1. Introduction
Research into calcium-ion batteries (CIBs), which utilize the redox reaction of calcium ions as an electrode process in secondary batteries, has gained significant momentum recently [
1,
2,
3,
4]. These batteries offer a promising alternative that could complement and diversify the energy storage landscape [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Calcium, being relatively abundant and cost-effective compared to certain other metals used in battery technologies, holds the potential to contribute to more sustainable and cost-efficient battery production. This abundance could play a crucial role in stabilizing renewable energy sources like solar and wind, thereby enhancing grid reliability. Moreover, by reducing reliance on materials with high environmental impact, such as cobalt and lithium, CIBs have the potential to foster more sustainable energy storage technologies.
CIBs are categorized into two primary groups determined by the nature of the electrolyte utilized: non-aqueous types, which employ organic materials similar to those found in commercially available lithium-ion batteries, and aqueous types, which use water-based materials. The choice between organic and aqueous electrolytes depends on specific battery application requirements, encompassing energy density, power output, safety considerations, and environmental impact. Organic electrolytes offer higher energy densities and broader voltage windows, while aqueous electrolytes provide enhanced safety and environmental benefits. Each type of electrolyte has its advantages and disadvantages, and the selection depends on the trade-offs acceptable for the particular battery system being developed. While most existing studies predominantly focus on the former category, there is a limited number of reports on the latter type.
The investigation of electrode materials for aqueous CIBs is an emerging research area. Our focus in this study was directed towards titanium disulfide (TiS
2). TiS
2 stands as a thoroughly investigated electrode material, recognized for its involvement in an intercalation-deintercalation reaction [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. This reaction involves the intercalation and deintercalation of metal ions within its layered crystal structure during charge and discharge cycles, enabling energy storage and release. Notably, this phenomenon holds true for non-aqueous CIBs as well [
24,
25]. Within non-aqueous solutions, the electrochemical intercalation and deintercalation of calcium ions into TiS
2 have been observed. However, it is surprising that TiS
2 has not been investigated as an electrode material for aqueous calcium CIBs. This gap in research served as the primary motivation behind the present study.
The purpose of this study is to understand the electrochemical redox reaction of calcium ions in TiS2 and, through this, to assess the applicability of TiS2 as an active material for aqueous CIBs. Additionally, the study aims to understand the effect of the electrolyte on the TiS2 electrode reaction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Electrode and Electrolytes
The working electrode was fabricated by blending TiS2 powder (Sigma-Aldrich, 99.9%, USA), carbon black (super P) (Alfa Aesar, 99+%, USA), graphite powder (SNO-15), and polyvinylidene fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, average Mw ~534,000 by GPC, powder, USA) in an 80:9:2:9 weight ratio. These constituents were gradually added to N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) (JUNSEI, 99+%, Japan) to form a slurry. The resultant slurry was coated onto a current collector and dried for 12 hours in a vacuum oven at 80 °C. Carbon cloth (Fuelcellearth, USA) and Ti foil (Nilaco, 99.5%, Japan) were used as current collectors for the Ca(NO3)2- and CaCl2-based electrolytes, respectively. For the counter electrode, a slurry was prepared by adding NMP dropwise to activated carbon (Sigma-Aldrich, -100 mesh particle size, USA) and polyvinylidene fluoride in a 9:1 weight ratio. This mixture was applied to the same current collector used for the working electrode and dried for 12 hours at 80 °C under vacuum. Electrolytes were formulated by dissolving Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (Alfa Aesar, 99–103%, USA) and CaCl2 (Alfa Aesar, 99.0–105.0%, USA) in pure water (Burdick & Jackson, HPLC grade, USA) respectively. Different electrolyte concentrations (1.0, 4.0, 7.0, and 8.0 mol dm–3 (M)) were employed to investigate variations in the electrochemical potential window and electrochemical performance based on concentration. The maximum concentration of 8.0 M was chosen considering the solubility of the calcium salts.
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
All electrochemical tests were performed using a custom-designed laboratory three-electrode cell within a battery test system (Wonatech, WBCS 3000, South Korea). The prepared TiS2 electrode served as the working electrode, while the activated carbon electrode was employed as the counter electrode. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) (Qrins, RE-2BP, 3.3 M potassium chloride, South Korea) was used as the reference electrode. Charge-discharge testing encompassed 5 cycles at a 0.1 C-rate (C), spanning a potential range of –1.0 to 0.76 V (vs. SCE). These tests were carried out using Ca(NO3)2 and CaCl2 electrolytes at varying concentrations.
