1. Introduction
For over thirty years, cosmologists have built up conclusive evidence that cosmic expansion is accelerating. To explain such observation, we need to assume that there is a mysterious new component: Dark Energy (DE) or a Cosmological Constant,
. This new term is usually interpreted as a repulsive force between galaxies that opposes gravity and dominates the expansion. Such strange behaviour is often flagged as one of the most important challenges to understand the laws of Physics today and could provide an observational window to understand Quantum Gravity ([
30]).
Cosmic acceleration is usually defined by the adimensional coefficient
, where
. For a universe with an equation of state
this results in
. For regular matter or radiation we have
so we expect the expansion to decelerate (
) because of gravity. However, concordant measurements from galaxy clustering (e.g. [
2,
3,
8]), Type Ia supernova ([
23,
26]) and CMB ([
24,
28]) all agree with an expansion that tends asymptotically to
or
(e.g. see [
7] and references therein for a review of more recent results, including weak gravitational lensing). This behaviour is very consistent with a Cosmological Constant
(see [
6,
22,
29]) where
tends to
and
q tends to
. What does this all mean?
The term Dark Energy (DE) was introduced by [
17] to refer for any component with
. However, there is no fundamental understanding of what DE is or why we measure a term with
. A natural candidate for DE is
, which is equivalent to
and can also be thought of as the ground state of a field (the DE), similar to the Inflaton but with a much smaller (
) energy scale.
can also be a fundamental constant in GR, but this has some other complications ([
6,
22,
29]).
2. Cosmic Acceleration
Current observations of the cosmos seem consistent with General Relativity (GR) with a flat FLRW (Friedmann–Lemaitre–Robertson–Walker) metric in comoving coordinates, corresponding to a homogeneous and isotropic space :
where we use units of
and
is the scale factor. For a classical perfect fluid with matter and radiation density
, the solution to Einstein’s field equations (called LCDM) is well known:
where
, where
and
represents the current (
) matter and radiation density,
and
. The cosmological constant (
