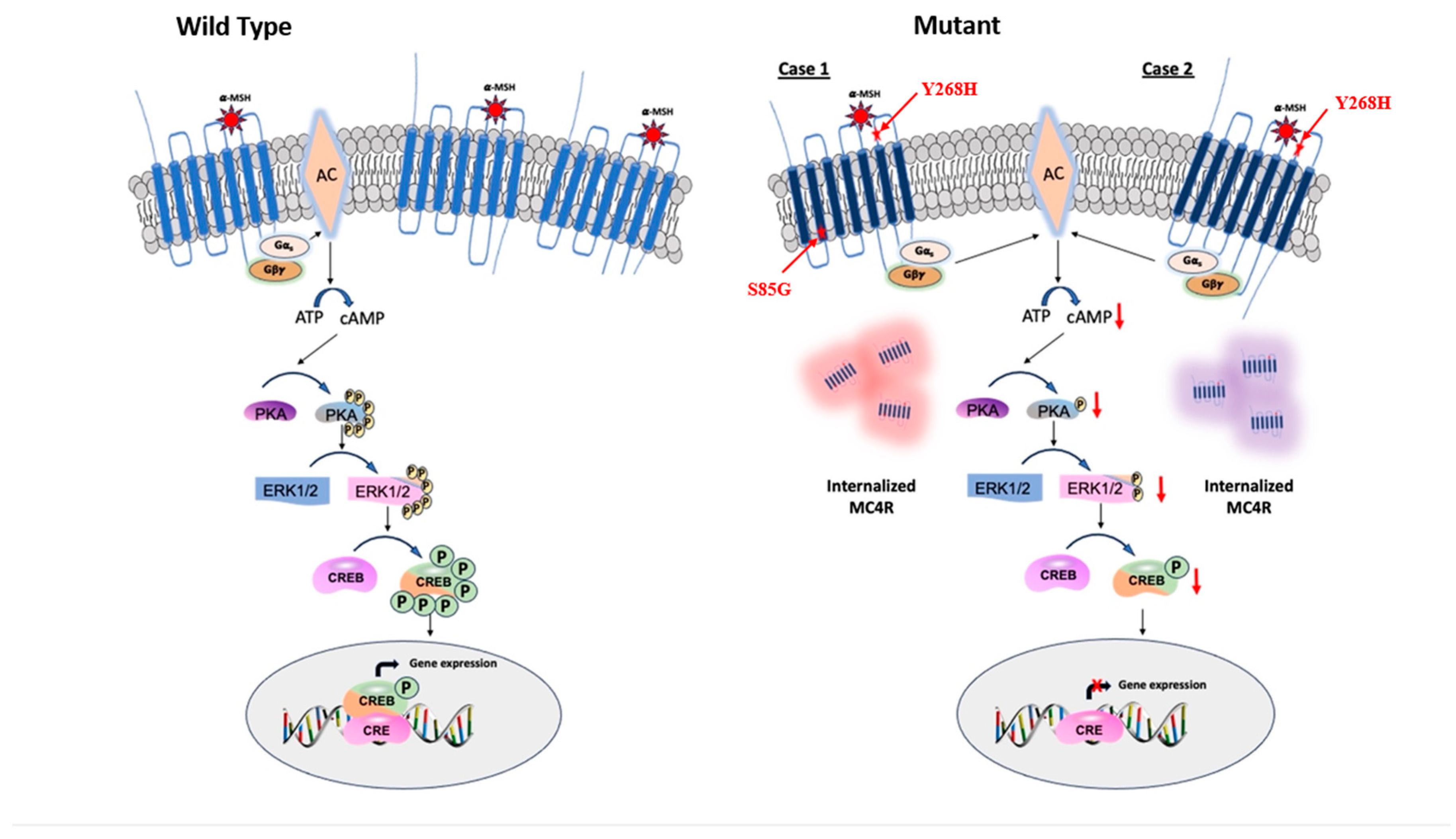
1. Background
Obesity is a complex condition caused by genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors , which has become a significant health problem worldwide (1). Monogenic obesity due to single-gene pathogenic variants in the leptin-melanocortin pathway, an essential energy homeostasis pathway accounts for 6% of severe early-onset obesity cases (2). The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) gene is a crucial component in this pathway and is predominantly expressed in the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) of the hypothalamus. The first evidence supporting the association of the MC4R with obesity was seen in mice in 1997 (3), and subsequently in humans in 1998 by two independent groups (4) (5). These studies showed that target disruption of the MC4R or frameshift mutation in the gene cause severe obesity accompanied by hyperphagia both in mice and humans (3–5). The MC4R gene is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds to its endogenous ligand the alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) and activates adenylate cyclase-3 (ADCY3). The activation of ADCY3 subsequently converts adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic monophosphate (cAMP), a secondary messenger vital in various downstream signaling cascades (6). The augmented intracellular cAMP levels, in turn, stimulate the activation of the downstream effectors such as extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and cyclic-AMP response element binding protein (CREB), which play an integral role in regulating energy intake and expenditure, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of obesity (7,8).
The MC4R gene, a one-exon gene, is localized on the long arm of human chromosome 18, 18q21.3. The gene encodes a 332 amino acid transmembrane receptor protein. The MC4R receptor binds to α-MSH, a peptide produced as a result of the cleavage of the POMC precursor by the pro-hormone convertase PC1/3 and PC2 (9). The MC4R gene regulates energy homeostasis by decreasing appetite and increasing satiety signaling downstream the POMC neurons (10). Pathogenic variants with complete or partial loss of function in MC4R are the most common cause of monogenic obesity, accounting for up to 6% of the severe early-onset form of obesity (11). Many of these genetic variations lead to reduced protein expression, hindered α-MSH binding, altered receptor trafficking, or inefficient coupling with the stimulatory G-protein, Gαs (12,13). Patients carrying disease-causing variants in the MC4R gene are characterized by extreme obesity, hyperphagia and increased linear growth (14). In most cases the mode of inheritance is autosomal dominant, while less frequently patients exhibit an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern (15). Patients with heterozygous MC4R variants are more common than homozygous or compound heterozygous carriers, where the latter develop more severe form of obesity c(3,16). So far, numerous heterozygous mutations in MC4R linked to obesity with variable severity have been studied functionally using in-vitro cell models, revealing a subset that disrupts G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) signaling. However, approximately 25% of MC4R mutations identified in obese cohorts do not affect the cAMP levels, mirroring WT traits, suggesting that the MC4R gene regulates weight through various cellular signaling mechanisms such as endocytosis and disruption of receptor homodimerization (17).
In this study, we performed clinical, genetic, and biochemical investigations of two patients in Qatar who exhibited pronounced early-onset obesity due to novel variants in the MC4R gene. We conducted in-vitro functional characterization, in silico prediction tools, and molecular dynamic stimulations to determine the pathogenicity and contribution of the variants to severe obesity.
2. Methodology
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) for the protection of human subjects in Sidra Medicine, Qatar (IRB reference number 1689931). Written consent was obtained from the patients and their parents for their participation in this study. Peripheral blood was collected from patients and available family members in EDTA tubes for DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using the QIAamp DNA blood midi kit (Cat. 51185, Qiagen, Germany) according to the manufacturer's recommendation. The concentrations and purities were assessed using Nanodrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermoscientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For Next generation sequencing, exonic regions of all genes of interest were captured using an optimized set of DNA hybridization probes. The captured DNA was sequenced by massively parallel sequencing using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform reversible dye terminator (RDT) (Illumina, San Diego, Ca, USA), detailed DNA sequencing and sequencing analysis methodology is described in our recently published article (18).
2.1. MC4R Cloning
The MC4R wild type and mutant cDNA (full length) were cloned into pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK vectors. These constructs were purchased from (GenScript). The plasmid contains DYKDDDK epitope, AMPr (ampicillin-resistant) for bacterial selection, and NeoR (Neomicin-resistant) for mammalian cell selection. The constructs were cloned in a CMV-driven and T7 promotor with a sequence of (TAATACGACTCACTATAG). The vector contained six restriction enzyme sites for Nhe I, Afl II, Hind III, Kpn I, and BamH I. The target gene was cloned after the Kozak sequence (GCCACC) in an open reading frame and was tagged with the DYK tag (DYKDDDDK). The DNA plasmids were transformed into chemically competent E.coli (Sigma Aldrich).
