Submitted:
15 September 2023
Posted:
18 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
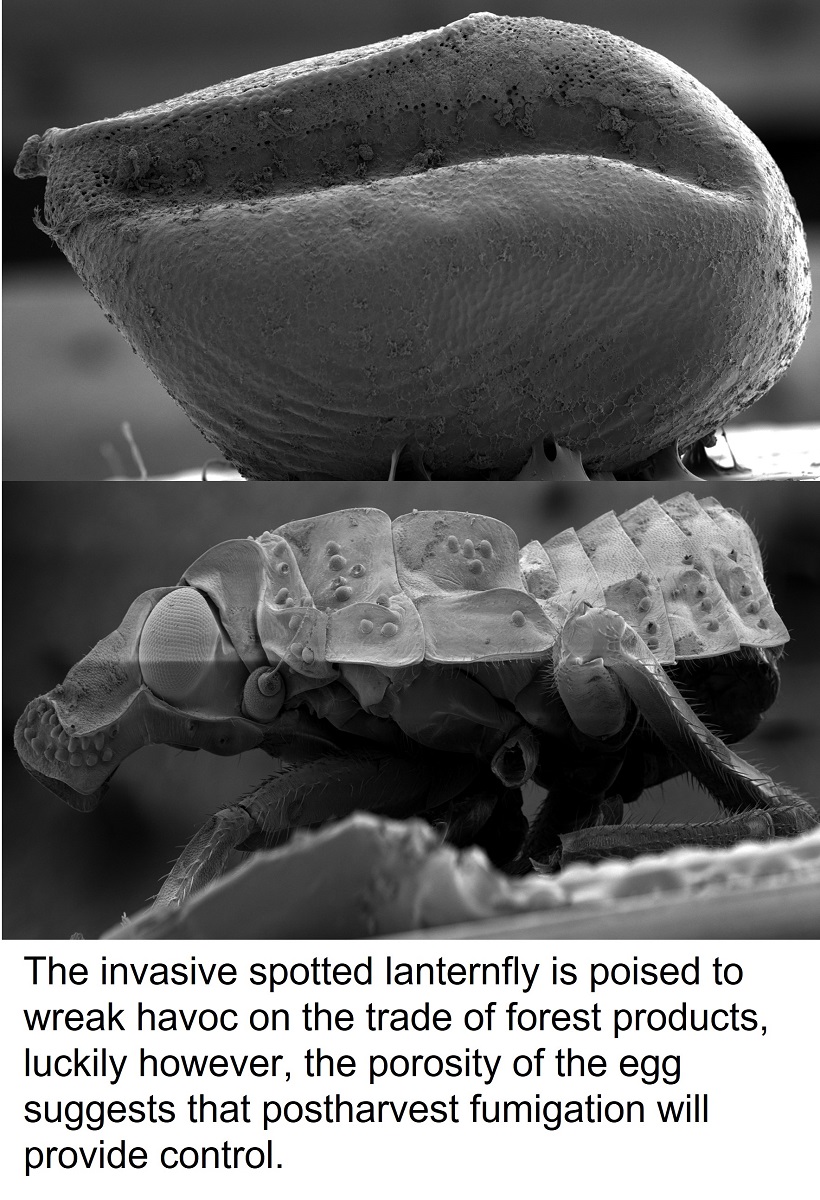
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1. Materials and Methods
1.1. Egg Collection
1.1. Microscopy
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.1. Time-lapse Light Microscopy
