Submitted:
15 September 2023
Posted:
18 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Diet-related diseases
2.1. Coeliac disease
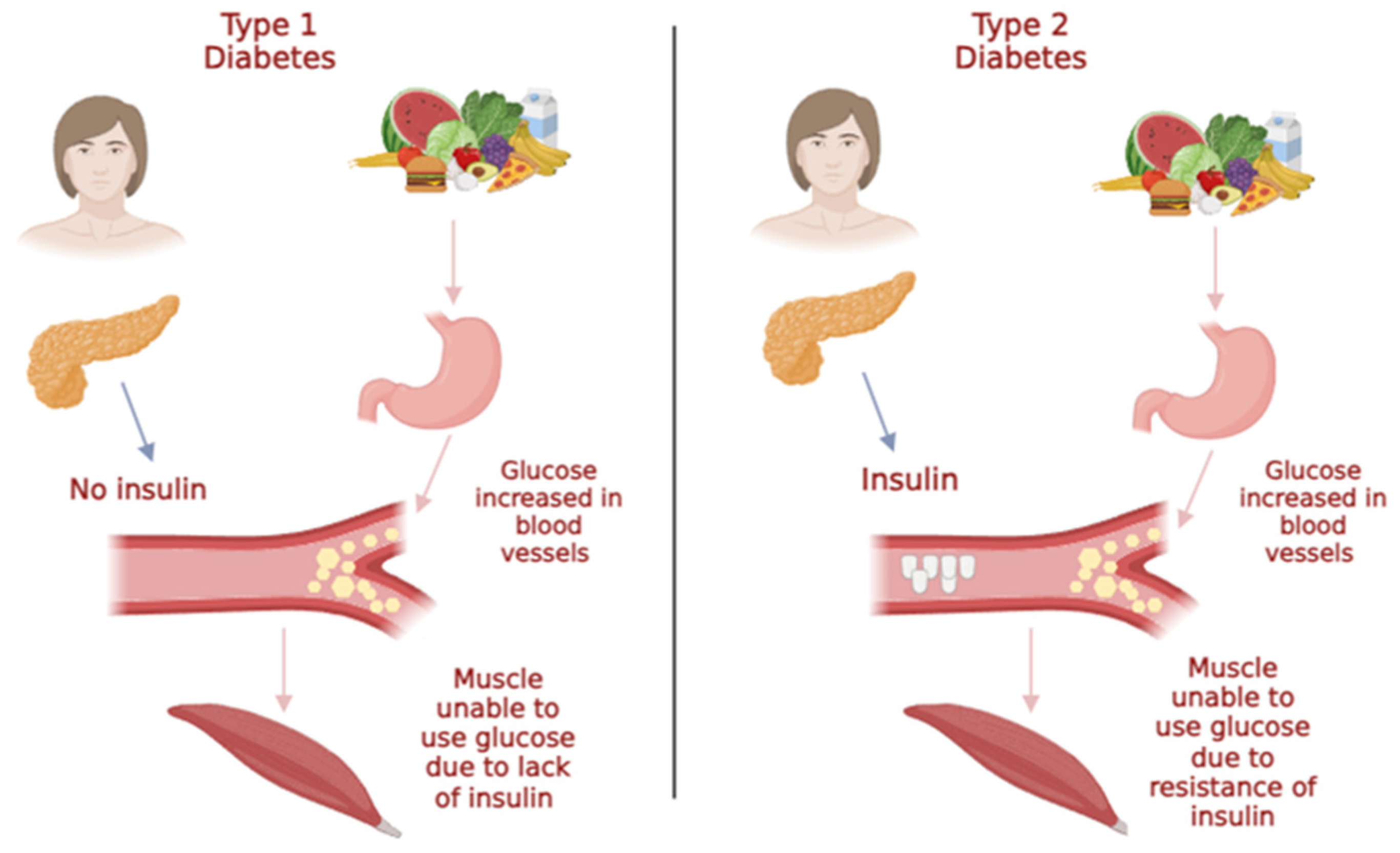
2.2. Diabetes mellitus (DM)
2.3. Cholesterol
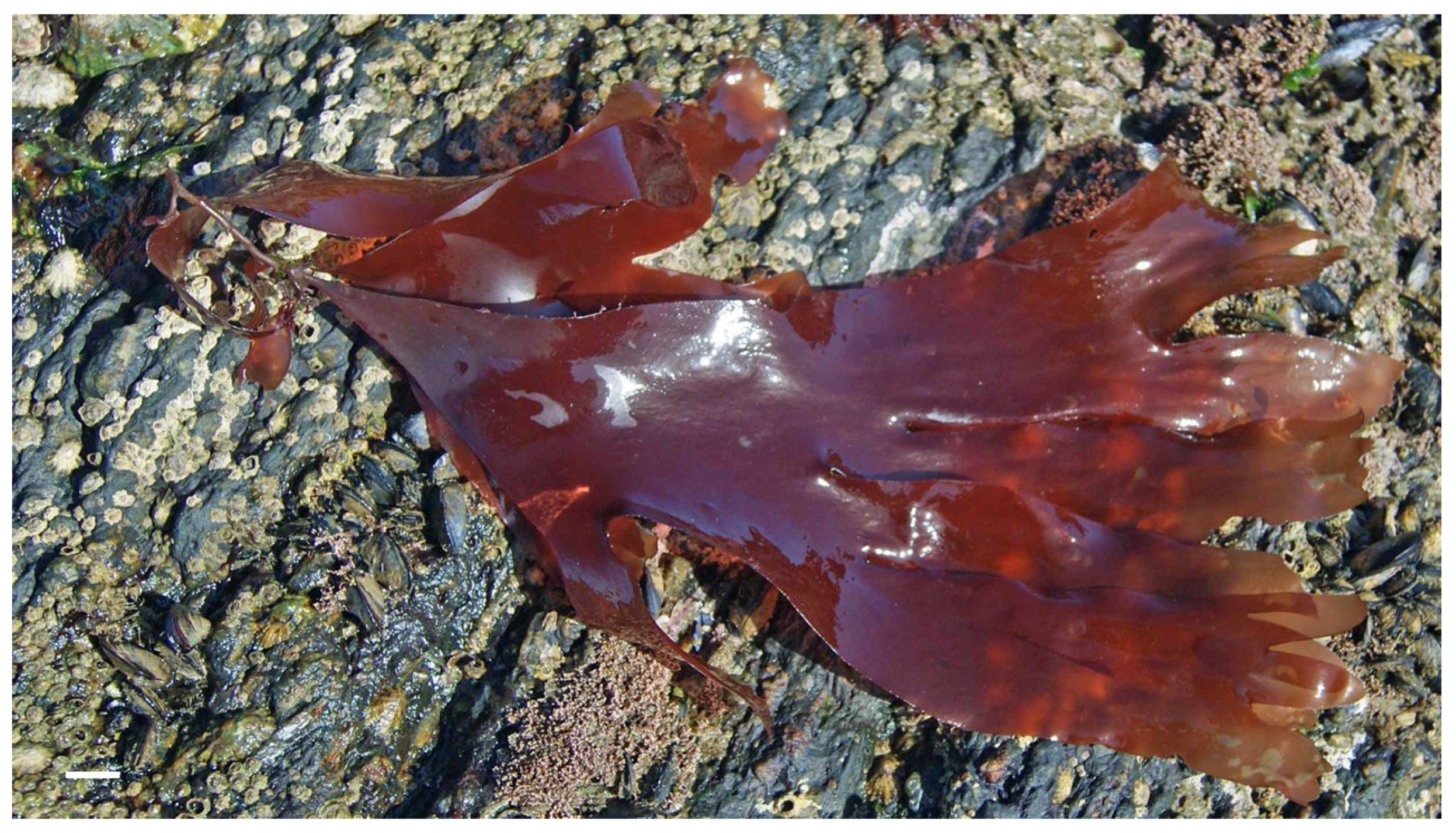
3. Macroalgae
3.1. Proteins
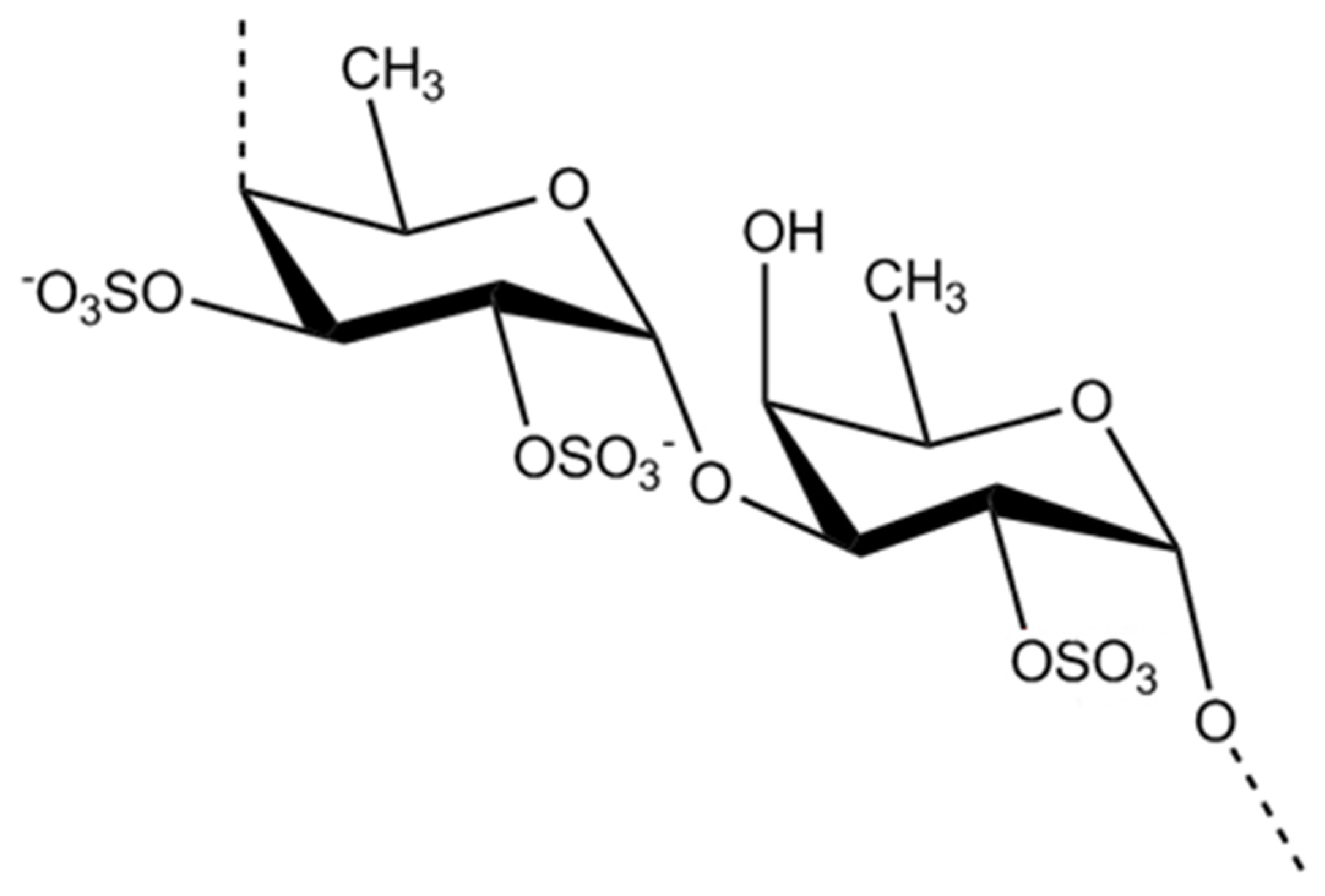
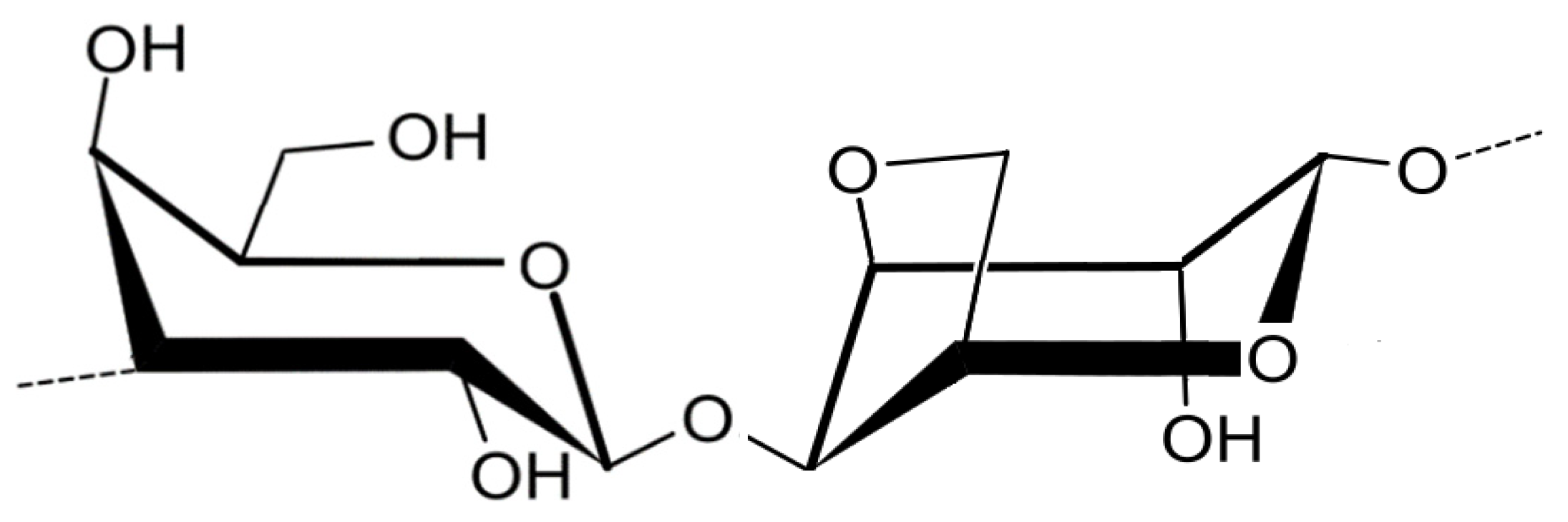
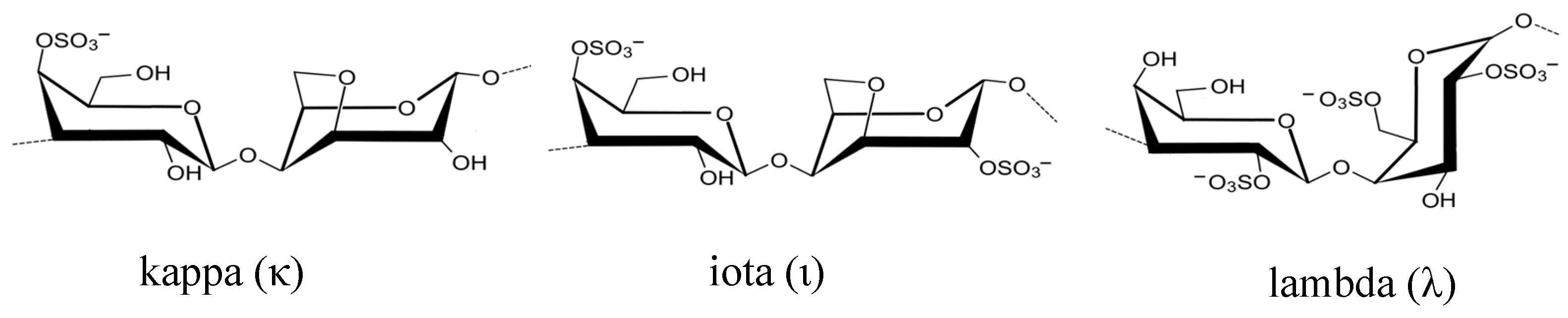
3.2. Polysaccharides from macroalgae
3.3. Natural antioxidants
3.4. Cholesterol
4. Algae Food Products as healthcare solution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, K.G.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. The Metabolic Syndrome—a New Worldwide Definition. The Lancet 2005, 366, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Peñalvo, J.L.; Cudhea, F.; Imamura, F.; Rehm, C.D.; Mozaffarian, D. Association Between Dietary Factors and Mortality from Heart Disease, Stroke, and Type 2 Diabetes in the United States. JAMA 2017, 317, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, R.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Shi, P.; Andrews, K.G.; Engell, R.E.; Mozaffarian, D. Global, Regional and National Consumption of Major Food Groups in 1990 and 2010: A Systematic Analysis Including 266 Country-Specific Nutrition Surveys Worldwide. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarnowski, A.; Jankowski, M.; Gujski, M. Public Awareness of Diet-Related Diseases and Dietary Risk Factors: A 2022 Nationwide Cross-Sectional Survey among Adults in Poland. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J. Current Evidence on Healthy Eating. Annu Rev Public Health 2013, 34, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettor, R. The Right Nutrition for the Nutrition Related Diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2020, 21, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, L.; Opie, R.S. A Nutrition Strategy to Reduce the Burden of Diet Related Disease: Access to Dietician Services Must Complement Population Health Approaches. Front Pharmacol 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klnc, B.; Cirik, S.; Turan, G.; Tekogul, H.; Koru, E. Seaweeds for Food and Industrial Applications. In Food Industry; InTech, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Seaweeds as Nutraceuticals for Health and Nutrition. Phycologia 2019, 58, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Leip, A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Slegers, P.M.; Ziegler, F.; Temme, E.H.M.; Herrero, M.; Tuomisto, H.; Valin, H.; Van Middelaar, C.E.; et al. The Potential of Future Foods for Sustainable and Healthy Diets. Nat Sustain 2018, 1, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascais, M.