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
GT1-7 mouse hypothalamic GnRH neuronal cells, obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM)-high glucose, enriched with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2 mM L-Glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. The cells were kept at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The growth medium was replenished with fresh medium every 48 hours while subculturing activities were carried out upon reaching 80% confluency. Transient transfection was carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions and 36 h post-transfection, the cells were used for the downstream analysis.
2.3. Isolation of Total/Cell Surface Proteins and Western Blotting
After transfecting GT1-7 cells with either wild-type or mutant MC4R, we extracted total protein by lysing the cells with RIPA buffer. For isolating cell surface proteins, we used the Pierce Cell Surface Protein Isolation Kit (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. First, the cells were chilled at 4 °C for 15-20 minutes and then biotinylated with EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin for 30 minutes at the same temperature. We then stopped the biotinylation process with a quenching buffer and lysed the cells on ice using the kit-provided lysis buffer. The biotinylated proteins were isolated by incubating the lysates with NeutrAvidin Agarose, washed thrice, and eluted using the kit's elution buffer, heated at 95°C for 5 minutes. The total and cell surface proteins were loaded onto a 4–12% Nupage gel and subsequently transferred onto a Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) membrane, blocked with a non-fat milk buffer, and incubated overnight at 4 °C with the appropriate primary antibody. The membrane was then incubated with an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody, and proteins were visualized using Chemdoc (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and quantified using ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.4. cAMP Assay
The cAMP assay was performed using the cAMP ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) from Cell Biolabs Inc., according to the manufacturer's instructions. GT1-7 cells were cultured in a 96-well plate until 80-90% confluence and then transfected with wild-type or mutant MC4R constructs. Cells were exposed to 0.5 mM IBMX for 10 min followed by subsequent stimulation with 100 nM α-MSH for 15 minutes. Post-stimulation, cells were lysed, and lysates were added to the pre-coated cAMP ELISA plate. The cAMP present in the lysate competed with cAMP conjugate for the anti-cAMP antibody binding sites during an incubation period at room temperature. After washing away unbound components, we added an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody was added and incubated the plate again for 2 hours. Following incubation, we added a colorimetric substrate for HRP, and the reaction was suspended after an appropriate period. The intensity of the color developed was inversely proportional to the amount of cAMP in the sample. The plate was read at 450 nm and the cAMP concentration in samples was determined by comparing with the standards.
2.5. Structure-based Prediction of Mutations on Protein Stability
Since the crystal structure of MC4R in complex with its native ligand, alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH), is not available, we instead used the recently resolved crystal structure of MC4R in complex with a synthetic analog of α-MSH, (Nle4, D-Phe7)-α-MSH (i.e., NDP-α-MSH), to study the structural and ligand-binding changes induced by the mutations in the complex (19). The crystal structure of the MC4R-NDP-α-MSH complex was obtained from the RCSB database (PDB: 7PIV, Chain P: NDP-α-MSH (aa:1 -13), Chain R: MC4R (aa 40-316) and Ca2+ (co-factor)). The effect of the mutations on the stability of the complex was assessed using computational prediction tools such as mCSM (20), Maestro (21), I-Mutant2.0 (22), and MUpro (23).
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
All-atom, explicit solvent, molecular dynamics simulations of MC4R in complex with NDP-α-MSH were performed using NAMD 3.0 software (24) and CHARMM36m force field (25). The topology and parameter input files required to simulate the wild type (WT) and mutant complexes were generated using the CHARMM-GUI server (26). Briefly, the complex structure was solvated in TIP3P cubic water box (27) with at least 10 Å distance between any of the atoms in the complex and edge of the water box. The biomolecular simulation system was then subjected to energy minimization and thermal equilibration with periodic boundary conditions (28). This was followed by 100 ns production simulation runs. The integration timestep was set up at 2 fs. A 12 Å cut-off with a 10 Å switching distance was chosen to handle short-range non-bonded interactions, while long-range non-bonded electrostatic interactions were conducted using a Particle-mesh scheme at 1 Å PME grid spacing (29–32). MD trajectories were analyzed using the available tools in VMD. Dynamic cross-correlation (DCC) analysis was performed for MC4R Cα atoms using the Bio3D R package. Results were represented as heatmaps that indicate the range of correlations from -1 to +1. A cut-off of 0.8 was applied to the positive and negative DCC values to investigate the changes in the lower and upper DCC extremes, and the results were represented as cartoon images.
2.7. Statical Analysis
Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cases Presentation
Case 1: Patient 1 is an 11-year-old Jordanian girl with morbid obesity. The patient had a birth weight of 3.5 kg and started to gain weight when she was a few months old. Her current weight is 72.5 kg, BMI of 36.4 Kg/m2 (Z-score of 2.88) and a BMI percentile of 99.8th centile. She has a strong family history of severe obesity; both her mother and father had gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity. All her baseline investigations were normal.
Case 2: Patient 2 is a 17-year-old Qatari boy with morbid obesity. His birth weight was 4 Kg, and he was born to consanguineous parents. He started to gain weight at the age of 2 years; his current weight is 277 with BMI of 88.4 Kg/m
2 (Z-score of +3.8) and a BMI percentile >99.99th centile. He has marked hyperphagia, difficulty breathing and elevated liver enzymes (ALT: 85U/L (5-30U/L), AST: 12U/L (0-39U/L), ALP: 191U/L (52-171U/L).
Table 1 summarizes the biochemical investigations of the two cases.
3.2. Genetic analysis
A targeted gene panel sequencing of 52 genes associated with obesity revealed two novel missense variants in
MC4R, c.253A>G p.Ser85Gly and c. 802T>C p.Tyr268H. Patient 1 had a compound heterozygous p.Ser85Gly and p.Tyr268His variants which was inherited from both parents who remained obese despite undergoing bariatric surgery (gastric bypass). Patient 2 had a heterozygous missense variant p.Tyr268His. The mother did not carry the variant, and the father's DNA was unavailable for genetic analysis.
A search in public databases such as gnomAD V2.1.1, 1000Genomes, TOPMED and GME Variome verified that these variants were not reported in the literature previously. To assess the pathogenic mechanism of these two MC4R variants, we performed in silico analysis; the variant p.Ser85Gly was predicted to affect the polarity of the protein due to the replacement of a highly polar (Serine) to a nonpolar (Glycine) residue. The variant is located on the second transmembrane helix of the MC4R gene in a highly conserved residue among diverse species suggesting it could have a deleterious effect on the protein. The second novel variant, p.Tyr268His resulted in amino acid substituting tyrosine (neutral) to histidine (positively charged) on residue 268 on the sixth transmembrane helix. These novel variants were strongly predicted to be deleterious to the MC4R gene using three independent in-silico prediction tools, SIFT, Polyphyne-2, and MutationTaster (Table 2).
