Submitted:
13 September 2023
Posted:
13 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
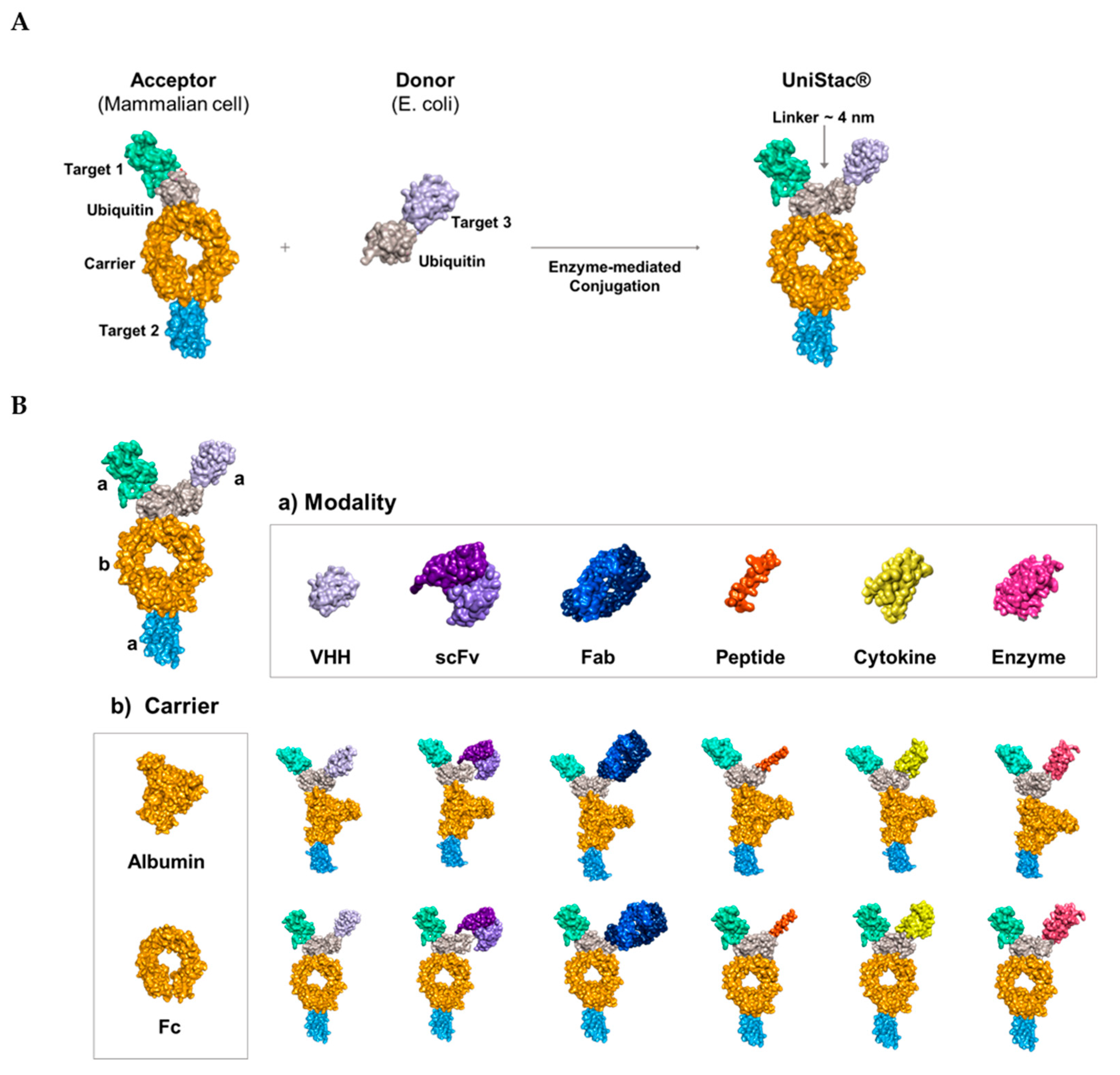
2.1. Conjugation of Multiple Targets Using a Novel Enzyme-mediated Platform—UniStac
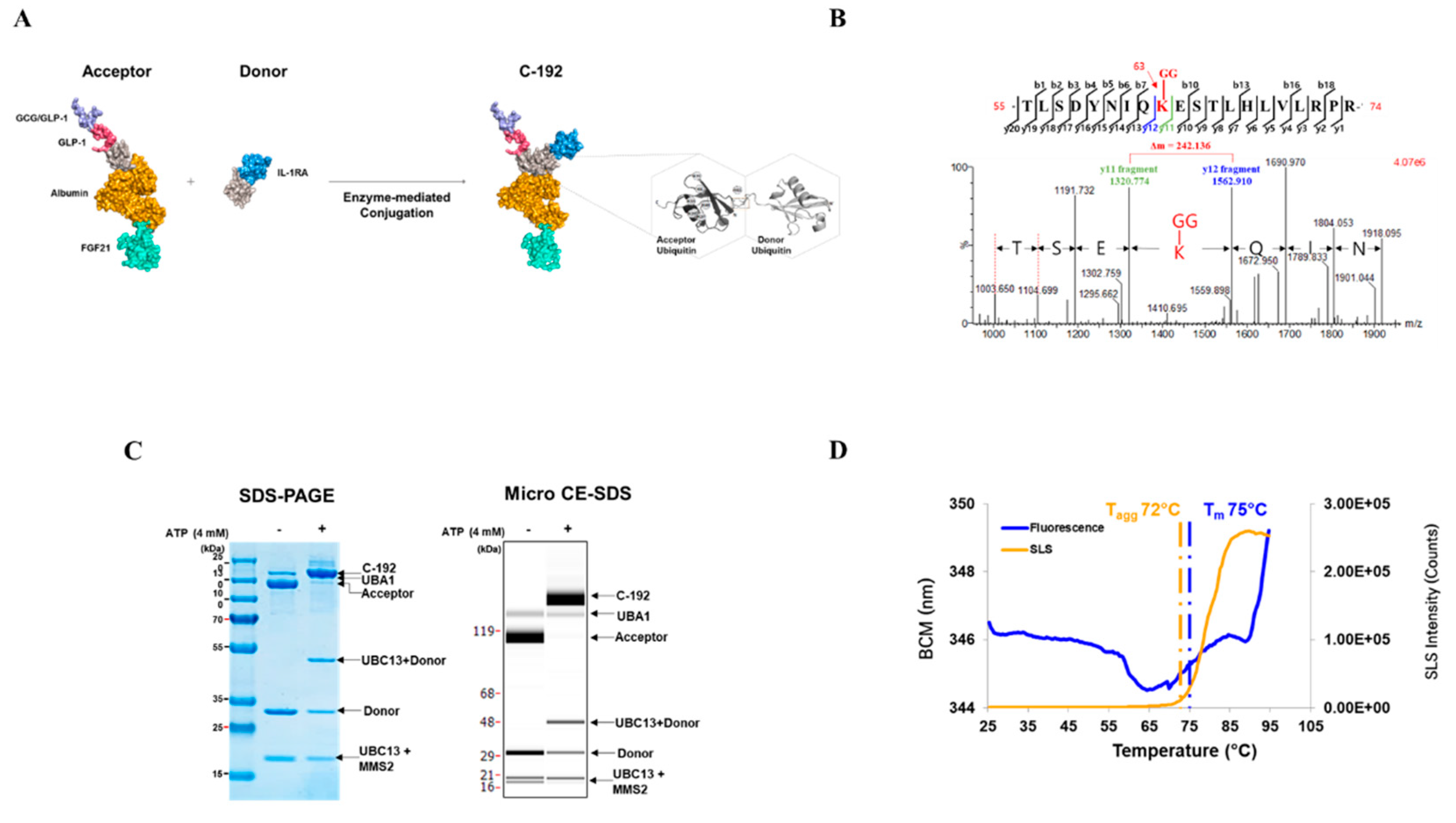
2.2. Development of the Novel Tetra-specific Drug C-192
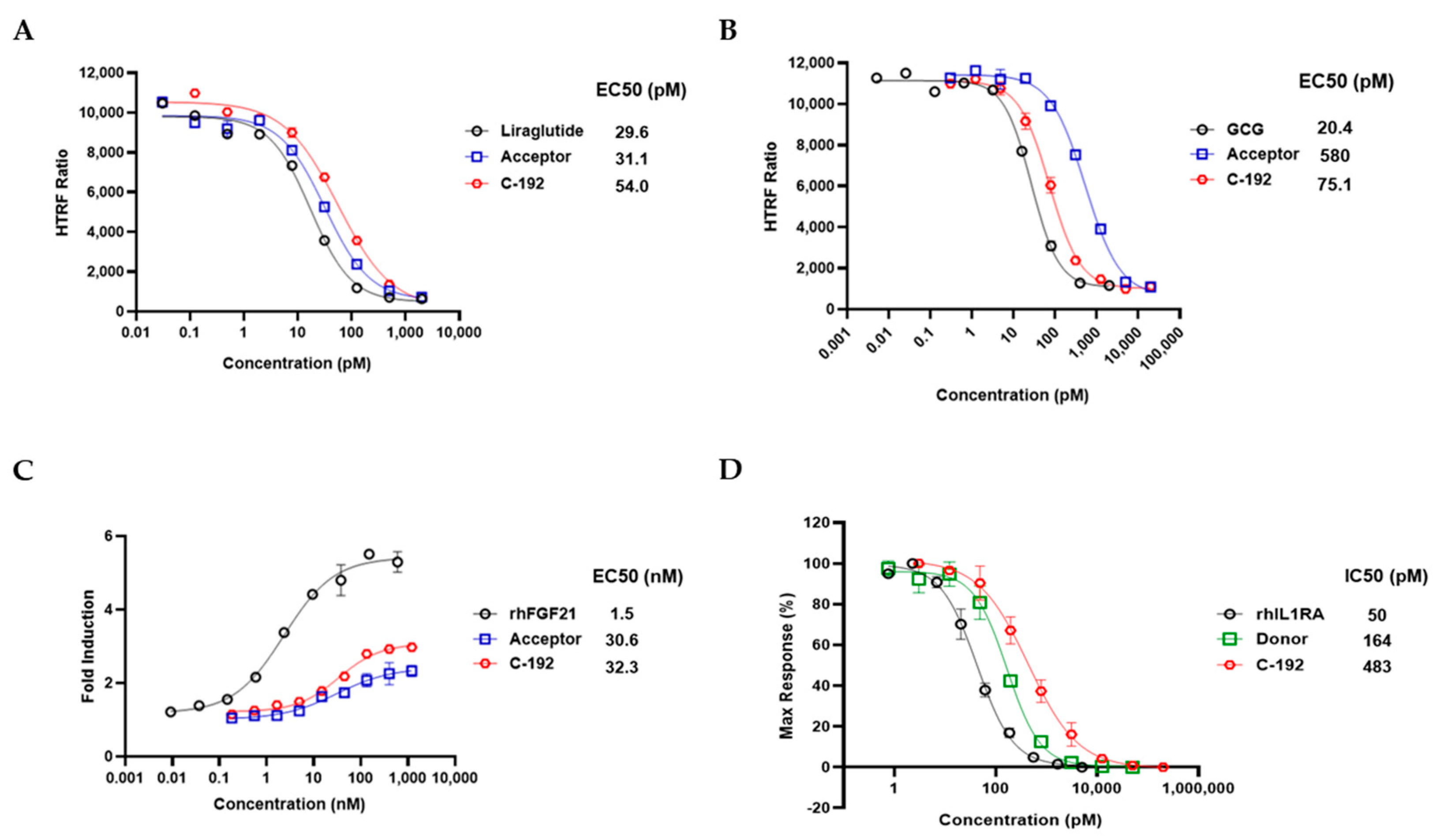
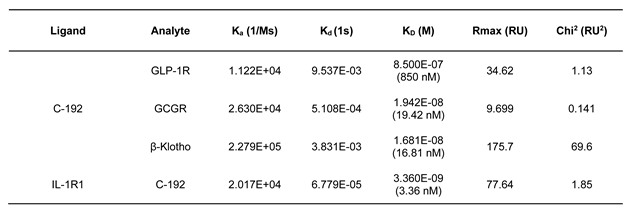
2.3. In Vitro Potencies of C-192 on target molecules
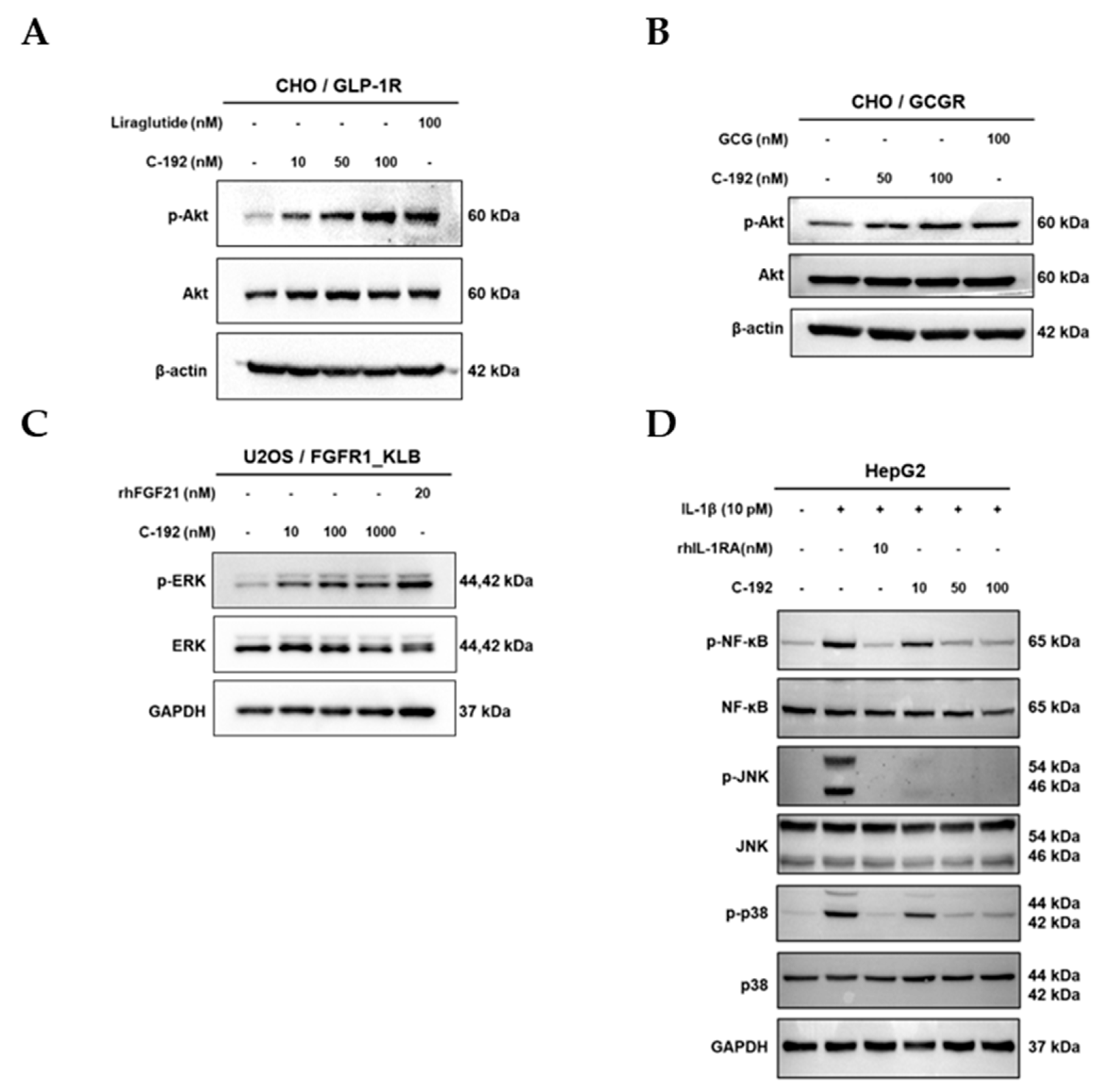
2.4. Downstream regulatory mechanism of Tetra-specific Targets in C-192
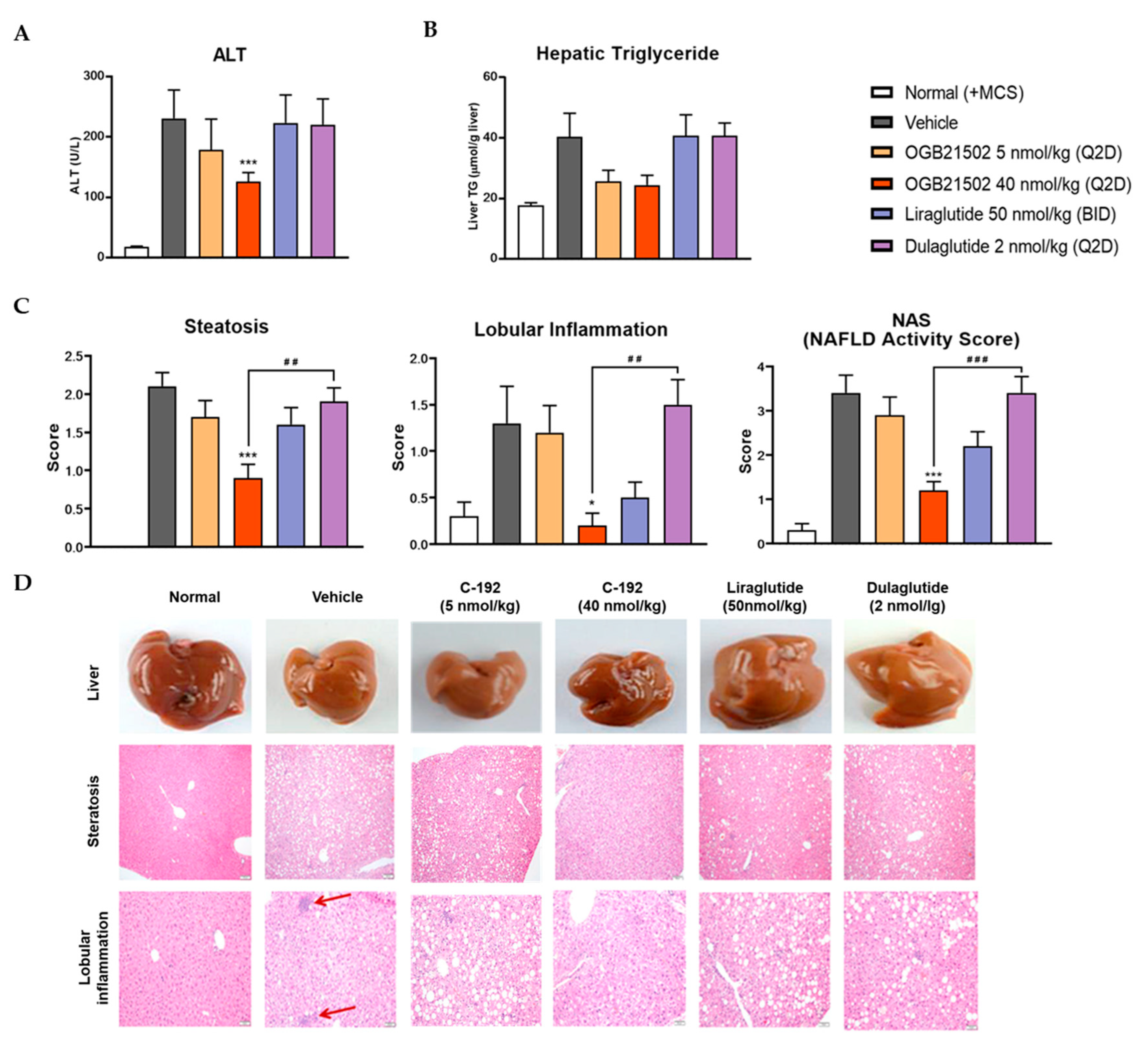
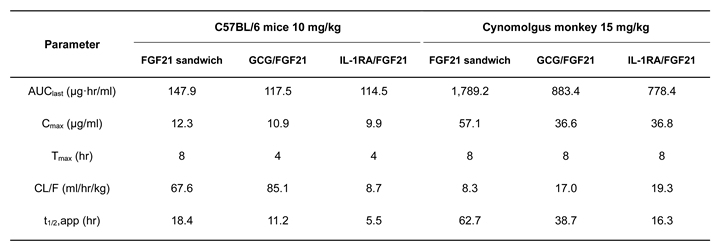
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Profile of C-192 and its Therapeutic Effects on MCD Diet-induced NASH Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. LC–MS/MS and Protein Purification
4.2. DSF Analysis
4.3. Affinity Measurement
4.4. In Vitro Biological Assays
4.5. Western Blotting Analysis
4.6. Pharmacokinetics of C-192 in Animal Models
4.7. MCD Diet-induced Mouse Model
4.8. Measurement of ALT Levels
4.9. Histological Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiess, C.; Zhai, Q.; Carter, P.J. Alternative molecular formats and therapeutic applications for bispecific antibodies. Mol Immunol 2015, 67, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Pyo, K.H.; Soo, R.A.; Cho, B.C. The promise of bispecific antibodies: Clinical applications and challenges. Cancer Treat Rev 2021, 99, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoba, X.H.; Viegas, C.; Mosa, R.A.; Viegas, F.P.D.; Pooe, O.J. Potential impact of the multi-target drug approach in the treatment of some complex diseases. Drug Des Devel Ther 2020, 14, 3235–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; McFarland, K.