Submitted:
13 September 2023
Posted:
14 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Case presentation
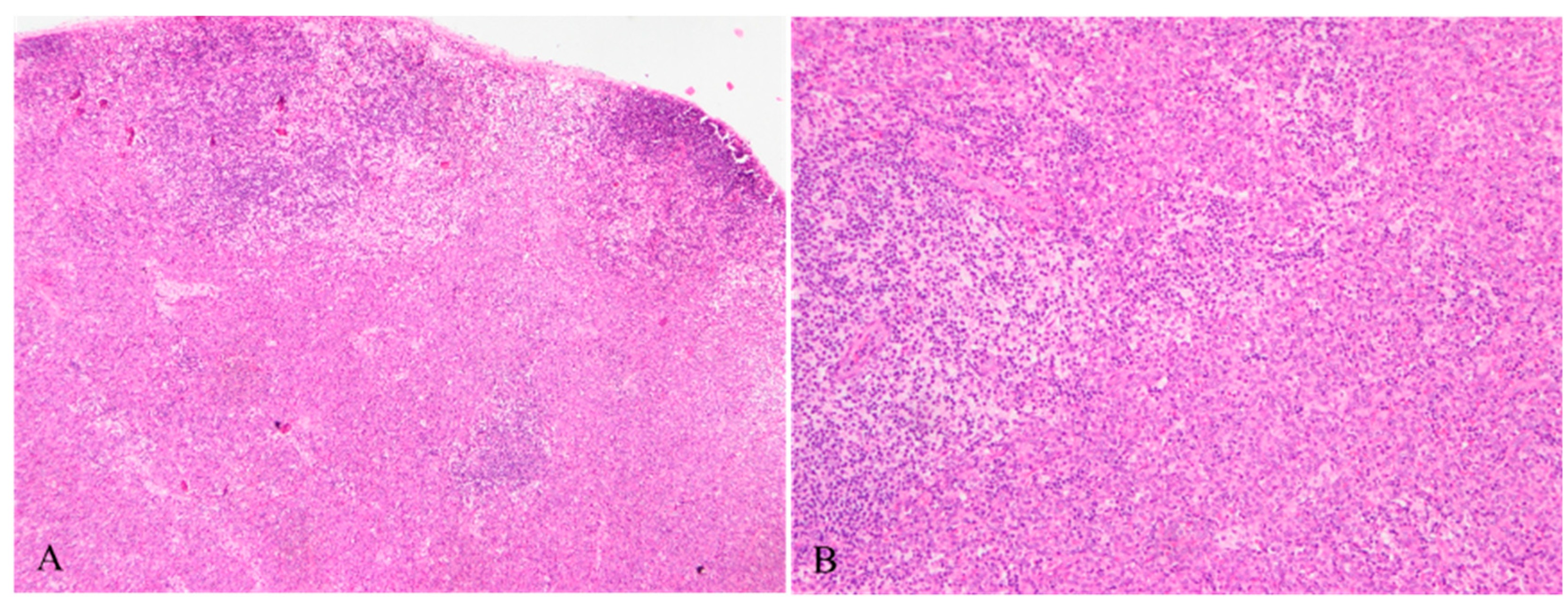
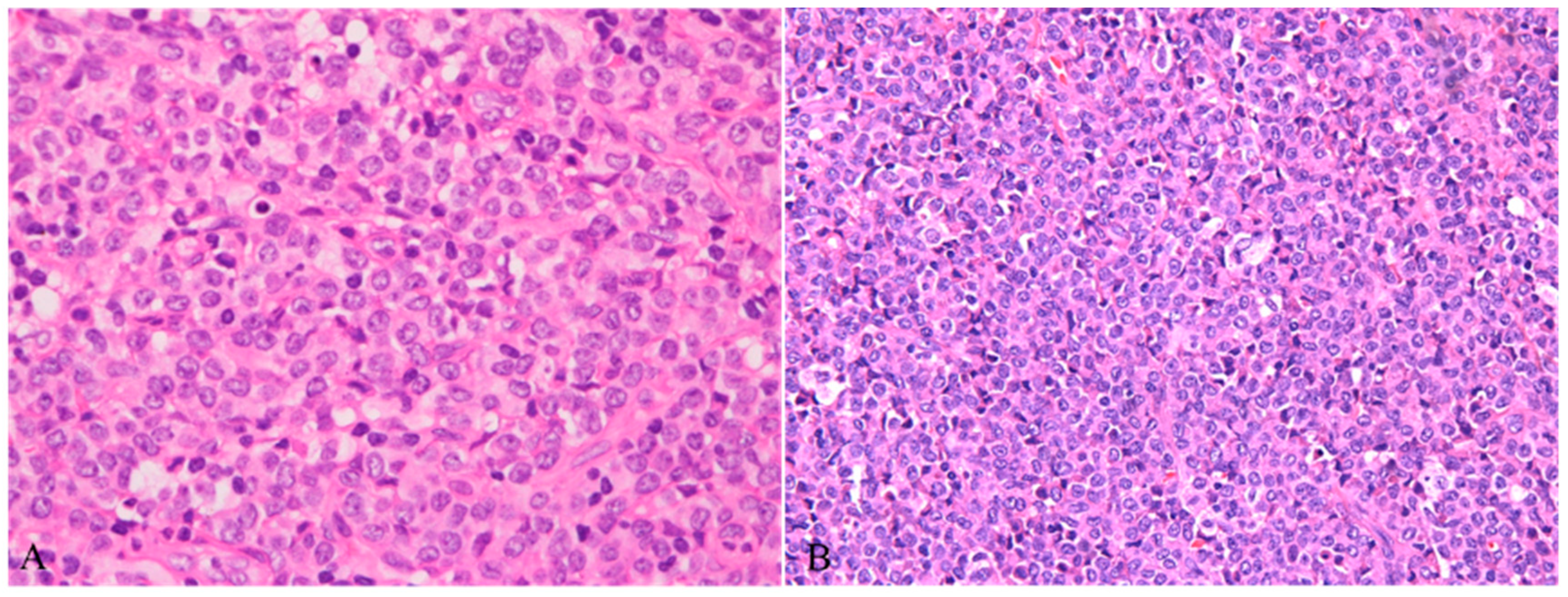
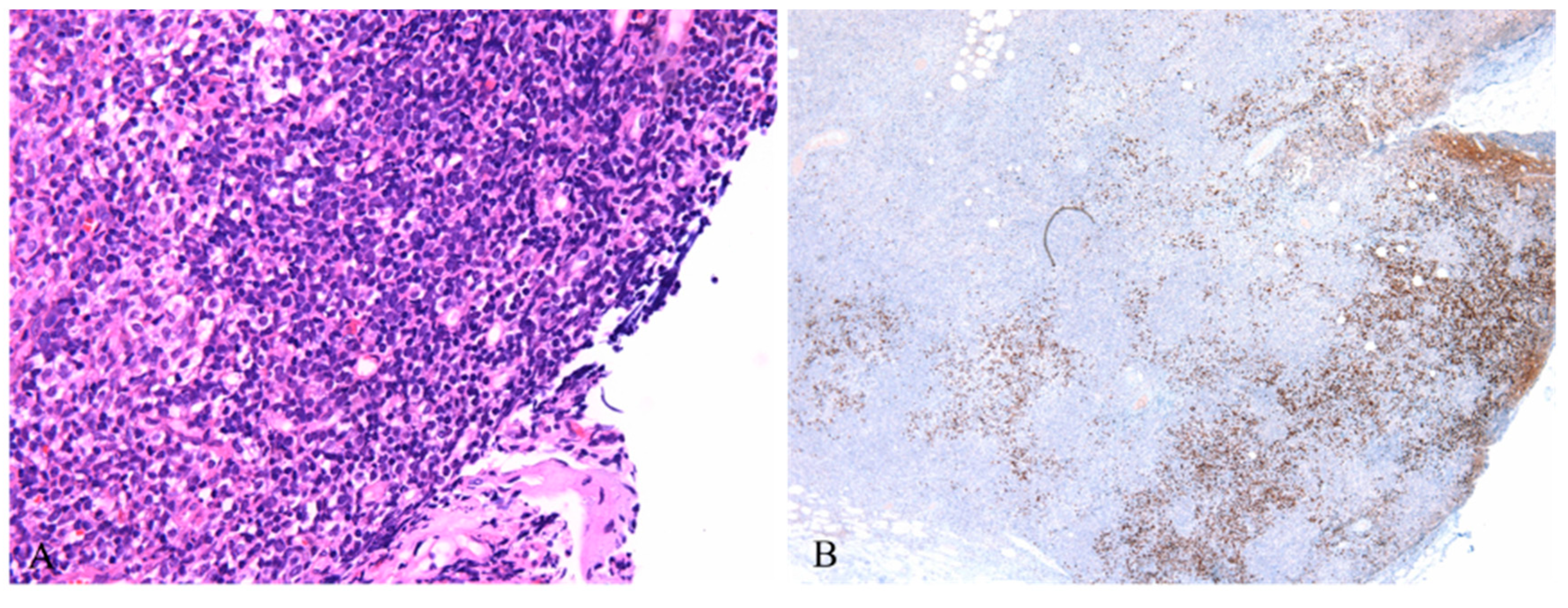
3. Discussion and Conclusions
| Report | Case | Gender | Age | Pattern | Destruction of normal structure | Location | Nodular Myeloid or lymphoid tumor | Associated tumor | Presentation | Follow-up time | Outcome |
| Muller et al. 1983 | 1 | M | 65 | NM | NM | NM | NM | Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | fatigu, weight loss,L,H,S | 7M | Dead |
| Grizzle et al.1985 | 2 | M | 86 | D | YES | NM | NO | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | weight loss,L,H,S | 3W | Dead |
| Beiske et al.1986 | 3 | M | 74 | N | NM | P | YES | Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | Weight loss,night sweat,L | 6M | Dead |
| Thomas et al.1991 | 4 | F | 6 | D | YES | P | NO | Atypical myeloproliferative disorder | L,H,S | NM | NM |
| Koo et al.1990 | 5 | F | 58 | D | YES | P,M | YES | Myeloproliferative disorder | aneimia,night sweat,L,H,S | 28M | Dead |
| Facchetti et al.1990 | 6 | M | 75 | N D | YES | P,C | YES | Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia | Weight loss,L,H,S | 16M | Dead |
| 7 | M | 66 | N | NO | P | YES | Acute nonB nonT lymphoblastic leukiemia | dyspnea fever,L,H,S | 20D | Dead | |
| Baddoura et al.1992 | 8 | M | 58 | D | YES | P,C,M | YES | Chronic myeloproliferative disorder | Fatigue fever weight loss ,L,H,S | Lost | Lost |
| 9 | M | 73 | N | NM | NM | NM | Acute monocytic leukemia | weight loss,fatigue ,L | Lost | Lost | |
| Harris et al.1991 | 10 | F | 54 | N | YES | P | YES | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia | fatigue ,weight loss,L,S | 84M | Dead |
| Vermi et al.2004 | 11 | M | 24 | N D | YES | NM | YES | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia | L,H,S | 8M | Dead |
| 12 | M | 50 | N | YES | NM | YES | Acute myelomonocytic leukaemia | L,H,S | 11M | Alive | |
| 13 | M | 58 | N | YES | NM | YES | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia | L,H | 84M | Dead | |
| 14 | F | 63 | N | YES | NM | YES | Unclassifiable chronic myeloproliferative disorder; | L,H | 15M | Dead | |
