Submitted:
17 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of HMA genes in Cucurbits
2.2. Chromosomal location and Gene Structure of HMA proteins
2.3. Phylogenetic analysis, synteny analysis, and gene duplication events of the Cucurbit HMA family
2.4. Motif Analysis and Promoter Cis-Element Identification
2.5. Gene ontology (GO) annotation of HMA proteins
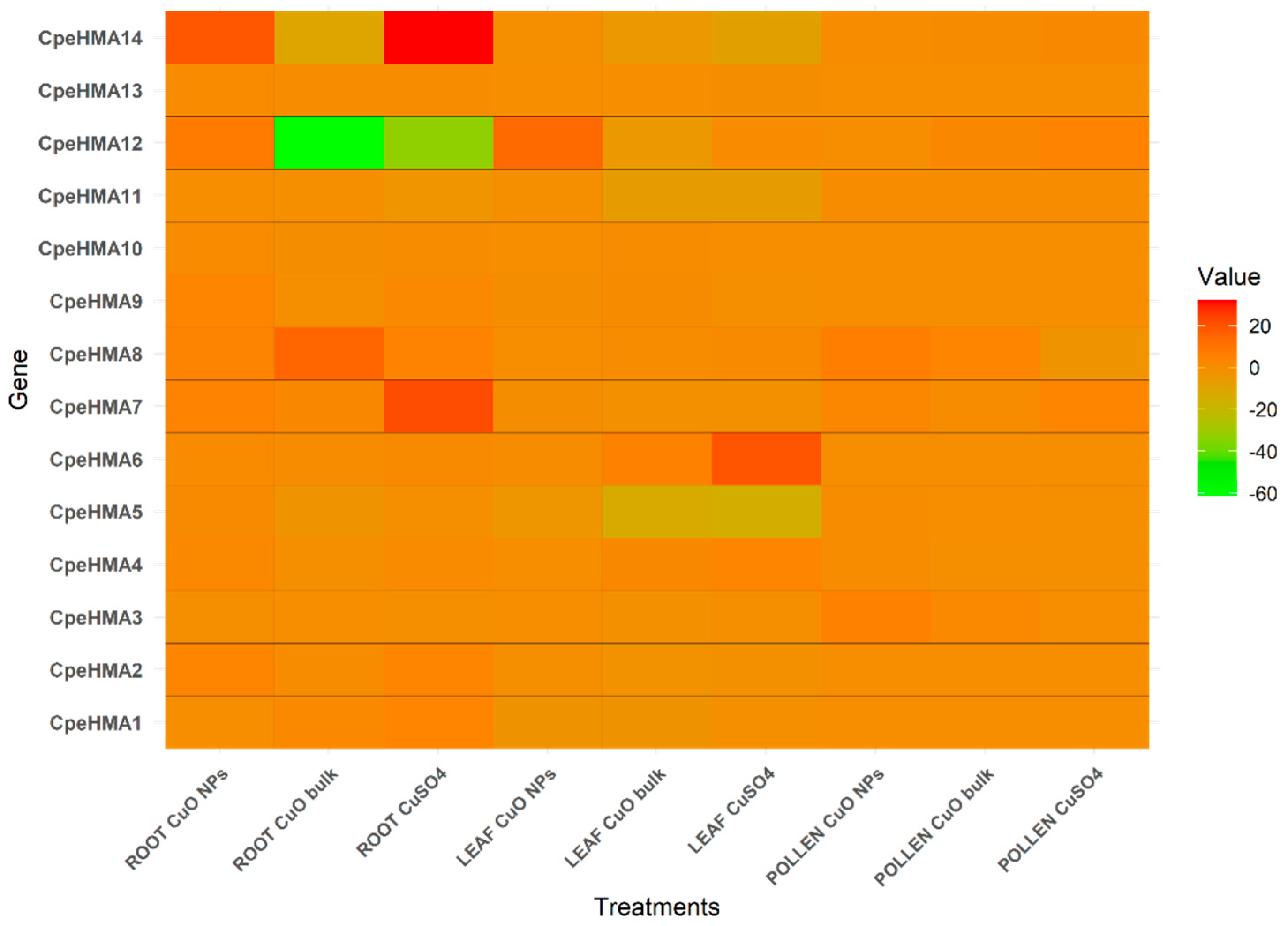
2.6. Expression pattern of the HMA family in Cucurbita pepo under different Cu treatments.
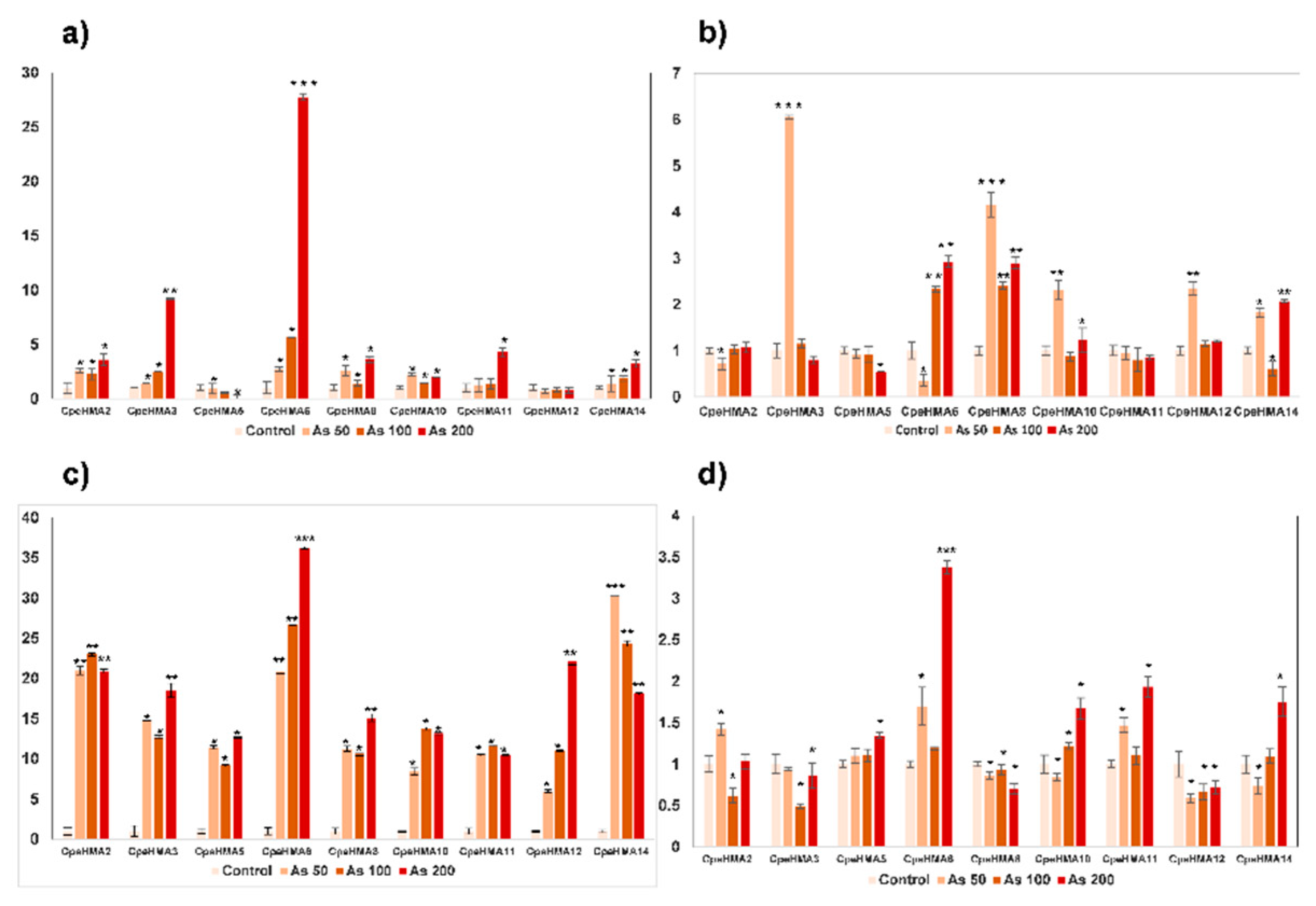
2.7. Expression pattern by RT-qPCR of the HMA family in Cucurbita pepo under As treatment
3. Results
3.1. Identification of HMA genes in Cucurbits
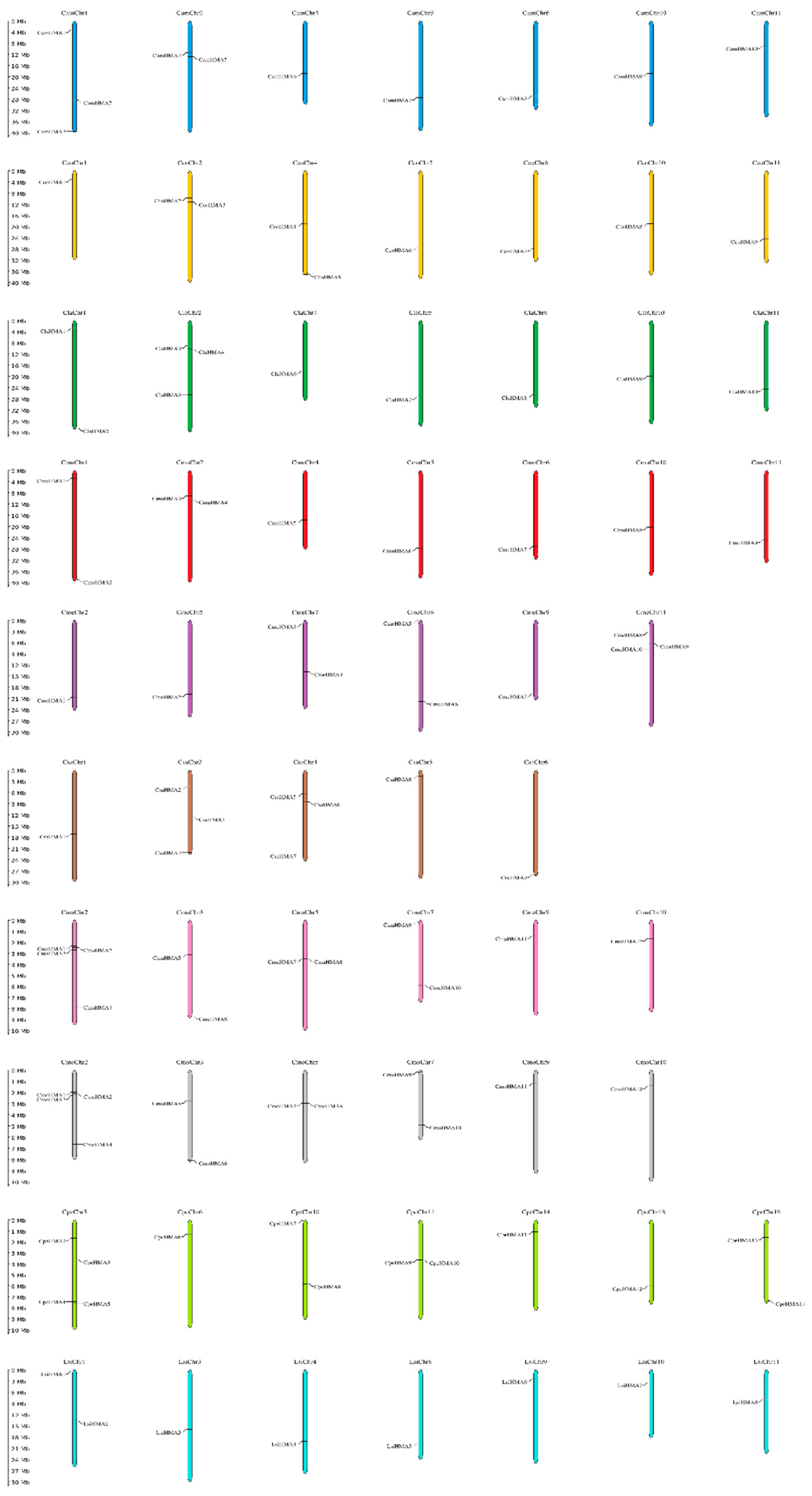
3.2. Chromosomal location and Gene structure of HMA Genes
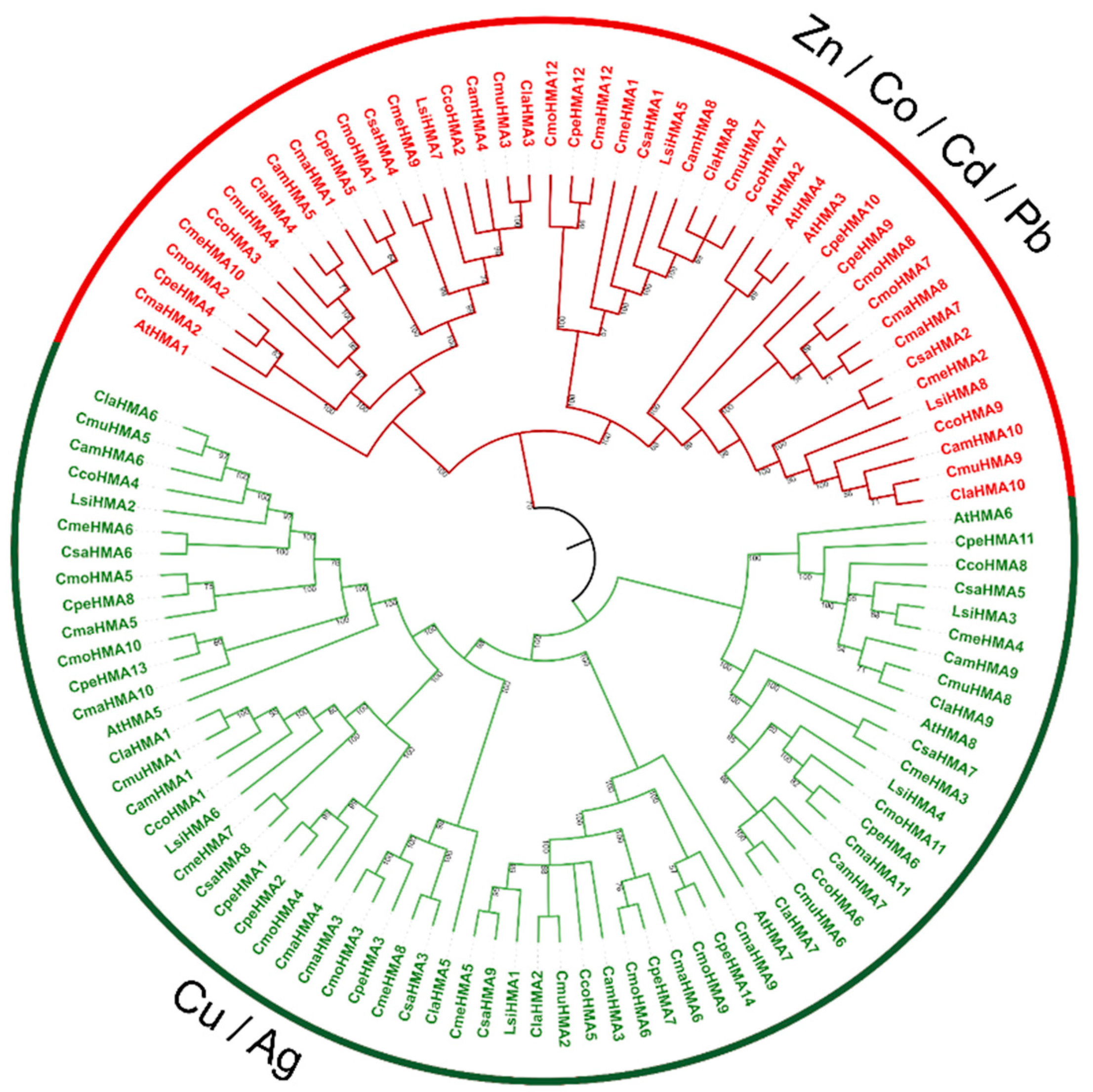
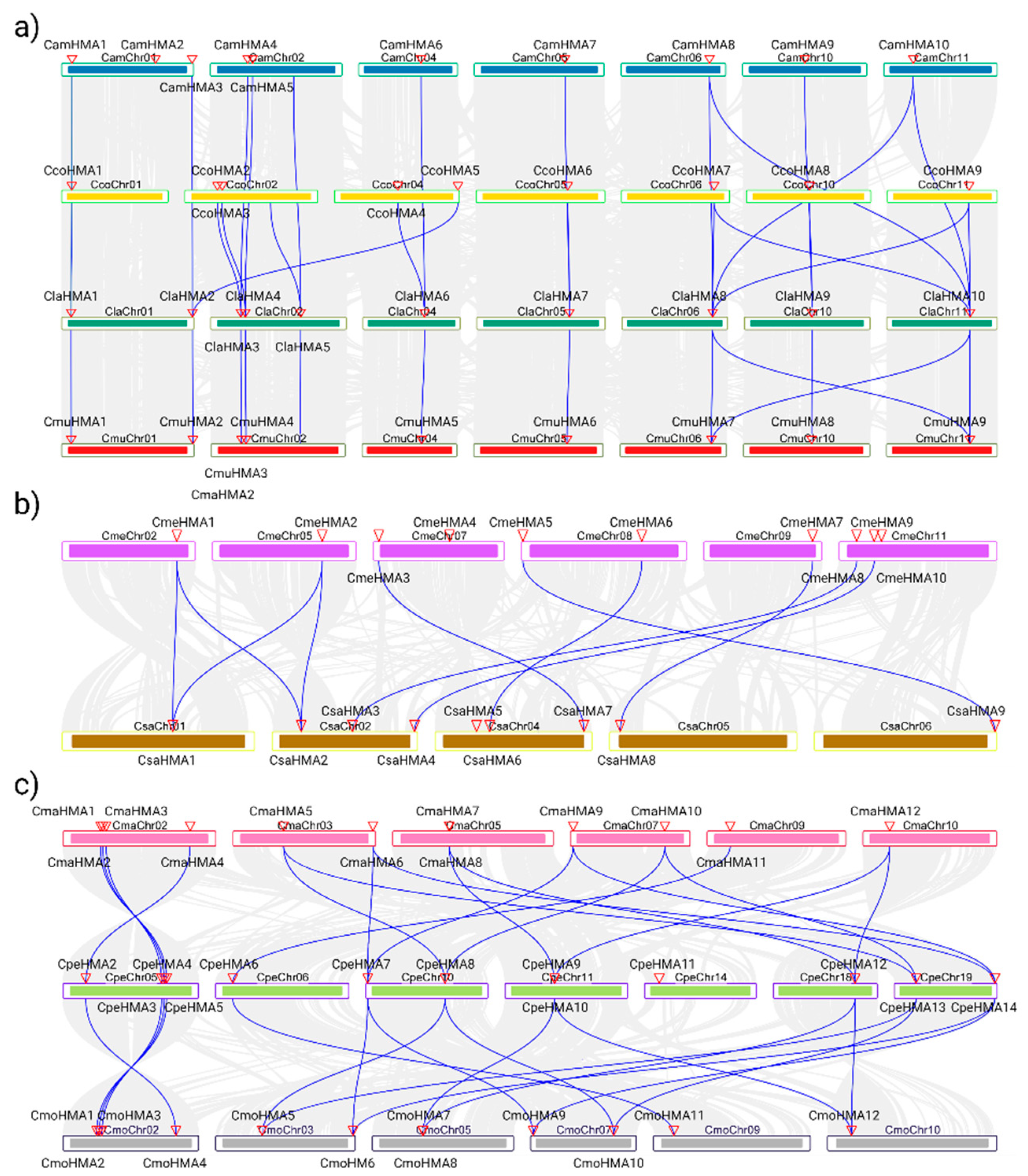