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Effects of Heat Treatment Processes: Health Benefits and Risks to the Consumer. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Seaweed’s Bioactive Candidate Compounds to Food Industry and Global Food Security. Life 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skendi, A.; Papageorgiou, M.; Varzakas, T. High Protein Substitutes for Gluten in Gluten-Free Bread. Foods 2021, Vol. 10, Page 1997 2021, 10, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Araya, M.; Roncoroni, L.; Doneda, L.; Elli, L. Dietary Gluten as a Conditioning Factor of the Gut Microbiota in Celiac Disease. Advances in Nutrition 2020, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesiekierski, J.R. What Is Gluten? Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Australia) 2017, 32, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac Disease: A Comprehensive Current Review. BMC Medicine 2019 17:1 2019, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendi, A.; Papageorgiou, M. Introduction in Wheat and Breadmaking. Trends in Wheat and Bread Making 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stef, D.-S.; Rivis, A.; Trasca, T.I.; Pop, M.; Heghedus-Mîndru, G.; Stef, L.; Marcu, A. The enrichment of bread with algae species. Animal Science Journal 2022, 558–566. [Google Scholar]
- Hager, A.S.; Wolter, A.; Czerny, M.; Bez, J.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K.; Czerny, M. Investigation of Product Quality, Sensory Profile and Ultrastructure of Breads Made from a Range of Commercial Gluten-Free Flours Compared to Their Wheat Counterparts. European Food Research and Technology 2012, 235, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, A.; Höchstötter, A.; Becker, T. Possibilities to Increase the Quality in Gluten-Free Bread Production: An Overview. European Food Research and Technology 2012, 235, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qi, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Ruan, R.; Yan, X.; Cheng, P. Macroalgae-Derived Multifunctional Bioactive Substances: The Potential Applications for Food and Pharmaceuticals. Foods 2022, Vol. 11, Page 3455 2022, 11, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federação Internacional de Diabetes (IDF). Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Abo-Shady, A.M.; Gheda, S.F.; Ismail, G.A.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L.; Abdel-Karim, O.H. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity of Algae. Life 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Valado, A. Unlocking Nature’s Treasures: Algae-Derived Natural Products in Diabetes and Its Complications-Current Advances and Future Prospects. Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, B.; Lin, L.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Yu, H.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Macroalgae and Their Hypoglycemic Benefits. Trends Food Sci Technol 2018, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S. Composition, Properties and Health Benefits of Indigestible Carbohydrate Polymers as Dietary Fiber: A Review. Int J Biol Macromol 2013, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, C.M.O.; Villar-Delfino, P.H.; Dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular Death, Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Diabetic Complications. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V. Role and Regulation of Autophagy in Cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009, 1793, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, T.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, N.; Cheng, X.; Lai, X.; Shunnar, A.; Singh, M.; et al. Prevention of Hyperglycemia-Induced Myocardial Apoptosis by Gene Silencing of Toll-like Receptor-4. J Transl Med 2010, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiris, K.; De Vreese, P.; De Cooman, L.; Muylaert, K. Rapid Screening and Guided Extraction of Antioxidants from Microalgae Using Voltammetric Methods. J Agric Food Chem 2012, 60, 7359–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, C.; Da Dalt, L.; Pirillo, A.; Galli, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Norata, G.D. Cholesterol Metabolism, Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Diabetes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2019, 1865, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Yang, R.; Luo, M.; Yu, C. Correlation between the Triglyceride-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Other Unconventional Lipid Parameters with the Risk of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: A RCSCD-TCM Study in China. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Rao-Balakrishna, P.; Malik, R.A.; Soran, H. Diabetes Dyslipidemia. Diabetes Therapy 2016, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzaro, G.; Vatland, A.K.; Pampanin, D.M. The One-Health Approach in Seaweed Food Production. Environ Int 2022, 158, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Rahikainen, M.; Camarena-Gómez, M.T.; Piiparinen, J.; Spilling, K.; Yang, B. European Union Legislation on Macroalgae Products. Aquaculture International 2021, 29, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, V.; Jayashree, S.; Kumar, G.; Aruna Sharmili, S.; Gopal, M.; Dharmaraj, S.; Chen, W.-H.; Kothari, R.; Manasa, I.; Hoon Park, J.; et al. Recent Technologies in Biorefining of Macroalgae Metabolites and Their Industrial Applications - A Circular Economy Approach. Bioresour Technol 2022, 127235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leandro, A.