1. Introduction
D-serine is a co-agonist of NMDA receptors [
1]. NMDA receptors are glutamate ionotropic receptors that play a major role in many physiological processes including learning and memory [
2], They are located at synaptic and extra-synaptic and responsible for inducing synaptic plasticity found in the CNS [
3], NMDAs require the binding of glutamate and other agonists (glycine and D-serine are co-agonist of NMDAs)[
3], NMDAR binds simultaneously to co-agonist D-serine through the GluN2 subunit, it acts as a major endogenous co-agonist of synaptic NMDARs [
4]. In this review, we review performed electrophysiological recordings to assess the distribution of D-serine. We also review studies on the pathway of synthesis and release of D-serine to determine:
Is D-Serine a gliotransmitter or neurotransmitter?
2. Controversy on D-serine glia transmission
There has been a big controversy surrounding D-serine, specifically the site of its synthesis and release. There are two main sides to this argument, proponents of the D-serine gliotransmission hypothesis which assumes that D-serine is a gliotransmitter, and those who are advocate for the D-serine shuttle hypothesis which believe D-serine to be of neuronal origin.
3. D-serine and the gliotransmission hypothesis
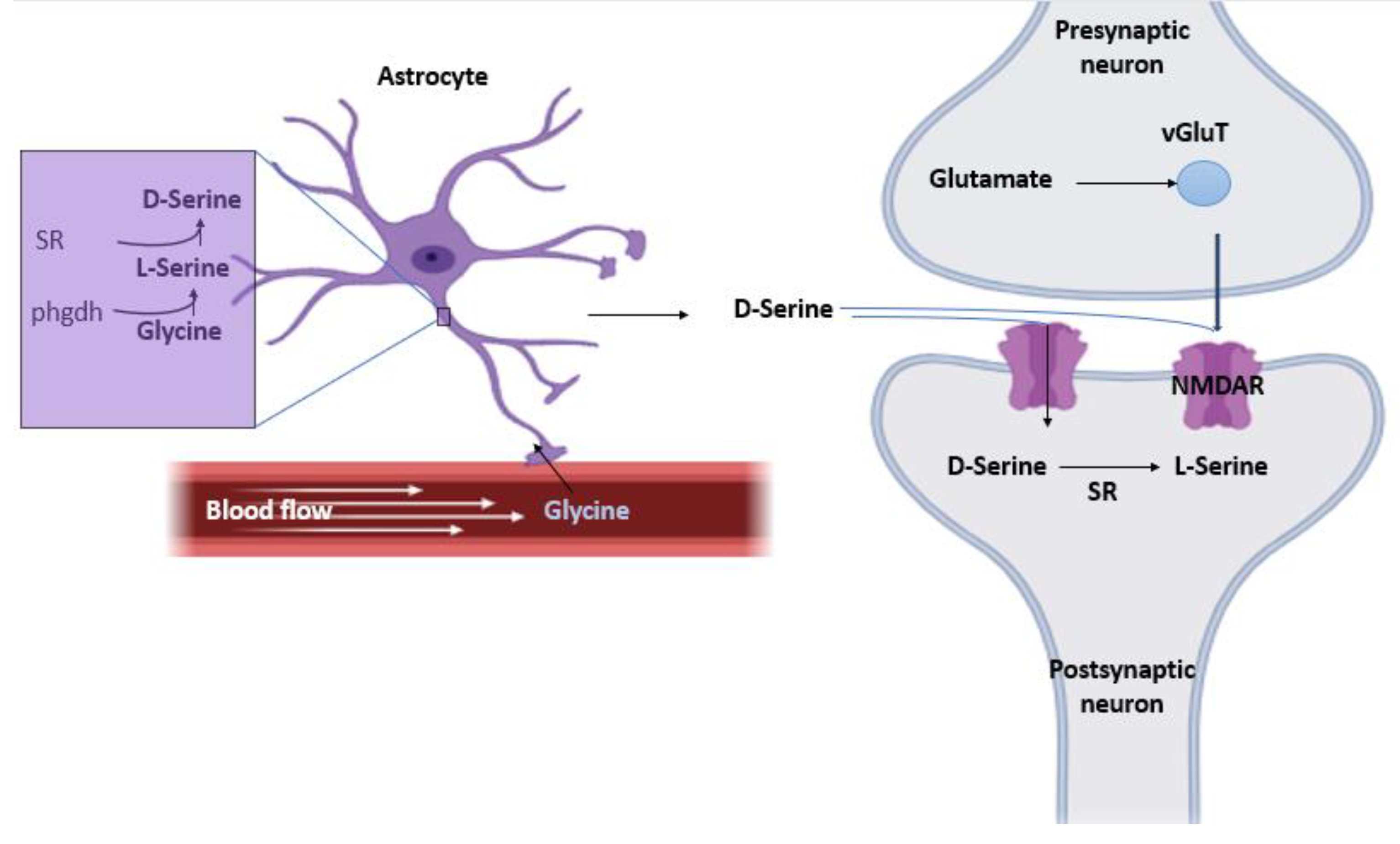
In this hypothesis, it’s believed that both serine racemase (SR) and D-serine are present mainly in astrocytes, therefore, the release of D-serine is astrocytic. glia modulates neurotransmission by releasing neuroactive substances (ATP. D-Serine. Glutamate.) that activate neuronal receptors (
Figure 1).