3.3. Phylogenetic analysis, synteny analysis, and gene duplication events of the Cucurbit HMA gene family
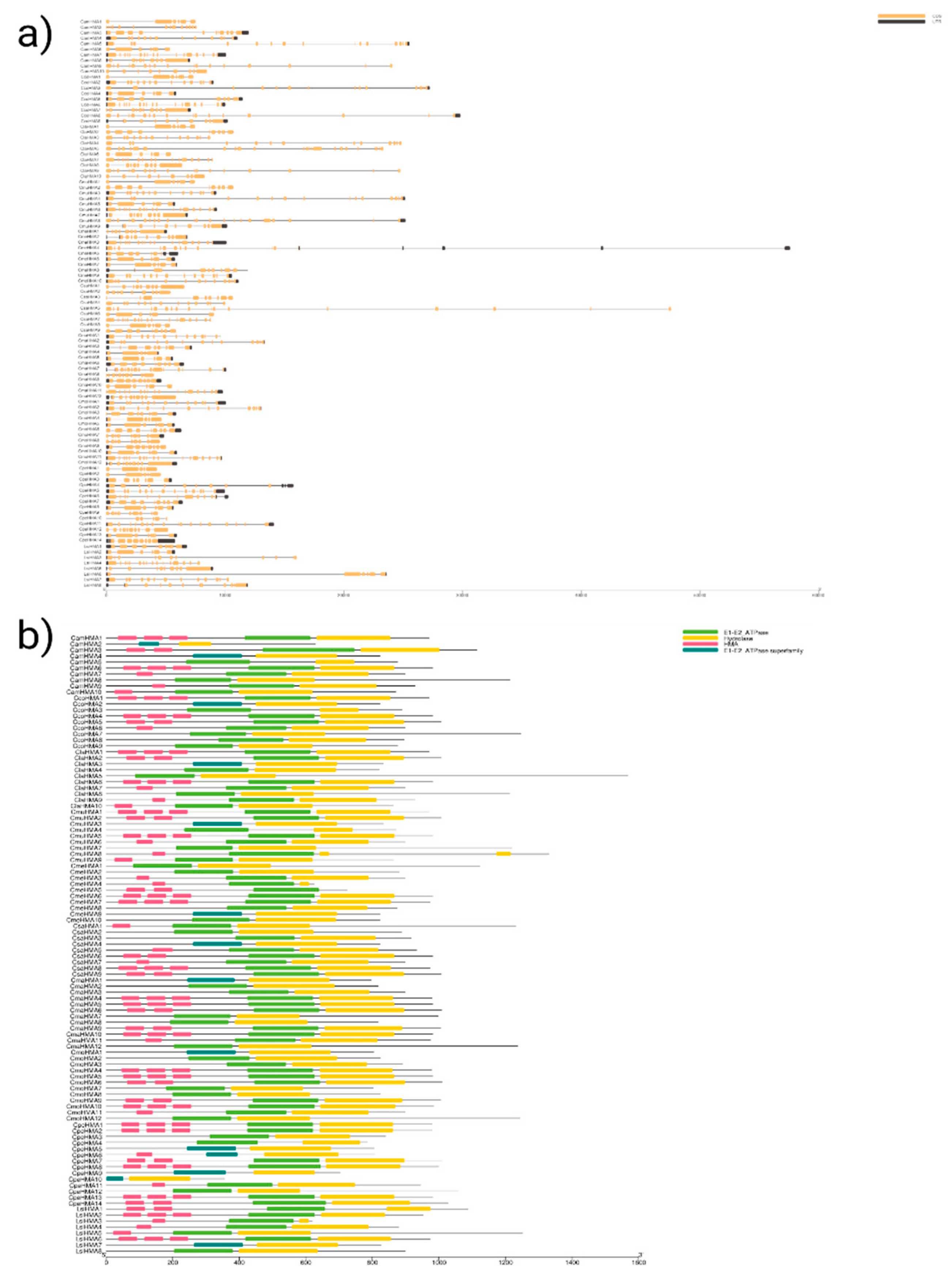
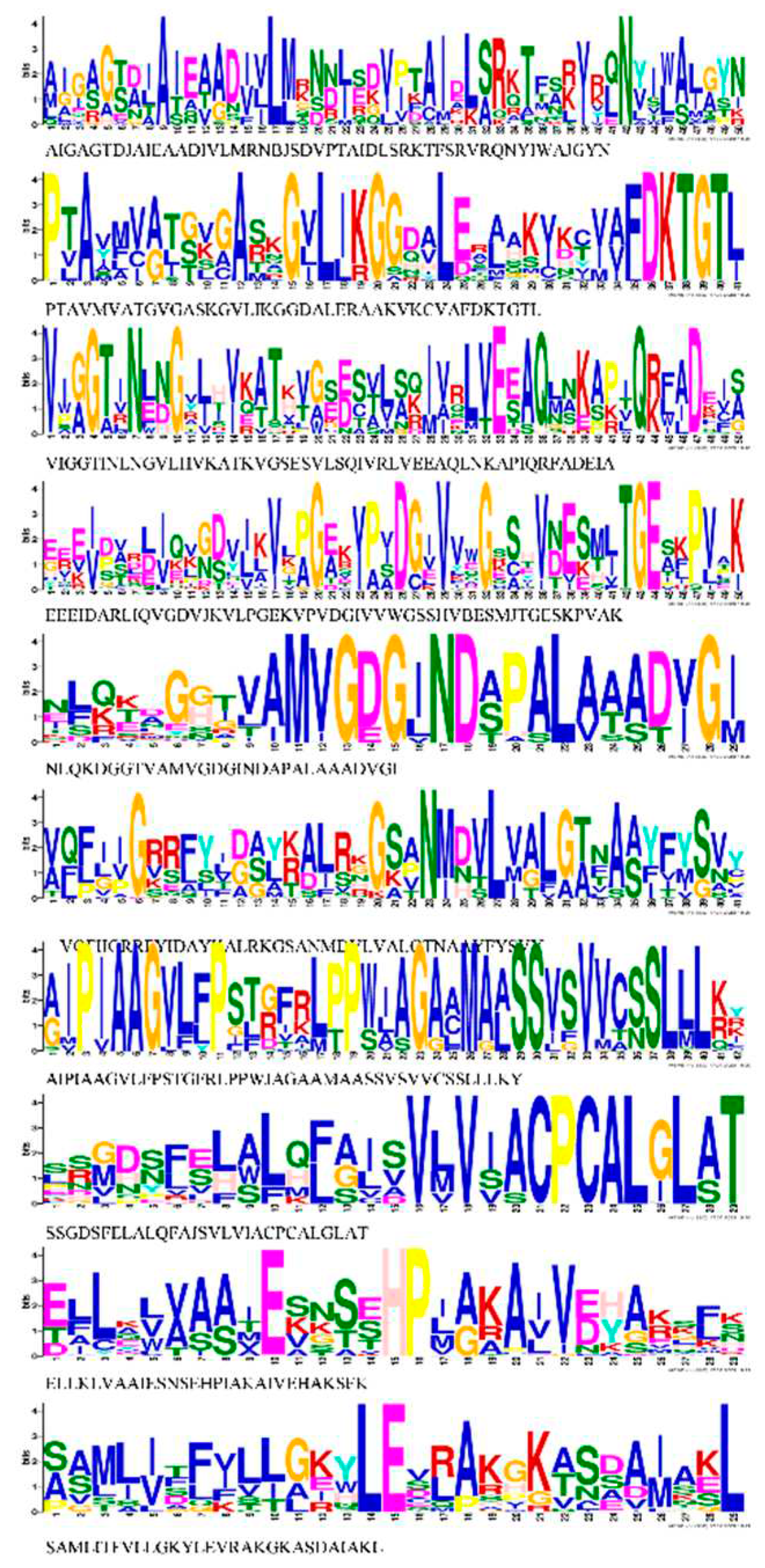
3.4. Conserved Motif Analysis and Cis-elements of HMA proteins
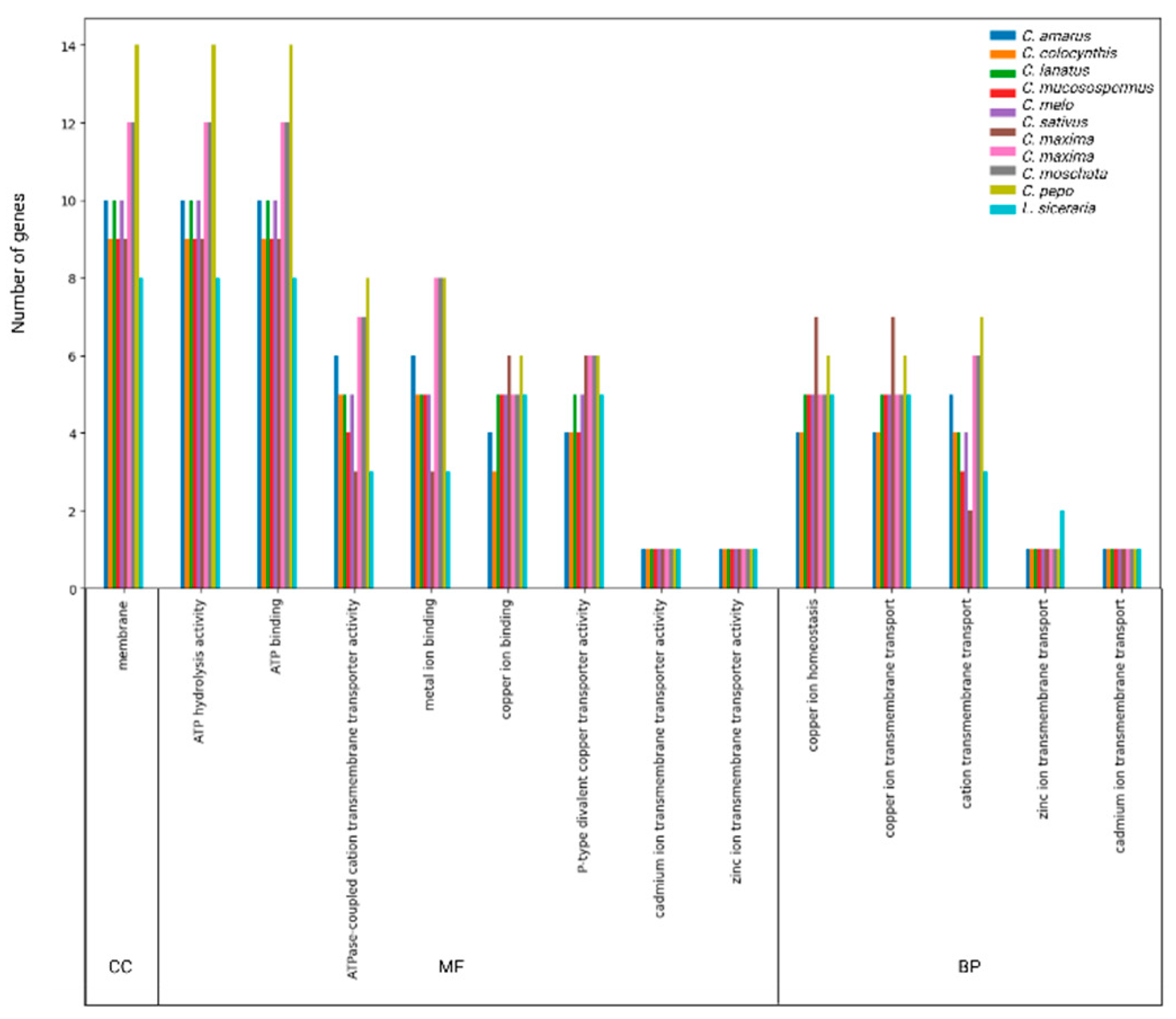
3.5. GO annotation of HMA proteins
3.6. Gene expression pattern of HMA genes in tissues of Cucurbita pepo under Cu and As treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chomicki, Guillaume, Hanno Schaefer, and Susanne S Renner. "Origin and Domestication of Cucurbitaceae Crops: Insights from Phylogenies, Genomics and Archaeology." New Phytologist 226, no. 5 (2020): 1240-55. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Xiulan, Zhouqing He, Nifan Chen, Zizhong Tang, Qiang Wang, and Yi Cai. "The Roles of Environmental Factors in Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Plant." BioMed research international 2019 (2019). [CrossRef]