3.3. Prediction analysis and molecular dynamics simulation
In order to investigate the effect of the identified mutations on the structural stability of MC4R protein, we used the online-available structure-based prediction tools (20–23,33,34). Results showed a destabilizing effect of these mutations on the protein structure (
Table 3). However, these tools do not provide a detailed picture of the structural dynamics of the complex. To get a detailed picture of how these mutations affect the structural dynamics, we performed 100 ns all-atom, explicit-solvent MD simulations of the WT and mutant complexes (
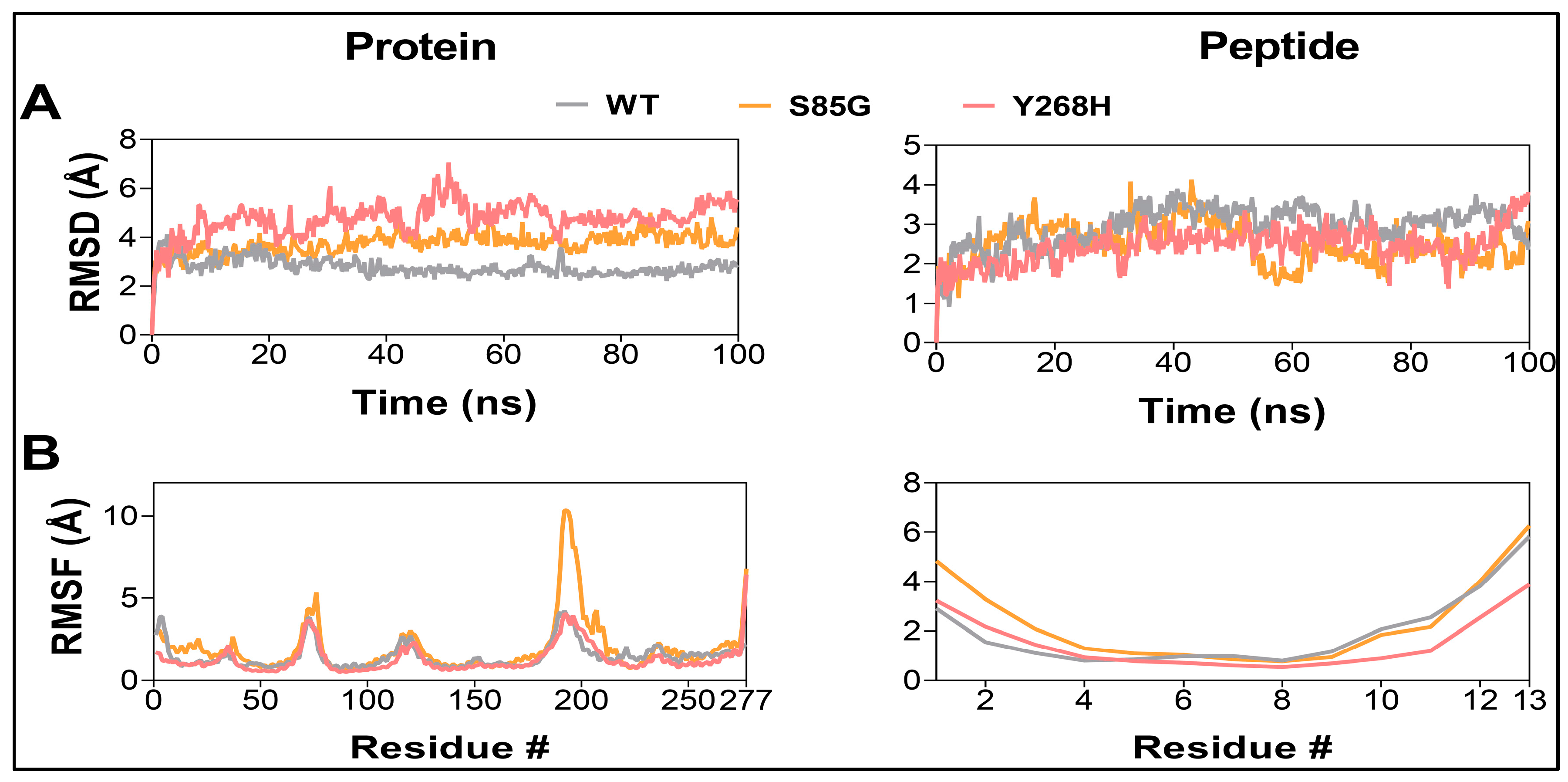
Figure 1). Analyzing MD trajectories showed an overall increase in the structural dynamics of the
MC4R mutants, as indicated by the increased RMSD and DCC values of the protein. No similar changes were observed in the peptide ligand (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). These destabilization effects could potentially impact the localization of the MC4R in the cell membrane and/or hinder the signal transmission that follows ligand binding.
3.4. The S85G and Y268H mutants reduce MC4R cell surface expression
GT1-7 cells derived from the murine hypothalamus are a widely recognized model for examining melanocortin-associated signaling pathways and energy homeostasis mechanisms. Thus, we used GT1-7 and overexpressed either the wild-type or mutant MC4R or empty vector (control). First, we sought to investigate the impact of S85G and Y268H substitution on the total protein level of Mc4R in cells with or without stimulating α-MSH. Notably, the level of MC4R was not altered in GT1-7 cells transfected with mutant MC4R compared with WT-transfected cells, suggesting that S85G and Y268H substitution did not affect protein expression (
Figure 3A,B). Moreover, no significant difference was observed in the total MC4R level in the cells after stimulation with α-MSH, indicating that ligand stimulation did not alter the MC4R protein synthesis.
Our next step was to delve into the membrane localization of the MC4R receptor. To this end, cell surface protein biotinylation was used to isolate the membrane MC4R in wild-type or mutant MC4R transfected cells with or without α-MSH stimulation. Interestingly, the membrane localization of MC4R was significantly increased in cells transfected with WT-MC4R compared with control. In contrast, S85G and Y268H substitution significantly affects the membrane localization of mutant MC4R when compared with control and WT-MC4R, suggesting that the mutant MC4R proteins are likely to be retained intracellularly, hinting at potential challenges in achieving proper membrane localization (
Figure 3C,D). Moreover, no significant difference was observed in MC4R membrane localization in cells stimulated with α-MSH when compared with their respective untreated group.
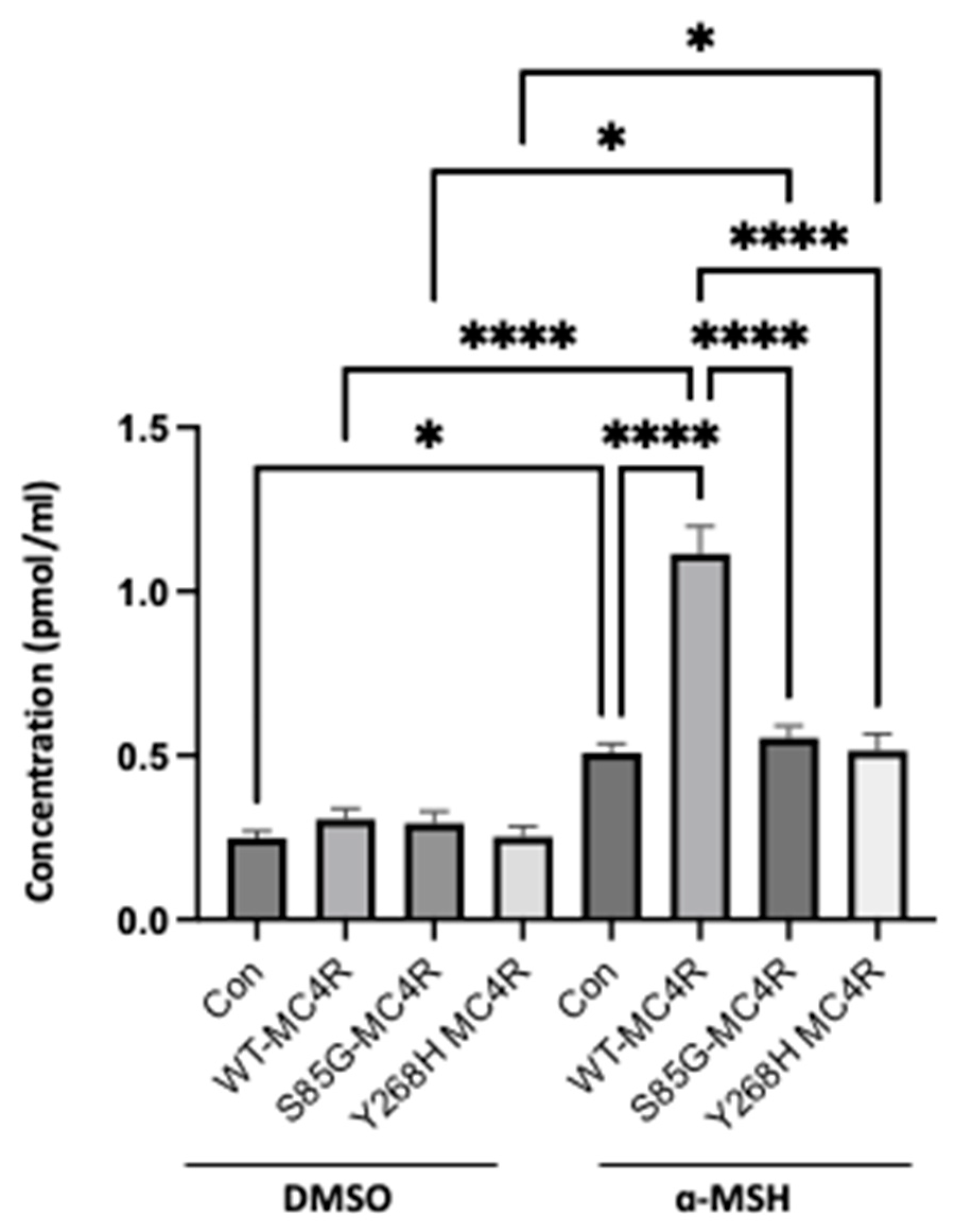
3.5. The S85G and Y268H mutants decrease agonist-stimulated cAMP accumulation
To understand the effect of S85G and Y268H variants on
MC4R functionality, we transfected GT1-7 cells with either the wild-type
MC4R (WT-MC4R) or its mutant counterparts. Post-transfection, cells were treated with 0.5 mM IBMX for a duration of 10 minutes and subsequently incubated with 100 nM α-MSH for an additional 15 minutes. While the basal cAMP levels remained unaltered, a distinct response pattern emerged upon agonist stimulation. Cells overexpressing the WT-MC4R displayed a pronounced surge in cAMP production. In contrast, cells bearing the novel
MC4R variants did not exhibit a significant increase in cAMP levels when compared with their respective unstimulated controls (
Figure 4).
