Introduction
Egypt is located in northeastern Africa and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Sudan to the south, Libya to the west, and Palestine and the Red Sea to the east (Rutherford & Sowers, 2018). The country has a total area of approximately 1,001,450 square kilometers (Rutherford & Sowers, 2018). The landscape of Egypt is characterized by a narrow strip of green along the Nile River, which fans into a verdant river delta, surrounded on both sides by vast deserts (Rutherford & Sowers, 2018). The Nile River is the lifeline of Egypt and has played a crucial role in the country's agriculture for thousands of years. The river provides water for irrigation, allowing for the cultivation of crops in an otherwise arid environment (Yeakel et al., 2014). The agricultural sector is one of Egypt's most important sectors and a principal economic and social concern (Abdelaal, 2021). The challenge for Egypt's agriculture is to sustainably expand agricultural production to meet escalating domestic demand for food and serve as a pathway out of poverty (Abdelaal, 2021). However, the agricultural sector faces many difficulties and challenges, including water stress and pressure on water resources (العال, 2021). The average amount of water withdrawn for agriculture in Egypt is about 82.43% (العال, 2021).
Nevertheless, the Egyptian landscape has undergone significant changes over time. During the Late Pleistocene/early Holocene, the region had a cooler, wetter climate driven by heavy monsoonal rains, known as the African Humid Period (AHP) (Yeakel et al., 2014). However, the region has experienced increasing aridification over time, leading to changes in the biological community and the extinction of certain animal species (Yeakel et al., 2014). The timing and pattern of animal extinctions in Egypt provide insights into how ecosystems can be affected by climate change and human activities (Yeakel et al., 2014). Desertification is also a significant issue in Egypt, particularly in the desert regions. Desertification processes and their impact on land cover changes have been analyzed using satellite data (Shalaby et al., 2004). The study found that certain parts of Egypt are at risk of desertification due to changing environmental conditions and land use (Shalaby et al., 2004). However, in terms of natural features, Egypt is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. The country has been studied for its biodiversity and the distribution of certain species, such as waterfowl and vultures (Henry et al., 2016; Mateo-Tomás & Olea, 2010). The Nile River and its surrounding areas provide important habitats for various species, including insects and parasites (Samy et al., 2014).
Figure 1.
Egypt map (source: Egyptian General Survey Authority).
Figure 1.
Egypt map (source: Egyptian General Survey Authority).
Challenges and Strategies for Closing the Food Gap and Achieving Food Security in Egypt
Egypt is currently facing a food gap due to several factors, including population growth, limited resources, and a struggling economy (Abdelaal & Thilmany, 2019). As the population continues to grow and opportunities for land reclamation remain limited, Egypt's reliance on food imports is expected to increase (Abdelaal & Thilmany, 2019). Additionally, food losses and wastage along the wheat value chain contribute to the food gap in Egypt (Yigezu et al., 2021). This food gap extends beyond grains and also affects other food commodities such as organic food products (Zayed et al., 2022), vegetable oils (El-Elsharkasy, 2023), sugar (Salah et al., 2020), and edible oils (Sherif & Alamry, 2023). Nevertheless, Water scarcity is a significant concern for Egypt's food security, especially considering the potential reduction in Nile flows (Abdelaal & Thilmany, 2019). Climate change further exacerbates the challenges faced by the agricultural sector, which is crucial for Egypt's food security (حافظ, 2017). Egypt shares similarities with Jordan in terms of food security, as both countries heavily rely on food imports and have limited capacity to absorb future price increases (Christoforidou et al., 2022). To address the food gap and enhance food security, various strategies can be implemented. These include (1) adopting advanced agricultural practices, developing innovative crop varieties, expanding land use, and promoting bio-saline agriculture (Almas & Usman, 2021). (2) Increasing agricultural trade between Egypt and Nile Basin countries can also contribute to food security by leveraging Egypt's surplus in certain crops and agricultural products (Ahmed, 2019). (3) Furthermore, supporting and activating agricultural and economic integration between Egypt and Sudan in grain production can help reduce the food gap and increase food security (الشاعر, 2015). On the other hand, understanding consumption patterns and expenditure on different food commodities is crucial for analyzing the food gap in Egypt (EL-Batran, 2019). It is also important to consider the impact of crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, on consumption spending and patterns (هاشم, 2023). By addressing these factors and implementing appropriate strategies, Egypt can work towards closing the food gap and achieving food security. However, the current situation of agriculture in Egypt is characterized by various opportunities and challenges. One of the major challenges is (1) soil degradation and soil sealing, which threatens agricultural development (Hendawy et al., 2019). (2) Urban expansion and uncontrolled urbanization are consuming vast areas of agricultural land, leading to environmental and social problems (Hendawy et al., 2019). (3) The loss of agricultural land to urbanization is a significant concern, as it reduces the available land for cultivation and affects food security (Hendawy et al., 2019). (4) Another challenge is the limited arable land base in Egypt, coupled with the erosion of land resources, loss of soil fertility, and salinity (Assem, 2014). These factors pose obstacles to agricultural productivity and sustainability. Additionally, the high rate of population growth in Egypt adds pressure to the agricultural sector, as it increases the demand for food (Assem, 2014). However, there are also opportunities for agricultural development in Egypt. The use of remote sensing data and GIS modeling allows for the monitoring and assessment of changes in land use and land cover, providing valuable information for land management and planning (Hendawy et al., 2019). This technology can help identify areas at risk of soil sealing and guide decision-making processes to protect agricultural land (Hendawy et al., 2019). Likewise, there are opportunities for commercializing biotech products in Egypt, such as (1) Bt maize (Assem, 2014). (2) Biotechnology can contribute to improving crop productivity, enhancing resistance to pests and diseases, and increasing agricultural efficiency (Assem, 2014). (3) The commercialization of biotech products can stimulate agricultural growth and contribute to food security in Egypt.
Bridging the Wheat Production Gap in Egypt: Challenges, Strategies
The situation of wheat and other grain crops in Egypt is characterized by a significant gap between production and demand, leading to heavy reliance on imports (
Table 1: Egypt Grains Production). Egypt currently produces around half of the 20 million tons of wheat it consumes, with the other half being imported (Asseng et al., 2018). The country is one of the largest importers of wheat in the world (Asseng et al., 2018). The demand for wheat in Egypt is projected to increase due to population growth, which is currently at a rate of 2.2% annually (Asseng et al., 2018). This increasing demand, coupled with limited domestic production, poses a challenge for achieving self-sufficiency in wheat (Asseng et al., 2018). The competition for water resources between agricultural irrigation and urban needs further complicates the situation (Asseng et al., 2018). Climate change is also expected to impact wheat production in Egypt. Combining multi-crop and climate models, it has been estimated that future wheat yields will decline primarily due to climate change, despite potential yield improvements from new technologies (Asseng et al., 2018). Rising temperatures are projected to hurt crop growth, outweighing any potential benefits from elevated atmospheric CO2 levels (Asseng et al., 2018). Efforts to address the wheat production gap in Egypt include the use of crop simulation models to estimate future production and water requirements for irrigation (Asseng et al., 2018). These models can help assess the impact of climate change and inform decision-making processes. Additionally, research has explored the response of wheat crops to different water requirements and weed management strategies (El-Metwally et al., 2015). Strategies such as bio-saline agriculture and the use of biochar have also been investigated to mitigate the adverse effects of saline water on soil properties and wheat production profitability (El-Sayed et al., 2021).
Table 1.
Egypt Grains Production.
Table 1.
Egypt Grains Production.
