Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
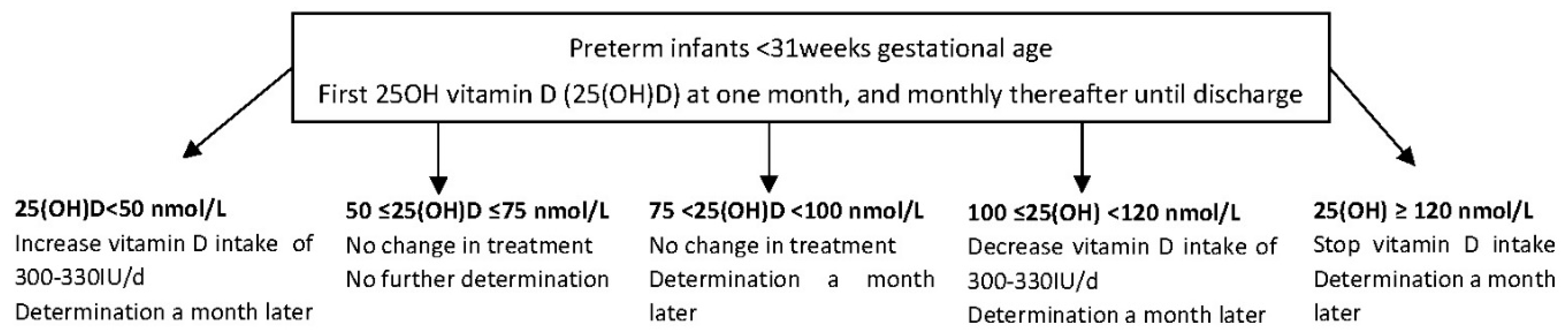
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
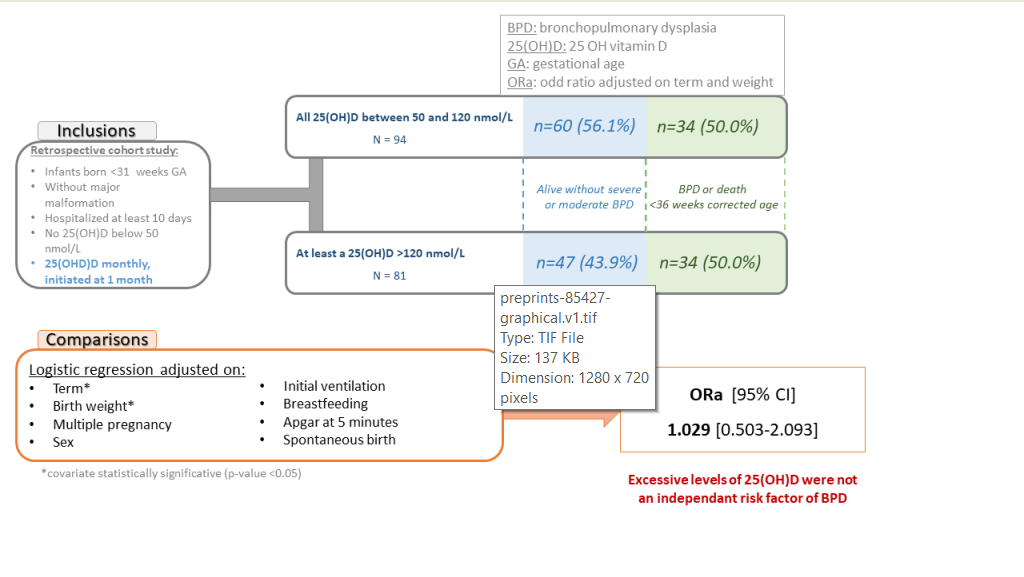
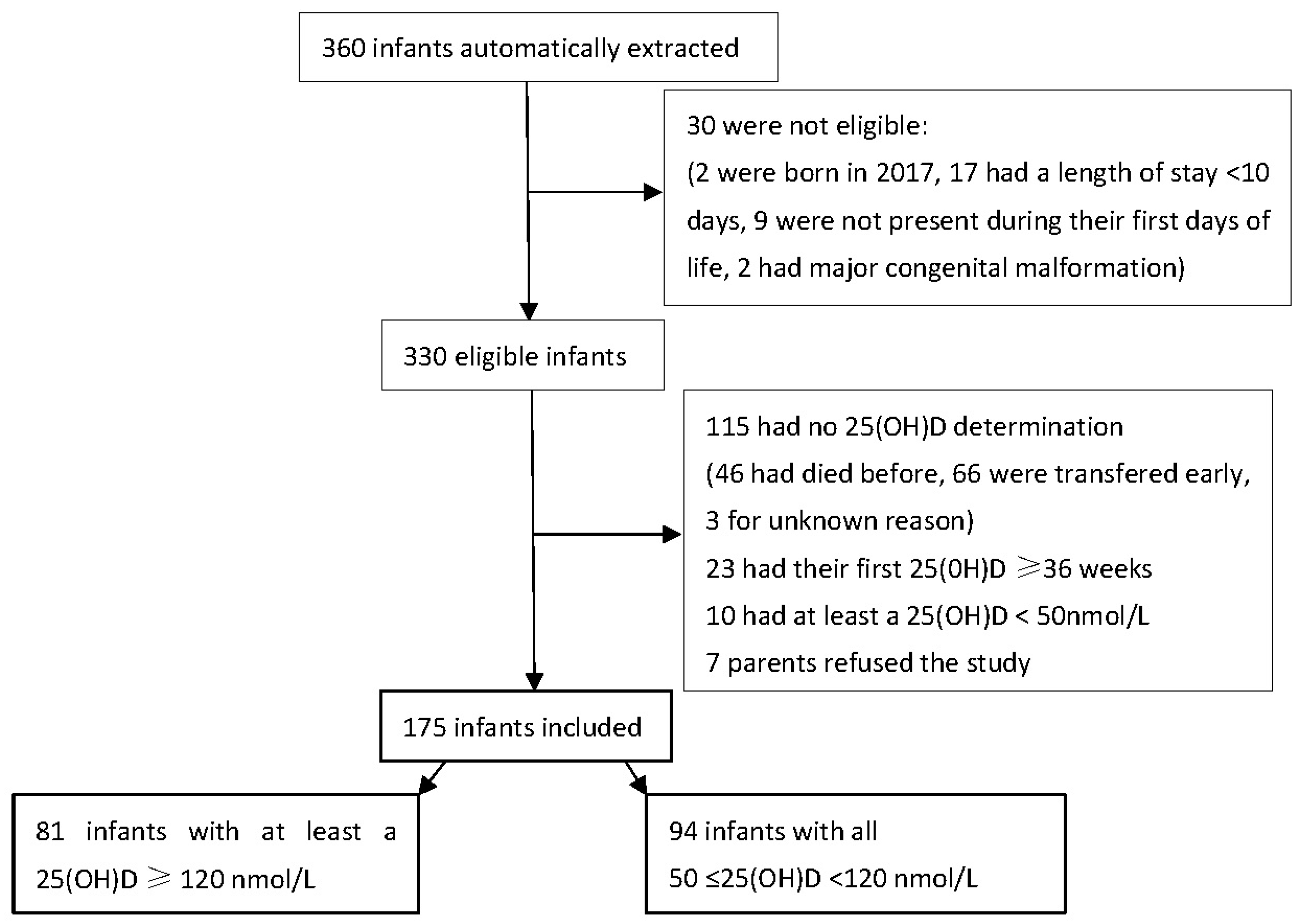
3.1. Population
3.1.1. Study flow-chart
3.1.2. Description of the population
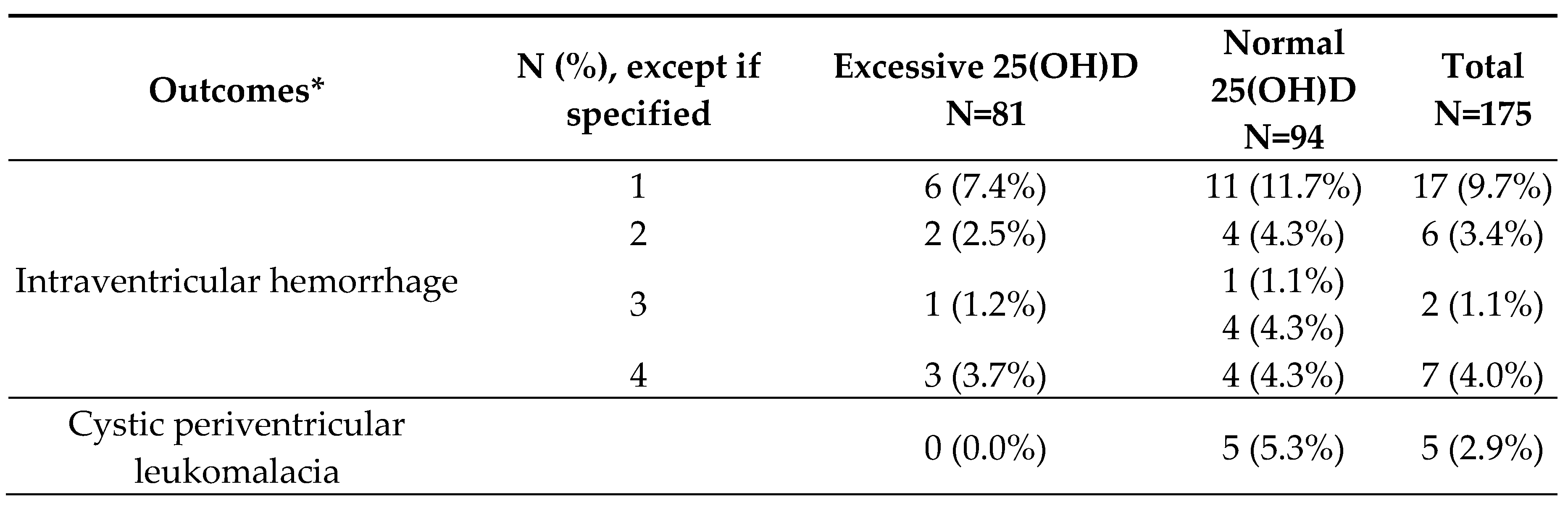
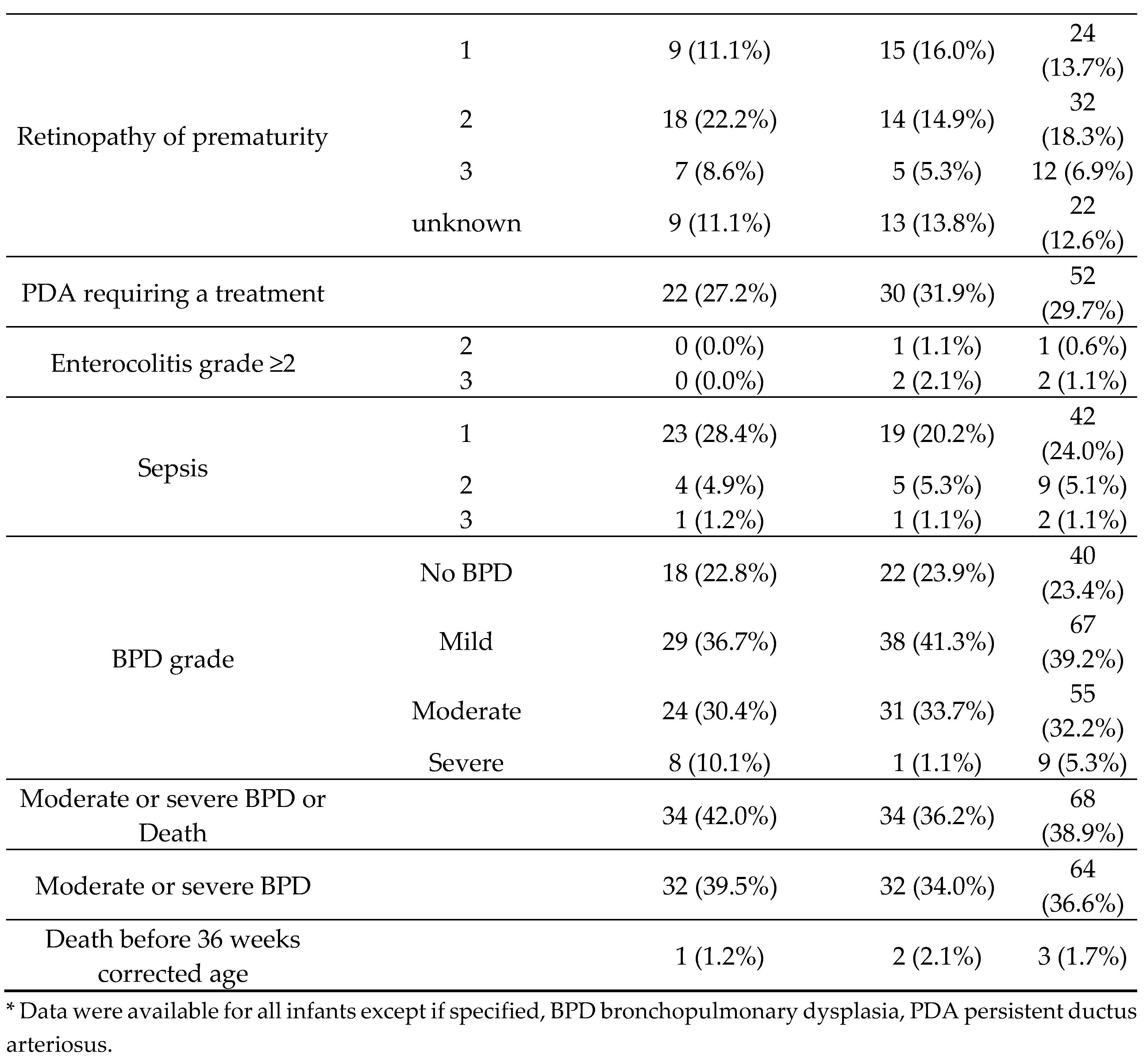
3.2. Outcomes
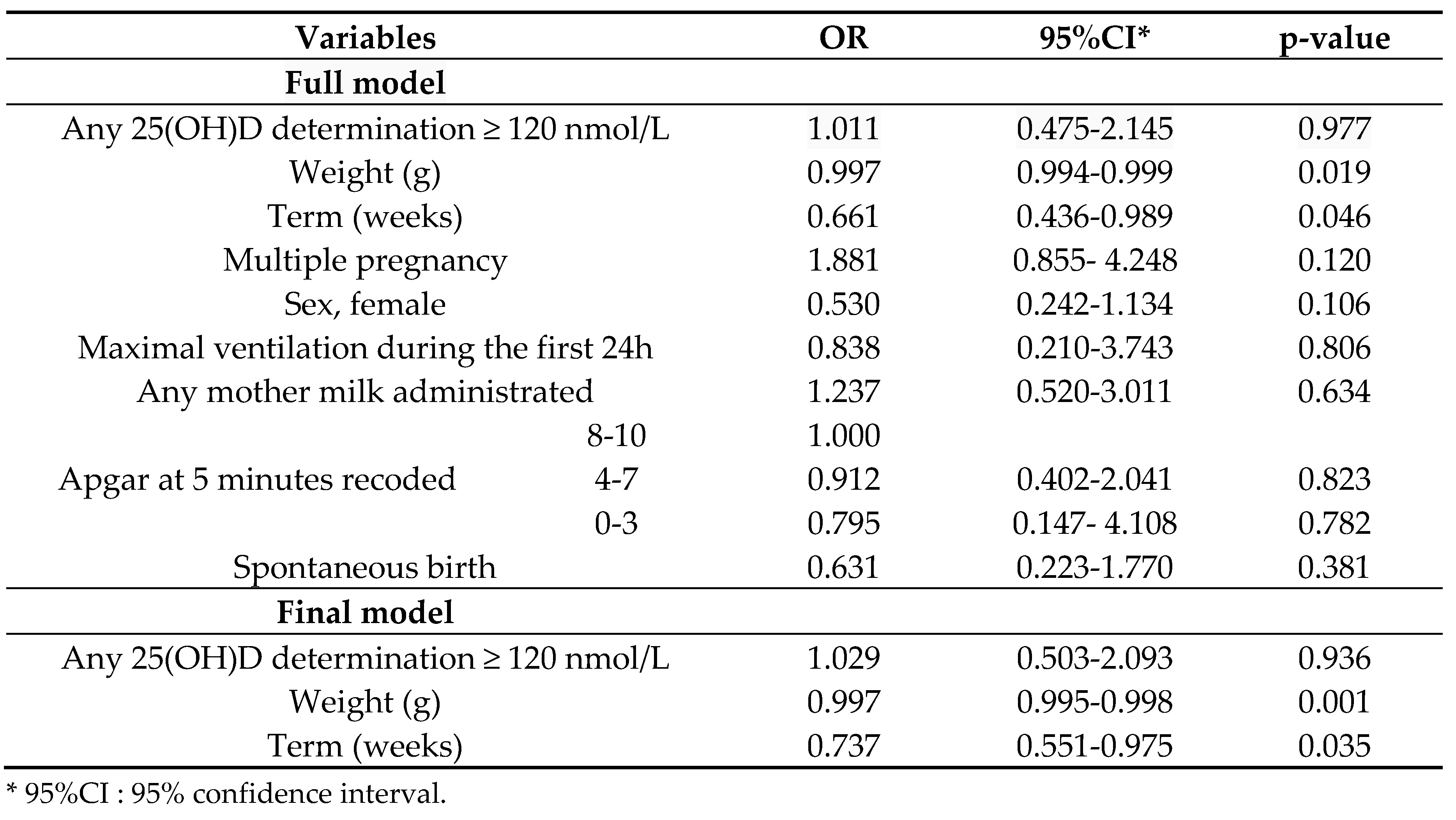
3.3. Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheong, J.L.Y.; Doyle, L.W. An Update on Pulmonary and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Semin. Perinatol. 2018, 42, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykkedegn, S.; Sorensen, G.L.; Beck-Nielsen, S.S.; Christesen, H.T. The Impact of Vitamin D on Fetal and Neonatal Lung Maturation. A Systematic Review. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L587–L602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fu, J.; Feng, Y. Utility of Umbilical Cord Blood 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels for Predicting Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants with Very Low and Extremely Low Birth Weight. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 956952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Lim, G.; Park, Y.-M.; Chang, M.; Son, J.S.; Lee, R. Association between Vitamin D Level and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0235332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.Y.; Bae, M.H.; Lee, N.R.; Han, Y.M.; Park, K.H. Association between Vitamin D Deficiency at One Month of Age and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e27966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, G.; Jie, Q.; Rui, C. Effect of Different Doses of Vitamin D Supplementation on Preterm Infants – an Updated Meta-Analysis. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristizabal, N.; Holder, M.P.; Durham, L.; Ashraf, A.P.; Taylor, S.; Salas, A.A. Safety and Efficacy of Early Vitamin D Supplementation in Critically Ill Extremely Preterm Infants: An Ancillary Study of a Randomized Trial. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 123, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, P.; Salas, A.A.; Nicola, T.; Craig, C.M.; Carlo, W.A.; Ambalavanan, N. A Comparison of 3 Vitamin D Dosing Regimens in Extremely Preterm Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, C.K.; Sankar, M.J.; Agarwal, R.; Pratap, O.T.; Jain, V.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, A.K.; Deorari, A.K.; Paul, V.K.; Sreenivas, V. Trial of Daily Vitamin D Supplementation in Preterm Infants. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e628–e634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierge, M.; Laborie, S.; Bertholet-Thomas, A.; Carlier, M.-C.; Picaud, J.-C.; Claris, O.; Bacchetta, J. Intoxication néonatale à la vitamine D chez des anciens prématurés : une série de 16 cas. Arch. Pédiatrie 2017, 24, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, R.; Singh, H.; Wang, Y.; Harb, A.; Gornes, C.; Liu, J.; Rehan, V.K. Effect of Perinatal Vitamin D Deficiency on Lung Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation and Injury Repair Potential. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 65, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurt, M.; Liu, J.; Sakurai, R.; Gong, M.; Husain, S.M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Husain, M.; Villarreal, P.; Akcay, F.; Torday, J.S.