2.3. Structure and Surface Analysis
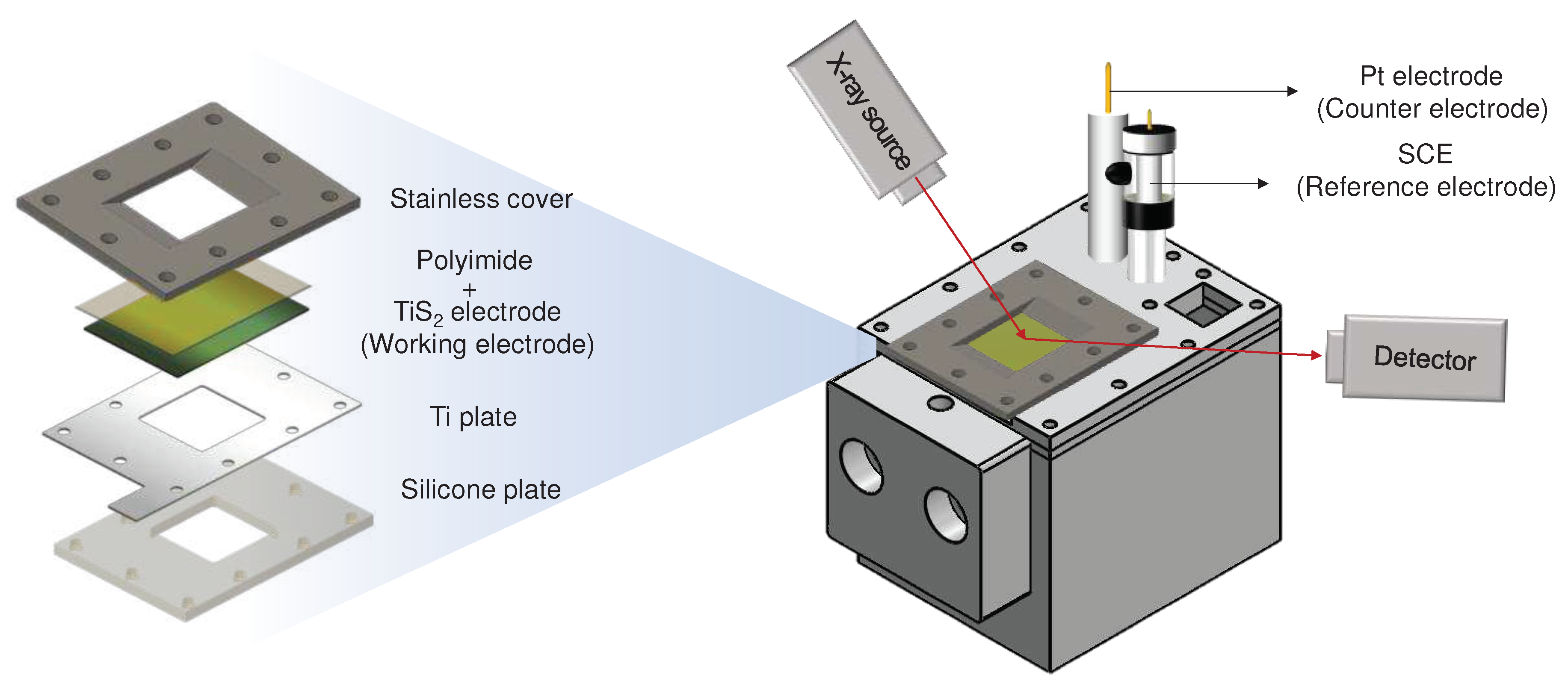
Modifications in the structure and surface composition of the TiS
2 electrode before and after charging and discharging were confirmed through X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Rigaku, Miniflex 600, Japan) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (Kratos Inc, Axis-Nova, USA) analyses. In-situ XRD analyses revealed alterations in interlayer spacing during the charging and discharging process of the TiS
2 electrode within the 2θ range of 10-80°. For in-situ XRD analysis, a self-fabricated laboratory cell (illustrated in
Figure 1) was employed. The working electrode was prepared by applying the slurry, as described in section 2.1, onto a polyimide film (DuPont, 25 µm thick Kapton
® 100HN film, USA), and then affixing the prepared film to a Ti plate (Nilaco, 0.15T, Japan), which served as the current collector. The counter electrode consisted of Pt mesh (WizMAC, net type, Korea), with SCE serving as the reference electrode. The electrolyte used was 8.0 M Ca(NO
3)
2, and charge/discharge test conditions matched those previously mentioned. Moreover, XPS was utilized to analyze the binding energy of calcium ions on the electrode surface after charging and discharging. Depth analysis was performed at 20 and 40 seconds after etching the surface with an argon ion laser.
3. Results and Discussion
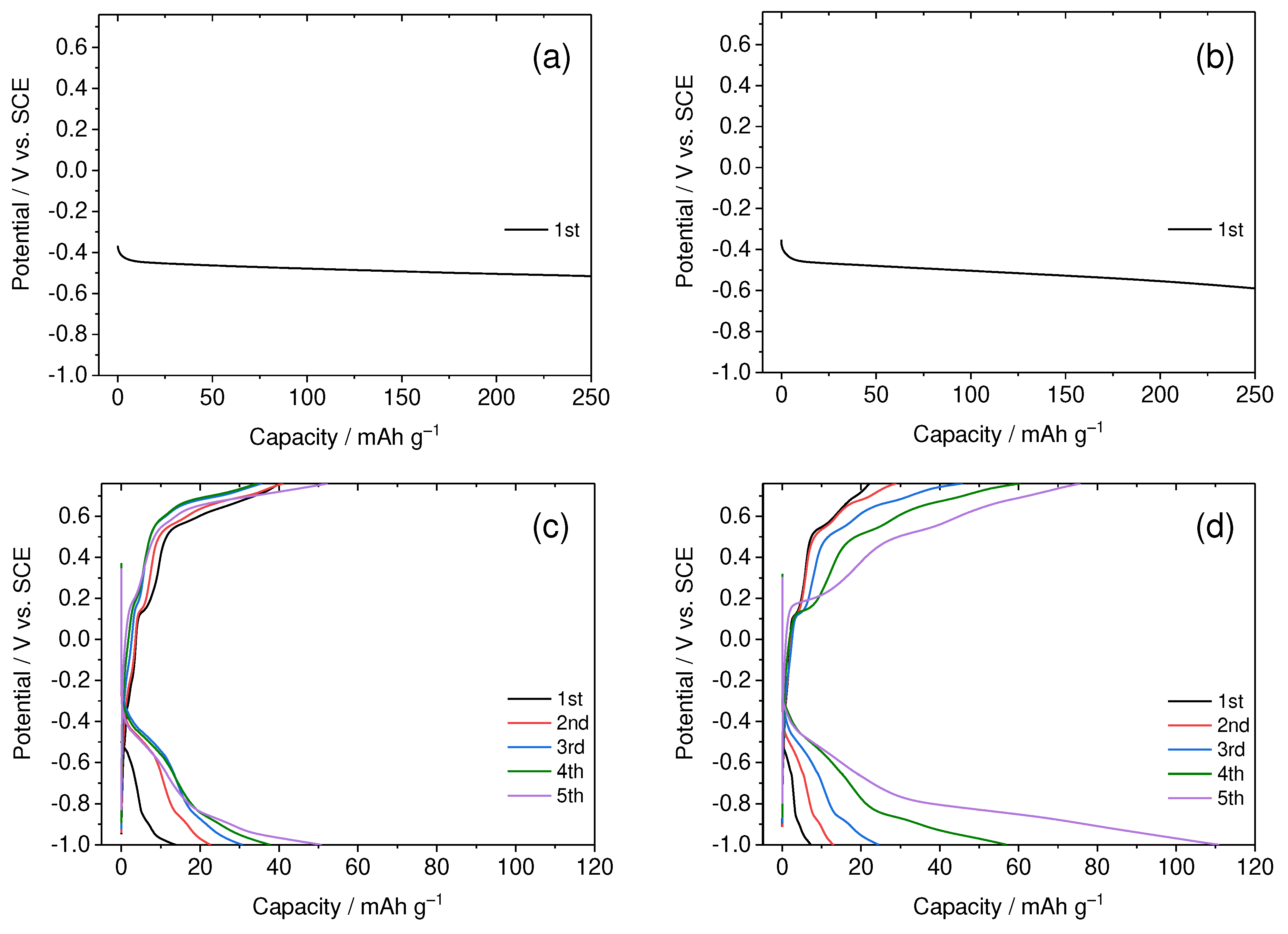
3.1. Dependence of Charge-Discharge Behavior on Electrolyte Concentration
Figure 2 depicts the electrochemical potential behavior of TiS
2 in aqueous solutions based on Ca(NO
3)
2 with varying concentrations. In both the 1.0 and 4.0 M electrolyte solutions, the TiS
2 electrode exhibited nearly identical potential behavior, maintaining a steady level around 0.5 V. It was visually confirmed that gas emerged from the electrode surface during this process. This gas is identified as hydrogen, resulting from the reductive decomposition of water molecules within the electrolyte solution. In other words, it means that TiS
2 does not function as an active material for aqueous CIBs due to the fact that the water decomposition reaction takes place prior (at a more positive potential) to the intercalation of calcium ions between the layers of TiS
2. In contrast, with the 7.0 and 8.0 M electrolyte solutions, the electrode potential dropped to –1.0 V during the reduction of Ca
2+ ions, resulting in verified charge capacity. Subsequently, discharge capacity from the oxidation reaction was also confirmed. This demonstrates the effectiveness of TiS
2 as an active material for aqueous CIBs, effectively suppressing the hydrogen generation reaction caused by water decomposition.
The suppression of the hydrogen generation reaction can be attributed to the decomposition of anions preceding water decomposition, resulting in a film forming on the electrode surface. This phenomenon is closely tied to changes in the solvation structure of Ca
2+ ions at higher concentrations. Increased concentration leads to higher counts of both Ca