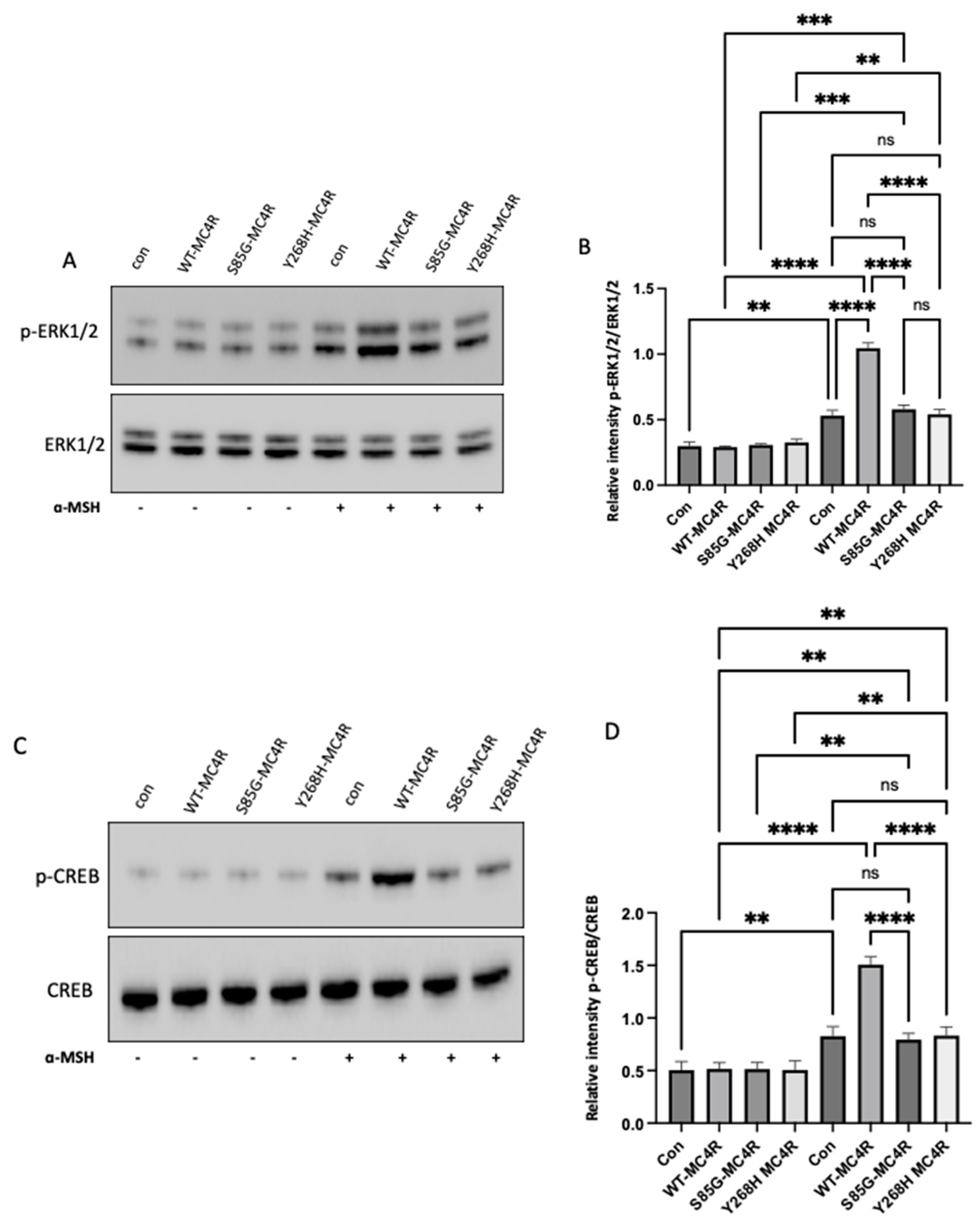
3.6. Mutant MC4R fails to activate the downstream signaling.
To delineate the downstream signaling dynamics mediated by mutant MC4R, GT1-7 cells were transfected with either WT-MC4R or its mutant variants. Following a 48-hour incubation post-transfection, these cells were exposed to 100 nm α-MSH for 3 hours. Consistent with the cAMP data, α-MSH stimulation led to a marked elevation in ERK1/2 phosphorylation in cells expressing WT-MC4R, as opposed to their unstimulated counterparts. Intriguingly, this agonist-mediated activation was conspicuously absent in cells harboring the mutant MC4R (
Figure 5A,B). Similarly, when observing CREB phosphorylation, cells transfected with WT-MC4R exhibited a significant boost in response to α-MSH stimulation. In contrast, cells expressing the mutant MC4Rs demonstrated minimal reactivity (
Figure 5C,D). This pattern indicates that the mutations could potentially hinder MC4R's capacity to effectively relay downstream signaling in the presence of the agonist. The mechanism by which loss of function variants on the
MC4R gene inactivate the downstream signaling cascade and dysregulate energy balance is summarized in
Figure 6.
4. Discussion
Monogenic obesity due to MC4R pathogenic variants is the most common cause of severe childhood obesity (2). We identified two novel missense variants in two unrelated patients (a Qatari and a Jordanian) with severe early-onset obesity. The patients described in this report resembled previously described cases of MC4R patients with early-onset obesity, hyperphagia, and increased linear growth(35). Patient 1 carried a compound heterozygous mutation (S85G and Y268H), while patient 2 had a heterozygous Y268H variant. To date, there are more than 200 MC4R variants reported in literature, out of which the homozygous and compound heterozygous variants are very rare but responsible for more severe phenotype compared to heterozygous variants (36). The mechanism by which the vast majority of these variants exert their effect is believed to be as a result of haploinsufficiency and loss of function of the gene. Not surprising gain of function variants were found to be protective against obesity and have negative association with the phenotype (35).
Generally, conserved amino acids are anticipated to have a significant role on protein function and stability. The amino acids found in our patients, serine at position 85 and tyrosine at position 268 in the MC4R gene, are highly conserved residues in the melanocortin receptors among different species (37). In addition, these two variants are located on the transmembrane helices of the MC4R gene. Transmembrane helices play a crucial role in the membrane proteins structure and folding. A large number of variants that localize on transmembrane helices are known to affect the localization of the protein and hinder the cell membrane signaling, consequently leading to severe obesity (2,38,39).
