1. Introduction
Impaired kidney function and/or chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, particularly in societies undergoing demographic change. Current worldwide prevalence of CKD is estimated at 8-16% [
3]. From 1960 to 2016, death due to CKD has increased by 98% to ≈ 1.2 million per year in 2016 [
4].
Detection of chronic kidney disease in first-line diagnostics is of high importance. It is a comorbidity and a severe risk factor of various diseases and influences the outcome after cardiologic interventions [
5,
6,
7,
8]. It must be taken into account for the dosage of potential nephrotoxic medications and the application of potentially kidney-damaging radiological procedures [
9].
This is true for critically ill and old patients with known kidney disease or high risk for such disease. But also, for supposedly healthy patients with no known kidney disease. Two sub-aspects are relevant here: Unknown kidney damage must be detected reliably. And the stage of kidney damage must be correctly assessed.
We wanted to find out whether the guidelines for the detection of chronic kidney disease are suitable for first-line detection and classification of chronic kidney diseases in elderly patients (aged > 60 years) admitted to a hospital.
To date, non-invasive assessment of renal function and dysfunction relies mostly on laboratory tests. Clinical stages of CKD as defined by the organization for Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) are entirely based on GFR values [
10]. The most reliable procedure for determining GFR is plasma clearance or urinary excretion of exogenous filtration markers such as inulin or iohexol [
11,
12]. However, these procedures are of little use in routine clinical health care. Measurement of the clearance of endogenous filtration markers, such as creatinine, is an alternative approach at exact GFR-determination. This approach is more practical in the clinical context. However, determination of endogenous creatinine clearance is also not widely used because it requires stringent collection of complete urine excretion over extended time periods. This procedure is cumbersome and impractical in most clinical situations. Instead, the estimation of GFR based on plasma levels of endogenous filtration markers has become the procedure of choice.
As recommended by international guidelines, initial screening of renal function is currently almost always based on GFR estimates derived from serum creatinine by the CKD-EPI formula [
10]. Various formulae for calculating GFR estimates (eGFR) have been established in routine clinical diagnostics [
13]. The CKD-EPI formula using serum creatinine is confounded by tubular secretion, muscle mass, food protein intake, and medication [
9]. Due to these confounders, serum creatinine does not increase until GFR drops by more than 50% [
14]. This limitation is crucial because a drop of GFR by more than 50% (i.e., below 60 ml/min entailing transition from CKD-stage 2 to CKD-stage 3) is associated with a significant increased mortality [
15] but not detected reliably by GFR-estimates based on creatinine. This shortcoming has prompted the search for more reliable filtration markers, such as the cysteine protease inhibitor cystatin C [
16]. But GFR estimates derived from serum cystatin C are rarely used and are not recommended as a primary diagnostic [
10] despite several studies indicating superiority of cystatin C as marker for estimating GFR and predicting kidney function [
8,
16,
17,
18,
19].
Consequently, here, we address two main questions:
1. Are kidney disease patients correctly identified by recommended first-line diagnostics?
For this purpose, we studied patients admitted to the hospital with a variety of diagnoses. These patients were selected as kidney-sane according to currently recommended first-line kidney diagnostics (eGFR CKD-EPI ≥ 60 ml/min and negative results of urine analysis). We rechecked their renal status by eGFR-cystatin C and used the coded diagnoses to judge the validity of the two procedures. We have here tested the CAPA formula, most widely implemented in routine healthcare.
2. Are patients with recommended first-line diagnostics assigned to the correct GFR stage?
For this purpose, we additionally studied patients considered
prima facie at risk for chronic kidney failure due to suffering from aortic valve stenosis and therefore being lined up for TAVI. Patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVI) can be expected to have a higher incidence of CKD than the normal population [
20]. In these patients we addressed the differences in the classification of manifest kidney-disfunction according to cystatin C- and creatinine-based GFR-estimations, as previously described by others [
8].
The recommended strategy may be particularly unsuitable for elderly individuals, most notably for elderly hospitalized patients. These patients are afflicted by co-morbidities compromising kidney dysfunction. They are often lined up for potentially nephrotoxic iatrogenic interventions. Furthermore, they are nota bene subjected to age-related decline in muscle mass and residual GFR-capacity, which compromises utility of creatinin-based GFR-estimation.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Participants: A total of 112 in- and out-patients of the University Hospital of the Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf were included and assigned to two cohorts. One cohort (N=61, 25 female, 36 male, mean age 71.89 years, median age 70.87 years) was denominated kidney-sane because these patients appear to be in good renal health after primary diagnostics, which are frequently used in clinical practice according to the guidelines. These patients were included based on the following criteria: age > 60 years, eGFR CKD-EPI ≥ 60 ml/min, total protein in urine < 150 mg/g creatinine or < 150 mg/l, white and red blood cell count in urine < 25/μl and < 23/μl, respectively, or corresponding negative results for white and red blood cells in urine test strip analysis. The true state of renal or non-renal diseases of these patients was determined ex post according to the etiology of the ICD-10-encoded diagnoses (see Appendix Table A1). We decided on this type of patient inclusion because for the treating physician in practice, in the primary diagnosis of patients without known CKD, it is precisely these laboratory parameters that are used to assess renal function.
The other cohort (N=51, 23 female, 28 male, mean age 81.48 years, median age of 82.69 years) was denominated
at risk (TAVI) due to suffering from aortic valve stenosis known to increase the risk of kidney dysfunction [
20]. These patients were admitted to the hospital for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) and included in the study if aged > 60 years.
Ethics: The investigation was approved by the local ethics board of the Medical Faculty of the Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (study number 2022-1839). Laboratory results and ICD-10-coded diagnoses retrieved for this study were anonymized prior to data analysis. The investigation conforms to the principles outlined by the Declaration of Helsinki of the World’s Medical Association. All patients have given informed consent.