2+ and NO
3– ions in the electrolyte. Previous studies have shown that not only water but also NO
3– ions coordinate with Ca
2+ ions under these conditions [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. Consequently, the number of water molecules coordinating with each Ca
2+ ion decreases. This results in the generation of numerous contact ion pairs in the electrolyte solution, leading to ion aggregation [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. In this process, NO
3– ions transfer electrons to Ca
2+ ions, resulting in a reduction of the energy level of the low unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of NO
3– ions [
18,
27,
28,
29,
31,
39]. Consequently, it is hypothesized that NO
3– ions undergo preferential reduction (at more positive potentials) prior to water decomposition. This preference leads to the generation of a film derived from NO
3– on the electrode surface. This can be comprehended as a phenomenon closely resembling the anion-derived solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formed on the surface of negative electrode when an aqueous solution with a high concentration of Li
+ ions is employed as the electrolyte [
39,
40,
41,
42]. Similarly, a NO
3–-derived SEI forms on the surface of TiS
2 electrode within an aqueous solution containing a high concentration of Ca
2+ ions, suppressing electrolyte decomposition reactions such as hydrogen generation and promoting intercalation and deintercalation reactions of Ca
2+ ions.
Another notable feature in
Figure 2c is the considerably larger discharge capacity compared to the charge capacity. Moreover, as cycling progressed, the charge capacity gradually increased, narrowing the gap between charging and discharging capacities. This suggests that, during discharge, the deintercalation of Ca
2+ ions occurred alongside the oxidation reaction of the electrolyte. The effectiveness of the NO
3–-derived film as an SEI improved over cycling. A similar trend is also evident in
Figure 2d. However, a slightly distinct observation is that the charge capacity exhibited a more pronounced increase than in
Figure 2c, implying a more effective SEI formation in higher concentrations. This supports the notion that the SEI formation is driven by the reduction of NO
3– ions with lower LUMO energy levels due to their coordination with Ca
2+ ions. This phenomenon is attributed to the greater presence of NO
3– ions with lower LUMO energy levels due to coordination with Ca
2+ ions in the 8.0 M aqueous solution compared to the 7.0 M solution.
3.2. In-Situ Structural Analysis of TiS2 during Charging and Discharging
The charge and discharge behavior of the TiS
2 electrode were significantly influenced by the electrolyte concentration, as discussed previously. To confirm the intercalation and deintercalation of Ca
2+ ions into and from TiS
2 at higher concentrations, we employed in-situ XRD. This technique allowed us to examine the associated structural modifications in detail.