GPCR receptors, upon binding to their ligand, activate a cascade of downstream signaling, one of the most common and vital genes in these cascades is ADCY3 which converts ATP into a secondary messenger, cAMP (40). Upregulation of cAMP plays a vital role in a variety of downstream signaling mechanisms, notably protein kinase A (PKA) (41). Once activated, PKA can then phosphorylate a diverse array of target proteins, ultimately leading to changes in cellular activity, including transcription, metabolism and ion channel activities (42). Conversely, pathogenic variants on the MC4R gene have shown profound impact in on cAMP production, subsequently, impairing the downstream of cAMP-PKA signaling mechanism that has impact in energy expenditure (42) (43) (44). Both variants identified in our study showed decreased cAMP generation even after stimulation with a-MSH. This finding is in concordance with previously reported cases that showed MC4R variants that lead to reduced cAMP generation cause severe obesity (8) (39) (45).
Agonist stimulation of MC4R has multifaceted downstream effects, including the activation of ERK and CREB, both of which play pivotal roles in translating MC4R signaling into cellular responses. When MC4R is stimulated by its agonists, it can activate a cascade of intracellular events that eventually lead to the activation of ERK1/2 (40). Activated ERK can translocate to the nucleus, where it can phosphorylate and activate various transcription factors, leading to the expression of target genes associated with cellular growth, differentiation, and survival (46). Parallel to the ERK pathway, MC4R activation also leads to the phosphorylation and activation of the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). The activation of CREB in the context of MC4R signaling is particularly relevant as it connects the dots between MC4R activation, and the regulation of genes associated with energy balance and appetite (42). In-vitro studies of the mutant MC4R variants demonstrated minimal reactivity of both p-ERK1/2 and p-CREB compared to the wild-type MC4R which exhibited a significant boost in response to α-MSH stimulation. These findings suggest that the mutations could potentially hinder MC4R's capacity to effectively activate downstream signaling in the presence of the agonist.
Functional in-vitro studies of the two novel variants, p.Ser85Gly and p.Tyr268His showed a loss of signal transduction activity of the mutant receptors. Despite the total protein expression of the wild-type and mutant alleles being comparably similar, the mutant variants' cell surface protein expression showed reduced expression than the wild-type cells upon stimulation with α-MSH, suggesting that the variants impair ligand binding. Worth noting, to date, most of the MC4R pathogenic variants that lead to loss of function were found to be affecting ligand binding affinity to the membrane receptor or intracellular retention of the receptor due to misfolding and trafficking (47). Receptor misfolding and intracellular retention of MC4R is the most common mechanisms that leads to severe childhood obesity (48). Thus, we assume the reduction of the cell membrane protein expression in the mutant cells in our study could probably be due to the retention of the misfolded protein in the endoplasmic reticulum and proteasomal degradation.
We performed molecular simulation dynamics prediction of the variants on MC4R protein structure. As shown previously, transmembrane helical contains remarkably high number of conserved residues compared to N-terminal and C-terminal loops (49). We tested the impact of the identified mutations on the structural stability of the MC4R protein, the result in accordance with previous report showed that the variants would not only destabilize the protein structure but also increase overall structure dynamics of the MC4R (50).
Interestingly, variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance have been reported in patients with mutations in the GPCRs, which could be due to mutations in modifier genes (10). Even though, both of our patients carry a shared variant p.Y268P, the severity in patient 2 (17-years old) is very remarkable (BMI 88.4Kg/m2) compared with patient 1 (11-years old, BMI 36.4 Kg/m2), this could potentially be explained by the fact that the severity of the phenotype might be exacerbated with age or due to variable expressivity of the variant.
Some in-vitro studies showed that chemical chaperones and a newly FDA approved drug, Setmelanotide (an MC4R agonist) could be used to treat some monogenic forms of obesity due to POMC, PCSK1, or LEPR deficiency. Setmelanotide can rescue some of the MC4R proteins which were retained in the endoplasmic reticulum and traffic the receptor to the plasma membrane via cell surface relocalization(6,51) (17). Further studies are required to understand whether obese subjects carrying variants like those identified in our patients affecting the membrane expression of MC4R may benefit from clinical chaperones or Setmelanotide for weight loss.
5. Conclusion
In summary, we identified two novel MC4R variants in patients with severe obesity. Both in silico investigation as well as in-vitro functional assessment substantiate the pathogenicity of the variants identified. While these variants do not affect total protein levels, they notably reduce the cell surface expression of the mutant proteins. The decreased cell surface expression is likely attributable to the post-translational modification causing misfolding of the mutant MC4R protein and subsequent retention within the endoplasmic reticulum. The identification of these variants in the population of Qatar further stresses the importance of looking into the genetic cause of obesity in patients presented with early onset severe obesity. These insights may pave the way for our patients to capitalize on the cutting-edge therapeutic advances tailored for monogenic obesity such as clinical chaperones and setmelanotide.
Funding
This research was supported by the Qatar National Research Fund [QNRF-NPRP 10-6100017-AXX] awarded to Professor Khalid Hussain.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) for the protection of human subjects in Sidra Medicine, Qatar (IRB reference number 1702007592). Informed consent forms were obtained from the parents as required. A copy of the written consent forms the parents is available for review by the editor of this journal.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for all the patients and their families who participated in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- Qi, L.; Cho, Y.A. Gene-environment interaction and obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Keogh, J.M.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Lank, E.J.; Cheetham, T.; O'Rahilly, S. Clinical Spectrum of Obesity and Mutations in the Melanocortin 4 Receptor Gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszar, D.; A Lynch, C.; Fairchild-Huntress, V.; Dunmore, J.H.; Fang, Q.; Berkemeier, L.R.; Gu, W.; A Kesterson, R.; A Boston, B.; Cone, R.D.; et al. Targeted Disruption of the Melanocortin-4 Receptor Results in Obesity in Mice. Cell 1997, 88, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisse, C.; Clement, K.; Guy-Grand, B.; Froguel, P. A frameshift mutation in human MC4R is associated with a dominant form of obesity. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.S.; Farooqi, I.S.; Aminian, S.; Halsall, D.J.; Stanhope, R.G.; O'Rahilly, S. A frameshift mutation in MC4R associated with dominantly inherited human obesity. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granell S, Mohammad S, Ramanagoudr-Bhojappa R, Baldini G. Obesity-Linked Variants of Melanocortin-4 Receptor Are Misfolded in the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Can Be Rescued to the Cell Surface by a Chemical Chaperone. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Sep 1;24(9):1805–21. [CrossRef]
- Patten, C.S.; Daniels, D.; Suzuki, A.; Fluharty, S.J.; Yee, D.K. Structural and signaling requirements of the human melanocortin 4 receptor for MAP kinase activation. Regul. Pept. 2007, 142, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tao, Y.-X. Defect in MAPK Signaling As a Cause for Monogenic Obesity Caused By Inactivating Mutations in the Melanocortin-4 Receptor Gene. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harno, E.; Ramamoorthy, T.G.; Coll, A.P.; White, A. POMC: The Physiological Power of Hormone Processing. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2381–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisse, C.; Clement, K.; Durand, E.; Hercberg, S.; Guy-Grand, B.; Froguel, P. Melanocortin-4 receptor mutations are a frequent and heterogeneous cause of morbid obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousidou, E.; Paeger, L.; Belgardt, B.F.; Pal, M.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Brönneke, H.; Collienne, U.; Hampel, B.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; et al. Distinct Roles for JNK and IKK Activation in Agouti-Related Peptide Neurons in the Development of Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillyard T, Fowler K, Williams SY, Cone RD. Obesity-associated mutant melanocortin-4 receptors with normal Gα s coupling frequently exhibit other discoverable pharmacological and biochemical defects. J Neuroendocrinol. 2019 Oct 15;31(10). [CrossRef]