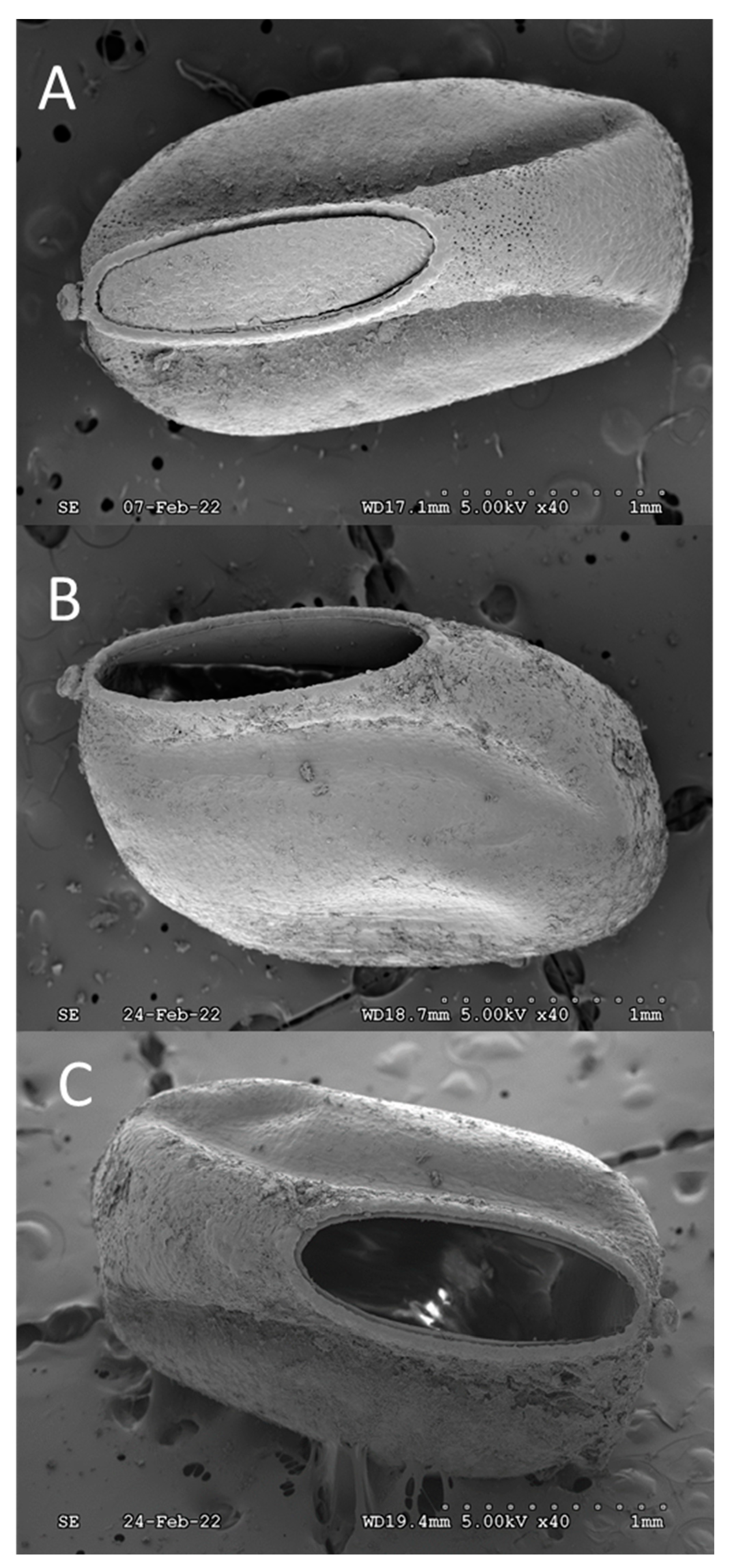
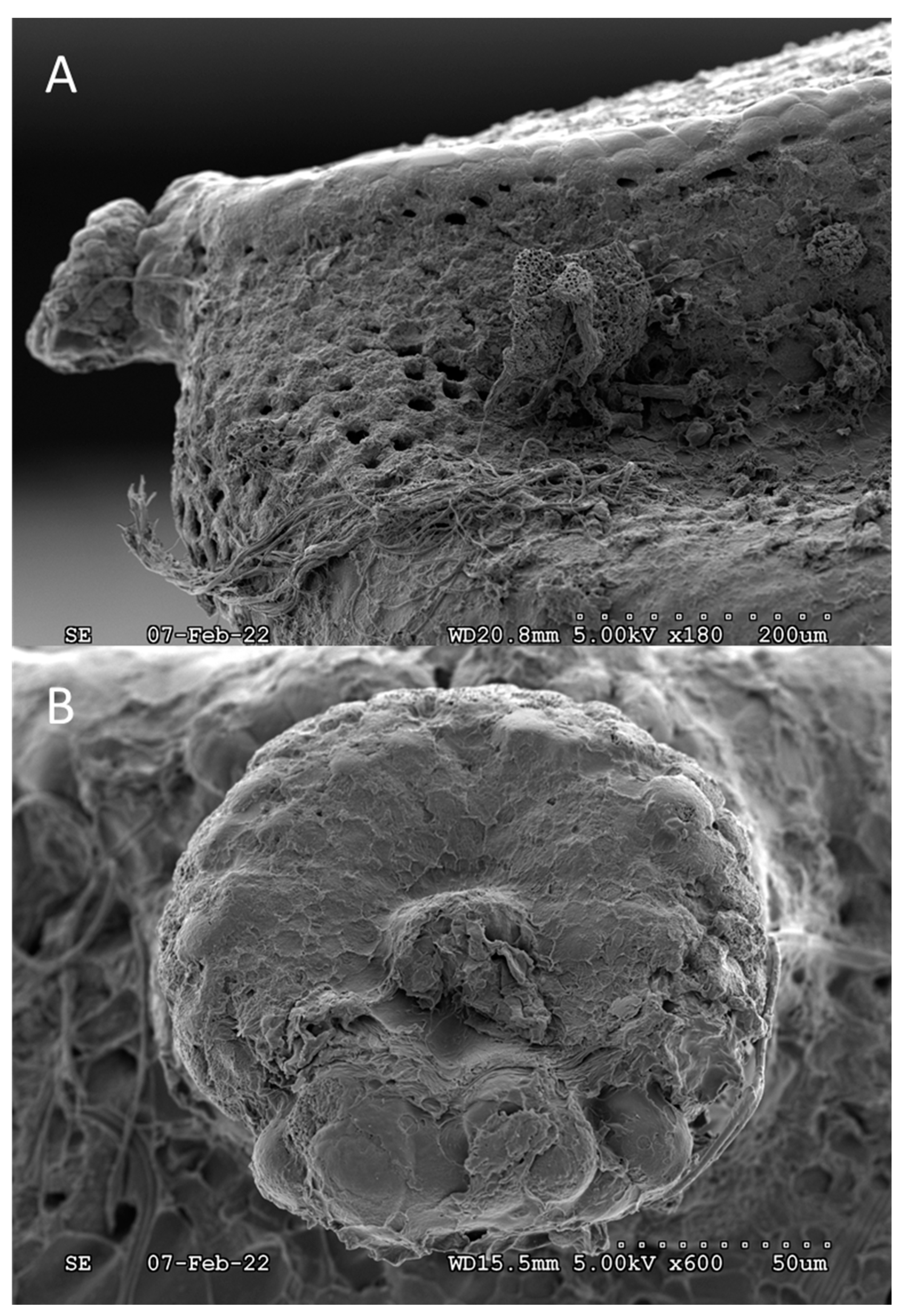
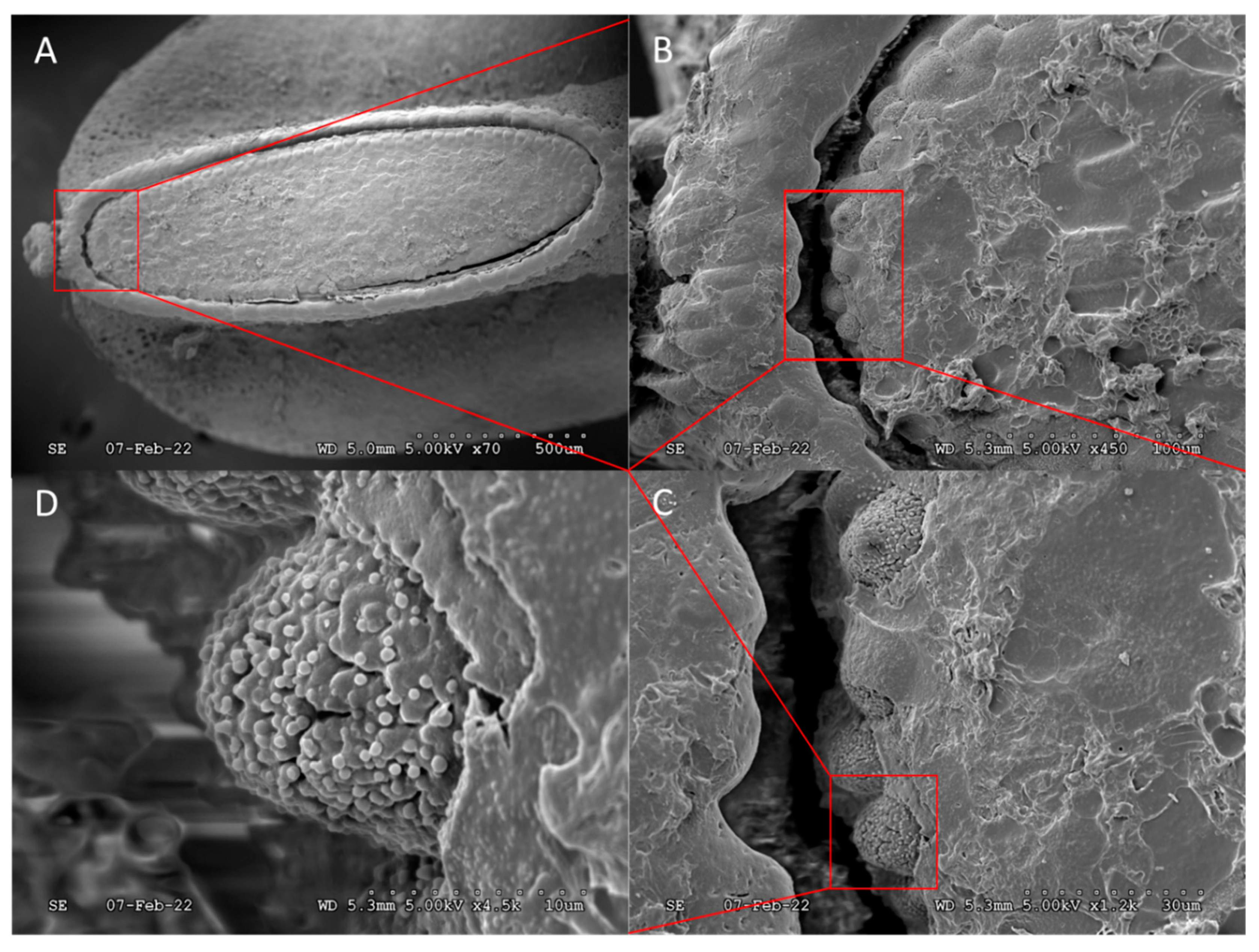
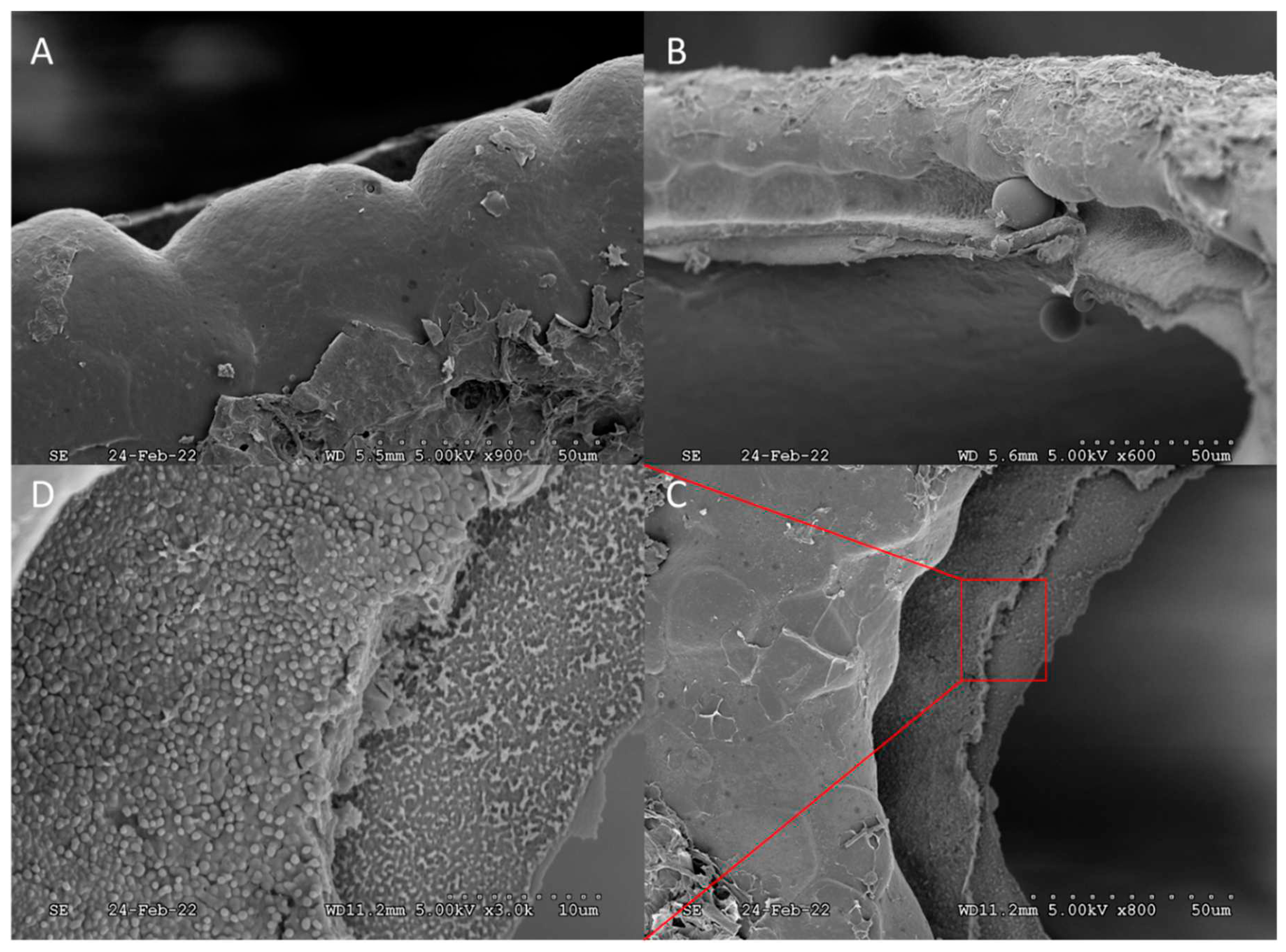
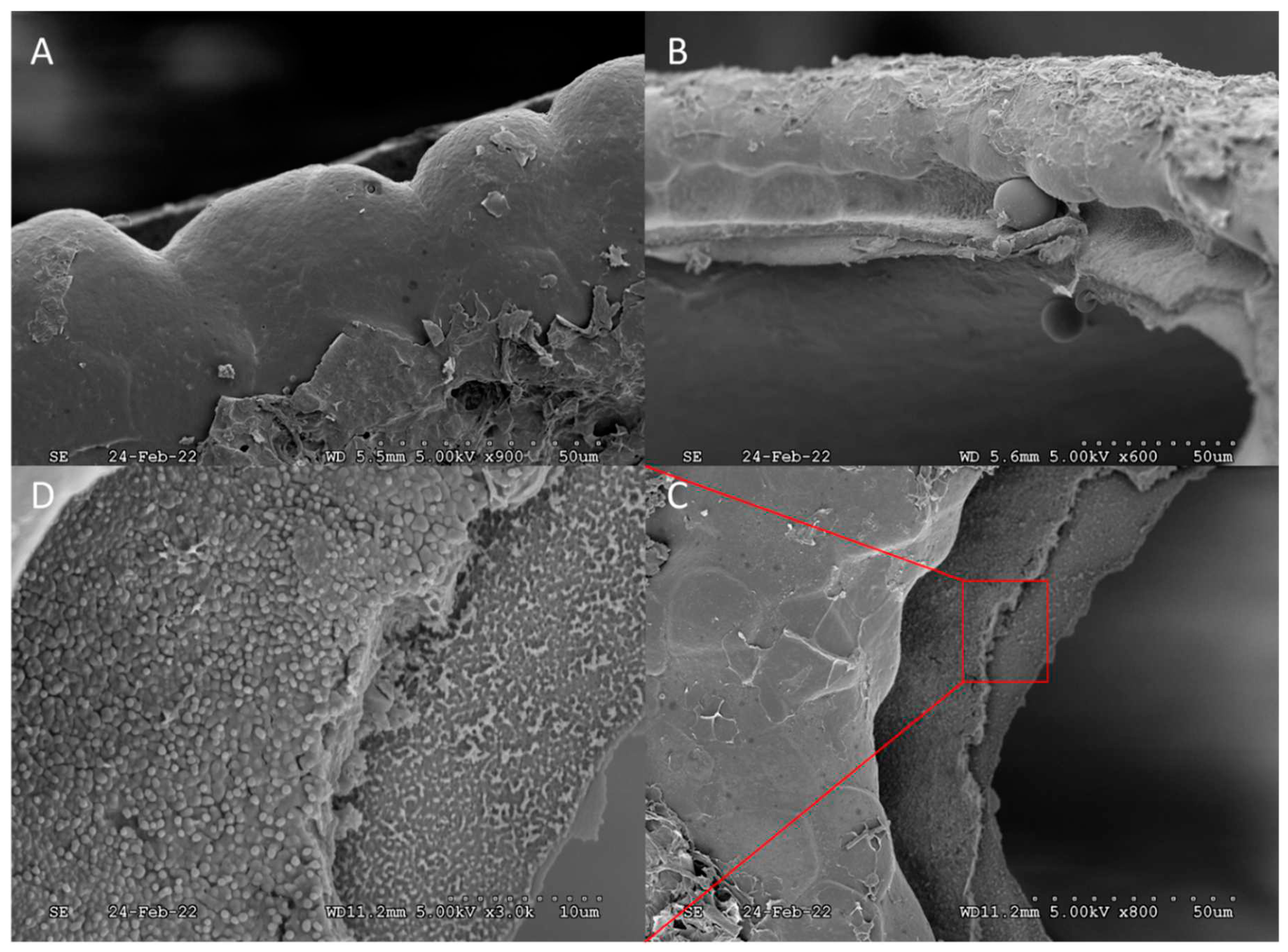
1. Results and Discussion
1. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barringer, L. E.; Donovall, L. R.; Spichiger, S.-E.; Lynch, D.; Henry, D. , The first new world record of Lycorma delicatula (Insecta: Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Entomological news 2015, 125, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, S. K.; Barringer, L.; Arthurs, S. P. , Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae): a new invasive pest in the United States. Journal of Integrated Pest Management 2015, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, N. I. Spotted Laternfly Map. https://www.stopslf.org/where-is-slf/slf-map/ (accessed 10/28/22).