) term corresponds to
where
Km/s/Mpc. Given
and
we can use the above equations to find
.
Cosmic acceleration is usually defined as
, where the dot represents a derivative with respect to proper time
. A derivative over Eq.
2 shows that:
For
Eq.
2-
3 indicate that as time passes (
) we have that
and
. This is because gravity opposes cosmic expansion and brings the expansion asymptotically to a halt. Including
brings the expansion to accelerate so that
and
. This is illustrated as black lines in
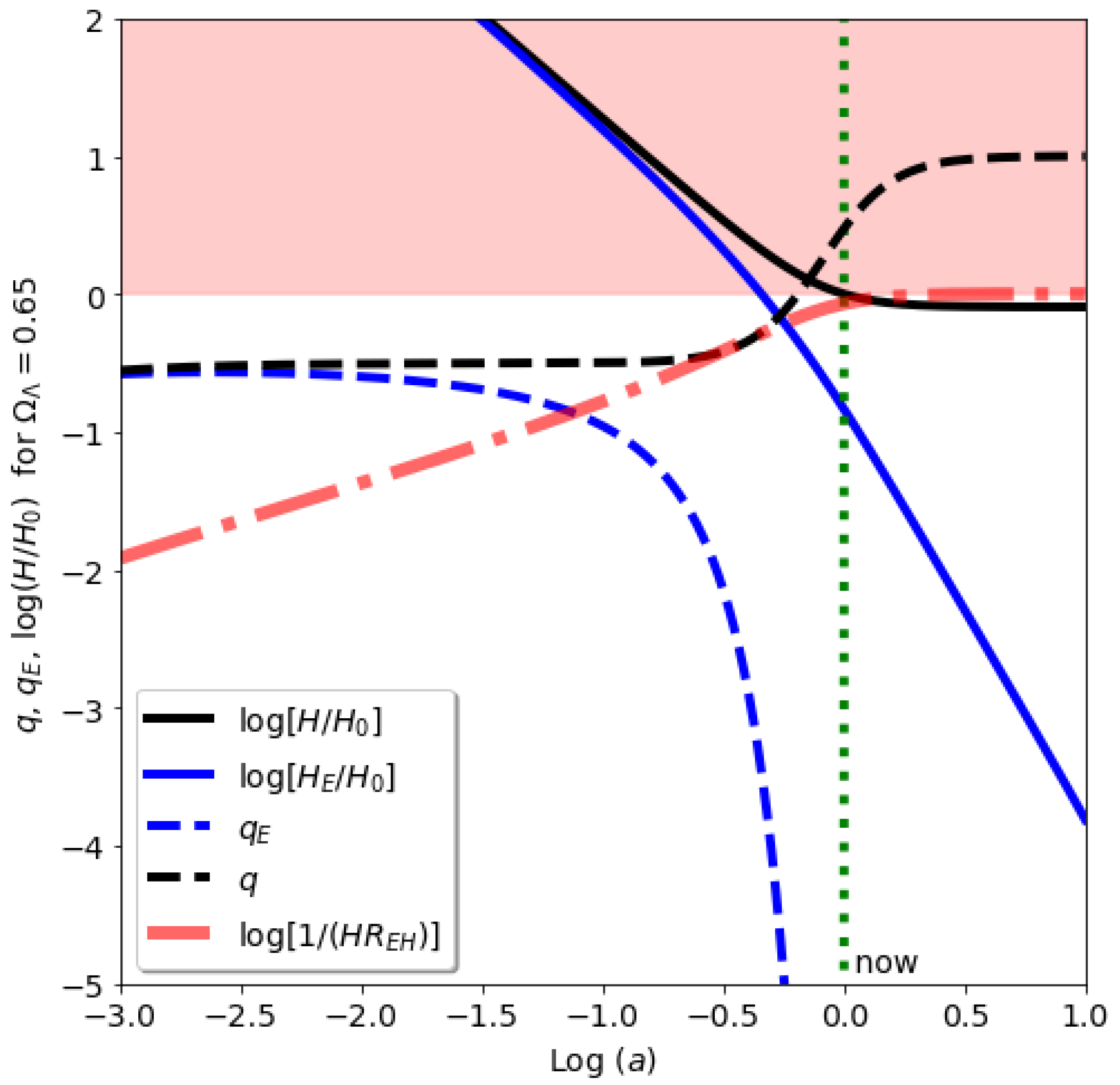
Figure 1 for
. The effect of
is then interpreted as a mysterious new repulsive force (or Dark Energy) that opposes gravity.
But this interpretation of acceleration, based on
, corresponds to the acceleration of 3D space-like events,
, of fixed comoving separation
:
so that
and
. Such events are not causally connected and correspond to a non-local theory of Gravity or to the Newtonian approximation of action at a distance where the speed of light is infinite. We need a better definition of acceleration to identify the nature of its physical causes within GR.
3. Event Acceleration
To have a coordinate invariant measurement of cosmic acceleration that is closer to actual observations, we need to use the distance between the events that are causally connected. This will help us to better interpret the effect of on cosmic expansion and therefore its possible mysterious meaning. To this end, we introduce here the event expansion rate and acceleration .
A photon emitted at time
can travel following an outgoing radial null geodesic
which from Eq.
1 implies
. The proper distance
traveled between the event at
and the future event at
is then (see e.g. [
9]):
Thus, we argue that we should use
R instead of
d in Eq.
4 as a measure of distance in cosmology to define cosmic acceleration and expansion rate. Such change is equivalent to a simple change of coordinates in the FLRW metric of Eq.
1, from comoving coordinates
to physical coordinates
:
which is just Minkowski’s metric in spherical coordinates with a radius
. We then have that:
. We can define the expansion rate between events as:
where the additional term,
corresponds to a friction term. There is an ambiguity in this definition because
R in Eq.
