Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
13 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Treatment approaches, advances and challenges:
1.2. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Overall survival and Current Findings
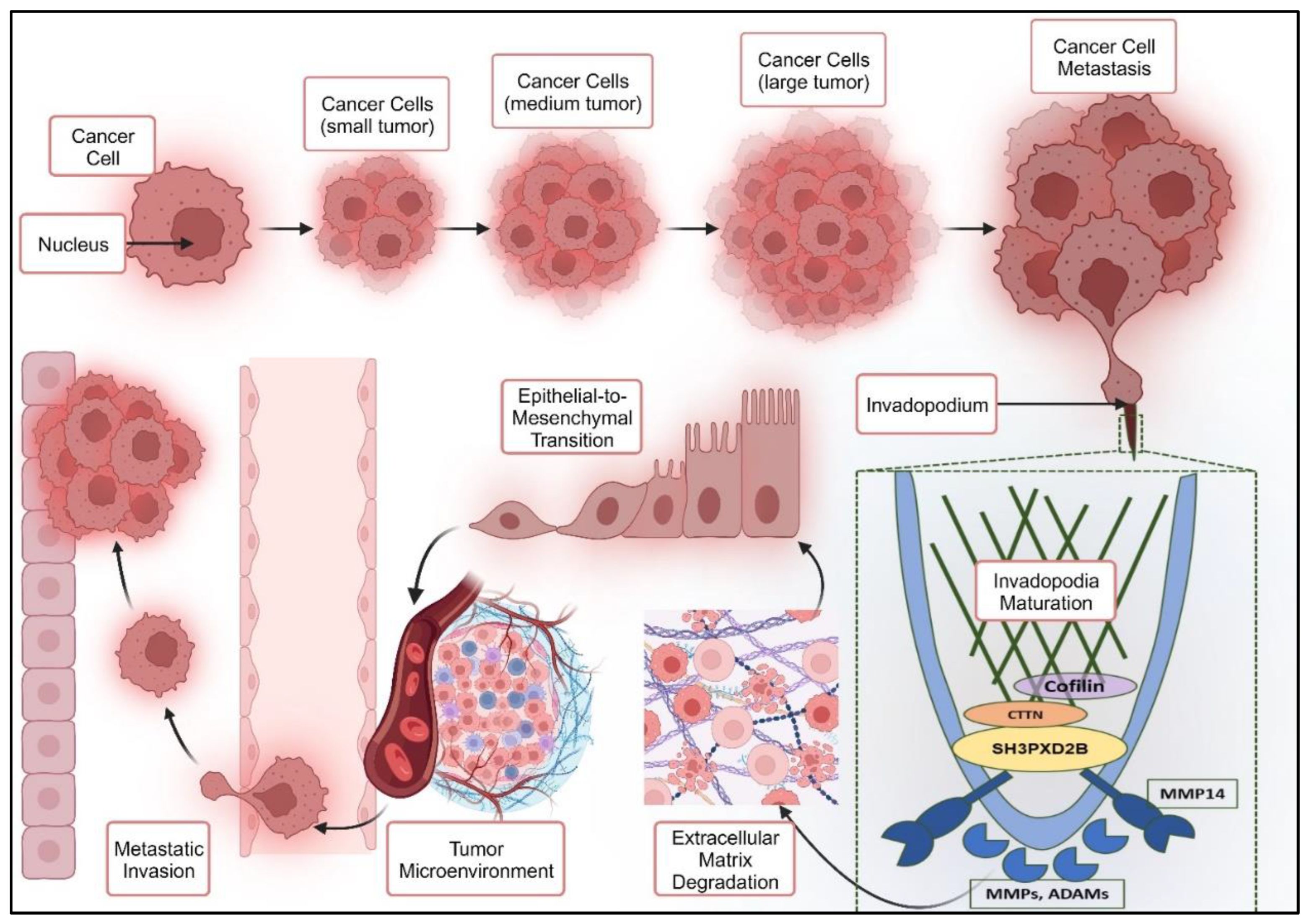
1.3. Breast Cancer – Lung Metastasis: EMT through Invadopodia formation
1.3.1. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition through Invadopodia Formation
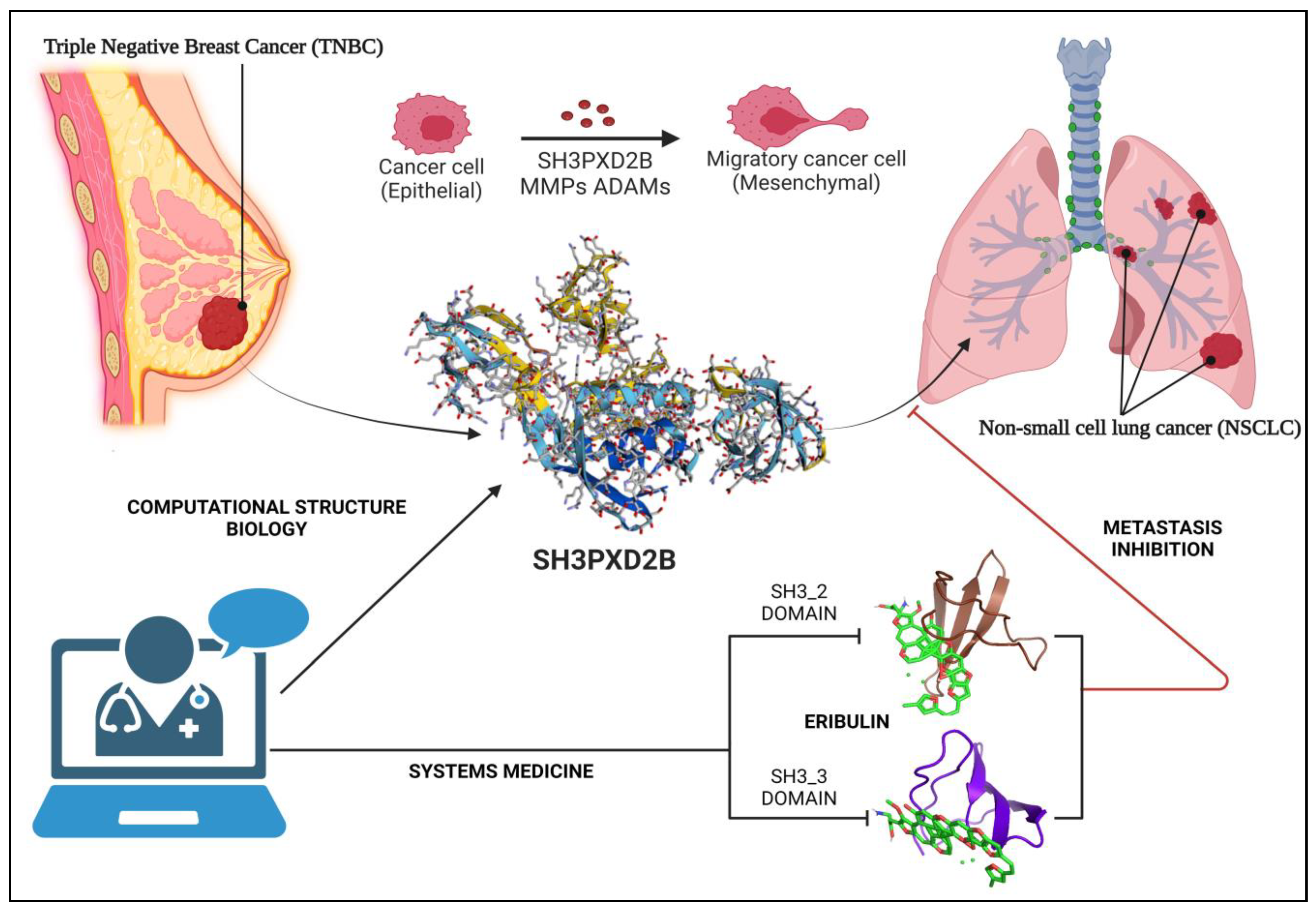
1.3.2. SH3PXD2B in Cancer Metastasis:
2. Methodology
2.1. Data acquisition and analysis
2.2. Overall Survival Analysis
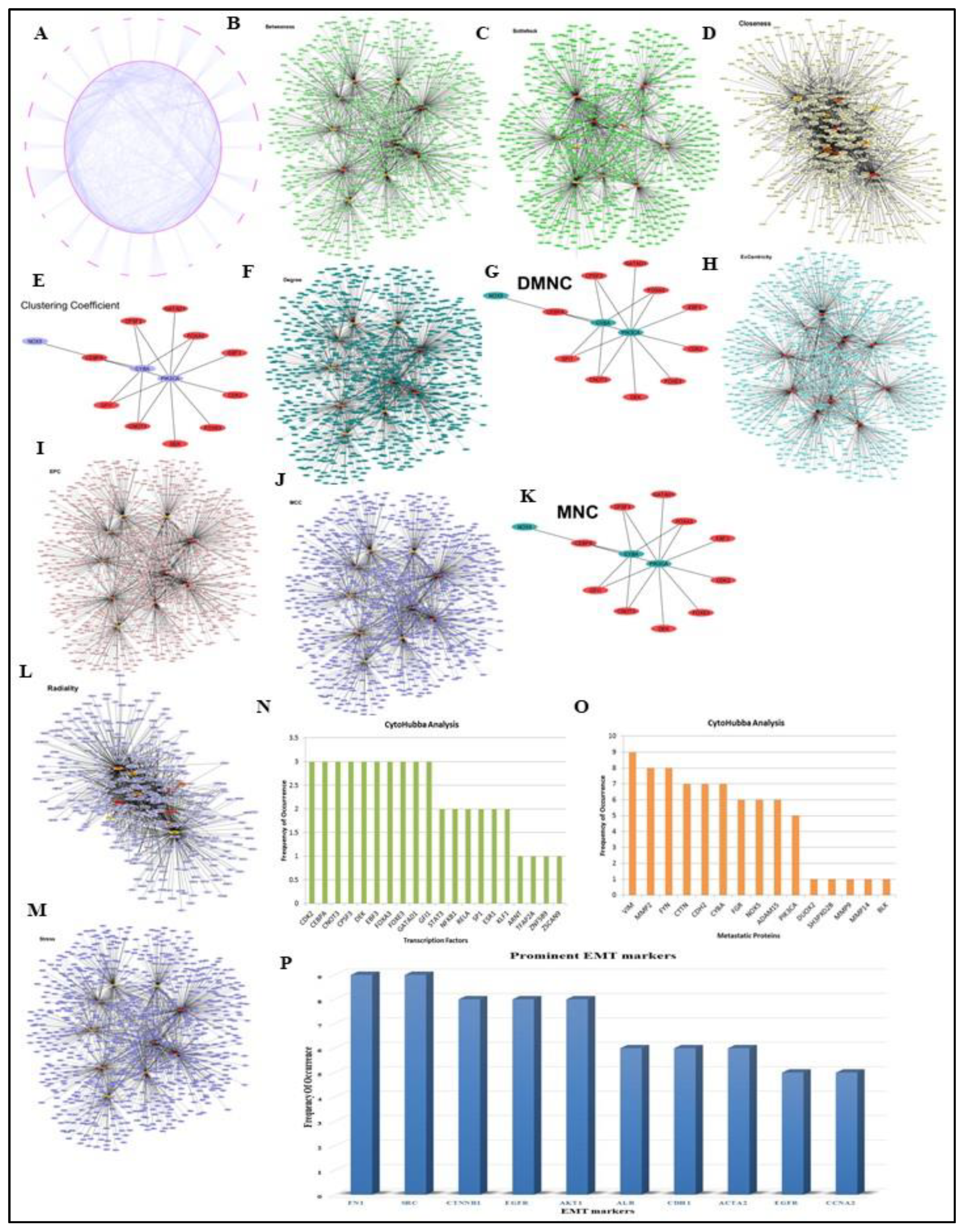
2.3. Reconstruction of Transcription Factor Target Gene (TFTG) Network and EMTome network
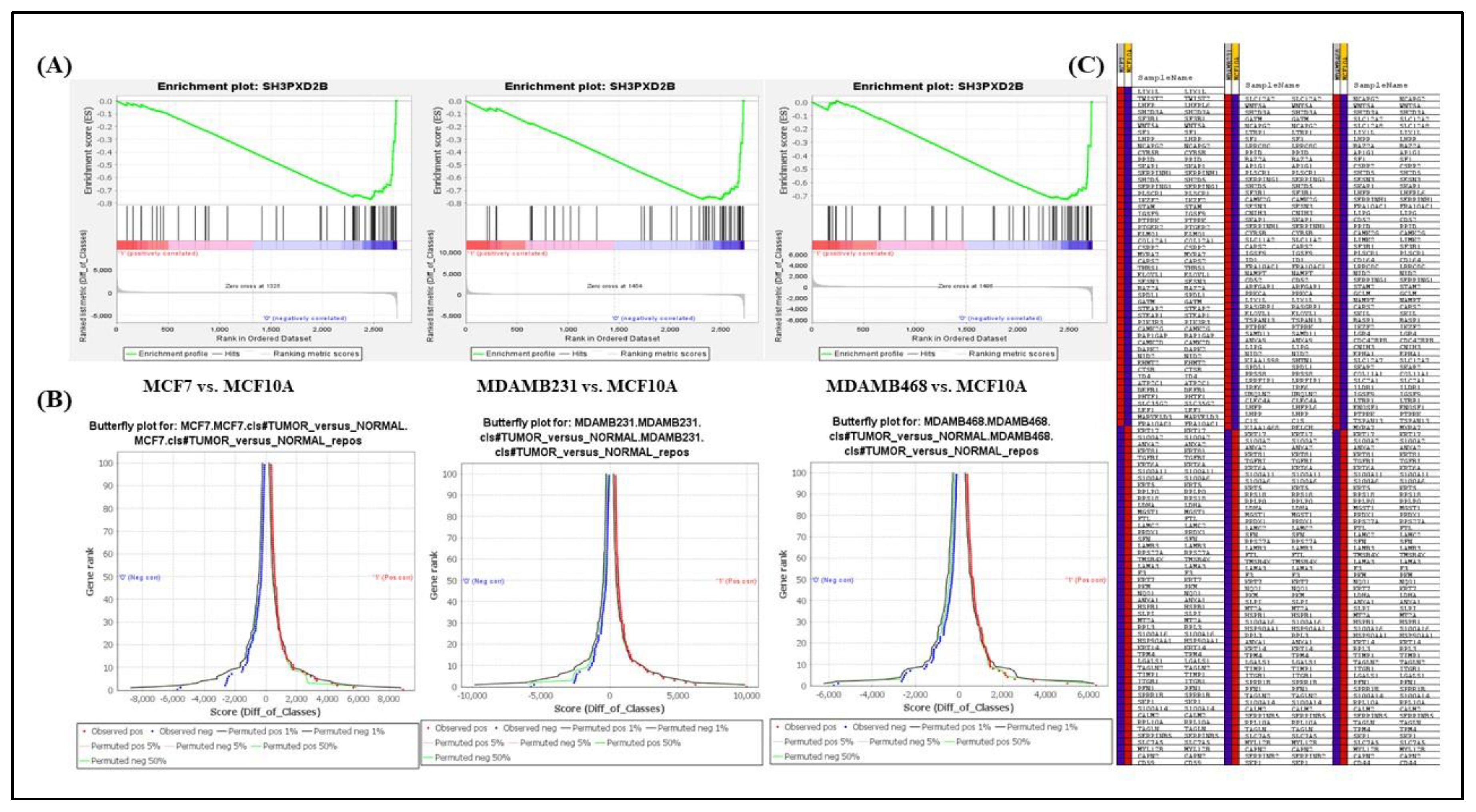
2.4. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.5. Cell Culture and maintenance
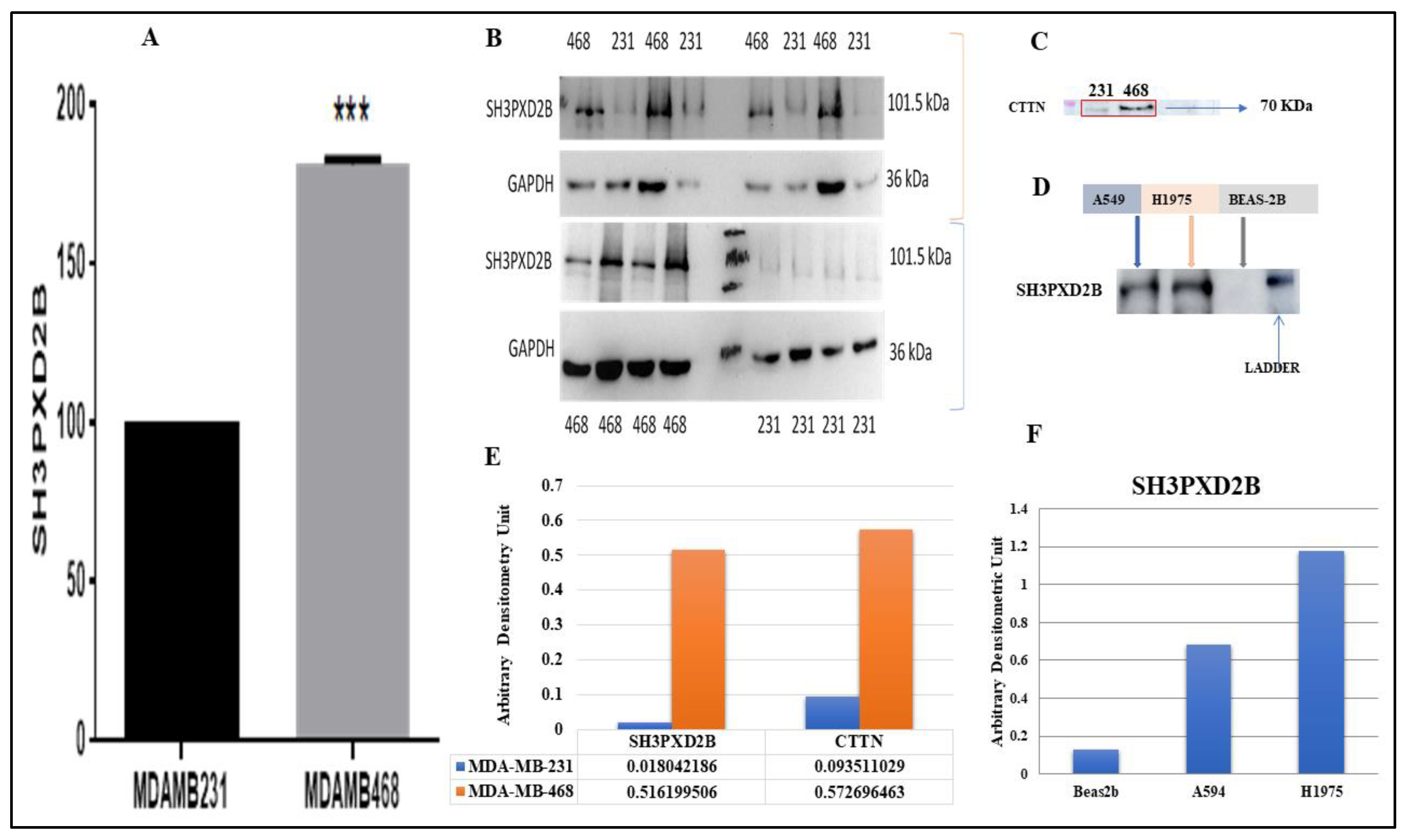
2.6. Proteomics and Western Blotting
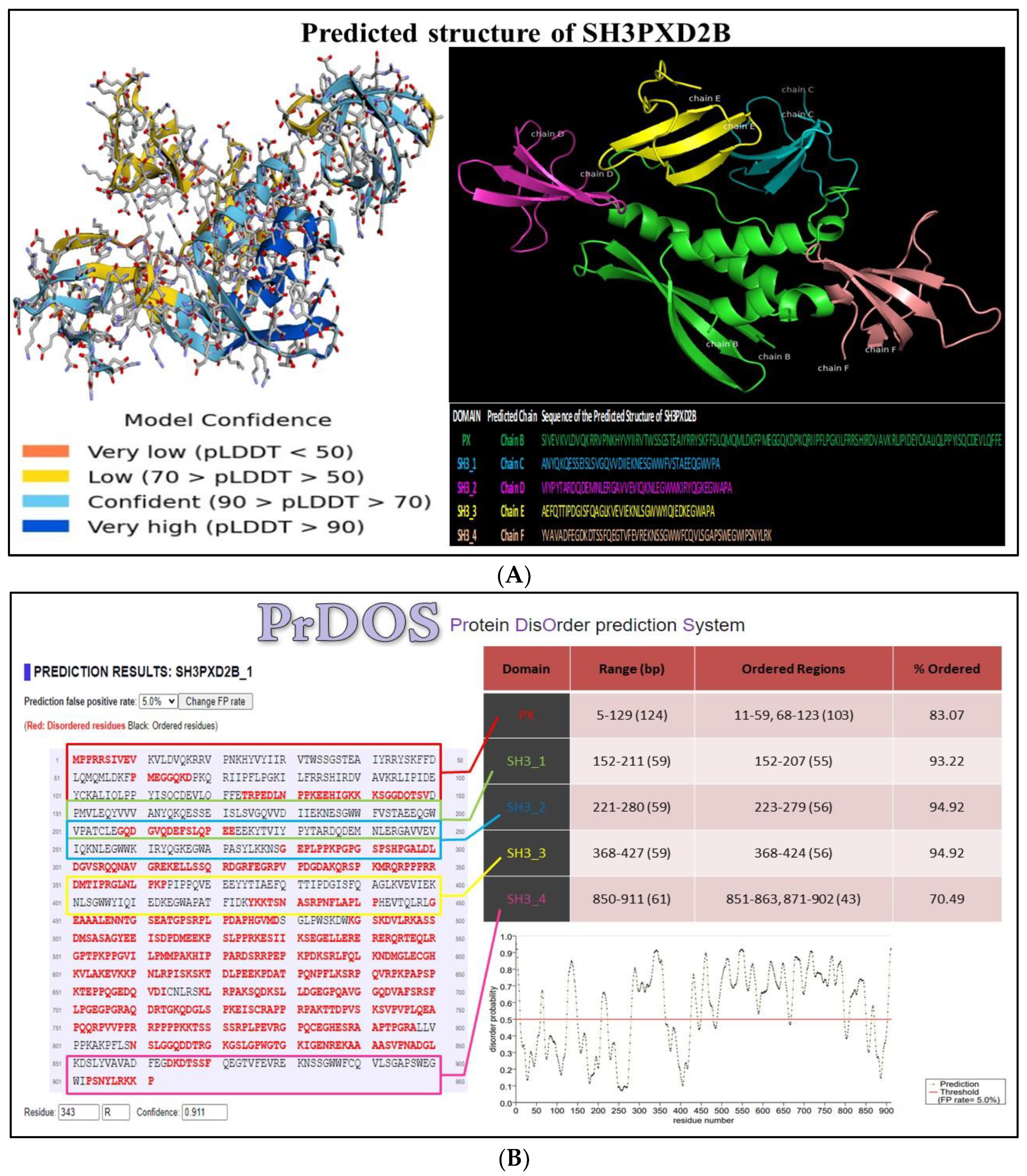
2.7. Structural aspects of SH3PXD2B
2.8. Molecular docking
2.9. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
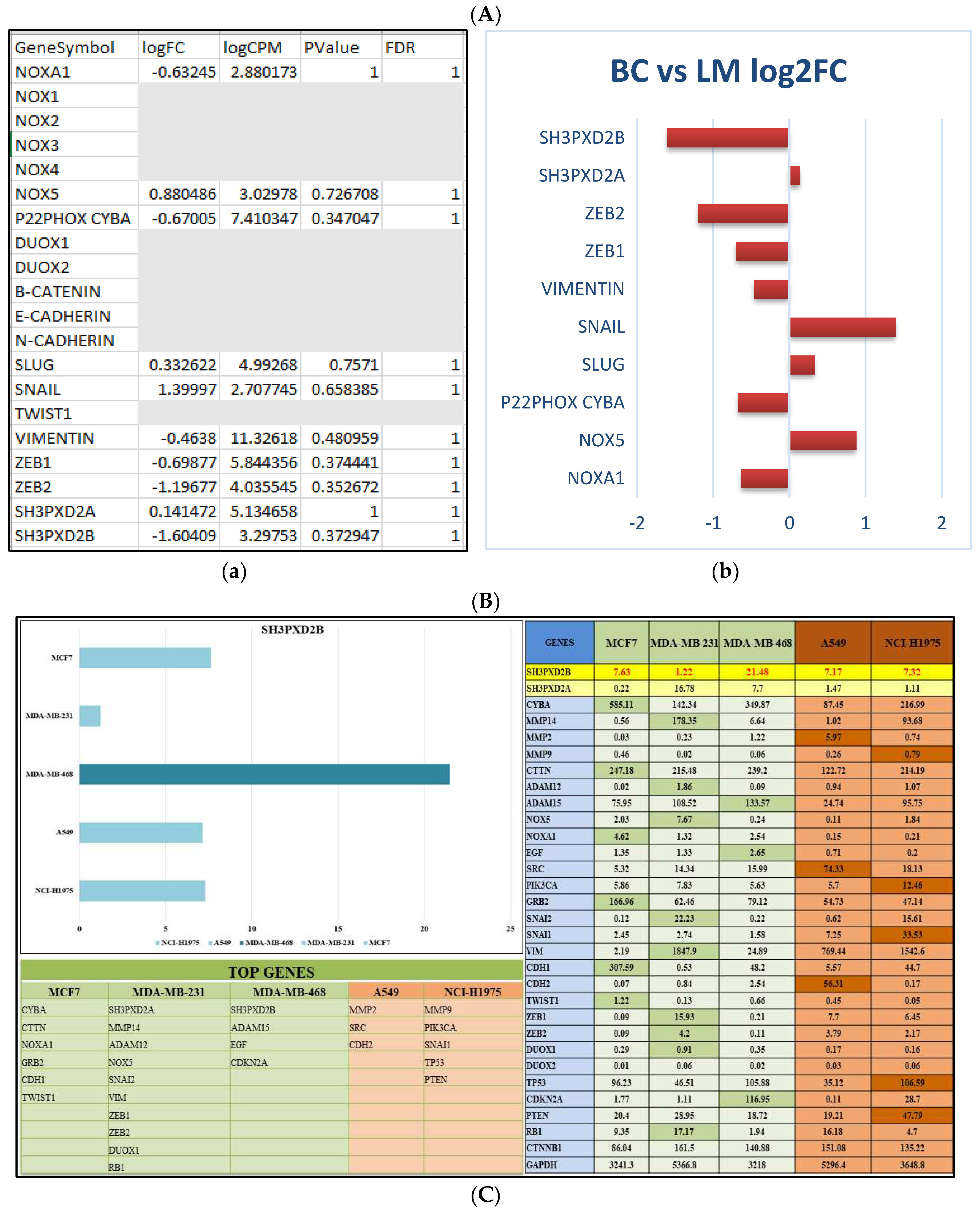
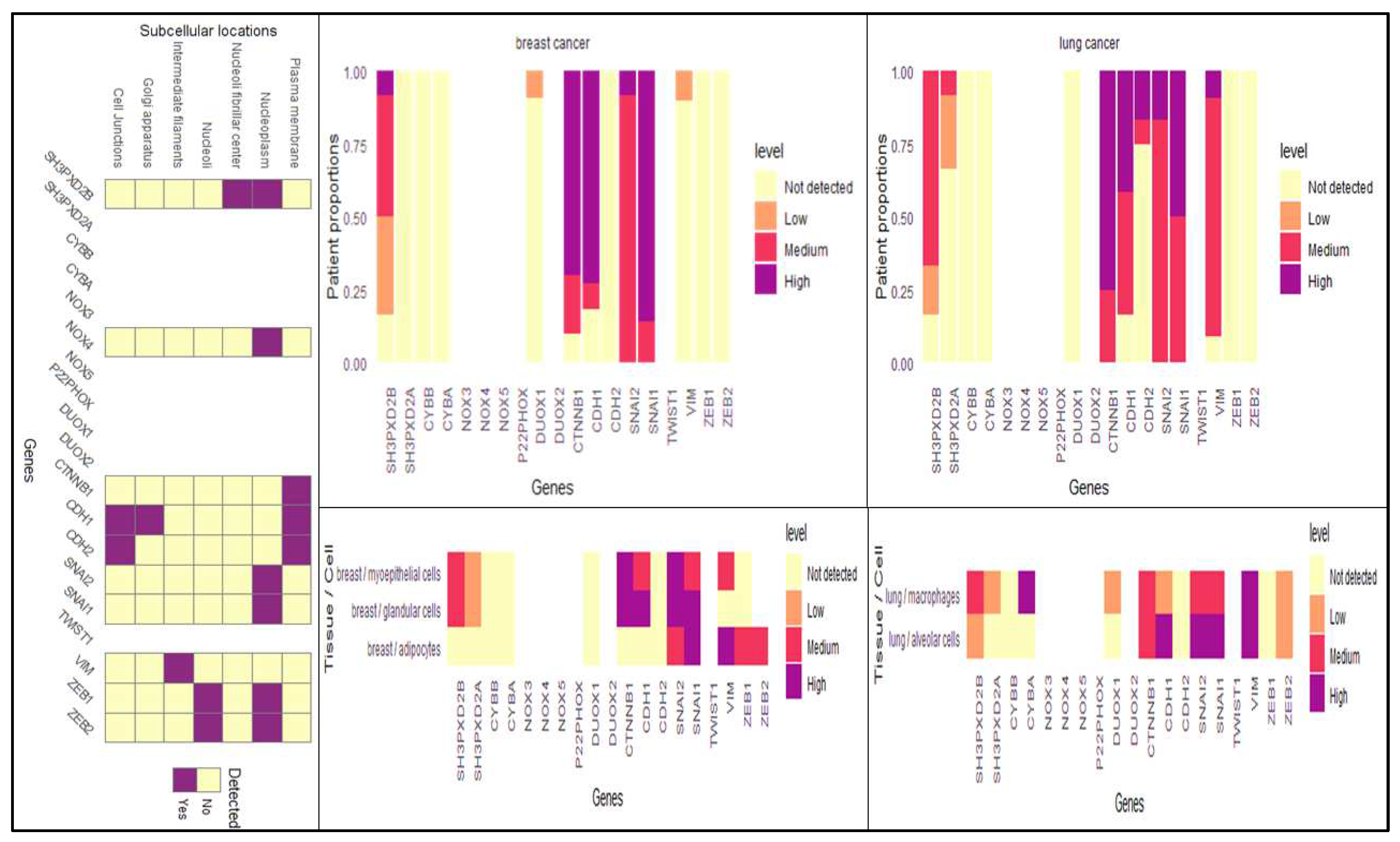
3.1. Differentially expressed genes in BC-LM
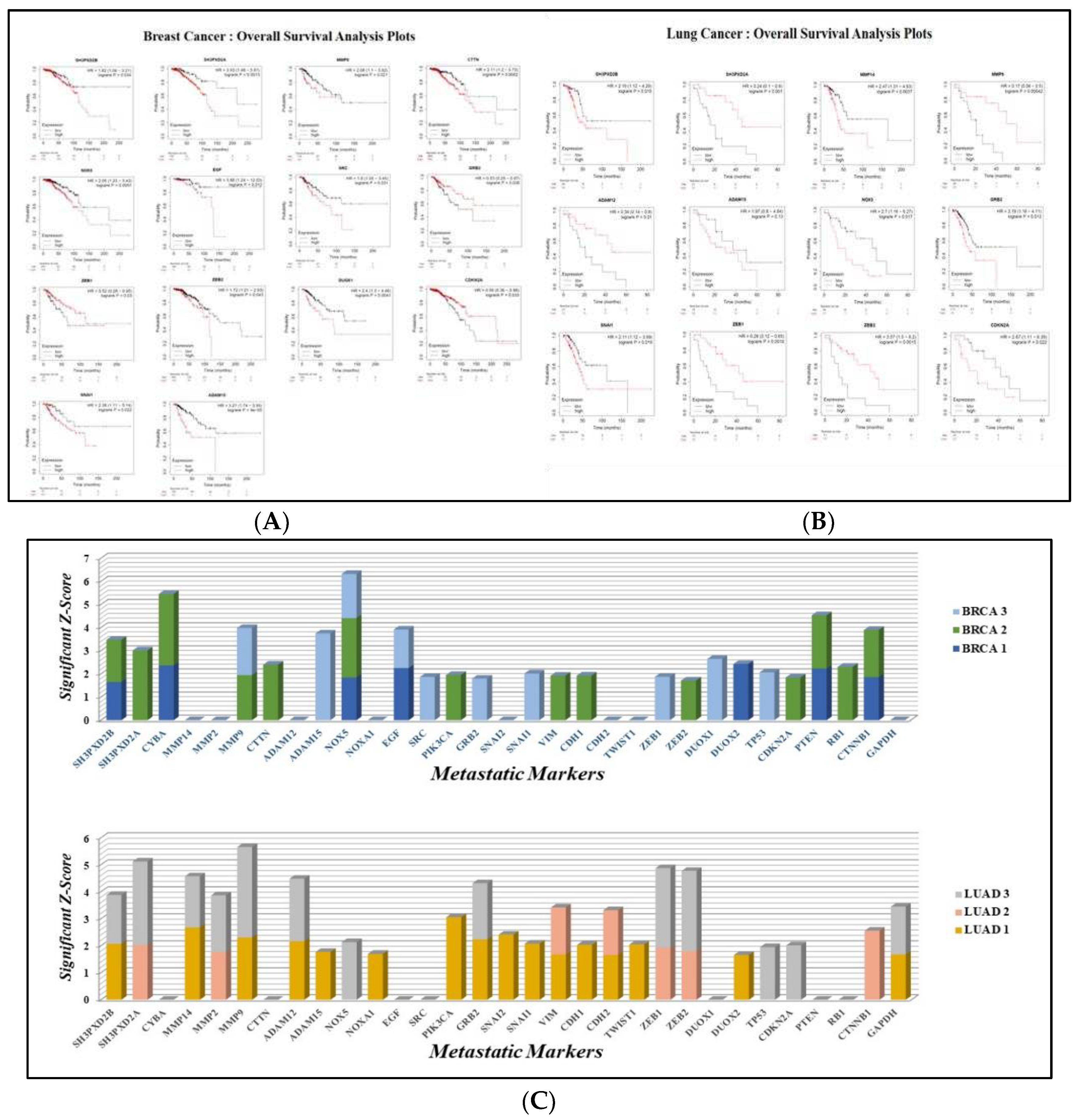
3.2. Overall Survival Analysis
3.3. TFTG and EMTome network analysis
3.4. Analysis of differentially expressed SH3PXD2B in BC cell-lines:
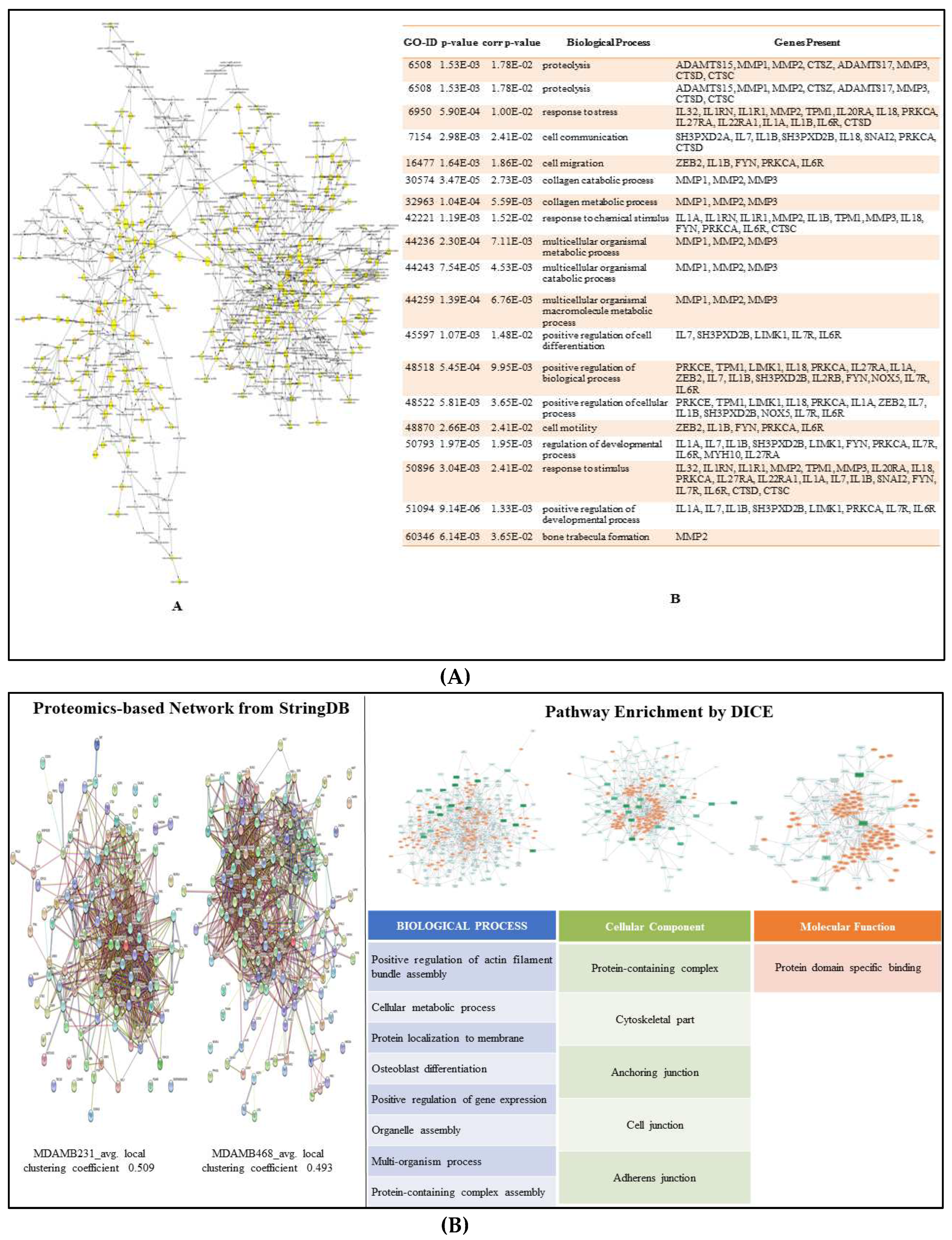
3.5. Proteomics and Western Blotting:
3.6. Structure
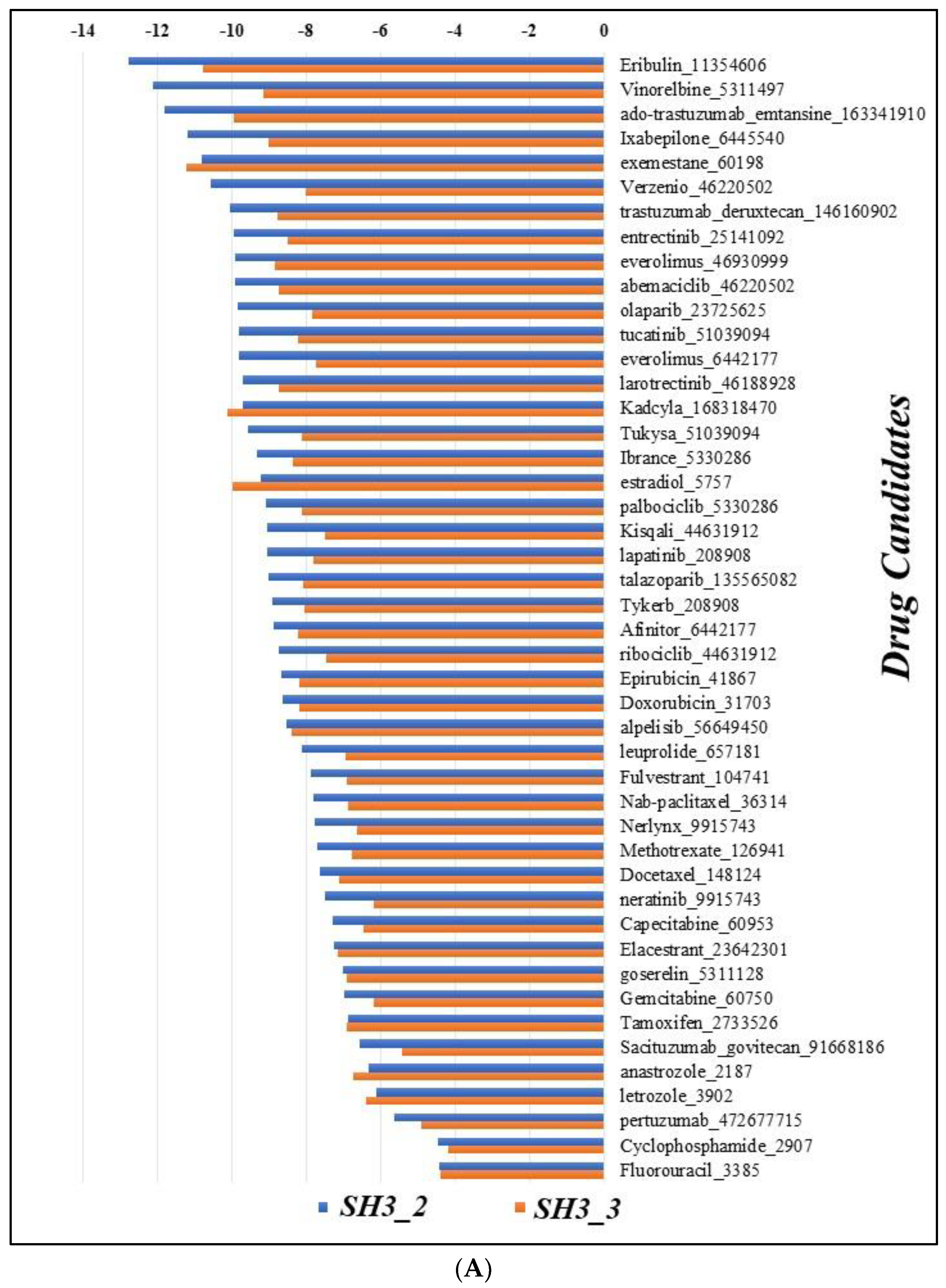
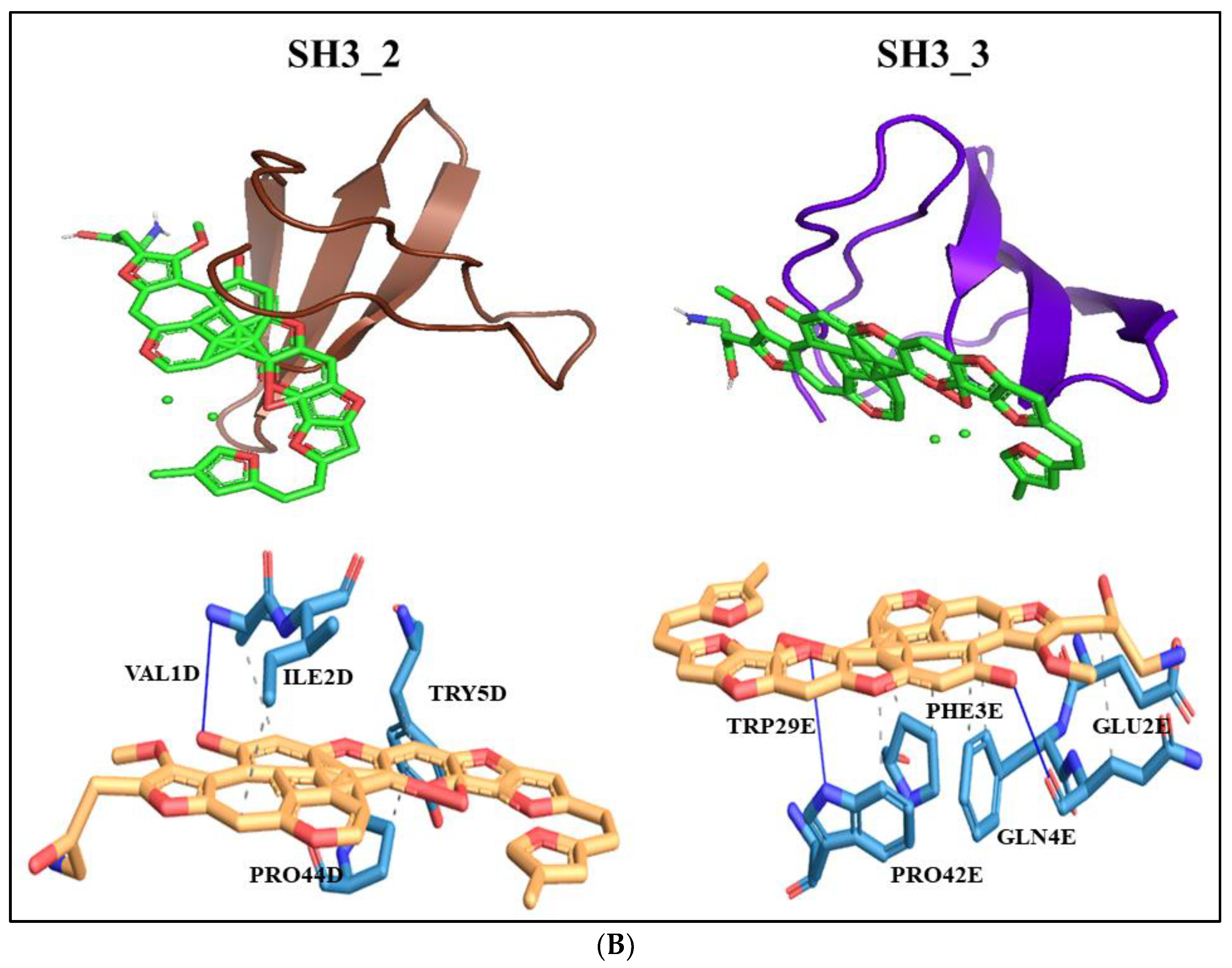