- ul Haq, Saeed, Abid Khan, Muhammad Ali, Abdul Mateen Khattak, Wen-Xian Gai, Huai-Xia Zhang, Ai-Min Wei, and Zhen-Hui Gong. "Heat Shock Proteins: Dynamic Biomolecules to Counter Plant Biotic and Abiotic Stresses." International journal of molecular sciences 20, no. 21 (2019): 5321. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Yanshan, Yong-He Han, Yue Cao, Yong-Guan Zhu, Bala Rathinasabapathi, and Lena Q Ma. "Arsenic Transport in Rice and Biological Solutions to Reduce Arsenic Risk from Rice." Frontiers in Plant Science 8 (2017): 268. [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, Joel, and Michael Berg. "Global Threat of Arsenic in Groundwater." Science 368, no. 6493 (2020): 845-50. [CrossRef]
- Garg, Neera, and Priyanka Singla. "Arsenic Toxicity in Crop Plants: Physiological Effects and Tolerance Mechanisms." Environmental chemistry letters 9 (2011): 303-21. [CrossRef]
- Raza, Ali, Ali Razzaq, Sundas Saher Mehmood, Xiling Zou, Xuekun Zhang, Yan Lv, and Jinsong Xu. "Impact of Climate Change on Crops Adaptation and Strategies to Tackle Its Outcome: A Review." Plants 8, no. 2 (2019): 34. [CrossRef]
- Smith, Aaron T, Kyle P Smith, and Amy C Rosenzweig. "Diversity of the Metal-Transporting P 1b-Type Atpases." JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry 19 (2014): 947-60. [CrossRef]
- Palmgren, Michael G, and Poul Nissen. "P-Type Atpases." Annual review of biophysics 40 (2011): 243-66.
- Mills, Rebecca F, Gerard C Krijger, Paul J Baccarini, JL Hall, and Lorraine E Williams. "Functional Expression of Athma4, a P1b-Type Atpase of the Zn/Co/Cd/Pb Subclass." The Plant Journal 35, no. 2 (2003): 164-76.