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Design and production of bispecific antibodies. Antibodies (Basel) 2019, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgundi, Z.; Reslan, M.; Cruz, E.; Sifniotis, V.; Kayser, V. The state-of-play and future of antibody therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2017, 122, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, U.; Kontermann, R.E. The making of bispecific antibodies. mAbs 2017, 9, 182–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Saxena, A.; Sidhu, S.S.; Wu, D. Fc engineering for developing therapeutic bispecific antibodies and novel scaffolds. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, L.D.; You, J.; Niles, E.G.; Pickart, C.M. E2/E3-mediated assembly of lysine 29-linked polyubiquitin chains. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 27299–27306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Lee, S.; Prag, G. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem J 2006, 399, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillich, F.F.; Imig, J.D.; Proschak, E. Multi-target approaches in metabolic syndrome. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 554961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, V.; Piater, B.; Zakeri, B.; Eichhorn, T.; Fischer, F.; Deutsch, C.; Becker, S.; Toleikis, L.; Hock, B.; Betz, U.A.; Kolmar, H. Spontaneous isopeptide bond formation as a powerful tool for engineering site-specific antibody-drug conjugates. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 39291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antos, J.M.; Ingram, J.; Fang, T.; Pishesha, N.; Truttmann, M.C.; Ploegh, H.L. Site-specific protein labeling via sortase-mediated transpeptidation. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 2017, 89, 15.3.1–15.3.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheka, A.C.; Adeyi, O.; Thompson, J.; Hameed, B.; Crawford, P.A.; Ikramuddin, S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J Gastroenterol 2018, 53, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Tian, L.; Chen, Q.; Ye, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Wu, P.; Yuan, W.; Qiu, Y. Recombinant human GLP-1 beinaglutide regulates lipid metabolism of adipose tissues in diet-induced obese mice. iScience 2021, 24, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somm, E.; Montandon, S.A.; Loizides-Mangold, U.; Gaïa, N.; Lazarevic, V.; De Vito, C.; Perroud, E.