| Crops |
5-yr Avg
(2018-2022)
(1000 Tons) |
2022/23
(1000 Tons) |
2023/24
(1000 Tons) |
% Change
2023-24/Avg |
| Wheat |
9,070 |
9,500 |
8,870 |
-2 |
| Corn |
6,896 |
7,440 |
7,600 |
10 |
| Rice |
3,520 |
3,600 |
3,780 |
7 |
| Sorghum |
767 |
750 |
750 |
-2 |
| Peanut |
207 |
205 |
205 |
-1 |
| Barley |
108 |
108 |
108 |
0 |
| Soybean |
40 |
56 |
85 |
113 |
| Sunflower seed |
23 |
38 |
50 |
116 |
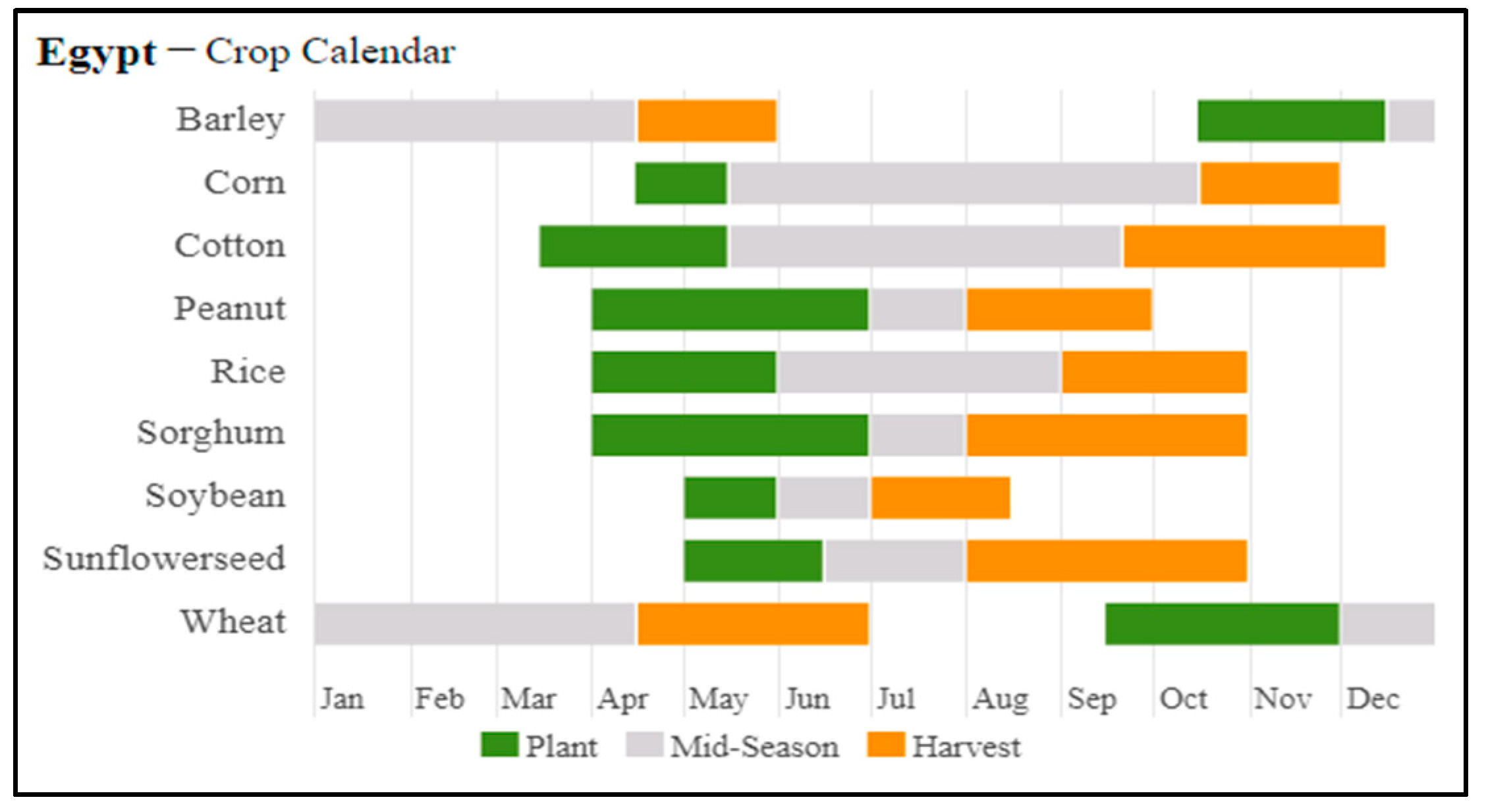
Figure 2.
Calendar of planting and harvesting grain crops in Egypt. Source (USDA.gov).
Figure 2.
Calendar of planting and harvesting grain crops in Egypt. Source (USDA.gov).
The Opportunity of Pseudocereals as Non-Traditional Crops in Egypt
Pseudocereals, such as quinoa, amaranth, buckwheat, tiff, and millet, offer high nutritional value and can be cultivated in marginal agricultural areas (Rodríguez et al., 2020). These crops are rich in protein, minerals, and other essential nutrients, making them a healthy and balanced food option (Rodríguez et al., 2020). Replacing low-nutritional raw materials used in gluten-free diets with pseudocereals can improve the nutritional quality of gluten-free diets and overcome mineral deficiencies (Nardo et al., 2019). Pseudocereals have the potential to enhance nutrient bioavailability and contribute to a more diverse and nutritious diet (Rodríguez et al., 2020). The cultivation of pseudocereals can make dry lands productive and ensure future food and nutritional security (Rodríguez et al., 2020). These crops have the advantage of being gluten-free, which is beneficial for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance (Rodríguez et al., 2020). Additionally, genomic information and advances in molecular breeding techniques have facilitated the development of molecular markers and the improvement of pseudocereal crops (Rodríguez et al., 2020). In Egypt, the cultivation of pseudocereals can diversify the agricultural sector and contribute to food security. These crops can be grown in marginal lands with limited water resources, making them suitable for the country's arid environment (Rodríguez et al., 2020). The high nutritional value of pseudocereals can also address nutrient deficiencies and improve the overall health and well-being of the population (Nardo et al., 2019). On the other hand, Nontraditional crops can play a significant role in closing the food gap in Egypt. By diversifying the agricultural sector and promoting the cultivation of nontraditional crops, Egypt can increase its food production and reduce its reliance on imports. Several studies have highlighted the potential of nontraditional crops to address the food gap and enhance food security in Egypt (Pradhan et al., 2015) Alobid et al., 2021). One approach to closing the food gap is by closing yield gaps in the currently cultivated land. By improving agricultural practices and increasing crop yields, it is possible to produce more crop calories on the existing cultivated land. This can be achieved through sustainable agricultural intensification methods, such as optimizing fertilizer use, improving soil management, and implementing advanced agricultural techniques (Pradhan et al., 2015). Another strategy is to focus on the highest production efficiency of nontraditional crops. By identifying crops that have the potential to thrive in Egypt's climate and soil conditions, farmers can maximize their yields and contribute to closing the food gap. This approach requires research and investment in the development of nontraditional crop varieties and the dissemination of best agricultural practices (Alobid et al., 2021). Also, it is important to note that closing the food gap through nontraditional crops should be done sustainably. This includes considering the environmental impact of agricultural practices and ensuring the efficient use of resources. Sustainable intensification methods, such as optimizing fertilizer use and improving water management, can help minimize negative externalities and promote long-term agricultural sustainability (Pradhan et al., 2015). Conversely, Nontraditional crops have the potential to contribute to closing the food gap in Egypt. Several studies have explored the suitability and potential of nontraditional crops in the country's agricultural sector. One study focused on the national water, food, and trade modeling framework in Egypt Abdelkader et al. (2018). The analysis revealed that non-water-based solutions, such as educational and health programs aimed at lowering population growth, are essential in solving Egypt's water and food problems. The study also projected similar trends in Egypt's food gap between national and global models. In terms of agricultural integration, a study examined the effect of activating the role of Egyptian-Sudanese integration in achieving food security for major grain crops, such as wheat, corn, and rice (الشاعر, 2015). A study conducted in Wadi Al-Natrun, Egypt, aimed to provide agricultural land use planning for uncultivated land (El-Kawy et al., 2019). The study assessed the suitability of the land for crop cultivation, considering factors such as soil quality and water availability. The adoption of export development for nontraditional crops in new lands in Egypt has also been explored (Abozied & Eldeep, 2013). These studies analyzed the possibilities of Egyptian export development for crops like mint and artichokes. Factors such as income from off-farm employment, production cost, and labor were considered in assessing the potential for export development. Furthermore, the economic efficiency and productivity of organic agriculture in Egypt have been studied (نصار, 2022). The research compared the traditional and organic systems and identified the problems facing organic agriculture in the country. Primary data collected through questionnaires were used to estimate the economic efficiency and productivity of organic fertilizers. Pseudo cereals crops, such as quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat, have the potential to contribute to addressing the nutrition gap in Egypt. These crops offer high nutritional value, including protein, minerals, and other essential nutrients (Nardo et al., 2019). By incorporating pseudo cereals into the diet, individuals can obtain a more balanced and nutritious food source. However, one of the key health challenges in Egypt is malnutrition, including both undernutrition and overnutrition. Pseudocereals, such as quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat, offer an opportunity to address these challenges due to their exceptional nutritional value (Zou et al., 2017). These crops are rich in protein, essential amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, making them a valuable addition to the diet (Zou et al., 2017). In Egypt, malnutrition is a significant concern, with a high prevalence of micronutrient deficiencies, particularly iron, vitamin A, and iodine (Zou et al., 2017). Pseudocereals, such as quinoa, are known for their high iron content, which can help address iron deficiency anemia, a common health issue in Egypt (Zou et al., 2017). Additionally, the high protein content and essential amino acid profile of pseudocereals can contribute to combating protein-energy malnutrition (Zou et al., 2017). Moreover, the consumption of pseudocereals can help address the rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in Egypt, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Pseudocereals have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels (Zou et al., 2017). Incorporating pseudocereals into the diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and support weight management, thus reducing the risk of obesity and related NCDs (Zou et al., 2017). The cultivation and consumption of pseudocereals also offer an opportunity to promote sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation. Pseudocereals are known for their adaptability to harsh environmental conditions, including drought and poor soil quality (Zou et al., 2017). By promoting the cultivation of pseudocereals, Egypt can diversify its agricultural sector, reduce water consumption, and minimize the use of chemical inputs, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Exploring the Nutritional Value and Health Benefits of Pseudo Cereals in Modern Diets
Pseudocereals are gluten-free and are considered safe for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance (Saturni et al., 2010). Some of the commonly used pseudo cereals in nutrition include amaranth, buckwheat, quinoa, sorghum, and teff (Saturni et al., 2010). These crops have been found to have higher protein content compared to wheat and are rich in essential amino acids (Saturni et al., 2010). They also contain dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious choice for a balanced diet (Theethira & Dennis, 2015). Amaranth is one of the most nutritious pseudo cereals and has been consumed since ancient times (Soriano-García et al., 2018). It is rich in protein, iron, and magnesium (Rybicka, 2018). Amaranth has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation-related diseases (Soriano-García et al., 2018). It is also considered a "superfood" due to its high nutraceutical value (Soriano-García et al., 2018). Buckwheat is another pseudocereal that is commonly used in nutrition. It is a good source of dietary fiber and contains essential amino acids (Janovská et al., 2021). Buckwheat has been found to affect the physical and nutritional quality of extruded breakfast cereals (Brennan et al., 2012). Quinoa is a pseudo cereal that is known for its high protein content and is considered a complete protein source (Saturni et al., 2010). It is also rich in dietary fiber and minerals such as magnesium and iron (Patil & Jena, 2020). Sorghum is a gluten-free pseudocereal that is rich in antioxidants and has been reported to have various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties (Saturni et al., 2010). Teff is a pseudocereal that is native to Ethiopia and is known for its high iron and calcium content (Saturni et al., 2010). The use of pseudo cereals in nutrition has gained popularity due to their nutritional value and health benefits. They are often used as alternatives to traditional cereals in gluten-free diets (Saturni et al., 2010). Pseudo cereals can provide complex carbohydrates, protein, fiber, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals (Theethira & Dennis, 2015). They can be incorporated into various food products, such as bread, breakfast cereals, and snacks, to enhance their nutritional value (Brennan et al., 2012). The consumption of pseudo cereals, along with whole grains, is considered to have a beneficial effect on reducing the risk of non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, gastrointestinal disorders, and type 2 diabetes (P & Joye, 2020).
