Submitted:
08 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
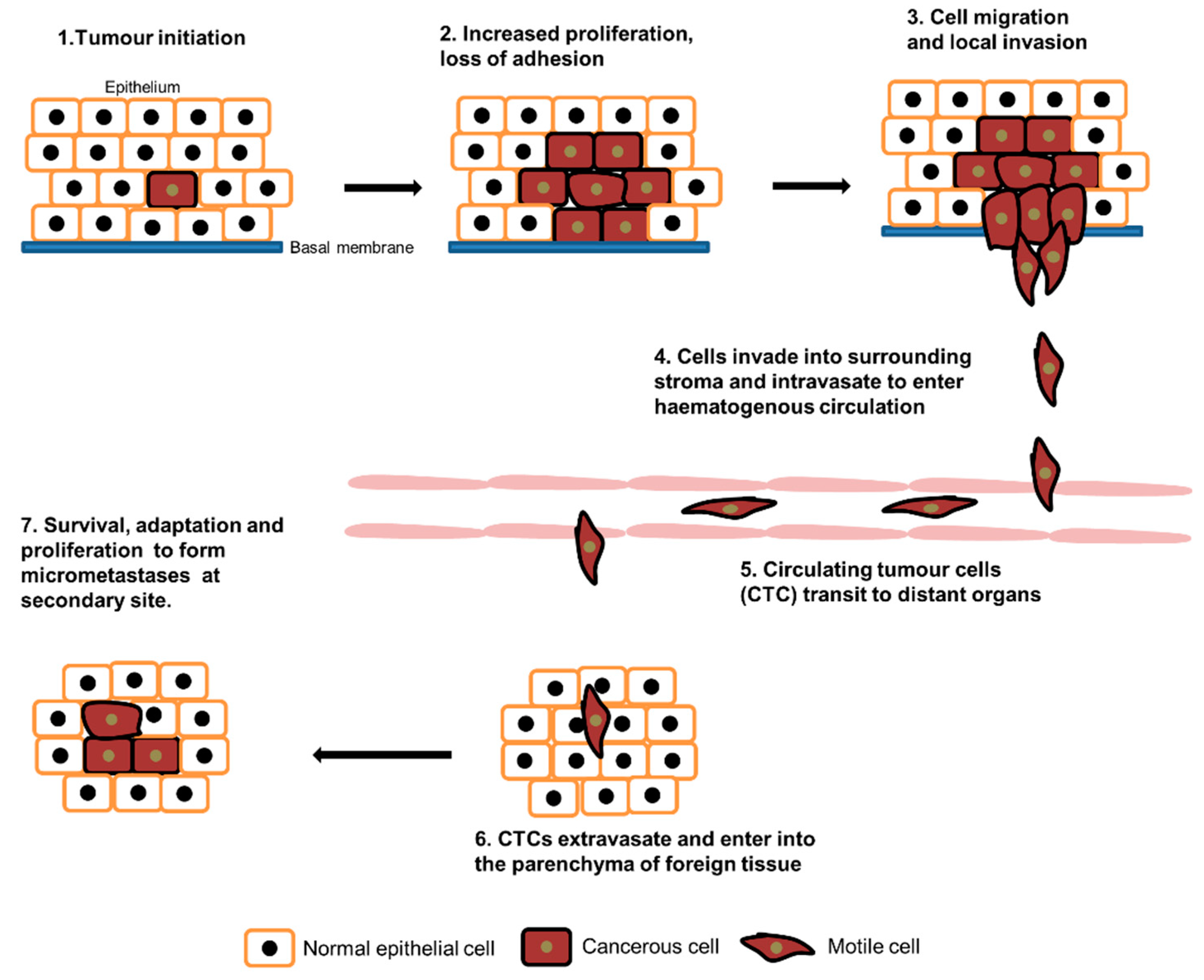
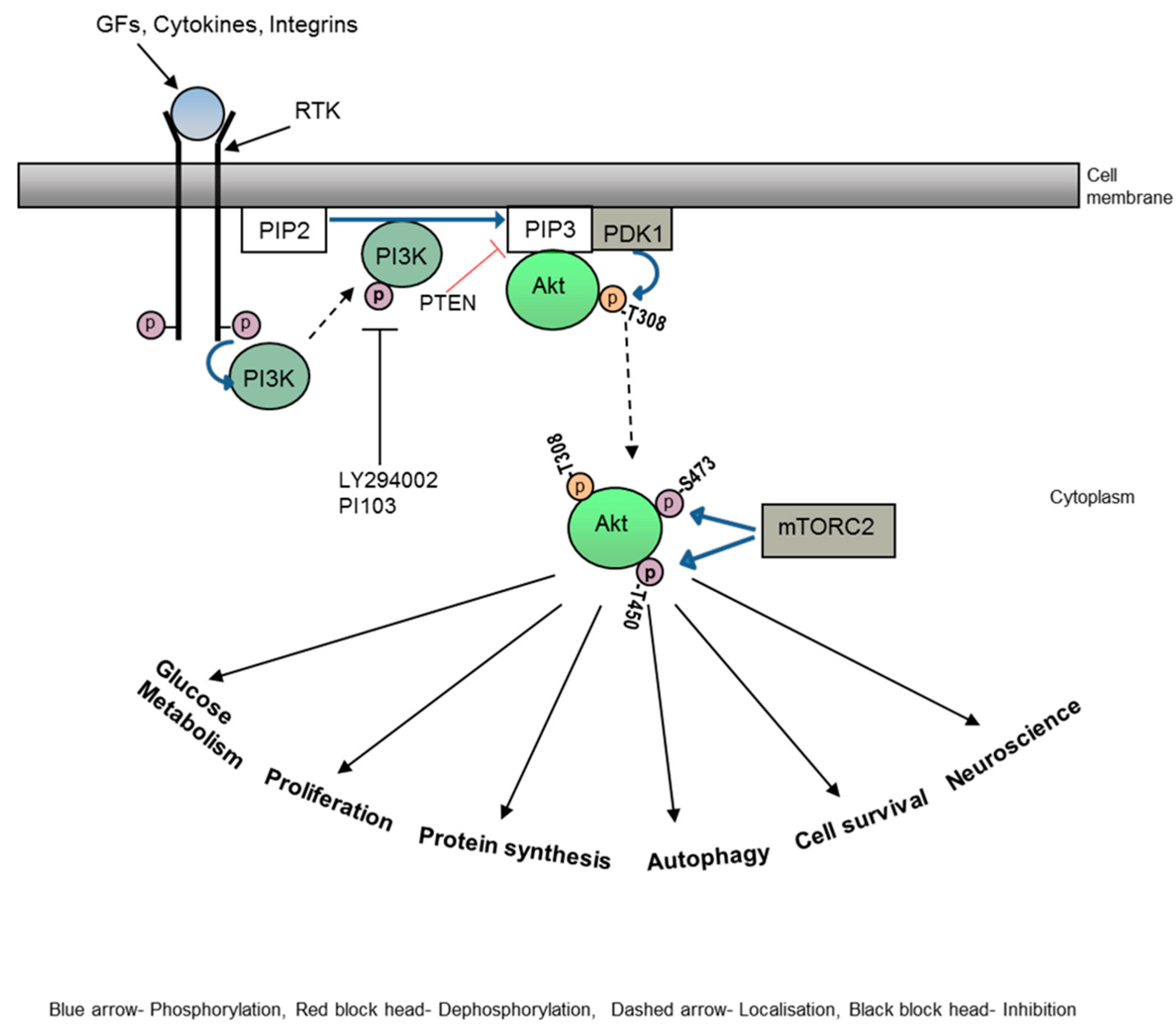
1. Introduction
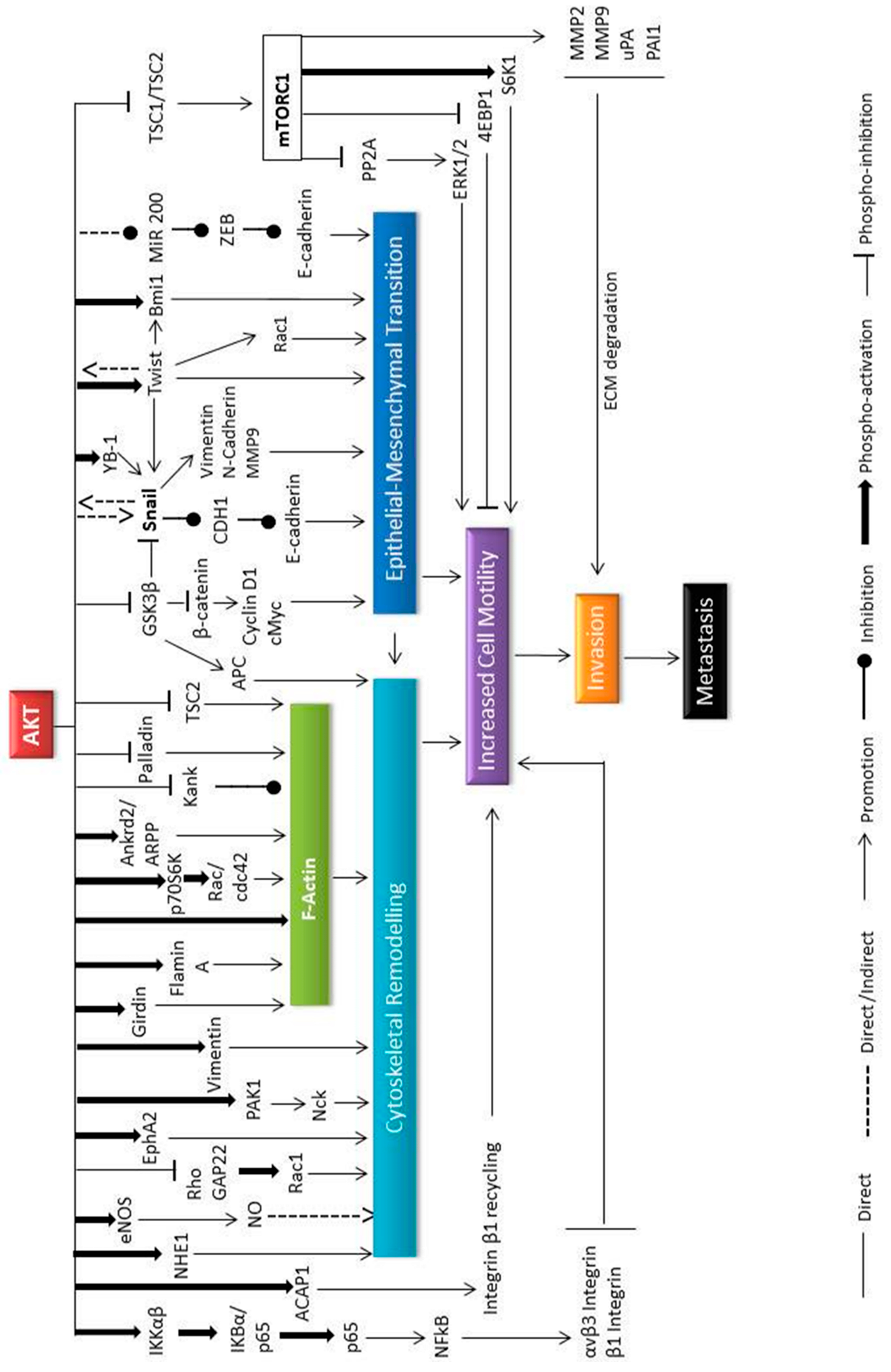
2. Akt in Cytoskeletal rearrangements
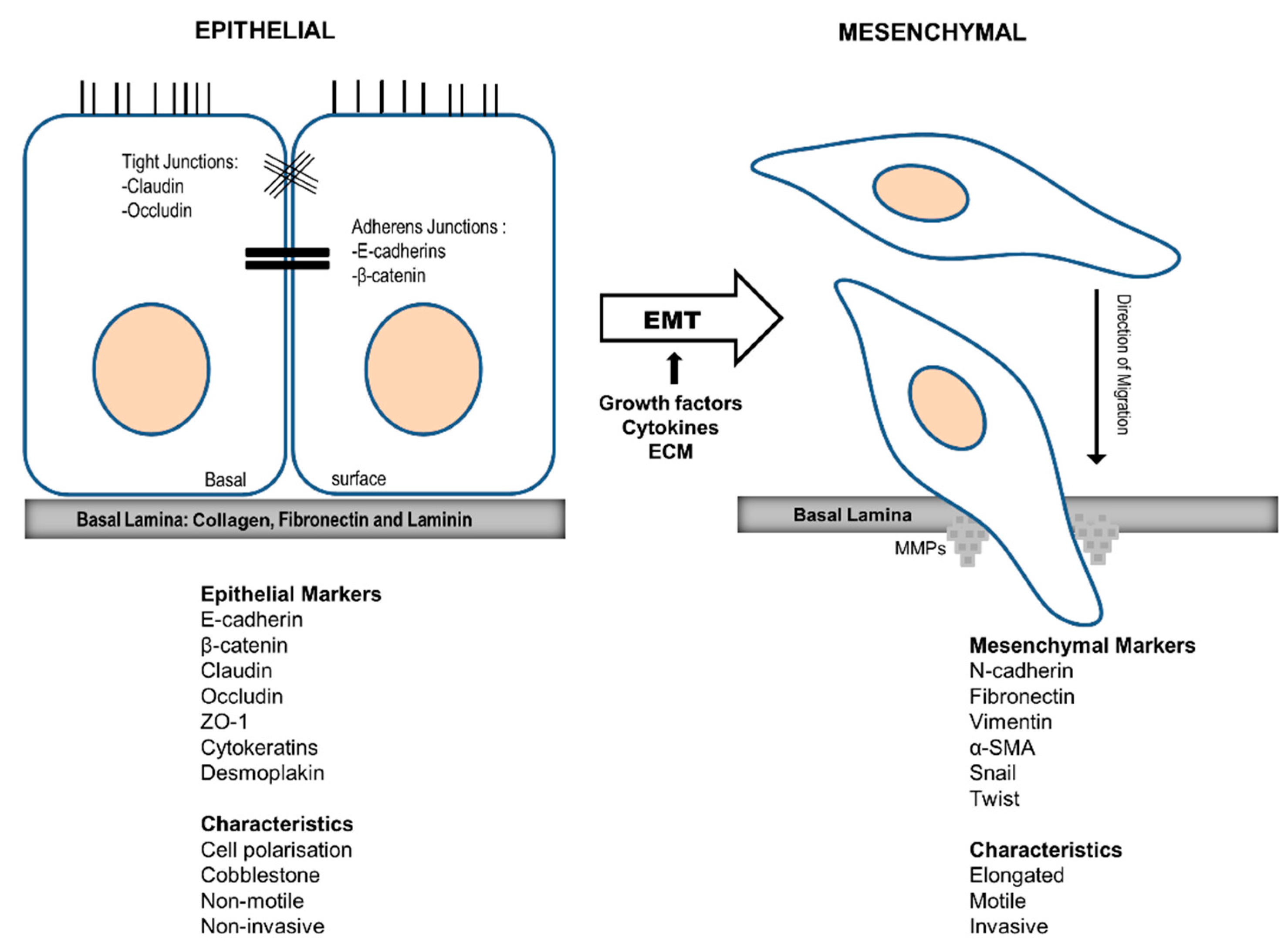
3. Akt in EMT
4. Akt in HNSCC metastasis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dillekås H, Rogers MS, Straume O. Are 90% of deaths from cancer caused by metastases? Cancer medicine. 2019;8(12):5574-6.
- Palmer TD, Ashby WJ, Lewis JD, Zijlstra A. Targeting tumor cell motility to prevent metastasis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(8):568-81.
- Leber MF, Efferth T. Molecular principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (review). Int J Oncol. 2009;34(4):881-95.
- Robert, J. Biology of cancer metastasis. Bulletin du cancer. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF, Liotta LA. General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer. 1997;80(8 Suppl):1529-37.
- Friedl P, Brocker EB. The biology of cell locomotion within three-dimensional extracellular matrix. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000;57(1):41-64.
- Friedl P, Wolf K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(5):362-74. [CrossRef]
- Zhou H, Huang S. Role of mTOR Signaling in Tumor Cell Motility, Invasion and Metastasis. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011;12(1):30-42.