Laboratory analyses
All analyses were performed by accredited standardized diagnostic procedures as part of routine diagnostic workup of the participants. Li-heparine-plasma or serum was obtained by vein puncture. Samples were analyzed within 2 h or stored for reflex testing at -20 °C for not more than eight weeks. Creatinine and cystatin C were determined on a Cobas 8000 analyzer (Roche; Basel, Switzerland) by enzymatic assay and particle-enhanced immunological turbidity assay, respectively.
Traceability: The method of creatinine determination was standardized against ID/MS (isotope dilution mass spectrometry) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The method of cystatin determination was standardized against the ERM-DA471/IFCC reference material according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Calculation of eGFR
Creatinine-based GFR estimates were calculated according to the CKD-EPI formula [
1], as follows: Females, plasma creatinine ≤ 0.7 mg/dl:
GFRCKD-EPI = 144 x (Creatinine [mg/dl] /0.7)-0.329 x 0.993age;
females, plasma creatinine > 0.7 mg/dl:
GFRCKD-EPI = 144 x (Creatinine [mg/dl] /0.7)-1.209 x 0.993age;
males, plasma creatinine ≤ 0.9 mg/dl:
GFRCKD-EPI = 141 x (Creatinine [mg/dl] /0.9)-0.411 x 0.993age;
males, plasma creatinine > 0.9 mg/dl:
GFRCKD-EPI = 141 x (Creatinine [mg/dl] /0.9)-1.209 x 0.993age.
Cystatin C–based GFR estimates were calculated according to the CAPA formula [
2]:
GFRCAPA = 130 x Cystatin C [mg/l] -1.069 x age-0.117 – 7.
Statistics
Graph Pad Prism 9 (Graph Pad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA: released in 2020. Graph Pad Prism 9 for Mac, San Diego, CA, USA: Graph Pad Inc.) and Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA: released in 2022. Microsoft Excel for Mac Version 16.67 Redmond, WA, USA: Microsoft Corp.) were used for analysis. Data were descriptively analyzed by mean and median values. Normal distribution was tested according to Shapiro-Wilk. Correlations were analyzed by Spearman’s correlation and assumed to be good at r ≥ 0.7 and moderate at r ≥ 0.5. Differences were analyzed by the Wilcoxon test for paired samples. For all tests, statistical significance was assumed at p < 0.05.
3. Results
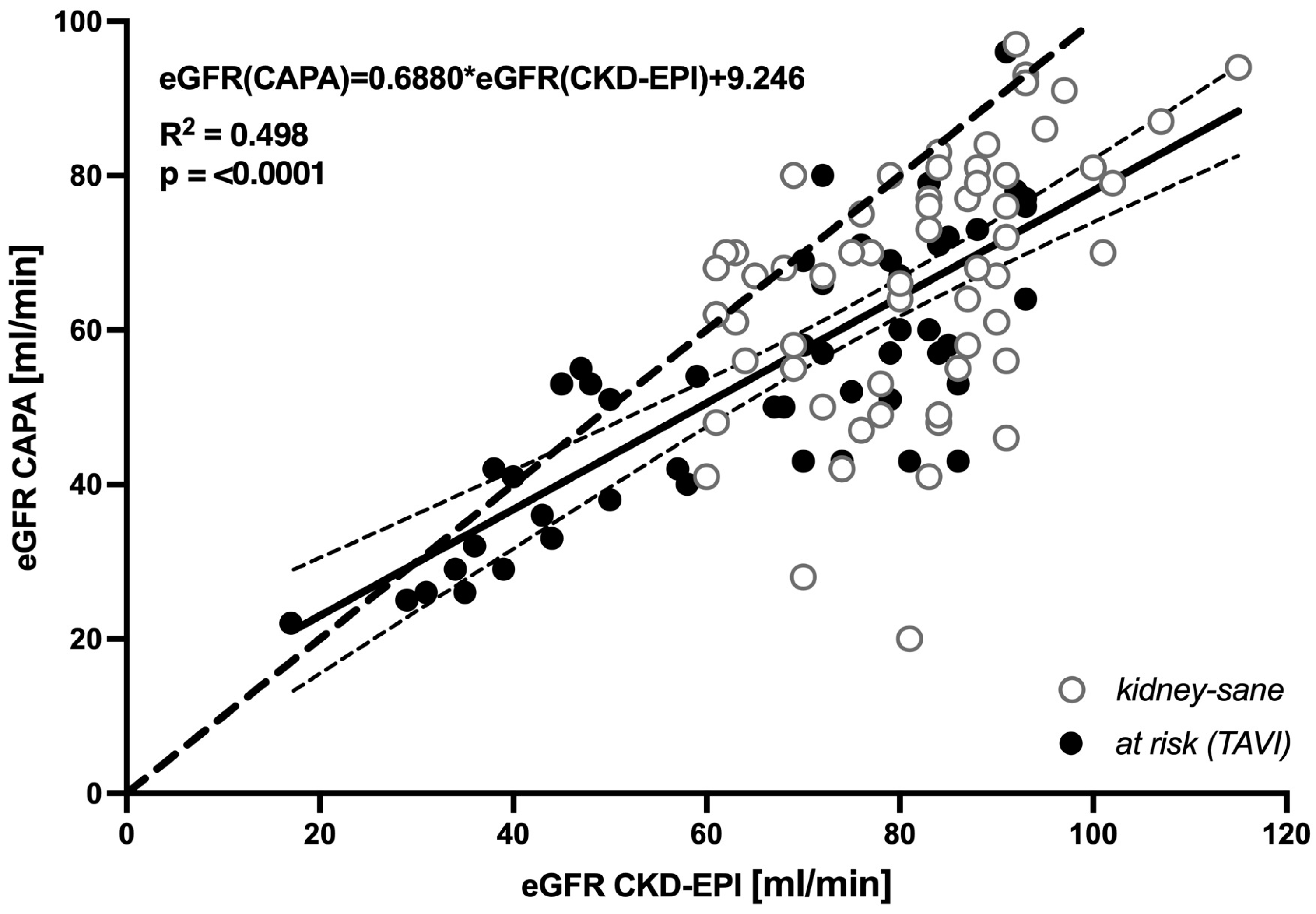
3.1. Cystatin C-based eGFR (CAPA) is linearly correlated with, but almost always lower than, creatinine-based eGFR (CKD-EPI)
Across the entire population of 112 elderly patients a systematic downward bias of cystatin C-based eGFR relative to creatinine-derived eGFR (CKD-EPI) was indicated by linear regression of the two datasets, yielding
eGFR(CAPA)=0.6880*eGFR(CKD-EPI)+9.246,
(R
2 = 0.498, p < 0.0001) (
Figure 1). Of note, at eGFR > 40 ml/min regression line and 95% confidence interval of regression were far beneath the hypothetical line of identity, supporting the notion that moderate decreases in GFR are indicated by cystatin C-based eGFR but not by creatinine-based eGFR.