- Gravot, Antoine, Aurélie Lieutaud, Frédéric Verret, Pascaline Auroy, Alain Vavasseur, and Pierre Richaud. "Athma3, a Plant P1b-Atpase, Functions as a Cd/Pb Transporter in Yeast." FEBS letters 561, no. 1-3 (2004): 22-28. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Dawar, Michael J Haydon, Yuwen Wang, Edwin Wong, Sarah M Sherson, Jeff Young, James Camakaris, Jeffrey F Harper, and Christopher S Cobbett. "P-Type Atpase Heavy Metal Transporters with Roles in Essential Zinc Homeostasis in Arabidopsis." The plant cell 16, no. 5 (2004): 1327-39. [CrossRef]
- Li, Jiaming, Minghui Zhang, Jian Sun, Xinrui Mao, Jingguo Wang, Hualong Liu, Hongliang Zheng, Xianwei Li, Hongwei Zhao, and Detang Zou. "Heavy Metal Stress-Associated Proteins in Rice and Arabidopsis: Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogenetics, Duplication, and Expression Profiles Analysis." Frontiers in Genetics 11 (2020): 477. [CrossRef]
- Zorrig, Walid, Chedly Abdelly, and Pierre Berthomieu. "The Phylogenetic Tree Gathering the Plant Zn/Cd/Pb/Co P1b-Atpases Appears to Be Structured According to the Botanical Families." Comptes Rendus Biologies 334, no. 12 (2011): 863-71. [CrossRef]
- Williams, Lorraine E, and Rebecca F Mills. "P1b-Atpases–an Ancient Family of Transition Metal Pumps with Diverse Functions in Plants." Trends in plant science 10, no. 10 (2005): 491-502. [CrossRef]
- Argüello, José M, Elif Eren, and Manuel González-Guerrero. "The Structure and Function of Heavy Metal Transport P 1b-Atpases." Biometals 20 (2007): 233-48. [CrossRef]
- Axelsen, Kristian B, and Michael G Palmgren. "Evolution of Substrate Specificities in the P-Type Atpase Superfamily." Journal of molecular evolution 46 (1998): 84-101. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Ryuichi, Khurram Bashir, Yasuhiro Ishimaru, Naoko K Nishizawa, and Hiromi Nakanishi. "The Role of Heavy-Metal Atpases, Hmas, in Zinc and Cadmium Transport in Rice." Plant signaling & behavior 7, no. 12 (2012): 1605-07. [CrossRef]
- Li, Dandan, Xuemei Xu, Xiaoqing Hu, Quangang Liu, Zhanchao Wang, Haizhen Zhang, Han Wang, Ming Wei, Hanzeng Wang, and Haimei Liu. "Genome-Wide Analysis and Heavy Metal-Induced Expression Profiling of the Hma Gene Family in Populus Trichocarpa." Frontiers in Plant Science 6 (2015): 1149. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Xiaolong, Lei Wang, Xiaojuan Deng, Peng Wang, Qibin Ma, Hai Nian, Yingxiang Wang, and Cunyi Yang. "Genome-Wide Characterization of Soybean P 1b-Atpases Gene Family Provides Functional Implications in Cadmium Responses." BMC genomics 17, no. 1 (2016): 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Zhiguo, E, LI Tingting, CHEN Chen, and WANG Lei. "Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of P1b-Atpases in Rice, Maize and Sorghum." Rice Science 25, no. 4 (2018): 208-17.
- Zhang, Chiran, Qianhui Yang, Xiaoqin Zhang, Xian Zhang, Tongyuan Yu, Yuhuan Wu, Yunxia Fang, and Dawei Xue. "Genome-Wide Identification of the Hma Gene Family and Expression Analysis under Cd Stress in Barley." Plants 10, no. 9 (2021): 1849. [CrossRef]
- Mills, Rebecca F, Kerry A Peaston, John Runions, and Lorraine E Williams. "Hvhma2, a P1b-Atpase from Barley, Is Highly Conserved among Cereals and Functions in Zn and Cd Transport." (2012). [CrossRef]
- Khan, Nadeem, Frank M You, Raju Datla, Sridhar Ravichandran, Bosen Jia, and Sylvie Cloutier. "Genome-Wide Identification of Atp Binding Cassette (Abc) Transporter and Heavy Metal Associated (Hma) Gene Families in Flax (Linum Usitatissimum L.)." BMC genomics 21 (2020): 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Li, Nannan, Hua Xiao, Juanjuan Sun, Shufeng Wang, Jingchao Wang, Peng Chang, Xinbin Zhou, Bo Lei, Kun Lu, and Feng Luo. "Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of the Hma Gene Family in Brassica Napus under Cd Stress." Plant and Soil 426 (2018): 365-81. [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, Muhammad Aamir, Xi Cheng, Guohui Li, Xueqiang Su, Muhammad Abdullah, and Yongping Cai. "Gene Structure, Evolution and Expression Analysis of the P-Atpase Gene Family in Chinese Pear (Pyrus Bretschneideri)." Computational Biology and Chemistry 88 (2020): 107346. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Wei, Changying Liu, Boning Cao, Meiling Qin, Dingpei Long, Zhonghuai Xiang, and Aichun Zhao. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Four Gene Families Putatively Involved in Cadmium Uptake, Translocation and Sequestration in Mulberry." Frontiers in Plant Science 9 (2018): 879. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Yitong, Na Wei, Qiuxia Wang, Zhipeng Liu, and Wenxian Liu. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Heavy Metal Atpase (Hma) Gene Family in Medicago Truncatula under Copper Stress." International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 193 (2021): 893-902. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Xueling, Changying Liu, Huiling Yan, Yan Wan, Qi Wu, Xiaoyong Wu, Gang Zhao, Liang Zou, and Dabing Xiang. "Genome-Wide Identification and Transcriptome Analysis of the Heavy Metal-Associated (Hma) Gene Family in Tartary Buckwheat and Their Regulatory Roles under Cadmium Stress." Gene 847 (2022): 146884. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Yu-Young, Hyunju Choi, Shoji Segami, Hyung-Taeg Cho, Enrico Martinoia, Masayoshi Maeshima, and Youngsook Lee. "Athma1 Contributes to the Detoxification of Excess Zn (Ii) in Arabidopsis." The Plant Journal 58, no. 5 (2009): 737-53. [CrossRef]
- Morel, Mélanie, Jérôme Crouzet, Antoine Gravot, Pascaline Auroy, Nathalie Leonhardt, Alain Vavasseur, and Pierre Richaud. "Athma3, a P1b-Atpase Allowing Cd/Zn/Co/Pb Vacuolar Storage in Arabidopsis." Plant physiology 149, no. 2 (2009): 894-904. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Huan, Haixia Zhao, Longhua Wu, Anna Liu, Fang-Jie Zhao, and Wenzhong Xu. "Heavy Metal Atpase 3 (Hma3) Confers Cadmium Hypertolerance on the Cadmium/Zinc Hyperaccumulator Sedum Plumbizincicola." New Phytologist 215, no. 2 (2017): 687-98. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Fenglin, Naoki Yamaji, Jixing Xia, and Jian Feng Ma. "A Member of the Heavy Metal P-Type Atpase Oshma5 Is Involved in Xylem Loading of Copper in Rice." Plant physiology 163, no. 3 (2013): 1353-62. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Shengjun, Yanghui Shen, Huinan Xu, Junyang Dong, Kexin Chen, Yu Xiang, Xianda Jiang, Chenjie Yao, Tao Lu, and Weiwei Huan. "Rna-Seq Identification of Cd Responsive Transporters Provides Insights into the Association of Oxidation Resistance and Cd Accumulation in Cucumis Sativus L." Antioxidants 10, no. 12 (2021): 1973. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Huili, Yiwei Gao, Lulu Wu, Luyao Wang, Tian Zhang, Changhua Dai, Wenxiu Xu, Lu Feng, Mi Ma, and Yong-Guan Zhu. "Potential Use of the Pteris Vittata Arsenic Hyperaccumulation-Regulation Network for Phytoremediation." Journal of hazardous materials 368 (2019): 386-96. [CrossRef]
- Axelsen, Kristian B., and Michael G. Palmgren. "Inventory of the Superfamily of P-Type Ion Pumps in Arabidopsis." Plant physiology 126, no. 2 (2001): 696-706. [CrossRef]