- Lauffenburger DA, Horwitz AF. Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process. Cell. 1996;84(3):359-69.
- Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, et al. Cell Migration: Integrating Signals from Front to Back. Science. 2003;302(5651):1704-9.
- Mitchison TJ, Cramer LP. Actin-based cell motility and cell locomotion. Cell. 1996;84(3):371-9.
- Schmidt A, Hall MN. Signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. 1998;14:305-38. [CrossRef]
- Pollard TD, Borisy GG. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 2003;112(4):453-65.
- Ahmed H, Ghoshal A, Jones S, Ellis I, Islam M. Head and Neck Cancer Metastasis and the Effect of the Local Soluble Factors, from the Microenvironment, on Signalling Pathways: Is It All about the Akt? Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(8). [CrossRef]
- Ellis IR, Islam MR, Aljorani L, Jones SJ. Fibronectin: the N-terminal region and its role in cell migration- implications for disease and healing. In: Beattie J, editor. Fibronectin: Current Concepts in Structure, Function and Pathology. Protein Biochemistry, Synthesis, Structure and Cellular Functions. New York: Nova Science publishers; 2012. p. 35-69.
- Friedl, P. Prespecification and plasticity: shifting mechanisms of cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16(1):14-23. [CrossRef]
- Inaki M, Vishnu S, Cliffe A, Rorth P. Effective guidance of collective migration based on differences in cell states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(6):2027-32. [CrossRef]
- Rorth, P. Whence directionality: guidance mechanisms in solitary and collective cell migration. Dev Cell. 2011;20(1):9-18. [CrossRef]
- Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E, Segall JE. Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(8):777-83.
- Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 2007;129(7):1261-74.
- Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes & development. 1999;13(22):2905-27. [CrossRef]
- Alessi DR, Cohen P. Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 1998;8(1):55-62. [CrossRef]
- Bozulic L, Hemmings BA. PIKKing on PKB: regulation of PKB activity by phosphorylation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2009;21(2):256-61.
- Feng J, Park J, Cron P, Hess D, Hemmings BA. Identification of a PKB/Akt Hydrophobic Motif Ser-473 Kinase as DNA-dependent Protein Kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(39):41189-96. [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307(5712):1098-101. [CrossRef]
- Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, et al. Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene. 1998;17(3):313-25. [CrossRef]
- Hart JR, Vogt PK. Phosphorylation of AKT: a mutational analysis. Oncotarget. 2011;2(6):467-76.
