Submitted:
12 September 2023
Posted:
13 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
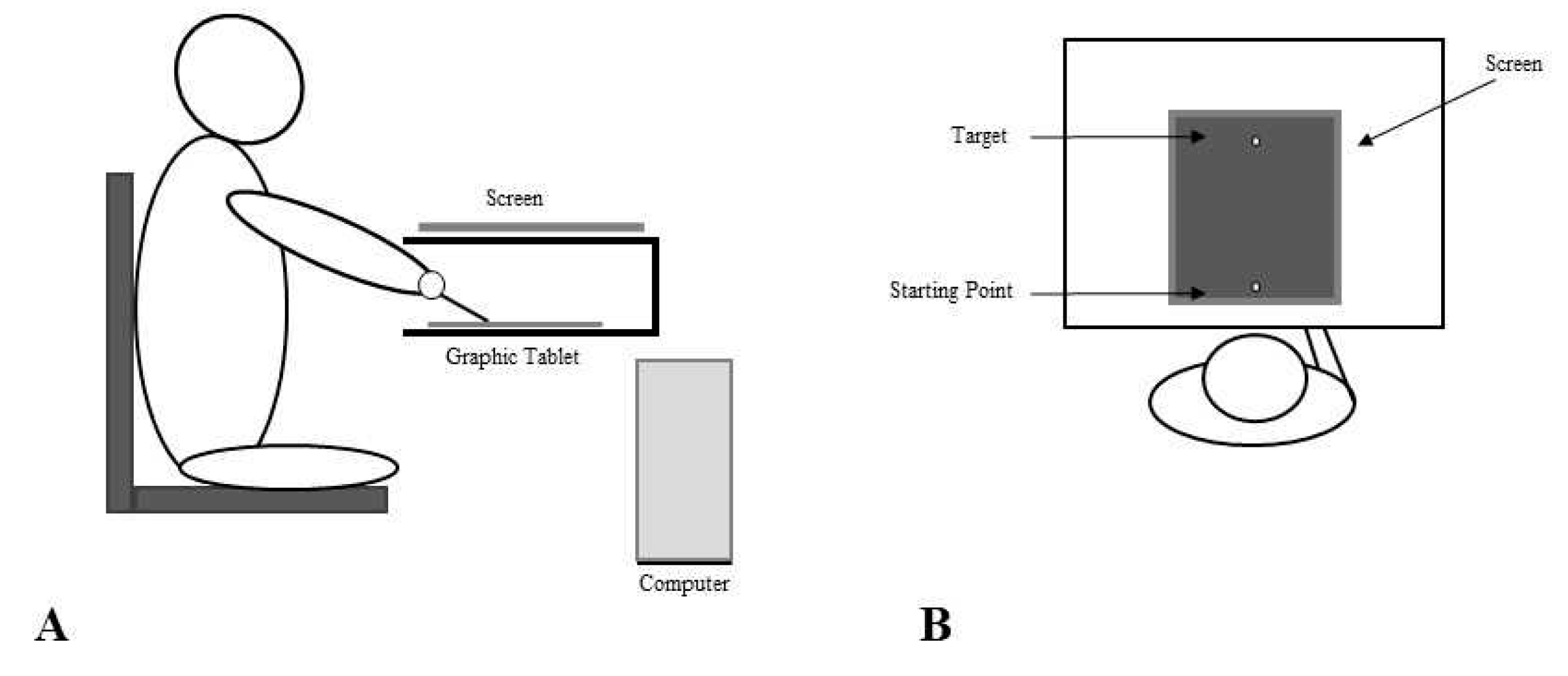
2.2. Set up
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
2.5. Data Analysis
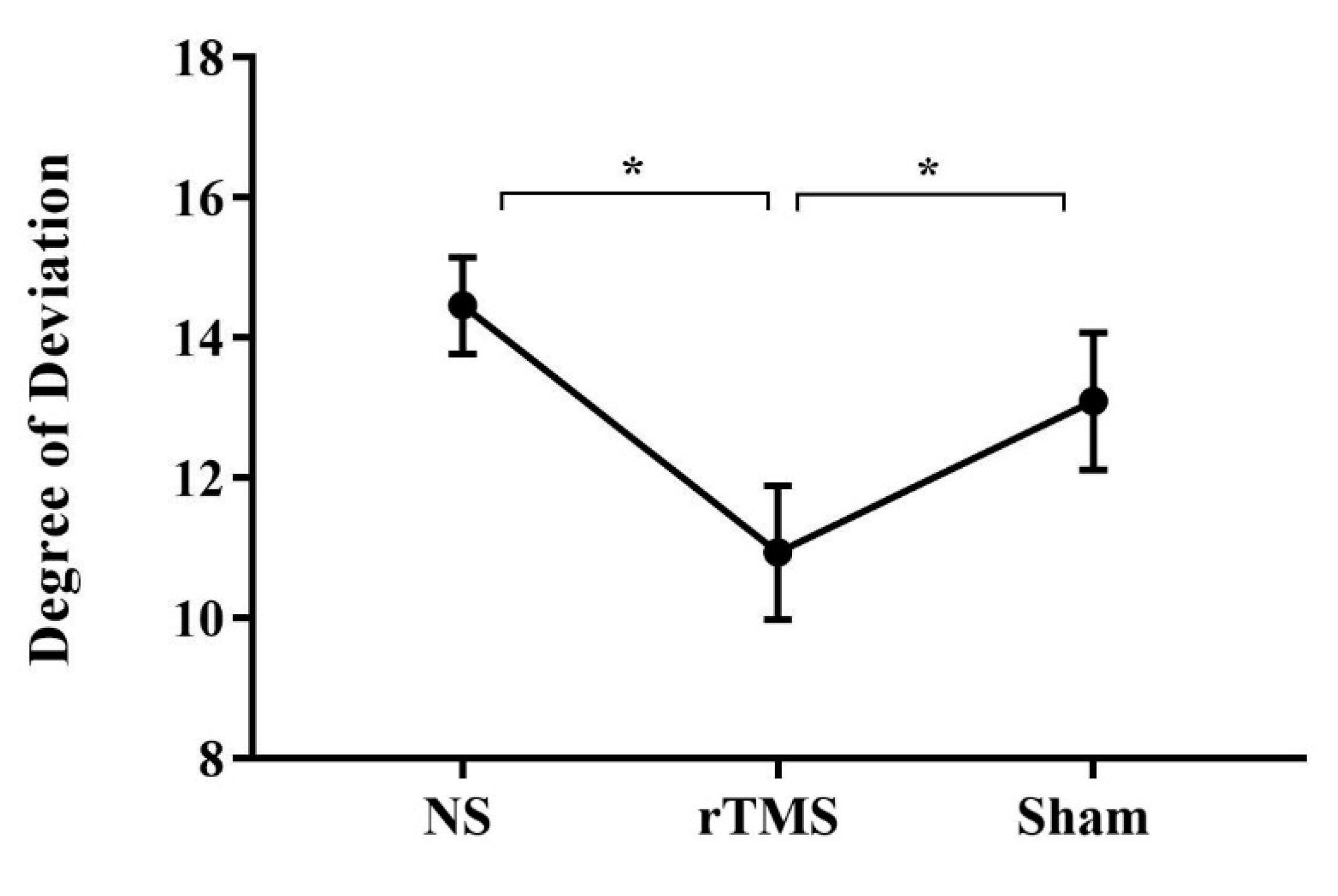
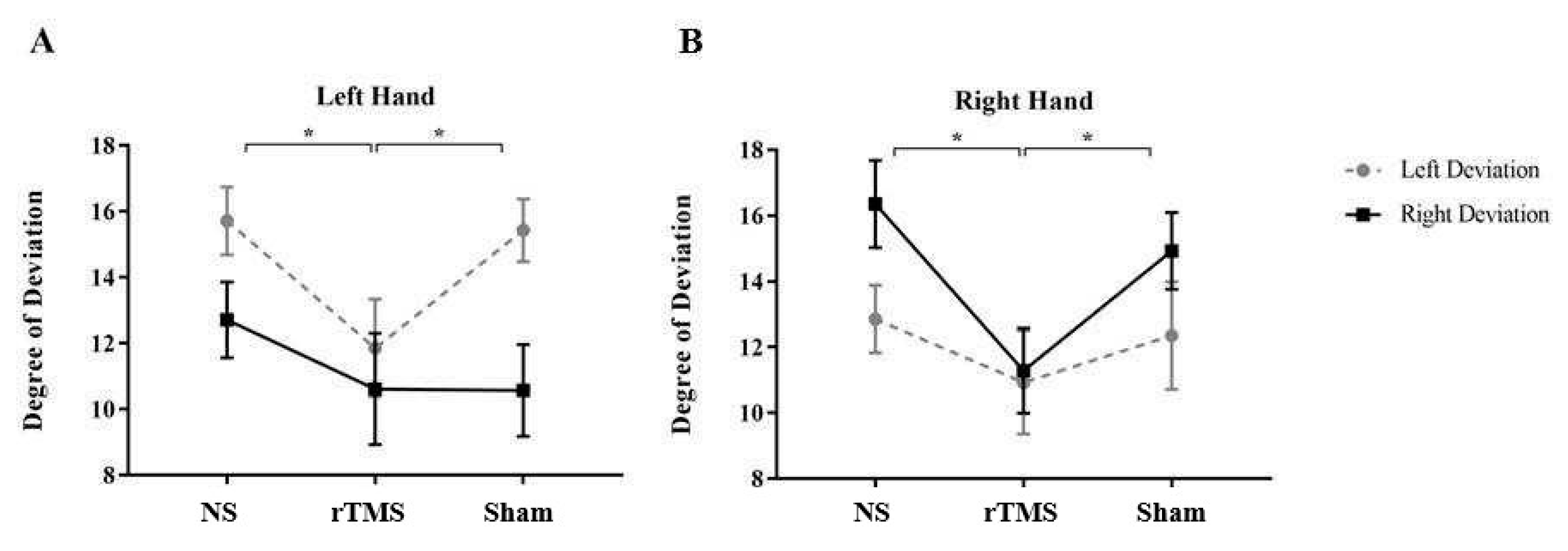
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blakemore, S.-J.; Wolpert, D.M.; Frith, C.D. Abnormalities in the awareness of action. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Association for Research into Nervous and Mental Diseases; Heilman, K.M.; Barrett, A.M.; Adair, J.C. Possible mechanisms of anosognosia: a defect in self–awareness. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 1998, 353, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frith, C.D.; Blakemore, S.-J.; Wolpert, D.M. Abnormalities in the awareness and control of action. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 1771–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libet, B. Unconscious cerebral initiative and the role of conscious will in voluntary action. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 1985, 8, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggard, P.; Magno, E. Localising awareness of action with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 127, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Bottini, G.; Gandola, M.; Pia, L.; Smania, N.; Stracciari, A.; Castiglioni, I.; Vallar, G.; Paulesu, E. Shared Cortical Anatomy for Motor Awareness and Motor Control. Science 2005, 309, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Pia, L. Understanding Motor Awareness Through Normal and Pathological Behavior. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarini, F.; Rabuffetti, M.; Piedimonte, A.; Pia, L.; Ferrarin, M.; Frassinetti, F.; Gindri, P.; Cantagallo, A.; Driver, J.; Berti, A. ‘Moving’ a paralysed hand: bimanual coupling effect in patients with anosognosia for hemiplegia. Brain 2012, 135, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pia, L.; Spinazzola, L.; Rabuffetti, M.; Ferrarin, M.; Garbarini, F.; Piedimonte, A.; Driver, J.; Berti, A. Temporal coupling due to illusory movements in bimanual actions: Evidence from anosognosia for hemiplegia. Cortex 2013, 49, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pia, L.; Neppi-Modona, M.; Ricci, R.; Berti, A. The anatomy of anosognosia for hemiplegia: a metanalysis. Cortex 2004, 40, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggard, P. Conscious intention and motor cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besharati, S.; Forkel, S.J.; Kopelman, M.; Solms, M.; Jenkinson, P.M.; Fotopoulou, A. The