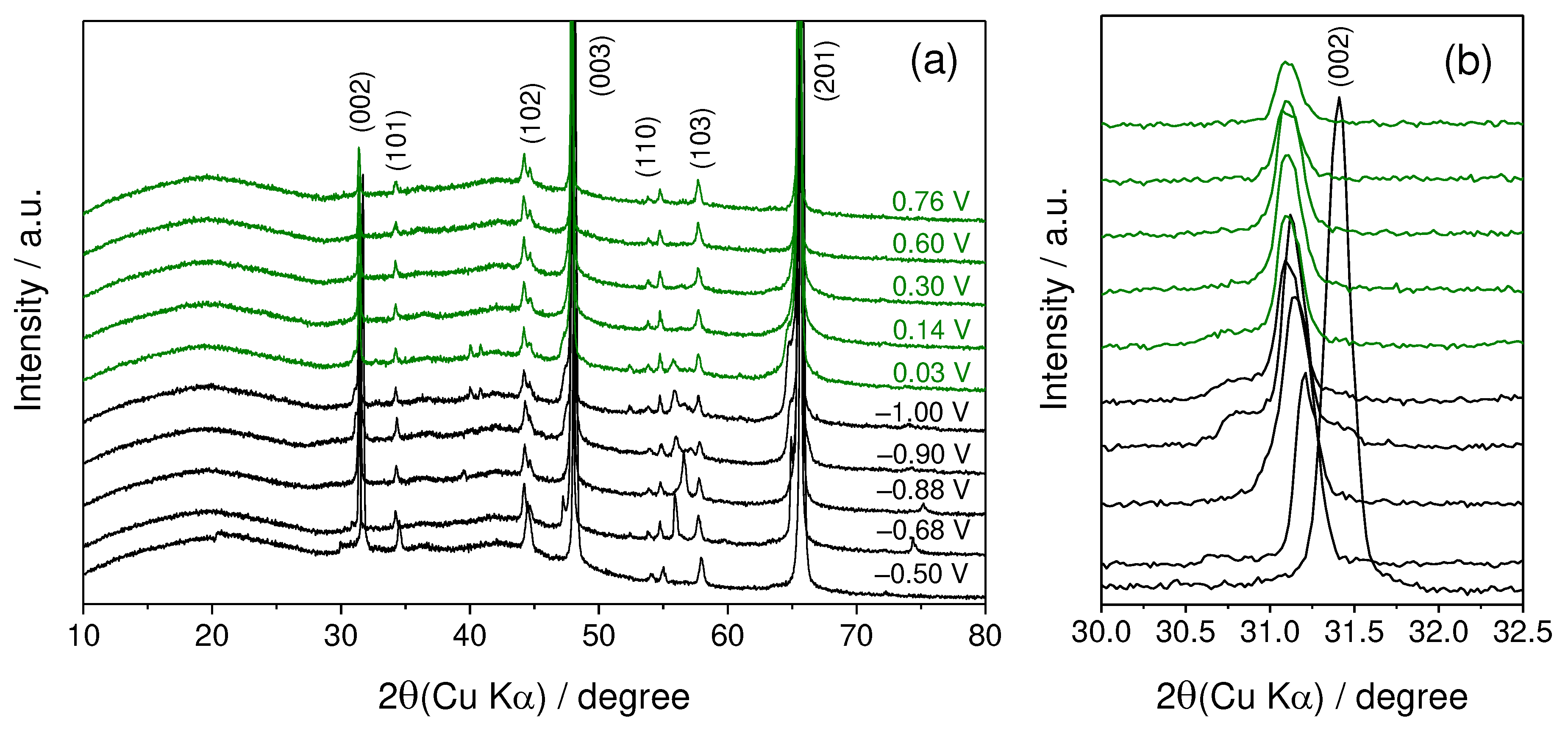
Figure 3 presents XRD patterns of TiS
2 in an 8.0 M Ca(NO
3)
2 solution collected during the charge and discharge processes using the three-electrode cell shown in
Figure 1. The strong (002) peak of the pristine electrode was observed at 31.4° in 2θ. This peak gradually shifted to a lower angle during the charging process, reaching 31.1° after being charged to –1.0 V. This shift corresponds to an expansion of the interlayer spacing due to the intercalation of Ca
2+ ions between TiS
2 layers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first confirmation of the electrochemical intercalation of calcium ions between TiS
2 layers in an aqueous electrolyte solution. While previous reports have described the insertion of calcium ions using an organic electrolyte with a wide potential window [
24,
25], there has been no prior report of calcium ion insertion using an aqueous solution with a much narrower potential window compared to the organic electrolyte. In other words, this suggests that TiS
2 can serve as an active material in aqueous CIBs.
On the other hand, the (002) peak, which shifted during charging, did not revert to its original position during discharge. Instead, it remained in the shifted position after charging was completed. This phenomenon likely results from the partial retention of Ca
2+ ions within the TiS
2 structure, as further explained in the XPS analysis results. These intercalated Ca
2+ ions do not completely deintercalate during discharge, continuing to occupy the interlayer spaces. Tchitchekova et al. conducted a study on the diffusion behavior of Ca
2+ ions when the interlayer spacing of TiS
2 expanded by 10% and 15%, based on DFT calculations [
24]. Their findings indicated a reduced activation barrier to Ca
2+ ion diffusion due to the expanded interlayer spacing. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that the observed expansion of the interlayer gap in
Figure 3, along with the improvements in the SEI described in the previous section, facilitated the diffusion of Ca
2+ ions, leading to an increase in capacity over cycling.
Another noteworthy observation in
Figure 3 is the broadening of the (002) peak after a single charge-discharge cycle. This suggests a decrease in the crystallinity of the TiS
2 active material. Although the exact cause remains unclear, one plausible explanation is the nonuniform diffusion of inserted ions [
43]. When metal ions intercalate between TiS
2 layers, they induce phase separation in TiS
2. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy results conducted by the Li group revealed that TiS
2 undergoes a stepwise phase transformation during the intercalation of K
+ ions, resulting in uneven diffusion of these ions [
22]. This stepwise phase transformation is not limited to K
+ ions; it also occurs during the intercalation of Na
+ ions [
44]. In essence, it is presumed that the crystallinity declined even after discharge due to the incomplete desorption of all unevenly intercalated Ca
2+ ions.
Figure 3.
(a) In-situ XRD patterns during the charge-discharge test of TiS2 electrode in an 8.0 M Ca(NO3)2 dissolved aqueous electrolyte at a voltage range between –1.0 and 0.76 V. (b) shows the expansion in the regions of the (002) peak.
Figure 3.
(a) In-situ XRD patterns during the charge-discharge test of TiS2 electrode in an 8.0 M Ca(NO3)2 dissolved aqueous electrolyte at a voltage range between –1.0 and 0.76 V. (b) shows the expansion in the regions of the (002) peak.