- Han, J. M.; Kim, H.; Lim, E. J.; Lee, S.; Kwon, Y. J.; Cho, S. , Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Fulgoridae: Aphaeninae) finally, but suddenly arrived in Korea. Entomological Research 2008, 38, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Park, Y.-L.; Leskey, T. C. , A review of biology and management of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae), an emerging global invasive species. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2019; 22, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Barringer, L.; Ciafré, C. M. , Worldwide feeding host plants of spotted lanternfly, with significant additions from North America. Environmental Entomology 2020, 49, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. , Oviposition substrate selection, egg mass characteristics, host preference, and life history of the spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) in North America. Environmental entomology 2019, 48, 1452–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheetham, T. , Pathological Alterations in Embryos of the Codling Moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Induced by Methyl Bromide. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 1990, 83, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.; Kamel, A.; El-Nahal, A.; El-Borollosy, F. , Toxicity of carbon bisulphide and methyl bromide to the eggs of four stored product insects. Journal of Stored Products Research 1972, 8, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, K.; Albee, R.; Mattsson, J.; Miller, R. , Incapacitation and treatment of rats exposed to a lethal dose of sulfuryl fluoride. Fundamental and applied toxicology 1986, 7, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrala, A.; Markham, D.; Eisenbrandt, D. , Rapid uptake, metabolism, and elimination of inhaled sulfuryl fluoride fumigant by rats. Toxicological Sciences 2005, 86, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, R.; Stewart, D.; Globus, O. , Fumigant mode of action, drywood termite metabolism of Vikane fumigant as shown by labeled pool technique. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 1963, 11, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, Y. H.; Kim, G.; Lee, B.-H.; Yang, J.-O.; Lee, S.-E. , Ethyl formate and phosphine fumigations on the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae and their biochemical responses. Applied Biological Chemistry 2019, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritos, V.; Dojchinov, G. , Cytochrome c oxidase inhibition in the rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae (L.) by formate, the toxic metabolite of volatile alkyl formates. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2003; 136, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, P. , Formate as an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 1975, 67, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, J. S.; Yang, J. O.; Lee, S.-E. , Biochemical mechanisms of fumigant toxicity by ethyl formate towards Myzus persicae nymphs. Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry 2017, 60, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPM) No. 28. 2007. Phytosanitary Treatments for Regulated Pests. Pp. 3- 11. http://www.furs.si/law/FAO/ZVR/ENG/184208_ISPM28_2007_E.
- United Nations Environment Program. 2010. Report of the Methyl Bromide Technical Options Committee (MBTOC) – 2010 Assessment http://www.mma.gov.br/estruturas/ozonio/_publicacao/130_publicacao19082011113643.
- Kenaga, E. E. , Some biological, chemical and physical properties of sulfuryl fluoride as an insecticidal fumigant. Journal of Economic Entomology 1957, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, C. Reichmuth, C.: Schöller, M.; Dugast, J.-F.; Drinkall, M. J., 1997. On the efficacy of sulphuryl fluoride against stored product pest moths and beetles, pp: 700. In: Donahaye, E.J., Navarro, S., Varnava, A. (eds.), proceedings of the Conference on Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products, 21-26 April, Nicosia, Cyprus, Pincto Ltd, Nicosia, Cyprus.
- United Nations Environment Program. 2011. Special review on achieving control of pest eggs by sulfuryl fluoride, pp. 110-136. In. Report of the Technology and Economic Assessment Panel. http://ozone.unep.org/Assessment_Panels/TEAP/Reports/TEAP_Reports/TEAP_Progress_Report_May_2011.pdf.
- Walse, S. S.; Gautam, S. G.; Opit, G. P.; Margosan, D.; Tebbets, J. S. , 2014. Sulfuryl fluoride-propylene oxide mixtures: applications and efficacy. proceedings of the International Working Congress on Stored Product Protection, , Chiang Mai, Thailand. http://spiru.cgahr.ksu.edu/proj/iwcspp/iwcspp11. 23 November.
- Baskin, S. I.; Brewer, T. G. , Cyanide Poisoning (From Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare, P 271-286, 1997, Frederick R. Sidell, MD, Ernest T. Takafuji, MD, eds, et al.,--See NCJ-190599). 1997.
- Sciuto, A. M.; Wong, B. J.; Martens, M. E.; Hoard-Fruchey, H.; Perkins, M. W. , Phosphine toxicity: a story of disrupted mitochondrial metabolism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2016, 1374, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, K.; Chefurka, W. , The effect of phosphine on the absorption and circular dichroic spectra of cytochrome c and cytochrome oxidase. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 1976, 6, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winks, R.; Waterford, C. , The relationship between concentration and time in the toxicity of phosphine to adults of a resistant strain of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). Journal of stored products research 1986, 22, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walse, S. S.; Jimenez, L. R. , Postharvest fumigation of fresh citrus with cylinderized phosphine to control bean thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Horticulturae 2021, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampiri, E.; Agrafioti, P.; Athanassiou, C. G. , Delayed mortality, resistance and the sweet spot, as the good, the bad and the ugly in phosphine use. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, E. J.; Dumas, T.; Hobbs, S. ,1984. Corrosion of metals by the fumigant phosphine. Journal of Stored Product Research.