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Dibner, C.; Schrenzel, J.; Jornayvaz, F.R. The GLP-1R agonist liraglutide limits hepatic lipotoxicity and inflammatory response in mice fed a methionine-choline deficient diet. Transl Res 2021, 227, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Poudel, A.; Welchko, R.; Mekala, N.; Chandramani-Shivalingappa, P.; Rosca, M.G.; Li, L. Liraglutide improves insulin sensitivity in high fat diet induced diabetic mice through multiple pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 2019, 861, 172594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L. A LEAN treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Lancet 2016, 387, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.S.; Harrison, S.A.; NN9931-4296 Investigators. A placebo-controlled trial of subcutaneous semaglutide in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor co-agonists for treating metabolic disease. Mol Metab 2021, 46, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; Funcasta-Calderón, R.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Castro-Quintela, E.; Carneiro-Freire, N. Metabolic effects of glucagon in humans. J Clin Transl Endocrinol 2019, 15, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galsgaard, K.D.; Pedersen, J.; Knop, F.K.; Holst, J.J.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J. Glucagon receptor signaling and lipid metabolism. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, J.J.; Parkes, D.; Feigh, M.; Suschak, J.J.; Harris, M.S. Effects of ALT-801, a GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist, in a translational mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, D.C.D.; Vincent, M.L.; Tan, T.M.M. Striking the balance: GLP-1/glucagon