Potentials of Pseudocereals for Egypt's Agriculture and Food Security
- I.
Amaranth
a pseudocereal crop that belongs to the Amaranthus genus. It is known for its high nutritional value and potential health benefits. Amaranth grains, particularly those from the species Amaranthus cruentus and Amaranthus hypochondriacus, are rich in macronutrients and micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals (Tang & Tsao, 2017). The proteins in amaranth are of high nutritional quality due to their balanced composition of essential amino acids (Tang & Tsao, 2017). The Amaranth seeds are also a good source of bioactive compounds, such as peptides, which have potential health benefits. Enzymatic hydrolysis and food processing can produce bioactive peptides from amaranth proteins (Montoya-Rodríguez et al., 2015). Lunasin, a bioactive peptide with anticarcinogenic properties, has been identified in amaranth seeds (Silva-Sanchez et al., 2008). Lunasin-like peptides and other potentially bioactive peptides have also been found in amaranth protein fractions (Silva-Sanchez et al., 2008). These peptides have the potential to prevent chronic diseases (Montoya-Rodríguez et al., 2015). In addition to its nutritional and bioactive properties, amaranth has been used for therapeutic purposes. It has been included in the human diet for a long time and is considered an important nutritional crop (Soriano-García et al., 2018). The Aztecs called amaranth "Huautli" and the Mayas named it "Xtes." In modern times, amaranth is being considered a "super crop" due to its high nutraceutical values (Soriano-García et al., 2018). It is also considered a "super food" because it is gluten-free and a relevant source of vegetable nutrients (Soriano-García et al., 2018). Amaranth is genetically diverse, with over 103 species of flowering plants in the Amaranthaceae family (Ozimede et al., 2019). It is an underutilized crop with diverse abiotic stress tolerance traits, making it suitable for cultivation in a rapidly changing climate (Jamalluddin et al., 2022). Genetic diversity analysis has been conducted to study the diversity of amaranth genotypes using molecular markers (Gelotar et al., 2019). This research can help in the conservation and improvement of amaranth crops. The nutritional and nutraceutical characteristics of amaranth can be affected by different processing methods, such as cooking, popping, or extrusion (Márquez-Molina & López-Martínez, 2020). These processes can alter the nutritional and bioactive compounds present in amaranth grains. Therefore, it is important to consider the effects of processing on the nutritional value of amaranth. Amaranth has also been studied in terms of its resistance to herbicides. Some populations of Palmer amaranth and waterhemp have evolved resistance to herbicides (Vieira et al., 2020). This resistance can have implications for weed control in amaranth crops and the development of sustainable agricultural practices. However, the cultivation and utilization of amaranth have the potential to contribute to closing the food gap in Egypt. Amaranth is a highly nutritious crop with the ability to thrive in adverse growing conditions, such as high temperatures, drought, and poor soil conditions (Alemayehu et al., 2014). Its nutritional value, including high-quality protein, dietary fiber, and essential minerals and vitamins, makes it a valuable addition to the diet (Waisundara, 2020). Additionally, amaranth has been shown to have potential health benefits and can be used to prevent chronic diseases (Montoya-Rodríguez et al., 2015). In East Africa, where there is a dire need for staple food supplements and alternatives, amaranth has been identified as a potential crop to support food security and mitigate the effects of climate change (Alemayehu et al., 2014). The expansion of amaranth cultivation in Egypt could provide a locally grown, nutrient-rich food source that can help meet the nutritional needs of the population. Amaranth is already cultivated in Kenya, and although its use in daily cooking is limited, it has the potential to be further integrated into the local food system (Alemayehu et al., 2014). By promoting the cultivation and consumption of amaranth in Egypt, the country can reduce its dependence on imported food and improve food self-sufficiency. Furthermore, amaranth can be grown as a second summer crop in double cropping systems after harvesting wheat and barley, providing an opportunity for farmers in Egypt to increase their agricultural productivity and income (Rahjerdi et al., 2015). The remaining growing season after harvesting wheat and barley can be utilized to grow a second crop of amaranth. To fully harness the potential of amaranth in closing the food gap in Egypt, it is important to consider the genetic diversity and genome evolution of amaranth. Single-molecule sequencing and proximity-guided assembly techniques have provided insights into the genome evolution of amaranth, which can aid in breeding programs and the development of improved varieties (Lightfoot et al., 2017).
- II.
Buckwheat
Buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp.) is a versatile crop that is cultivated for its seeds, which are used for various purposes, including human consumption, animal feed, and as a cover crop (Liu et al., 2019). Buckwheat cultivation, agronomy, and distribution have been the subject of several studies, providing insights into its nutritional properties, starch characteristics, and effects on pest control. Buckwheat seeds contain a cereal-like starchy endosperm, making them suitable for the production of various food products (Skrabanja et al., 2000). The nutritional properties of buckwheat starch have been studied to identify its potential for reducing post-meal metabolic responses (Skrabanja et al., 2000). Boiled buckwheat groats have been found to have a high satiety score and lower glycemic index (GI), indicating their potential use in the design of foods with lower GI properties (Skrabanja et al., 2000). The rate of starch hydrolysis and the formation of resistant starch (RS) in buckwheat products have also been investigated (Skrabanja et al., 2000). Boiled buckwheat groats have been found to have the highest concentration of RS (Skrabanja et al., 2000). Buckwheat cultivation practices and agronomy vary depending on the region and purpose of cultivation. Buckwheat is known for its adaptability to different environmental conditions, including poor soils and cool climates (Berndt et al., 2002). It is often grown as a cover crop in vineyards to enhance biological control of pests by providing nutrients to parasitoids (Berndt et al., 2002). The presence of buckwheat flowers in agricultural ecosystems has been found to benefit parasitoids, such as braconidae, which can help control leafroller pests (Berndt et al., 2002). The distribution of buckwheat is widespread, with different species found in various regions. Buckwheat is cultivated in many countries, including China, Russia, and the United States (Liu et al., 2019). It is an important crop in regions where it is traditionally consumed, such as Japan and Eastern Europe (Liu et al., 2019). The distribution of buckwheat and its cultivation practices have implications for its genetic diversity and potential for crop improvement. Buckwheat presents several opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. The cultivation and utilization of buckwheat can contribute to addressing food security challenges and improving nutrition in the country. Buckwheat is a versatile crop with various benefits that make it suitable for Egypt's agricultural landscape. One of the key advantages of buckwheat is its ability to tolerate high salinity in the soil (Chen et al., 2007). This is particularly relevant for Egypt, where soil salinity is a significant challenge in many agricultural areas. Buckwheat has been found to grow, flower, and accumulate important nutrients even in the presence of high levels of sodium chloride in the soil (Chen et al., 2007). This tolerance to salinity makes buckwheat a valuable crop for agricultural use in saline environments, contributing to increased agricultural productivity and food security. Additionally, buckwheat has a relatively short growing season, allowing for multiple harvests in a year (Li et al., 2009). This characteristic makes it suitable for rotation with other crops, providing farmers with the opportunity to diversify their agricultural practices and improve soil fertility. Buckwheat can also be grown in marginal lands that are not suitable for other crops, further expanding the agricultural potential in Egypt. Buckwheat is a highly nutritious crop, rich in protein, dietary fiber, and essential minerals (Chen et al., 2007). The seeds of buckwheat contain 10-12.5% protein and have high nutritional value (Chen et al., 2007). They also contain flavones, flavonoids, and sterols, which have been associated with various health benefits (Chen et al., 2007). Incorporating buckwheat into the diet can help address malnutrition and provide a balanced source of nutrients. Furthermore, buckwheat has economic opportunities. It can be processed into various functional food products, such as noodles, pasta, bread, tea, spirits, and vinegar (Qin et al., 2011). The production and value addition of buckwheat-based products can create employment opportunities and contribute to the country's economy. Buckwheat tea, in particular, is a popular and healthy product in several countries, including China, Japan, South Korea, and European countries (Qin et al., 2011).