- Paisdzior, S.; Dimitriou, I.M.; Schöpe, P.C.; Annibale, P.; Scheerer, P.; Krude, H.; Lohse, M.J.; Biebermann, H.; Kühnen, P. Differential Signaling Profiles of MC4R Mutations with Three Different Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, Farooqi IS, Murad MH, Silverstein JH, et al. Pediatric Obesity—Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Mar 1;102(3):709–57. [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, I.S.; O'Rahilly, S. Mutations in ligands and receptors of the leptin–melanocortin pathway that lead to obesity. Nat. Clin. Pr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.S.; Metzger, J.M.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Guan, X.-M.; Yu, H.; Frazier, E.G.; Marsh, D.J.; Forrest, M.J.; Gopal-Truter, S.; Fisher, J.; et al. Role of the melanocortin-4 receptor in metabolic rate and food intake in mice. Transgenic Res. 2000, 9, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet T-H, Dubern B, Mokrosinski J, Connors H, Keogh JM, Mendes de Oliveira E, et al. Evaluation of a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist (Setmelanotide) in MC4R deficiency. Mol Metab. 2017 Oct;6(10):1321–9. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Haris, B.; Al-Barazenji, T.; Vasudeva, D.; Tomei, S.; Al Azwani, I.; Dauleh, H.; Shehzad, S.; Chirayath, S.; Mohamadsalih, G.; et al. Understanding the Genetics of Early-Onset Obesity in a Cohort of Children From Qatar. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyder, N.A.; Kleinau, G.; Speck, D.; Schmidt, A.; Paisdzior, S.; Szczepek, M.; Bauer, B.; Koch, A.; Gallandi, M.; Kwiatkowski, D.; et al. Structures of active melanocortin-4 receptor–Gs-protein complexes with NDP-α-MSH and setmelanotide. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Ascher, D.B.; Blundell, T.L. mCSM: predicting the effects of mutations in proteins using graph-based signatures. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laimer, J.; Hofer, H.; Fritz, M.; Wegenkittl, S.; Lackner, P. MAESTRO - multi agent stability prediction upon point mutations. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P.; Casadio, R. I-Mutant2.0: predicting stability changes upon mutation from the protein sequence or structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W306–W310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Randall, A.; Baldi, P. Prediction of protein stability changes for single-site mutations using support vector machines. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 62, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. CHARMM36m: an improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, A.M.; Ahmed, W.S.; Biswas, K.H. Reversal of the unique Q493R mutation increases the affinity of Omicron S1-RBD for ACE2. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.S.; Philip, A.M.; Biswas, K.H. Decreased interfacial dynamics caused by the N501Y mutation in the SARS-Cov-2 s1 spike:ACE2 complex. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 39a–39a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethakumari AM, Ahmed WS, Rasool S, Fatima A, Nasir Uddin SM, Aouida M, et al. A genetically encoded BRET-based SARS-CoV-2 Mpro protease activity sensor. Commun Chem. 2022 Sep 28;5(1):117. [CrossRef]
- Altamash, T.; Ahmed, W.; Rasool, S.; Biswas, K.H. Intracellular Ionic Strength Sensing Using NanoLuc. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad N, Laurent-Rolle M, Ahmed WS, Hsu JC-C, Mitchell SM, Pawlak J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins ORF7a and ORF3a use distinct mechanisms to down-regulate MHC-I surface expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2023 Jan 3;120(1). [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, A.P.; Ochoa-Montaño, B.; Ascher, D.B.; Blundell, T.L. SDM: a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W229–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, V.; Gromiha, M.M.; Schomburg, D. CUPSAT: prediction of protein stability upon point mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W239–W242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzmann, F.; Tan, K.; Vatin, V.; Dina, C.; Jouret, B.; Tichet, J.; Balkau, B.; Potoczna, N.; Horber, F.; O'Rahilly, S.; et al. Prevalence of Melanocortin-4 Receptor Deficiency in Europeans and Their Age-Dependent Penetrance in Multigenerational Pedigrees. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabkin, M.; Birk, O.S.; Birk, R. Heterozygous versus homozygous phenotype caused by the same MC4R mutation: novel mutation affecting a large consanguineous kindred. BMC Med Genet. 2018, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyder, N.; Kleinau, G.; Szczepek, M.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Speck, D.; Soletto, L.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Krude, H.; Kühnen, P.; Biebermann, H.; et al. Signal Transduction and Pathogenic Modifications at the Melanocortin-4 Receptor: A Structural Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.-X. The Melanocortin-4 Receptor: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiology. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 506–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinney, A.; Hohmann, S.; Geller, F.; Vogel, C.; Hess, C.; Wermter, A.-K.; Brokamp, B.; Goldschmidt, H.; Siegfried, W.; Remschmidt, H.; et al. Melanocortin-4 Receptor Gene: Case-Control Study and Transmission Disequilibrium Test Confirm that Functionally Relevant Mutations Are Compatible with a Major Gene Effect for Extreme Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4258–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-K.; Hou, Z.-S.; Tao, Y.-X. Biased signaling in naturally occurring mutations of G protein-coupled receptors associated with diverse human diseases. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1867, 165973–165973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.R.; Almeida, H.; Gouveia, A.M. Intracellular signaling mechanisms of the melanocortin receptors: current state of the art. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 72, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glas, E.; Mückter, H.; Gudermann, T.; Breit, A. Exchange factors directly activated by cAMP mediate melanocortin 4 receptor-induced gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32776–32776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.-L.; Yang, R.; Tao, Y.-X. Functions of transmembrane domain 3 of human melanocortin-4 receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 49, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Mahalingam, K. Molecular genetics of human obesity: A comprehensive review. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2017, 340, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, W.A.J.; Garner, K.M.; van Rozen, R.J.; Adan, R.A.H. Poor Cell Surface Expression of Human Melanocortin-4 Receptor Mutations Associated with Obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22939–22945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebratu Y, Tesfaigzi Y. How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 15;8(8):1168–75. [CrossRef]
- Lubrano-Berthelier, C. Intracellular retention is a common characteristic of childhood obesity-associated MC4R mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 2003 Jan 15;12(2):145–53. [CrossRef]
- Lotta LA, Mokrosiński J, Mendes de Oliveira E, Li C, Sharp SJ, Luan J, et al. Human Gain-of-Function MC4R Variants Show Signaling Bias and Protect against Obesity. Cell. 2019 Apr;177(3). [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Harmon, C.M. Molecular signatures of human melanocortin receptors for ligand binding and signaling. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, J.M.; Farrens, D.L. Assessing structural elements that influence Schiff base stability: mutants E113Q and D190N destabilize rhodopsin through different mechanisms. Vis. Res. 2003, 43, 2991–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- René, P.; Le Gouill, C.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Lee, G.; Mosberg, H.I.; Farooqi, I.S.; Valenzano, K.J.; Bouvier, M. Pharmacological Chaperones Restore Function to MC4R Mutants Responsible for Severe Early-Onset Obesity. Experiment 2010, 335, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
MC4R mutants result in a destabilization of the MC4R protein. Root-mean-square deviation analysis (A) and Root-mean-square fluctuation values (B) of MC4R (left) and peptide ligand (right) in the WT (gray), S85G (yellow), and Y268H (red) protein-peptide complexes.
Figure 1.
MC4R mutants result in a destabilization of the MC4R protein. Root-mean-square deviation analysis (A) and Root-mean-square fluctuation values (B) of MC4R (left) and peptide ligand (right) in the WT (gray), S85G (yellow), and Y268H (red) protein-peptide complexes.
