Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
13 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology
3. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia interconnection
4. Target lipid levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus
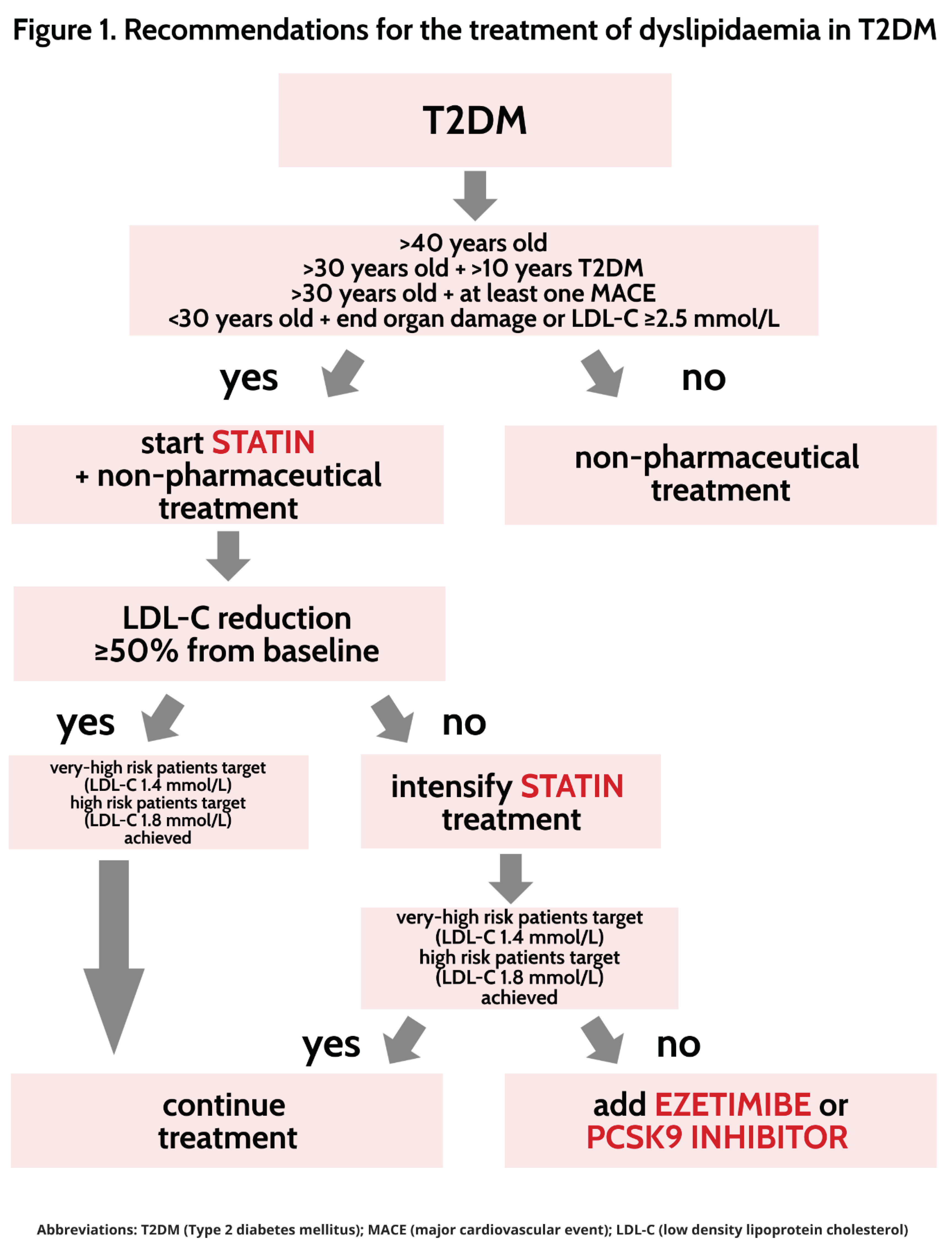
5. Treatment of dyslipidaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus
5.1. Statins
5.2. Ezetimibe
5.3. PCSK9 inhibitors
5.4. Fibrates
5.5. Omega-3 fatty acids
5.6. Non-pharmaceutical treatment
6. Conclusion
References
- Khan, M. A. B.; Hashim, M. J.; King, J. K.; Govender, R. D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes – Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends: J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T. R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U. H. Economic Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Value Health 2018, 21, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A. V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V. A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A. N. The Diabetes Mellitus–Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21 (5), 1835. B. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidaemia: Where Are We? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 21, We. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Stančáková, A.; Soininen, P.; Kangas, A. J.; Paananen, J.; Kuusisto, J.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Laakso, M. Lipoprotein Subclass Profiles in Individuals with Varying Degrees of Glucose Tolerance: A Population-Based Study of 9399 Finnish Men: Lipids and Glucose Tolerance. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, M.-R.; Nikkil, E. A.; Kuusi, T.; Harno, K. Lipoprotein Lipase Activity and Serum Lipoproteins in Untreated Type 2 (Insulin-Independent) Diabetes Associated with Obesity. Diabetologia 1982, 22, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiels, M.; Taskinen, M.-R.; Packard, C.; Caslake, M. J.; Soro-Paavonen, A.; Westerbacka, J.; Vehkavaara, S.; Häkkinen, A.; Olofsson, S.-O.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Borén, J. Overproduction of Large VLDL Particles Is Driven by Increased Liver Fat Content in Man. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, T.; Tanaka, A.; Nakano, T.; Nakajima, K.; Numano, F. Importance of Glycation in the Acceleration of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Uptake into Macrophages in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. Angiol. J. Int. Union Angiol. 1999, 18, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Duvillard, L.; Pont, F.; Florentin, E.; Gambert, P.; Vergès, B. Inefficiency of Insulin Therapy to Correct Apolipoprotein A-I Metabolic Abnormalities in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2000, 152, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R. American Diabetes Association Releases 2023 Standards of Care in Diabetes to Guide Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment for People Living with Diabetes.
- Solano, M. P.; Goldberg, R. B. Lipid Management in Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. DIABETES 2006, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A. L.; Koskinas, K. C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M. J.; De Backer, G. G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B. A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G. B. J.; Hegele, R. A.; Leiter, L. A. Dyslipidemia. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, S178–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy of Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy in 18 686 People with Diabetes in 14 Randomised Trials of Statins: A Meta-Analysis. The Lancet 2008, 371, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colhoun, H. M.; Betteridge, D. J.; Durrington, P. N.; Hitman, G. A.; Neil, H. A. W.; Livingstone, S. J.; Thomason, M. J.; Mackness, M. I.; Charlton-Menys, V.; Fuller, J. H. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with Atorvastatin in Type 2 Diabetes in the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS): Multicentre Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. The Lancet 2004, 364, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, R. H.; d’Emden, M.; Smilde, J. G.; Pocock, S. J.; on behalf of the ASPEN Study Group. Efficacy and Safety of Atorvastatin in the Prevention of Cardiovascular End Points in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganda, O. P. Statin-Induced Diabetes: Incidence, Mechanisms, and Implications. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Uribe, K. B.; Siddiqi, H.; Ostolaza, H.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Statin Treatment-Induced Development of Type 2 Diabetes: From Clinical Evidence to Mechanistic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Lamendola, C.; Harris, C. S.; Harris, V.; Tsai, M.-S.; Tripathi, P.; Abbas, F.; Reaven, G. M.; Reaven, P. D.; Snyder, M. P.; Kim, S. H.; Knowles, J. W. Statins Are Associated With Increased Insulin Resistance and Secretion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T. M. E.; Badshah, I.; Chubb, S. A. P.; Davis, W. A. Dose-Response Relationship between Statin Therapy and Glycaemia in Community-Based Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merćep, I.; Strikić, D.; Slišković, A. M.; Reiner, Ž. New Therapeutic Approaches in Treatment of Dyslipidaemia—A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J. M.; Pocock, S. J.; Bhatt, D. L.; Quesada, A. J.; Owen, R.; Fernandez-Ortiz, A.; Sanchez, P. L.; Marin Ortuño, F.; Vazquez Rodriguez, J. M.; Domingo-Fernández, A.; Lozano, I.; Roncaglioni, M. C.; Baviera, M.; Foresta, A.; Ojeda-Fernandez, L.; Colivicchi, F.; Di Fusco, S. A.; Doehner, W.; Meyer, A.; Schiele, F.; Ecarnot, F.; Linhart, A.; Lubanda, J.-C.; Barczi, G.; Merkely, B.; Ponikowski, P.; Kasprzak, M.; Fernandez Alvira, J. M.; Andres, V.; Bueno, H.; Collier, T.; Van De Werf, F.; Perel, P.; Rodriguez-Manero, M.; Alonso Garcia, A.; Proietti, M.; Schoos, M. M.; Simon, T.; Fernandez Ferro, J.; Lopez, N.; Beghi, E.; Bejot, Y.; Vivas, D.; Cordero, A.; Ibañez, B.; Fuster, V. Polypill Strategy in Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandor, A.; Ara, R. M.; Tumur, I.; Wilkinson, A. J.; Paisley, S.; Duenas, A.; Durrington, P. N.; Chilcott, J. Ezetimibe Monotherapy for Cholesterol Lowering in 2,722 People: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C. P.; Blazing, M. A.; Giugliano, R. P.; McCagg, A.; White, J. A.; Theroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B. S.; Ophuis, T. O.; Jukema, J. W.; De Ferrari, G. M.; Ruzyllo, W.; De Lucca, P.; Im, K.; Bohula, E. A.; Reist, C.; Wiviott, S. D.; Tershakovec, A. M.; Musliner, T. A.; Braunwald, E.; Califf, R. M. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R. P.; Cannon, C. P.; Blazing, M. A.; Nicolau, J. C.; Corbalán, R.; Špinar, J.; Park, J.-G.; White, J. A.; Bohula, E. A.; Braunwald, E. Benefit of Adding Ezetimibe to Statin Therapy on Cardiovascular Outcomes and Safety in Patients With Versus Without Diabetes Mellitus: Results From IMPROVE-IT (Improved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial). Circulation 2018, 137, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoglou, T.; Statkevich, P.; Johnson-Levonas, A. O.; Paolini, J. F.; Bergman, A. J.; Alton, K. B. Ezetimibe: A Review of Its Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 467–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M. S.; Giugliano, R. P.; Keech, A. C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S. D.; Murphy, S. A.; Kuder, J. F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S. M.; Sever, P. S.; Pedersen, T. R. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K. K.; Colhoun, H. M.; Szarek, M.; Baccara-Dinet, M.; Bhatt, D. L.; Bittner, V. A.; Budaj, A. J.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S. G.; Hanotin, C.; et al. Effects of Alirocumab on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with or without Diabetes: A Prespecified Analysis of the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Reid, J.; Rosenwasser, J. N.; Lewis, T.; Sheikh-Ali, M.; Choksi, R. R.; Goldfaden, R. F. A Spotlight on Alirocumab in High Cardiovascular Risk Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Mixed Dyslipidemia: A Review on the Emerging Data. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, Volume 12, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugo, S.; Sirtori, C. R.; Corsini, A.; Tokgozoglu, L.; Ruscica, M. PCSK9 Inhibition and Risk of Diabetes: Should We Worry? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, R.; Malek, R.; Munir, K. M. Doubling of Hemoglobin A1c on PCSK9 Inhibitor Therapy. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, e17–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civeira, F.; Pedro-Botet, J. Cost-Effectiveness Evaluation of the Use of PCSK9 Inhibitors. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. Engl. Ed 2021, 68, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Dallongeville, J.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Leitersdorf, E.; Fruchart, J.-C. Mechanism of Action of Fibrates on Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Circulation 1998, 98, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effects of Long-Term Fenofibrate Therapy on Cardiovascular Events in 9795 People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (the FIELD Study): Randomised Controlled Trial. The Lancet 2005, 366, 1849–1861. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effects of Combination Lipid Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1563–1574. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W. C. The Role of Dietary N-6 Fatty Acids in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 8 (Suppl 1), S42–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, M.; Origasa, H.; Matsuzaki, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Sasaki, J.; Hishida, H.; Itakura, H.; Kita, T.; Kitabatake, A.; Nakaya, N.; Sakata, T.; Shimada, K.; Shirato, K. Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Major Coronary Events in Hypercholesterolaemic Patients (JELIS): A Randomised Open-Label, Blinded Endpoint Analysis. The Lancet 2007, 369, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D. L.; Steg, P. G.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E. A.; Jacobson, T. A.; Ketchum, S. B.; Doyle, R. T.; Juliano, R. A.; Jiao, L.; Granowitz, C.; Tardif, J.-C.; Ballantyne, C. M. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction with Icosapent Ethyl for Hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, J.; Anzalone, D.; Hilleman, D.; Catini, J. The Clinical Relevance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Management of Hypertriglyceridemia. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J. S.; Tanenbaum, M. L.; Commissariat, P. V. Psychosocial Factors in Medication Adherence and Diabetes Self-Management: Implications for Research and Practice. Am. Psychol. 2016, 71, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D. K.; Blumenthal, R. S.; Albert, M. A.; Buroker, A. B.; Goldberger, Z. D.; Hahn, E. J.; Himmelfarb, C. D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J. W.; Michos, E. D.; Miedema, M. D.; Muñoz, D.; Smith, S. C.; Virani, S. S.; Williams, K. A.; Yeboah, J.; Ziaeian, B. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, e177–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfvenborg, J. E.; Andersson, T.; Carlsson, P.