Submitted:
17 September 2023
Posted:
18 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Flexible regulation capacity of flexible DERs in smart building system
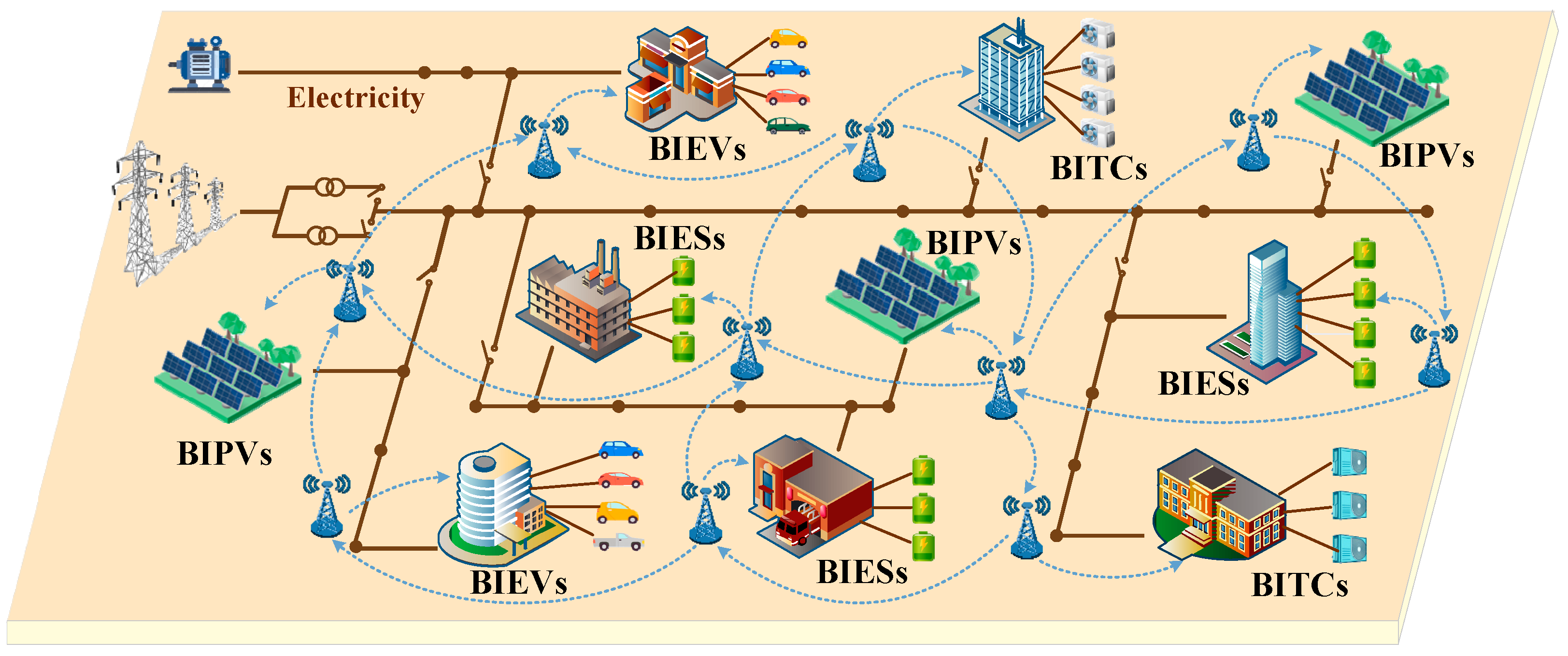
2.1. Smart building system
2.2. Battery model of ES in the smart building system
2.2. Virtual battery (VB) model in the smart building system
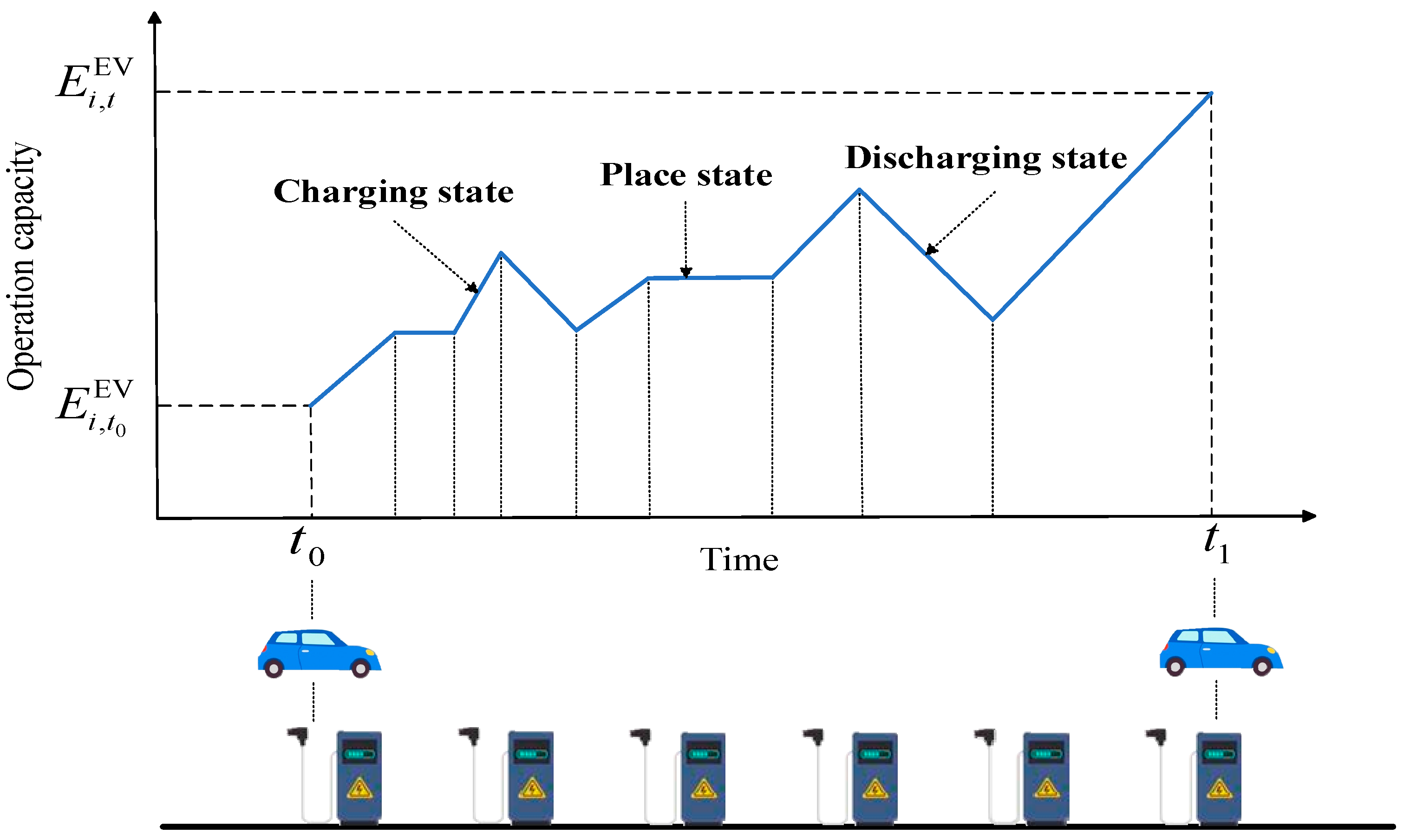
2.3. VB model of EV in the smart building system
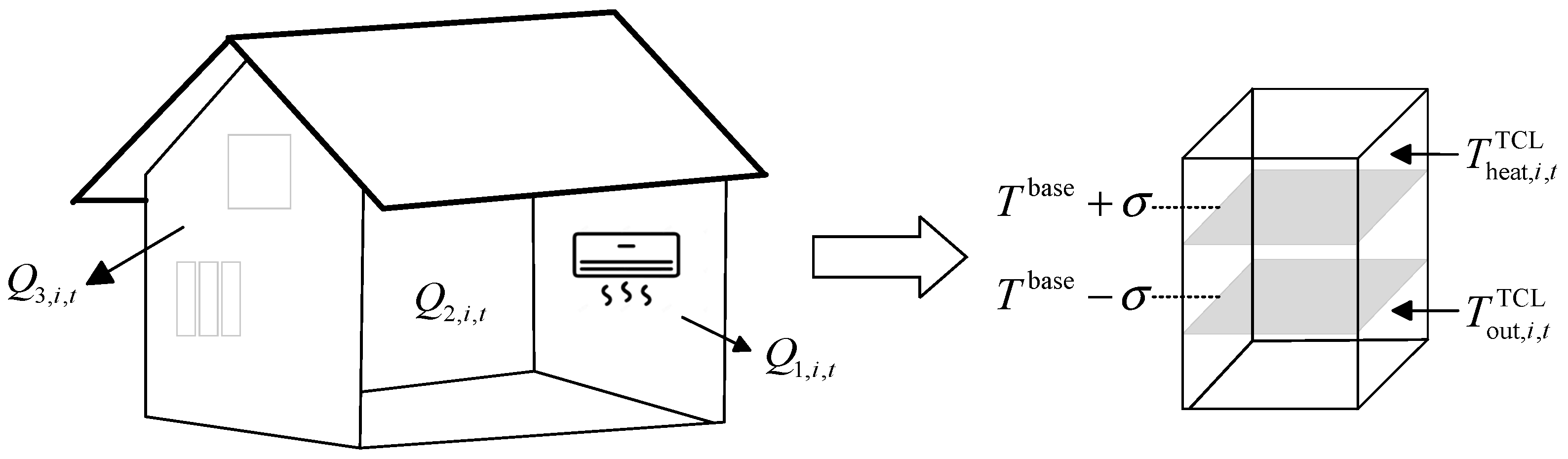
2.4. VB model of TCL in the smart building system