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation Blocks Pulmonary Structural and Functional Changes in a Rat Model of Perinatal Vitamin D Deficiency. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L859–L867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Weng, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, C.; Jin, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, A.; Sun, Y. Low-Dose Vitamin D Protects Hyperoxia-Induced Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Inhibiting Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborie, S.; Denis, A.; Raverot, V.; Claris, O.; Bacchetta, J.; Butin, M. A Third of Premature Neonates Displayed Inadequate 25-hydroxyvitamin D Levels before Being Discharged from a French Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathilde, M.; Butin, M.; Pascal, R.; Plaisant, F.; Laborie, S.; Bacchetta, J. Local Protocol Helped to Deliver Vitamin D Levels More Accurately in Preterm Infants. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczyk-Nowotarska, A.; Bokiniec, R.; Seliga-Siwecka, J. Monitored Supplementation of Vitamin D in Preterm Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, O.; Laughon, M.; Lehert, P. Survival without Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia of Extremely Preterm Infants: A Predictive Model at Birth. Neonatology 2021, 118, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughon, M.M.; Langer, J.C.; Bose, C.L.; Smith, P.B.; Ambalavanan, N.; Kennedy, K.A.; Stoll, B.J.; Buchter, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; et al. Prediction of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Postnatal Age in Extremely Premature Infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapcharoensap, W.; Gage, S.C.; Kan, P.; Profit, J.; Shaw, G.M.; Gould, J.B.; Stevenson, D.K.; O’Brodovich, H.; Lee, H.C. Hospital Variation and Risk Factors for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in a Population-Based Cohort. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, e143676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegler, J.; Preuß, M.; Gebauer, C.; Bendiks, M.; Herting, E.; Göpel, W.; Bendiks, M.; Berghäuser, M.A.; Böckenholt, K.; Bohnhorst, B.; et al. Does Breastmilk Influence the Development of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia? J. Pediatr. 2016, 169, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Revise the Fenton Growth Chart for Preterm Infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborie, S. Les Surdosages En 25 OHD Pendant Les Premiers Mois de Vie Sont-Ils Un Facteur de Risque de Dysplasie Bronchopulmonaire ? Presented at the JFRN 2022, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shroff, R.; Wan, M.; Nagler, E.V.; Bakkaloğlu, S.; Fischer, D.-C.; Bishop, N.; Cozzolino, M.; Bacchetta, J.; Edefonti, A.; Stefanidis, C.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Recommendations for Native Vitamin D Therapy in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 2–5 and on Dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1098–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, H.H.; Van Marter, L.J.; McElrath, T.F.; Tabatabai, P.; Litonjua, A.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Christou, H. Vitamin D Status among Preterm and Full-Term Infants at Birth. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassai, M.S.; Cafeo, F.R.; Affonso-Kaufman, F.A.; Suano-Souza, F.I.; Sarni, R.O.S. Vitamin D Plasma Concentrations in Pregnant Women and Their Preterm Newborns. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuneme, C.; Martin, F.; McCarthy, R.; Carroll, A.; Segurado, R.; Murphy, J.; Twomey, A.; Murphy, N.; Kilbane, M.; McKenna, M.; et al. The Association of Vitamin D Status with Acute Respiratory Morbidity in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courbebaisse, M.; Souberbielle, J.-C.; Baptiste, A.; Taieb, J.; Tsatsaris, V.; Guibourdenche, J.; Senat, M.-V.; Haidar, H.; Jani, J.; Guizani, M.; et al. Vitamin D Status during Pregnancy and in Cord Blood in a Large Prospective French Cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalia, H.; Samonini, A.; Buffat, C.; Gras, E.; des Robert, C.; Landrier, J.-F.; Pauly, V.; Boubred, F. Low Vitamin D Levels at Birth and Early Respiratory Outcome in Infants With Gestational Age Less Than 29 Weeks. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 790839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetta, J.; Schmitt, C.P.; Bakkaloglu, S.A.; Cleghorn, S.; Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Prytula, A.; Ranchin, B.; Schön, A.; Stabouli, S.; Van de Walle, J.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Mineral and Bone Disorders in Infants with CKD: Clinical Practice Points from the ESPN CKD-MBD and Dialysis Working Groups and the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetta, J.; Edouard, T.; Laverny, G.; Bernardor, J.; Bertholet-Thomas, A.; Castanet, M.; Garnier, C.; Gennero, I.; Harambat, J.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Vitamin D and Calcium Intakes in General Pediatric Populations: A French Expert Consensus Paper. Arch. Pédiatrie 2022, 29, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.D.; Moltu, S.J.; Lapillonne, A.; van den Akker, C.H.P.; Carnielli, V.; Fusch, C.; Gerasimidis, K.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Haiden, N.; Iacobelli, S.; et al. Enteral Nutrition in Preterm Infants (2022): A Position Paper from the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition and Invited Experts. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, Publish Ahead of Print. [CrossRef]
