1. Introduction
Due to their unique characteristics and morphological peculiarities, seahorses (
Hippocampus sp.) have captured the interest of the community, thereby enhancing their cultural, scientific, educational, and economic value. As a result of this growing interest, seahorse exploitation, both for traditional medicines and the ornamental fish trade, has increased. This has led to a decline in natural populations [
1] and an amplified focus on their cultivation worldwide [
2].
Presently, seahorse species encounter conservation challenges, with habitat degradation and overfishing being the two primary causes of significant declines in most wild populations over the past decades. These issues have resulted in these species becoming an integrant part of the IUCN Red List and Appendix II of CITES. Therefore, seahorse aquaculture holds significant potential as a conservation tool for these species, but also as a growing business, owing to the high demand for these species and their substantial market values. Presently, it is known that at least 13 species of seahorses are commercially produced [
2] at different commercial scales.
Currently, there are 42 identified seahorse species, including
Hippocampus hippocampus, which is found in the northeastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea [
3]. Although there is insufficient information to assess the conservation status of this species, natural populations in Portugal have exhibited a declining trend. Additionally, within the Mediterranean Sea, the species is already considered as Near Threatened [
4]. This situation has promoted research into various wild populations, often with a focus on their long-term conservation, as well as increased investigation into their captive production. Therefore, this remains a recent topic, and numerous gaps in knowledge regarding seahorse aquaculture, including
H.
hippocampus, persist [
2]. To prevent, or at the very least, mitigate the problems stemming from the illegal capture of seahorses, aquaculture can provide animals for international trade, thereby promoting the recovery of wild stocks and ensuring the conservation of natural populations [
5].
It is widely acknowledged that captive breeding contributes significantly to preventing species extinction [
6], and in this regard, seahorse captive breeding also assumes a preventive role in terms of species extinction [
7]. Given the limited current understanding of the dietary requirements of
H.
hippocampus, the utilization and development of diets that align with the nutritional needs of the juveniles hold paramount importance.
Artemia and rotifers have historically been utilized as live prey for feeding seahorses [
7]. However, both
Artemia nauplii and rotifers have consistently demonstrated nutritional deficiencies as food sources for larval and juvenile marine fishes, largely due to their inadequate fatty acid profiles and low levels of free amino acids [
8]. Through enrichment, these live prey organisms can supply essential nutrients to the target species, with
Artemia often serving as a carrier of essential fatty acids (EFA) [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. Feeding on
Artemia or copepods has resulted in high rates of survival and growth during the rearing of multiple seahorse species [
5,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22].
Numerous studies have also confirmed the significance of fatty acids in seahorse growth by enhancing
Artemia with various emulsions e.g., [
23,
24,
25]. This fact is related with the basis of the trophic chains because marine and freshwater trophic chains are distinct in terms of fatty acid profile. Producers of marine food webs are unicellular algae rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), mainly from the ω3 family, while freshwater food chain producers have a higher content of PUFAs from the ω6 family [
26].
Because marine fish acquire substantial PUFA levels directly from their diet, their capacity to elongate and desaturate PUFAs has diminished, owing to a reduction in the associated enzymatic processes [
27]. Considering this aspect, it can be asserted that the majority of marine species exhibit limited, inadequate, or in some instances, even non-existent abilities to elongate and desaturate linoleic acid (LA; C18:2ω6) and α-linolenic acid (ALA; C18:3ω3) is low, insufficient or, in some cases, even null as they receive high amounts of these fatty acids directly from the diet [
28,
29]. In contrast, freshwater fish have higher levels of PUFAs with 18-carbon chains (i.e., AL, LA, and ALA) and possess substantial quantities of AA (C20:4 ω6), EPA (C20:5ω3), and DHA (C22:6ω3) resulting from metabolism [
27,
29,
30].
When comparing the lipid composition of eggs between the vast majority of marine fish species and seahorses, it becomes evident that the former is characterized by having eggs with high concentrations of palmitic acid (PA, C16:0) (20.0%), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA: 17.4%), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA: 13.2%). Additionally, they contain, to a lesser extent, oleic acid (C18:1ω9), stearic acid (C18:0), palmitoleic acid (C16:1ω7), and vaccenic acid (C18:1ω7) [
29].
However, as mentioned earlier, seahorse juveniles have a low content of essential fatty acids (EFAs), namely EPA and DHA [
31], which are typically associated with their survival and growth performance [
32,
33]. As marine fish, seahorses have high requirements for fatty acids from the ω3 family, which must be supplied through their diets [
23,
34,
35,
36]. Furthermore, the prey sizes may also restrict the ingesting capacity of seahorses [
37]. In their natural habitat, copepods are the preferred prey for most marine fish larvae [
38], including seahorses. Multiple studies have indicated that the preference for copepods among marine fish larvae is attributed to their nutritional composition [
39,
40] and the provision of numerous enzymes that aid in the digestive process [
41]. Consequently, in the realm of fish larval culturing, copepods are generally considered superior to rotifers and
Artemia [
42]. However, the utilization of copepods as larval fish feed is hindered by their limited availability and the challenges associated with intensive production [
43].
Hence, as copepods are a more nutritionally suitable prey,
Artemia cultivation is a more feasible option and, through enrichment, can serve as a "vehicle" to fulfil the nutritional requirements of seahorses through a process known as “bio-encapsulation”. Conversely, advancements have been made in marine fish incubation techniques over recent years. Nonetheless, these improvements have not fully addressed the mortality issues observed during the early developmental stages of certain marine juvenile fish species [
7,
44,
45], which are often linked to feeding, feeding behavior, and periods of food scarcity [
46,
47,
48].
Considering the above, the objective of this study was to address some of the existing gaps in understanding the dietary requirements of the short-snout seahorse, H. hippocampus, during its early life stages, through the utilization of different live feed (Artemia) dietary enrichments and the implementation of an appropriate copepod co-feeding protocol.