- Soderstrom, E. L.; Brandl, D. G. , Hartsell, P. L.; Mackey, B., Fumigants as treatments for harvested citrus fruits infested with Asynonychus godmani (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Journal of Economic Entomology 1991, 84, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C. , The tolerance of developmental stages of four stored product moths to phosphine. Journal of Stored Products Research 1976, 12, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.-Y.; Scheffrahn, R. H. , Efficacy of sulfuryl fluoride against four beetle pests of museums (Coleoptera: Dermestidae, Anobiidae). Journal of Economic Entomology 1990, 83, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Savvidou, N. , The toxicity of Vikane (sulfuryl fluoride) to age groups of eggs of the Mediterranean flour moth (Ephestia kuehniella). Journal of Stored Products Research 1999, 35, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, D.; Klementz, D.; Gerowitt, B.; Drinkall, M.; Reichmuth, C. , Lethal effects of sulfuryl fluoride on eggs of different ages and other life stages of the warehouse moth Ephestia elutella (Hübner). Journal of Stored Products Research 2009, 45, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonjour, E.; Opit, G.; Hardin, J.; Jones, C.; Payton, M.; Beeby, R. , Efficacy of ozone fumigation against the major grain pests in stored wheat. Journal of Economic Entomology 2011, 104, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C. G.; Phillips, T. W.; Aikins, M. J.; Hasan, M. M.; Throne, J. E. , Effectiveness of sulfuryl fluoride for control of different life stages of stored-product psocids (Psocoptera). Journal of Economic Entomology 2012, 105, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenaga, E. E. , Time, temperature and dosage relationships of several insecticidal fumigants. Journal of Economic Entomology 1961, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C. In Factors affecting the efficacy of sulphuryl fluoride as a fumigant, Proceedings of the Ninth International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, ABRAPOS Rodovia, Brazil: 2006; pp 519-526.