Step 1: the Phgdh enzyme, exclusively located in astrocytes, converts glycine into L-serine [
5].
Step 2: SR present in astrocytes then synthesizes D-serine from L-serine [
6].
Step 3: Synthesized D-serine is then stored in vesicles to protect it from α, β-elimination by SR. This results in high concentration of L-serine in the astrocytes and almost no D-serine which favors the synthetic effect of SR as opposed to its degrading activity [
6].
Step 4: D-serine is released in Ca2+- and SNARE-dependent manner to act as a glutamate co-agonist at the NMDA receptors and is then up-taken by the neurons upon its accumulation hypothetically through ASC-1 where it is degraded by SR [
1,
6].
4. D-serine shuttle model hypothesis
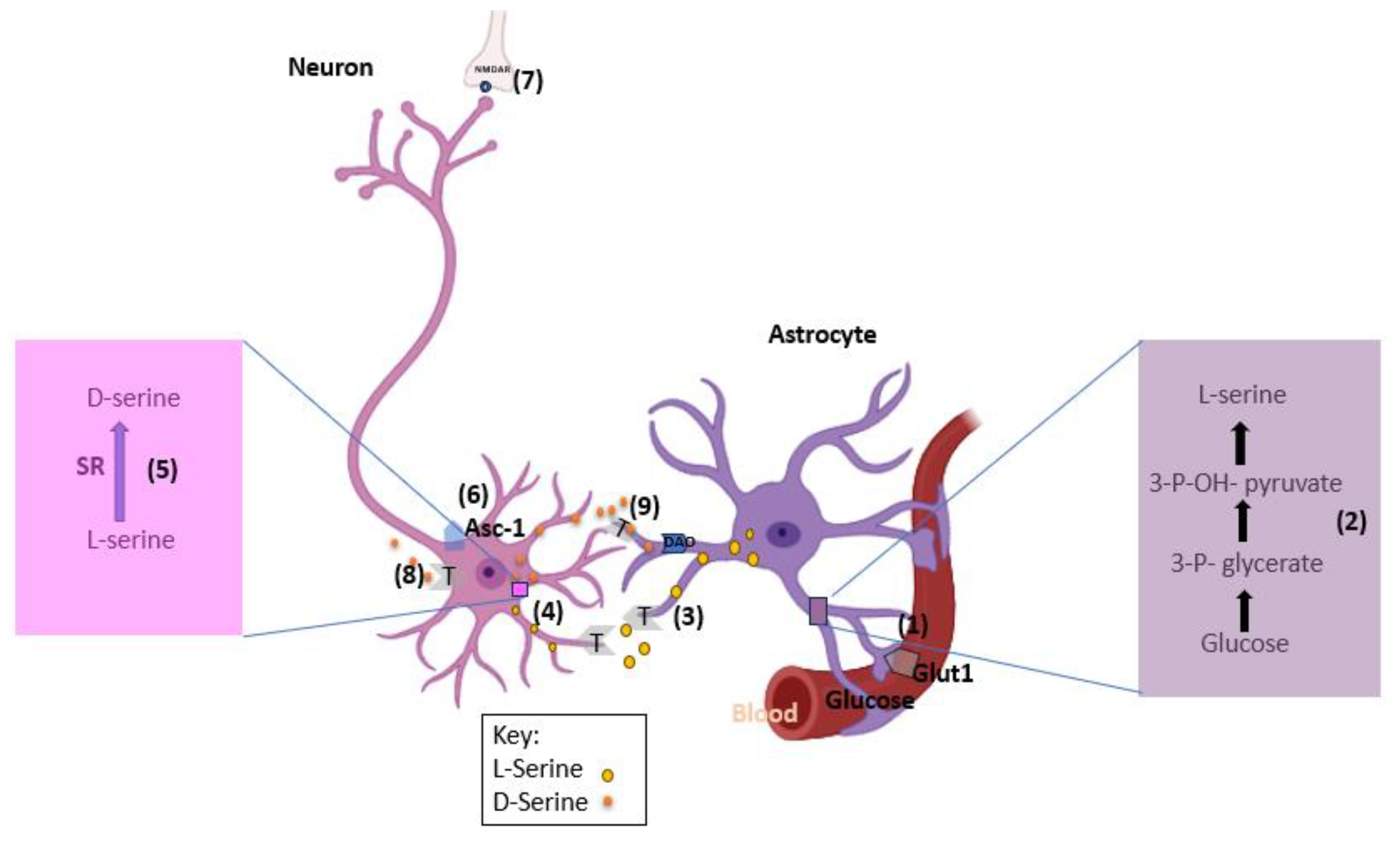
Proponents of D-serine being of neuronal origins use this model to explain the synthesis and release of D-serine in neurons as opposed to astrocytes (
Figure 2). Astrocytes produces required enzymes to convert glucose into L-serine de novo. L-serine is then shuttled to the neurons where it is converted into D-serine [
7].
Step 1: Astrocytes obtain glucose from blood vessels through glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1).
Step 2: Glucose is converted into L-serine in several steps, with the committed step catalyzed by the 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase enzyme.
Step 3: L-Serine exits the astrocytes by neutral amino acid exchangers, such as ASCT1 (Slc1a4) and system N transporters (T).
Step 4: Neurons take up L-serine by neutral amino acid antiporters or system A transporter (T).
Step 5: Neuronal SR converts L-serine into D-serine.
Step 6: D-Serine is subsequently released from neurons by Asc-1 (Slc7a10) or other transporters.
Step 7: Released D-serine allows synaptic NMDAR activation.
Step 8: D-Serine signaling may terminate through neuronal reuptake.
Step 9: or low-affinity astrocytic uptake and subsequent metabolism by the peroxisomal DAO [
8].
5. D-serine is not a gliotransmitter
5.1. Immunostaining
Kartvelishvily et al.[
17] showed by performing immunostaining using selective antibodies that expression of SR and D-serine is more prominent in neurons of rat forebrain and is synthesized by primary neuronal cultures [