- III.
Quinoa
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) has the potential to contribute to closing the food gap in Egypt. Quinoa is a high-quality grain crop that is resistant to abiotic stresses such as drought, cold, and salt (Bazile et al., 2016). It offers an optimal source of protein and has undergone a major expansion in recent years (Bilalis et al., 2019). Several studies have explored the suitability and potential of quinoa in Egypt's agricultural sector. Field evaluations of quinoa were conducted in Egypt, among other countries, to assess its adaptability and potential (Shams, 2018). These evaluations revealed that some quinoa genotypes showed higher yields and greater adaptation to new environmental conditions (Shams, 2018). Quinoa's ability to grow in different environments contributes to production stability, which is crucial under climate change uncertainty (Bazile et al., 2016). A study conducted in Egypt evaluated the agronomic potential, chemical composition, and economic opportunity of quinoa under arid sandy soil conditions (Shams, 2018). The study identified nine quinoa genotypes, including Peruvian varieties, and assessed their protein content and saponin content (Shams, 2018). The results showed variations in protein content and saponin content among the different genotypes (Shams, 2018). Genetic characterization studies have also been conducted on quinoa genotypes introduced to Egypt (Saad-Allah & Youssef, 2018). These studies used molecular markers to evaluate genetic relationships among the genotypes and assess their phytochemical traits. The results confirmed reasonable variation in phytochemical traits among the quinoa genotypes (Saad-Allah & Youssef, 2018). Quinoa's nutritional value and bioactive properties have also been highlighted (Ahmed et al., 2021). Quinoa is known for its adaptability to harsh environmental conditions and high nutritional value. It is considered suitable for gluten-free and functional foods (Ahmed et al., 2021). However, its consumption is not widespread due to a lack of knowledge regarding its nutritional and health benefits among consumers (Ahmed et al., 2021). Quinoa is a facultative halophyte plant with exceptional nutritional properties (Pitzschke, 2016). It is highly adaptable to various environmental conditions, including high levels of salinity and drought stress (Pitzschke, 2016). This adaptability makes it suitable for cultivation in Egypt, where arid and marginal soils are prevalent (Sosa-Zuniga et al., 2017). From an agricultural perspective, quinoa exhibits unique developmental peculiarities and seed-borne endophytes that contribute to its resilience and fitness (Pitzschke, 2016). The presence of robust Bacilli endophytes in quinoa seeds enhances their ability to withstand extreme conditions during seed rehydration and seedling establishment (Pitzschke, 2016). These endophytes potentially manipulate the host plant's redox status and contribute to its overall fitness (Pitzschke, 2016). Quinoa's rapid germination and regeneration capabilities make it a valuable crop for agricultural production (Pitzschke, 2016). It can germinate within minutes, even under hostile conditions, and broken seeds or split embryos can regenerate (Pitzschke, 2016). This resilience and adaptability make quinoa a promising crop for cultivation in Egypt's challenging agricultural environment. From a nutritional perspective, quinoa seeds are considered a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals (Saad-Allah & Youssef, 2018). They contain high-quality protein, essential amino acids, and antioxidants (Saad-Allah & Youssef, 2018). Quinoa is gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease (Saad-Allah & Youssef, 2018). Its nutritional value and adaptability to different environmental conditions make it a valuable addition to the diet and a potential solution for addressing nutritional deficiencies in Egypt. Furthermore, the expansion of quinoa cultivation in Egypt can have implications for land use management and agricultural sustainability (Bedoya-Perales et al., 2018). The variability of quinoa expansion rates at the regional level requires attention to ensure sustainable land use practices and soil management (Bedoya-Perales et al., 2018).
- IV.
Sorghum:
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is a versatile and multipurpose crop that is ranked among the top five cereal crops in the world (Gaffa et al., 2004). It is cultivated for various purposes, including food, fodder, feed, and fuel (Gaffa et al., 2004). The genus Sorghum consists of diverse species, with different distributions and characteristics (Ananda et al., 2020). Sorghum cultivation, agronomy, and distribution have been the subject of several studies, providing insights into its genetic diversity, adaptation to different environments, and potential for crop improvement. Sorghum cultivation practices and agronomy vary depending on the region and purpose of cultivation. Sorghum can withstand severe droughts, making it suitable for cultivation in regions where other major crops struggle to grow (White et al., 2015). It is known for its heat and drought tolerance, which contributes to its resilience in challenging environments (White et al., 2015). Agronomic practices for sorghum cultivation include land preparation, planting methods, fertilization, weed control, and pest management (White et al., 2015). The use of improved varieties and crop management techniques can enhance sorghum yields and quality (White et al., 2015). The distribution of sorghum is diverse, with different species found in various regions. Some sorghum species are widely distributed, while others are more restricted in their range (Ananda et al., 2020). For example, in Australia, there are 17 native sorghum species, none of which have been cultivated (Ananda et al., 2020). The wild relatives of sorghum, found in different regions, are valuable genetic resources for crop improvement (Ananda et al., 2020). The wild gene pool of sorghum harbors genes for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance, which can be introduced into cultivated varieties (Ananda et al., 2020). The distribution of sorghum and its wild relatives has implications for conservation and gene flow. Ecogeographical databases are important tools for managing genetic resources and understanding the overlaps in ecological and geographical distributions between crops and their wild relatives (Mutegi et al., 2009). The overlap in flowering periods and the tillering ability of wild sorghum contribute to the potential for crop-to-wild gene flow (Mutegi et al., 2009). Intermediate forms between wild and cultivated sorghum have been observed in areas where sorghum is predominantly grown, indicating the occurrence of gene flow (Mutegi et al., 2009). The taxonomy and classification of the genus Sorghum are still not fully resolved, with alternative classifications proposed (Ananda et al., 2020). The exact number of species in the genus is also not well established, but it is known to consist of multiple species distributed across different regions (Ananda et al., 2020). Understanding the genetic diversity and evolutionary history of sorghum and its wild relatives is important for crop improvement and the development of more resilient crops (Ananda et al., 2020). Sorghum presents several opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. The cultivation and utilization of sorghum can contribute to addressing food security challenges and improving nutrition in the country. Sorghum is a versatile crop with various benefits that make it suitable for Egypt's agricultural landscape. One of the key advantages of sorghum is its ability to tolerate drought and heat stress (Mundia et al., 2019). This is particularly relevant for Egypt, where water scarcity and high temperatures are significant challenges in many agricultural areas. Sorghum has evolved mechanisms to cope with these adverse conditions, making it a valuable crop for agricultural use in arid and semiarid regions. Its ability to produce reasonable yields under limited water availability can contribute to increased agricultural productivity and food security. Additionally, sorghum is a highly nutritious crop, rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and essential minerals (Sorour et al., 2017). It is also gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Sorghum can be used as a staple food, animal feed, or processed into various food products such as flour, porridge, and snacks. Incorporating sorghum into the diet can help diversify food sources, improve nutrition, and contribute to food security. Furthermore, sorghum has economic opportunities. It can be used as a forage crop for livestock feed, providing an alternative to corn forage (Getachew et al., 2016). Sorghum is adapted to a variety of soil types and can tolerate soil salinity, making it suitable for cultivation in different regions of Egypt (Getachew et al., 2016). It can also be grown in rotation with other crops, contributing to soil fertility and sustainable agricultural practices. The production and value addition of sorghum-based products can create employment opportunities and contribute to the country's economy. In terms of climate change resilience, sorghum has the potential to withstand the impacts of climate change, such as increased temperature and water scarcity (Mundia et al., 2019). Its ability to produce reasonable yields under adverse conditions can help mitigate the negative effects of climate change on agricultural productivity and food security.
- V.