affective modulation of motor awareness in anosognosia for hemiplegia: Behavioural and lesion evidence. Cortex 2014, 61, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbarini, F.; Cecchetti, L.; Bruno, V.; Mastropasqua, A.; Fossataro, C.; Massazza, G.; Sacco, K.; Valentini, M.C.; Ricciardi, E.; Berti, A. To Move or Not to Move? Functional Role of Ventral Premotor Cortex in Motor Monitoring During Limb Immobilization. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 29, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnath, O. Awareness of the functioning of one's own limbs mediated by the insular cortex? J Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7134–8 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, V.; Pernigo, S.; Zapparoli, P.; Cordioli, Z.; Aglioti, S.M. Phenomenology and neural correlates of implicit and emergent motor awareness in patients with anosognosia for hemiplegia. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.C.; Rogers, R.D.; Haggard, P.; Passingham, R.E. Attention to intention. Science 2004, 303, 1208–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, I.; Mukamel, R.; Kreiman, G. Internally Generated Preactivation of Single Neurons in Human Medial Frontal Cortex Predicts Volition. Neuron 2011, 69, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmurget, M.; Reilly, K.T.; Richard, N.; Szathmari, A.; Mottolese, C.; Sirigu, A. Movement Intention After Parietal Cortex Stimulation in Humans. Science 2009, 324, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognini, N.; Zigiotto, L.; Carneiro, M.I.S.; Vallar, G. “How Did I Make It?”: Uncertainty about Own Motor Performance after Inhibition of the Premotor Cortex. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 28, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, V.; Fossataro, C.; Bolognini, N.; Zigiotto, L.; Vallar, G.; Berti, A.; Garbarini, F. The role of premotor and parietal cortex during monitoring of involuntary movement: A combined TMS and tDCS study. Cortex 2017, 96, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Walsh, V.; Rothwell, J. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in cognitive neuroscience – virtual lesion, chronometry, and functional connectivity. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2000, 10, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwinska, M.W.; Vitello, S.; Devlin, J.T. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Investigating Causal Brain-behavioral Relationships and their Time Course. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourneret, P.; Jeannerod, M. Limited conscious monitoring of motor performance in normal subjects. Neuropsychologia 1998, 36, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slachevsky, A.; Pillon, B.; Fourneret, P.; Pradat-Diehl, P.; Jeannerod, M.; Dubois, B. Preserved Adjustment but Impaired Awareness in a Sensory-Motor Conflict following Prefrontal Lesions. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slachevsky, A.; Pillon, B.; Fourneret, P.; Renié, L.; Levy, R.; Jeannerod, M.; Dubois, B. The prefrontal cortex and conscious monitoring of action: An experimental study. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.I. VOLITION: A NEW EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH. Scand. J. Psychol. 1963, 4, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.S.; Lundbye-Jensen, J.; Grey, M.J.; Vejlby, A.D.; Belhage, B.; Nielsen, J.B. Illusory Sensation of Movement Induced by Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e13301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, A.; Salatino, A.; Giromini, L.; Ricci, R.; Pignolo, C.; Cristofanelli, S.; Ferro, L.; Viglione, D.J.; Zennaro, A. Embodied simulation and ambiguous stimuli: The role of the mirror neuron system. Brain Res. 2015, 1629, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, R.; Salatino, A.; Siebner, H.R.; Mazzeo, G.; Nobili, M. Normalizing Biased Spatial Attention With Parietal rTMS in a Patient With Focal Hand Dystonia. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino, A.; Berra, E.; Troni, W.; Sacco, K.; Cauda, F.; D’agata, F.; Geminiani, G.; Duca, S.; Dimanico, U.; Ricci, R. Behavioral and neuroplastic effects of low-frequency rTMS of the unaffected hemisphere in a chronic stroke patient: A concomitant TMS and fMRI study. Neurocase 2013, 20, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino, A.; Momo, E.; Nobili, M.; Berti, A.; Ricci, R. Awareness of Symptoms Amelioration Following Low-frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in a Patient With Tourette Syndrome and Comorbid Obsessive-compulsive Disorder. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino, A.; Chillemi, G.; Gontero, F.; Poncini, M.; Pyasik, M.; Berti, A.; Ricci, R. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of Posterior Parietal Cortex Modulates Line-Length Estimation but Not Illusory Depth Perception. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.D.