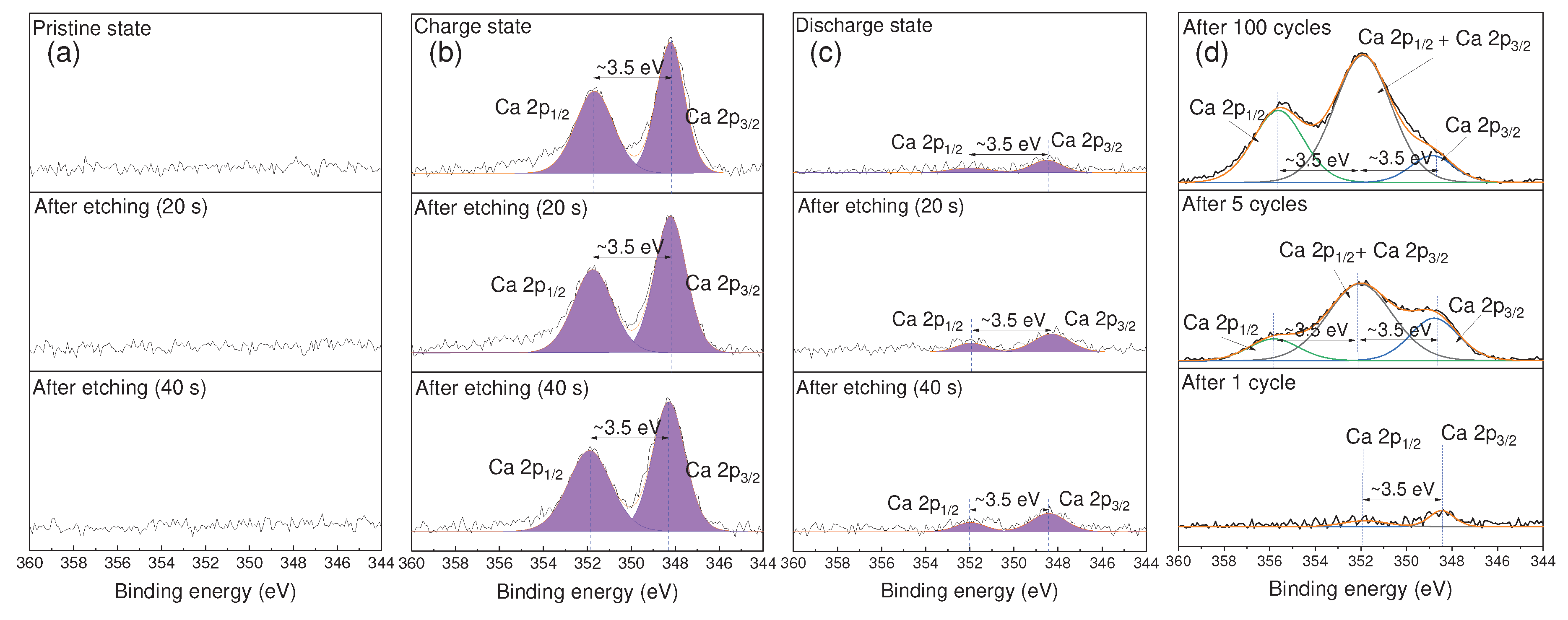
3.3. XPS Analysis of TiS2 Electrode Before and After Discharging
To investigate the intercalation-deintercalation behavior of Ca
2+ ions and the formation of an SEI, we conducted XPS analysis on TiS
2 electrodes in both their charged and discharged states, and the results are depicted in
Figure 4. After charging (
Figure 4b), two distinct peaks emerged at approximately 348.4 eV and 351.9 eV, corresponding to the binding energies of Ca 2p
3/2 and Ca 2p
1/2, respectively [
45]. The approximately 3.5 eV difference between these peaks is attributed to spin-orbit splitting. These peaks indicate the formation of calcium compounds on the electrode surface as a result of anion reduction coordinated with Ca
2+ ions. Even after etching for 40 seconds, these peaks persisted, suggesting the presence of Ca atoms not only on the electrode surface but also within the TiS
2 layers. This implies the intercalation of Ca
2+ ions between TiS
2 layers, indicating that the calcium compound generated on the electrode surface functions as the SEI. This SEI may either dissolve or undergo changes in its properties when exposed to free water molecules that are not coordinated to Ca
2+ ions [
30]. However, in high-concentration electrolyte solutions, where free water molecules are scarce, the SEI is believed to function effectively.
On the other hand, in the discharged state (
Figure 4c), the peak intensity decreased compared to the charged state but did not vanish entirely. Two peaks were observed at the same positions as in the charged state, indicating that some Ca
2+ ions remained intercalated between the TiS
2 layers. These remaining Ca
2+ ions may have been directly responsible for both maintaining the expanded interlayer gap of TiS
2 and lowering the crystallinity of TiS
2 even after discharge previously described in
Figure 3.
To further investigate the evolution of the SEI on the surface of the TiS
2 electrode as cycling progressed, the Ca 2p binding energy on the TiS
2 electrode was examined after 1, 5, and 100 cycles, as shown in
Figure 4d. As cycling continued, the peak area increased, indicating an increase in calcium compounds due to electrolyte decomposition during the repair of the damaged SEI caused by the expansion and contraction of the active material (TiS
2) over 100 charge-discharge cycles. Furthermore, with ongoing cycling, the peak area around ~348.4 eV decreased, while the area around ~351.9 eV increased, and a new peak emerged at ~355.4 eV. This change in peak area and the appearance of a new peak can be attributed to a peak shift of Ca 2p by approximately ~3.5 eV in some of the initially formed calcium compounds. Such shifts usually occur due to changes in the chemical environment of the calcium atom. While it remains unclear which specific factors induce these shifts and why only some Ca 2p peaks are affected, identifying these factors will be crucial for future research in this study.
Figure 4.
(a-d) The Ca 2p region of XPS spectra of the TiS2 electrode, including both unetched and etched samples at 20 and 40 seconds. (a) Pristine, (b) charge, and (c) discharge states. (d) Ca 2p region of the XPS spectra in the pristine state, after 1, 5, and 100 cycles of the TiS2 electrode.
Figure 4.
(a-d) The Ca 2p region of XPS spectra of the TiS2 electrode, including both unetched and etched samples at 20 and 40 seconds. (a) Pristine, (b) charge, and (c) discharge states. (d) Ca 2p region of the XPS spectra in the pristine state, after 1, 5, and 100 cycles of the TiS2 electrode.