Teff:
Teff (Eragrostis tef) is a unique grain that is primarily cultivated for human consumption and livestock feed (Abewa et al., 2019). It is an indigenous annual crop in Ethiopia and Eritrea, where it is mainly grown for its small grains used in the preparation of a staple food called injera (Kim et al., 2020). Teff cultivation is primarily concentrated in these regions, but its popularity is rapidly increasing worldwide due to its attractive nutritional and functional properties (Kim et al., 2020). Teff is known for its small grain size, with a length of about 1.0 mm and a width of about 0.60 mm, making it one of the smallest whole flour grains in the world (Kim et al., 2020). Despite its small size, teff has gained attention for its nutritional composition and health benefits. It is rich in essential amino acids, minerals (such as iron and calcium), and dietary fiber (Kim et al., 2020). The grain is also gluten-free, which allows for flexibility in food utilization as it can be directly substituted for gluten-containing products (Kim et al., 2020). The cultivation of teff faces certain challenges. The average yield of teff is lower compared to other cereals such as wheat and barley, primarily due to the lack of available agronomic technology and low yield potential (Mihretie et al., 2020). However, teff is known for its adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, ranging from lowlands to highlands, and its tolerance to storage pests (Abewa et al., 2019). This makes it a low-risk crop that can be cultivated in various regions. Teff cultivation has significant agronomic and utilization benefits. The crop is preferred by both farmers and consumers due to its beneficial traits and genetic diversity (Nascimento et al., 2018). It is considered a national treasure in Ethiopia and has the potential for global importance (Nascimento et al., 2018). Teff can be processed and utilized in various food applications, including the production of gluten-free products (Nascimento et al., 2018). Its nutritional value and functional properties make it an attractive option for new food uses. In terms of distribution, teff cultivation is primarily concentrated in Ethiopia and Eritrea, where it has been cultivated for thousands of years (Kim et al., 2020). However, the demand for teff and its products has been increasing globally, leading to its commercialization and distribution in other countries (Barretto et al., 2020). The crop's nutritional value and gluten-free nature have contributed to its popularity and expansion beyond its traditional cultivation regions. Teff presents several opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. The cultivation and utilization of teff can contribute to addressing food security challenges and improving nutrition in the country. Teff is a versatile crop with various benefits that make it suitable for Egypt's agricultural landscape. One of the key advantages of teff is its ability to tolerate harsh environmental conditions and grow over a wider range of ecologies compared to other cereals (Gebremariam et al., 2013). It is known for its environmental flexibility and can tolerate drought, heat, and poor soil conditions (Gebremariam et al., 2013). This makes teff a valuable crop for agricultural use in Egypt, where water scarcity and desertification are significant challenges. The cultivation of teff can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices and enhance agricultural productivity in arid and semiarid regions. Additionally, teff is a highly nutritious crop, rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and essential minerals (Gebremariam et al., 2013). It is also gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Teff has a high nutritional value and is considered a complete protein source (Gebremariam et al., 2013). Incorporating teff into the diet can help diversify food sources, improve nutrition, and contribute to food security. Furthermore, teff has economic opportunities. It is used in various food applications, including baking, brewing, and as a staple food (Gebremariam et al., 2013). Teff flour is used to make traditional Ethiopian flatbread called injera, which is a staple in Ethiopian cuisine. The production and value addition of teff-based products can create employment opportunities and contribute to the country's economy. In terms of water efficiency, teff has the potential to contribute to water conservation in agriculture. Egypt faces water scarcity and low water use efficiency in the agricultural sector (El-Shirbeny et al., 2014). Teff is known for its relatively low water requirements compared to other cereal crops (El-Shirbeny et al., 2014). By promoting the cultivation of teff, Egypt can improve water use efficiency and reduce the pressure on water resources in agriculture.
- VI.
Millet
Millet is a type of grain that has been consumed by humans for thousands of years. It has been an important staple food in many cultures, particularly in Asia and Africa. Millet is known for its nutritional value, as it is rich in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals (John & Babu, 2021). There are several different types of millet, including proso millet, foxtail millet, and pearl millet, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. One of the key aspects of millet is its dietary diversity and consumption of significant C4 resources, such as millets (Wang et al., 2017). Millet consumption has been found to provide direct evidence of unique dietary diversity, as indicated by the large range of δ13C values (Wang et al., 2017). This diversity in millet consumption is important for understanding the dietary habits and cultural practices of ancient populations. Cooking methods can have an impact on the nutritional composition and digestibility of millet. For example, heating has been found to reduce the digestibility of proso millet proteins (Gulati et al., 2017). This reduction in digestibility is attributed to the formation of hydrophobic aggregates during the cooking process (Gulati et al., 2017). Similarly, the digestibility of protein in proso millet flour is significantly lower compared to unprocessed flour, even after cooking with reducing agents (Gulati et al., 2017). These findings highlight the importance of considering cooking methods when assessing the nutritional value of millet. addition to its nutritional value, millet has also been studied for its potential health benefits. Research has shown that protein isolates from both raw and cooked foxtail millet can attenuate the development of type 2 diabetes in diabetic mice (Fu et al., 2021). The protein isolate from cooked foxtail millet has been found to improve glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, as well as alleviate lipid disorders (Fu et al., 2021). These findings suggest that millet protein isolates may have potential as a dietary intervention for managing type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, millet has been found to have antioxidant activity. The phenolic contents of cookies containing millet flour were found to be higher compared to cookies prepared from plain wheat flour (Hussain et al., 2019). The antioxidant activity of millet can be influenced by different processing methods, such as cooking and steaming (Zhang et al., 2017). However, the antioxidant activity measured by different assays may not be consistent with each other (Zhang et al., 2017). This indicates that the antioxidant activity of millet is complex and may vary depending on the specific method of analysis. The cooking process can also affect the morphological and physicochemical properties of millet grains. Waxy and non-waxy proso millet grains have been found to undergo gelatinization during cooking, with non-waxy grains being more resistant to cooking (Yang et al., 2019). Changes in the morphological and physicochemical properties of proso millet grains during cooking have been rarely reported, highlighting the need for further research in this area (Yang et al., 2019). Millet cultivation is an important agricultural practice in many regions, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa and the arid and semi-arid tropics of Asia (Jukanti et al., 2016). In Niger, pearl millet is a staple crop that covers more than 65% of the total cultivated area (Mariac et al., 2006). Pearl millet is primarily cultivated for grain production, but its stover is also valued as dry fodder (Jukanti et al., 2016). It is known for its resilience to climate change, as it is adaptable to drought and high temperatures (Jukanti et al., 2016). Millets, including pearl millet, have been cultivated as a food and feed crop for a long time due to their nutritional value and other merits (Matsuura et al., 2016). Genetic diversity is an important aspect of millet cultivation. Studies have shown that wild pearl millet accessions have higher genetic diversity compared to cultivated accessions (Mariac et al., 2006). However, there is evidence of introgressions between cultivated and wild accessions, indicating some level of gene flow between the two groups (Mariac et al., 2006). Understanding the genetic diversity and dynamics of pearl millet is crucial for germplasm conservation and breeding programs (Mariac et al., 2006). Millet cultivation practices vary depending on the region and purpose. In West Africa, pearl millet is often cultivated as a monocrop, but it can also be intercropped with legumes such as cowpea, groundnut, and grain sorghum (Jukanti et al., 2016). In India, pearl millet is grown as an irrigated summer crop, resulting in higher yields and better-quality grain (Jukanti et al., 2016). Recommended production practices for pearl millet include stand establishment, row spacing, plant population, fertilization, and pest management (Assis et al., 2017). The use of pearl millet as a cover crop between soybean or maize production is also recommended to reduce crop losses from nematodes (Assis et al., 2017). Millet cultivation has several advantages. It has fewer pests and disease problems compared to other cereals and is suited to different cropping systems (Jukanti et al., 2016). Millets are also known for their climate resilience and ability to grow in marginal soils (Grovermann et al., 2018). They are highly responsive to improved crop management practices, which can lead to increased yields and better-quality grain (Jukanti et al., 2016). Millets, including pearl millet, are considered important sources of food security, nutrition, and health in regions with arid and semi-arid climates (Jukanti et al., 2016).
Millet presents several opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. The cultivation and utilization of millet can contribute to addressing food security challenges and improving nutrition in the country. Millet is a versatile crop with various benefits that make it suitable for Egypt's agricultural landscape. One of the key advantages of millet is its ability to tolerate drought and heat stress Deng et al. (2017). This is particularly relevant for Egypt, where water scarcity and high temperatures are significant challenges in many agricultural areas. Millet has evolved mechanisms to cope with these adverse conditions, making it a valuable crop for agricultural use in arid and semiarid regions. Its ability to produce reasonable yields under limited water availability can contribute to increased agricultural productivity and food security. Additionally, millet is a highly nutritious crop, rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and essential minerals (Fu et al., 2010). It is also gluten-free, making it suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Millet can be used as a staple food, animal feed, or processed into various food products such as flour, porridge, and snacks. Incorporating millet into the diet can help diversify food sources, improve nutrition, and contribute to food security. Furthermore, millet has economic opportunities. It can be used as a forage crop for livestock feed, providing an alternative to other feed sources (Wilkinson et al., 2011). Millet is adapted to a variety of soil types and can tolerate soil salinity, making it suitable for cultivation in different regions of Egypt (Wilkinson et al., 2011). It can also be grown in rotation with other crops, contributing to soil fertility and sustainable agricultural practices. The production and value addition of millet-based products can create employment opportunities and contribute to the country's economy. In terms of climate change resilience, millet has the potential to withstand the impacts of climate change, such as increased temperature and water scarcity (Wilkinson et al., 2011). Its ability to produce reasonable yields under adverse conditions can help mitigate the negative effects of climate change on agricultural productivity and food security.