- Programme, U. N. E. , Special review on achieving control of pest eggs by sulfuryl fluoride. Report of the Technology and Economic Assessment Panel. 2011, 110–136. [Google Scholar]
- Outram, I. , Factors affecting the resistance of insect eggs to sulphuryl fluoride—I: The uptake of sulphuryl-35S fluoride by insect eggs. Journal of Stored Products Research 1967, 3, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outram, I. , Factors affecting the resistance of insect eggs to sulphuryl fluoride—II: The distribution of sulphuryl-35S fluoride in insect eggs after fumigation. Journal of Stored Products Research 1967, 3, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Opit, G.; Margosan, D.; Tebbets, J.; Walse, S. , Egg morphology of key stored-product insect pests of the United States. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 2014, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Opit, G.; Margosan, D.; Hoffmann, D.; Tebbets, J.; Walse, S. , Comparative egg morphology and chorionic ultrastructure of key stored-product insect pests. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 2015, 108, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, H. E. , Respiratory systems. Biology of insect eggs 1981, 1, 95–148. [Google Scholar]
- Trougakos, I. P.; Margaritis, L. H. , Novel morphological and physiological aspects of insect eggs. Chemoecology of insect eggs and egg deposition 2003, 2–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kučerová, Z.; Stejskal, V. , Comparative egg morphology of silvanid and laemophloeid beetles (Coleoptera) occurring in stored products. Journal of Stored Products Research 2002, 38, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, J.; Russel, L. , Electron Microscopy, Specimen Preparation for Scanning Electron Microscopy. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston: 1992.