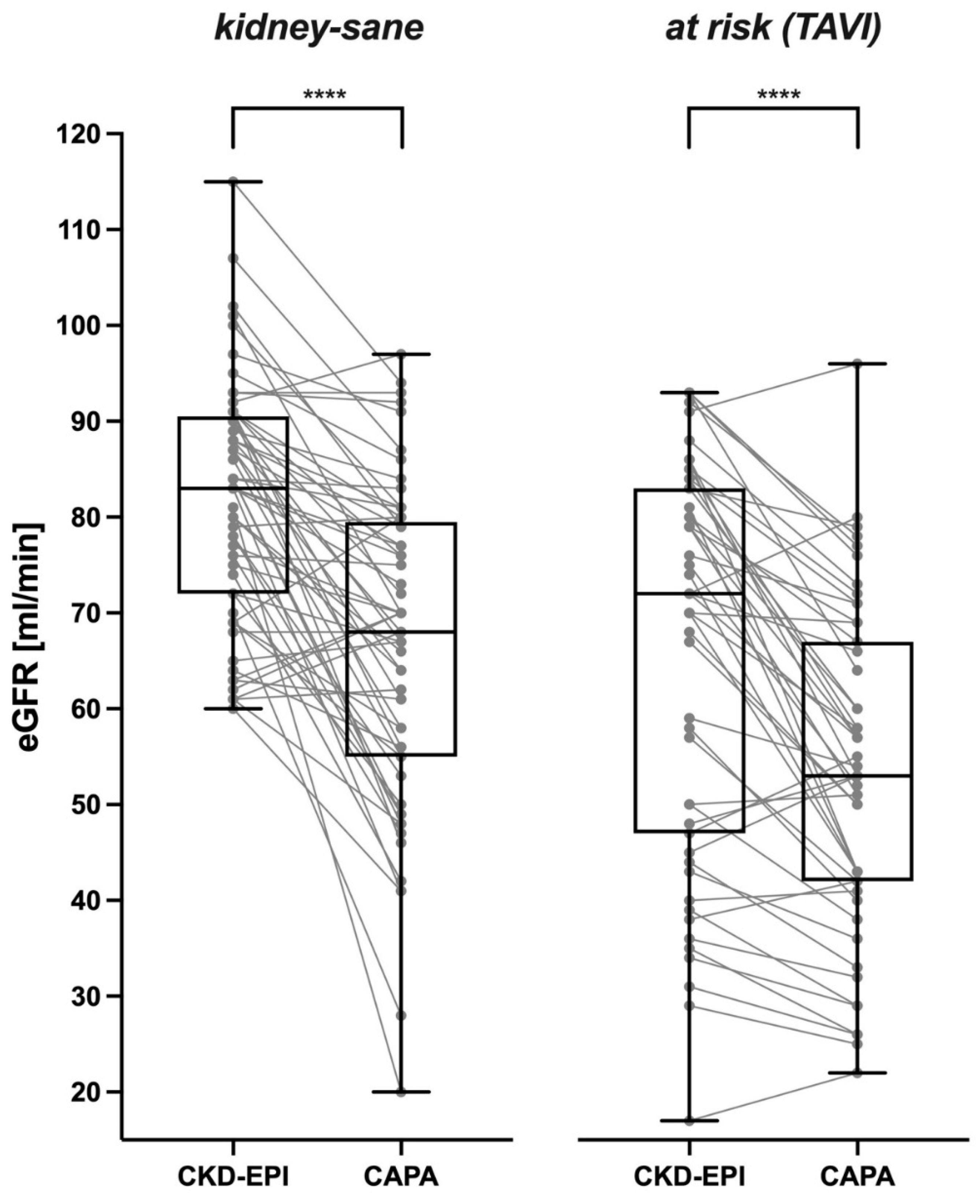
Correspondingly, in a vast majority of the analyzed cases, cystatin C-based eGFR was distinctively lower than creatinine-based eGFR. This was likewise true for the
kidney-sane patients (
Figure 2 left panel) and for the
at risk (TAVI) patients suffering from manifest kidney disease or bearing an increased risk therefore (
Figure 1 right panel). Cystatin C-derived eGFR was lower than creatinine-derived eGFR in ≈ 84% of
kidney-sane and ≈ 82% of
at risk (TAVI) cases.
In the kidney-sane patients CKD-EPI-calculated eGFR was 81.56 ± 12.41 ml/min in the mean and 83 ml/min in the median. In contrast, eGFR derived from serum/plasma cystatin C (CAPA formula) was 66.38 ± 16.60 ml/min in the mean and 68 ml/min in the median. The prevalent downward bias of cystatin C-based eGFR (-21.35 ± 18.64 and -13.50 ± 18.31% for males and females, respectively) was highly significant (p < 0.0001).