Conclusion:
Egypt is characterized by its unique geography, with a narrow strip of green along the Nile River surrounded by vast deserts. The agricultural sector plays a crucial role in the country's economy but faces challenges such as water stress and pressure on resources. The landscape has changed over time due to climate change and human activities, leading to the extinction of certain species. Desertification is also a significant issue in certain parts of Egypt. However, the current situation of agriculture in Egypt presents both challenges and opportunities. Soil degradation, urban expansion, and limited arable land are among the challenges that need to be addressed. However, the use of remote sensing and GIS modeling, as well as the potential for biotech product commercialization, offer opportunities for sustainable agricultural development in Egypt. However, the situation of wheat and other grain crops in Egypt is characterized by a significant gap between production and demand, leading to heavy reliance on imports. Population growth, competition for water resources, and the impact of climate change pose challenges to achieving self-sufficiency in wheat. However, the use of crop simulation models, research on water management and weed control, and the exploration of innovative agricultural practices offer opportunities to address these challenges and enhance wheat production in Egypt. On the other hand, nontraditional crops have the potential to play a significant role in closing the food gap in Egypt. By focusing on sustainable agricultural intensification, promoting the cultivation of nontraditional crops, and enhancing agricultural trade, Egypt can increase its food production and achieve greater food security. However, the cultivation of pseudo cereals, such as quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat, presents an opportunity for Egypt's agricultural sector. These crops offer high nutritional value, can be grown in marginal lands, and contribute to food security and dietary diversity. Further research and promotion of pseudo cereals cultivation can enhance the agricultural landscape and improve the nutritional status of the population. However, nontraditional crops have been studied and explored in Egypt's agricultural sector. These crops, such as date palms and crops suitable for export, have the potential to contribute to closing the food gap in the country. Factors such as land suitability, agricultural integration, and the adoption of sustainable practices, including organic agriculture, are important considerations in promoting the cultivation of nontraditional crops. However, the pseudo cereals crops have the potential to contribute to addressing the nutrition gap in Egypt. By incorporating these crops into the diet and promoting nutritional education, individuals can obtain a more balanced and nutritious food source. Further research and promotion of pseudo cereals cultivation and consumption can help improve the nutritional status of the population and bridge the nutrition gap in Egypt. Also, it presents significant opportunities to address current health challenges in Egypt. Their exceptional nutritional value, including high protein content, essential amino acids, and micronutrients, can help combat malnutrition and address deficiencies in iron and other essential nutrients. Additionally, the low glycemic index and potential for weight management make pseudocereals valuable in addressing the rising prevalence of NCDs. Promoting the cultivation and consumption of pseudocereals can contribute to sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation in Egypt. However, Pseudo cereals such as amaranth, buckwheat, quinoa, sorghum, and teff are commonly used in nutrition due to their nutritional value and health benefits. These crops are gluten-free and provide protein, dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They can be incorporated into various food products to enhance their nutritional value and are considered safe for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. The consumption of pseudo cereals, along with whole grains, is recommended for a balanced and healthy diet. Buckwheat presents significant opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. Its tolerance to soil salinity, short growing season, nutritional value, and economic potential make it a promising crop. By promoting the cultivation and utilization of buckwheat, Egypt can enhance food security, improve nutrition, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Quinoa has the potential to contribute to closing the food gap in Egypt. Its adaptability to different environmental conditions, high nutritional values, and resistance to abiotic stresses make it a promising nontraditional crop. Sorghum presents significant opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. Its tolerance to drought and heat stress, nutritional value, adaptability to different soil types, and economic potential make it a promising crop. By promoting the cultivation and utilization of sorghum, Egypt can enhance food security, improve nutrition, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Teff presents significant opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. Its environmental flexibility, nutritional value, economic potential, and water efficiency make it a promising crop. By promoting the cultivation and utilization of teff, Egypt can enhance food security, improve nutrition, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Millet presents significant opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. Its tolerance to drought and heat stress, nutritional value, economic potential, and climate change resilience make it a promising crop. By promoting the cultivation and utilization of millet, Egypt can enhance food security, improve nutrition, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Millet presents significant opportunities for Egypt's agriculture and food security. Its tolerance to drought and heat stress, nutritional value, economic potential, and climate change resilience make it a promising crop. By promoting the cultivation and utilization of millet, Egypt can enhance food security, improve nutrition, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices.
References
- Abdelaal, H. (2021). Food security concerns and sustainable agricultural production in Egypt. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Social Sciences, 12(6), 529-534. [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, H. and Thilmany, D. (2019). Grains production prospects and long run food security in egypt. Sustainability, 11(16), 4457. [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A., Elshorbagy, A., Tuninetti, M., Laio, F., Ridolfi, L., Fahmy, H., … & Hoekstra, A. (2018). National water, food, and trade modeling framework: the case of egypt. The Science of the Total Environment, 639, 485-496. [CrossRef]
- Abewa, A., Adgo, E., Yitaferu, B., Alemayehu, G., Assefa, K., Solomon, J., … & Payne, W. (2019). Teff grain physical and chemical quality responses to soil physicochemical properties and the environment. Agronomy, 9(6), 28. 6. [CrossRef]
- Abozied, D. and Eldeep, S. (2013). The adoption of exports development for some non-traditional crops in new lands in egypt. Egyptian Journal of Desert Research, 63(1), 87-96. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I., Al-Juhaimi, F., & Özcan, M. (2021). Insights into the nutritional value and bioactive properties of quinoa (chenopodium quinoa): past, present and future prospective. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 56(8), 3726-3741. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. (2019). The potential of enhancing agricultural trade to achieve food security between egypt and nile basin countries. Fayoum Journal of Agricultural Research and Development, 33(2), 142-159. [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, F., Bendevis, M., & Jacobsen, S. (2014). The potential for utilizing the seed crop amaranth (amaranthus.
- Almas, L. and Usman, M. (2021). Determinants of wheat consumption, irrigated agriculture, and food security challenges in egypt. Wseas Transactions on Environment and Development, 17, 696-712. [CrossRef]
- Alobid, M., Derardja, B., & Szűcs, I. (2021). Food gap optimization for sustainability concerns, the case of egypt. Sustainability, 13(5), 2999. 5. [CrossRef]
- Ananda, G., Myrans, H., Norton, S., Gleadow, R., Furtado, A., & Henry, R. (2020). Wild sorghum as a promising resource for crop improvement. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. [CrossRef]
- Assem, S. (2014). Opportunities and challenges of commercializing biotech products in egypt: bt maize: a case study., 37-51. [CrossRef]
- Asseng, S., Kheir, A., Kassie, B., Hoogenboom, G., Abdelaal, A., Haman, D., … & Ruane, A. (2018). Can egypt become self-sufficient in wheat?. Environmental Research Letters, 13(9), 094012. [CrossRef]
- Assis, R., Freitas, R., & Mason, S. (2017). Pearl millet production practices in brazil: a review. Experimental Agriculture, 54(5), 699-718. [CrossRef]
- Barretto, R., Buenavista, R., Rivera, J., Wang, S., Prasad, P., & Siliveru, K. (2020). Teff (eragrostis tef) processing, utilization and future opportunities: a review. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 56(7), 3125-3137. [CrossRef]
- Bazile, D., Pulvento, C., Verniau, A., Al-Nusairi, M., Ba, D., Breidy, J., … & Padulosi, S. (2016). Worldwide evaluations of quinoa: preliminary results from post international year of quinoa fao projects in nine countries. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7. [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Perales, N., Pumi, G., Mujica, A., Talamini, E., & Padula, A. (2018). Quinoa expansion in peru and its implications for land use management. Sustainability, 10(2), 532. 2. [CrossRef]
- Berndt, L., Wratten, S., & Hassan, P. (2002). Effects of buckwheat flowers on leafroller (lepidoptera: tortricidae) parasitoids in a new zealand vineyard. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 4(1), 39-45. [CrossRef]
- Bilalis, D., Roussis, I., Kakabouki, I., & Folina, A. (2019). Quinoa (chenopodium quinoa willd.) crop under mediterranean conditions: a review. Ciencia e investigación agraria, 46(2), 51-68. [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M., Menard, C., Roudaut, G., & Brennan, C. (2012). Amaranth, millet and buckwheat flours affect the physical properties of extruded breakfast cereals and modulates their potential glycaemic impact. Starch - Stärke, 64(5), 392-398. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Zhang, B., & Xu, Z. (2007). Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of arabidopsis vacuolar na+/h+ antiporter gene atnhx1 in common buckwheat (fagopyrum esculentum). Transgenic Research, 17(1), 121-132. [CrossRef]
- Christoforidou, M., Borghuis, G., Seijger, C., Halsema, G., & Hellegers, P. (2022). Food security under water scarcity: a comparative analysis of egypt and jordan. Food Security, 15(1), 171-185. [CrossRef]
- Crop Explorer Country Summary for Major Crop Regions - United States Department of Agriculture, 2023, ipad.fas.usda.gov/countrysummary/default.aspx?id=EG.