5 depends also on the arbitrary time
use to define
R. To break this ambiguity we arbitrarily fix
R to be the distance to
(which corresponds to a possible Event Horizon):
where
. As we will see in next section, this choice implies that
is zero unless
. So this new invariant way to define cosmic expansion reproduces the standard definition when
. But for
we have that the event expansion halts
(blue line in in
Figure 1) due to the friction term (red line) for
, while the standard Hubble rate definition approaches a constant
(black line). This might seem irrelevant at first look, but the resulting physical interpretation is quite different. In the standard definition,
H, the expansion with
becomes asymptotically exponential (or inflationary expansion). While in our new definition,
, the expansion becomes static (as in the static de-Sitter metric).
The event acceleration can then be measured as:
As before, for
the friction term,
, makes little difference between
q and
. For
the friction term asymptotically cancels the
term in
(i.e. Eq.
3) so that
is always negative, no matter how large is
(
and
). The net effect of the
term is to bring the expansion of events to a faster stop (
) that in the case with gravity alone. This is illustrated in
Figure 1. The
term produces a faster deceleration (than with gravity alone). This corresponds to an attracting (and not repulsive) force, as explained in more detail in the Appendix.
4. Event Horizon
What is more relevant to understand the meaning of
is that the additional deceleration brings the expansion to a halt within a finite proper distance between the events, creating an Event Horizon (EH). The EH is the maximum distance that a photon emitted at time
can travel following the outgoing radial null geodesic:
For
we have
, so there is no EH. But for
we have that
(red line in
Figure 1). We can then see that
corresponds to a causal horizon or boundary term. The analog force behaves like a rubber band between observed galaxies (null events) that prevents them crossing some maximum stretch (i.e. the EH). We can interpret such force as a boundary term that just emerges from the finite speed of light (see the Appendix).
The FLRW metric with
, asymptotically tends to the de-Sitter metric, which can be written as:
