ischemia (10 min), followed by cardiac reperfusion, and subsequent ECG monitoring for 100 min for determination of the VA, AVB and LET incidence;
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
References
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2015 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian, D. ; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, T.; Reis, V.A.; Linke, S.E.; Greenberg, B.H.; Mills, P.J. Depression in Heart Failure a Meta-Analytic Review of Prevalence, Intervention Effects, and Associations with Clinical Outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.; Ortengren, A.R.; Zeitler, E.P. Arrhythmias After Acute Myocardial Infarction. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2023, 96, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naryzhnaya, N. V.; Maslov, L.N.; Derkachev, I.A.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Prasad, N.R.; Singh, N.; Fu, F.; Pei, J.-M.; Sarybaev, A.; et al. The Effect of an Adaptation to Hypoxia on Cardiac Tolerance to Ischemia/Reperfusion. J. Biomed. Res. 2022, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricati-Neto, A.; Errante, P.R.; Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S. Recent Advances in Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies of Cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Tavares, J.G.P.; Vasques, E.R.; Errante, P.R.; Araújo, E.A. de; Pires-Oliveira, M.; Scorza, C.A.; Scorza, F.A.; Taha, M.O.; Caricati-Neto, A. Cardioprotective Effects of Pharmacological Blockade of the Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter on Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Acta Cir. Bras. 2020, 35, e202000306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Errante, P.R.; Ferreira, R.M.; Tavares, J.G.P.; Paula, L. de; Araújo, E.A.; Govato, T.C.P.; Tikazawa, E.H.; Reis, M. do C.M.; Luna-Filho, B.; et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Lipstatin Derivative Orlistat on Normotensive Rats Submitted to Cardiac Ischemia and Reperfusion. Acta Cir. Bras. 2018, 33, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Errante, P.R.; Tavares, J.G.P.; Ferraz, R.R.N.; Gomes, W.J.; Taha, M.O.; Scorza, C.A.; Scorza, F.A.; Caricati-Neto, A. Pharmacological Modulation of B-Adrenoceptors as a New Cardioprotective Strategy for Therapy of Myocardial Dysfunction Induced by Ischemia and Reperfusion. Acta Cir. Bras. 2019, 34, e201900505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, J.G.P.; Vasques, E.R.; Arida, R.M.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Cabral, F.R.; Torres, L.B.; Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Caricati-Neto, A.; Godoy, C.M.G.; et al. Epilepsy-Induced Electrocardiographic Alterations Following Cardiac Ischemia and Reperfusion in Rats. Brazilian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrao Tavares, J.G.; Menezes Rodrigues, F.S.; Vasques, E.R.; Maia Reis, M. do C.; Paula, L. de; Luna Filho, B.; Errante, P.R.; Caricati Neto, A.; Bergantin, L.B. A Simple and Efficient Methodology for the Study of Cardioprotective Drugs in Animal Model of Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion. J. Mol. Imaging Dyn. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, J.G.P.; Errante, P.R.; Govato, T.C.P.; Vasques, Ê.R.; Ferraz, R.R.N.; Taha, M.O.; Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Caricati-Neto, A. Cardioprotective Effect of Preconditioning Is More Efficient than Postconditioning in Rats Submitted to Cardiac Ischemia and Reperfusion1. Acta Cir. Bras. 2018, 33, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Diego, J.M.; Antzelevitch, C. Cellular Basis for ST-Segment Changes Observed during Ischemia. J. Electrocardiol. 