9]. Miya et al. performed immunostaining in presence of SR(-/-) mice to act as negative control. They showed the presence of SR in the glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons of mouse forebrain and not astrocytes [
10]. To determine antibody specificity, more selective Abs were used and Knockout or SR (Srr -/-) mice as controls. Mori's group was able to observe neuronal staining for RS and D-serine in the tissues of Srr -/- mice. While no staining was detectable in astrocytes [
10].
5.2. Cell selective mutations in SR expression
Bennyworth et al [
11]. engineered mice with cell-selective suppression of SR (serine racemase) expression, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter D-serine. They achieved this by flanking exon 1 in the SR gene with loxP sites and crossing these mice with transgenic counterparts expressing Cre-recombinase under the control of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) promoters in forebrain glutamatergic neurons and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoters in astrocytes [
11]. This strategy yielded three experimental groups: aSRCKO (astrocyte-specific SR knockout), nSRCKO (neuron-specific SR knockout), and a control group with floxed alleles (fl/fl) [
11]. Notably, they observed a substantial (~65%) reduction in SR expression in the hippocampus of nSRCKO mice but only a modest (~15%) decrease in aSRCKO mice[
11], indicating a pronounced impact in neurons compared to astrocytes. Furthermore, their electrophysiological investigations of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus revealed that aSRCKO mice exhibited no significant alterations [
11], while nSRCKO mice displayed a significant 70% reduction in LTP induction. Additionally, nSRCKO mice exhibited decreased postsynaptic NMDA currents [
11], although there was no discernible effect on AMPA receptors. These findings underscore the critical role of SR in regulating synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission, with neuron-specific SR deficiency having a more pronounced impact on LTP and synaptic NMDA currents in the hippocampus [
11].