The at risk (TAVI) patients exhibited lower eGFR values than the kidney-sane patients. CKD-EPI-derived eGFR was 66.14 ± 20.71 ml/min in the mean and 72 ml/min in the median. Nevertheless, cystatin C-based eGFR was even lower (53.53 ± 16.92 ml/min in the mean and 53 ml/min in the median). Again, the downward bias of cystatin C-based eGFR (-15.70 ± 19.16 and -18.09 ± 14.53% for males and females, resp.) was highly significant (p < 0.0001).
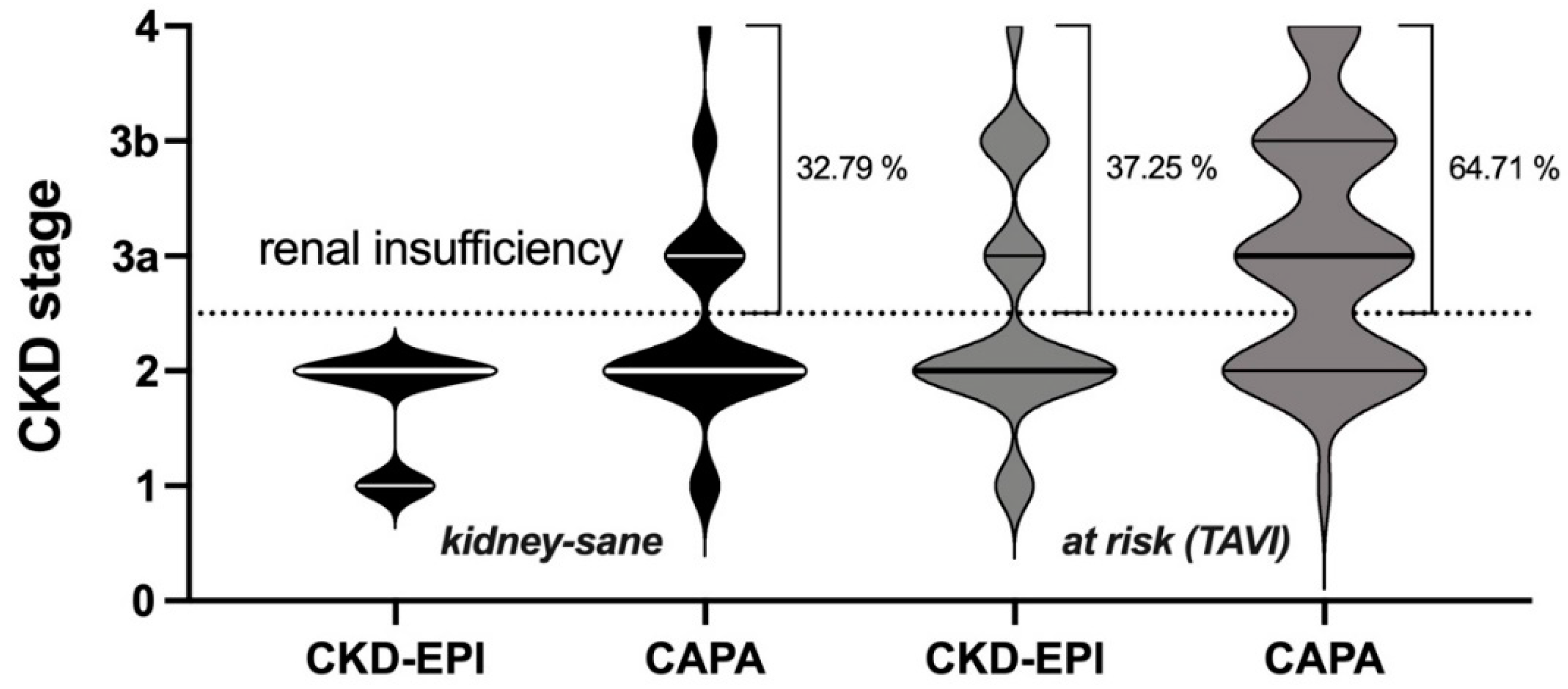
3.2. Potential impact of eGFR (CAPA) on CKD-stage and clinical classification of kidney disease
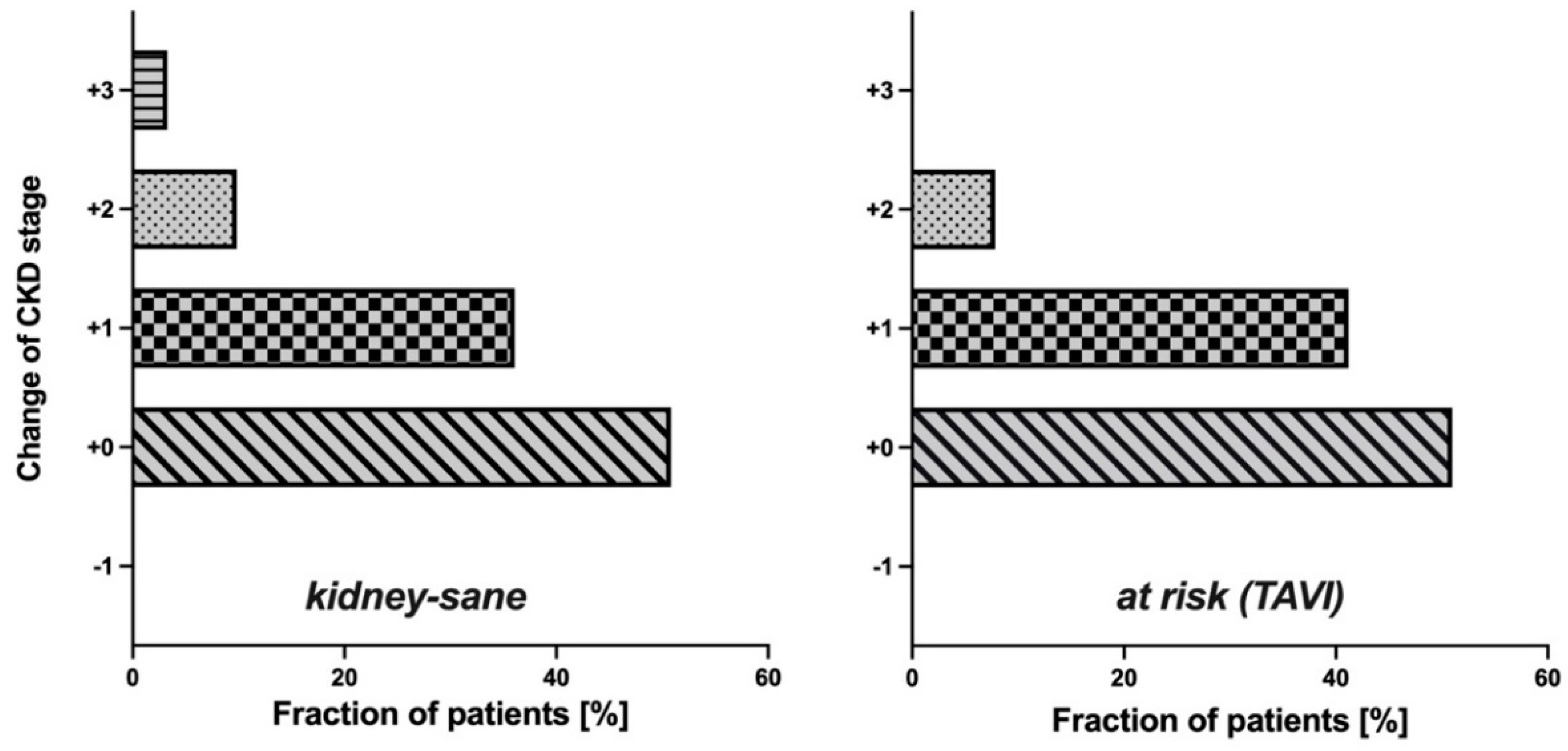
Since in both groups cystatin C-based eGFR (CAPA) was notably lower than eGFR (CKD-EPI), the question arose whether the use of eGFR (CAPA) instead of eGFR (CKD-EPI) would result in assignments of the patients to different CDK-stages. This question seemed particularly interesting for the
kidney-sane group, i. e. the patients classified as
not suffering from kidney disease according to eGFR (CKD-EPI). While half of these patients (50.82%) remained in the same CKD-stage upon reclassification according to eGFR (CAPA), the rest moved one (36.07%), two (9.84%) or even three (3.28%) CKD-stages downwards (
Figure 3, left). More relevant, for one third of these patients, reclassification according to eGFR (CAPA) resulted in a CKD-stage indicative of kidney dysfunction or even kidney disease, while all these patients were judged
kidney-sane according to eGFR (CKD-EPI). Thus, reclassification did not only alter CKD-stage but also clinical classification of kidney disease state for a significant portion of the patients. A similar observation was made in the
at risk (TAVI) group: Half of these (49.02%) were down-graded by one or two CKD-stages (
Figure 3, right), and 27.45% of the cases were moved to a worse clinical disease classification, i. e. from CKD-stages 1/2 to CKD-stages 3a/b or even 4 (
Figure 4). It should be noted that there was not a single patient in both groups, whose CKD-stage or disease classification improved when based on eGFR (CAPA) instead of eGFR (CKD-EPI).
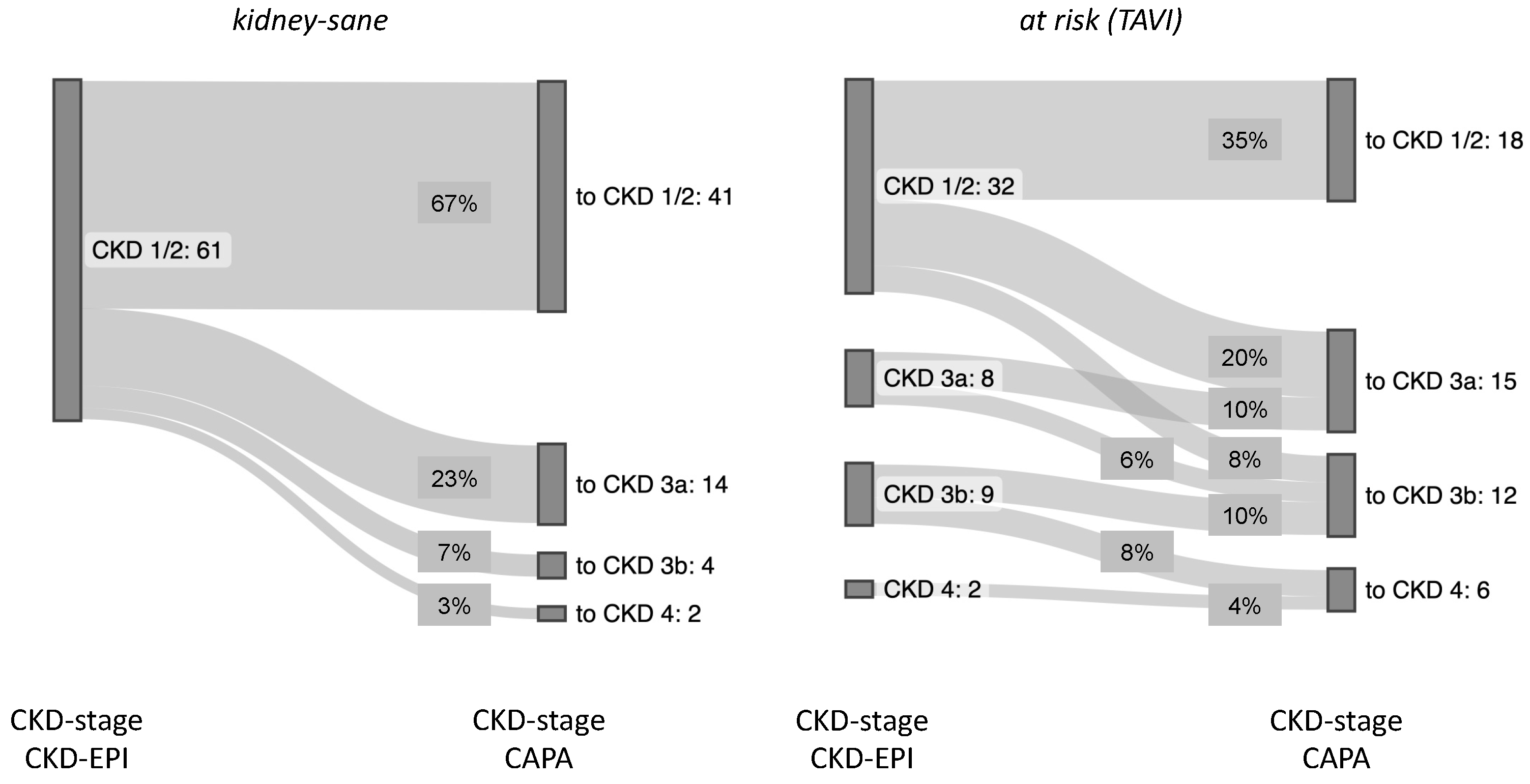
Overall, the