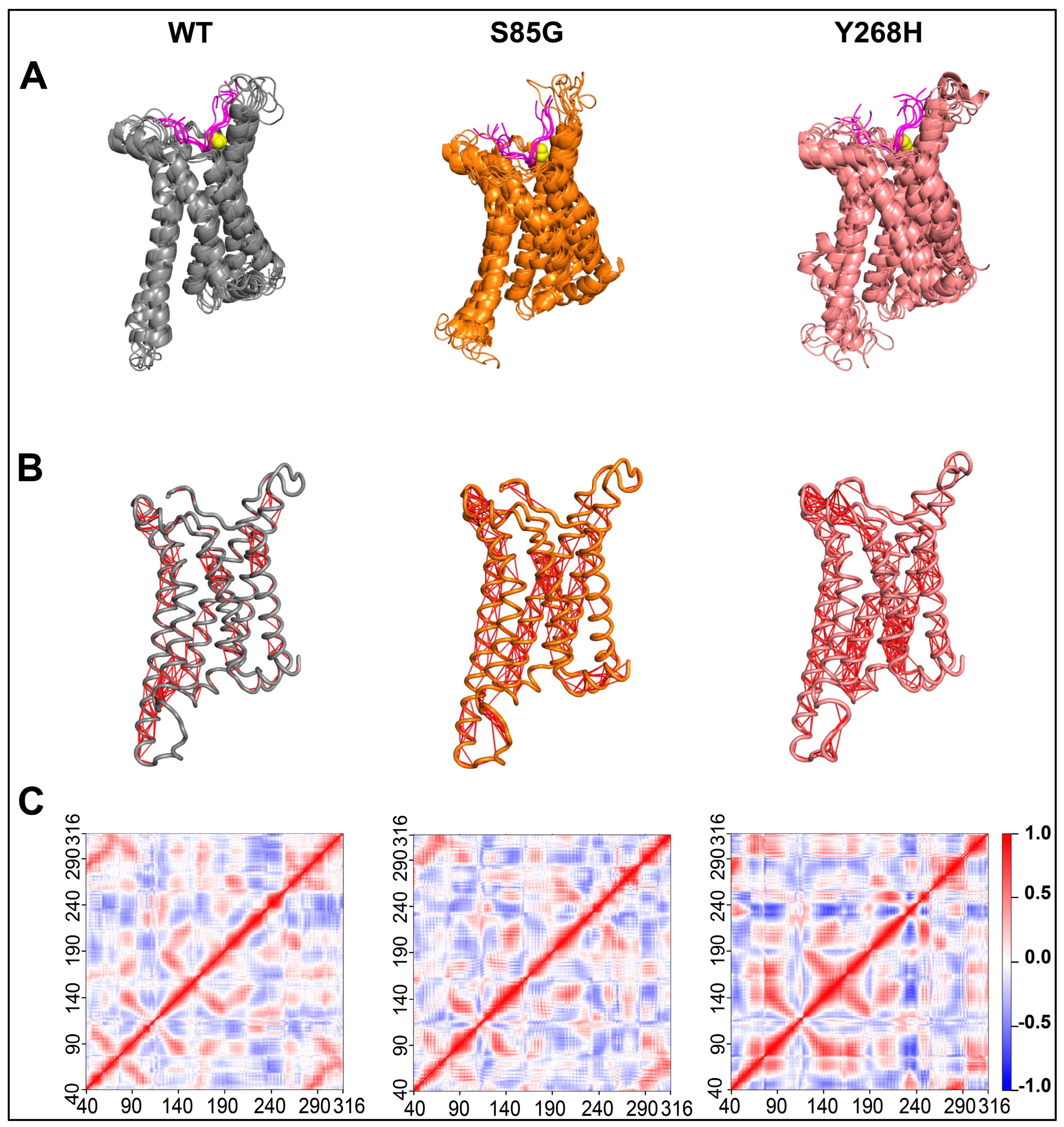
Figure 2.
The MC4R mutations increase the structural dynamics of the protein. (A) Composite image of cartoon snapshots representing 100 ns of MD simulation, taken 20 ns apart. (B) Cartoon image representing MC4R Cα atom dynamic cross-correlation (DCC) values obtained from 100 ns MD simulations after applying a DCC value cut-off of ± 0.8. (C) Heatmap showing MC4R Cα atom DCC values obtained from 100 ns MD simulations of the MC4R WT (left panel), MC4R(S85G) (middle panel), and Y268H (right panel). Note the impact of the mutations on the overall dynamics of the protein.
Figure 2.
The MC4R mutations increase the structural dynamics of the protein. (A) Composite image of cartoon snapshots representing 100 ns of MD simulation, taken 20 ns apart. (B) Cartoon image representing MC4R Cα atom dynamic cross-correlation (DCC) values obtained from 100 ns MD simulations after applying a DCC value cut-off of ± 0.8. (C) Heatmap showing MC4R Cα atom DCC values obtained from 100 ns MD simulations of the MC4R WT (left panel), MC4R(S85G) (middle panel), and Y268H (right panel). Note the impact of the mutations on the overall dynamics of the protein.
Figure 3.
Analysis of MC4R Expression and Membrane Localization in GT1-7 Cells. (A) Western blot analysis showing the total protein levels of MC4R in GT1-7 cells transfected with wild-type (WT) MC4R, mutant MC4R (S85G and Y268H), or empty vector (control). Representative immunoblots shown were probed for MC4R and β-tubulin (loading control). (B) Quantitative analysis of the MC4R protein expression derived from independent experiments. The densitometric evaluation was used to ascertain the relative intensity of MC4R bands against the β-tubulin signals, serving as the normalization factor. Graphically illustrated data represents mean ± SEM gathered from a minimum of three separate experiments. (C) GT1-7 cells were transfected with either WT or mutant MC4R. After 36 h of transfection, cells were stimulated with 100 nm α-MSH for 12h. Representative western blot images illustrating the membrane localization of MC4R following cell surface protein biotinylation. TfR was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometric quantification of membrane-bound MC4R based on several independent experiments. The intensity of MC4R bands was normalized to the signals from TfR. The compiled data, representing the mean ± SEM, was sourced from at least three individual experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
Figure 3.
Analysis of MC4R Expression and Membrane Localization in GT1-7 Cells. (A) Western blot analysis showing the total protein levels of MC4R in GT1-7 cells transfected with wild-type (WT) MC4R, mutant MC4R (S85G and Y268H), or empty vector (control). Representative immunoblots shown were probed for MC4R and β-tubulin (loading control). (B) Quantitative analysis of the MC4R protein expression derived from independent experiments. The densitometric evaluation was used to ascertain the relative intensity of MC4R bands against the β-tubulin signals, serving as the normalization factor. Graphically illustrated data represents mean ± SEM gathered from a minimum of three separate experiments. (C) GT1-7 cells were transfected with either WT or mutant MC4R. After 36 h of transfection, cells were stimulated with 100 nm α-MSH for 12h. Representative western blot images illustrating the membrane localization of MC4R following cell surface protein biotinylation. TfR was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometric quantification of membrane-bound MC4R based on several independent experiments. The intensity of MC4R bands was normalized to the signals from TfR. The compiled data, representing the mean ± SEM, was sourced from at least three individual experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
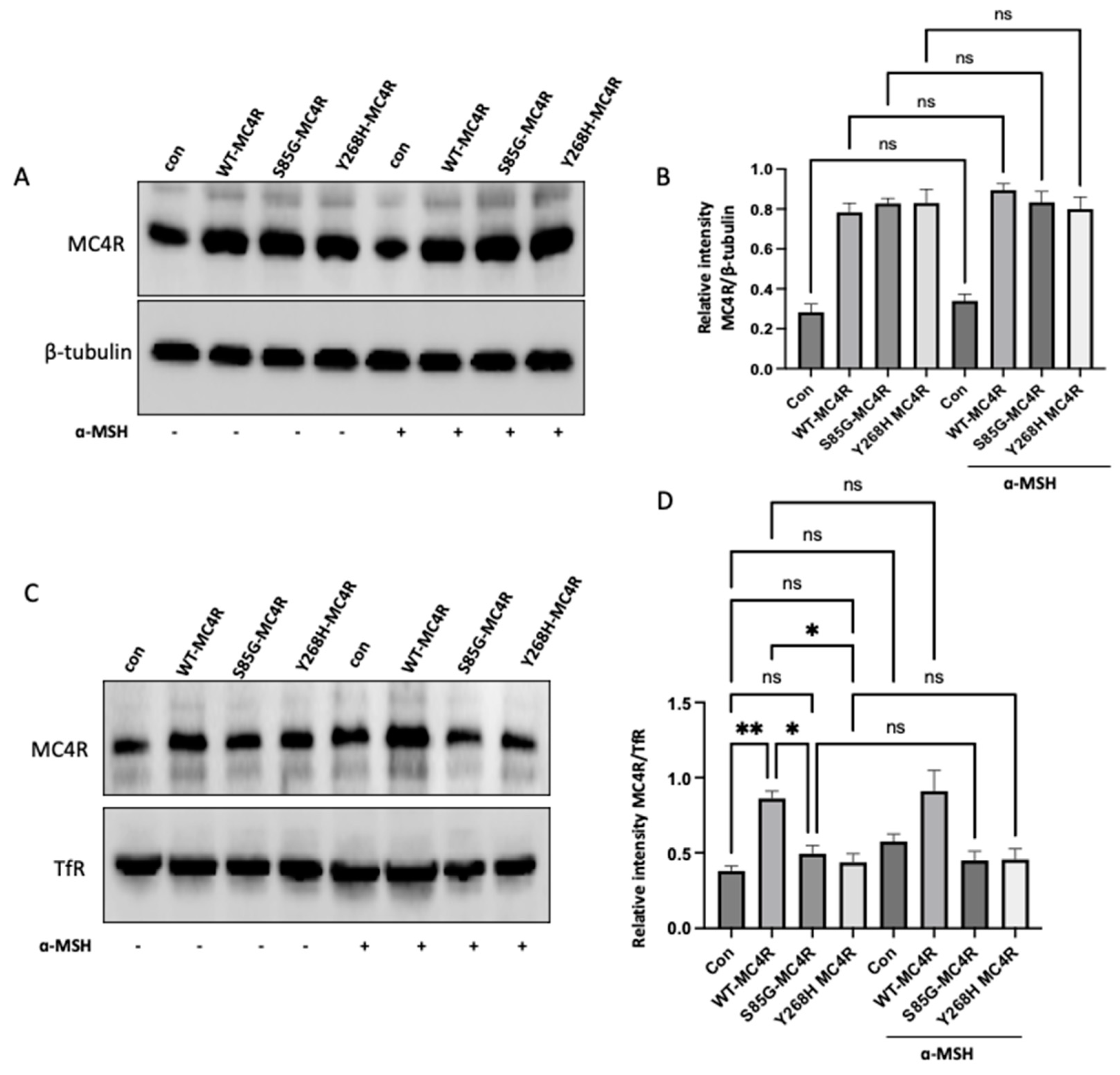
Figure 4.
MC4R variants diminish cAMP accumulation. GT1-7 cells were transfected with either WT-MC4R or mutant MC4R variants and subsequently subjected to IBMX treatment (0.5 mM) for 10 minutes, followed by a 15-minute incubation with 100 nM α-MSH. Intracellular cAMP content was measured by ELISA. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
Figure 4.