co-agonism as a treatment strategy for obesity. Front Endocrinol 2021, 12, 735019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, M.L.; Laker, R.C.; Mather, K.; Nawrocki, A.; Oldham, S.; Boland, B.B.; Lewis, H.; Conway, J.; Naylor, J.; Guionaud, S.; Feigh, M.; Veidal, S.S.; Lantier, L.; McGuinness, O.P.; Grimsby, J.; Rondinone, C.M.; Jermutus, L.; Larsen, M.R.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Rhodes, C.J. Resolution of NASH and hepatic fibrosis by the GLP-1R/GCGR dual-agonist cotadutide via modulating mitochondrial function and lipogenesis. Nat Metab 2020, 2, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvert, R.; Herling, A.W.; Bossart, M.; Weiss, T.; Zhang, B.; Wenski, P.; <monospace> </monospace>Wandschneider, J.; Kleutsch, S.; Butty, U.; Kannt, A.; Wagner, M.; Haack, T.; Evers, A.; Dudda, A.; Lorenz, M.; Keil, S.; Larsen, P.J. Running on mixed fuel-dual agonistic approach of GLP-1 and GCG receptors leads to beneficial impact on body weight and blood glucose control: A comparative study between mice and non-human primates. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018, 20, 1836–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Yan, Z.; Yang, R.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Wu, S.; Luo, S.; Ye, S.; Lin, R.; Sun, X.; Xie, J.; Lan, T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, R.; Jiang, X. Design of a highly potent GLP-1R and GCGR dual-agonist for recovering hepatic fibrosis. Acta Pharm Sin B 2022, 12, 2443–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, A.; Melander, S.A.; Khan, S.; Andreassen, K.V.; Karsdal, M.A.; Henriksen, K. The effects of dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonists with different receptor selectivity in mouse models of obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2023, 384, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kang, Y.E.; Chang, J.Y.; Park, K.C.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.J.; Yi, H.S.; Shong, M.; Chung, H.K.; Kim, K.S. An engineered FGF21 variant, LY2405319, can prevent non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by enhancing hepatic mitochondrial function. Am J Transl Res 2016, 8, 4750–4763. [Google Scholar]