- Ikenoue T, Inoki K, Yang Q, Zhou X, Guan K-L. Essential function of TORC2 in PKC and Akt turn motif phosphorylation, maturation and signalling. EMBO J. 2008;27(14):1919-31. doi: http://www.nature.com/ emboj/journal/v27/ n14/ suppinfo/emboj2008119a_S1.html.
- De Marco C, Rinaldo N, Bruni P, Malzoni C, Zullo F, Fabiani F, et al. Multiple genetic alterations within the PI3K pathway are responsible for AKT activation in patients with ovarian carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55362. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Ferrer-Lozano J, Stemke-Hale K, Sahin A, Liu S, Barrera JA, et al. PI3K pathway mutations and PTEN levels in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Molecular cancer therapeutics. 2011;10(6):1093-101.
- Wu R, Baker SJ, Hu TC, Norman KM, Fearon ER, Cho KR. Type I to Type II Ovarian Carcinoma Progression: Mutant Trp53 or Pik3ca Confers a More Aggressive Tumor Phenotype in a Mouse Model of Ovarian Cancer. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(4):1391-9.
- Xue G, Hemmings BA. PKB/Akt-Dependent Regulation of Cell Motility. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(6):393-404. [CrossRef]
- Yoeli-Lerner M, Toker A. Akt/PKB Signaling in Cancer: A Function in Cell Motility and Invasion. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(6):603-5.
- Frixione, E. Recurring views on the structure and function of the cytoskeleton: a 300-year epic. Cell motility and the cytoskeleton. 2000;46(2):73-94. [CrossRef]
- Bonello T, Coombes J, Schevzov G, Gunning P, Stehn J. Therapeutic Targeting of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Cancer. In: Kavallaris M, editor. Cytoskeleton and Human Disease. New York: Humana Press; 2012. p. 181-200.
- Bugyi B, Carlier MF. Control of actin filament treadmilling in cell motility. Annual review of biophysics. 2010;39:449-70. [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995;1(1):27-31.
- Morales-Ruiz M, Fulton D, Sowa G, Languino LR, Fujio Y, Walsh K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ Res. 2000;86(8):892-6.
- Dimmeler S, Dernbach E, Zeiher AM. Phosphorylation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase at ser-1177 is required for VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration. FEBS Lett. 2000;477(3):258-62.
- Dimmeler S, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Hermann C, Busse R, Zeiher AM. Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature. 1999;399(6736):601-5. [CrossRef]
- Qian Y, Corum L, Meng Q, Blenis J, Zheng JZ, Shi X, et al. PI3K induced actin filament remodeling through Akt and p70S6K1: implication of essential role in cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286(1):C153-63. [CrossRef]
- Qian Y, Zhong X, Flynn DC, Zheng JZ, Qiao M, Wu C, et al. ILK mediates actin filament rearrangements and cell migration and invasion through PI3K/Akt/Rac1 signaling. Oncogene. 2005;24(19):3154-65. [CrossRef]
- Ip CKM, Cheung ANY, Ngan HYS, Wong AST. p70 S6 kinase in the control of actin cytoskeleton dynamics and directed migration of ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 2011;30(21):2420-32. [CrossRef]
- Chodniewicz D, Zhelev DV. Chemoattractant receptor-stimulated F-actin polymerization in the human neutrophil is signaled by 2 distinct pathways. Blood. 2003;101(3):1181-4. [CrossRef]
- Yang L, Dan HC, Sun M, Liu Q, Sun XM, Feldman RI, et al. Akt/protein kinase B signaling inhibitor-2, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Akt signaling with antitumor activity in cancer cells overexpressing Akt. Cancer Res. 2004;64(13):4394-9. [CrossRef]
- Amiri A, Noei F, Jeganathan S, Kulkarni G, Pinke DE, Lee JM. eEF1A2 activates Akt and stimulates Akt-dependent actin remodeling, invasion and migration. Oncogene. 2007;26(21):3027-40. [CrossRef]
- Cenni V, Sirri A, Riccio M, Lattanzi G, Santi S, de Pol A, et al. Targeting of the Akt/PKB kinase to the actin skeleton. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(12):2710-20. [CrossRef]
- Ho YP, Kuo CW, Hsu YT, Huang YS, Yew LP, Huang WF, et al. beta-Actin is a downstream effector of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in myeloma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;348(1-2):129-39. [CrossRef]
- Zhou GL, Zhuo Y, King CC, Fryer BH, Bokoch GM, Field J. Akt phosphorylation of serine 21 on Pak1 modulates Nck binding and cell migration. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(22):8058-69.
- Chung CY, Potikyan G, Firtel RA. Control of cell polarity and chemotaxis by Akt/PKB and PI3 kinase through the regulation of PAKa. Mol Cell. 2001;7(5):937-47.
- Chhabra ES, Higgs HN. The many faces of actin: matching assembly factors with cellular structures. nature cell biology. 2007;9(10):1110-21.
- Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, Morone N, Watanabe T, Kawai K, et al. Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility via Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 2005;9(3):389-402. [CrossRef]
- Jiang P, Enomoto A, Jijiwa M, Kato T, Hasegawa T, Ishida M, et al. An actin-binding protein Girdin regulates the motility of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68(5):1310-8. [CrossRef]
- Natsume A, Kato T, Kinjo S, Enomoto A, Toda H, Shimato S, et al. Girdin maintains the stemness of glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene. 2012;31(22):2715-24. [CrossRef]
- Weng L, Enomoto A, Ishida-Takagishi M, Asai N, Takahashi M. Girding for migratory cues: roles of the Akt substrate Girdin in cancer progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Science. 2010;101(4):836-42. [CrossRef]
- Shibata T, Matsuo Y, Shamoto T, Hirokawa T, Tsuboi K, Takahashi H, et al. Girdin, a regulator of cell motility, is a potential prognostic marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(6):2127-32. [CrossRef]
- Yamamura Y, Asai N, Enomoto A, Kato T, Mii S, Kondo Y, et al. Akt–Girdin Signaling in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Contributes to Tumor Progression. Cancer Research. 2015;75(5):813-23. [CrossRef]
- Cenni V, Bavelloni A, Beretti F, Tagliavini F, Manzoli L, Lattanzi G, et al. Ankrd2/ARPP is a novel Akt2 specific substrate and regulates myogenic differentiation upon cellular exposure to H(2)O(2). Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(16):2946-56. [CrossRef]
- Feng Y, Walsh CA. The many faces of filamin: a versatile molecular scaffold for cell motility and signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(11):1034-8. [CrossRef]
- Ravid D, Chuderland D, Landsman L, Lavie Y, Reich R, Liscovitch M. Filamin A is a novel caveolin-1-dependent target in IGF-I-stimulated cancer cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(15):2762-73. [CrossRef]
- Stossel TP, Condeelis J, Cooley L, Hartwig JH, Noegel A, Schleicher M, et al. Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2(2):138-45. [CrossRef]
- Ravid D, Maor S, Werner H, Liscovitch M. Caveolin-1 inhibits cell detachment-induced p53 activation and anoikis by upregulation of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors and signaling. Oncogene. 2005;24(8):1338-47. [CrossRef]
- Nallapalli RK, Ibrahim MX, Zhou AX, Bandaru S, Sunkara SN, Redfors B, et al. Targeting filamin A reduces K-RAS-induced lung adenocarcinomas and endothelial response to tumor growth in mice. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:50. [CrossRef]
- Meima ME, Webb BA, Witkowska HE, Barber DL. The sodium-hydrogen exchanger NHE1 is an Akt substrate necessary for actin filament reorganization by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(39):26666-75. [CrossRef]
- Denker SP, Barber DL. Cell migration requires both ion translocation and cytoskeletal anchoring by the Na-H exchanger NHE1. J Cell Biol. 2002;159(6):1087-96. [CrossRef]
- Martin C, Pedersen SF, Schwab A, Stock C. Intracellular pH gradients in migrating cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300(3):C490-5. [CrossRef]
- Stock C, Schwab A. Role of the Na/H exchanger NHE1 in cell migration. Acta physiologica (Oxford, England). 2006;187(1-2):149-57. [CrossRef]
- Stuwe L, Muller M, Fabian A, Waning J, Mally S, Noel J, et al. pH dependence of melanoma cell migration: protons extruded by NHE1 dominate protons of the bulk solution. The Journal of physiology. 2007;585(Pt 2):351-60. [CrossRef]
- Clement DL, Mally S, Stock C, Lethan M, Satir P, Schwab A, et al. PDGFRalpha signaling in the primary cilium regulates NHE1-dependent fibroblast migration via coordinated differential activity of MEK1/2-ERK1/2-p90RSK and AKT signaling pathways. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 4):953-65. [CrossRef]
- Chang L, Goldman RD. Intermediate filaments mediate cytoskeletal crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5(8):601-13. [CrossRef]
- Helfand BT, Chang L, Goldman RD. Intermediate filaments are dynamic and motile elements of cellular architecture. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 2):133-41. [CrossRef]
- Zhu QS, Rosenblatt K, Huang KL, Lahat G, Brobey R, Bolshakov S, et al. Vimentin is a novel AKT1 target mediating motility and invasion. Oncogene. 2011;30(4):457-70. [CrossRef]
- Lahat G, Zhu QS, Huang KL, Wang S, Bolshakov S, Liu J, et al. Vimentin is a novel anti-cancer therapeutic target; insights from in vitro and in vivo mice xenograft studies. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10105. [CrossRef]
- Satelli A, Li S. Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(18):3033-46. [CrossRef]
- Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker A, Wei W. Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(4):397-408. [CrossRef]
- Lin HK, Wang G, Chen Z, Teruya-Feldstein J, Liu Y, Chan CH, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cytosolic localization and oncogenic function of Skp2 by Akt/PKB. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(4):420-32. [CrossRef]
- Hong KO, Kim JH, Hong JS, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, Hong SP, et al. Inhibition of Akt activity induces the mesenchymal-to-epithelial reverting transition with restoring E-cadherin expression in KB and KOSCC-25B oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR. 2009;28:28. [CrossRef]
- McPhee TR, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Dedhar S. Integrin-linked kinase regulates E-cadherin expression through PARP-1. Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists. 2008;237(10):2737-47. [CrossRef]
- Onishi K, Higuchi M, Asakura T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y. The PI3K-Akt pathway promotes microtubule stabilization in migrating fibroblasts. Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms. 2007;12(4):535-46. [CrossRef]
- Ridnour LA, Barasch KM, Windhausen AN, Dorsey TH, Lizardo MM, Yfantis HG, et al. Nitric oxide synthase and breast cancer: role of TIMP-1 in NO-mediated Akt activation. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44081. [CrossRef]
- Xu W, Liu LZ, Loizidou M, Ahmed M, Charles IG. The role of nitric oxide in cancer. Cell Res. 2002;12(5-6):311-20. [CrossRef]
- Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(5):397-407. [CrossRef]
- Lee MJ, Thangada S, Paik JH, Sapkota GP, Ancellin N, Chae SS, et al. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 is required for endothelial cell chemotaxis. Mol Cell. 2001;8(3):693-704. [CrossRef]
- Ozaki H, Hla T, Lee MJ. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in endothelial activation. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. 2003;10(3):125-31.
- Miao H, Li DQ, Mukherjee A, Guo H, Petty A, Cutter J, et al. EphA2 mediates ligand-dependent inhibition and ligand-independent promotion of cell migration and invasion via a reciprocal regulatory loop with Akt. Cancer Cell. 2009;16(1):9-20. [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, EB. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(3):165-80. [CrossRef]
- Kawai H, Kobayashi M, Hiramoto-Yamaki N, Harada K, Negishi M, Katoh H. Ephexin4-mediated promotion of cell migration and anoikis resistance is regulated by serine 897 phosphorylation of EphA2. FEBS Open Bio. 2013;3(0):78-82. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Ballif BA, Powelka AM, Dai J, Gygi SP, Hsu VW. Phosphorylation of ACAP1 by Akt regulates the stimulation-dependent recycling of integrin beta1 to control cell migration. Dev Cell. 2005;9(5):663-73. [CrossRef]
- Rowland AF, Larance M, Hughes WE, James DE. Identification of RhoGAP22 as an Akt-dependent regulator of cell motility in response to insulin. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(23):4789-800. [CrossRef]
- Berven LA, Willard FS, Crouch MF. Role of the p70(S6K) pathway in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 2004;296(2):183-95. [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara K, Liu B, Hollenbeck S, Kent KC. Rapamycin inhibits fibronectin-induced migration of the human arterial smooth muscle line (E47) through the mammalian target of rapamycin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288(6):H2861-8. [CrossRef]
- Inoki K, Li Y, Zhu T, Wu J, Guan KL. TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(9):648-57. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Li F, Cardelli JA, Martin KA, Blenis J, Huang S. Rapamycin inhibits cell motility by suppression of mTOR-mediated S6K1 and 4E-BP1 pathways. Oncogene. 2006;25(53):7029-40. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Chen L, Chung J, Huang S. Rapamycin inhibits F-actin reorganization and phosphorylation of focal adhesion proteins. Oncogene. 2008;27(37):4998-5010. [CrossRef]
- Benefield J, Meisinger J, Petruzzelli GJ, Young MR. Endothelial cell response to human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas involves downregulation of protein phosphatases-1/2A, cytoskeletal depolymerization and increased motility. Invasion & metastasis. 1997;17(4):210-20.