- Deng, Z., Hung, H., Fan, X., & Lu, H. (2017). The ancient dispersal of millets in southern china: new archaeological evidence. The Holocene, 28(1), 34-43. [CrossRef]
- Egyptian General Survey Authority. (2023). Egypt map, accessed via: Egy_2m.pdf (esa.gov.eg).
- EL-Batran, M. (2019). An economic study of food consumption patterns in egypt. Egyptian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 70(4), 277-290. [CrossRef]
- El-Elsharkasy, S. (2023). Some economic indicators of the current situation of food vegetable oils in egypt and its future prospects. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal, 10(6), 77-97. [CrossRef]
- El-Kawy, O., Flous, G., Abdel-Kader, F., & Suliman, A. (2019). Land suitability analysis for crop cultivation in a newly developed area in wadi al-natrun, egypt. Alexandria Science Exchange Journal, 40(6), 683-657. [CrossRef]
- El-Metwally, I., Abdelraouf, R., Ahmed, M., Mounzer, O., Alarcón, J., & Abdelhamid, M. (2015). Response of wheat (triticum aestivum l.) crop and broad-leaved weeds to different water requirements and weed management in sandy soils. Agriculture (Pol Nohospodárstvo), 61(1), 22-32. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M., Hazman, M., El-Rady, A., Almas, L., McFarland, M., Din, A., … & Burian, S. (2021). Biochar reduces the adverse effect of saline water on soil properties and wheat production profitability. Agriculture, 11(11), 1112. 11. [CrossRef]
- El-Shirbeny, M., Ali, A., & Saleh, N. (2014). Crop water requirements in egypt using remote sensing techniques. Journal of Agricultural Chemistry and Environment, 03(02), 57-65. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q., Jin, S., Hu, Y., Ma, Z., Pan, J., & Wang, C. (2010). Agricultural development and human diets in gouwan site, xichuan, henan. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(7), 614-620.
- Fu, Y., Yin, R., Guo, E., Cheng, R., Diao, X., Xue, Y., … & Shen, Q. (2021). Protein isolates from raw and cooked foxtail millet attenuate development of type 2 diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 65(6). [CrossRef]
- Gaffa, T., Yoshimoto, Y., Hanashiro, I., Honda, O., Kawasaki, S., & Takeda, Y. (2004). Physicochemical properties and molecular structures of starches from millet (pennisetum typhoides) and sorghum (sorghum bicolorl. moench) cultivars in nigeria. Cereal Chemistry, 81(2), 255-260. 2. [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, M., Zarnkow, M., & Becker, T. (2013). Effect of teff (eragrostis tef) variety and storage on malt quality attributes. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 119(1-2), 64-70. [CrossRef]
- Gelotar, M., Dharajiya, D., Solanki, S., Prajapati, N., & Tiwari, K. (2019). Genetic diversity analysis and molecular characterization of grain amaranth genotypes using inter simple sequence repeat (issr) markers. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 43(1). [CrossRef]
- Getachew, G., Putnam, D., Ben, C., & Peters, E. (2016). Potential of sorghum as an alternative to corn forage. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 07(07), 1106-1121. 07. [CrossRef]
- Grovermann, C., Umesh, K., Quiédeville, S., Kumar, B., S., S., & Moakes, S. (2018). The economic reality of underutilised crops for climate resilience, food security and nutrition: assessing finger millet productivity in india. Agriculture, 8(9), 131. [CrossRef]
- Gulati, P., Li, A., Holding, D., Santra, D., Zhang, Y., & Rose, D. (2017). Heating reduces proso millet protein digestibility via formation of hydrophobic aggregates. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(9), 1952-1959. 9. [CrossRef]
- Hazzouri, K., Flowers, J., Visser, H., Khierallah, H., Rosas, U., Pham, G., … & Purugganan, M. (2015). Whole genome re-sequencing of date palms yields insights into diversification of a fruit tree crop. Nature Communications, 6(1). [CrossRef]
- Hendawy, E., Belal, A., Mohamed, E., Elfadaly, A., Murgante, B., Aldosari, A., … & Lasaponara, R. (2019). The prediction and assessment of the impacts of soil sealing on agricultural land in the north nile delta (egypt) using satellite data and gis modeling. Sustainability, 11(17), 4662. [CrossRef]
- Henry, D., Ament, J., & Cumming, G. (2016). Exploring the environmental drivers of waterfowl movement in arid landscapes using first-passage time analysis. Movement Ecology, 4(1). [CrossRef]
- Hg, L., Kreft, I., & Im, B. (2000). Nutritional properties of starch in buckwheat products: studies in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(1), 490-496. [CrossRef]
- Hoidal, N., Jacobsen, S., Odone, A., & Alandia, G. (2020). Defoliation timing for optimal leaf nutrition in dual-use amaranth production systems. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 100(13), 4745-4755. [CrossRef]
- Hooda, B. and Hooda, E. (2019). A new index for evaluation of g×e interaction in pearl millet using ammi and gge biplot analyses. Indian Journal of Agricultural Research, (of). [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S., Mohamed, A., Alamri, M., Ibraheem, M., Qasem, A., El-Din, M., … & Almaiman, S. (2019). Wheat–millet flour cookies: physical, textural, sensory attributes and antioxidant potential. Food Science and Technology International, 26(4), 311-320. [CrossRef]
- Jamalluddin, N., Massawe, F., Mayes, S., Ho, W., & Symonds, R. (2022). Genetic diversity analysis and marker-trait associations in amaranthus species. Plos One, 17(5), e0267752. [CrossRef]
- Janovská, D., Jágr, M., Svoboda, P., Dvořáček, V., Meglič, V., & Čepková, P. (2021). Breeding buckwheat for nutritional quality in the czech republic. Plants, 10(7), 1262. [CrossRef]
- John, D. and Babu, G. (2021). Lessons from the aftermaths of green revolution on food system and health. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 5. [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A., Gowda, C., Rai, K., Manga, V., & Bhatt, R. (2016). Crops that feed the world 11. pearl millet (pennisetum glaucum l.): an important source of food security, nutrition and health in the arid and semi-arid tropics. Food Security, 8(2), 307-329. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K., Sbhatu, D., & Kim, K. (2020). Nutritional composition and health benefits of teff (eragrostis tef (zucc.) trotter). Journal of Food Quality, 2020, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Shang, X., Dodson, J., & Zhou, X. (2009). Holocene agriculture in the guanzhong basin in nw china indicated by pollen and charcoal evidence. The Holocene, 19(8), 1213-1220. [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot, D., Jarvis, D., Ramaraj, T., Lee, R., Jellen, E., & Maughan, P. (2017). Single-molecule sequencing and hi-c-based proximity-guided assembly of amaranth (amaranthus hypochondriacus) chromosomes provide insights into genome evolution. BMC Biology, 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., lv, M., Peng, Q., Shan, F., & Wang, M. (2015). Physicochemical and textural properties of tartary buckwheat starch after heat-moisture treatment at different moisture levels. Starch - Stärke, 67(3-4), 276-284. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Cai, C., Yao, Y., & Xu, B. (2019). Alteration of phenolic profiles and antioxidant capacities of common buckwheat and tartary buckwheat produced in china upon thermal processing. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(12), 5565-5576. [CrossRef]
- Mariac, C., Luong, V., Kapran, I., Mamadou, A., Sagnard, F., Deu, M., … & Vigouroux, Y. (2006). Diversity of wild and cultivated pearl millet accessions (pennisetum glaucum [l.] r. br.) in niger assessed by microsatellite markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 114(1), 49-58. [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Molina, O. and López-Martínez, L. (2020). Effect of various process conditions on the nutritional and bioactive compounds of amaranth. [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Tomás, P. and Olea, P. (2010). Diagnosing the causes of territory abandonment by the endangered egyptian vulture neophron percnopterus: the importance of traditional pastoralism and regional conservation. Oryx, 44(3), 424-433. [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, A., An, P., Murata, K., & Inanaga, S. (2016). Effect of pre- and post-heading waterlogging on growth and grain yield of four millets. Plant Production Science, 19(3), 348-359. [CrossRef]
- Mihretie, F., Tsunekawa, A., Bitew, Y., Chakelie, G., Derebe, B., Getahun, W., … & Asfaw, M. (2020). Teff [eragrostis tef (zucc.)] rainfed yield response to planting method, seeding density, and row spacing. Agronomy Journal, 113(1), 111-122. [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Rodríguez, A., Gómez-Favela, M., Reyes-Moreno, C., Milán-Carrillo, J., & Mejia, E. (2015). Identification of bioactive peptide sequences from amaranth (amaranthus hypochondriacus) seed proteins and their potential role in the prevention of chronic diseases. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 14(2), 139-158. [CrossRef]
- . Mundia, C., Secchi, S., Akamani, K., & Wang, G. (2019). A regional comparison of factors affecting global sorghum production: the case of north america, asia and africa’s sahel. Sustainability, 11(7), 2135. [CrossRef]