3. Active-reactive power collaborative optimization scheduling of distribution network cluster with the aggregation of flexible DERs in smart building system
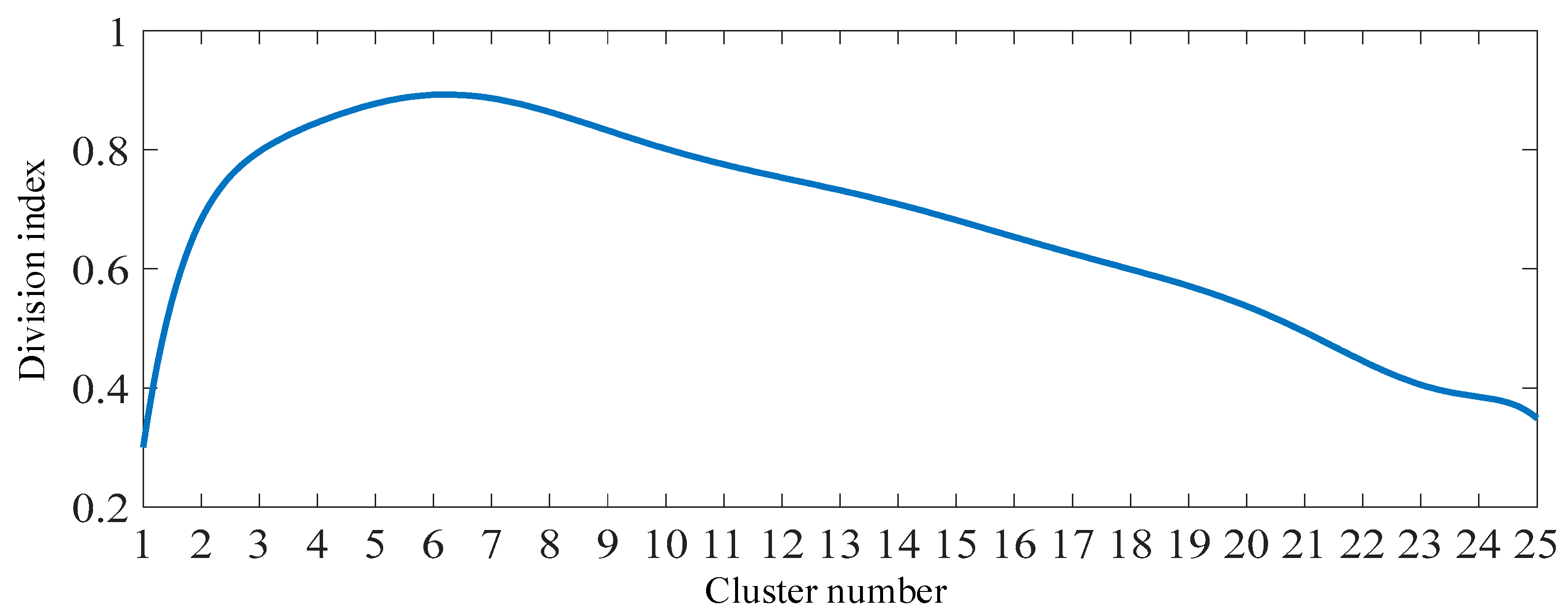
3.1. Cluster division index of building-integrated flexible DERs
3.1.1. Module degree index
3.1.2. Flexible balance contribution index
- Each node in the distribution network is regarded as a separate cluster initially to calculate the cluster division index of the building-integrated flexible DERs based on formula (10);
- Node is randomly selected from the remaining other nodes to merge with node forming a new cluster , and then the variation of the cluster division index can be derived from the division index of cluster . When reaches the maximum positive value, the two nodes can be divided into the same cluster;
- The new cluster will be regarded as a new node to repeating the second procedure. The division procedures will be stopped until the nodes in the network cannot merge and the cluster division index of the building-integrated flexible DERs reaches the maximum.
