Submitted:
12 September 2023
Posted:
14 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:

Introduction
2. Results
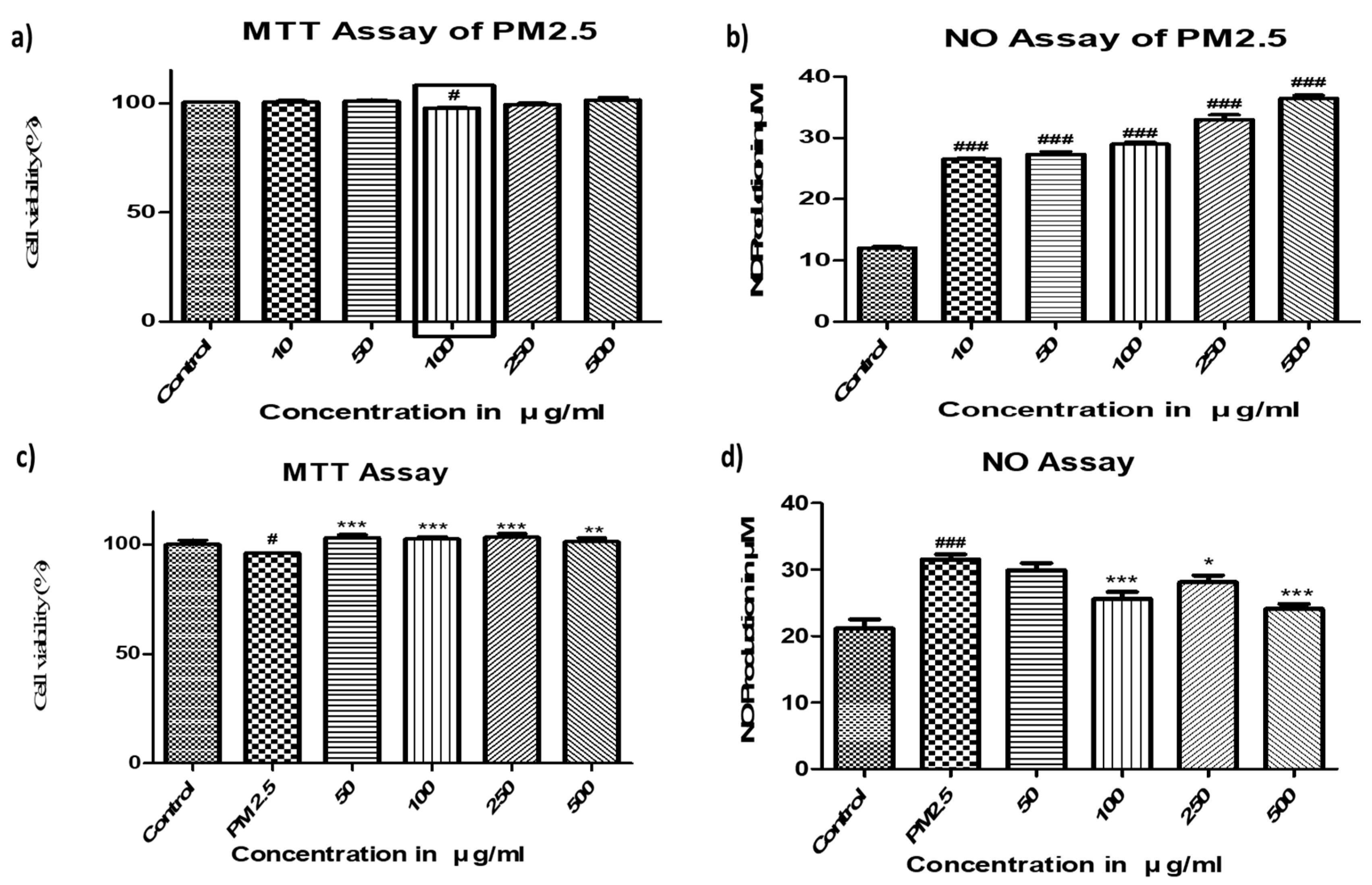
2.1. Toxicity of PM2.5 and Protective Effects of FBBR in SH-SY5Y cells
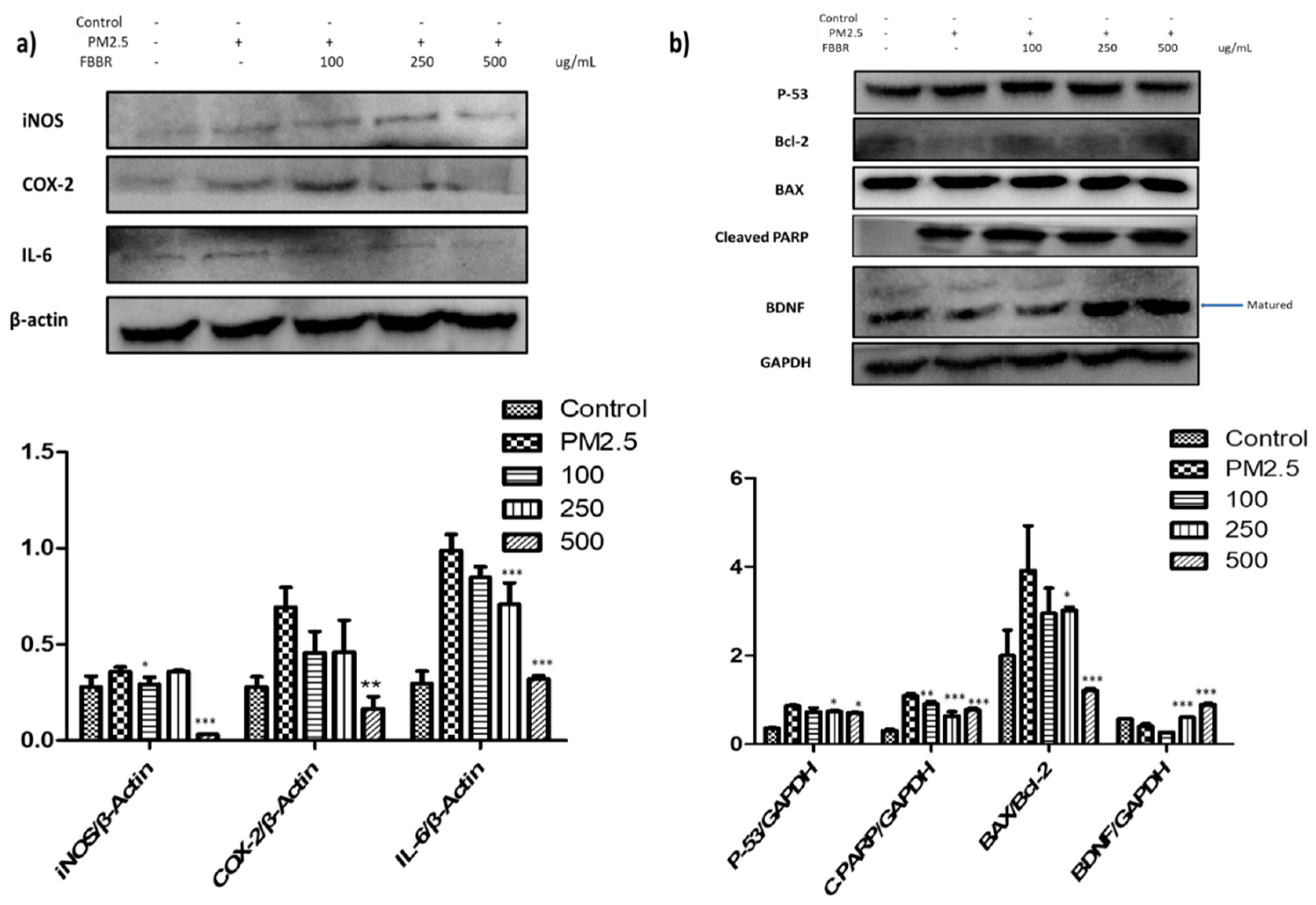
2.2. Effects of FBBR on Inflammatory markers iNOS, COX-2, IL-6 and Apoptotic Proteins Expression in PM2.5-induced SH-SY5Y cells
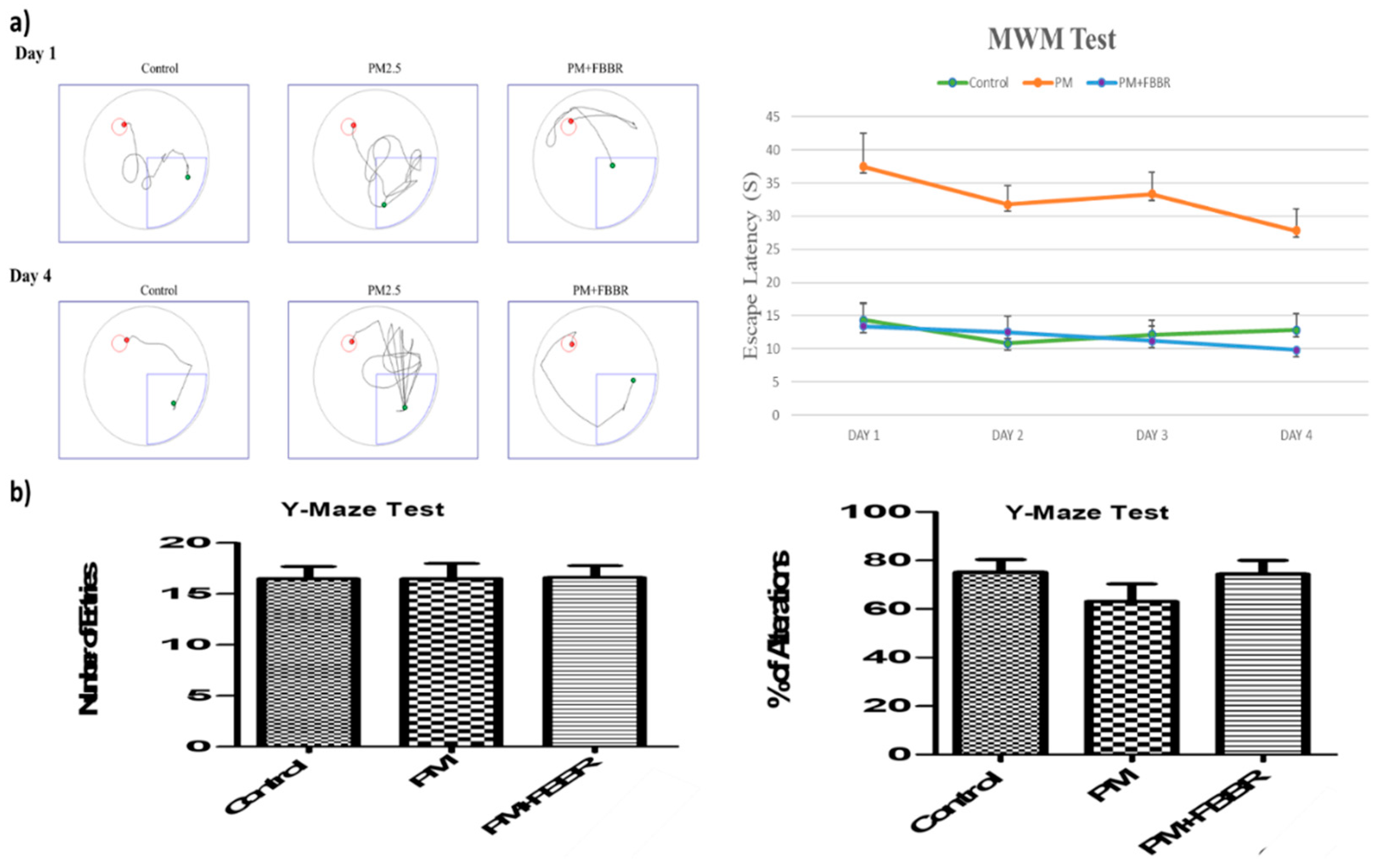
2.3. Effects of FBBR on Cognitive Impairment by PM2.5-induced Mice
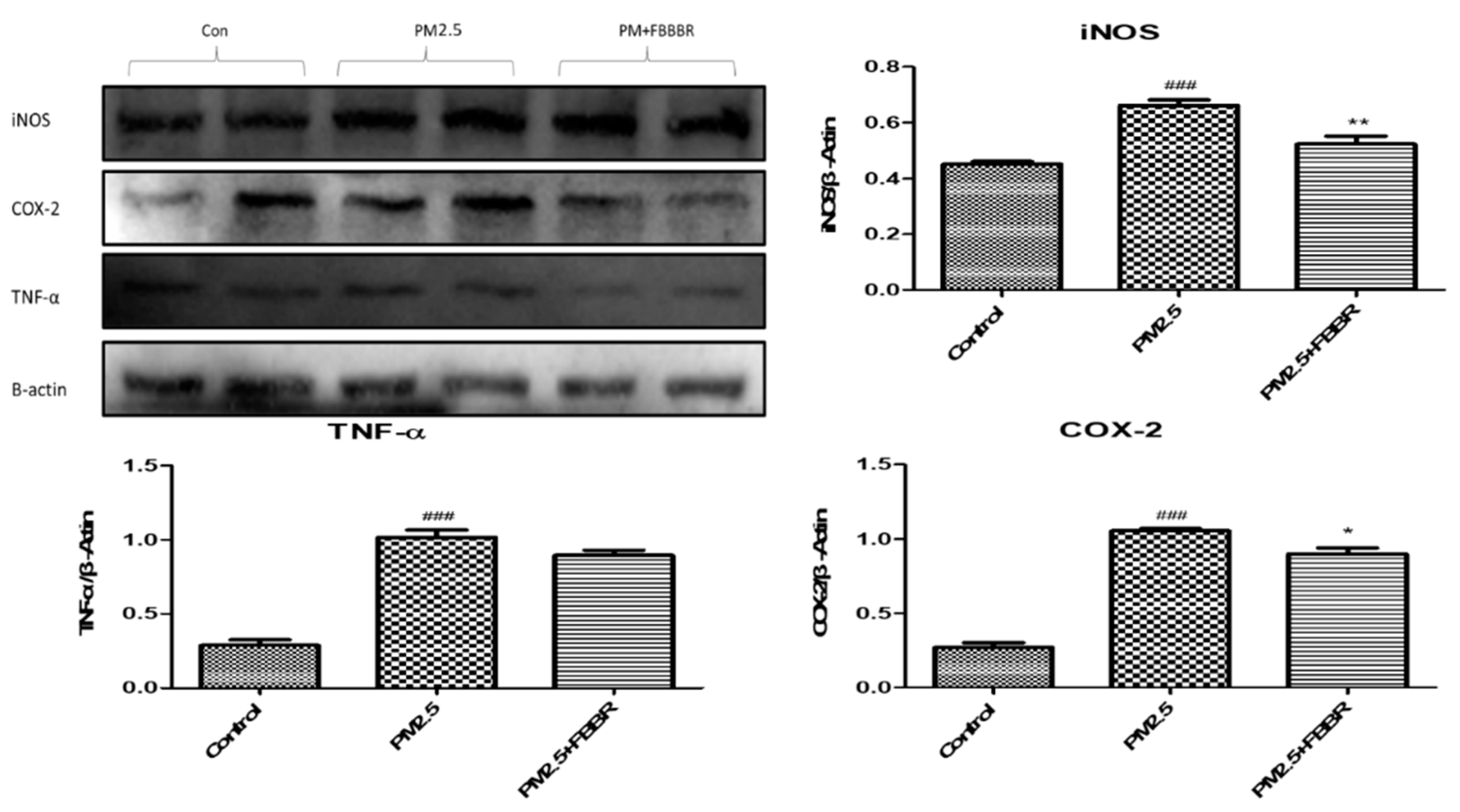