- Mistry, Jaina, Sara Chuguransky, Lowri Williams, Matloob Qureshi, Gustavo A Salazar, Erik L L Sonnhammer, Silvio C E Tosatto, Lisanna Paladin, Shriya Raj, Lorna J Richardson, Robert D Finn, and Alex Bateman. "Pfam: The Protein Families Database in 2021." Nucleic Acids Research 49, no. D1 (2020): D412-D19. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Chengjie, Hao Chen, Yi Zhang, Hannah R. Thomas, Margaret H. Frank, Yehua He, and Rui Xia. "Tbtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data." Molecular Plant 13, no. 8 (2020): 1194-202. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Sudhir, Glen Stecher, and Koichiro Tamura. "Mega7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets." Molecular Biology and Evolution 33, no. 7 (2016): 1870-74. [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A., G. Blackshields, N.P. Brown, R. Chenna, P.A. McGettigan, H. McWilliam, F. Valentin, I.M. Wallace, A. Wilm, R. Lopez, J.D. Thompson, T.J. Gibson, and D.G. Higgins. "Clustal W and Clustal X Version 2.0." Bioinformatics 23, no. 21 (2007): 2947-48. [CrossRef]
- Moniz de Sá, M, and G Drouin. "Phylogeny and Substitution Rates of Angiosperm Actin Genes." Molecular Biology and Evolution 13, no. 9 (1996): 1198-212. [CrossRef]
- Marmiroli, Marta, Luca Pagano, Riccardo Rossi, Roberto De La Torre-Roche, Giovanni Orazio Lepore, Roberta Ruotolo, Gianluca Gariani, Valentina Bonanni, Simone Pollastri, and Alessandro Puri. "Copper Oxide Nanomaterial Fate in Plant Tissue: Nanoscale Impacts on Reproductive Tissues." Environmental science & technology 55, no. 15 (2021): 10769-83. [CrossRef]
- Obrero, Ángeles, Jose V. Die, Belén Román, Pedro Gómez, Salvador Nadal, and Clara I. González-Verdejo. "Selection of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Studies in Zucchini (Cucurbita Pepo) Using Qpcr." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 59, no. 10 (2011): 5402-11. [CrossRef]
- Obrero, Ángeles, Clara I. González-Verdejo, Jose V. Die, Pedro Gómez, Mercedes Del Río-Celestino, and Belén Román. "Carotenogenic Gene Expression and Carotenoid Accumulation in Three Varieties of Cucurbita Pepo During Fruit Development." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 61, no. 26 (2013): 6393-403. [CrossRef]
- Livak, Kenneth J., and Thomas D. Schmittgen. "Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative Pcr and the 2−Δδct Method." Methods 25, no. 4 (2001): 402-08. [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, Andreas, Harm Nijveen, Xiangyu Rao, Ton Bisseling, René Geurts, and Jack A.M. Leunissen. "Primer3plus, an Enhanced Web Interface to Primer3." Nucleic Acids Research 35, no. suppl_2 (2007): W71-W74. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Honghe, Shan Wu, Guoyu Zhang, Chen Jiao, Shaogui Guo, Yi Ren, Jie Zhang, Haiying Zhang, Guoyi Gong, and Zhangcai Jia. "Karyotype Stability and Unbiased Fractionation in the Paleo-Allotetraploid Cucurbita Genomes." Molecular Plant 10, no. 10 (2017): 1293-306. [CrossRef]
- Montero-Pau, Javier, José Blanca, Aureliano Bombarely, Peio Ziarsolo, Cristina Esteras, Carlos Martí-Gómez, María Ferriol, Pedro Gómez, Manuel Jamilena, and Lukas Mueller. "De Novo Assembly of the Zucchini Genome Reveals a Whole-Genome Duplication Associated with the Origin of the Cucurbita Genus." Plant biotechnology journal 16, no. 6 (2018): 1161-71.
- Garcia-Mas, Jordi, Andrej Benjak, Walter Sanseverino, Michael Bourgeois, Gisela Mir, Víctor M. González, Elizabeth Hénaff, Francisco Câmara, Luca Cozzuto, Ernesto Lowy, Tyler Alioto, Salvador Capella-Gutiérrez, Jose Blanca, Joaquín Cañizares, Pello Ziarsolo, Daniel Gonzalez-Ibeas, Luis Rodríguez-Moreno, Marcus Droege, Lei Du, Miguel Alvarez-Tejado, Belen Lorente-Galdos, Marta Melé, Luming Yang, Yiqun Weng, Arcadi Navarro, Tomas Marques-Bonet, Miguel A. Aranda, Fernando Nuez, Belén Picó, Toni Gabaldón, Guglielmo Roma, Roderic Guigó, Josep M. Casacuberta, Pere Arús, and Pere Puigdomènech. "The Genome of Melon (<I>Cucumis Melo</I> L.)." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 109, no. 29 (2012): 11872-77. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Shaogui, Jianguo Zhang, Honghe Sun, Jerome Salse, William J. Lucas, Haiying Zhang, Yi Zheng, Linyong Mao, Yi Ren, Zhiwen Wang, Jiumeng Min, Xiaosen Guo, Florent Murat, Byung-Kook Ham, Zhaoliang Zhang, Shan Gao, Mingyun Huang, Yimin Xu, Silin Zhong, Aureliano Bombarely, Lukas A. Mueller, Hong Zhao, Hongju He, Yan Zhang, Zhonghua Zhang, Sanwen Huang, Tao Tan, Erli Pang, Kui Lin, Qun Hu, Hanhui Kuang, Peixiang Ni, Bo Wang, Jingan Liu, Qinghe Kou, Wenju Hou, Xiaohua Zou, Jiao Jiang, Guoyi Gong, Kathrin Klee, Heiko Schoof, Ying Huang, Xuesong Hu, Shanshan Dong, Dequan Liang, Juan Wang, Kui Wu, Yang Xia, Xiang Zhao, Zequn Zheng, Miao Xing, Xinming Liang, Bangqing Huang, Tian Lv, Junyi Wang, Ye Yin, Hongping Yi, Ruiqiang Li, Mingzhu Wu, Amnon Levi, Xingping Zhang, James J. Giovannoni, Jun Wang, Yunfu Li, Zhangjun Fei, and Yong Xu. "The Draft Genome of Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) and Resequencing of 20 Diverse Accessions." Nature Genetics 45, no. 1 (2013): 51-58. [CrossRef]
- David, Rakesh, Caitlin S Byrt, Stephen D Tyerman, Matthew Gilliham, and Stefanie Wege. "Roles of Membrane Transporters: Connecting the Dots from Sequence to Phenotype." Annals of Botany 124, no. 2 (2019): 201-08. [CrossRef]
- Wong, Chong Kum Edwin, Renée S Jarvis, Sarah M Sherson, and Christopher S Cobbett. "Functional Analysis of the Heavy Metal Binding Domains of the Zn/Cd-Transporting Atpase, Hma2, in Arabidopsis Thaliana." New Phytologist 181, no. 1 (2009): 79-88.
- Leonhardt, Nathalie, Pierre Cun, Pierre Richaud, and Alain Vavasseur. "Zn/Cd/Co/Pb P1b-Atpases in Plants, Physiological Roles and Biological Interest." In Metal Toxicity in Plants: Perception, Signaling and Remediation, 227-48: Springer, 2011.
- Wu, Danxia, Muhammad Saleem, Tengbing He, and Guandi He. "The Mechanism of Metal Homeostasis in Plants: A New View on the Synergistic Regulation Pathway of Membrane Proteins, Lipids and Metal Ions." Membranes 11, no. 12 (2021): 984. [CrossRef]
- Smith, Aaron T., Dulmini Barupala, Timothy L. Stemmler, and Amy C. Rosenzweig. "A New Metal Binding Domain Involved in Cadmium, Cobalt and Zinc Transport." Nature Chemical Biology 11, no. 9 (2015): 678-84. [CrossRef]
- Arnesano, Fabio, Lucia Banci, Ivano Bertini, Simone Ciofi-Baffoni, Elena Molteni, David L. Huffman, and Thomas V. O'Halloran. "Metallochaperones and Metal-Transporting Atpases: A Comparative Analysis of Sequences and Structures." Genome Research 12, no. 2 (2002): 255-71. [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Yoshiaki, Carolyn Lim, Takehiko Tosha, Koki Yoshida, Tomoaki Hagai, Shuji Akiyama, Shoji Watanabe, Kenta Nakagome, and Yoshitsugu Shiro. "Identification of a Novel Zinc-Binding Protein, C1orf123, as an Interactor with a Heavy Metal-Associated Domain." PLOS ONE 13, no. 9 (2018): e0204355. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Qingyu, Wenmin Qiu, Miao Yu, Shaocui Li, Zhuchou Lu, Yue Zhu, Xianzhao Kan, and Renying Zhuo. "Genome-Wide Characterization of Sedum Plumbizincicola&Nbsp;Hma Gene Family Provides Functional Implications in Cadmium Response." Plants 11, no. 2 (2022): 215. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Ghulam, Behzad Murtaza, Irshad Bibi, Muhammad Shahid, Nabeel Khan Niazi, Muhammad Imran Khan, Muhammad Amjad, Munawar Hussain, and Natasha. "Arsenic Uptake, Toxicity, Detoxification, and Speciation in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Aspects." International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 1 (2018): 59.