kidney-sane patient collective was entirely assigned to CKD-stage 1 or 2 according to eGFR (CKD-EPI) and gained roughly one third of cases of more or less advanced kidney insufficiency, when reclassified according eGFR (CAPA). Similarly, in the
at risk (TAVI) group roughly one more third of the cases was judged to be at risk for chronic kidney failure, when analyzed according eGFR (CAPA) (summarized in
Figure 5).
3.3. Sensitivity of eGFR (CKD-EPI) and eGFR (CAPA) for kidney-relevant clinical diagnoses
To test whether the reclassification according to eGFR (CAPA) from presumably
kidney sane to presumed renal insufficiency (i.e., from CKD ≤ 2 to CKD > 2) was plausible in clinical terms, we unblinded the ICD-10-coded diagnoses of the (based on laboratory parameters)
kidney-sane group and therefrom identified etiologies plausibly encompassing or entailing kidney dysfunction or not. As summarized in
Table 1, the vast majority ( > 90%) of those patients remaining in CKD-stage 1 or 2 after recalculation of eGFR using cystatin C were indeed not diagnosed to suffer from primary or secondary renal disease. In contrast, a significant fraction (30%) of those patients that according to eGFR (CAPA) were moved from
kidney-sane to kidney insufficient state (i.e., from CKD stage ≤ 2 to CKD-stage >2) had indeed diagnoses encompassing renal insufficiency.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sensitivity of first-line diagnostic for kidney dysfunction
Our data suggest that in multimorbid elderly persons (as typically hospitalized in a university hospital) GFR-estimations based on serum creatinine according to the CKD-EPI formula are prompting an over-optimistic clinical assessment of kidney function. As a consequence, unknown/hidden kidney disease is overlooked in up to 30% of cases with undetermined state of kidney function. In the collective of elderly hospitalized patients analyzed here GFR-estimation based on cystatin C appeared more sensitive for, and less prone to overlooking, manifest kidney insufficiency than creatinine-based GFR estimations. Our observation that GFR is frequently underestimated by the CKD-EPI formula in elderly patients is plausible, given that the CKD-EPI formula has been developed based on a collective encompassing relatively few individuals aged 60 years or more [