5.3. Use of EGFP
In this study [
4], BAC transgenic mice were employed to investigate the Crypto-SR hypothesis in astrocytes, utilizing enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) as a key tool. The EGFP expression was controlled by the Srr promoter [
4], which serves as a sensitive surrogate marker for cells expressing serine racemase (SR). Consequently, EGFP accumulation was observed primarily in cell bodies rather than in small astrocytic processes [
4]. The results revealed predominant neuronal staining for EGFP [
4], with a particular emphasis on cortical neurons expressing EGFP under the regulation of the Srr promoter [
4], as evidenced by concurrent staining for EGFP and cell-specific markers, shedding light on the intriguing role of SR and its expression in specific neuronal populations [
4].
5.4. In vivo microdialysis in the hippocampus of glutamatergic neurons in Srr -/-
Under physiological conditions, neurons were found to release D-serine primarily through the mediation of Asc-1 [
7], a mechanism that facilitates the release of neuronal tonic D-serine rather than its uptake [
7]. To substantiate this hypothesis, Toru Nishikawa conducted an experiment employing in vivo microdialysis in the hippocampus of targeted glutamatergic neurons within Srr -/- mice [
7]. The results of this study revealed a notable 50% reduction in the levels of extracellular D-serine [
7], coinciding with the emergence of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the altered hippocampus [
7]. In contrast, the LTP in Srr -/- mouse astrocytes remained unaffected [
7], offering compelling evidence for the pivotal role of Asc-1-mediated D-serine release by neurons in modulating synaptic plasticity and hippocampal function.
6. Counterarguments and Rebuttal
Studies carried out in at least 6 laboratories demonstrate that neurons are the main sources of D-serine and its synthetic enzyme SR (serine racemase) in the normal brain [
8]. However, a rebuttal letter sent by Papouin et al. [
12] contradicts this hypothesis citing evidence that lacks adequate control to ensure specificity of staining for SR and D-serine at the astrocyte level, but also failure to apply other detection methods such as biosensors [
12,
13,
14].
It’s important to acknowledge some of the reasons that have misled these scholars into believing astrocytes to be the origin site of D-serine synthesis and release. Here, we will mention some of their arguments and show how they don’t make much sense in the light of the current literature we have.
6.1. Cultured astrocytes show immunoreactivity to D-serine which undergoes exocytosis in vitro
That’s one thing that proponents of the gliotransmission hypothesis always bring up. There are many parts to why this is not the case. While it is true that earlier studies have shown astrocytic immunoreactivity to D-serine in cultured tissues [
15,
16], it is important to notice how that was reversed when more selective antibodies. As we mentioned earlier, using more selective antibodies by Kartvelishvily et al. [
17] have shown prominent expression of D-serine in neurons as opposed to astrocytes [
17].
Another point they got wrong here is how they miss how results obtained from experiments in vitro aren’t always representative of how things actually work in vivo [
18]. Cultured astrocytes are more representative of pathological conditions like in the case of neuroinflammation or stroke [
19]. Even though cultured astrocytes did show Ca+2 dependent vesicular release of D-serine that stopped upon adding intracellular or extracellular Ca+2 chelating agents [
20], Another study has shown that the release of D-serine from astrocytes was not vascular and was at least partially due to volume-regulation channels opening [
21]. It is worth mentioning that cultured neurons also show D-serine release by depolarization [
22]. In fact, when rat brain slices were studied as opposed to cultured astrocytes, there was inhibition of D-serine release upon adding Ca+2 chelating agents [
16]. This further proves that the release of D-serine in cultured astrocytes is not a good representative of what actually happens in vivo.