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Gould, I.C.; English, T.; Garavan, H.; McNaught, E.; Kamke, M.; Mattingley, J.B. Dissociable Mechanisms of Cognitive Control in Prefrontal and Premotor Cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroojerdi, B.; Phipps, M.; Kopylev, L.; Wharton, C.; Cohen, L.; Grafman, J. Enhancing analogic reasoning with rTMS over the left prefrontal cortex. Neurology 2001, 56, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dräger, B.; Breitenstein, C.; Helmke, U.; Kamping, S.; Knecht, S. Specific and nonspecific effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on picture–word verification. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Antal, A.; Bestmann, S.; Bikson, M.; Brewer, C.; Brockmöller, J.; Carpenter, L.L.; Cincotta, M.; Chen, R.; Daskalakis, J.D.; et al. Safety and recommendations for TMS use in healthy subjects and patient populations, with updates on training, ethical and regulatory issues: Expert Guidelines. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 132, 269–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, R.; Salatino, A.; Li, X.; Funk, A.P.; Logan, S.L.; Mu, Q.; Johnson, K.A.; Bohning, D.E.; George, M.S. Imaging the neural mechanisms of TMS neglect-like bias in healthy volunteers with the interleaved TMS/fMRI technique: preliminary evidence. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberley, T.J.; Borich, M.R.; Arora, S.; Siebner, H.R. Multiple sessions of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in focal hand dystonia: clinical and physiological effects. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniussi, C.; Rossini, P.M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in cognitive rehabilitation. Neuropsychol. Rehabilitation 2011, 21, 579–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur-Moreau, J.; Brunelin, J.; Fecteau, S. Non-invasive brain stimulation can induce paradoxical facilitation. Are these neuroenhancements transferable and meaningful to security services? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasso, P.; Ninghetto, M.; Salatino, A.; Ronga, I.; Bongiardina, A.; Iarrobino, I.; Neppi-Modona, M.; Ricci, R. Everything is (still) illuminated: Dual right cathodal-left anodal tDCS of PPC prevents fatigue on a visual detection task. Brain Stimul. 2018, 12, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Làdavas, E.; Petronio, A.; Umiltà, C. The Deployment of Visual Attention in the Intact Field of Hemineglect Patients. Cortex 1990, 26, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, N. Paradoxical functional facilitation in brain-behaviour research. Brain 1996, 119, 