1]. Moreover, the here observed downward bias of serum cystatin C-based relative to creatinine-based GFR-estimates conforms to many previous findings [
8,
16,
21].
4.2. Correct assessment of CKD-stage
Our data obtained in a group of TAVI patients suggest that severity of manifest kidney disease is often underestimated by GFR-estimates based on serum creatinine according to the CKD-EPI formula. In the case of TAVI patients under-determination of kidney insufficiency is particularly unfortunate, because patients with renal dysfunction have a worse outcome after TAVI [
6,
7,
8]. In addition to the current status assessment of renal function, the GFR determined by cystatin C in TAVI patients with a GFR of 3b or worse also seems to be better suited for the prognostic assessment of the patients. This is true for the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular impairment [
8].
This is relevant, because our data show that the proportion of these patients is in fact higher than assumed according to standard diagnostics. Thus, correct pre-interventional assessment of renal function is essential for post-interventional monitoring of these patients.
4.3. What is the ultimative filtration marker?
In agreement with many previous studies [
8,
16,
17,
18,
19], our data strongly suggest that cystatin C is superior to creatinine as a filtration marker. Nevertheless, cystatin C based eGFR estimates can also be subject to error, because serum levels of cystatin C are confounded by extra-renal factors such as age, gender, body mass, body length, cigarette smoking, high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, obesity, diabetes and inflammation [
22,
23]. Moreover, the clinical relevance of differences between eGFR values based on cystatin C and creatinen seems unclear. Thus, it has been shown that the use of eGFR-CKD-EPI-Cystatin C (in contrast to the CAPA-formula employed here), especially to predict disease progression and mortality in patients with mild CKD, offers no benefits and only increases costs [
24].