- Jackson JL, Young MR. Protein phosphatase-2A regulates protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in Lewis lung carcinoma tumor variants. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20(4):357-64.
- Li Y, Wang X, Yue P, Tao H, Ramalingam SS, Owonikoko TK, et al. Protein phosphatase 2A and DNA-dependent protein kinase are involved in mediating rapamycin-induced Akt phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Chen L, Luo Y, Chen W, Zhou H, Xu B, et al. Rapamycin inhibits IGF-1 stimulated cell motility through PP2A pathway. PLoS One. 2010;5(5):e10578. [CrossRef]
- Wlodarski P, Grajkowska W, Lojek M, Rainko K, Jozwiak J. Activation of Akt and Erk pathways in medulloblastoma. Folia neuropathologica / Association of Polish Neuropathologists and Medical Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences. 2006;44(3):214-20.
- Fong Y-C, Hsu S-F, Wu C-L, Li T-M, Kao S-T, Tsai F-J, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 increases cell migration and β1 integrin up-regulation in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2009;64(1):13-21. [CrossRef]
- Yeh Y-Y, Chiao C-C, Kuo W-Y, Hsiao Y-C, Chen Y-J, Wei Y-Y, et al. TGF-β1 increases motility and αvβ3 integrin up-regulation via PI3K, Akt and NF-κB-dependent pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2008;75(6):1292-301. [CrossRef]
- Busch S, Renaud SJ, Schleussner E, Graham CH, Markert UR. mTOR mediates human trophoblast invasion through regulation of matrix-remodeling enzymes and is associated with serine phosphorylation of STAT3. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(10):1724-33. [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma N, Roy BC, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Kiyama R. Kank regulates RhoA-dependent formation of actin stress fibers and cell migration via 14-3-3 in PI3K-Akt signaling. J Cell Biol. 2008;181(3):537-49. [CrossRef]
- Chin YR, Toker A. The Actin-Bundling Protein Palladin Is an Akt1-Specific Substrate that Regulates Breast Cancer Cell Migration. Molecular Cell. 2010;38(3):333-44. [CrossRef]
- Chin YR, Toker A. Akt2 regulates expression of the actin-bundling protein palladin. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(23):4769-74. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Radisky DC, Nelson CM, Zhang H, Fata JE, Roth RA, et al. Mechanism of Akt1 inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion reveals a protumorigenic role for TSC2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(11):4134-9. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, MA. The ins and outs of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. 2011;27:347-76. [CrossRef]
- Yang J, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 2008;14(6):818-29. [CrossRef]
- Larue L, Bellacosa A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene. 2005;24(50):7443-54. [CrossRef]
- Zheng H, Kang Y. Multilayer control of the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Thompson EW, Williams ED. EMT and MET in carcinoma--clinical observations, regulatory pathways and new models. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008;25(6):591-2. [CrossRef]
- Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A, Testa JR. Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for therapeutic targeting. Advances in cancer research. 2005;94:29-86. [CrossRef]
- Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, Gonzalez-Baron M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer treatment reviews. 2004;30(2):193-204. [CrossRef]
- Ringel MD, Hayre N, Saito J, Saunier B, Schuppert F, Burch H, et al. Overexpression and overactivation of Akt in thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61(16):6105-11.
- Testa JR, Bellacosa A. AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(20):10983-5. [CrossRef]
- Wu HT, Ko SY, Fong JH, Chang KW, Liu TY, Kao SY. Expression of phosphorylated Akt in oral carcinogenesis and its induction by nicotine and alkaline stimulation. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38(2):206-13.
- Bellacosa A, de Feo D, Godwin AK, Bell DW, Cheng JQ, Altomare DA, et al. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1995;64(4):280-5.
- Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, Klein-Szanto AJ, Van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W, et al. The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer research. 2003;63(9):2172-8.
- Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1420-8. [CrossRef]
- Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139(5):871-90. [CrossRef]
- Bellacosa A, Larue L. PI3K/AKT Pathway and the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. In: Thomas-Tikhonenko A, editor. Cancer Genome and Tumor Microenvironment. New York: Springer Science+Business Media; 2010. p. 11-31.
- Katoh M, Katoh M. Cross-talk of WNT and FGF signaling pathways at GSK3beta to regulate beta-catenin and SNAIL signaling cascades. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5(9):1059-64.
- Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M, et al. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(10):931-40. [CrossRef]
- Ha G-H, Park J-S, Breuer E-KY. TACC3 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Letters. 2013;332(0):63-73. [CrossRef]
- Smith A, Teknos TN, Pan Q. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013;49(4):287-92. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Wang H-S, Zhou B-H, Li C-L, Zhang F, Wang X-F, et al. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Induced by TNF-α Requires AKT/GSK-3β-Mediated Stabilization of Snail in Colorectal Cancer. PLOS ONE. 2013;8(2):e56664. [CrossRef]
- Wu K, Fan J, Zhang L, Ning Z, Zeng J, Zhou J, et al. PI3K/Akt to GSK3β/β-catenin signaling cascade coordinates cell colonization for bladder cancer bone metastasis through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Cellular Signalling. 2012;24(12):2273-82. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Zhou H, Ni H, Shen X. COL11A1-Driven pithelialMesenchymal Transition and Stemness of Pancreatic Cancer Cells Induce Cell Migration and Invasion by Modulating the AKT/GSK-3β/Snail Pathway. Biomolecules. 2022;12(3):391.