- Garbinski, Luis D, Barry P Rosen, and Jian Chen. "Pathways of Arsenic Uptake and Efflux." Environment international 126 (2019): 585-97. [CrossRef]
- Li, Nannan, Jingchao Wang, and Won-Yong Song. "Arsenic Uptake and Translocation in Plants." Plant and Cell Physiology 57, no. 1 (2016): 4-13. [CrossRef]
- Bali, Aditi Shreeya, and Gagan Preet Singh Sidhu. "Arsenic Acquisition, Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants-from Physiology to Remediation: A Review." Chemosphere 283 (2021): 131050.
- Song, Won-Yong, Jiyoung Park, David G Mendoza-Cózatl, Marianne Suter-Grotemeyer, Donghwan Shim, Stefan Hörtensteiner, Markus Geisler, Barbara Weder, Philip A Rea, and Doris Rentsch. "Arsenic Tolerance in Arabidopsis Is Mediated by Two Abcc-Type Phytochelatin Transporters." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107, no. 49 (2010): 21187-92. [CrossRef]
- Song, Won-Yong, Tomohiro Yamaki, Naoki Yamaji, Donghwi Ko, Ki-Hong Jung, Miho Fujii-Kashino, Gynheung An, Enrico Martinoia, Youngsook Lee, and Jian Feng Ma. "A Rice Abc Transporter, Osabcc1, Reduces Arsenic Accumulation in the Grain." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111, no. 44 (2014): 15699-704.
- Yamaji, Naoki, Gen Sakurai, Namiki Mitani-Ueno, and Jian Feng Ma. "Orchestration of Three Transporters and Distinct Vascular Structures in Node for Intervascular Transfer of Silicon in Rice." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112, no. 36 (2015): 11401-06. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Zhong, Yi Chen, Fei Chen, Yuchen Ji, and Fang-Jie Zhao. "Osptr7 (Osnpf8. 1), a Putative Peptide Transporter in Rice, Is Involved in Dimethylarsenate Accumulation in Rice Grain." Plant and Cell Physiology 58, no. 5 (2017): 904-13. [CrossRef]
- Mathews, Shiny, Bala Rathinasabapathi, and Lena Q. Ma. "Uptake and Translocation of Arsenite by Pteris Vittata L.: Effects of Glycerol, Antimonite and Silver." Environmental Pollution 159, no. 12 (2011): 3490-95. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V., and Stephen Ebbs. "Transport of Arsenite by the Arsenic Hyperaccumulating Brake Fern Pteris Vittata Is Inhibited by Monovalent Silver." Indian Journal of Plant Physiology 12 (2007): 312-16.
- Mayerhofer, Hubert, Emeline Sautron, Norbert Rolland, Patrice Catty, Daphné Seigneurin-Berny, Eva Pebay-Peyroula, and Stéphanie Ravaud. "Structural Insights into the Nucleotide-Binding Domains of the P1b-Type Atpases Hma6 and Hma8 from Arabidopsis Thaliana." PLOS ONE 11, no. 11 (2016): e0165666. [CrossRef]
- Sautron, Emeline, Cécile Giustini, ThuyVan Dang, Lucas Moyet, Daniel Salvi, Serge Crouzy, Norbert Rolland, Patrice Catty, and Daphné Seigneurin-Berny. "Identification of Two Conserved Residues Involved in Copper Release from Chloroplast P<Sub>Ib-1</Sub>-Atpases *." Journal of Biological Chemistry 291, no. 38 (2016): 20136-48. [CrossRef]
- Sautron, Emeline, Hubert Mayerhofer, Cécile Giustini, Danièle Pro, Serge Crouzy, Stéphanie Ravaud, Eva Pebay-Peyroula, Norbert Rolland, Patrice Catty, and Daphné Seigneurin-Berny. "Hma6 and Hma8 Are Two Chloroplast Cu+-Atpases with Different Enzymatic Properties." Bioscience Reports 35, no. 3 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Shingles, Richard, Larry E Wimmers, and Richard E McCarty. "Copper Transport across Pea Thylakoid Membranes." Plant physiology 135, no. 1 (2004): 145-51. [CrossRef]
- Gresser, M. J. "Adp-Arsenate. Formation by Submitochondrial Particles under Phosphorylating Conditions." Journal of Biological Chemistry 256, no. 12 (1981): 5981-83. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Yuriko, Keishi Kuroda, Keisuke Kimura, Jennafer L Southron-Francis, Aya Furuzawa, Kazuhiko Kimura, Satoshi Iuchi, Masatomo Kobayashi, Gregory J Taylor, and Hiroyuki Koyama. "Amino Acid Polymorphisms in Strictly Conserved Domains of a P-Type Atpase Hma5 Are Involved in the Mechanism of Copper Tolerance Variation in Arabidopsis." Plant physiology 148, no. 2 (2008): 969-80. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Yanzhi, Chen Hao, Jianmei Du, Lei Xu, Zhonglong Guo, Dong Li, Huaqing Cai, Hongwei Guo, and Lei Li. "The Carboxy Terminal Transmembrane Domain of Spl7 Mediates Interaction with Ran1 at the Endoplasmic Reticulum to Regulate Ethylene Signalling in Arabidopsis." New Phytologist 236, no. 3 (2022): 878-92. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, Elinea O., Bruno P. Melo, Isabela T. Lourenço-Tessutti, Fabrício B. M. Arraes, Regina M. Amorim, Maria E. Lisei-de-Sá, Julia A. Costa, Ana G. B. Leite, Muhammad Faheem, Márcio A. Ferreira, Carolina V. Morgante, Elizabeth P. B. Fontes, and Maria F. Grossi-de-Sa. "Identification and Characterization of the Gmrd26 Soybean Promoter in Response to Abiotic Stresses: Potential Tool for Biotechnological Application." BMC Biotechnology 19, no. 1 (2019): 79. [CrossRef]
| Species | HMA clade | Total | |
| Zn/Cd/Co/Pb | Cu/Ag | ||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Citrullus amarus | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Citrullus colocynthis | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| Citrullus lanatus | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Citrullus mucusospermus | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| Cucumis melo | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Cucumis sativus | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| Cucurbita maxima | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Cucurbita moschata | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Cucurbita pepo | 5 | 9 | 14 |
| Legenaria siceraria | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Species | Pair# | Gene names | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks ratio | Duplication type | MYA1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. amarus | 1 | CamHMA2-CamHMA3 | 0.5081 | 0.4684 | 1.0846 | Tandem | 35.70 |
| 2 | CamHMA1-CamHMA6 | 0.1036 | 0.4185 | 0.2474 | Segmental | 31.90 | |
| 3 | CamHMA8-CamHMA10 | 0.1208 | 0.3328 | 0.3629 | Segmental | 25.36 | |
| 4 | CamHMA7-CamHMA9 | 0.2087 | 0.4635 | 0.4503 | Segmental | 35.33 | |
| 5 | CamHMA4-CamHMA5 | 0.0796 | 0.2789 | 0.2855 | Tandem | 21.25 | |
| C. colocynthis | 1 | CcoHMA1-CcoHMA4 | 0.1056 | 0.4402 | 0.2400 | Segmental | 33.55 |
| 2 | CcoHMA7-CcoHMA9 | 0.1192 | 0.3347 | 0.3562 | Segmental | 25.51 | |
| 3 | CcoHMA6-CcoHMA8 | 0.2019 | 0.4616 | 0.4374 | Segmental | 35.18 | |
| 4 | CcoHMA2-CcoHMA3 | 0.0823 | 0.2832 | 0.2907 | Tandem | 21.59 | |
| C. lanatus | 1 | ClaHMA2-ClaHMA8 | 0.3042 | 0.4742 | 0.6415 | Segmental | 36.14 |
| 2 | ClaHMA1-ClaHMA6 | 0.1059 | 0.4301 | 0.2463 | Segmental | 32.78 | |
| 3 | ClaHMA5-ClaHMA10 | 0.1174 | 0.3248 | 0.3615 | Segmental | 24.75 | |
| 4 | ClaHMA7-ClaHMA9 | 0.2128 | 0.4653 | 0.4573 | Segmental | 35.46 | |
| 5 | ClaHMA3-ClaHMA4 | 0.0832 | 0.2848 | 0.2922 | Tandem | 21.70 | |
| C. mucusospermus | 1 | CmuHMA1-CmuHMA5 | 0.1075 | 0.4420 | 0.2431 | Segmental | 33.69 |