2. Materials and Methods
A total of 420
H.
hippocampus juveniles obtained from a captive-bred broodstock kept at the Ramalhete research station, CCMAR – Universidade do Algarve, Portugal were used to conduct two different rearing trials. The broodstock fish were kept in one 250 L plastic tank assembled in a semi-open flow system with a water turnover of approximately 125 L/h per tank. Holdfast units were added to provide support for seahorses [
49]. Individuals were daily fed a mix of live mysid shrimp (
Mesopodopsis slabberi and
Leptomysis sp.) in different proportions, depending on availability. After natural spawning, juvenile seahorses from a single brood were randomly collected and used in the trials just after release from the male’s pouch. Juvenile seahorses were gently transferred to the rearing tanks using a 250 ml beaker and with utmost caution to avoid exposure to air.
In this study, two rearing trials were conducted. The first one, referred to as preliminary trial, was designed to test an enrichment protocol for seahorse´s feeding regime. The second, the experimental trial, was developed using the information obtained in the preliminary trial, to create an optimized feeding protocol that will be later described. In both trials, the rearing tanks (10 L glass rectangular tanks) were supplied with water at a stable flow rate within a semi-closed recirculation system. Prior to being introduced into the rearing tanks, water was circulated from the reservoir tank through a UV sterilization unit. To ensure that dissolved oxygen was always kept close to saturation, water was vigorously aerated in a filtration reservoir (sump). To prevent bubbling, rearing tanks water inflow was made through a transparent plastic tube ending below the water surface. The water outflow structure was assembled in the corner of the tanks. It consisted of a black polystyrene tube covered at the water surface with a 150 μm diameter mesh to prevent live feed from being flushed from the tanks. To improve prey detection, lateral and back tank walls were covered with a black adhesive like [
50], whilst the front wall remained uncovered for observation. Each of the rearing tanks had two artificial holdfasts adjusted to juvenile size. For illumination, 2 x 36 W fluorescent tubes were placed above the tanks. The light intensity at the water surface was around 900 ± 40 lux, and a photoperiod of 16L: 8D (06:00 – 22:00 h), controlled by a timer. Water temperature and chemical parameters pH, salinity, and dissolved oxygen were recorded daily and maintained at 20.4 ± 0.3 ºC, 7.8, 37.5 ± 0.1 and 7.6 ± 0.1 mg/L, respectively. Seawater quality parameters were recorded biweekly, values of ammonia were always below detectable levels, values of nitrate < 0.3 mg/L and values of nitrite < 1.25 mg/L. The tanks were daily cleaned by siphoning to remove faeces, uneaten feed, and dead juvenile seahorses (accounted for mortality).
2.1. Live Feed Culture and Enrichment
AF
Artemia cysts (Sanders®, Ogden, UT, USA) were hatched according to the procedures described by [
51]. Phytobloom Prof
Isochrysis galbana and Phytobloom Prof
Nannochloropsis spp. pure powders from Necton’s Phytobloom Green Formula (Necton, S.A, Olhão, PT) were used as enrichment according to the manufacturer specifications. In brief, each microalgae quantity was weighted individually, added to 250 ml of seawater, mixed and left to hydrate for 15 minutes. The mix was then poured into a blender and homogenized for 2 min. The
Artemia (approx. 48 000 nauplii) were added into the enrichment cup in a volume not higher than 750 ml and the enrichment media was added. This procedure was repeated for each dietary treatment.
Artemia nauplii were left to enrich for 24h at room temperature (20-22 °C), under continuous moderate aeration and illumination.
2.2. Copepod Harvesting
Copepods (Acartia clausi) were naturally produced in the outflow pond of the Ramalhete research station and collected daily using a 60 μm hand net. After acclimation to room temperature, copepods were strained through a 150 μm sieve to remove large plankters and debris and were counted to the adequate feed ratio.
2.3. Feeding Trials
In the preliminary trial, the single use of enriched Artemia was tested. For this, three different enrichment media with different DHA/EPA ratios were tested using two microalgae in different proportions: I. galbana, rich in DHA, and Nannochloropsis sp., rich in EPA. The calculations of the DHA and EPA ratios were derived from the fatty acid (FA) profile provided by the manufacturers. A total of 180 juvenile H. hippocampus from the same brood were distributed across nine rearing tanks using a completely randomized design, with three replicate tanks allocated to each dietary treatment. 20 juvenile H. hippocampus were stocked in each replicate tank. The first dietary treatment (Art2:1), contained Artemia metanauplii enriched with 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio; the second (Art1:1), Artemia metanauplii enriched with 1:1 DHA/EPA ratio; and the third (Art1:2), Artemia metanauplii enriched with 1:2 DHA/EPA ratio. The experiment was designed to last 28 days.
In the experimental trial, based on the results of the preliminary trial, the minimum copepod (A. clausi) addition to sustain optimal growth and survival of juvenile H. hippocampus was evaluated and compared to copepod and Artemia diets. 240 juvenile H. hippocampus from a same brood were assembled into twelve rearing tanks according to a completely randomised design, with three replicate tanks assigned to each dietary treatment. 20 juvenile H. hippocampus were stocked in each replicate tanks at a density of 2 fish l-1. All groups were first fed natural copepods from 0 – 7 days post-parturition (DPP), and only on the 8th day the transition to each of the following dietary treatments was made. The first dietary treatment (Cop), consisted in daily captured copepods (control diet); the second dietary treatment (ArtDHA/EPA), of 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii used in the previous trial (dietary treatment Art2:1); the third (ArtDHA/EPA5%), a mixture of 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; and the fourth dietary treatment (ArtDHA/EPA10%), a mixture of 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods. The experiment lasted for 28 days.
2.4. Sampling, Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
To obtain the accurate weight and length information at 0 DPP, due to the small size and to avoid morphological distortions, ten juveniles were immediately and rapidly sacrificed with an excess of anaesthetic (2-phenoxyethanol solution, 0.40 mg L
-1). Individuals were placed in the anaesthetic solution for at least 20 minutes and removed no less than 10 minutes after ventilation stopped. Fish were than weighted using a high precision scale and measurements (total length as the sum of the head, trunk, and tail length) were done using a binocular microscope associated with an image analysis software (DinoCapture 2.0 (AnMo Electronics Corporation, Sanchong, New Taipei City, Taiwan)). Later, experimental fish were sampled at 14 and 28 DPP for growth performance analysis. To determine the total length, the sum of the head length and the height of the fish were considered. Head length was measured as the distance from the rostral zone of the snout (maxillary) to the midpoint of the cleithral ring. The height of the seahorse was measured by the length between the cleithral ring to the end of the tail, considering it in extension (Annex I), as suggested by [
52]. This procedure was related to the adoption of a methodology that would inflict the least possible stress on seahorses, which is more advantageous than the traditional three-measurement method proposed by [
53]. Mortality was monitored daily.