- Evdokimova V, Tognon C, Ng T, Ruzanov P, Melnyk N, Fink D, et al. Translational activation of snail1 and other developmentally regulated transcription factors by YB-1 promotes an epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(5):402-15. [CrossRef]
- Villagrasa P, Diaz VM, Vinas-Castells R, Peiro S, Del Valle-Perez B, Dave N, et al. Akt2 interacts with Snail1 in the E-cadherin promoter. Oncogene. 2012;31(36):4022-33. [CrossRef]
- Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun CD, Wang LH. Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 2007;67(5):1979-87. [CrossRef]
- Xue G, Restuccia DF, Lan Q, Hynx D, Dirnhofer S, Hess D, et al. Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-beta signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(3):248-59. [CrossRef]
- Yao K, Ye PP, Tan J, Tang XJ, Shen Tu XC. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in TGF-beta2-mediated epithelial mesenchymal transition in human lens epithelial cells. Ophthalmic research. 2008;40(2):69-76. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama K, Kimoto K, Itoh Y, Nakatsuka K, Matsuo N, Yoshioka H, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the expression of type I collagen induced by TGF-beta2 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2012;250(1):15-23. [CrossRef]
- Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, Wang HJ, Lan HY, Yang WH, et al. Bmi1 is essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(10):982-92. [CrossRef]
- Nacerddine K, Beaudry JB, Ginjala V, Westerman B, Mattiroli F, Song JY, et al. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Bmi1 modulates its oncogenic potential, E3 ligase activity, and DNA damage repair activity in mouse prostate cancer. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(5):1920-32. [CrossRef]
- Guo BH, Feng Y, Zhang R, Xu LH, Li MZ, Kung HF, et al. Bmi-1 promotes invasion and metastasis, and its elevated expression is correlated with an advanced stage of breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2011;10(1):10. [CrossRef]
- Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu LJ, et al. The polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(12):3626-36. [CrossRef]
- Ahn J, Sanz-Moreno V, Marshall CJ. The metastasis gene NEDD9 product acts through integrin beta3 and Src to promote mesenchymal motility and inhibit amoeboid motility. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 7):1814-26. [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Moreno, V. Tumour invasion: a new twist on Rac-driven mesenchymal migration. Curr Biol. 2012;22(11):R449-51. [CrossRef]
- Yang W-H, Lan H-Y, Huang C-H, Tai S-K, Tzeng C-H, Kao S-Y, et al. RAC1 activation mediates Twist1-induced cancer cell migration. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(4):366-74. doi: http://www.nature.com/ncb/ journal/ v14/n4/ abs/ ncb2455.html#supplementary-information.
- Hill L, Browne G, Tulchinsky E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: at the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(4):745-54. [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos D, Polytarchou C, Hatziapostolou M, Kottakis F, Maroulakou IG, Struhl K, et al. MicroRNAs differentially regulated by Akt isoforms control EMT and stem cell renewal in cancer cells. Sci Signal. 2009;2(92):ra62. [CrossRef]
- Gillison ML, Koch WM, Capone RB, Spafford M, Westra WH, Wu L, et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(9):709-20.
- Neville BW, Day TA. Oral cancer and precancerous lesions. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2002;52(4):195-215.
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2018;68(6):394-424. [CrossRef]
- Islam MR, Ellis IR, Macluskey M, Cochrane L, Jones SJ. Activation of Akt at T308 and S473 in alcohol, tobacco and HPV-induced HNSCC: is there evidence to support a prognostic or diagnostic role? Exp Hematol Oncol. 2014;3(1):25. [CrossRef]
- Islam MR, Jones SJ, Macluskey M, Ellis IR. Is there a pAkt between VEGF and oral cancer cell migration? Cellular Signalling. 2014;26(6):1294-302. [CrossRef]
- Amornphimoltham P, Sriuranpong V, Patel V, Benavides F, Conti CJ, Sauk J, et al. Persistent activation of the Akt pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential target for UCN-01. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(12 Pt 1):4029-37. [CrossRef]
- Amornphimoltham P, Patel V, Molinolo A, Gutkind JS. Head and Neck Cancer and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Network: Novel Molecular Targeted Therapy. In: Glick AB, Van Waes C, editors. Signaling Pathways in Squamous Cancer. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC; 2011. p. 407-30.
- Marquard FE, Jücker M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as a molecular target in head and neck cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;172:113729. [CrossRef]
- Massarelli E, Liu DD, Lee JJ, El-Naggar AK, Lo Muzio L, Staibano S, et al. Akt activation correlates with adverse outcome in tongue cancer. Cancer. 2005;104(11):2430-6. [CrossRef]
- Yu Z, Weinberger PM, Sasaki C, Egleston BL, Speier WFt, Haffty B, et al. Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) predicts poor clinical outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16(3):553-8. [CrossRef]
- Pontes HA, de Aquino Xavier FC, da Silva TS, Fonseca FP, Paiva HB, Pontes FS, et al. Metallothionein and p-Akt proteins in oral dysplasia and in oral squamous cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38(8):644-50. [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa J, Mitoro A, Kawashiri S, Chada KK, Imai K. Expression of Mesenchyme-Specific Gene HMGA2 in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Cavity. Cancer Research. 2004;64(6):2024-9.
- Maeda G, Chiba T, Okazaki M, Satoh T, Taya Y, Aoba T, et al. Expression of SIP1 in oral squamous cell carcinomas: implications for E-cadherin expression and tumor progression. International journal of oncology. 2005;27(6):1535-41.
- Yokoyama K, Kamata N, Hayashi E, Hoteiya T, Ueda N, Fujimoto R, et al. Reverse correlation of E-cadherin and snail expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro. Oral Oncology. 2001;37(1):65-71.
- Taki M, Kamata N, Yokoyama K, Fujimoto R, Tsutsumi S, Nagayama M. Down-regulation of Wnt-4 and up-regulation of Wnt-5a expression by epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Science. 2003;94(7):593-7.
- Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure J, Nelles L, van Roy F, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene. 2007;26(53):7445-56. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Wang Q, Ling MT, Wong YC, Leung SC, Wang X. Anti-apoptotic role of TWIST and its association with Akt pathway in mediating taxol resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(9):1891-8. [CrossRef]
- Onoue T, Uchida D, Begum NM, Tomizuka Y, Yoshida H, Sato M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 system in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. International Journal of Oncology. 2006;29(5):1133-8.
- Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, Kostic AD, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 2011;333(6046):1157-60. [CrossRef]
- Zheng Y, Wang Z, Xiong X, Zhong Y, Zhang W, Dong Y, et al. Membrane-tethered Notch1 exhibits oncogenic property via activation of EGFR–PI3K–AKT pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2019;234(5):5940-52. [CrossRef]
- Vasko V, Saji M, Hardy E, Kruhlak M, Larin A, Savchenko V, et al. Akt activation and localisation correlate with tumour invasion and oncogene expression in thyroid cancer. J Med Genet. 2004;41(3):161-70.
- Wang R, Brattain MG. AKT can be activated in the nucleus. Cell Signal. 2006;18(10):1722-31.
- Alkhadar H, Macluskey M, White S, Ellis I. Nerve growth factor-induced migration in oral and salivary gland tumour cells utilises the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway: Is there a link to perineural invasion? J Oral Pathol Med. 2020;49(3):227-34. [CrossRef]
- Islam M, Alghamdi A, Sriramula P, Shalgm B, Jones S, Ellis I. Is it all just an Akt - you'd be SMAD to believe it! Role of TGFβ1 in oral cancer metastasis. Science Repository (Dental Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research). 2018;1(3). [CrossRef]
- Thwe AM, Mossey P, Ellis IR. Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in Asian head and neck cancer cell lines. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021;50(10):1031-9. [CrossRef]
- Khattri A, Sheikh N, Acharya R, Tan Y-HC, Kochanny S, Lingen MW, et al. Mechanism of acquired resistance to cetuximab in head and neck cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2018;36(15_suppl):e18061-e. [CrossRef]
- Montagut C, Dalmases A, Bellosillo B, Crespo M, Pairet S, Iglesias M, et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):221-3. [CrossRef]
- Zaryouh H, De Pauw I, Baysal H, Pauwels P, Peeters M, Vermorken JB, et al. The Role of Akt in Acquired Cetuximab Resistant Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An In Vitro Study on a Novel Combination Strategy. Frontiers in Oncology. 2021;11(3658). [CrossRef]
- Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-11. [CrossRef]
- Chen D, Wu M, Li Y, Chang I, Yuan Q, Ekimyan-Salvo M, et al. Targeting BMI1(+) Cancer Stem Cells Overcomes Chemoresistance and Inhibits Metastases in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(5):621-34.e6. [CrossRef]
- Lai YJ, Yu WN, Kuo SC, Ho CT, Hung CM, Way TD, et al. CSC-3436 inhibits TWIST-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the suppression of Twist/Bmi1/Akt pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):9118-29. [CrossRef]
- Institute NC: Akt Inhibitor MK2206 in Treating Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01349933 (2011). Accessed. 04 April.
- Ma BB, Goh BC, Lim WT, Hui EP, Tan EH, Lopes Gde L, et al. Multicenter phase II study of the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma from patients in the mayo phase II consortium and the cancer therapeutics research group (MC1079). Invest New Drugs. 2015;33(4):985-91. [CrossRef]
- Ho AL, Foster NR, Meyers JP, Vasudeva SD, Katabi N, Antonescu CR, et al. Alliance A091104: A phase II trial of MK-2206 in patients (pts) with progressive, recurrent/metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2015;33(15_suppl):6039-. [CrossRef]
- University Y: An Open Label, Single Arm, Multicenter Phase II Study of BYL719 in Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck Who Failed to Respond to Platinum-based Therapy. (2016). Accessed.
- Kim HR, Kang HN, Yun MR, Lim SM, Kim CG, Ahn M-J, et al. Clinical trials outcomes of combined BKM120 and cetuximab compared to BKM120 in recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (R/M-SCCHN). Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2015;33(15_suppl):6049-. [CrossRef]
- Rodon J, Curigliano G, Delord J-P, Harb W, Azaro A, Han Y, et al. A Phase Ib, open-label, dose-finding study of alpelisib in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Oncotarget. 2018;9(60):31709-18. [CrossRef]
- Institute D-FC, Pharmaceuticals N: Phase Ib Study of BKM120 With Cisplatin and XRT in High Risk Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Cancer of Head and Neck. (2014). Accessed.
- Hospital SNU, Group KCS, Hospital CNU: Korean Cancer Study Group: Translational bIomarker Driven UMbrella Project for Head and Neck (TRIUMPH), Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma- Part 1 (HNSCC). (2017). Accessed.
- Chicago Uo, Institute NC: PI3K Inhibitor BKM120 and Cetuximab in Treating Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. (2013). Accessed.
| Trial identifier | Phase | Stage/type of HNSCC | Inhibitor | Combination | Result | Ref |
| NCT01349933 | II | IV/recurrent NPC | MK2206 (Akt inhibitor) | None | CR-0%, PR-4.8%, stable disease 52.4%, OS-10 months, PFS-3.5 months | [175] |
| NCT01370070 | II | Recurrent NPC | MK2206 | None | CR-0%, PR-5%, Stable disease-52%, OS-10 months, PFS-3.5 months | [176] |
| NCT01604772 | II | IV/recurrent ADCC | MK2206 | None | CR/PR-0%, Stable disease-81%, PFS-9.7 months, OS-18 months | [177] |
| NCT02145312 | II | Recurrent/metastatic HNSCC | BYL719/ Alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor) | None | Not published | [178] |
| NCT01527877 | II | Recurrent/metastatic HNSCC | BKM120/ Buparlisib (PI3K inhibitor) | None | RR-3%, Stable disease-49%, PFS-63 days, OS-143 days | [179] |
| NCT02021751 | Ib | Recurrent/metastatic HNSCC | BYL719 | Paclitaxel | Challenging safety profile, dose expansion phase was not initiated | [180] |
| NCT02113878 | Ib | Locally advanced HNSCC | BKM120 | Cisplatin/RT | Not published yet | [181] |
| NCT03292250 | II | HNSCC | BYL719 | Poziotinib (EGFR inhibitor) | Not published yet | [182] |
| NCT01816984 | I/II | Recurrent/metastatic HNSCC | BKM120 | Cetuximab | OS-9.3 months, PFS-2 months, RR-8-9% | [183] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