This form corresponds to a static 4D hyper-sphere of radius . So in this (rest) frame, events can only travel a finite distance within a static 3D surface of the imaginary 4D hyper-sphere. Thus there is a frame duality that allows us to equivalently describe de-Sitter space as either static (in proper or physical coordinates and t) or exponentially expanding (in comoving coordinates and ).
This frame duality can be understood as a Lorentz contraction
, where
. An observer in the rest frame, sees the moving fluid element
contracted by the Lorentz factor
. Therefore, the FLRW metric becomes de-Sitter:
This radial element corresponds to the metric of a hypersphere of radius
that expands towards a constant event horizon
(see also [
19] and the Appendix in [
12]). This duality is better understand using our new measures for the expansion rate
and cosmic deceleration
based on the distance between causal events.
5. Comparison to Data
We show next how to estimate the new measure of cosmic acceleration,
, using direct astrophysical observations. As an example consider the Supernovae Ia (SNIa) data as given by the ’Pantheon Sample’ compilation ([
27]) consisting on 1048 SNIas between
. Each SNIa provides a direct estimate of the luminosity distance
at a given measured redshift
z. This corresponds to the comoving look-back distance:
so that
gives us directly
. The second derivative gives us the acceleration:
is given by the model prediction in Eq.
10 (arbitrarily fixed at
in both data and models). We adopt here the approach presented in [
18], who used an empirical fit to the luminosity distance measurements, based on a third-order logarithmic polynomial:
where
. [
18] find a good fit to:
and
to the full SNIa ’Pantheon Sample’. We use these values of
A and
B and its corresponding errors to estimate
H,
q and
using the above relations. Results for
H and
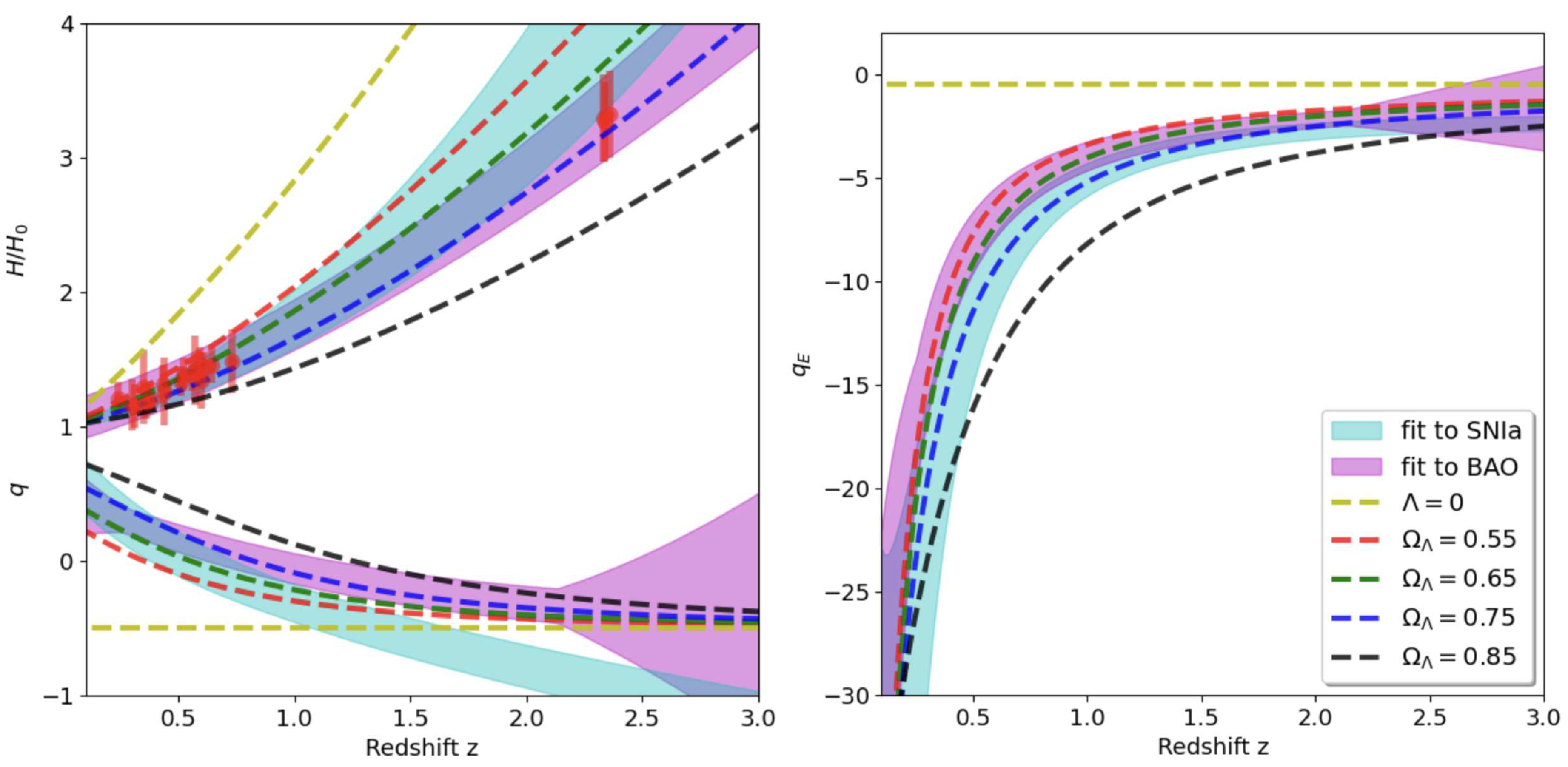
q are shown as shaded cyan regions in the left panel
Figure 2. They are compared to the LCDM predictions in Eq.
2 and
3.
There is a very good agreement in
for
. At
, the
estimates are also consistent with the
predictions. But the detailed
evolution with redshift in the SNIa data does not seem to follow any of the model predictions, specially for
. The
estimates are too steep compare to the different models predictions. If we compare instead the
estimates (see right panel of
Figure 2) we find a much better agreement with the model predictions. This seems to validate our
approach, but it is not clear from this comparison alone if this is caused by the fitting function use in Eq.
15.