1775–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buetefisch, C.M.; Hines, B.; Shuster, L.; Pergami, P.; Mathes, A.; Wischnewski, M.; Kowalski, G.M.; Rink, F.; Belagaje, S.R.; Haut, M.W.; et al. Motor demand-dependent improvement in accuracy following low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation of left motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanzino, L.; Bove, M.; Trompetto, C.; Tacchino, A.; Ogliastro, C.; Abbruzzese, G. 1-Hz repetitive TMS over ipsilateral motor cortex influences the performance of sequential finger movements of different complexity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzkopf, D.S.; Silvanto, J.; Rees, G. Stochastic Resonance Effects Reveal the Neural Mechanisms of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3143–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone, A. , Horvath, J.C., Robertson, E.M. “Enhancement of normal cognitive abilities through noninvasive brain stimulation” in Cortical Connectivity: Brain Stimulation for Assessing and Modulating Cortical Connectivity and Function, eds R. Chen, and J.C. Rothwell (Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer), 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ianì, F.; Burin, D.; Salatino, A.; Pia, L.; Ricci, R.; Bucciarelli, M. The beneficial effect of a speaker’s gestures on the listener’s memory for action phrases: The pivotal role of the listener’s premotor cortex. Brain Lang. 2018, 180-182, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, B.; Vucurevic, G.; Müller-Forell, W.; Glassl, O.; Geber, C.; Dieterich, M.; Karnath, H.-O. Anosognosia for hemiparesis after left-sided stroke. Cortex 2014, 61, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornia, L.; Puglisi, G.; Leonetti, A.; Bello, L.; Berti, A.; Cerri, G.; Garbarini, F. Direct electrical stimulation of the premotor cortex shuts down awareness of voluntary actions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, K.M. , Valenstein, E., Watson, R.T. Neglect and related disorders. Semin Neurol. 2000, 20, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J. R. The effects of an irrelevant directional cue on human information processing. In R. W. Proctor & T. G. Reeve (Eds.), Stimulus-response compatibility (pp. 31-86). 1990, Amsterdam: North-Holland.
- Umiltá, C. , Nicoletti, R. Spatial Stimulus-Response Compatibility. Advances in Psychology 1990, 65, 89–116. [Google Scholar]
- Freud, E.; Aisenberg, D.; Salzer, Y.; Henik, A.; Ganel, T. Simon in action: the effect of spatial congruency on grasping trajectories. Psychol. Res. 2013, 79, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