Given the limitations of both creatinine and cystatin C, other markers for measuring kidney function are currently the subject of research. In critically ill sepsis patients, for example, proenkephalin exhibited a more precise correlation with the GFR than creatinine [
25,
26]. Unfortunately, proenkephalin has not yet been extensively compared to cystatin C. Thus, it remains to be found out whether it is superior to it.
4.4. Limitations of our study
Limitations of our study are the small case number and the lack of GFR-validation by a gold-standard GFR procedure. However, since many studies show that cystatin C appears superior to creatinine, it seemed sufficient to evaluate the additional value of cystatin C as compared to creatinine in terms of clinical utility.
5. Conclusions
In the first-line diagnostics of elderly, hospitalized patients for the detection of previously unrecognized renal dysfunction, the sole use of creatinine as a GFR marker seems insufficient. Nevertheless, this procedure is still recommended in the German S2k Interdisciplinary Guidelines and the international KDIGO Guidelines [
10,
27].
Furthermore, creatinine-based GFR estimation underestimates existing renal dysfunction compared to cystatin C-based measurement..
Pending corroboration by a larger study, our result suggest that a modification of guidelines and recommendations with respect to elderly hospitalized patients could be heralded. It could be imagined that elderly hospitalized patients would significantly profit from cystatin C derived determination of eGFR (CAPA) as obligatory diagnostic reflex, whenever creatinine-based eGFR (CKD-EPI) appears normal (i.e., is above 60 ml/min).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G. and F.B.; methodology, D.G. and F.B.; software, Graph Pad Prism 9 (Graph Pad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA: released in 2020. Graph Pad Prism 9 for Mac, San Diego, CA, USA: Graph Pad Inc.) and Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA: released in 2022. Microsoft Excel for Mac Version 16.67 Redmond, WA, USA: Microsoft Corp.); data curation, D.G., R.E.W., L.H.; writing—original draft preparation, D.G. and F.B.; writing—review and editing, D.G. and F.B..; visualization, D.G. and F.B.; helpful discussions: R.E.W, L.H.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty of the Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (study number 2022-1839, 07.02.2022).” for studies involving humans
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Excellent technical assistance is gratefully acknowledged to Birgit Hanzen. Support and helpful discussions are acknowledged to Dr. Karin Schulze-Bosse and Dr. Derek Hermsen.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| CAPA |
Caucasian, Asian, Pediatric and Adult |
| CKD |
Chronic kidney disease |
| CKD-EPI |
Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration |
| CVD |
cardiovascular disease |
| eGFR |
estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| GFR |
Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ICD-10 |
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems |
| IFFC |
International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine |
| KDIGO |
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| TAVI |
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation |
Appendix
Table A1.
caption.
| etiology |
Main or kidney-relevant secondary diagnosis (ICD-10-encoded) |
| Renal disease |
|
| Acute or chronic kidney disease |
Chronic kidney disease
Acute renal failure, Crush kidney with acute renal failure
State after acute renal failure |
| Kidney transplant |
Follow-up examination after organ transplantation
condition after kidney transplantation |
| Neoplasia (kidney) or loss of the kidney |
Multilocular cystic neoplasia of the kidney with low malignancy potential, status after renal cell carcinoma
Loss of kidneys, Follow-up care after living kidney donation
Pulmonary and osseous metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Malignant neoplasm of the kidney, angiomyolipoma at the upper pole of the right kidney |
| Non-renal disease |
|
| Athropathy |
Other unspecified crystal athropathies: shoulder region |
| Autoimmune disease |
Progressive systemic sclerosis, other overlap syndromes, seronegative chronic polyarthritis: multiple localizations
Other giant cell arteritis
MS with a secondary chronic course with indication of an acute exacerbation or progression
Other forms of systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Cardiovascular disease |
Arterial hypertension WHO grade II, no sec. cause of hypertension |
| Disease of the bile ducts |
Cholecystolithiasis |
| Disease of the eyes |
Suspected scleritis
Zoster ophthalmicus
Corneal dystrophy |
| Dysphagia |
Other and unspecified dysphagia |
| Flanks/abdominal pain |
Pain localized in other parts of the lower abdomen
Other and unspecified abdominal pain, Personal history of malignant neoplasms of other organs or systems, Hypothyroidism after medical interventions |
| Gait and mobility disorders |
Weakness |
| Hematological disease |
Anemia
Status after hematopetic stem cell transplantation, acute myeloid leukemia |
| Infectious disease |
Vesicular stomatitis with enterovirus exanthema
Infection by corona viruses of unspecified location |
| Neoplasia/dysplasia (non-renal) |
Malignant neoplasm of the rectum
Prostate dysplasia, Foreskin hypertrophy, phimosis and paraphimosis
Prostate adenocarcinoma
Malignant neoplasm of the prostate
Malignant neoplasm in the temporal lobe
Malignant neoplasm in the frontal lobe
Olfactory meningioma
Malignant neoplasm: urinary bladder, several parts overlapping
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Locoregionally recurrent, bipulmonary and lymphogenous metastatic p16-positive oropharyngeal carcinoma |
| Neurological diseases |
Uninhibited neurogenic voiding, not elsewhere classified
Cerebral infarction due to embolism of cerebral arteries
Gait disturbance/ataxia |
| Rheumatic disease |
Other seropositive chronic polyarthritis: Multiple localizations
Other seropositive chronic polyarthritis: Multiple localizations, systemic lupus erythematosus involving organs and organ systems
Other specified chronic polyarthritis: several localizations
Seronegative chronic polyarthritis: multiple localizations
Felty syndrome: Multiple localizations
Psoriatic arthropathy
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Giant cell arteritis in polymyalgia rheumatica, other polyarthrosis
Wegener’s granulomatosis |
| Unknown/others |
Unknown
Follow-up control with no evidence of neoplasia
Preliminary examination: living kidney donation |
References
- Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF, 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604-12.