3.4. Anion Dependence of Charge-Discharge Behavior
As previously mentioned, we have confirmed the occurrence of electrochemical intercalation-deintercalation reactions involving Ca
2+ ions at the TiS
2 electrode. This confirmation was achieved using aqueous solutions containing a high concentration of Ca(NO
3)
2 as the electrolyte. The enabling factor for this intercalation process lies in the formation of the SEI on the surface of the TiS
2 electrode. Our interpretation is that the reduction of anions plays a crucial role in SEI generation. To further substantiate this interpretation, we prepared an aqueous solution with a high concentration of CaCl
2 instead of Ca(NO
3)
2 and subsequently investigated the charging and discharging behavior within this solution. Essentially, we altered the anion coordinated with Ca
2+ ions from NO
3– to Cl
– to assess the impact of the anion on the charge and discharge behavior. The results of this experiment are presented in
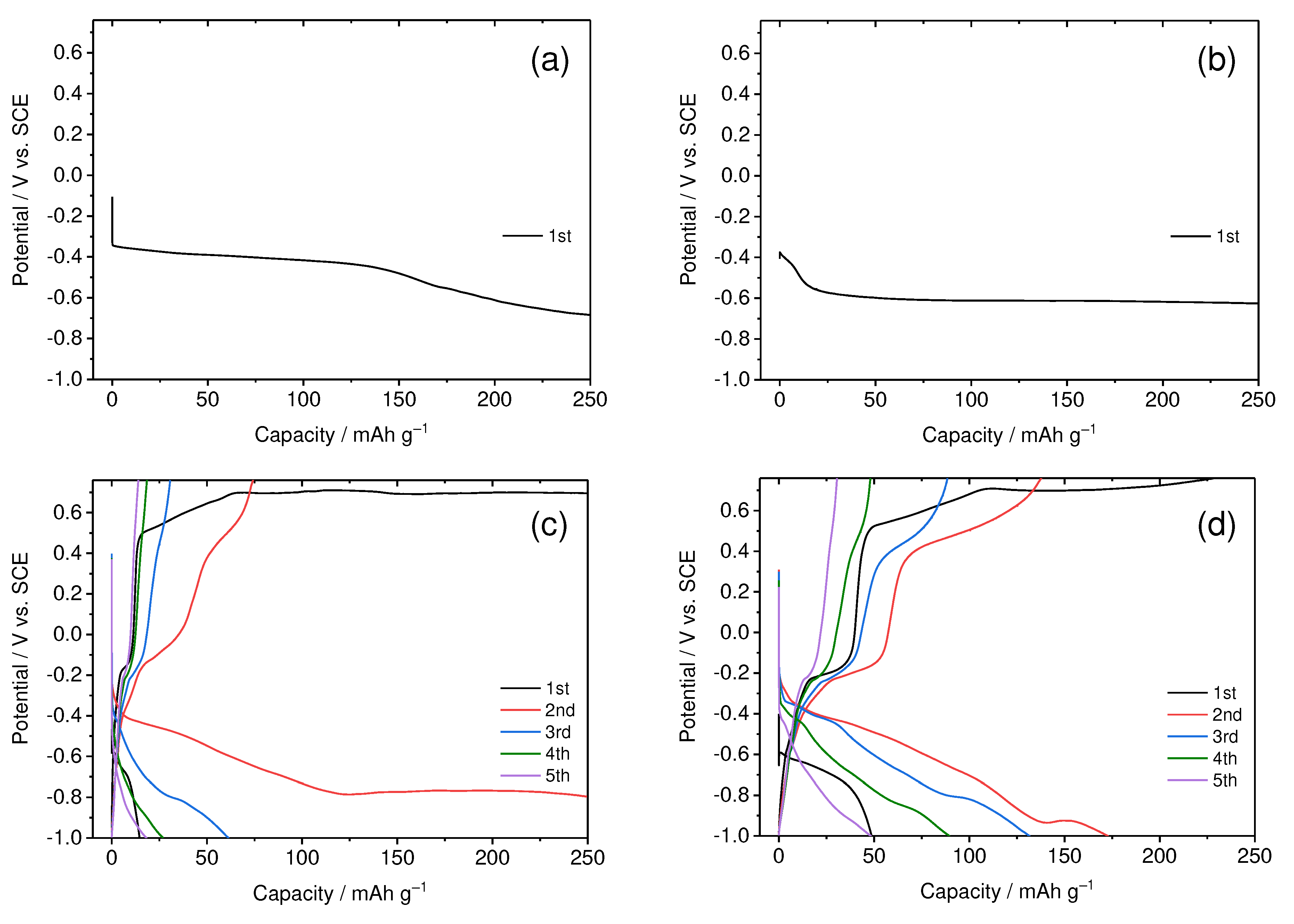
Figure 5.
In the CaCl
2-based aqueous solution, we observed a charge-discharge behavior similar to what was obtained in the Ca(NO
3)
2-based aqueous solution (as confirmed in
Figure 2). Notably, charging and discharging of the TiS
2 electrode were not possible at 1.0 and 4.0 M concentrations, but they became feasible at 7.0 and 8.0 M. Previous research has noted that at high concentrations, CaCl
2-based aqueous solutions form contact ion pairs similar to those in Ca(NO
3)
2-based aqueous solutions [
46,
47]. Consequently, the coordination of Ca
2+ ions with water molecules decreases while Cl
– ions become involved in coordination [
46,
47]. In high-concentration environments, it can be anticipated that the energy level of the LUMO of Cl
– ions will decrease, resulting in a higher reduction potential. With this understanding, we can explain the stark differences in charge and discharge behavior shown in
Figure 5 by dividing it into two cases: first, the reduction reaction of water molecules generating hydrogen occurs, preventing charge and discharge (
Figure 5a,b); second, the reduction reaction of Cl
– ions, producing an SEI, takes place first, allowing for subsequent charging and discharging (
Figure 5c,d).
Notably, the irreversible capacity and cycling behavior exhibited significant deviations from those observed in the Ca(NO3)2-based aqueous solution. In the initial cycle, the discharge capacity surpassed the charge capacity, suggesting that, in addition to the deintercalation of Ca2+ ions during discharge, there were concurrent decomposition reactions involving the electrolyte or SEI formed during charging. Furthermore, as the cycling continued, there was a rapid decrease in discharge capacity. We attribute these differences in irreversible capacity and cycling behavior to variations in the properties of the SEI formed in each electrolyte solution. In essence, once the SEI forms through electrolyte decomposition, it should ideally restrain further electrolyte decomposition while allowing the smooth passage of metal ions during subsequent cycles to maintain stability. Consequently, it is evident that discrepancies in charging and discharging behavior arise due to differences in the SEI's ability to fulfill these essential functions.