Seahorse’s wet weight and total length, as well as mortality, were used to calculate: Survival (S) = ((𝑁
𝑖−𝑀
𝑖𝑗)/𝑁
𝑖) × 100, where Ni is the initial number of seahorses placed on each tank on day 1 and M
ij the total number of surviving individuals at the end of the trial; Condition Factor (CF) = (WW/L
3) × 100, where WW is the wet weight (g) and L the total length (cm); Mean Length Gain (LG) (cm/fish) =(L
f/L
i)/t, where L
f is the final length (cm), L
i is the initial length (cm) and t is the number of experimental days; Mean Weight Gain (WG) (mg/fish) = (W
f-W
i)/t, where W
f is the final wet weight (mg), W
i is the initial wet weight (mg) and t is the number of experimental days and the Thermal-unit Growth Coefficient (𝑇𝐺𝐶) (modified from [
54] by [
55]) = [(W
f1/3-W
i1/3)/Σ(T✕D)] × 100, where W
f is the final seahorse wet weight (g), W
i is the initial wet weight (g), T is the water temperature (°C), and D is the number of days in each trial. Data processing and statistical analysis were conducted using the statistical analysis program package GraphPad Prism (version 8.4.2 for Windows, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). All data were tested for normality and homogeneity of variances. To study the effect of the diets on growth performance (Weight gain, Length gain, Thermal-unit Coefficient, Condition Factor, and Accumulative survival) between groups, a One-Way ANOVA, using Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons was used.
2.5. Dietary Treatments Proximate Analysis and Fatty Acid Composition
To analyse the nutritional quality of prey and the dietary treatments used in the experimental trial, samples of natural copepods (Cop), unenriched Artemia (ArtRef) 24h enriched Artemia plus 5% copepods (ArtDHA/EPA5%) and enriched Artemia plus 10% copepods (ArtDHA/EPA10%) were collected. Even though unenriched Artemia (ArtRef) was not a dietary treatment tested in any of the groups, it was analysed along with all the regimes for comparison purposes and to determine the efficiency of the enrichment used and copepod addition.
The four dietary treatments and the unenriched
Artemia were analyzed following the procedures outlined in [
56]. In brief, the dry matter was analyzed by drying samples at 105 °C to constant weight; ash by incineration of samples at 550 °C for 5 h; crude protein (N × 6.25) using a Leco nitrogen analyzer (Leco Corporation, St. Joseph, USA); total lipid by extraction according to the method of [
57], using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) and lyophilized samples.; crude fiber by acid and basic digestion (Fibertec System M., 1020 Hot Extractor, Tecator) and gross energy content using an automatic oxygen bomb calorimeter (Parr 6400, U.S.A.) according to ISO 9831.
For the fatty acid analysis, to achieve the extract derivatization, total lipids were transferred to methylation tubes using 1.5 mL of CHCl
3/MeOH (3:2) solution and placed under a nitrogen stream to evaporate the transfer solvent and dry the extract for saponification and methylation. For methylation phase, the samples were cooled for approx. 1 min and 1 mL of BF
3-methanol was added, the tubes were then heated at 70°C for 10 min. Once methylation was complete, the solution was cooled to room temperature, 2 mL of distilled water and 2 mL of petroleum ether were added and stirred vigorously. The tubes were then placed in the fridge for 12 h, at 2°C. After separation of the phases was verified, each sample’s supernatant (1.5 mL) was collected into 2 mL vials, which were hermetically sealed, labelled, and laced in the fridge until further use. Chromatographic analysis of methyl esters was performed as described by [
58]. In brief, the analysis of the peaks and their respective MS was obtained by electronic impact at 70 eV, with a sweep of m/z= 40 to 450 and analyzed using MSWS 8.2 software. The Fame standards used were 37-component FAME MIX and BAME MIX 26 (Supelco). Fatty acids were designated according to the nomenclature of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) for carbon chain length: number of double bonds and position of the double bond closest to the omega carbon.
2.6. Ethical Statement
CCMAR facilities and the research is certified to house and conduct experiments with live animals (Group-C licenses by the Direção Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária, Ministério da Agricultura, Florestas e Desenvolvimento Rural, Portugal). The experimental design of the present study was part of the Projects HIPPONUTRE (reference 1602-01-FMP-54) and HIPPOSAVE (reference MAR-01.04.02-FEAMP-0029), which obtained approval from the ethics committee of the Veterinary Medicines Directorate, Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries, Portugal. The study adhered to the guidelines outlined by the European Union Council (86/609/EU) and the relevant Portuguese legislation concerning the use of laboratory animals.
3. Results
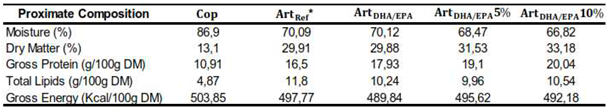
The proximate composition of each dietary treatment is presented in
Table 1. The dry matter of
Cop dietary treatment was considerably lower (13.1%) compared to the remaining diets (ranged between 29.9 and 33.2%). As for the gross protein, the
ArtDHA/EPA10% had the highest content (20 g/100g DM), followed by
ArtDHA/EPA5% (19.1 g/100g DM),
ArtDHA/EPA (17.9 g/100g DM),
ArtRef (16.5g/100g DM) and
Cop (10.9 g/100g DM). Concerning the total lipids content,
Cop diet had the lowest value of total lipids, (4.9 g/100g DM), a value twofold lower than all other dietary treatments. Conversely,
Cop diet had the higher gross energy content (503.9 Kcal/100g DM), followed by
ArtDHA/EPA5% (495.62 Kcal/100g DM),
ArtDHA/EPA10% (492.18 Kcal/100g DM), and
ArtDHA/EPA (489.84 Kcal/100g DM) (
Table 1).