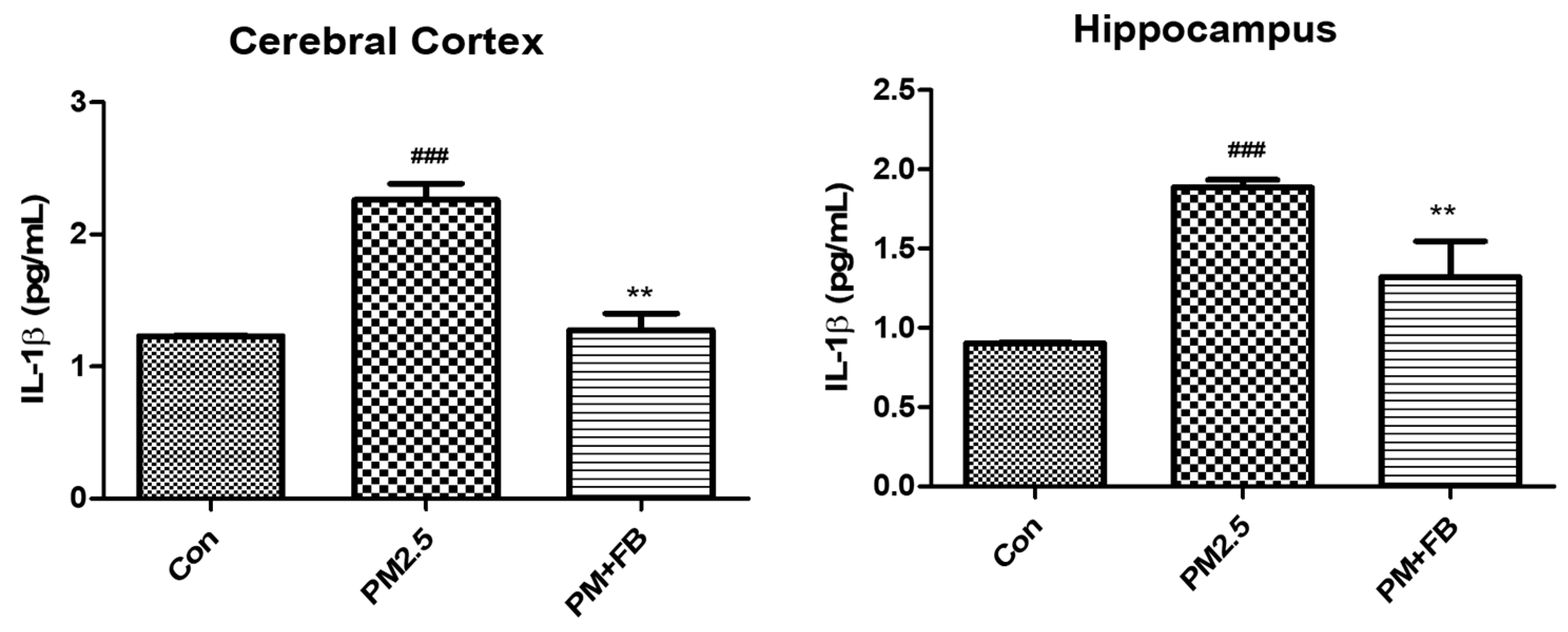
2.4. Effects of FBBR on Neuroinflammation in PM2.5-induced Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.2. Sample Preparations
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. MTT and NO Assay
4.5. Animal Model Design
4.6. Morris Water Maze Test
4.7. Y-Maze Test
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. IL-1β Level Detection
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ku, T., et al., NF-κB-regulated microRNA-574-5p underlies synaptic and