To test this further we use measurements of the radial BAO data to estimate
. Such measurements give us a direct estimate of
(as first demonstrated by [
15,
16]) so they have the advantage over SNIa that we only need to do a first order derivative, to estimate
q or
:
As an illustration we use
measurements presented in Table 2 in [
20]. This compilation of
is shown as red points with
errorbars in the left panel
Figure 2. The compilation include values from the clustering of galaxies (
) and Ly-alpha forest in QSO (
). The combination of two separate ranges of redshift allows for a very good measurement of
at the intermediate redshift (
), where we found the discrepancies in SNIa for
q and
model comparison (see above). The radial BAO provides a very good constraint on cosmic acceleration, independent of possible calibration errors in
or sampling errors (from small area samples). This is something that we can not yet do with the current SNIa data, but will be very interesting to see in the near future with upcoming data from wider and deeper surveys.
We fit a quadratic polynomial to the radial BAO data:
We have checked that the results presented here are very similar if we use a cubic polynomial. In units of Km/s/Mpc, we find
,
and
, with strong covariance between the errors (the cross-correlation coefficient between
and
is
). The value of
is in good agreement with the Planck CMB fit ([
24]) but in some tension with the SNIa local calibration:
(see [
25]). This corresponds to either a local calibration problem (in SNIa, in radial BAO or in both) or a tension in the
CDM model at different times or distances (see e.g. [
1]). We ignore this normalization problem here and just focus on the evolution of
to measure cosmic acceleration
q or
(which are fairly independent of
).
In the right panel of
Figure 2 we show (as shaded regions) the measurements for
given by combining Eq.
15 with Eq.
14 and Eq.
17 with Eq.
16. The measurements clearly favour models with large negative cosmic event acceleration
, which supports our interpretation of
as a friction term.
Comparing left and right panels in
Figure 2 we see that both
q and
are rougthly consistent with models with
( or
) in good concordance with
in the upper left panel of
Figure 2.
Even when the underlying model for
q and
is the same, note how the measured
q and
data have different tensions with the model predictions as a function of redshift. In particular, the radial BAO and SNIa data sets show inconsistencies among them for
q around
. This is a well known tension (see e.g. 17 in [
4]). This tension disappears when we use the corresponding estimates for
. Thus, data is more consistent with the
than with the
q description.
One would expect that a perfect realizations of the LCDM model in Eq.
2 would produce consistent results in both
q and
. But deviations from LCDM and systematic effects can produce tensions in data, specially if we use a parametrization, like
q, which refers to events that we never observe. The
q and
parametrization of acceleration are more general than the particular LCDM model and the fact that data prefers
is an important indication. Data lives in the light-cone, which corresponds to
rather than
q. At
the difference between a light-cone and space-like separations is very significant and any discrepancies in the data or model will show more pronounced in the
q modeling.
We conclude that the data shows some tensions with LCDM predictions (as indicated by q) but confirms that cosmic expansion is clearly decelerating (as indicated by ) so that events are trapped inside an Event Horizon ().
6. Discussion & Conclusions
We have shown here that the measured
term, which is usually interpreted as causing cosmic acceleration (see
Section 2), results in a faster cosmic deceleration of events (than that caused by gravity alone, see
Section 3). This explains the origin of the Event Horizon (EH, see
Section 4) that results from an expansion dominated by
. It points in the direction that
is not a new form of vacuum energy ([
6,
22,
29]) but a boundary or surface term in the field equations.
The EH measured in our cosmic expansion behaves like the interior of a Schwarzschild Black Hole (BH) and it is identical to it if we just assume that the space outside
is approximately empty (see [
12]). We can also conjecture from this, that the interior dynamics of the Schwarzschild BH radius,
, could also have a similar
surface term
, as part of its field equations, at least for expanding interior BH solutions. The
term becomes the actual mechanism that prevents anything from escaping the BH interior (see [
13]).
The Event Horizon
measured with
(i.e. Eq.
10, which is equivalent to the presence of
) also tell us that there is a finite mass
trapped within
. If we assume that the space outside
is approximately empty, such finete mass
provides the explanation for the observed
and therefore for
: i.e.
(see [
14]).
That is fixed by the total mass of our universe is in good agreement with the physical interpretation presented here that corresponds to a friction (attractive) force that decelerates cosmic events. In the Appendix we elaborate in this idea and revisit the Newtonian limit to show that corresponds to an additional (attractive) Hooke’s term to the inverse square gravitational law. A rubber band Universe.