6.2. Inhibition of astrocyte-gliotransmission via calcium clamping or fluoroacetate and decreased synapse in nearby astrocytes
As we mentioned before, proponents of the D-serine glio-transmission hypothesis use the argument that cultured astrocytes release D-serine via a Ca+2 dependent vesicular release. We’ve already shown the problems with such an argument. While it’s true that Henneberg et al. have found that calcium clamping (i.e. chelating Ca+2) in the hippocampal Schaffer collateral CA-1 synapse causes decrease in synaptic formation in nearby astrocytes [
17], that was not the case with McCarthy et al. interestingly, McCarthy and colleagues used mice engineered to increase only intracellular Ca+2 in astrocytes when Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member A1 (MRGA1) receptors are stimulated. However, McCarthy and colleagues didn’t observe that same effect previously found by Henneberg. There was no change in the short- or long-term potentiation in the hippocampal Schaffer collateral CA-1 synapse [
18]. There are also other problems with using gliotoxins. The effect of gliotoxins such as fluoroacetate is likely to be due to its disruption of the serine shuttle which would result in less L-serine available to be transported to neurons and converted to D-serine [
23]. Gliotoxins have other non-specific effects like disrupting general astrocytic metabolism as well as dysregulation of levels of extracellular K+ [
24,
25]. Calcium clamping is also not an ideal method since it too can produce non-specific effects due to possible inhibition of various Ca2+-binding proteins which in turn affects multiple astrocytic functions [
8].
6.3. Small volume of astrocytic processes compared to that of neurons
Proponents of the D-serine glio-transmission hypothesis also bring up how astrocytes only possess 5-7% of the volume of the neuropil as compared to neurons that occupy 70% of the volume [
26]. However, cell selective conditional silencing of SR expression has shown otherwise. The results are reliable here since such a method is not affected by the different volumes. Silencing SR expression in astrocytes with glial fibrillary associated protein (GFAP) promoter-Cre showed insignificant effect in the cortex. On the other hand, deletion of Srr in glutamergic neurons showed a decrease in SR expression in (CAMKIIα–Cre) Srr −/− mice [
11].
6.4. ASC-1 is a bidirectional mediator
Another argument used is that D-serine found in neurons is there to be degraded and that alanine/serine/cysteine transporter ASC-1 which is supposed to be responsible for D-serine efflux can also account for its uptake [
21]. This argument stems from lack of understanding of ASC-1 in the serine shuttle model. Also, this argument is not consistent with the findings of many other studies that found that release levels of endogenous D-serine as well as microdialysis levels of extracellular D-serine in vivo actually decrease upon treatment with ASC-1 inhibitors [
27,
28]. These findings confirm that ASC-1 role in neurons is mainly release not uptake.
6.5. SR in neurons is responsible for degradation of D-serine
In their letter of rebuttal Papouin et al. argue that SR enzyme works in the neurons as a degrading enzyme for D-serine [
12]. This argument is too bizarre since they do in the same letter claim that SR is present predominantly in astrocytes. They then claim its presence in neurons is for degradation of D-serine. So which one is it? The efficiency of SR synthetic activity of L-serine to D-serine is five folds higher than that of its catabolic activity of D-serine into pyruvate by α,β elimination [
29]. While it is true that α,β elimination is responsible in D-serine submaximal synthesis, the high concentration of SR in neurons makes it unlikely for it to have exclusively catabolic activity [
12,
30].
7. Conclusions
D-Serine modulates NMDARs and regulates synaptic plasticity. However, the primary site of D-serine synthesis and release remains controversial, with some arguing that it is a gliotransmitter and others defining it as a neuronal co-transmitter, even though controversy and debate are major aspects of scientific discoveries. We can see that in science there are no absolutes. It’s an ongoing process of evidence-backed hypotheses that can be later replaced by a newer hypothesis that makes more sense. When it comes to our topic of D-serine, it’s important to remember that when there’s an obvious, simple, straightforward answer it’s probably the right answer. The main issue with the gliotransmission hypothesis discourse is that it tends to complicate things far more than they should be. Looking objectively at the data presented in this review, it’s clear that although astrocytes are essential for L-serine synthesis, D-serine is in fact neuronal and not astrocytic. The serine shuttle hypothesis remains the most probable one which makes good sense in the light of what we know now according to the current available literature.
Author Contributions
EE conceptualized and designed the review, conducted the literature review, gathered and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Forsythe et al., 1988, Johnson and Ascher, 1987; Kleckner and Dingledine, 1988.