cognitive impairment in response to atmospheric PM2.5 aspiration. Particle and Fibre Toxicology, 2017. 14(1): p. 34.
- Tseng, C.-Y., et al., The Effect of Ganoderma Microsporum immunomodulatory proteins on alleviating PM2.5-induced inflammatory responses in pregnant rats and fine particulate matter-induced neurological damage in the offsprings. Scientific Reports, 2019. 9(1): p. 6854. [CrossRef]
- Block, M.L. and L. Calderón-Garcidueñas, Air pollution: mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends in Neurosciences, 2009. 32(9): p. 506-516.
- Bayazid, A.B., et al., Sodium butyrate ameliorates neurotoxicity and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in high fat diet-fed mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2022. 159: p. 112743. [CrossRef]
- Jabri, M.-A., K. Rtibi, and H. Sebai, Chamomile decoction mitigates high fat diet-induced anxiety-like behavior, neuroinflammation and cerebral ROS overload. Nutritional Neuroscience, 2020: p. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, G., et al., High-fat diet induces neuroinflammation and mitochondrial impairment in mice cerebral cortex and synaptic fraction. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 2019. 13: p. 509. [CrossRef]
- Song, J., et al., Protective effects of quercetin on traumatic brain injury induced inflammation and oxidative stress in cortex through activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 2021. 39: p. 73-84.
- Sablina, A.A., et al., The antioxidant function of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nature Medicine, 2005. 11(12): p. 1306-1313.