| 2 | CmuHMA7-CmuHMA9 | 0.1212 | 0.3426 | 0.3538 | Segmental | 26.11 | |
| 3 | CmuHMA6-CmuHMA8 | 0.2076 | 0.4521 | 0.4591 | Segmental | 34.46 | |
| 4 | CmuHMA3-CmuHMA4 | 0.0847 | 0.2817 | 0.3009 | Tandem | 21.47 | |
| C. melo | 1 | CmeHMA6-CmeHMA7 | 0.1115 | 0.4288 | 0.2599 | Segmental | 32.68 |
| 2 | CmeHMA2-CmeHMA4 | 0.2848 | 0.3743 | 0.7608 | Segmental | 28.52 | |
| 3 | CmeHMA9-CmeHMA10 | 0.0771 | 0.2719 | 0.2835 | Tandem | 20.72 | |
| 4 | CmeHMA3-CmeHMA5 | 0.2542 | 0.3687 | 0.6894 | Segmental | 28.10 | |
| C. sativus | 1 | CsaHMA6-CsaHMA8 | 0.1077 | 0.4426 | 0.2434 | Segmental | 33.73 |
| 2 | CsaHMA1-CsaHMA2 | 0.1225 | 0.3678 | 0.3330 | Segmental | 28.03 | |
| 3 | CsaHMA5-CsaHMA7 | 0.2109 | 0.4253 | 0.4958 | Segmental | 32.41 | |
| 4 | CsaHMA4-CsaHMA9 | 0.3201 | 0.4293 | 0.7455 | Segmental | 32.72 | |
| C. maxima | 1 | CmaHMA7-CmaHMA8 | 0.0256 | 0.0308 | 0.8303 | Tandem | 2.35 |
| 2 | CmaHMA6-CmaHMA9 | 0.0272 | 0.1394 | 0.1951 | Segmental | 10.62 | |
| 3 | CmaHMA1-CmaHMA2 | 0.0703 | 0.2765 | 0.2543 | Tandem | 21.07 | |
| 4 | CmaHMA3-CmaHMA11 | 0.2830 | 0.4255 | 0.6651 | Segmental | 32.43 | |
| 5 | CmaHMA5-CmaHMA10 | 0.0186 | 0.1056 | 0.1762 | Segmental | 8.05 | |
| C. moschata | 1 | CmoHMA3-CmoHMA11 | 0.3381 | 0.5363 | 0.6304 | Segmental | 40.88 |
| 2 | CmoHMA1-CmoHMA2 | 0.0874 | 0.3327 | 0.2628 | Tandem | 25.36 | |
| 3 | CmoHMA5-CmoHMA10 | 0.0190 | 0.1179 | 0.1612 | Segmental | 8.99 | |
| 4 | CmoHMA6-CmoHMA9 | 0.0241 | 0.1136 | 0.2125 | Segmental | 8.66 | |
| 5 | CmoHMA7-CmoHMA8 | 0.0130 | 0.0167 | 0.7802 | Tandem | 1.27 | |
| C. pepo | 1 | CpeHMA4-CpeHMA5 | 0.0981 | 0.3070 | 0.3196 | Tandem | 23.39 |
| 2 | CpeHMA7-CpeHMA14 | 0.0294 | 0.1337 | 0.2198 | Segmental | 10.19 | |
| 3 | CpeHMA6-CpeHMA11 | 0.2511 | 0.4202 | 0.5975 | Segmental | 32.03 | |
| 4 | CpeHMA9-CpeHMA10 | 0.0170 | 0.0301 | 0.5649 | Tandem | 2.29 | |
| 5 | CpeHMA8-CpeHMA13 | 0.0183 | 0.1176 | 0.1562 | Segmental | 8.96 | |
| L. siceraria | 1 | LsiHMA5-LsiHMA8 | 0.1290 | 0.3793 | 0.3400 | Segmental | 28.91 |
| 2 | LsiHMA3-LsiHMA4 | 0.2196 | 0.4498 | 0.4881 | Segmental | 34.28 | |
| 3 | LsiHMA1-LsiHMA7 | 0.2933 | 0.3786 | 0.7748 | Segmental | 28.85 | |
| 4 | LsiHMA2-LsiHMA6 | 0.0856 | 0.3274 | 0.2615 | Segmental | 24.95 |
| Cis-regulatory element | Expression pattern | Signal sequence |
| 3-AF1 binding site | light responsive element | TAAGAGAGGAA |
| AAGAA-motif | binding site in many light-regulated gene | GAAAGAA |
| ABRE | cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | ACGTG |
| ABRE4 | early responsive to dehydration | CACGTA |
| ACE | cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness | CTAACGTATT |
| AE-box | part of a module for light response | AGAAACAA |
| AP-1 | cis-acting element for proline | TGAGTTAG |
| ARE | cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | AAACCA |
| as-1 | transcriptional activation of several genes by auxin and/or salicylic acid; May be relevant to light regulation | TGACG |
| AT~TATA-box | Critical for accurate initiation of transcription | TATATA |
| AT1-motif | part of a light responsive module | AATTATTTTTTATT |
| ATCT-motif | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | AATCTAATCC |
| AT-rich element | binding site of AT-rich DNA binding protein (ATBP-1) | ATAGAAATCAA |
| AT-rich sequence | element for maximal elicitor-mediated activation (2copies) | TAAAATACT |
| AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness | GGTCCAT |
| Box 4 | part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | ATTAAT |
| Box II | part of a light responsive element | TGGTAATAA |
| Box III | protein binding site | ATCATTTTCACT |
| CAAT-box | common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | CAAAT |
| CAT-box | cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression | GCCACT |
| CCAAT-box | MYBHv1 binding site | CAACGG |
| CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | CGTCA |
| chs-CMA1a | part of a light responsive element | TTACTTAA |
| circadian | cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control | CAAAGATATC |
| DRE1 | expressed during late embryogenesis, induced by ABA | ACCGAGA |
| ERE | ethylene-induced activation | ATTTTAAA |
| GA-motif | part of a light responsive element | ATAGATAA |
| Gap-box | part of a light responsive element | CAAATGAAGA |
| GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element | TCTGTTG |
| GATA-motif | part of a light responsive element | AAGGATAAGG |
| G-box | cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | CAGACGTGGCA |
| GCN4_motif | cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression | TGAGTCA |
| GT1-motif | light responsive element | GGTTAA |
| H-box | Essential for both light regulation and elicitor induction | CCTACCNNNNNNNCTNNNNA |
| HD-Zip 1 | element involved in differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | CAATAATTG |
| I-box | part of a light responsive element | TGATAATGT |
| LAMP-element | part of a light responsive element | CTTTATCA |
| L-box | part of a light responsive element | ATCCCACCTAC |
| LTR | cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | CCGAAA |
| MBS | MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | CAACTG |
| MBSI | MYB binding site involved in flavonoid biosynthetic genes regulation | TTTTTACGGTTA |
| MRE | MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | AACCTAA |
| MYB | Involved in regulation of genes that are responsive to water stress | CAACAG |
| MYB recognition site | Involved in regulation of genes that are responsive to water stress | CCGTTG |
| Myb-binding site | gibberellin-responsive element | CAACAG |
| MYB-like sequence | Involved in regulation of genes that are responsive to water stress | TAACCA |
| MYC | Related to cold and dehydration responsiveness | CAATTG |
| O2-site | cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation | GATGACATGG |
| P-box | gibberellin-responsive element | CCTTTTG |
| Sp1 | light responsive element | GGGCGG |
| TATA | core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | TATAAAAT |
| TATA-box | core promoter element around -30 of transcription start | ATATAT |
| TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness | TATCCCA |
| TCA | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | TCATCTTCAT |
| TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | CCATCTTTTT |
| TCCC-motif | characteristic of the promoters activated in infected cells DE of root nodules | TCTCCCT |
| TC-rich repeats | cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | GTTTTCTTAC |
| TCT-motif | part of a light responsive element | TCTTAC |
| TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | TGACG |
| TGA-element | auxin-responsive element | AACGAC |
| W box | involved in elicitor-responsive transcription of defense genes | TTGACC |
| WRE3 | RRE (R response element) | CCACCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