Table 1.
Proximate composition of the four tested dietary treatments used (per 100g of Dry Matter (g/100g DM)). * Although ArtRef was not directly tested is presented for comparison purposes, as it is the basis for the dietary treatments with enriched Artemia used. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA - 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods.
Table 1.
Proximate composition of the four tested dietary treatments used (per 100g of Dry Matter (g/100g DM)). * Although ArtRef was not directly tested is presented for comparison purposes, as it is the basis for the dietary treatments with enriched Artemia used. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA - 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods.
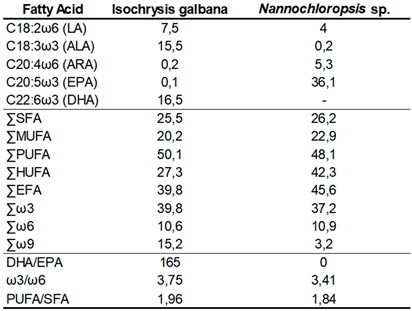
Regarding the presence of EFAs in the two microalgae used,
I.
galbana had the higher percentages of LA (C18:2ω6) (7.5%), ALA (C18:3ω3) (15.5%) and DHA (C22:6ω3) (16.5%), than
Nannochloropsis sp. Conversely, although
Nannochloropsis sp. did not contain any DHA in its profile, it had a higher concentration of ARA (C20:4ω6) (5.3%) and a substantially more EPA (C20:5ω3) (36.1%) (
Table 2). Concerning fatty acid classes (SFA, MUFA, PUFA and HUFA) and families (ω3, ω6 and ω9), the biggest differences were in the percentage of HUFAs, EFAs and ω9 fatty acids.
Nannochloropsis sp. presented higher amounts of HUFAs (42.3%) and EFAs (45,6%), while
I.
galbana showed a greater percentage in ω9 fatty acids, with a value of 15.2%. As for the ratios,
I.
galbana shows higher values for all the ratios presented, especially the very high DHA/EPA ratio (165) whereas
Nannochloropsis sp. has a value of 0 for the same ratio (
Table 2).
Table 2.
Fatty acid profile of the two microalgae used as Artemia nauplii enrichment, in the diets, ArtDHA/EPA, ArtDHA/EPA5%, and ArtDHA/EPA10%.
Table 2.
Fatty acid profile of the two microalgae used as Artemia nauplii enrichment, in the diets, ArtDHA/EPA, ArtDHA/EPA5%, and ArtDHA/EPA10%.
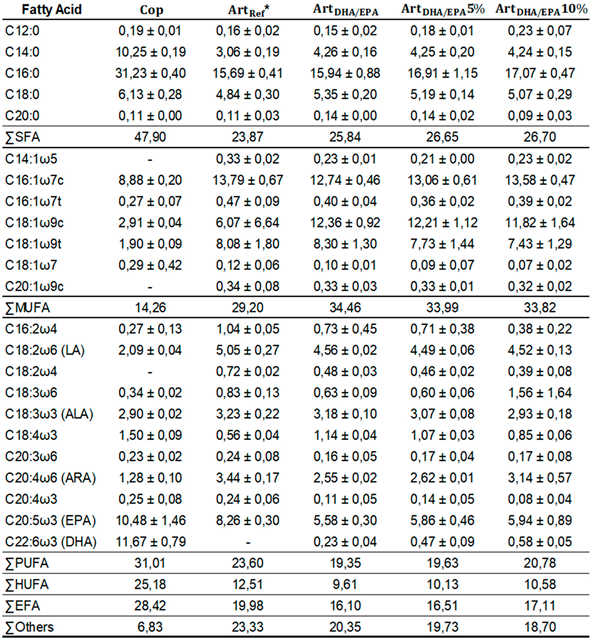
The lipid profile of the control diet (Cop) and tested dietary treatments (
Cop,
ArtDHA/EPA,
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10%)
, and the additional
ArtRef, for the most expressive fatty acids and respective sums of SFA, MUFA, PUFA, HUFA and EFA are detailed in
Table 3. The
Cop diet contained high values of all fatty acid classes, but MUFA.
Cop and
ArtRef diets also revealed the highest percentage values for PUFA and HUFA. Regarding PUFA,
Cop diet showed a value of 31%, followed by
ArtRef with 23.6%, and by the three diets including enriched
Artemia. Dietary treatments with enriched
Artemia had much higher values of MUFA (≈34%) and, consequently, lower PUFA and HUFA values (≈ 20% and 10%, respectively).