- Hayat, P. , Techniques of electron microscopy. Biological Applications 2000, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Matesco, V. C.; Fürstenau, B.; Bernardes, J. L.; Schwertner, C. F.; Grazia, J. , Morphological features of the eggs of Pentatomidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Zootaxa 2009, 1984, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesco, V. C.; Bianchi, F. M.; Fürstenau, B. B. R. J.; Da Silva, P. P.; Campos, L. A.; Grazia, J. , External egg structure of the Pentatomidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) and the search for characters with phylogenetic importance. Zootaxa, 2014; 3768, 351–385. [Google Scholar]
- Javahery, M. , Development of eggs in some true bugs (Hemiptera–Heteroptera). Part I. Pentatomoidea. The Canadian Entomologist 1994, 126, 401–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilimova, J.; Rohanova, M. , The external morphology of eggs of three Rhopalidae species (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) with a review of the eggs of this family. Acta Entomol Musei Natioalis Pragae 2010, 50, 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Arbogast, R. T.; Lecato, G. L.; Byrd, R. V. , External morphology of some eggs of stored-product moths (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae, Gelechiidae, Tineidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1980, 9, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C. H.; Price, N.; Chakrabarti, B. The Methyl Bromide Issue; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, 1997. [Google Scholar]
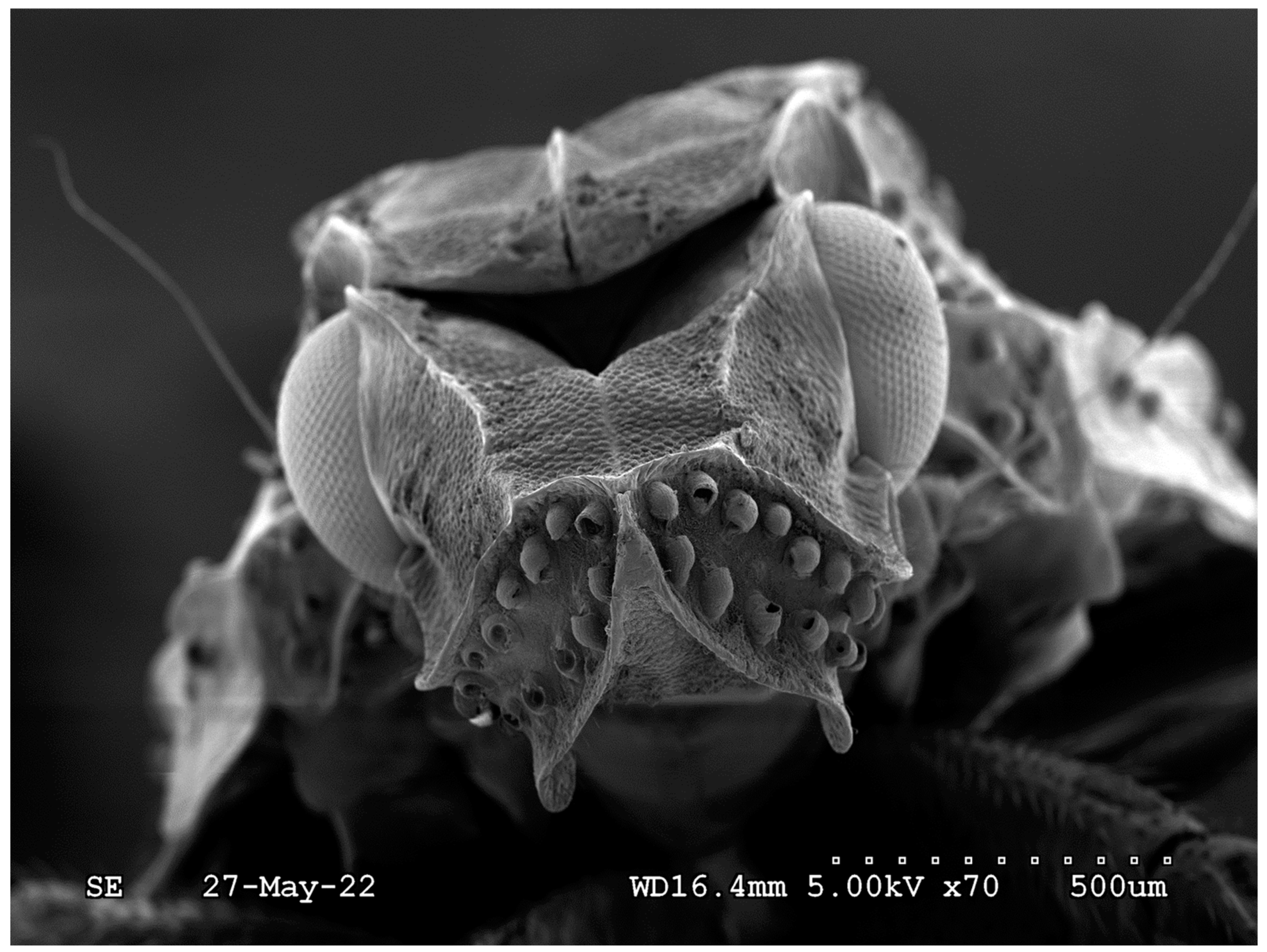
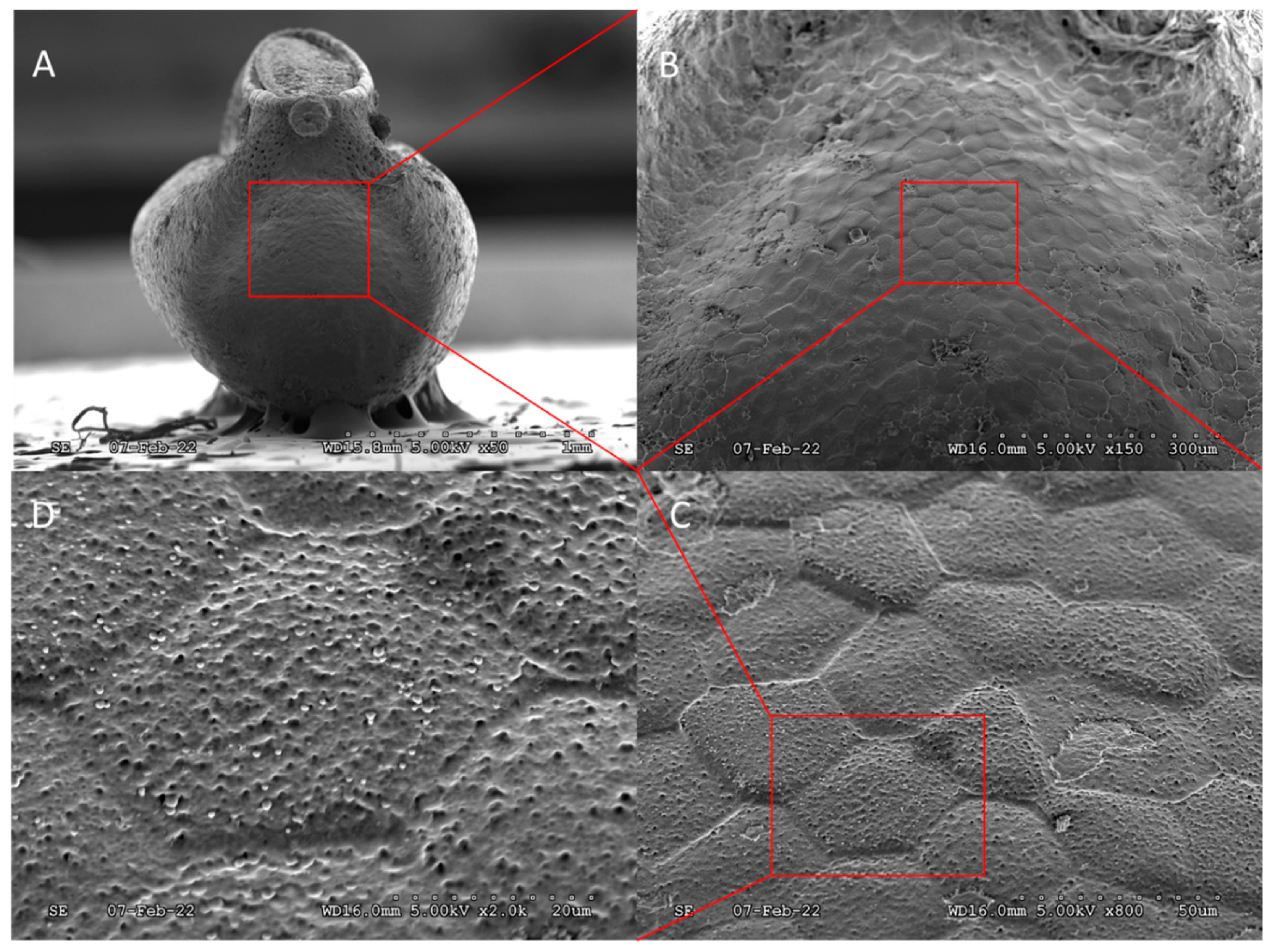


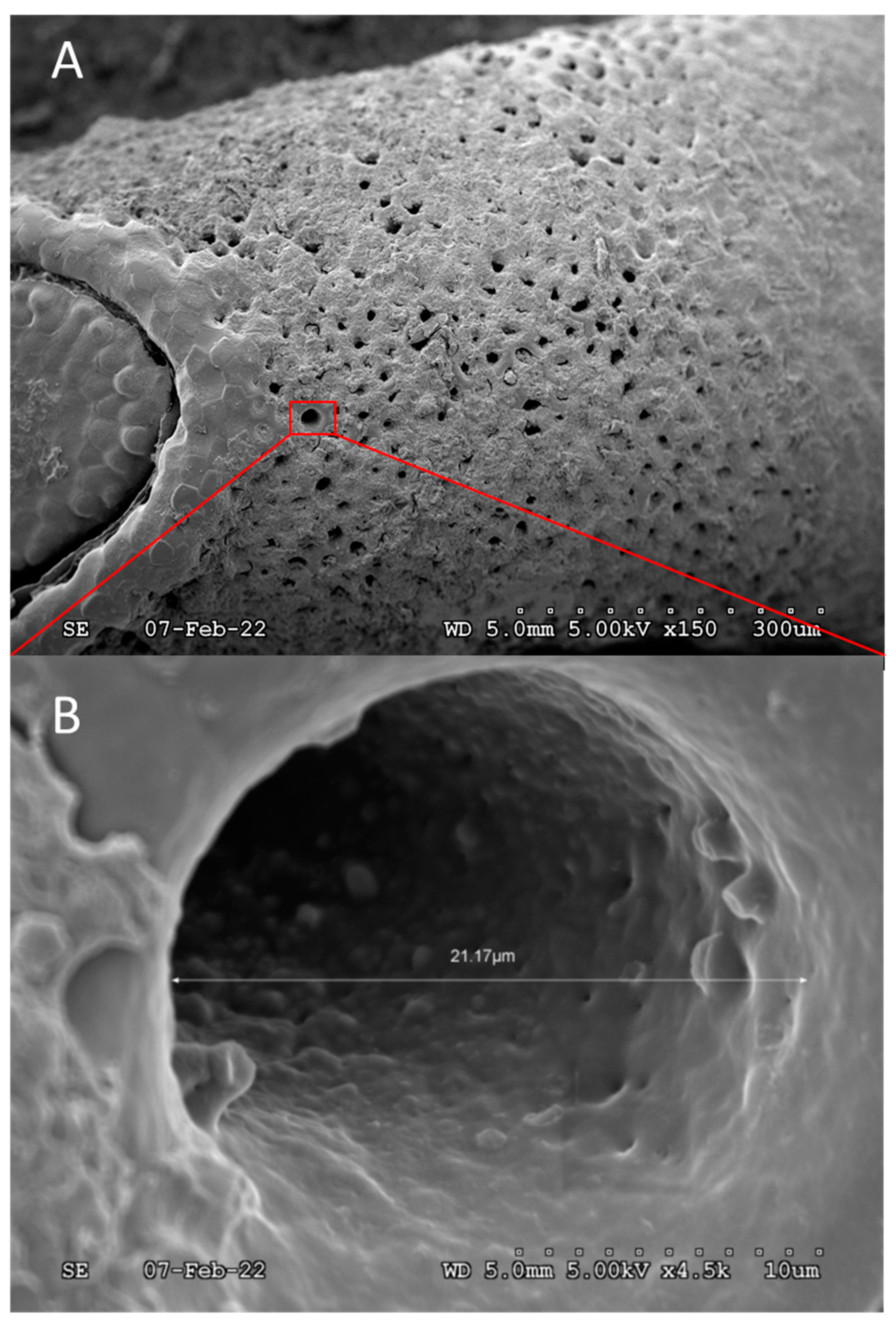
| Fumigant | Molecule diameter (nm) | Molecular area (nm2) | # molecules per pore (billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ethyl formate | 0.557 | 0.2435 | 1.15 |
| sulfuryl fluoride | 0.259 | 0.0527 | 5.31 |
| phosphine | 0.255 | 0.0510 | 5.48 |
| methyl bromide | 0.221 | 0.0383 | 7.29 |
| hydrogen cyanide | 0.219 | 0.0376 | 7.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