- Bliss, T.V.P. , and Collingridge, G.L. (1993). A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39.
- Liu et al., 2004; Massey et al., 2004; Morishita et al., 2007; Berberich et al., 2005. 2005.
- Henneberger et al., 2010; Mothet et al., 2000; Schell et al., 1995; Yang et al., 2003.
- Ehmsen, J.T. et al. (2013) D-serine in glia and neurons derives from phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. J. Neurosci. 33, 12464.
- Astroglial versus Neuronal D-Serine: Fact Checking Thomas Papouin,1 Christian Henneberger,2,3,4 Dmitri A. Rusakov,3 and Stéphane H.R. Oliet5. Astroglial versus Neuronal D-Serine: Fact Checking.
- Schell, M.J. et al. (1995) D-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator: localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92, 3948–3952.
- Wolosker H, et al. The rise and fall of the D-serine-mediated gliotransmission hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 2016; 39:712–721. [PubMed: 27742076].
- Kartvelishvily, E. et al. (2006) Neuron-derived D-serine release provides a novel means to activate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 14151–14162.
- Miya, K. et al. (2008) Serine racemase is predominantly localized in neurons in mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 510, 641–654.
- Benneyworth, M.A. et al. (2012) Cell selective conditional null mutations of serine racemase demonstrate a predominate localization in cortical glutamatergic neurons. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 32, 613–624.
- Papouin, T. , et al. Astroglial versus neuronal D-serine: fact checking. Trends Neurosci. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Balu DT, et al. D-serine and serine racemase are localized to neurons in the adult mouse and human fore-brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 34:419–435.
- Ehmsen JT, et al. D-serine in glia and neurons derives from 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. J Neurosci. 2013; 33:12464–12469.
- Traynelis, S.F. et al. (2010) Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 62, 405–496.
- Balu, D.T. and Coyle, J.T. (2015) The NMDA receptor ‘glycine modulatory site’ in schizophrenia: D-serine, glycine, and beyond. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 20, 109–115.
- Kartvelishvily, E. et al. (2006) Neuron-derived D-serine release provides a novel means to activate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 14151–14162.
- Cahoy, J.D. et al. (2008) A transcriptome database for astrocytes, neurons, and oligodendrocytes: a new resource for understanding brain development and function. J. Neurosci. 28, 264–278.
- Zamanian, J.L. et al. (2012) Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J.
- Mothet, J.P. et al. (2005) Glutamate receptor activation triggers a calcium-dependent and SNARE protein-dependent release of the gliotransmitter D-serine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 5606–5611.
- Rosenberg, D. et al. (2010) Neuronal release of D-serine: a physiological pathway controlling extracellular D-serine concentration. FASEB J. 24, 2951–2961.
- Henneberger, C. et al. (2010) Long-term potentiation depends on release of D-serine from astrocytes. Nature 463, 232–236.
- Hassel, B. et al. (1997) Trafficking of amino acids between neurons and glia in vivo. Effects of inhibition of glial metabolism by fluoroacetate. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 1230–1238.
- Fonnum, F. et al. (1997) Use of fluorocitrate and fluoroacetate in the study of brain metabolism. Glia 21, 106–113.
- Largo, C. et al. (1996) The effect of depressing glial function in rat brain in situ on ion homeostasis, synaptic transmission, and neuron survival. J. Neurosci. 16, 1219–12.
- Medvedev, N. et al. (2014) Glia selectively approach synapses on thin dendritic spines. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 369, 20140047.
- Sason H, et al. Asc-1 transporter regulation of synaptic activity via the tonic release of D-serine in the forebrain. Cereb Cortex. 2017; 27:1573–1587.
- Sakimura K, et al. A novel Na+-independent alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 1 inhibitor inhibits both influx and efflux of D-serine. J Neurosci Res. 2016; 94:888–895.
- Strisovsky K, et al. Dual substrate and reaction specificity in mouse serine racemase: identification of high-affinity dicarboxylate substrate and inhibitors and analysis of the beta-eliminase activity. Biochemistry. 2005; 44:13091–13100.
- Balu DT, et al. D-serine and serine racemase are localized to neurons in the adult mouse and human fore-brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 34:419–435.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).