The most relevant SFA were C12:0, C14:0, C16:0, C18:0, and C20:0. C16:0 was the SFA with the highest value in all tested diets, with
Cop diet having 31.2%, followed by
ArtDHA/EPA10% (17.1%),
ArtDHA/EPA5% (16.9%),
ArtDHA/EPA (16%) diets (
Table 3). The second most expressive SFA was C14:0, as for C18:0, there were no major differences between dietary treatments. Amongst the PUFA, all EFAs (LA, ARA, ALA, EPA, and DHA) were present in the tested dietary treatments (
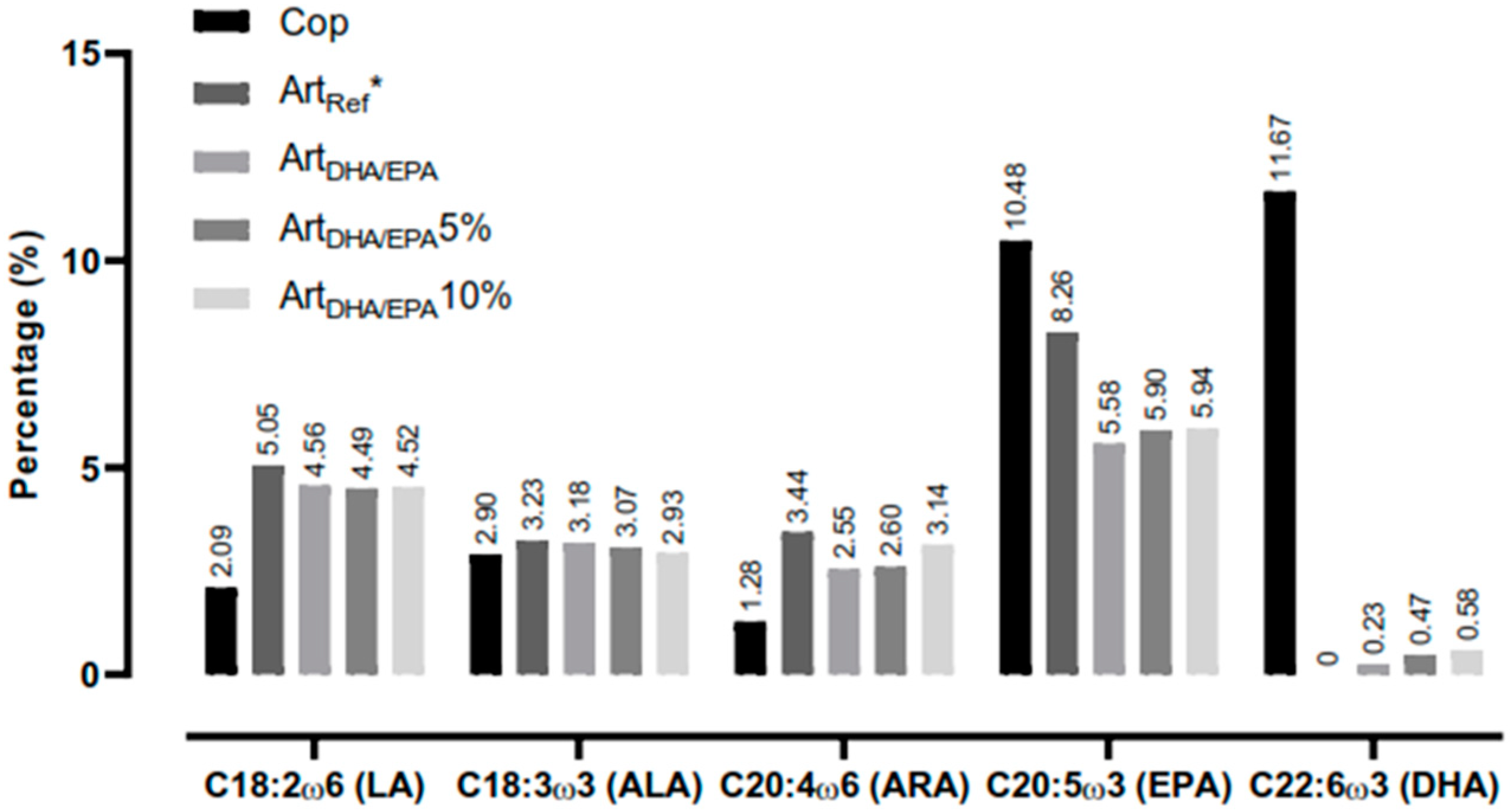
Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Essential fatty acids (EFA) present in each tested dietary treatment. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; - ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods. LA - Linoleic acid; ALA - Alpha-Linolenic acid; ARA – Arachidonic; EPA - Eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA - Docosahexaenoic acid.
Figure 1.
Essential fatty acids (EFA) present in each tested dietary treatment. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; - ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods. LA - Linoleic acid; ALA - Alpha-Linolenic acid; ARA – Arachidonic; EPA - Eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA - Docosahexaenoic acid.
Regarding LA and ARA, all diets containing
Artemia (
ArtDHA/EPA,
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10%) had about twice the amount of these fatty acids compared to the
Cop control diet (
Table 3). No relevant differences in the ALA amount (≈3%) were found among dietary treatments. Regarding EPA,
Cop control diet had the highest value (10.48%), followed by
ArtRef, and 8.26%, while the remaining samples have very similar amounts (≈6%). The
Cop dietary treatment contained a high percentage of DHA (11.7%), compared to the remaining diets, with concentrations ranging between 0.2% and 0.6%). It is however noteworthy, that the low DHA concentrations in the Art
DHA/EPA5% and Art
DHA/EPA10% were present on the expanses of the 5 and 10% copepod inclusion, as in the Art
Ref the DHA concentration was 0% (
Table 3).