- Maor-Nof, M., et al., p53 is a central regulator driving neurodegeneration caused by C9orf72 poly(PR). Cell, 2021. 184(3): p. 689-708.e20. [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, A.B. and B.O. Lim, Quercetin Is An Active Agent in Berries against Neurodegenerative Diseases Progression through Modulation of Nrf2/HO1. Nutrients, 2022. 14(23): p. 5132.
- Quiñones, M., et al., p53 in AgRP neurons is required for protection against diet-induced obesity via JNK1. Nature Communications, 2018. 9(1): p. 1-16.
- Bayazid, A.B., et al., Sodium Butyrate Alleviates Potential Alzheimer’s Disease In Vitro by Suppressing Aβ and Tau Activation and Ameliorates Aβ-induced Toxicity Food and Agricultural Immunology, 2023. 34.
- Park, S.H., et al., Fermented black rice and blueberry with Lactobacillus plantarum MG4221 improve UVB-induced skin injury. Food and Agricultural Immunology, 2021. 32(1): p. 499-515. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M., et al., Fermented blueberry and black rice containing Lactobacillus plantarum MG4221: a novel functional food for particulate matter (PM 2.5)/dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-induced atopic dermatitis. Food&Function, 2021. 12(8): p. 3611-3623.
- Wang, D.-M., et al., Effects of Long-Term Treatment with Quercetin on Cognition and Mitochondrial Function in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochemical Research, 2014. 39(8): p. 1533-1543. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., et al., Melatonin alleviates cognition impairment by antagonizing brain insulin resistance in aged rats fed a high-fat diet. Journal of Pineal Research, 2019. 67(2): p. e12584. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.L., et al., Seasonal variation of chemical characteristics of fine particulate matter at a high-elevation subtropical forest in East Asia. Environmental Pollution, 2019. 246: p. 668-677. [CrossRef]
- Ansarin, K., M. Khoubnasabjafari, and A. Jouyban, Reliability of malondialdehyde as a biomarker of oxidative stress in psychological disorders. 2015. 5(3): p. 123-127.
- Saw, C.L.L., et al., The berry constituents quercetin, kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive oxygen species: Involvement of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2014. 72: p. 303-311. [CrossRef]
- Emerit, J., M. Edeas, and F. Bricaire, Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomedicine&pharmacotherapy, 2004. 58(1): p. 39-46. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X., et al., Coeloglossum viride var. bracteatum extract improves cognitive deficits by restoring BDNF, FGF2 levels and suppressing RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated neuroinflammation in a 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Functional Foods, 2021. 85: p. 104612.
- TANIGAWA, S., M. FUJII, and D.-X. HOU, Stabilization of p53 Is Involved in Quercetin-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2008. 72(3): p. 797-804. [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T., et al., Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. The Lancet Neurology, 2015. 14(4): p. 388-405.
- Priprem, A., et al., Anxiety and cognitive effects of quercetin liposomes in rats. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2008. 4(1): p. 70-78. [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, A.B. and B.O. Lim, Quercetin Is An Active Agent in Berries against Neurodegenerative Diseases Progression through Modulation of Nrf2/HO1. 2022. 14(23): p. 5132.
- Ajayi, A.M., et al., Repeated social defeat stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioural deficits in mice: ameliorative role of Chrysophyllum albidum fruit extract through anti-neuroinflammation, antioxidant and neurochemical balance. Metabolic Brain Disease, 2022. 37(7): p. 2467-2481. [CrossRef]
- Plazas, E., et al., Natural isoquinoline alkaloids: Pharmacological features and multi-target potential for complex diseases. Pharmacological Research, 2022. 177: p. 106126. [CrossRef]
- Hadrich, F., M. Chamkha, and S. Sayadi, Protective effect of olive leaves phenolic compounds against neurodegenerative disorders: Promising alternative for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases modulation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2022. 159: p. 112752. [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, N., et al., Chromatography analysis, in light of vitro antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiobesity, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and three-dimensional cancer spheroids’ formation blocking activities of Laurus nobilis aromatic oil from Palestine. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 2023. 10(1): p. 25.
- Shawahna, R. and N.A. Jaradat, Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used by patients with psoriasis in the West Bank of Palestine. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2017. 17(1): p. 4. [CrossRef]
- Jia, G., et al., Neural stem cell-conditioned medium ameliorates Aβ25–35-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells by protecting mitochondrial function. Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 2021. 21(2): p. 179-186. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