3.7. Docking
3.8. Enriched Pathways
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, Hyuna, et al. "Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 71.3 (2021): 209-249. [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, Erasmo, et al. "Subtypes of breast cancer." Breast Cancer [Internet] (2022).
- Łukasiewicz, Sergiusz, et al. "Breast cancer—epidemiology, risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment strategies—an updated review." Cancers 13.17 (2021): 4287. [CrossRef]
- Leong, Stanley PL, et al. "Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries?." World journal of surgery 34 (2010): 2308-2324. [CrossRef]
- Green, Michael, and Vinod Raina. "Epidemiology, screening and diagnosis of breast cancer in the Asia–Pacific region: current perspectives and important considerations." Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology 4 (2008): S5-S13. [CrossRef]
- Sung, Hyuna, et al. "Female breast cancer incidence among Asian and Western populations: more similar than expected." Journal of the National Cancer Institute 107.7 (2015): djv107. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Peng-Jhen, et al. "Urban–Rural Disparity in Birth Cohort Effects on Breast Cancer Incidence." Journal of Urban Health (2023): 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Lim, Yu Xian, et al. "Breast cancer in Asia: incidence, mortality, early detection, mammography programs, and risk-based screening initiatives." Cancers 14.17 (2022): 4218. [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer [accessed on September 2, 2023] (https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en).