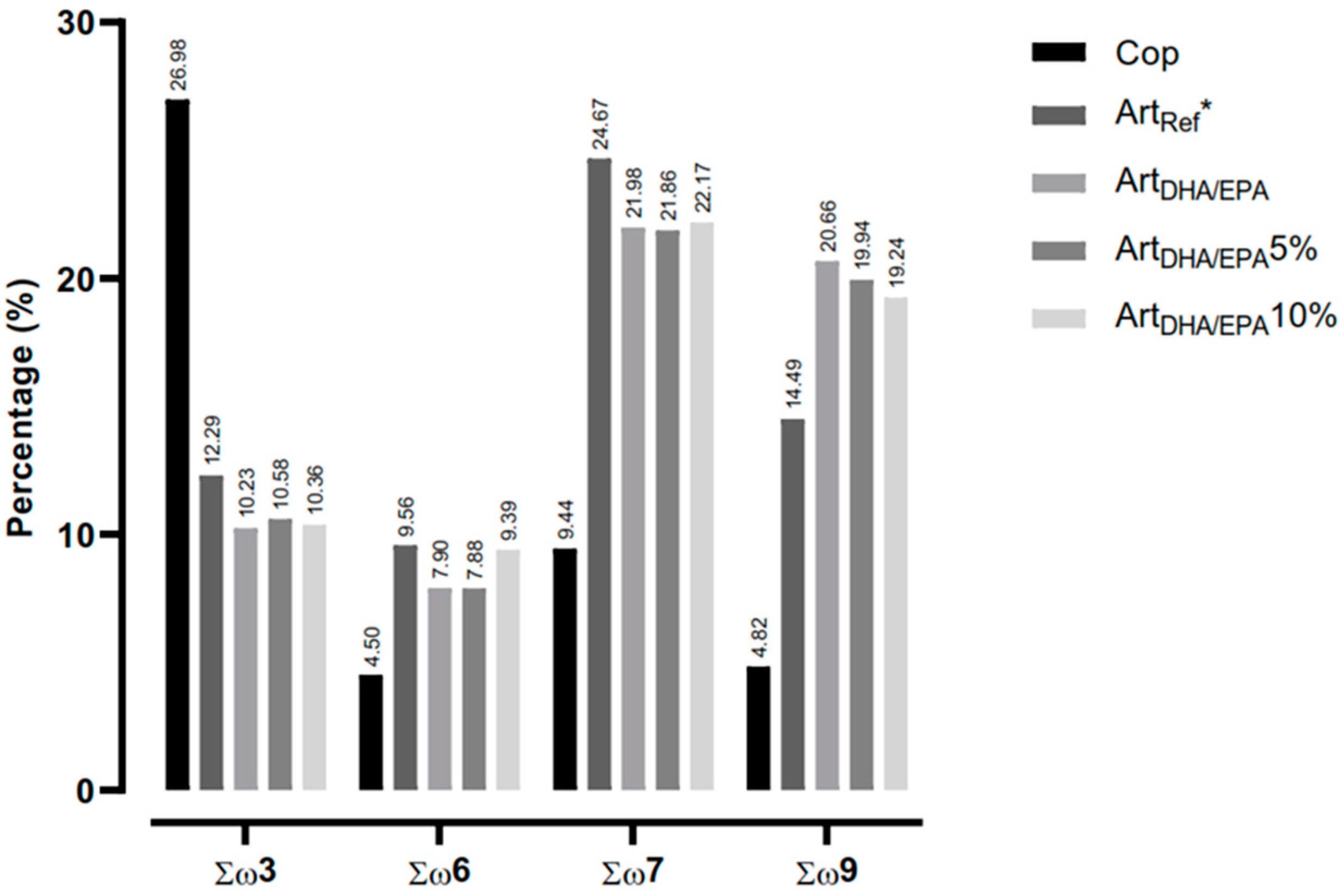
Figure 2. shows the distribution of fatty acid families by dietary treatment. The Cop control diet had the highest value of ω3 fatty acids (27%), followed by the
ArtRef (12.3%),
ArtDHA/EPA5% (10.5%),
ArtDHA/EPA10% (10.4%) and the
ArtDHA/EPA (10.2%). Concerning the ω6, ω7 and ω9 fatty acid families, all diets but Cop revealed higher percentages. The diets with the highest ω6 fatty acids were
ArtDHA/EPA10% (9.4%),
ArtDHA/EPA (7.9%) and
ArtDHA/EPA5% (7.9%). Regarding the ω7 fatty acids, all regimes with enriched Artemia revealed to have high concentrations with similar values (approximately 22%) and Cop diet with half the concentration of the remaining diets (9.4%). Finally, for ω9 fatty acids, it was observed that the
ArtDHA/EPA regime presented the highest value (20.7%), followed by
ArtDHA/EPA5% (19.9%) and
ArtDHA/EPA10% (19.2%). Cop diet presented the lowest value of ω9 fatty acids, with 4.8%.
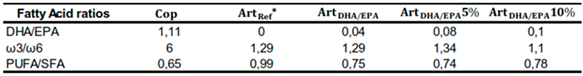
Some relevant ratios in terms of nutritional assessment of the tested diets are presented in
Table 4. DHA/EPA and ω3/ω6 ratios in
Cop diet revealed the highest values (1.11 and 6, respectively). As for the DHA/EPA ratio in the
ArtRef it was 0. Regarding the PUFA/SFA ratio,
ArtRef presented the higher value (0.99), followed by
ArtDHA/EPA10% (0.78),
ArtDHA/EPA (0.75),
ArtDHA/EPA5% (0.74) and
Cop (0.65) dietary treatments.
Table 3.
Fatty acid profile of each dietary treatment (mean ± standard deviation) expressed in percentage (%) relative to the total of fatty acids identified in the samples.
Table 3.
Fatty acid profile of each dietary treatment (mean ± standard deviation) expressed in percentage (%) relative to the total of fatty acids identified in the samples.
Figure 2.
- Characterization of the fatty acid families ω3, ω6, ω7 and ω9 in each of the four tested dietary treatments. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; - ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods.
Figure 2.
- Characterization of the fatty acid families ω3, ω6, ω7 and ω9 in each of the four tested dietary treatments. Cop - Natural copepods; ArtRef - Unenriched Artemia nauplii; ArtDHA/EPA5% - 95% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 5% natural copepods; - ArtDHA/EPA10% - 90% 2:1 DHA/EPA ratio enriched Artemia metanauplii and 10% natural copepods.
Table 4.
Main fatty acid ratios in each of the four tested dietary treatments.
Table 4.
Main fatty acid ratios in each of the four tested dietary treatments.
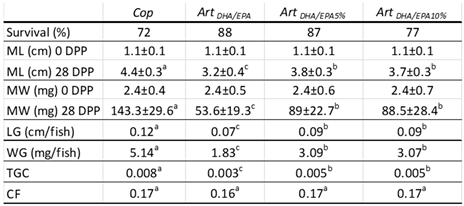
3.1. Growth Trials
In the preliminary trial, all dietary treatments (
Art2/1,
Art1/1, and
Art1/2) resulted in 100% mortality by the 9th DPP, leading to the termination of the trial at that point. Regarding the subsequent experimental trial, comprehensive data regarding the survival and growth performance of juvenile
H.
hippocampus fed each of the four dietary treatments (
Cop,
ArtDHA/EPA,
ArtDHA/EPA5%, and
ArtDHA/EPA10%) are presented in
Table 5. It was observed that both the
ArtDHA/EPA and
ArtDHA/EPA5% groups exhibited similar survival rates, 88% and 87%, respectively. The
ArtDHA/EPA10% group followed with a survival rate of 77%, and the
Cop group had the lowest survival rate at 72% (
Table 5).
Table 5.
- Survival and growth parameters of juvenile Hippocampus hippocampus fed each the four tested dietary treatments.