3.2. Active-reactive power collaborative optimization scheduling within clusters
3.2.1. Optimization objective
3.2.2. Operation constraints
3.2.3. Solution methodology
4. Discussion
4.1. System data
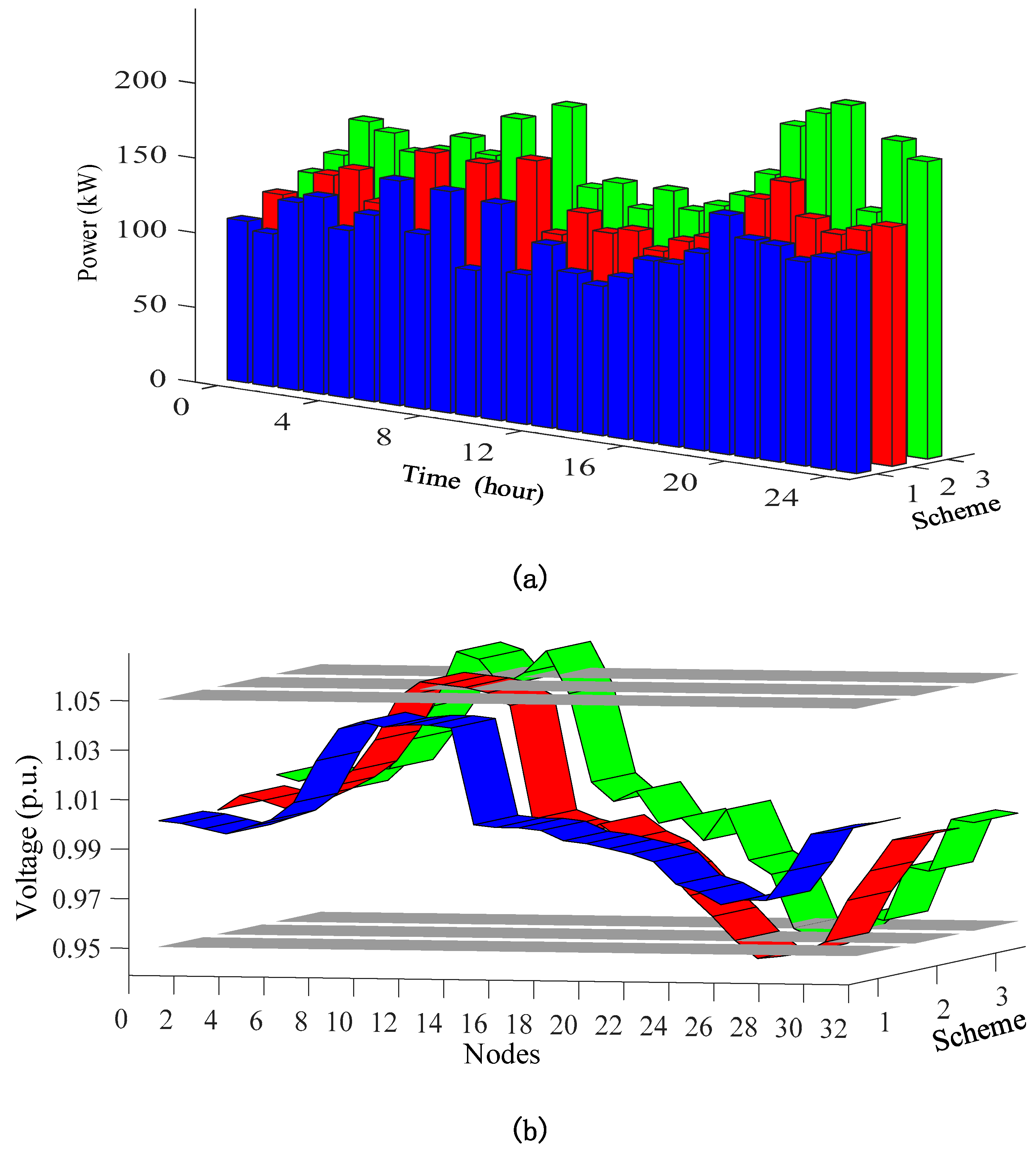
4.2. Comparative Results and Analysis
- Scheme 1 performs the proposed optimization scheduling of distribution network with cluster division for flexible DERs integrated into the smart building system in Section 3.
- Scheme 2 adopts the centralized optimization scheduling of distribution network without considering the cluster division.
- Scheme 3 is the initial distribution network before the optimization scheduling.