- Cancer Research UK [accessed on September 2, 2023] (https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/aboutcancer/breast-cancer/survival).
- Caswell-Jin, Jennifer L., et al. "Change in survival in metastatic breast cancer with treatment advances: meta-analysis and systematic review." JNCI cancer spectrum 2.4 (2018): pky062. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Xin, and Ping Mu. "Targeting breast cancer metastasis." Breast cancer: basic and clinical research 9 (2015): BCBCR-S25460. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Mi-Young, et al. "Tumor self-seeding by circulating cancer cells." Cell 139.7 (2009): 1315-1326. [CrossRef]
- Comen, Elizabeth, Larry Norton, and Joan Massague. "Clinical implications of cancer self-seeding." Nature reviews Clinical oncology 8.6 (2011): 369-377. [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Anne C., and Joan Massagué. "Molecular basis of metastasis." New England Journal of Medicine 359.26 (2008): 2814-2823. [CrossRef]
- Keefe, Dorothy MK, and Emma H. Bateman. "Tumor control versus adverse events with targeted anticancer therapies." Nature reviews Clinical oncology 9.2 (2012): 98-109. [CrossRef]
- Park, Misung, et al. "Breast cancer metastasis: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.12 (2022): 6806. [CrossRef]
- Shafei, Ayman, et al. "A review on the efficacy and toxicity of different doxorubicin nanoparticles for targeted therapy in metastatic breast cancer." Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 95 (2017): 1209-1218. [CrossRef]