- Durup, D.; Jørgensen, H.L.; Christensen, J.; Schwarz, P.; Heegaard, A.M.; Lind, B. A Reverse J-Shaped Association of All-Cause Mortality with Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in General Practice: The CopD Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempos, C.T.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Yetley, E.A.; Looker, A.C.; Schleicher, R.L.; Cao, G.; Burt, V.; Kramer, H.; Bailey, R.L.; et al. Is There a Reverse J-Shaped Association Between 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and All-Cause Mortality? Results from the U.S. Nationally Representative NHANES. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3001–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandai, R.; Jajoo, M.; Singh, A.; Mandal, A.; Jain, R. Association of Vitamin D Deficiency with an Increased Risk of Late-Onset Neonatal Xepsis. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cizmeci, M.N.; Kanburoglu, M.K.; Akelma, A.Z.; Ayyildiz, A.; Kutukoglu, I.; Malli, D.D.; Tatli, M.M. Cord-Blood 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and Risk of Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis: A Case–Control Study from a Tertiary Care Center in Turkey. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Say, B.; Uras, N.; Sahin, S.; Degirmencioglu, H.; Oguz, S.S.; Canpolat, F.E. Effects of Cord Blood Vitamin D Levels on the Risk of Neonatal Sepsis in Premature Infants. Korean J. Pediatr. 