- Mutegi, E., Sagnard, F., Muraya, M., Kanyenji, B., Rono, B., Mwongera, C., … & Labuschagne, M. (2009). Ecogeographical distribution of wild, weedy and cultivated sorghum bicolor (l.) moench in kenya: implications for conservation and crop-to-wild gene flow. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 57(2), 243-253. [CrossRef]
- Nardo, G., Villa, M., Conti, L., Ranucci, G., Pacchiarotti, C., Principessa, L., … & Parisi, P. (2019). Nutritional deficiencies in children with celiac disease resulting from a gluten-free diet: a systematic review. Nutrients, 11(7), 1588. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, K., Paes, S., Oliveira, I., Reis, I., & Augusta, I. (2018). Teff: suitability for different food applications and as a raw material of gluten-free, a literature review. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 6(2), 74-81. [CrossRef]
- Ozimede, C., Obute, G., & Nyananyo, B. (2019). Genetic diversity on <i>amaranthus hybridus l., amaranthus viridis l.</i> and<i> amaranthus spinosus l.</i> in parts of rivers state, nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 23(10), 1881-1885. [CrossRef]
- P, N. and Joye, I. (2020). Dietary fibre from whole grains and their benefits on metabolic health. Nutrients, 12(10), 3045. [CrossRef]
- Pastor, K. and anski, M. (2018). The chemistry behind amaranth grains. Journal of Nutritional Health & Food Engineering, 8(5). [CrossRef]
- Patil, S. and Jena, S. (2020). Utilization of underrated pseudo-cereals of north east india: a systematic review. Nutrition & Food Science, 50(6), 1229-1240. [CrossRef]
- Pitzschke, A. (2016). Developmental peculiarities and seed-borne endophytes in quinoa: omnipresent, robust bacilli contribute to plant fitness. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7. [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P., Fischer, G., Velthuizen, H., Reusser, D., & Kropp, J. (2015). Closing yield gaps: how sustainable can we be?. Plos One, 10(6), e0129487. [CrossRef]
- Qin, P., Ma, T., Wu, L., Shan, F., & Ren, G. (2011). Identification of tartary buckwheat tea aroma compounds with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Food Science, 76(6), S401-S407. [CrossRef]
- Rahjerdi, N., Rouzbehan, Y., Fazaeli, H., & Rezaei, J. (2015). Chemical composition, fermentation characteristics, digestibility, and degradability of silages from two amaranth varieties (kharkovskiy and sem), corn, and an amaranth–corn combination. Journal of Animal Science, 93(12), 5781. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J., Rahman, H., Thushar, S., & Singh, R. (2020). Healthy and resilient cereals and pseudo-cereals for marginal agriculture: molecular advances for improving nutrient bioavailability. Frontiers in Genetics, 11. [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, B. and Sowers, J. (2018). The rise of modern egypt. [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, I. (2018). The handbook of minerals on a gluten-free diet. Nutrients, 10(11), 1683. [CrossRef]
- Saad-Allah, K. and Youssef, M. (2018). Phytochemical and genetic characterization of five quinoa (chenopodium quinoa willd.) genotypes introduced to egypt. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 24(4), 617-629. [CrossRef]
- Salah, S., Shelaby, A., Othman, E., & Tawab, D. (2020). Analysis study of the food security factor for sugar in egypt. Fayoum Journal of Agricultural Research and Development, 34(2), 101-107. [CrossRef]
- Samy, A., Campbell, L., & Peterson, A. (2014). Leishmaniasis transmission: distribution and coarse-resolution ecology of two vectors and two parasites in egypt. Revista Da Sociedade Brasileira De Medicina Tropical, 47(1), 57-62. [CrossRef]
- Saturni, L., Ferretti, G., & Bacchetti, T. (2010). The gluten-free diet: safety and nutritional quality. Nutrients, 2(1), 16-34. [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A., Ghar, M., & Tateishi, R. (2004). Desertification impact assessment in egypt using low resolution satellite data and gis. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 61(4), 375-383. [CrossRef]
- Shams, A. (2018). Preliminary evaluation of new quinoa genotypes under sandy soil conditions in egypt. Agricultural Sciences, 09(11), 1444-1456. [CrossRef]
- Sherif, S. and Alamry, N. (2023). The problems of edible oils and the means of their development in egypt: a study in economic geography. Journal of Sustainable Development in Social and Environmental Sciences, 2(2), 67-87. [CrossRef]
- Silva-Sanchez, C., Rosa, A., León-Galván, M., Lumen, B., León-Rodríguez, A., & Mejía, E. (2008). Bioactive peptides in amaranth (amaranthus hypochondriacus) seed. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(4), 1233-1240. [CrossRef]
- Soriano-García, M., Arias-Olguín, I., Montes, J., Ramírez, D., Figueroa, J., Flores-Valverde, E., … & Valladares-Rodríguez, M. (2018). Nutritional functional value and therapeutic utilization of amaranth. Journal of Analytical & Pharmaceutical Research, 7(5). [CrossRef]
- Sorour, M., Mehanni, A., Taha, E., & Rashwan, A. (2017). Changes of total phenolics, tannins, phytate and antioxidant activity of two sorghum cultivars as affected by processing. Journal of Food and Dairy Sciences, 8(7), 267-274. [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Zuniga, V., Brito, V., Fuentes, F., & Steinfort, U. (2017). Phenological growth stages of quinoa (chenopodium quinoaspp.) in east africa as an alternative crop to support food security and climate change mitigation. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 201(5), 321-329. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. and Tsao, R. (2017). Phytochemicals in quinoa and amaranth grains and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential health beneficial effects: a review. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 61(7), 1600767. [CrossRef]
- Theethira, T. and Dennis, M. (2015). Celiac disease and the gluten-free diet: consequences and recommendations for improvement. Digestive Diseases, 33(2), 175-182. [CrossRef]
- Vieira, B., Luck, J., Amundsen, K., Werle, R., Gaines, T., & Kruger, G. (2020). Herbicide drift exposure leads to reduced herbicide sensitivity in amaranthus spp.. Scientific Reports, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Waisundara, V. (2020). Nutritional value of amaranth. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Wei, D., Chang, X., Yu, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, C., … & Fuller, B. (2017). Tianshanbeilu and the isotopic millet road: reviewing the late neolithic/bronze age radiation of human millet consumption from north china to europe. National Science Review, 6(5), 1024-1039. [CrossRef]
- White, J., Alagarswamy, G., Ottman, M., Porter, C., Singh, U., & Hoogenboom, G. (2015). An overview of ceres–sorghum as implemented in the cropping system model version 4.5. Agronomy Journal, 107(6), 1987-2002. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A., Hu, Y., Zhu, J., Zhou, M., Wang, C., & Richards, M. (2011). Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope evidence of human and pig diets at the qinglongquan site, china. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(4), 519-527. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q., Liu, L., Zhang, W., Li, J., Gao, X., & Feng, B. (2019). Changes in morphological and physicochemical properties of waxy and non-waxy proso millets during cooking process. Foods, 8(11), 583. [CrossRef]
- Yeakel, J., Pires, M., Rudolf, L., Dominy, N., Koch, P., Guimarães, P., … & Gross, T. (2014). Collapse of an ecological network in ancient egypt. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(40), 14472-14477. [CrossRef]
- Yigezu, Y., Moustafa, M., Mohiy, M., Ibrahim, S., Ghanem, W., Niane, A., … & Halila, H. (2021). Food losses and wastage along the wheat value chain in egypt and their implications on food and energy security, natural resources, and the environment. Sustainability, 13(18), 10011. 13, 18, 10011. [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M., Gaber, H., & Essawi, N. (2022). Examining the factors that affect consumers’ purchase intention of organic food products in a developing country. Sustainability, 14(10), 5868. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Li, J., Han, F., Ding, Z., & Fan, L. (2017). Effects of different processing methods on the antioxidant activity of 6 cultivars of foxtail millet. Journal of Food Quality, 2017, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Zou, C., Chen, A., Xiao, L., Muller, H., Ache, P., Haberer, G., … & Zhu, J. (2017). A high-quality genome assembly of quinoa provides insights into the molecular basis of salt bladder-based salinity tolerance and the exceptional nutritional value. Cell Research, 27(11), 1327-1340. [CrossRef]
- حافظ, م. (2017). التغيرات المناخية والتأثير المحتمل في الأمن الغذائي المصري. مجلة کلية الآداب جامعة الإسکندرية, 87(87), 1-36. [CrossRef]
- الشاعر, ا. (2015). إ مکانیة تحقیق التکامل الاقتصادی بین مصر والسودان فی محاصیل الحبوب الرئیسیة. مجلة الإقتصاد الزراعى و التنمیة الریفیة, 1(1), 1-9. [CrossRef]
- العال, ح. (2021). دراسة تحليلية لبعض مؤشرات التنمية الزراعية المستدامة في مصر. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Social Sciences, 12(12), 1125-1128. [CrossRef]
- نصار, ز. (2022). دراسة اقتصادیة تحلیلیة لأسلوبی الزراعة العضویة والتقلیدیة فى مصر. المجلة المصریة للاقتصاد الزراعی, 32(2), 402-419. [CrossRef]
- هاشم, ا. (2023). أثر أزمة «كورونــــــــــــا» علي الإنفاق الاستهلاكي في مصر. المجلة العربیة للإدارة, 43(1), 361-378. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).