- Helsby, Nuala, et al. "Cyclophosphamide bioactivation pharmacogenetics in breast cancer patients." Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 88.3 (2021): 533-542. [CrossRef]
- Miranda Furtado, Cristiana Libardi, et al. "Epidrugs: targeting epigenetic marks in cancer treatment." Epigenetics 14.12 (2019): 1164-1176. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Enyong, et al. "Epigenetic modulation of antitumor immunity for improved cancer immunotherapy." Molecular cancer 20.1 (2021): 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Schmid, Peter, et al. "Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer." New England Journal of Medicine 379.22 (2018): 2108-2121. [CrossRef]
- Corso, Giovanni, et al. "Metaplastic breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic considerations." Journal of Surgical Oncology 123.1 (2021): 61-70. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, Erica L., et al. "A Phase I dose-escalation study of the VEGFR inhibitor tivozanib hydrochloride with weekly paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer." Breast cancer research and treatment 140 (2013): 331-339. [CrossRef]
- Cortés, Javier, et al. "Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine for breast cancer." New England Journal of Medicine 386.12 (2022): 1143-1154. [CrossRef]
- Geyer, Charles E., et al. "Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer." New England journal of medicine 355.26 (2006): 2733-2743. [CrossRef]
- Finn, Richard S., et al. "Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer." New England journal of medicine 375.20 (2016): 1925-1936. [CrossRef]
- Von Minckwitz, Gunter, et al. "Adjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in early HER2-positive breast cancer." New England Journal of Medicine 377.2 (2017): 122-131.
- Plosker, G.L. , Faulds D. Epirubicin. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in cancer chemotherapy. Drugs. 1993;45:788–856. [CrossRef]
- Zardavas, Dimitrios, José Baselga, and Martine Piccart. "Emerging targeted agents in metastatic breast cancer." Nature reviews Clinical oncology 10.4 (2013): 191-210. [CrossRef]
- Shah, Sohrab P., et al. "Mutational evolution in a lobular breast tumour profiled at single nucleotide resolution." Nature 461.7265 (2009): 809-813. [CrossRef]
- Amir, Eitan, et al. "Prospective study evaluating the impact of tissue confirmation of metastatic disease in patients with breast cancer." Journal of clinical oncology 30.6 (2012): 587. [CrossRef]
- Lindström, Linda Sofie, et al. "Clinically used breast cancer markers such as estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 are unstable throughout tumor progression." J Clin Oncol 30.21 (2012): 2601-2608. [CrossRef]
- Bedard, Philippe L., et al. "Tumour heterogeneity in the clinic." Nature 501.7467 (2013): 355-364. [CrossRef]
- Van Denderen, Bryce JW, and Erik W. Thompson. "The to and fro of tumour spread." Nature 493.7433 (2013): 487-488.