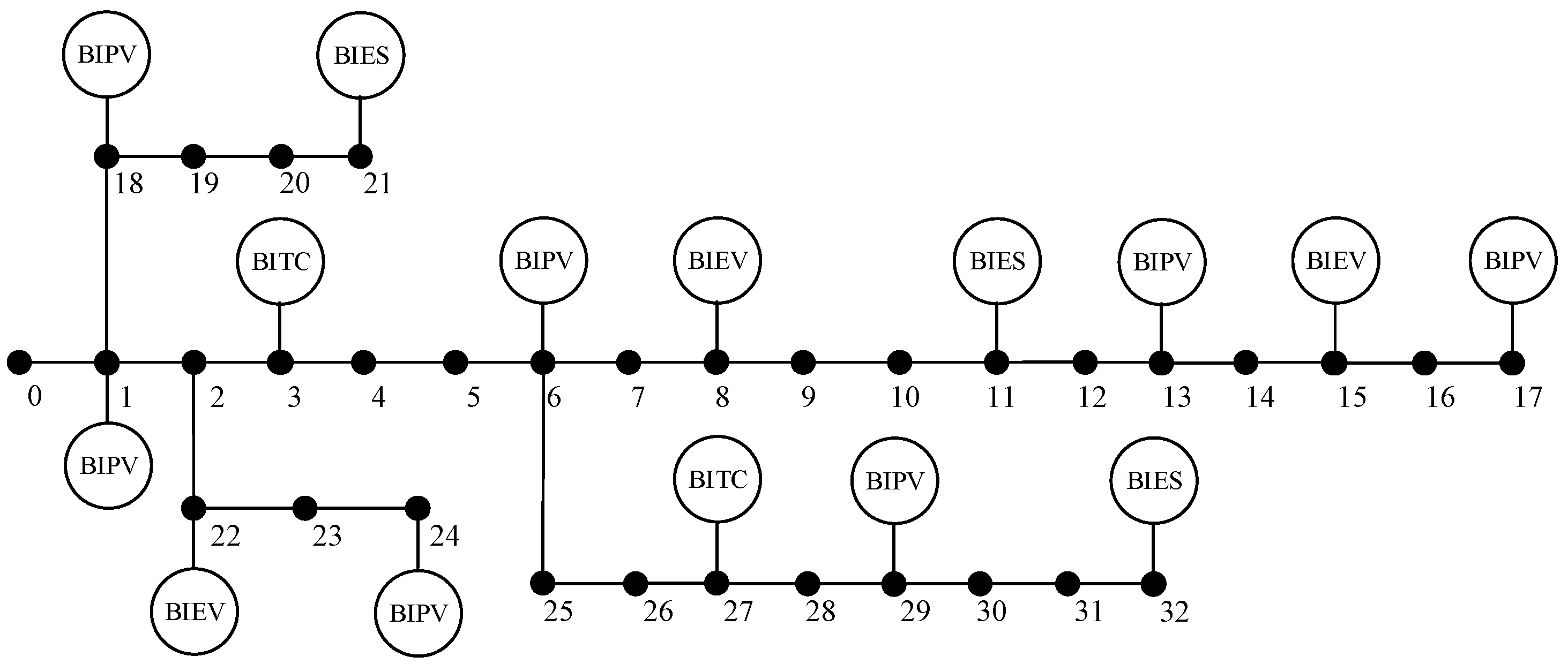
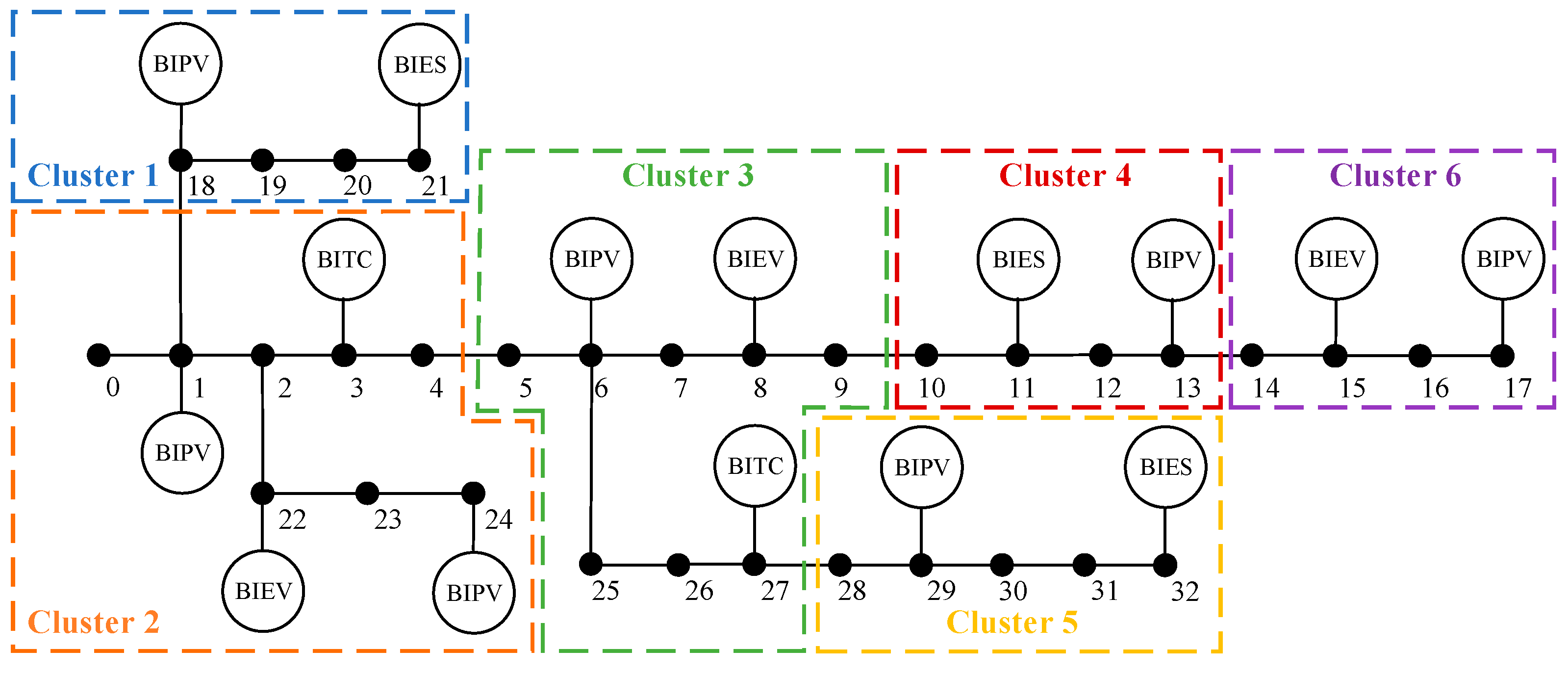
4.2.1. Cluster division of the building-integrated flexible DERs
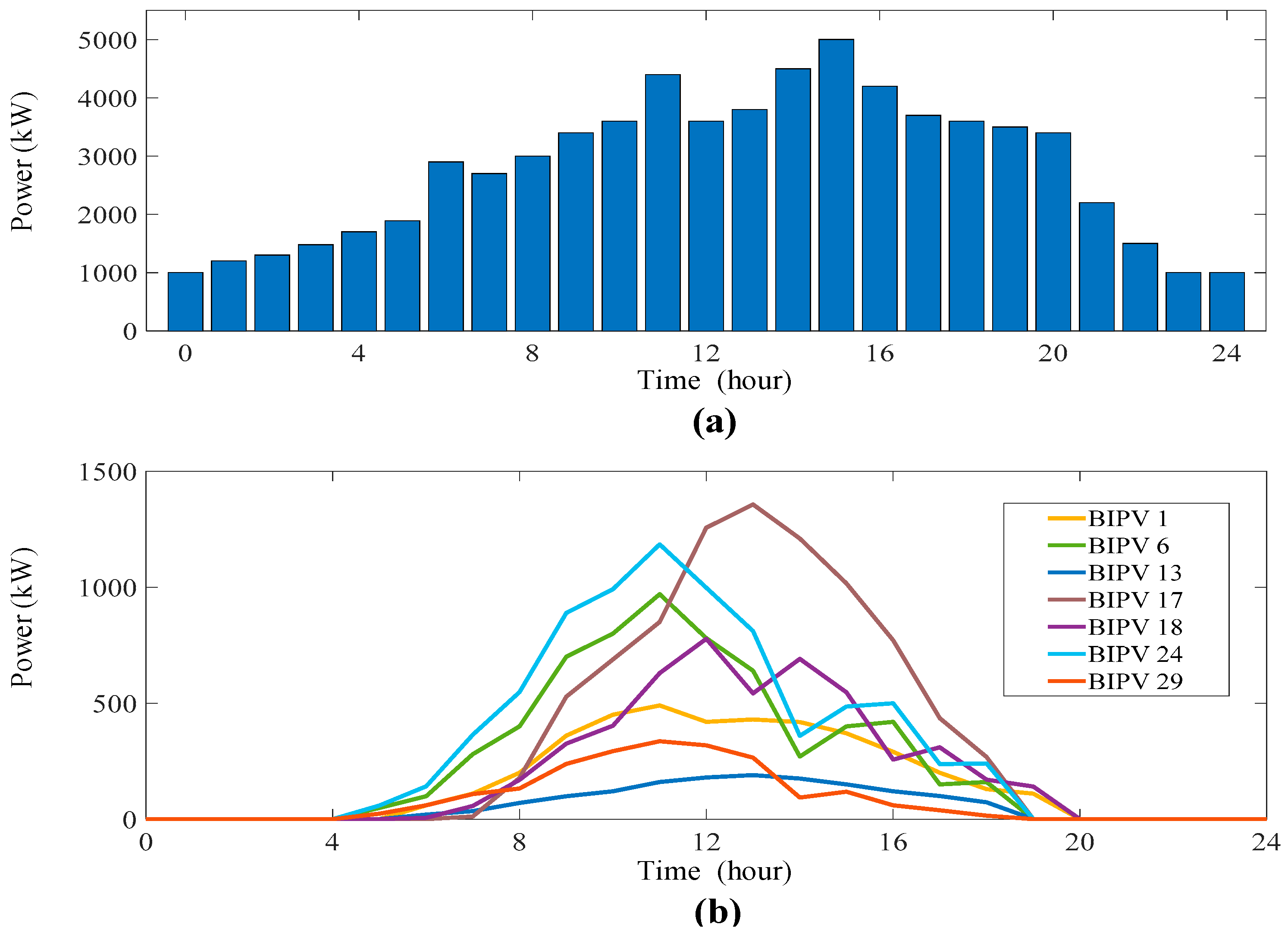