- Grubb A, Horio M, Hansson LO, Björk J, Nyman U, Flodin M, et al. Generation of a new cystatin C-based estimating equation for glomerular filtration rate by use of 7 assays standardized to the international calibrator. Clin Chem. 2014;60(7):974-86. [CrossRef]
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382(9888):260-72. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y, Bowe B, Mokdad AH, Xian H, Yan Y, Li T, et al. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018;94(3):567-81. [CrossRef]
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Hypertension. 2003;42(5):1050-65.
- Gupta T, Goel K, Kolte D, Khera S, Villablanca PA, Aronow WS, et al. Association of Chronic Kidney Disease With In-Hospital Outcomes of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10(20):2050-60. [CrossRef]
- Thourani VH, Forcillo J, Beohar N, Doshi D, Parvataneni R, Ayele GM, et al. Impact of Preoperative Chronic Kidney Disease in 2,531 High-Risk and Inoperable Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the PARTNER Trial. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102(4):1172-80. [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara K, Zen K, Yashige M, Takamatsu K, Ito N, Kadoya Y, et al. Cystatin C in risk prediction after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a retrospective analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2022;9(4):2601-9. [CrossRef]
- Raman M, Middleton RJ, Kalra PA, Green D. Estimating renal function in old people: an in-depth review. International Urology and Nephrology. 2017;49(11):1979-88. [CrossRef]
- KDIGO. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. kdigo.org: KDIGO; 2013.
- Delanaye P, Ebert N, Melsom T, Gaspari F, Mariat C, Cavalier E, et al. Iohexol plasma clearance for measuring glomerular filtration rate in clinical practice and research: a review. Part 1: How to measure glomerular filtration rate with iohexol? Clin Kidney J. 2016;9(5):682-99.
- Delanaye P, Melsom T, Ebert N, Bäck SE, Mariat C, Cavalier E, et al. Iohexol plasma clearance for measuring glomerular filtration rate in clinical practice and research: a review. Part 2: Why to measure glomerular filtration rate with iohexol? Clin Kidney J. 2016;9(5):700-4.
- Thomas, L. Labor und Diagnose Indikation und Bewertung von Laborbefunden für die medizinische Diagnostik 1. Frankfurt/Main: Th-Books-Verl.-Ges.; 2012.
- Shemesh O, Golbetz H, Kriss JP, Myers BD. Limitations of creatinine as a filtration marker in glomerulopathic patients. Kidney Int. 1985;28(5):830-8. [CrossRef]
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(13):1296-305. [CrossRef]
- Newman DJ, Thakkar H, Edwards RG, Wilkie M, White T, Grubb AO, et al. Serum cystatin C measured by automated immunoassay: a more sensitive marker of changes in GFR than serum creatinine. Kidney Int. 1995;47(1):312-8. [CrossRef]
- Luis-Lima S, Escamilla-Cabrera B, Negrín-Mena N, Estupiñán S, Delgado-Mallén P, Marrero-Miranda D, et al. Chronic kidney disease staging with cystatin C or creatinine-based formulas: flipping the coin. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(2):287-94. [CrossRef]
- Svensson-Färbom P, Ohlson Andersson M, Almgren P, Hedblad B, Engström G, Persson M, et al. Cystatin C identifies cardiovascular risk better than creatinine-based estimates of glomerular filtration in middle-aged individuals without a history of cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med. 2014;275(5):506-21. [CrossRef]
- Shlipak MG, Matsushita K, Ärnlöv J, Inker LA, Katz R, Polkinghorne KR, et al. Cystatin C versus creatinine in determining risk based on kidney function. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(10):932-43. [CrossRef]
- Hensey M, Murdoch DJ, Sathananthan J, Wood DA, Webb JG. Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Decision Making and Management in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Interventions. Can J Cardiol. 2019;35(9):1188-94. [CrossRef]
- Potok OA, Katz R, Bansal N, Siscovick DS, Odden MC, Ix JH, et al. The Difference Between Cystatin C- and Creatinine-Based Estimated GFR and Incident Frailty: An Analysis of the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS). Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76(6):896-8. [CrossRef]
- Knight EL, Verhave JC, Spiegelman D, Hillege HL, de Zeeuw D, Curhan GC, et al. Factors influencing serum cystatin C levels other than renal function and the impact on renal function measurement. Kidney Int. 2004;65(4):1416-21. [CrossRef]
- Glassock RJ, Rule AD. Optimally predicting mortality with kidney function markers is not the same as optimally determining how kidney function predicts mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32(4):585-7. [CrossRef]
- Shardlow A, McIntyre NJ, Fraser SDS, Roderick P, Raftery J, Fluck RJ, et al. The clinical utility and cost impact of cystatin C measurement in the diagnosis and management of chronic kidney disease: A primary care cohort study. PLoS Med. 2017;14(10):e1002400. [CrossRef]
- Beunders R, van Groenendael R, Leijte GP, Kox M, Pickkers P. Proenkephalin Compared to Conventional Methods to Assess Kidney Function in Critically Ill Sepsis Patients. Shock. 2020;54(3):308-14. [CrossRef]
- von Groote T, Albert F, Meersch M, Koch R, Porschen C, Hartmann O, et al. Proenkephalin A 119-159 predicts early and successful liberation from renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a post hoc analysis of the ELAIN trial. Crit Care. 2022;26(1):333. [CrossRef]
- (DGKL) DGfrNDDGfrKCuLeV. Interdisziplinäre S2k-Leitlinie: Rationelle Labordiagnostik zur Abklärung Akuter Nierenschädigungen und Progredienter Nierenerkrankungen: Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften e. V. (AWMF); 2021 [Available from: https://register.awmf.org/assets/guidelines/115-001l_S2k_Rationelle_Labordiagnostik_Abklärung_Nierenschädigungen_Nierenerkrankungen_2021-09_01.pdf.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).