- Valachis, Antonis, et al. "Overall survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer in Sweden: a nationwide study." British Journal of Cancer 127.4 (2022): 720-725. [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Castro, Ana C., Nancy U. Lin, and Kornelia Polyak. "Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast cancer: improving patient selection for treatment." Cancer discovery 9.2 (2019): 176-198. [CrossRef]
- Dent, Rebecca, et al. "Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence." Clinical cancer research 13.15 (2007): 4429-4434. [CrossRef]
- Andre, F. , and C. C. Zielinski. "Optimal strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with currently approved agents." Annals of oncology 23 (2012): vi46-vi51. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Weikai, et al. "Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of distant metastasis at initial diagnosis: a population-based study." Cancer management and research (2018): 5329-5338. [CrossRef]
- Zardavas, Dimitros, et al. "The AURORA initiative for metastatic breast cancer." British journal of cancer 111.10 (2014): 1881-1887. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, Susana, et al. "Multiomics in primary and metastatic breast tumors from the AURORA US network finds microenvironment and epigenetic drivers of metastasis." Nature Cancer 4.1 (2023): 128-147. [CrossRef]
- Paget, Stephen. "The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast." The Lancet 133.3421 (1889): 571-573. [CrossRef]
- Gennari, Alessandra, et al. "Survival of metastatic breast carcinoma patients over a 20-year period: A retrospective analysis based on individual patient data from six consecutive studies." Cancer 104.8 (2005): 1742-1750.