2003, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.-X.; Lankipalli, R.S.; Burke, J.F.; Musco, S.; Kowey, P.R. Ventricular Repolarization Components on the Electrocardiogram: Cellular Basis and Clinical Significance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.J.; Curtis, M.J.; Hearse, D.J.; Campbell, R.W.; Janse, M.J.; Yellon, D.M.; Cobbe, S.M.; Coker, S.J.; Harness, J.B.; Harron, D.W. The Lambeth Conventions: Guidelines for the Study of Arrhythmias in Ischaemia Infarction, and Reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 1988, 22, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, C.E.; Bell, J.R.; Pepe, S.; Delbridge, L.M.D. Benchmarking Ventricular Arrhythmias in the Mouse--Revisiting the “Lambeth Conventions” 20 Years On. Heart. Lung Circ. 2008, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
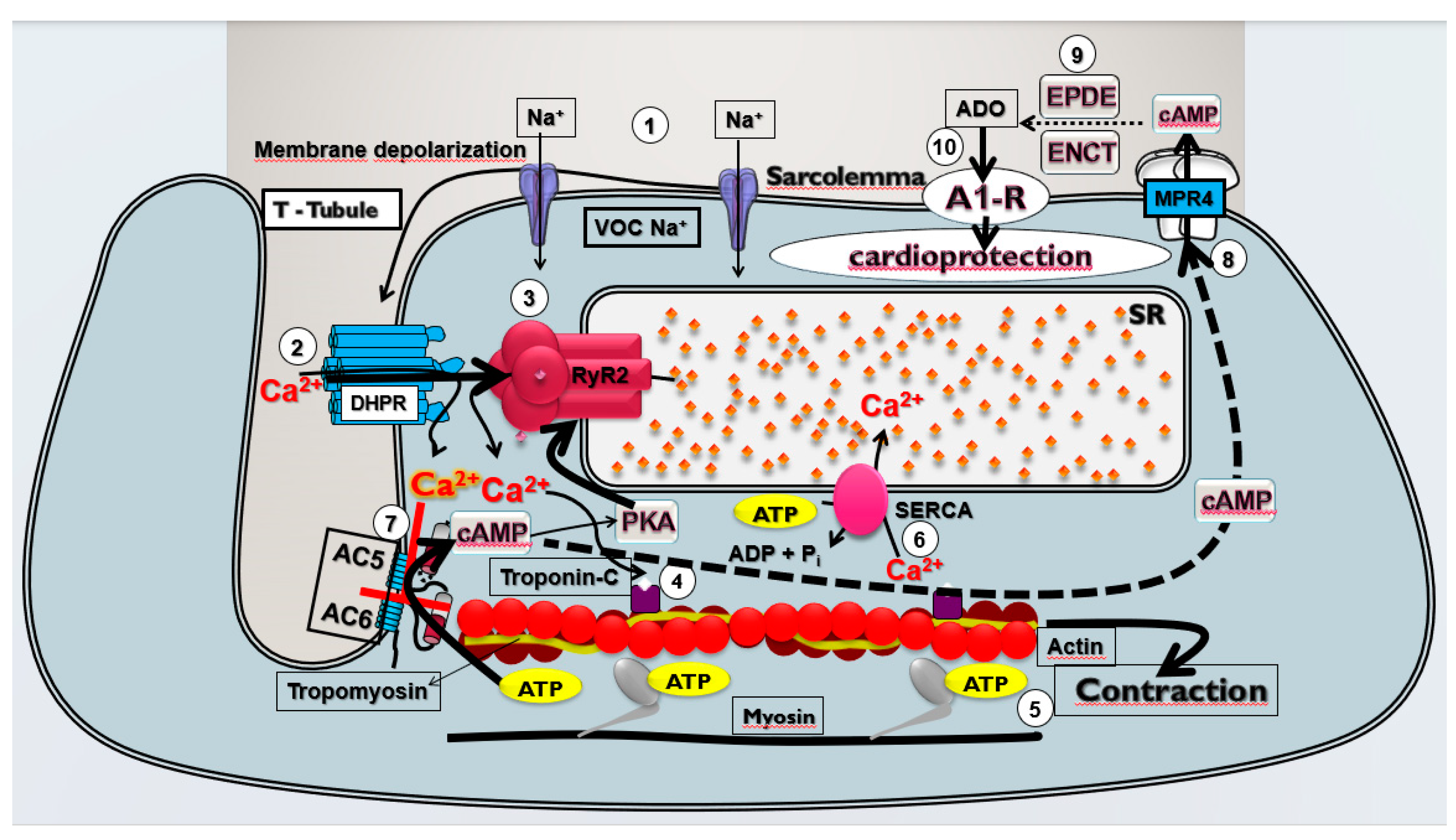
- Bers, D.M. Calcium Cycling and Signaling in Cardiac Myocytes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Maier, L.S.; Bers, D.M. Role of Sodium and Calcium Dysregulation in Tachyarrhythmias in Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1956–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halestrap, A.P.; Clarke, S.J.; Khaliulin, I. The Role of Mitochondria in Protection of the Heart by Preconditioning. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-H.H.; Weiss, J.N. Arrhythmogenic Consequences of Intracellular Calcium Waves. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H997–H1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Pires-Oliveira, M.; Duarte, T.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Chiavegatti, T.; Godinho, R.O. Calcium Influx through L-Type Channels Attenuates Skeletal Muscle Contraction via Inhibition of Adenylyl Cyclases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 720, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.J.; Ma, H.; Green, R.D.; Yu, H.; Ma, H.; Green, R.D.; Yu, H.J.; Ma, H.; Green, R.D. Calcium Entry via L-Type Calcium Channels Acts as a Negative Regulator of Adenylyl Cyclase Activity and Cyclic AMP Levels in Cardiac Myocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 44, 689–693. [Google Scholar]
- Halls, M.L.; Cooper, D.M.F. Regulation by Ca2+-Signaling Pathways of Adenylyl Cyclases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, Z.M.; Naren, A.P.; Xiang, Y.; Best, P.M. MRP4 and CFTR in the Regulation of cAMP and β-Adrenergic Contraction in Cardiac Myocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 681, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, N.; Shneyvays, V.; Balas, N.; Jacobson, K.A.; Nawrath, H.; Shainberg, A. Cardioprotective Effects of Adenosine A1 and A3 Receptor Activation during Hypoxia in Isolated Rat Cardiac Myocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 217, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Gao, Z.-G.; Nithipatikom, K.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Veldhoven, J.P.D. van; Jacobson, K.A.; Gross, G.J.; Auchampach, J.A. Protection from Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by a Positive Allosteric Modulator of the A₃ Adenosine Receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.E.B.; Barbosa, A.H.P.; Nicolau, L.A.D.; Medeiros, J.V.R.; Pires-Oliveira, M.; Póvoa, R.M.; Govato, T.C.P.; Júnior, H.J.F.; de Carvalho, R.G.; Luna-Filho, B.