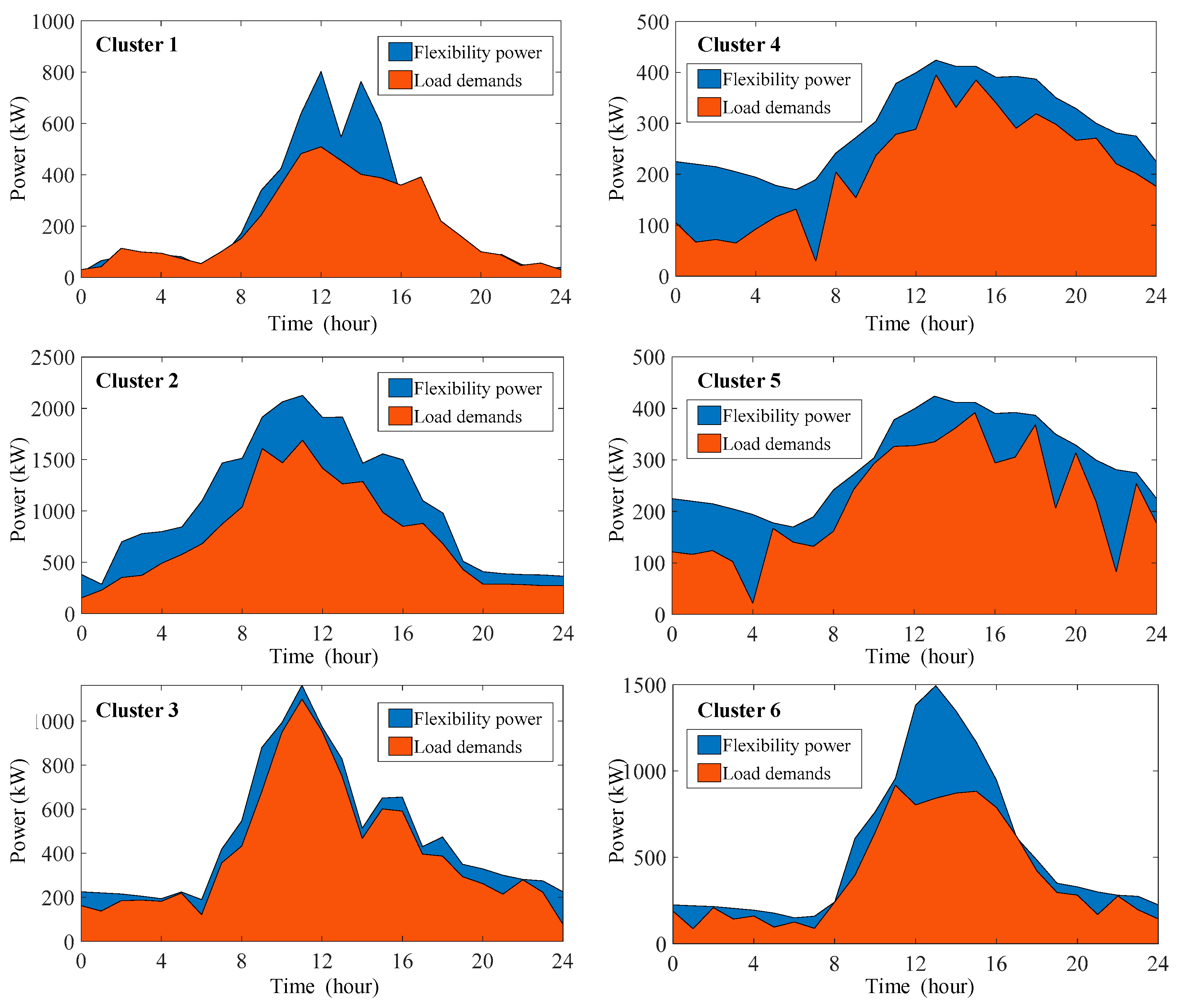
4.2.2. Flexible regulation capacity results of the building-integrated flexible DERs
4.2.3. Optimization scheduling results with scheme 1-3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA, World Energy Outlook 2022: An updated roadmap to Net Zero Emissions by 2050. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/75cd37b8-e50a-4680-bfd7-0424e 04a1968/WorldEnergyOutlook2022.pdf.