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Diverse Applications of Marine Macroalgae. Mar Drugs 2019, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D. Extração de Agar de Algas Vermelhas Do Género Gracilaria; Coimbra, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, L.; Monteiro, P.; Cotas, J.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Fernandes, C.; Gonçalves, T.; Pereira, L. Seaweeds’ Pigments and Phenolic Compounds with Antimicrobial Potential. Biomol Concepts 2022, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal Extracts: Technology and Advances. Eng Life Sci 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Poza, S.G. Brown Seaweed Polysaccharides - A Roadmap as Biomolecules; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Agregán, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Dominguez, R.; Carballo, J.; Franco, D. Assessment of the Antioxidant Activity of Bifurcaria bifurcata Aqueous Extract on Canola Oil. Effect of Extract Concentration on the Oxidation Stability and Volatile Compound Generation during Oil Storage. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.-J. Enzyme-Assistant Extraction (EAE) of Bioactive Components: A Useful Approach for Recovery of Industrially Important Metabolites from Seaweeds: A Review. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Kim, S.K. Nutritional and Digestive Health Benefits of Seaweed. Adv Food Nutr Res 2011, 64, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Valado, A. The Seaweed Diet in Prevention and Treatment of the Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mar Drugs 2021, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, J.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Pérez-Jiménez, J. Design of Low Glycemic Response Foods Using Polyphenols from Seaweed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.R.; Tiwari, U.; Rajauria, G. Seaweed Nutraceuticals and Their Therapeutic Role in Disease Prevention. Food Science and Human Wellness 2019, 8, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgougnon, N.; Burlot, A.S.; Jacquin, A.G. Algae for Global Sustainability? Adv Bot Res 2021, 100, 145–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, R.; Hameed Hassoon, W.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Siastała, M.; Dziki, D. Study on the Physical and Antioxidant Properties of Gluten-Free Bread with Brown Algae. http://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/tcyt 2016, 15, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M. Estudo Bioquímico e Fisiológico Aplicado à Macroalga Saccorhiza polyschides, 2021.