| 15 | M | 80 | D | YES | NM | NO | Unclassifiable myeloproliferative/myelodysplastic disorder | L,H,S | 43M | Dead | |
| 16 | F | 62 | N | YES | NM | YES | Acute monocytic leukemia | L | 15M | Dead | |
| 17 | M | 52 | N | YES | NM | YES | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia | L,H | 13M | Alive | |
| Song et al.2012 | 18 | M | 55 | N D | YES | NM | YES | Acute myeloid leukaemia | weigh loss,L | 17D | Dead |
| Bodmer et al.2017 | 19 | M | 65 | N | NM | P | NM | Myelodysplastic syndromes | L | 28M | Dead |
| present | 20 | F | 65 | D | YES | P,C,M | YES | T lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia | L | 3M | Alive |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lennert, K.; Remmele, W. [Karyometric research on lymph node cells in man. I. Germinoblasts, lymphoblasts & lymphocytes]. Acta Haematol 1958, 19, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Siegal, F.P.; Kadowaki, N.; Shodell, M.; Fitzgerald-Bocarsly, P.A.; Shah, K.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Liu, Y.J. The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 1999, 284, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, M.; Jarrossay, D.; Facchetti, F.; Alebardi, O.; Nakajima, H.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Colonna, M. Plasmacytoid monocytes migrate to inflamed lymph nodes and produce large amounts of type I interferon. Nat Med 1999, 5, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegalian, A.G.; Facchetti, F.; Jaffe, E.S. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Physiologic roles and pathologic states. Adv Anat Pathol 2009, 16, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchetti, F.; Cigognetti, M.; Fisogni, S.; Rossi, G.; Lonardi, S.; Vermi, W. Neoplasms derived from plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mod Pathol 2016, 29, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathan, T.S.; Figdor, C.G.; Buschow, S.I. Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells: From molecules to intercellular communication network. Front Immunol 2013, 4, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Chow, K.V.; Soo, P.; Xu, Z.; Brady, J.L.; Lawlor, K.E.; Masters, S.L.; O'Keeffe, M.; Shortman, K.; Zhang, J.G.; et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are short-lived: Reappraising the influence of migration, genetic factors and activation on estimation of lifespan. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchetti, F.; Vermi, W.; Mason, D.; Colonna, M. The plasmacytoid monocyte/interferon producing cells. Virchows Arch 2003, 443, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchetti, F.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; van den Oord, J.J.; De Vos, R.; Desmet, V.J. Plasmacytoid T cells: A cell population normally present in the reactive lymph node. An immunohistochemical and electronmicroscopic study. Hum Pathol 1988, 19, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stary, G.; Bangert, C.; Tauber, M.; Strohal, R.; Kopp, T.; Stingl, G. Tumoricidal activity of TLR7/8-activated inflammatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med 2007, 204, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaperot, L.; Blum, A.; Manches, O.; Lui, G.; Angel, J.; Molens, J.P.; Plumas, J. Virus or TLR agonists induce TRAIL-mediated cytotoxic activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Immunol 2006, 176, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urosevic, M.; Dummer, R.; Conrad, C.; Beyeler, M.; Laine, E.; Burg, G.; Gilliet, M. Disease-independent skin recruitment and activation of plasmacytoid predendritic cells following imiquimod treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005, 97, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Stein, H.; Steinmann, G.; Lennert, K. Malignant lymphoma of plasmacytoid T-cells. Morphologic and immunologic studies characterizing a special type of T-cell. Am J Surg Pathol 1983, 7, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koo, C.H.; Mason, D.Y.; Miller, R.; Ben-Ezra, J.; Sheibani, K.; Rappaport, H. Additional evidence that "plasmacytoid T-cell lymphoma" associated with chronic myeloproliferative disorders is of macrophage/monocyte origin. Am J Clin Pathol 1990, 93, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchetti, F.