- Xue, Q.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, Q.Y. Multi-objective optimization of building design for life cycle cost and CO2 emissions: A case study of a low-energy residential building in a severe cold climate. Build. Simul. 2022, 15, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.P.; Cerio Mendaza, I.D.; Myers, K.S.; Bak-Jensen, B.; Paudyal, S. Optimum Aggregation and control of spatially distributed flexible resources in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5311–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousoglou, G.; Sartzetakis, I.; Makris, P.; Efthymiopoulos, N.; Varvarigos, E.; Paterakis, N.G. Flexibility aggregation of temporally coupled resources in real-time balancing markets using machine learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2022, 18, 4342–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, M.; Adelmanesh, B.; Shirdare, E. Intelligent energy management based on SCADA system in a real microgrid for smart building applications. Renew. Energ. 2021, 171, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eini, R.; Linkous, L.; Zohrabi, N.; Abdelwahed, S. Smart building management system: performance specifications and design requirements. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 39, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Li, H. Optimal control strategy of distributed energy storage cluster for prompting renewable energy accomodation in distribution network. Automat. Electron. Power Syst. 2018, 45, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.Q.; Wu, Z.X.; Lv, X.X.; Dinavahi, V. Robust secondary frequency control for virtual synchronous machine-based microgrid cluster using equivalent modeling. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2021, 12, 2879–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, B. Multi-agent Classified Voltage Regulation Method for Photovoltaic User Group. Automat. Electron. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 20–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Liu, X.F.; Bi, R.; Hu, D. Method for cluster partition of high-penetration distributed generators based on comprehensive performance index. Automat. Electron. Power Syst. 2018, 42, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, X.Y.; Sun, M.Q.; Dong, L.; Yang, X.W. Distributed source-load coordinated dispatching considering flexible aggregated power. Automat. Electron. Power Syst. 2021, 45, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Li, T.; Wu, W.C. Minkowski sum based flexibility aggregating method of load dispatching for heat pumps. Automat. Electron. Power Syst. 2019, 43, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.M.; Huang, H.J.; Zhu, J.Q. Flexible resource cluster response based on inner approximate and constraint space integration. Power Syst. Tenchno. 2023, 47, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, J.; Li, P.; Ji, H.R.; Bai, L.Q. DLMP-based quantification and analysis method of operational flexibility in flexible distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 2353–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Z.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Song, Y.H. Modeling and integration of flexible demand in heat and electricity integrated energy system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 19, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, M.; Zare, K. Integration of smart energy hubs in distribution networks under uncertainties and demand response concept. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.R.; Cao, Y.J.; Shi, X.H.; Zhang, Z. Coordination of multiple flexible resources considering virtual power plants and emergency frequency control. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Q.S.; Fukuda, H. Thermal performance and optimizing of composite trombe wall with temperature-controlled dc fan in winter. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Si, W.G.; Luo, S.J.; Zhao, J. Real-time demand response strategy of temperature-controlled load for high elastic distribution network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 69418–69425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Nie, S.L.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dong, J. Optimization of peer-to-peer power trading in a microgrid with distributed pv and battery energy storage systems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.S.; Jiao, F.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.G. A Short-Term Power Output forecasting model based on correlation analysis and elm-lstm for distributed pv system. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Khodayar, M.E.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B. Data-driven distributionally robust co-optimization of P2P energy trading and network operation for interconnected microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5172–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaifallah, M.; Alaas, Z.; Rezvani, A.; Le, B.N.; Samad, S. Optimal day-ahead economic/emission scheduling of renewable energy resources based microgrid considering demand side management. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, H.; El-Taweel, N.; Farag, H.E.Z. Supervisory scheduling of storagebased hydrogen fueling stations for transportation sector and distributed operating reserve in electricity markets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2020, 16, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| BIES | =300kW | =300kW | =0.95 |
| =1200kWh | =200kWh | =0.95 | |
| BIEV | =400kW | =400kW | =0.95 |
| =800kWh | =0.95 | ||
| BITCL | =8.16 | =35 | =1.25kJ/℃ |
| =0.80 | =0.85 | =0.95 | |
| Unit prices | =1.2 $/kW | =0.5 $/kW | = 0.8 $/kW |
| =0.8 $/kW | =1.1 $/kW | =0.9 $/kW | |
| Scheme | Operation cost ($) | Network loss cost ($) | Flexibility deficiency cost ($) |
| 1 | 5697.8 | 3089.6 | 2608.2 |
| 2 | 6027.1 | 3254.3 | 2872.8 |
| 3 | 6452.6 | 3438.1 | 3014.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