- Rosemary, T.; Arulkumar, A.; Paramasivam, S.; Mondragon-Portocarrero, A.; Miranda, J.M. Biochemical, Micronutrient and Physicochemical Properties of the Dried Red Seaweeds Gracilaria edulis and Gracilaria corticata. Molecules 2019, Vol. 24, Page 2225 2019, 24, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Pereira, L. A Comprehensive Review of the Nutraceutical and Therapeutic Applications of Red Seaweeds (Rhodophyta). Life 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, L.E.; Zhu, X.; Pojić, M.; Sullivan, C.; Tiwari, U.; Curtin, J.; Tiwari, B.K. Biomolecules from Macroalgae—Nutritional Profile and Bioactives for Novel Food Product Development. Biomolecules 2023, Vol. 13, Page 386 2023, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliapietra, B.L.; Clerici, M.T.P.S. Brown Algae and Their Multiple Applications as Functional Ingredient in Food Production. Food Research International 2023, 167, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Miyoshi, T. Algal Fermentation—The Seed for a New Fermentation Industry of Foods and Related Products. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly: JARQ 2013, 47, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, M.; Allahgholi, L.; Sardari, R.R.R.; Hreggviosson, G.O.; Karlsson, E.N. Extraction and Modification of Macroalgal Polysaccharides for Current and Next-Generation Applications. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.L.L. de; Araújo, M.L.H.; Benevides, N.M.B.; Mattos, A.L.A.; Araújo, I.M. da S.; Silva, E.M.C. Sequential Extraction Process and Physicochemical Characterization of R-Phycoerythrin and Agar from Red Macroalgae Gracilaria birdiae. Algal Res 2023, 69, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamede, M.; Cotas, J.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Polysaccharides in Agriculture: A Next Step towards Sustainability. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.V. Seaweed Polysaccharides–Food Applications. In Handbook of Marine Macroalgae; Wiley, 2011; pp. 541–555. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, L.; Bhattamisra, S.K.; Panigrahy, R.C.; Parida, S.K. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Hypoglycaemic and Anti-Diabetic Activities of Some Seaweed Collected from the East Coast of India. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal 2016, 9, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reka, P.; A., T.B.; Seethalakshmi, M. Alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibition activity of selected edible seaweeds from south coast area of india. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2017, 9, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, P.S.; Suthindhiran, K.; Jayasri, M.A. Alpha-Amylase Inhibition and Antioxidant Activity of Marine Green Algae and Its Possible Role in Diabetes Management. Pharmacogn Mag 2015, 11, S511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, N.A.H.K.; Siam, A.A.; El-Manawy, I.M.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-Microbial and Anti-Diabetic Activity of Six Seaweeds Collected from the Red Sea, Egypt. CATRINA 2019, 19, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, S.S. Effects of Seaweed Supplementation on Blood Glucose Concentration, Lipid Profile, and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutr Res Pract 2008, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandini, S.K.; Ganesan, P.; Bhaskar, N. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities of Three Selected Brown Seaweeds of India. Food Chem 2008, 107, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motshakeri, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Goh, Y.M.; Matanjun, P.; Mohamed, S. Sargassum polycystum Reduces Hyperglycaemia, Dyslipidaemia and Oxidative Stress via Increasing Insulin Sensitivity in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes. J Sci Food Agric 2013, 93, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaraweera, A.M.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Kurukulasuriya, M.S. Industrial Applications of Macroalgae; John Wiley and Sons, 2012; ISBN 9780470979181. [Google Scholar]
- Elangovan, M.; Noorjahan, A.; Anantharaman, P. Extraction of Metabolites and Screening Their Antioxidant Potential From Marine Macro Algae. International journal of scientific & technology research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Azzawie, H.F.; Alhamdani, M.S.S. Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Effect of Oleuropein in Alloxan-Diabetic Rabbits. Life Sci 2006, 78, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.Y.M.; Saber, A.A.; Hammad, H.B.I. The Possible Role of the Seaweed Ulva fasciata on Ameliorating Hyperthyroidism-Associated Heart Inflammations in a Rat Model. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 6830–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, L.; Lima, E.; Neto, A.I.; Baptista, J. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity, Antioxidant Properties, Phenolic Content and Amino Acid Profiles of Fucus Spiralis L. Protein Hydrolysate Fractions. Mar Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilam, Y.; Pintel, N.; Khattib, H.; Shagug, N.; Taha, R.; Avni, D. Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism by Phytochemicals Derived from Algae and Edible Mushrooms in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, Vol. 23, Page 13667 2022, 23, 13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.T.V.; Tsou, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Lu, W.J.; Hwang, P.A. Effects of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan and High Stability Fucoxanthin on Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Function in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes. Marine Drugs 2017, Vol. 15, Page 113 2017, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Beppu, F.; Hosokawa, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Nutraceutical Characteristics of the Brown Seaweed Carotenoid Fucoxanthin. Arch Biochem Biophys 2020, 686, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, R.T.; Marçal, C.; Queirós, A.S.; Abreu, H.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Screening of Ulva Rigida, Gracilaria sp., Fucus vesiculosus and Saccharina latissima as Functional Ingredients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, Vol. 19, Page 2987 2018, 19, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, R.; Guedes, L.; Melo, R.; Ascensão, L.; Pacheco, R.; Vaz, P.D.; Serralheiro, M.L. Effect of Food Preparations on In Vitro Bioactivities and Chemical Components of Fucus Vesiculosus. Foods 2020, Vol. 9, Page 955 2020, 9, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.W.; Kim, W.K. The Effect of Fucoxanthin Rich Power on the Lipid Metabolism in Rats with a High Fat Diet. Nutr Res Pract 2013, 7, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Gong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Ye, Y.; Lin, W. Sulfated Polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera Suppress SREBP-2 and HMG-CoA Reductase Expression and Attenuate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet. Food Funct 2017, 8, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.C.