- Smid, Marcel, et al. "Subtypes of breast cancer show preferential site of relapse." Cancer research 68.9 (2008): 3108-3114. [CrossRef]
- Dan, Zhaoling, et al. "A pH-responsive host-guest nanosystem loading succinobucol suppresses lung metastasis of breast cancer." Theranostics 6.3 (2016): 435.
- Foulkes, William D., Ian E. Smith, and Jorge S. Reis-Filho. "Triple-negative breast cancer." New England journal of medicine 363.20 (2010): 1938-1948.
- Jin, Liting, et al. "Breast cancer lung metastasis: Molecular biology and therapeutic implications." Cancer biology & therapy 19.10 (2018): 858-868. [CrossRef]
- Soh, Junichi, Yoshifumi Komoike, and Tetsuya Mitsudomi. "Surgical therapy for pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer." Translational Cancer Research 9.8 (2020): 5044. [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, Hagen, et al. "Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes." Journal of clinical oncology 28.20 (2010): 3271-3277. [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, Cornelia, et al. "Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer." Journal of clinical oncology 26.8 (2008): 1275-1281. [CrossRef]
- Dent R, Hanna WM, Trudeau M, et al. Pattern of metastatic spread in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;115:423-8. [CrossRef]
- Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1938-48. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Qi, et al. "Breast cancer subtypes predict the preferential site of distant metastases: a SEER based study." Oncotarget 8.17 (2017): 27990. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Fengwei, et al. "Case Report Second primary lung cancer after a first breast cancer: a case report and critical literature review." Int J Clin Exp Med 11.2 (2018): 1049-1054.
- Langerød, Anita, et al. "TP53 mutation status and gene expression profiles are powerful prognostic markers of breast cancer." Breast cancer research 9 (2007): 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, Fernando, et al. "Cancer stem cell markers in breast neoplasias: their relevance and distribution in distinct molecular subtypes." Virchows Archiv 460 (2012): 545-553. [CrossRef]
- Honeth, Gabriella, et al. "The CD44+/CD24-phenotype is enriched in basal-like breast tumors." Breast Cancer Research 10.3 (2008): 1-12.
- Hu, Jing, et al. "A CD44v+ subpopulation of breast cancer stem-like cells with enhanced lung metastasis capacity." Cell death & disease 8.3 (2017): e2679-e2679. [CrossRef]
- McGovern, Marie, et al. "A “latent niche” mechanism for tumor initiation." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106.28 (2009): 11617-11622.
- Harrison, Hannah, et al. "Regulation of breast cancer stem cell activity by signaling through the Notch4 receptor." Cancer research 70.2 (2010): 709-718. [CrossRef]
- Sansone P, Storci G, Giovannini C, Pandolfi S, Pianetti S, Taffurelli M, Santini D, Ceccarelli C, Chieco P, Bonafé M. p66Shc/Notch-3 interplay controls self-renewal and hypoxia survival in human stem/progenitor cells of the mammary gland expanded in vitro as mammospheres. Stem Cells. 2007;25(3):807–15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal D, Kolluru V, Chandrasekaran B, Baby BV, Aman M, Suman S, Sirimulla S, Sanders MA, Alatassi H, Ankem MK, et al. Targeting aberrant expression of Notch-1 in ALDH+ cancer stem cells in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2017;56(3):1127–1136. [CrossRef]
- Suman S, Das TP, Damodaran C. Silencing NOTCH signaling causes growth arrest in both breast cancer stem cells and breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(10):2587–96. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khramtsov, Andrey I., et al. "Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome." The American journal of pathology 176.6 (2010): 2911-2920. [CrossRef]
- Geyer, Felipe C., et al. "β-Catenin pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with triple-negative phenotype but not with CTNNB1 mutation." Modern pathology 24.2 (2011): 209-231. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Hisaki, and Tsutomu Kume. "Forkhead transcription factors regulate expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in endothelial cells and CXCL12-induced cell migration." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 367.3 (2008): 584-589. [CrossRef]
- Han, Bingchen, et al. "FOXC1 activates smoothened-independent hedgehog signaling in basal-like breast cancer." Cell reports 13.5 (2015): 1046-1058. [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Hou Dong, and W. Wu Yao. "The role and the potential regulatory pathways of high expression of forkhead box C1 in promoting tumor growth and metastasis of basal-like breast cancer." J BUON 21.4 (2016): 818-25.
- Liu, Jiao, et al. "Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through chemokine-activated hedgehog and TGF-β pathways." Cancer letters 379.1 (2016): 49-59. [CrossRef]
- Pires, Bruno Ricardo Barreto, et al. "Targeting cellular signaling pathways in breast cancer stem cells and its implication for cancer treatment." Anticancer research 36.11 (2016): 5681-5691. [CrossRef]
- Zardawi, Sarah J., et al. "Dysregulation of Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways in breast cancer." Histology and histopathology (2009).
- Okuhashi, Yuki, Mai Itoh, and Shuji Tohda. "Hedgehog stimulation suppresses clonogenicity and activates NOTCH signalling in T-lymphoblastic leukaemia Jurkat cells." Anticancer Research 37.9 (2017): 5005-5009. [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, Mikala, Elizabeth S. Nakasone, and Zena Werb. "Tumors as organs: complex tissues that interface with the entire organism." Developmental cell 18.6 (2010): 884-901. [CrossRef]
- Polyak, Kornelia, and Raghu Kalluri. "The role of the microenvironment in mammary gland development and cancer." Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 2.11 (2010): a003244. [CrossRef]
- Yu, P. F. , et al. "TNFα-activated mesenchymal stromal cells promote breast cancer metastasis by recruiting CXCR2+ neutrophils." Oncogene 36.4 (2017): 482-490. [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, Swarnali, and Joan Massague. "Arresting supporters: targeting neutrophils in metastasis." Cell research 26.3 (2016): 273-274. [CrossRef]
- Wculek, Stefanie K., and Ilaria Malanchi. "Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells." Nature 528.7582 (2015): 413-417. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jingqi, et al. "CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3." Cancer cell 19.4 (2011): 541-555. [CrossRef]
- Li, Xiu Juan, et al. "Role of pulmonary macrophages in initiation of lung metastasis in anaplastic thyroid cancer." International Journal of Cancer 139.11 (2016): 2583-2592. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Haiqiang, et al. "Liposomes coated with isolated macrophage membrane can target lung metastasis of breast cancer." ACS nano 10.8 (2016): 7738-7748. [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, Surya Kumari, et al. "Studying the role of alveolar macrophages in breast cancer metastasis." JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) 112 (2016): e54306.
- Chen, Qing, Xiang H-F. Zhang, and Joan Massagué. "Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs." Cancer cell 20.4 (2011): 538-549. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Kun, et al. "The fibroblast Tiam1-osteopontin pathway modulates breast cancer invasion and metastasis." Breast cancer research 18.1 (2016): 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Hye Min, Woo Hee Jung, and Ja Seung Koo. "Expression of cancer-associated fibroblast related proteins in metastatic breast cancer: an immunohistochemical analysis." Journal of translational medicine 13.1 (2015): 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M. Angela, et al. "EMT: 2016." Cell 166.1 (2016): 21-45.
- Gonzalez, David M., and Damian Medici. "Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition." Science signaling 7.344 (2014): re8-re8. [CrossRef]
- Linder, Stefan, Christiane Wiesner, and Mirko Himmel. "Degrading devices: invadosomes in proteolytic cell invasion." Annual review of cell and developmental biology 27 (2011): 185-211.
- Weaver, Alissa M. "Invadopodia: specialized cell structures for cancer invasion." Clinical & experimental metastasis 23 (2006): 97-105. [CrossRef]
- Schoumacher, Marie, et al. "Actin, microtubules, and vimentin intermediate filaments cooperate for elongation of invadopodia." Journal of Cell Biology 189.3 (2010): 541-556. [CrossRef]
- Petrie, Ryan J., Andrew D. Doyle, and Kenneth M. Yamada. "Random versus directionally persistent cell migration." Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 10.8 (2009): 538-549. [CrossRef]
- Artym, Vira V., et al. "Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function." Cancer research 66.6 (2006): 3034-3043. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, Danielle A., and Sara A. Courtneidge. "The'ins' and'outs' of podosomes and invadopodia: characteristics, formation and function." Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 12.7 (2011): 413-426.