2017, 60, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinkaya, M.; Cekmez, F.; Buyukkale, G.; Erener-Ercan, T.; Demir, F.; Tunc, T.; Aydın, F.N.; Aydemir, G. Lower Vitamin D Levels Are Associated with Increased Risk of Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis in Term Infants. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pregnancy characteristics* | Excessive 25(OH)D N=81 | Normal 25(OH)D N=94 |
Total N=175 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parity | 1 | 29 (35.8%) | 40 (42.6%) | 69 (39.4%) | |
| 2 | 25 (30.9%) | 31 (33.0%) | 56 (32.0%) | ||
| 3 | 19 (23.5%) | 14 (14.9%) | 33 (18.9%) | ||
| ≥4 | 8 (9.9%) | 8 (8.5%) | 16 (9.1%) | ||
| Unknown | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.6%) | ||
| Multiple pregnancy | 30 (37.5%) | 25 (26.6%) | 56 (32.0%) | ||
| Any hypertension during pregnancy | 19 (23.5%) | 21 (22.3%) | 40 (22.9%) | ||
| Preterm premature rupture of membranes | 26 (32.1%) | 27 (28.7%) | 53 (30.3%) | ||
| Any diabetes during pregnancy | 8 (9.9%) | 13 (13.8%) | 21 (12.0%) | ||
| Histological chorioamnionitis | 21 (25.9%) | 13 (13.8%) | 34 (19.4%) | ||
| Unavailable | 0 (0%) | 3 (3.2%) | 3 (1.7%) | ||
| Clinical chorioamnionitis | 11 (13.6%) | 7 (7.4%) | 18 (10.3%) | ||
| Unknown | 1/1.2%) | 3 (3.2%) | 4 (2.3%) | ||
| Any antenatal corticosteroids | 76 (93.8%) | 83 (88.3%) | 159 (90.9%) | ||
| Neonatal characteristics* | N (%), except if specified | Excessive 25(OH)D N=81 | Normal 25(OH)D N=94 |
Total N=175 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth Season | Summer | 19 (23.5%) | 32 (34.0%) | 51 (29.1%) |
| Fall | 20 (24.7%) | 26 (27.7%) | 46 (26.3%) | |
| Winter | 21 (25.9%) | 18 (19.1%) | 39 (22.3%) | |
| Spring | 21 (25.9%) | 18 (19.1%) | 39 (22.3%) | |
| Sex | Male | 39 (48.1%) | 51 (54.3%) | 90 (51.4%) |