- Tillman, E.J.; Rolph, T. FGF21: An emerging therapeutic target for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and related metabolic diseases. Front Endocrinol 2020, 11, 601290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Fibroblast growth factor 21 analogs for treating metabolic disorders. Front Endocrinol 2015, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keinicke, H.; Sun, G.; Mentzel, C.M.J.; Fredholm, M.; John, L.M.; Andersen, B.; Raun, K.; Kjaergaard, M. FGF21 regulates hepatic metabolic pathways to improve steatosis and inflammation. Endocr Connect 2020, 9, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Chui, P.C.; Nasser, I.A.; Popov, Y.; Cunniff, J.C.; Lundasen, T.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Schuppan, D.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast growth factor 21 limits lipotoxicity by promoting hepatic fatty acid activation in mice on methionine and choline-deficient diets. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Parlee, S.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Li, P.; Pan, J.; Mroz, P.A.; Hansen, A.M.K.; Andersen, B.; Finan, B.; Kharitonenkov, A.; DiMarchi, R. Molecular elements in FGF19 and FGF21 defining KLB/FGFR activity and specificity. Mol Metab 2018, 13, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, D.M.; Rocheleau, J.V. The FGF21 receptor signaling complex: Klothoβ, FGFR1c, and other regulatory interactions. Vitam Horm 2016, 101, 17–58. [Google Scholar]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; Ma, T.; Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Zhang, L.; Habegger, K.M.; Fischer, K.; Campbell, J.E. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat Med 2015, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, C.A.; Capozzi, M.E.; Varanko, A.K.; Tong, J.; D'alessio, D.A.; Campbell, J.E.; Chilkoti, A. Sustained release of a GLP-1 and FGF21 dual agonist from an injectable depot protects mice from obesity and hyperglycemia. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaaz9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Shang, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, W. Rational design of a GLP-1/GIP/Gcg receptor triagonist to correct hyperglycemia, obesity and diabetic nephropathy in rodent animals. Life Sci 2020, 260, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, H.; Cai, X.; Hayashi, S. Interleukin-1 family cytokines in liver diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015, 630265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Lamacchia, C.; Palmer, G. IL-1 pathways in inflammation and human diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2010, 6, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, L.; Ferhat, M.; Salamé, E.; Robin, A.; Herbelin, A.; Gombert, J.M. ; Silvain, C; Barbarin, A. Interleukin-1 family cytokines: Keystones in liver inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mirea, A.M.; Tack, C.J.; Chavakis, T.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Toonen, E.J.M. IL-1 family cytokine pathways underlying NAFLD: Towards new treatment strategies. Trends Mol Med 2018, 24, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.P.H.; Meyer, J.; Montanari, E.; Lacotte, S.; Balaphas, A.; Muller, Y.D.; Clément, S.; Negro, F.; Toso, C.; Morel, P.; Buhler, L.H. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist modulates liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice in a model-dependent manner. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, W.P.; Malyak, M.; Guthridge, C.J.; Gabay, C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: Role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol 1998, 16, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wree, A.; Broderick, L.