Figure 5.
Charge and discharge curves of TiS2 electrode in aqueous solutions with varied CaCl2 concentrations: (a) 1.0, (b) 4.0, (c) 7.0, and (d) 8.0 M. The measurements were conducted at a 0.1 C-rate.
Figure 5.
Charge and discharge curves of TiS2 electrode in aqueous solutions with varied CaCl2 concentrations: (a) 1.0, (b) 4.0, (c) 7.0, and (d) 8.0 M. The measurements were conducted at a 0.1 C-rate.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we explored the potential of TiS2 as an active material for CIBs. Our investigation focused on the electrochemical redox reaction of calcium ions in TiS2 and its applicability as an active material for aqueous CIBs. We examined the dependence of charge-discharge behavior on electrolyte concentration, revealing that TiS2 effectively suppresses hydrogen generation and functions as an active material for aqueous CIBs in higher electrolyte concentrations. This suppression is attributed to the formation of an anion-derived SEI on the electrode surface, facilitated by changes in the solvation structure of Ca2+ ions at higher concentrations. Additionally, in-situ structural analysis using XRD confirmed the intercalation of Ca2+ ions into TiS2 during charging, marking the first confirmation of this electrochemical intercalation in an aqueous electrolyte solution. The XPS analysis further supported this finding, indicating the presence of Ca atoms not only on the electrode surface but also within the TiS2 layers. Furthermore, our study investigated the influence of anions on charge-discharge behavior by comparing Ca(NO3)2 and CaCl2-based electrolytes. The results showed that the choice of anion had a significant impact on SEI formation and consequently on the charge–discharge behavior. While both electrolytes allowed for TiS2 to function as an active material at higher concentrations, variations in irreversible capacity and cycling behavior highlighted the importance of SEI properties in dictating the performance of CIBs. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that TiS2 holds promise as an active material for aqueous CIBs, providing insights into the crucial role of SEI formation and anion choice in influencing CIB performance. This study contributes to the growing body of research in the field of CIBs, offering potential solutions for sustainable and environmentally friendly energy storage technologies. Further exploration of TiS2 and SEI engineering in CIBs may lead to improved energy storage solutions with broader applications in the renewable energy sector and beyond.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S., H.L., and S.-K.J.; Methodology, H.L., P.M.N., and Y.K.; Formal Analysis, S.S., H.L., S.L., and C.L.; Investigation, S.S. and H.L.; Resources, S.S. and H.L.; Data Curation, S.S. and H.L.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, S.S., H.L., and S.L.; Writing-Review & Editing, S.S., S.L., and S.-K.J.; Supervision, S.-K.J.; Project Administration, S.-K.J.; Funding Acquisition, S.-K.J.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1I1A3060329). This work was supported by Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (1415182582, Automotive Industry Technology Development). This work also received support from the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zaman, W.; Hatzell, K.B. Processing and manufacturing of next generation lithium-based all solid-state batteries. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2022, 26, 101003. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jeong, S.R.; Tao, S. Key materials and future perspective for aqueous rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100096. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Choi, J.W. Opportunities and Reality of Aqueous Rechargeable Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001386 . [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.-K.; Mevawalla, A.; Aziz, A.; Panchal, S.; Xie, Y.; Fowler, M. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Runaway Modeling and Diagnosis Approaches. Processes 2022, 10, 1192 . [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; He, H.; Yao, W.; Tang, Y. Recent Advances and Perspectives on Calcium-Ion Storage: Key Materials and Devices. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, e2005501 . [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Huang, W. Solvation Structures in Aqueous Metal-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202068. [CrossRef]
- Gheytani, S.; Liang, Y.; Wu, F.; Jing, Y.; Dong, H.; Rao, K.K.; Chi, X.; Fang, F.; Yao, Y. An aqueous ca-ion battery. Advanced Science 2017, 4, 1700465.
- Lee, C.; Jeong, S.-K. A novel strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of a prussian blue an-alogue electrode for calcium-ion batteries. Electrochemistry 2018, 86, 134-137.
- Purbarani, M.E.; Hyoung, J.; Hong, S.-T. Crystal-water-free potassium vanadium bronze (K0. 5V2O5) as a cathode material for ca-ion batteries. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2021, 4, 7487-7491.
- Alvarez Ferrero, G.; Åvall, G.; Mazzio, K.A.; Son, Y.; Janßen, K.; Risse, S.; Adelhelm, P. Co-intercalation batteries (CoIBs): Role of TiS2 as electrode for storing solvated Na ions. Advanced Energy Materials 2022, 12, 2202377.
- Whittingham, M.S. Electrical Energy Storage and Intercalation Chemistry. Science 1976, 192, 1126–1127 . [CrossRef]
- Whittingham, M. Chemistry of intercalation compounds: Metal guests in chalcogenide hosts. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1978, 12, 41–99 . [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Xia, W.; Ming, C.; Han, Y.; Cao, L.; Lu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; et al. Semimetal or Semiconductor: The Nature of High Intrinsic Electrical Conductivity in TiS2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 6996–7001 . [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bates, J.B.; Hart, F.X.; Sales, B.C.; Zuhr, R.A.; Robertson, J.D. Characterization of Thin-Film Rechargeable Lithium Batteries with Lithium Cobalt Oxide Cathodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3203–3213 . [CrossRef]
- Striebel, K.A.; Deng, C.Z.; Wen, S.J.; Cairns, E.J. Electrochemical Behavior of LiMn2 O 4 and LiCoO2 Thin Films Produced with Pulsed Laser Deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 1821–1827 . [CrossRef]
- Prosini, P.P.; Lisi, M.; Zane, D.; Pasquali, M. Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4. Solid State Ionics 2002, 148, 45–51 . [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bonnick, P.; Nazar, L.F. Layered TiS2 positive electrode for Mg batteries. ACS Energy Letters 2016, 1, 297-301.