Table 5.
- Survival and growth parameters of juvenile Hippocampus hippocampus fed each the four tested dietary treatments.
3.2. Top of Form
At the end of the trial, juvenile
H.
hippocampus fed the
Cop diet, grew significantly more (P < 0.05) than all the remaining groups.
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10% attained an intermediate growth performance, non-significantly different (P<0.05) among the two, and the group fed
ArtDHA/EPA grew significantly less (P < 0.05) than all the remaining (
Table 5 and
Figure 3).
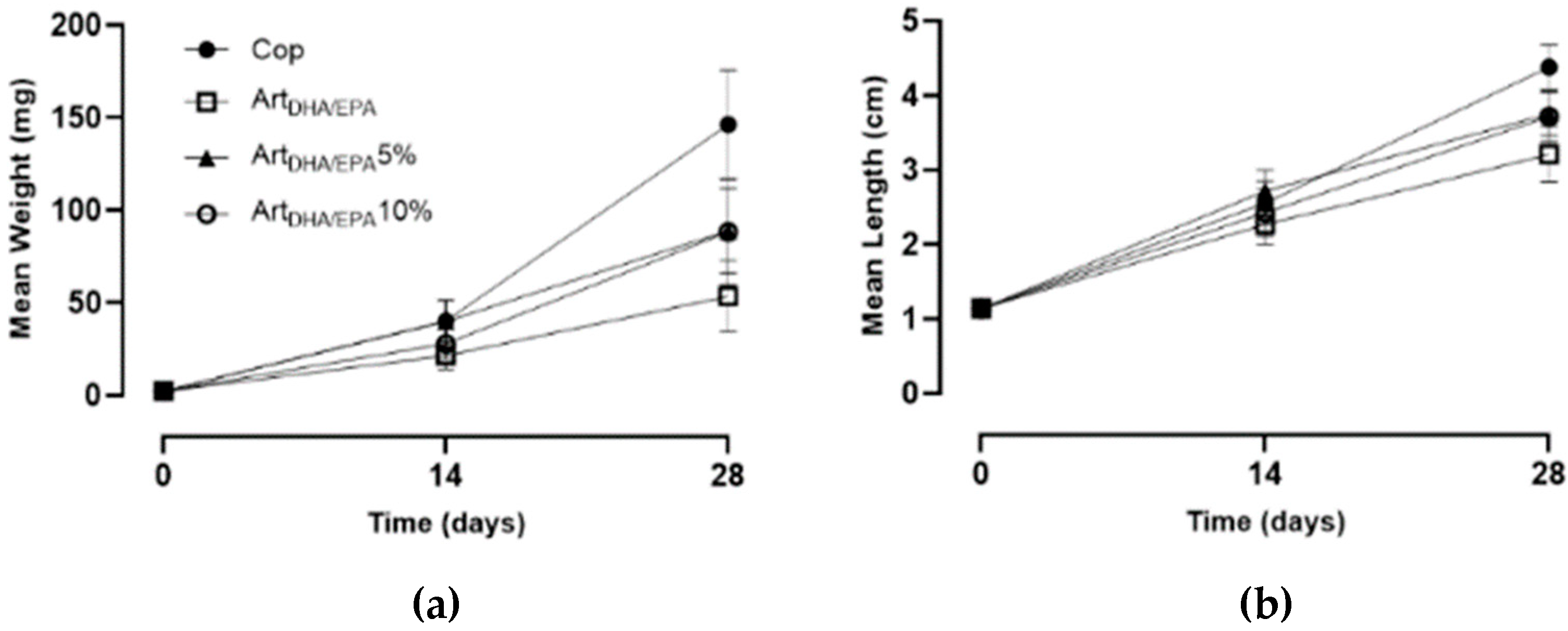
Figure 3.
Mean weight (a) and mean length (b) gain of juvenile Hippocampus hippocampus fed each the four tested dietary treatments during the 28-day experiment.
Figure 3.
Mean weight (a) and mean length (b) gain of juvenile Hippocampus hippocampus fed each the four tested dietary treatments during the 28-day experiment.
This is corroborated by a Cop group WG of 5.1 mg d-1, and a final MW of 146.3 ± 29.6 mg at 28 DPP, the highest observed. The ArtDHA/EPA5% and ArtDHA/EPA10% groups showed identical WG (3.09 and 3.07 mg d-1, correspondingly) and a MW of 89 ± 22.7 mg and 88.5 ± 28.4 mg, respectively. The group fed with the ArtDHA/EPA attained a WG of 1.8 mg d-1 and a final MW of 53.6 ± 19.3 mg, showing the lowest growth performance.
Concordantly, the
Cop group had the highest LG (0.12 cm d
-1) averaging 4.4 ± 0.3 cm at the end of the experiment.
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10% groups weren’t significantly different (P > 0.05), and the LG was 0.09 cm d
-1, resulting in 0.03 cm d
-1 less than the
Cop group. The lowest LG and ML values were observed for the
ArtDHA/EPA regime group, with 0.07 cm d
-1, and a ML of 3.2 ± 0.4 cm (
Table 5).
Concerning the TGC, the highest value was observed in
Cop group (0.008), followed by both
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10% groups (0.005) and the
ArtDHA/EPA group (0.003) the lowest TGC value was observed. All groups attained similar, and non-significantly different (P>0.05) CF values at the end of the experiment (
Table 5).
4. Discussion
Juvenile seahorses require large amounts of good quality live feed [
2] in which the fatty acids are a prevalent nutritional requirement. However, ensuring its appropriate provision remains one of the most significant challenges in successful seahorse mass farming.
Artemia is a commonly used feed for seahorses due to its easy cultivation and commercial availability [
14,
16] but available
Artemia enrichments are still inadequate for most seahorse species.
Artemia nauplii has been identified as deficient in highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFAs) [
5,
11], requiring HUFA enrichment media [
14,
25,
59,
60]. Conversely, copepods are regarded as an ideal diet for marine fish larvae, seahorse included, primarily due to their well-balanced fatty acid composition. However, copepods often cannot be cultured at high densities under controlled conditions as other live food options, because they need the use of larger volumes of water and larger culture vessels [
61]. this, enriched
Artemia-based diets cannot be ignored and can be used as an alternative or complement to an exclusive copepod-based diet if its enrichment is adequately tailored to the target species. Additionally, its utilization can also offer advantages by potentially reducing associated contaminants, as copepods frequently originate from wild populations and can introduce pathogens [
62].