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Kennes, C.; Rossi, G.; De Vos, R.; van den Oord, J.J.; Desmet, V.J. Leukemia-associated lymph node infiltrates of plasmacytoid monocytes (so-called plasmacytoid T-cells). Evidence for two distinct histological and immunophenotypical patterns. Am J Surg Pathol 1990, 14, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermi, W.; Facchetti, F.; Rosati, S.; Vergoni, F.; Rossi, E.; Festa, S.; Remotti, D.; Grigolato, P.; Massarelli, G.; Frizzera, G. Nodal and extranodal tumor-forming accumulation of plasmacytoid monocytes/interferon-producing cells associated with myeloid disorders. Am J Surg Pathol 2004, 28, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddoura, F.K.; Hanson, C.; Chan, W.C. Plasmacytoid monocyte proliferation associated with myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer 1992, 69, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasthofer, E.F.; Prchal, J.T.; Grizzle, W.E.; Grossi, C.E. Plasmacytoid T-cell lymphoma associated with chronic myeloproliferative disorder. Am J Surg Pathol 1985, 9, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N.L.; Demirjian, Z. Plasmacytoid T-zone cell proliferation in a patient with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Histologic and immunohistologic characterization. Am J Surg Pathol 1991, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiske, K.; Langholm, R.; Godal, T.; Marton, P.F. T-zone lymphoma with predominance of 'plasmacytoid T-cells' associated with myelomonocytic leukaemia--a distinct clinicopathological entity. J Pathol 1986, 150, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargent, J.L.; Henne, S.; Pranger, D.; Balzarini, P.; Sartenaer, D.; Bulliard, G.; Rack, K.; Facchetti, F. Tumor-forming plasmacytoid dendritic cells associated with myeloid neoplasms. Report of a peculiar case with histopathologic features masquerading as lupus erythematosus. J Cutan Pathol 2016, 43, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.O.; Beiske, K.; Hann, I.; Koo, C.; Mason, D.Y. Immunohistological diagnosis of "plasmacytoid T cell lymphoma" in paraffin wax sections. J Clin Pathol 1991, 44, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, A.; Menter, T.; Juskevicius, D.; Arranto, C.; Wenzel, F.