MC4R variants diminish cAMP accumulation. GT1-7 cells were transfected with either WT-MC4R or mutant MC4R variants and subsequently subjected to IBMX treatment (0.5 mM) for 10 minutes, followed by a 15-minute incubation with 100 nM α-MSH. Intracellular cAMP content was measured by ELISA. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
Figure 5.
MC4R variants impair the ERK1/2 and CREB Activation in GT1-7 Cells. (A) Representative Western blot images showing the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pThr202/Tyr204-ERK1/2) and total ERK in GT1-7 cells transfected with either wild-type MC4R (WT-MC4R) or its mutant counterparts. Following a 48-hour post-transfection period, cells were exposed to 100 nm α-MSH for 3 hours. (B) Analogous Western blot images illustrating the levels of phosphorylated CREB (pSer133-CREB) and total CREB post-transfection and α-MSH treatment. (B and D) Densitometric analyses of p-ERK1/2 and p-CREB signals normalized to their respective total protein levels. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
Figure 5.
MC4R variants impair the ERK1/2 and CREB Activation in GT1-7 Cells. (A) Representative Western blot images showing the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pThr202/Tyr204-ERK1/2) and total ERK in GT1-7 cells transfected with either wild-type MC4R (WT-MC4R) or its mutant counterparts. Following a 48-hour post-transfection period, cells were exposed to 100 nm α-MSH for 3 hours. (B) Analogous Western blot images illustrating the levels of phosphorylated CREB (pSer133-CREB) and total CREB post-transfection and α-MSH treatment. (B and D) Densitometric analyses of p-ERK1/2 and p-CREB signals normalized to their respective total protein levels. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s analysis.
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of agonist-induced MC4R signaling in energy homeostasis. MC4R Mutants Decreased intracellular cAMP leads to downregulation of PKA which, in turn, inactivates ERK1/2 and CREB and imbalances the energy homeostasis.
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of agonist-induced MC4R signaling in energy homeostasis. MC4R Mutants Decreased intracellular cAMP leads to downregulation of PKA which, in turn, inactivates ERK1/2 and CREB and imbalances the energy homeostasis.
Table 1.
Clinical and biochemical features of the two cases.
Table 1.
Clinical and biochemical features of the two cases.
| Test |
Value |
| |
Patient 1 |
Reference |
Patient 2 |
Reference |
| Age of onset |
3 months |
|
2 years |
|
| BMI (Kg/m2) |
36.4 |
|
88.4 |
|
| ALT |
14 |
10-25 U/L |
85 U/L (H) |
5-30 U/L |
| AST |
20 |
20-38 U/L |
128 U/L (H) |
0-39 U/L |
| GGT |
15 |
6 - 18 U/L |
NA |
NA |
| ALP |
NA |
NA |
191 U/L (H) |
52-171 U/L |
| HBA1c |
5.70 |
<6.% |
5.40 |
<6.% |
| Total Cholesterol |
5 |
3.1-5.9 mmol/L |
5.11 |
3.1-5.9 mmol/L |
| Trig |
1.8 |
0.6-2.5 mmol/L |
2.5 (H) |
1.8-2.2 mmol/L |
| HDL |
1.1 |
0.9-1.7 mmol/L |
0.3 (L) |
0.9-1.7 mmol/L |
| LDL |
3.6 |
1.4-4.2 mmol/L |
3.7 (H) |
<3.4 mmol/L |
| TSH |
2.80 |
0.76-4.64 mIU/L |
4.58 (H) |
0.5-4.3 mIU/L |
| Free T4 |
12.7 |
8.1 - 14.9 pmol/L |
13.1 |
12.9 - 20.6 pmol/L |
| Insulin |
NA |
NA |
41.1 |
1.4-47 mc unit/mL |
| Leptin |
NA |
NA |
34 (H) |
0.7-5.3 ng/mL |
Table 2.
Summary of the in-silico predictions of the two novel MC4R variants.
Table 2.
Summary of the in-silico predictions of the two novel MC4R variants.
| Chromosomal location (GRCh37) |
MC4R variant |
Amino acid change |
SIFT |
Polyphen-2 |
Mutation Taster |
gnomAD MAF |
GME MAF |
| Chr18: 58039330 |
c.253A>G |
p.Ser85Gly |
Deleterious |
Probably Damaging |
Disease Causing |
0 |
0 |
| Chr18:58038781 |
c.802T>C |
p.Thy268His |
Deleterious |
Probably Damaging |
Disease Causing |
0 |
0 |
Table 3.
Prediction of the changes in Gibb's free energy (kcal/mol) induced by the indicated single point mutation obtained using various bioinformatics prediction tools.
Table 3.
Prediction of the changes in Gibb's free energy (kcal/mol) induced by the indicated single point mutation obtained using various bioinformatics prediction tools.
| Bioinformatics tool |
MC4R(S85G) |
Outcome |
MC4R(Y268H) |
Outcome |
| ΔΔG mCSM |
-1.282 |
Destabilizing |
-1.81 |
Destabilizing |
| ΔΔG MUpro |
-1.54 |
Destabilizing |
-1.28 |
Destabilizing |
| ΔΔG I-Mutant 2.0 |
-2.33 |
Destabilizing |
-1.83 |
Destabilizing |
| ΔΔG Maestro |
1.9994 |
Destabilizing |
2.85 |
Destabilizing |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).