-O.; Dorkhan, M.; Groop, L.; Martinell, M.; Tuomi, T.; Wolk, A.; Carlsson, S. Sweetened Beverage Intake and Risk of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA) and Type 2 Diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boule, N. G.; Haddad, E.; Kenny, G. P.; Wells, G. A.; Sigal, R. J. Effects of Exercise on Glycemic Control and Body Mass in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials: Sports Medicine Update. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2002, 12, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, C.; Després, J.-P.; Lamarche, B.; Bergeron, J.; Gagnon, J.; Leon, A. S.; Rao, D. C.; Skinner, J. S.; Wilmore, J. H.; Bouchard, C. Effects of Endurance Exercise Training on Plasma HDL Cholesterol Levels Depend on Levels of Triglycerides: Evidence From Men of the Health, Risk Factors, Exercise Training and Genetics (HERITAGE) Family Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W. E.; Houmard, J. A.; Duscha, B. D.; Knetzger, K. J.; Wharton, M. B.; McCartney, J. S.; Bales, C. W.; Henes, S.; Samsa, G. P.; Otvos, J. D.; Kulkarni, K. R.; Slentz, C. A. Effects of the Amount and Intensity of Exercise on Plasma Lipoproteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzynski, M. A.; Ruiz-Ramie, J. J.; Barber, J. L.; Slentz, C. A.; Apolzan, J. W.; McGarrah, R. W.; Harris, M. N.; Church, T. S.; Borja, M. S.; He, Y.; Oda, M. N.; Martin, C. K.; Kraus, W. E.; Rohatgi, A. Effects of Increasing Exercise Intensity and Dose on Multiple Measures of HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C. K.; Ng, C.; Hama, S.; Eliseo, A. J.; Barnard, R. J. Effect of a Short-Term Diet and Exercise Intervention on Inflammatory/Anti-Inflammatory Properties of HDL in Overweight/Obese Men with Cardiovascular Risk Factors. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 101, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, M.; Liang, J.; He, G.; Chen, N. Ketogenic Diet Benefits to Weight Loss, Glycemic Control, and Lipid Profiles in Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, Z. Z. X.; Guelfi, K. J.; Davis, E. A.; Jones, T. W.; Fournier, P. A. The Glycaemic Benefits of a Very-Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus May Be Opposed by Increased Hypoglycaemia Risk and Dyslipidaemia. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhayany, A.; Lustman, A.; Abel, R.; Attal-Singer, J.; Vinker, S. A Low Carbohydrate Mediterranean Diet Improves Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Diabetes Control among Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 1-Year Prospective Randomized Intervention Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Leone, L.; Agostoni, C.; Pali-Schöll, I. The Secrets of the Mediterranean Diet. Does [Only] Olive Oil Matter? Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covas, M.-I.; Nyyssönen, K.; E. Poulsen, H.; Kaikkonen, J.; F. Zunft, H.-J.; Kiesewetter, H.; Gaddi, A.; Torre, R. de la; Mursu, J.; Bäumler, H.; Nascetti, S.; T. Salonen, J.; Fitó, M.; Virtanen, J.; Marrugat, J.; Group, for the E. S. The Effect of Polyphenols in Olive Oil on Heart Disease Risk Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Peña, J. D.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Delgado-Casado, N.; Gomez-Luna, P.; Alcala-Diaz, J. F.; Yubero-Serrano, E. M.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Leon-Acuña, A.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Camargo, A.; Tinahones, F. J.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Ordovas, J. M.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Lopez-Miranda, J. Mediterranean Diet Improves Endothelial Function in Patients with Diabetes and Prediabetes: A Report from the CORDIOPREV Study. Atherosclerosis 2018, 269, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