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, H.J. Effects of 12-Week Oral Supplementation of Ecklonia cava Polyphenols on Anthropometric and Blood Lipid Parameters in Overweight Korean Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Phytotherapy Research 2012, 26, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, X.Q.; Xiao, J.J.; Zhang, H.N.; Wang, J.H.; Pan, L.H.; Yang, X.F.; Luo, J.P. Polysaccharides in Laminaria japonica (LP): Extraction, Physicochemical Properties and Their Hypolipidemic Activities in Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Food Chem 2012, 134, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, E.I.; Kalyuzhnaya, A.M.; Panchenko, A.K.; Krasil’nikova, S. V.; Petrenko, E.B. Amino Acids from Algae-Valuable Bread Additives. Khlebopekarnaya I Konditerskaya Promyshlennost 1969, 13, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mamat, H.; Matanjun, P.; Ibrahim, S.; Siti, S.F.; Abdul Hamid, M.; Rameli, A.S. The Effect of Seaweed Composite Flour on the Textural Properties of Dough and Bread. J Appl Phycol 2014, 26, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsopp, P.; Crowe, W.; Bahar, B.; Harnedy, P.A.; Brown, E.S.; Taylor, S.S.; Smyth, T.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Magee, P.J.; Gill, C.I.R.; et al. The Effect of Consuming Palmaria palmata-Enriched Bread on Inflammatory Markers, Antioxidant Status, Lipid Profile and Thyroid Function in a Randomised Placebo-Controlled Intervention Trial in Healthy Adults. Eur J Nutr 2016, 55, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradinho, P.; Raymundo, A.; Sousa, I.; Domínguez, H.; Torres, M.D. Edible Brown Seaweed in Gluten-Free Pasta: Technological and Nutritional Evaluation. Foods 2019, Vol. 8, Page 622 2019, 8, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, B.S.; Coelho, M.S.; Meza, S.L.R.; Salas-Mellado, M.; Souza, M.R.A.Z. Macroalgal Biomass as an Additional Ingredient of Bread. Int Food Res J 2015, 22, 819–824. [Google Scholar]
- Derosa, G.; Pascuzzo, M.D.; D’Angelo, A.; Maffioli, P. Ascophyllum Nodosum, Fucus vesiculosus and Chromium Picolinate Nutraceutical Composition Can Help to Treat Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2019, Volume 12, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qi, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Ruan, R.; Yan, X.; Cheng, P. Macroalgae-Derived Multifunctional Bioactive Substances: The Potential Applications for Food and Pharmaceuticals. Foods 2022, 11, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñalver, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ros, G.; Amarowicz, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nieto, G. Seaweeds as a Functional Ingredient for a Healthy Diet. Mar Drugs 2020, 18, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouritsen, O.G.; Dawczynski, C.; Duelund, L.; Jahreis, G.; Vetter, W.; Schröder, M. On the Human Consumption of the Red Seaweed Dulse (Palmaria palmata (L.) Weber & Mohr). J Appl Phycol 2013, 25, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, C.; Gallagher, E.; Doran, L.; Auty, M.; Prieto, J.; Hayes, M. Increasing the Health Benefits of Bread: Assessment of the Physical and Sensory Qualities of Bread Formulated Using a Renin Inhibitory Palmaria palmata Protein Hydrolysate. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2014, 56, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilaka, T.L.; Samarakoon, K.; Ranasinghe, P.; Peiris, L.D.C. Antidiabetic Potential of Marine Brown Algae—a Mini Review. J Diabetes Res 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Sellappa, S.; Prakash, S. Antidiabetic Activity of Aqueous Extract of Padina boergesenii in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2014, 6, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Gholampour, H.; Farzadinia, P.; Daneshi, A.; Ramavandi, B.; Moazzeni, A.; Keshavarz, M.; Bargahi, A. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Sargassum oligocystum on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2018, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotama, T.L.; Husni, A. Ustadi Antidiabetic Activity of Sargassum hystrix Extracts in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Prev Nutr Food Sci 2018, 23, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.; Almeida, J.; Coelho, I.; Delgado, I.; Gomes, R.; Quintã, R.; Bandarra, N.M.; Afonso, C. Farming a Wild Seaweed and Changes to Its Composition, Bioactivity, and Bioaccessibility: The Saccorhiza polyschides Case Study. Aquaculture 2023, 566, 739217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Oliva-Teles, M.T.; Pinto, E.; Nastić, N.; Savić, S.; Almeida, A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Mineral Composition of Subcritical Water Extracts of Saccorhiza polyschides, a Brown Seaweed Used as Fertilizer in the North of Portugal. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2020, Vol. 8, Page 244 2020, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocanegra, A.; Macho-González, A.; Garcimartín, A.; Benedí, J.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J. Whole Alga, Algal Extracts, and Compounds as Ingredients of Functional Foods: Composition and Action Mechanism Relationships in the Prevention and Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, R.; Correia, A.P.; Pires, D.; Pires, P.; Ferreira, I.; Simões, M.; do Carmo, B.; Santos, P.; Pombo, A.; Afonso, C.; et al. Potential Use of Macroalgae Gracilaria gracilis in Diets for European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Health Benefits from a Sustainable Source. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2021, 119, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Franchi, M.; Monteleone, M.; Caroppo, C. The Red Seaweed Gracilaria gracilis as a Multi Products Source. Mar Drugs 2013, 11, 3754–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.L.; Potin, P.; Craigie, J.S.; Raven, J.A.; Merchant, S.S.; Helliwell, K.E.; Smith, A.G.; Camire, M.E.; Brawley, S.H. Algae as Nutritional and Functional Food Sources: Revisiting Our Understanding. J Appl Phycol 2017, 29, 949–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
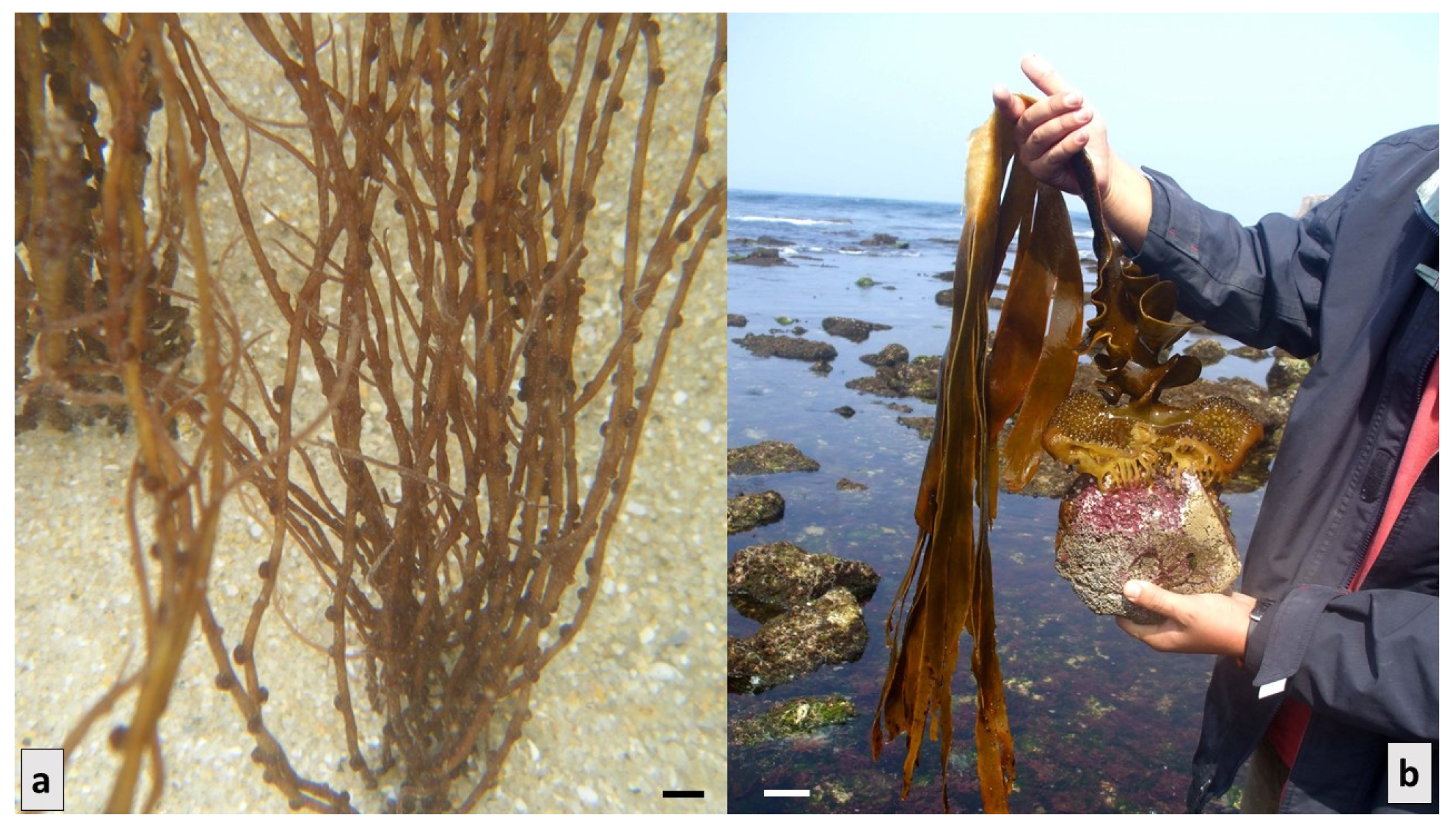
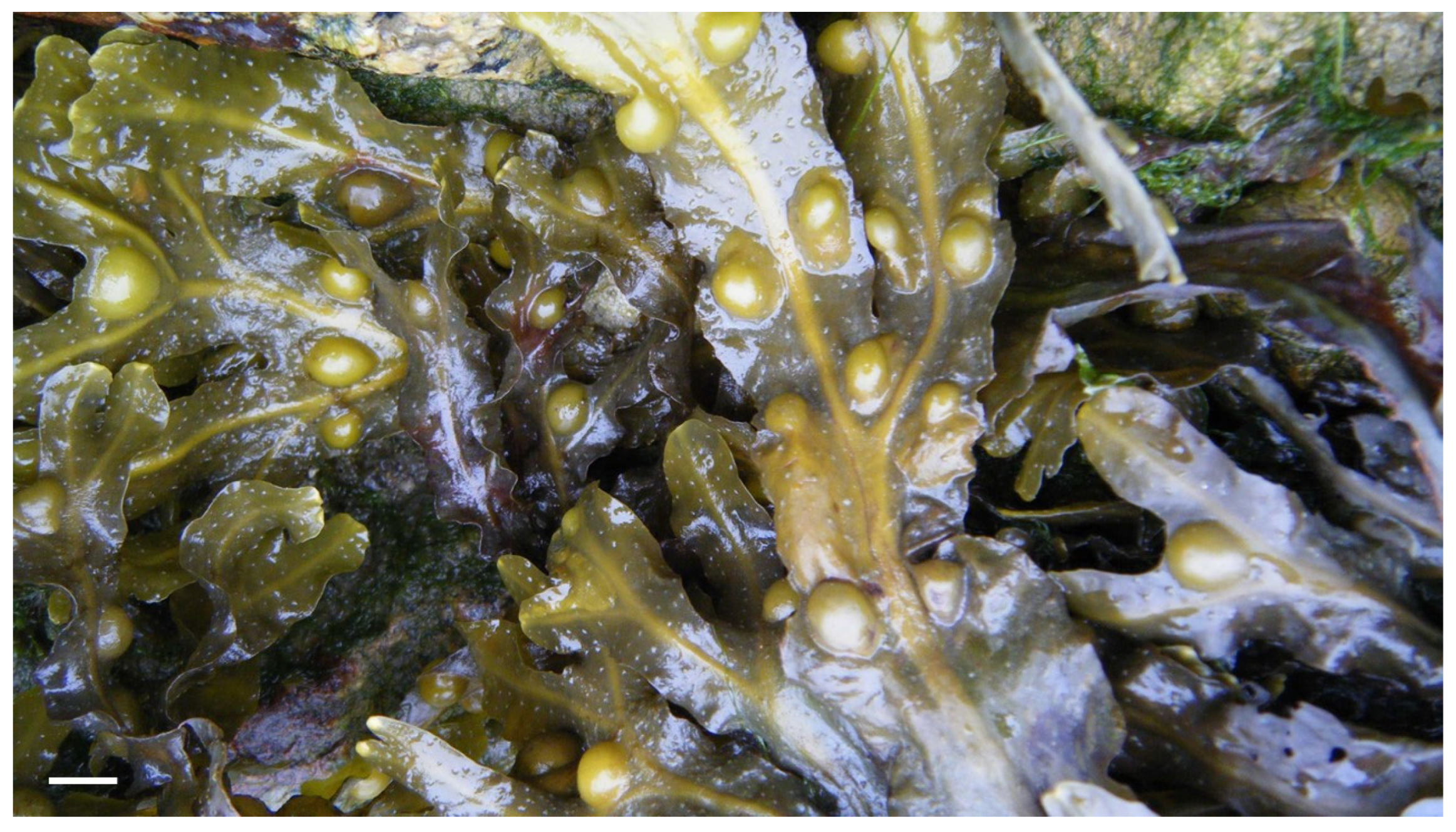
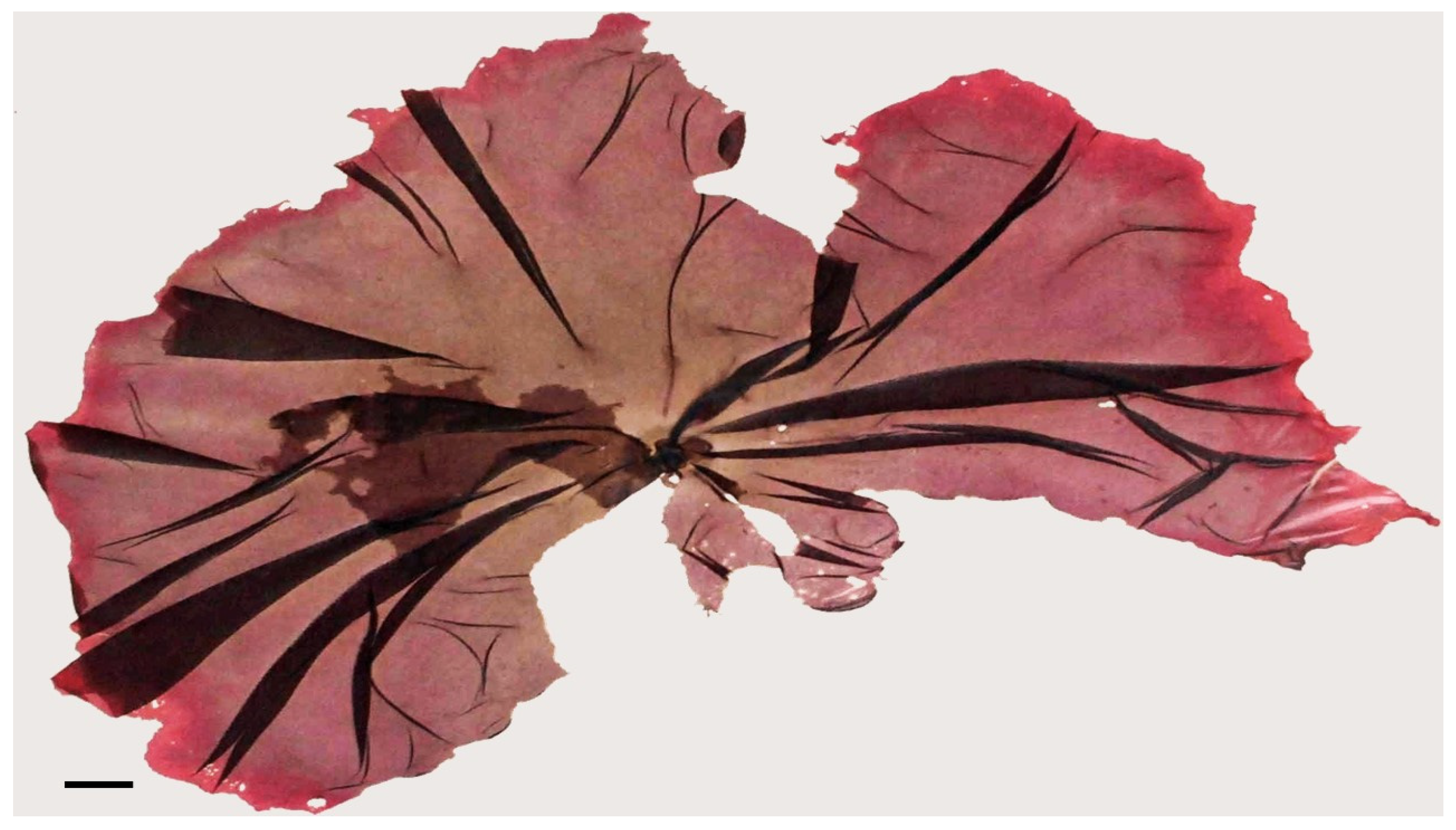






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