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H.M.; Feldstein, A.E. From NAFLD to NASH to cirrhosis-New insights into disease mechanisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013, 10, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Walters, K.J. Multitasking with ubiquitin through multivalent interactions. Trends Biochem Sci 2010, 35, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappadocia, L.; Lima, C.D. Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation: Structures, chemistry, and mechanism. Chem Rev 2018, 118, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heride, C.; Urbé, S.; Clague, M.J. Ubiquitin code assembly and disassembly. Curr Biol 2014, 24, R215–R220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasser, L.; Brik, A. Chemistry and biology of the ubiquitin signal. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2012, 51, 6840–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.W.; Saunders, G.F. Structure of the human glucagon gene. Nucleic Acids Res 1986, 14, 4719–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.; Spyracopoulos, L.; Moraes, T.; Pastushok, L.; Ptak, C.; Xiao, W.; Ellison, M.J. Noncovalent interaction between ubiquitin and the human DNA repair protein Mms2 is required for Ubc13-mediated polyubiquitination. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 40120–40126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, V. Combination therapy. Neurol Sci 2006, 27 Suppl 5, S350–S354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudega, M.; Bradbury, E.J.; Ramer, M.S. Combination therapies. Handb Clin Neurol 2012, 109, 617–636. [Google Scholar]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Larkin, J.; Tabernero, J.; Bonini, C. Enhancing anti-tumour efficacy with immunotherapy combinations. Lancet 2021, 397, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurs, F.V.