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation by Low Molecular Weight Heparin of Purinergic Signaling in Cardiac Cells Prevents Arrhythmia and Lethality Induced by Myocardial Infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, J.; Flood, A.; Linden, J.; Matherne, G.P.; Headrick, J.P. Adenosine-Mediated Cardioprotection in Ischemic-Reperfused Mouse Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasley, R.D.; Rhee, J.W.; Van Wylen, D.G.; Mentzer, R.M. Adenosine A1 Receptor Mediated Protection of the Globally Ischemic Isolated Rat Heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1990, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasley, R.D.; Mentzer, R.M. Dose-Dependent Effects of Adenosine on Interstitial Fluid Adenosine and Postischemic Function in the Isolated Rat Heart. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 286, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Lasley, R.D.; Kristo, G.; Keith, B.J.; Mentzer, R.M. The A2a/A2b Receptor Antagonist ZM-241385 Blocks the Cardioprotective Effect of Adenosine Agonist Pretreatment in in Vivo Rat Myocardium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H426–H431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalla, A.K.; Shryock, J.C.; Shreeniwas, R.; Belardinelli, L. Pharmacology and Therapeutic Applications of A1 Adenosine Receptor Ligands. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G.; Pelleg, A. Cardiac Purinergic Signalling in Health and Disease. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardinelli, L.; Lerman, B.B. Adenosine: Cardiac Electrophysiology. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1991, 14, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shryock, J.C.; Belardinelli, L. Adenosine and Adenosine Receptors in the Cardiovascular System: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Pharmacology. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 79, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, E.; McIntosh, V.J.; Lasley, R.D. Adenosine A₂A and A₂B Receptors Are Both Required for Adenosine A₁ Receptor-Mediated Cardioprotection. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1183–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmaliya, V.B.; Church, J.E.; Coupar, I.M.; Rose’Meyer, R.B.; Pouton, C.W.; White, P.J. Cardioprotection Induced by Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonists in a Cardiac Cell Ischemia Model Involves Cooperative Activation of Adenosine A2A and A2B Receptors by Endogenous Adenosine. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; de Oliveira, M.P.; Araújo, EA.; Ferraz, HB.; Finsterer, J.; Olszewer, E.; Taha, M.O.; Scorza, C.A.; Caricati-Neto, A.; Scorza, F.A. Role of cardiac β1-adrenergic and A1-adenosine receptors in severe arrhythmias related to Parkinson's disease. Clinics. 2023, 78, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Rodrigues, F.S.; Tavares, J.G.P.; Errante, P.R.; Vasques, E.V.; Reis, M.C.M.; Luna-Filho, B.; Scorza, F.A.; Caricati-Neto, A.; Bergantin, L.B. Role of the Extracellular Ca2+/cyclic AMP-Adenosine Signaling Pathways in Cardioprotection. J. Thrombo. Cir. 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthal, A.P.; Kulkarni, R.; Kumar, D.; Bagul, C.; Mukherjee-Kandhare, A.A.; Kandhare, A.D.; Ambavade, S.D.; Wagh, V.; Bodhankar, S.L. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate: Recent and future perspectives on various diseases. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