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. Sharing of a PTPN11 mutation by myelodysplastic bone marrow and a mature plasmacytoid dendritic cell proliferation provides evidence for their common myelomonocytic origin. Virchows Arch 2017, 470, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chou, J.M.; Ketterling, R.P.; Letendre, L.; Li, C.Y. Histologic and immunohistochemical study of bone marrow monocytic nodules in 21 cases with myelodysplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 2003, 120, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargent, J.L.; Delannoy, A.; Pieron, P.; Husson, B.; Debecker, C.; Petrella, T. Cutaneous accumulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells associated with acute myeloid leukemia: A rare condition distinct from blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. J Cutan Pathol 2011, 38, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, W.; Peters, M.S.; Reed, K.B.; Ketterling, R.P.; Dogan, A.; Gibson, L.E. Atypical generalized eruptive histiocytosis clonally related to chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with loss of Y chromosome. J Cutan Pathol 2013, 40, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Breton, G.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Aljoufi, A.; Puhr, S.; Cameron, M.J.; Sekaly, R.P.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Liu, K. Restricted dendritic cell and monocyte progenitors in human cord blood and bone marrow. J Exp Med 2015, 212, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Chang, K.C. Tumorous proliferations of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and Langerhans cells associated with acute myeloid leukaemia. Histopathology 2012, 61, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Liedtke, M.; Silva, O. Case Report: Mature Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Proliferation Associated With a Lymphoid Neoplasm. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 903113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
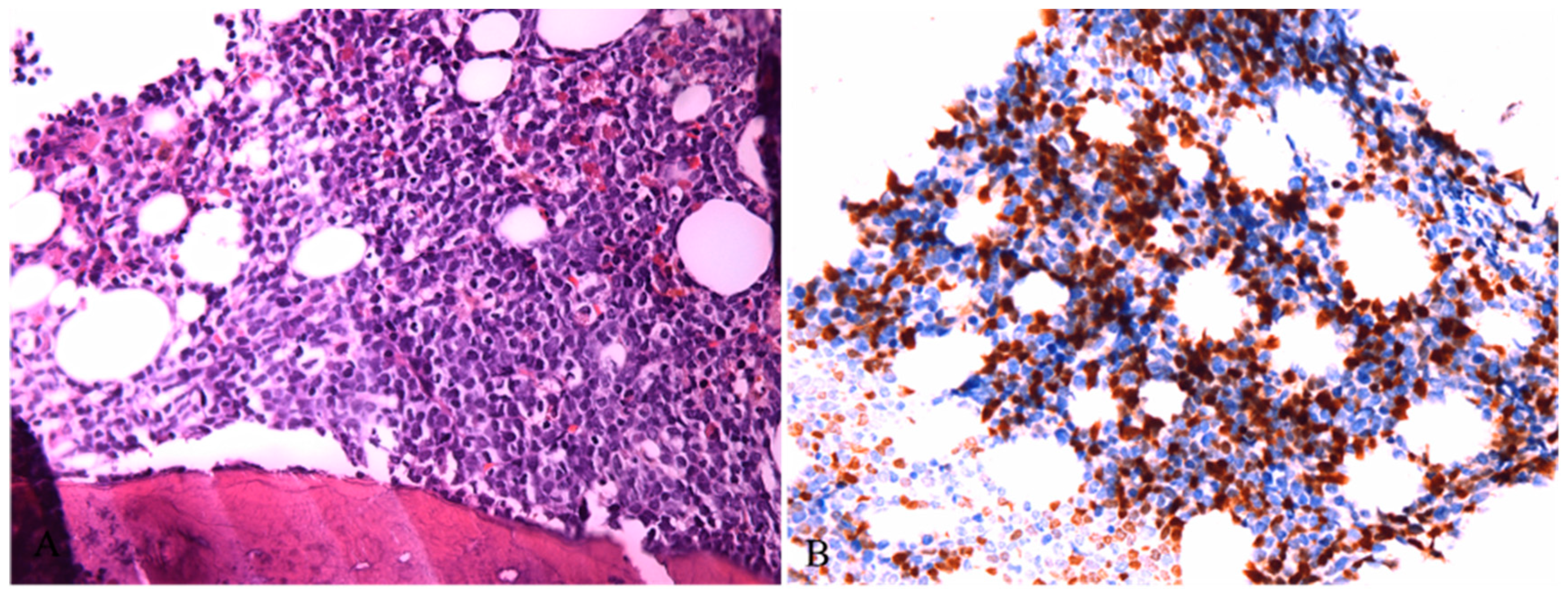
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