| Term (weeks) | Mean (SD) | 27.58 (1.84) | 27.88 (1.56) | 27.74 (1.70) |
| Weight (g) | Mean (SD) | 938 ( 272) | 998 ( 305) | 970 (291) |
| Height (cm) | Mean (SD) | 35.05 (3.11) | 35.15 ( 3.98) | 35.11 (3.60) |
| Head circumference (cm) | Mean (SD) | 24.83 ( 2.19) | 25.44 (2.72) | 25.16 (2,50) |
| Small for gestational age* | 14 (17.3%) | 17 (18.1%) | 31 (17.7%) | |
| Apgar at 5 minutes | 8-10 | 55 (67.9%) | 52 (55.3%) | 107 (61.1%) |
| 4-7 | 21 (25.9%) | 37 (39.4%) | 58 (33.1%) | |
| 0-3 | 4 (4.9%) | 4 (4.3%) | 8 (4.6%) | |
| Not available | 1 (1.2%) | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (1.1%) | |
| Maximum ventilation during the first 24h | FiO2<30% and non invasive ventilation | 7 (8.6%) | 6 (6.4%) | 13 (7.4%) |
| Assisted ventilation and FiO2<30% | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (0.6%) | |
| Assisted ventilation or FiO2≥ 30% | 74 (91.4%) | 87 (92.6%) | 161 (92.0%) | |
| Parenteral nutrition (days) | Median | 14 | 13 | 14 |
| Interquartile range | 7 -23 | 7 -20 | 7 -21 | |
| Enteral feeding | Maternal or donor milk | 17 (21.0%) | 19 (20.2%) | 36 (20.6%) |
| Mixed | 50 (61.7%) | 49 (52.1%) | 99 (56.6%) | |
| Formula or donor milk | 14 (17.3%) | 26 (27.7%) | 40 (22.9%) | |
| Any mother milk given | 66 (81.5%) | 68 (72.3%) | 134 (76.6%) | |
| First determination of 25(OH)D (nmol/L) | Mean (SD) | 139.4 (43.1) | 86.1 (19.6) | 110.8 (42.1) |
| Corrected age at first 25(OH)D determination | Mean (SD) | 32.4 (1.9) | 32.5 (1.5) | 32.4 (1.7) |
| Second determination of 25(OH)D (nmol/L) | 25 (30.9%) | 20 (21.3%) | 45 (25.7%) | |
| Mean (SD) | 144.40 (29.58) | 85.20 (17.76) | 118.1 (38.7) | |
| Corrected age at second determination of 25(OH)D | Mean (SD) | 34.2 (1.2) | 34.2 (1.5) | 34.2 (1.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