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G.; de Groot, D.J.A. A review of bispecific antibodies and antibody constructs in oncology and clinical challenges. Pharmacol Ther 2019, 201, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H. Bispecific antibodies and antibody–drug conjugates for cancer therapy: Technological considerations. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazor, Y.; Oganesyan, V.; Yang, C.; Hansen, A.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Sachsenmeier, K.; Carlson, M.; Gadre, D.V.; Borrok, M.J.; Yu, X.Q. Improving target cell specificity using a novel monovalent bispecific IgG design. MAbs 2015, 7, 77–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godar, M.; de Haard, H.; Blanchetot, C.; Rasser, J. Therapeutic bispecific antibody formats: A patent applications review (1994-2017). Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018, 28, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshiaty, M.; Schindler, H.; Christopoulos, P. Principles and current clinical landscape of multispecific antibodies against cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yi, M.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, K. Recent advances and challenges of bispecific antibodies in solid tumors. Exp Hematol Oncol 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D.; Lord, C.J.; Scheel, H.; Swift, S.; Hofmann, K.; Ashworth, A.; Barford, D. The structure of the CYLD USP domain explains its specificity for Lys63-linked polyubiquitin and reveals a B box module. Mol Cell 2008, 29, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Dikic, I.; Heilemann, M. Visualizing ubiquitination in mammalian cells. EMBO Rep 2019, 20, e46520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.S.; Zhang, M.; Meng, Y.G.; Kadkhodayan, M.; Kirchhofer, D.; Combs, D.; Damico, L.A. Albumin binding as a general strategy for improving the pharmacokinetics of proteins. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 35035–35043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Yeh, M. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