- Chan, Keefe T., Christa L. Cortesio, and Anna Huttenlocher. "FAK alters invadopodia and focal adhesion composition and dynamics to regulate breast cancer invasion." Journal of Cell Biology 185.2 (2009): 357-370. [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, Shinji, et al. "The role of Tks adaptor proteins in invadopodia formation, growth and metastasis of melanoma." Oncotarget 7.48 (2016): 78473.
- Buschman, Matthew D., et al. "The novel adaptor protein Tks4 (SH3PXD2B) is required for functional podosome formation." Molecular biology of the cell 20.5 (2009): 1302-1311. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Yoshifumi, and Motoharu Seiki. "MT1-MMP: a potent modifier of pericellular microenvironment." Journal of cellular physiology 206.1 (2006): 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Uekita, Takamasa, et al. "Cytoplasmic tail–dependent internalization of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is important for its invasion-promoting activity." The Journal of cell biology 155.7 (2001): 1345-1356. [CrossRef]
- Lehti, Kaisa, et al. "Regulation of membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activity by its cytoplasmic domain." Journal of Biological Chemistry 275.20 (2000): 15006-15013. [CrossRef]
- Hotary, Kevin B., et al. "Membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase usurps tumor growth control imposed by the three-dimensional extracellular matrix." Cell 114.1 (2003): 33-45. [CrossRef]
- Gianni, Davide, et al. "c-Src–mediated phosphorylation of NoxA1 and Tks4 induces the reactive oxygen species (ROS)–dependent formation of functional invadopodia in human colon cancer cells." Molecular biology of the cell 21.23 (2010): 4287-4298. [CrossRef]
- Leong, Hon S., et al. "Invadopodia are required for cancer cell extravasation and are a therapeutic target for metastasis." Cell reports 8.5 (2014): 1558-1570. [CrossRef]
- Mitre, Geovanni Pereira, et al. "Key proteins of invadopodia are overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma suggesting an important role of MT1-MMP in the tumoral progression." Diagnostic Pathology 16 (2021): 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Kui, Xiang, et al. "Prognostic value of SH3PXD2B (Tks4) in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a combined multi-omics and experimental study." BMC Medical Genomics 14.1 (2021): 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Kudlik, Gyöngyi, et al. "Advances in understanding TKS4 and TKS5: Molecular scaffolds regulating cellular processes from podosome and invadopodium formation to differentiation and tissue homeostasis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.21 (2020): 8117. [CrossRef]
- Saini, Priyanka, and Sara A. Courtneidge. "Tks adaptor proteins at a glance." Journal of cell science 131.1 (2018): jcs203661. [CrossRef]
- Bögel, Gábor, et al. "Frank-ter Haar syndrome protein Tks4 regulates epidermal growth factor-dependent cell migration." Journal of Biological Chemistry 287.37 (2012): 31321-31329. [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, Rohan D., and Brett M. Collins. "Insights into the PX (phox-homology) domain and SNX (sorting nexin) protein families: structures, functions and roles in disease." Biochemical Journal 441.1 (2012): 39-59.
- Mao, Mao, et al. "The podosomal-adaptor protein SH3PXD2B is essential for normal postnatal development." Mammalian genome 20 (2009): 462-475. [CrossRef]
- Szeder, Bálint, et al. "Absence of the Tks4 scaffold protein induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like changes in human colon cancer cells." Cells 8.11 (2019): 1343. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Wesley L., et al. "Specific chromatin landscapes and transcription factors couple breast cancer subtype with metastatic relapse to lung or brain." BMC medical genomics 13.1 (2020): 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Pertea, Mihaela, et al. "Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown." Nature protocols 11.9 (2016): 1650-1667.
- Lánczky, András, and Balázs Győrffy. "Web-based survival analysis tool tailored for medical research (KMplot): development and implementation." Journal of medical Internet research 23.7 (2021): e27633.
- Goel, Manish Kumar, Pardeep Khanna, and Jugal Kishore. "Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate." International journal of Ayurveda research 1.4 (2010): 274. [CrossRef]
- Rich, Jason T., et al. "A practical guide to understanding Kaplan-Meier curves." Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery 143.3 (2010): 331-336. [CrossRef]
- Eckert MA, Santiago-Medina M, Lwin TM, Kim J, Courtneidge SA, Yang J. ADAM12 induction by Twist1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis via regulation of invadopodia and focal adhesions. J Cell Sci. 2017 Jun 15;130(12):2036-2048. Epub 2017 May 3. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martner A, Aydin E, Hellstrand K. NOX2 in autoimmunity, tumor growth and metastasis. J Pathol. 2019 Feb;247(2):151-154. Epub 2018 Nov 29. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li Y, Zhang H, Gong H, Yuan Y, Li Y, Wang C, Li W, Zhang Z, Liu M, Liu H, Chen J. miR-182 suppresses invadopodia formation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting cortactin gene. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 9;37(1):141. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li X, Yang J, Wang X, Li X, Liang J, Xing H. Role of TWIST2, E-cadherin and Vimentin in epithelial ovarian carcinogenesis and prognosis and their interaction in cancer progression. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2016;37(1):100-8. [PubMed]
- Mrozik KM, Blaschuk OW, Cheong CM, Zannettino ACW, Vandyke K. N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a therapeutic target in cancer. BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 1;18(1):939. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, K. , Tang, Z., Huang, A., Chen, P., Liu, P., Yang, J., Lu, W., Liao, J., Sun, Y., Wen, S., Hu, Y., Huang, P."Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promotes cancer growth and metastasis through upregulation of SNAIL expression". International Journal of Oncology 50.1 (2017): 252-262. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X, Zhou BP. The Role of Snail in EMT and Tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Nov;13(9):963-972. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan L, Lei H, Zhang S, Peng Y, Fu C, Shu G, Yin G. Non-canonical signaling pathway of SNAI2 induces EMT in ovarian cancer cells by suppressing miR-222-3p transcription and upregulating PDCD10. Theranostics. 2020 Apr 27;10(13):5895-5913. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang P, Sun Y, Ma L. ZEB1: at the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(4):481-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, Hye-Ran, et al. “Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 2 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Various Cancers and Its Correlation with Infiltrating Immune Cells in Ovarian Cancer.” Current Issues in Molecular Biology, vol. 44, no. 3, Mar. 2022, pp. 1203–14. Crossref. [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya VM, Ho B, Conroy J, Liu S, Wang D, Cance WG. Gene Expression Profiling Identifies Important Genes Affected by R2 Compound Disrupting FAK and P53 Complex. Cancers (Basel). 2014 Jan 21;6(1):166-78. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vasaikar, Suhas V., et al. "EMTome: A resource for pan-cancer analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition genes and signatures." British journal of cancer 124.1 (2021): 259-269. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, Aravind, et al. "Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 102.43 (2005): 15545-15550. [CrossRef]
- Jumper, John, et al. "Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold." Nature 596.7873 (2021): 583-589. [CrossRef]
- Trott, Oleg, and Arthur J. Olson. "AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading." Journal of computational chemistry 31.2 (2010): 455-461.
- Morris, Garrett M., et al. "AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility." Journal of computational chemistry 30.16 (2009): 2785-2791. [CrossRef]
- Rastelli G, et al. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(11): 879-891. [CrossRef]
- Morris GM, Lim-Wilby M. Molecular docking. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;443:365-382. [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, Roman A., and Mark B. Swindells. "LigPlot+: multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery." (2011): 2778-2786. [CrossRef]
- Damian Szklarczyk and others, The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D605–D612. [CrossRef]
- Steven Maere and others, BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of Gene Ontology categories in Biological Networks, Bioinformatics, Volume 21, Issue 16, August 2005, Pages 3448–3449. [CrossRef]
- Tom Brody,Chapter 9 - Biostatistics—Part I,Editor(s): Tom Brody, Clinical Trials (Second Edition), Academic Press, 2016,Pages 203-226,ISBN 9780128042175. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Meysam, et al. "Organ-specific metastasis of breast cancer: molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying lung metastasis." Cellular Oncology 41 (2018): 123-140. [CrossRef]
- Balch, William E., et al. "Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention." science 319.5865 (2008): 916-919. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Xiao-Qiong, et al. "Protein homeostasis in aging and cancer." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 11 (2023): 1143532.
- Brancolini, Claudio, and Luca Iuliano. "Proteotoxic stress and cell death in cancer cells." Cancers 12.9 (2020): 2385. [CrossRef]
- Merő, Balázs, et al. "Characterization of the intramolecular interactions and regulatory mechanisms of the scaffold protein Tks4." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.15 (2021): 8103. [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, Douglas B., et al. "Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications." Nature reviews Drug discovery 3.11 (2004): 935-949. [CrossRef]
- Pizzuti, Laura, et al. "Eribulin in triple negative metastatic breast cancer: critic interpretation of current evidence and projection for future scenarios." Journal of Cancer 10.24 (2019): 5903. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