- Zhang, L.; Hou, X.; Edström, K.; Berg, E.J. Reactivity of TiS2 anode towards electrolytes in aqueous lithium-ion batteries. Batteries & Supercaps 2022, 5, e202200336.
- Sun, W.; Suo, L.; Wang, F.; Eidson, N.; Yang, C.; Han, F.; Ma, Z.; Gao, T.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. “Wa-ter-in-salt” electrolyte enabled LiMn2O4/TiS2 lithium-ion batteries. Electrochemistry Communications 2017, 82, 71-74.
- Chung, S.-H.; Luo, L.; Manthiram, A. TiS2–polysulfide hybrid cathode with high sulfur loading and low electrolyte consumption for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Energy Letters 2018, 3, 568-573.
- Tian, B.; Tang, W.; Leng, K.; Chen, Z.; Tan, S.J.R.; Peng, C.; Ning, G.-H.; Fu, W.; Su, C.; Zheng, G.W.; et al. Phase Transformations in TiS2 during K Intercalation. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1835–1840 . [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zou, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, G.; Bai, J.; Gao, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.-S.; et al. TiS2 as a high performance potassium ion battery cathode in ether-based electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 12, 216–222 . [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tai, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.W.; Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Lai, W.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Ultrathin 2D TiS2 nanosheets for high capacity and long-life sodium ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2019, 9, 1803210.
- Tchitchekova, D.; Ponrouch, A.; Verrelli, R.; Broux, T.; Frontera, C.; Sorrentino, A.; Bardé, F.; Biskup, N.; Arroyo-de Dompablo, M.E.; Palacín, M.R. Electrochemical Intercalation of Calcium and Magnesium in TiS2: Fundamental Studies Related to Multivalent Battery Applications. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 847–856 . [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, Y.-T.; Nogales, P.M.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Yin, R.-Z.; Jeong, S.-K. Electrochemical interca-lation of Ca2+ ions into TiS2 in organic electrolytes at room temperature. Electrochemistry Communications 2019, 98, 115-118.
- Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, Z.; Cai, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, H.; Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Shu, J. Organic interlayer engineering of TiS2 for enhanced aqueous Zn ions storage. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 135–141 . [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Borodin, O.; Gao, T.; Olguin, M.; Ho, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, K. “Water-in-salt” elec-trolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries. Science 2015, 350, 938-943.
- Yamada, Y.; Usui, K.; Sodeyama, K.; Ko, S.; Tateyama, Y.; Yamada, A. Hydrate-melt electrolytes for high-energy-density aqueous batteries. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16129 . [CrossRef]
- Kühnel, R.-S.; Reber, D.; Battaglia, C. A High-Voltage Aqueous Electrolyte for Sodium-Ion Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2005–2006 . [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.J.; Chang, D.; Kim, J.; Moon, S.; Oh, K.; Park, K.-Y.; Seong, W.M.; Park, H.; Kwon, G.; et al. Toward a low-cost high-voltage sodium aqueous rechargeable battery. Mater. Today 2019, 29, 26–36 . [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Jaumaux, P.; Gao, X.; Fu, Y. A universal strategy towards high–energy aqueous multivalent–ion batteries. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 2857.
- Cao, L.; Li, D.; Hu, E.; Xu, J.; Deng, T.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.-Q.; Wang, C. Solvation Structure Design for Aqueous Zn Metal Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21404–21409 . [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Pan, L.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Lin, H.; Mao, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, L.; Liu, H.; Pan, K.; et al. Electrolyte additive engineering for aqueous Zn ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 51, 733–755 . [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, S.-K. Modulating the hydration number of calcium ions by varying the electrolyte concen-tration: Electrochemical performance in a prussian blue electrode/aqueous electrolyte system for calci-um-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2018, 265, 430-436.
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Fu, J.; Feng, G. Progress on predicting the electrochemical stability window of electrolytes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 34, 101030. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Feng, G.; Qiao, R. Water-in-salt electrolytes: An interfacial perspective. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 47, 99–110 . [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, S.; Yan, J.; Mao, B.; Kornyshev, A.A.; Feng, G. Minimizing the electrosorption of water from humid ionic liquids on electrodes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9 . [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, J.; Ye, T.; Ye, J.; Zhao, C.; Bi, S.; Yan, J.; Mao, B.; Feng, G. Adding salt to expand voltage window of humid ionic liquids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10 . [CrossRef]
- Vatamanu, J.; Borodin, O. Ramifications of Water-in-Salt Interfacial Structure at Charged Electrodes for Electrolyte Electrochemical Stability. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 4362–4367 . [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Suo, L. Water-in-salt widens the electrochemical stability window: Thermodynamic and kinetic factors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 29, 100818 . [CrossRef]
- Adil; Ghosh, A.; Mitra, S. Water-in-Salt Electrolyte-Based Extended Voltage Range, Safe, and Long-Cycle-Life Aqueous Calcium-Ion Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25501–25515 . [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Oh, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Borodin, O.; Gao, T.; Wang, F.; Kushima, A.; Wang, Z.; Kim, H.-C.; et al. How Solid-Electrolyte Interphase Forms in Aqueous Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18670–18680 . [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, J.; Luo, B.; Knibbe, R.; Lin, T.; Hu, H.; Rana, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gu, Q. Sandwich-like ultrathin TiS2 nanosheets confined within N, S codoped porous carbon as an effective polysulfide promoter in lithium-sulfur batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2019, 9, 1901872.
- Starnberg, H. Recent developments in alkali metal intercalation of layered transition metal dichalcogeni-des. Modern Physics Letters B 2000, 14, 455-471.
- Bezerra, C.d.S.; Valerio, M.E.G. Structural and optical study of CaF2 nanoparticles produced by a mi-crowave-assisted hydrothermal method. Physica B: Condensed Matter 2016, 501, 106-112.
- Rudolph, W.W.; Irmer, G. Hydration of the calcium (II) ion in an aqueous solution of common anions (ClO4–, Cl–, Br–, and NO3–). Dalton Transactions 2013, 42, 3919-3935.
- Li, M.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Weare, J. The structure, dynamics and solvation mechanisms of ions in water from long time molecular dynamics simulations: a case study of CaCl2(aq) aqueous solutions. Mol. Phys. 2008, 106, 2685–2697 . [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).