In the current study, all dietary treatments containing
Artemia (
ArtDHA/EPA,
ArtDHA/EPA5%, and
ArtDHA/EPA10%) had higher levels of total protein and total lipids compared to the
Cop control diet. This difference could be attributed to the greater moisture content in the
Cop diet (86.9%) compared to that of the Art
Ref (70.1%). However, it was the
Cop diet that yielded a higher gross energy content. This same trend in gross energy content was observed when
ArtDHA/EPA was supplemented with 5% and 10% copepod inclusion, resulting in an increase in gross energy content in these dietary treatments. From a nutritional perspective, dietary lipids have been shown to play a critically important role in the early development of marine finfish larvae [
29]. They serve as the primary energy source for larvae and are a vital source of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) and essential fatty acids (EFA), which are necessary for the development of new cellular structures. Additionally, they contribute to normal larval growth, morphogenesis, and bone formation [
63]. Therefore, a deficiency in HUFA levels in prey can lead to detrimental effects on juvenile seahorse performance, including reduced feeding and swimming activity, as well as a delay in the settlement process, as observed in previous studies where
Artemia was used, due to its incomplete assimilation [
2,
5]. Concordantly, a correlation between the type of prey enrichment and the occurrence of gas bubble disorder has also been observed. [
17] reported that juveniles of
H.
guttulatus fed
Artemia enriched with microalgae exhibited a significantly lower incidence of this disorder compared to those fed on
Artemia enriched with commercial products. Similarly, it was noted that
H.
guttulatus juveniles fed DHA-Selco® enriched
Artemia metanauplii displayed symptoms of gas bladder overinflation and intestinal disorders, unlike individuals fed solely on natural copepods [
59].
In the present study, the selection of the two microalgae for Artemia enrichment was based on their DHA and EPA profiles. The analysis revealed that I. galbana had a higher proportion of C22:6ω3 (DHA) in its profile (16.5%), while Nannochloropsis sp. lacked any significant concentration of this essential fatty acid. On the contrary, Nannochloropsis sp. exhibited a substantial percentage of C20:5ω3 (EPA) (36.1%), while I. galbana displayed only a trace amount of this fatty acid. The presence of EPA in Nannochloropsis sp. notably influenced the HUFA content, leading to a 55% increase compared to that of I. galbana. Moreover, I. galbana was rich in ω9 HUFAs (15.2%), largely attributed to its high content of oleic acid (C18:1ω9) (15%), which represented 99% of ω9 HUFAs in this species. On its turn, the Cop diet had a higher PUFA percentage than ArtRef, base diet. Notably, out of the PUFA content (31%) in the Cop diet, 79.9% comprised HUFA, indicating a significant presence of EPA and DHA in comparison to the ArtRef base diet. In contrast, only 53.4% of PUFA in the ArtRef diet constituted HUFA. Additionally, the analysis of both ArtRef and ArtDHA/EPA diets unveiled that the enrichment process contributed to elevate the SFA and MUFA content. Conversely, the incorporation of 5% or 10% copepods in combination with the enriched Artemia increased the PUFA and HUFA content.
Regarding the fatty acid families, the
Cop diet showed high concentrations of ω3 PUFA. Its fatty acid profile showed that EPA and DHA were the predominant polyunsaturated fatty acids. Furthermore, the substantial presence of C16:1ω7c (palmitoleic acid) in the
Artemia profile contributes to the heightened ω7 content in
Artemia-based dietary treatments (
ArtDHA/EPA,
ArtDHA/EPA 5% and
ArtDHA/EPA 10%). Moreover, the enriched
Artemia diets exhibited notably high levels of ω9 fatty acids, which declined with the incorporation of copepods. This outcome is attributed to the elevated concentration of C18:1ω9 (olieic acid) in the
I.
galbana, as mentioned earlier. The analysis of essential fatty acid profiles in the tested dietary treatments revealed the presence of all five essential fatty acids (LA, ALA, ARA, EPA, and DHA), standing out the content of EFA in the
Cop diet (∑EFA = 28.4%) (
Table 3). The higher content of these fatty acids in the
Cop diet could potentially justify a better lipid profile of this diet when compared to that of
Artemia for juvenile seahorses, since high levels of these fatty acids are typically found in marine fish eggs [
29]. In comparison, the EFA content in the
ArtRef base diet was significantly lower than that of the
Cop diet, which can be attributed to the instability of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFAs) and their metabolism in
Artemia [
31].
In the preliminary growth trial, the survival rate was 0% after 9 days of the experimental trial across all dietary treatments. This result suggests that the exclusive use of enriched
Artemia diets since 0 DPP, even with differing DHA/EPA ratios, is not a viable alternative to copepods as a suitable diet for
H.
hippocampus juveniles. While these diets match the necessary fatty acid profile, the outcome agreed with the findings from other studies, in which, their authors linked this observation with the underdeveloped nature of a seahorse’s digestive tract in the initial phase of its life cycle. Consequently, the correct assimilation of nutrients is hindered [
7,
64,
65]. As
Artemia can be more difficult to be digested by fish compared to other live prey such as copepods, when prey densities are high, continuous feeding reduces digestion time lowering the assimilation efficiency in the gut, possibly leading to an intact passage through the digestive tract. In some cases, preys might even remain alive upon passage [
18], occasionally maintaining vitality [
25]. In their natural habitat, newly born seahorses might exhibit preferences for specific prey items, making it advantageous to perform gut content analysis to assess prey preferences as they develop [
66]. Since copepods constitute the primary prey for wild juvenile seahorses, it is expected that seahorses possess a greater capacity for digesting copepods compared to other prey. This capability could arise from an adaptive evolution of the gastrointestinal system and its secretions tailored for copepod digestion [
60,
67,
68]. Moreover, the composition and permeability of the exoskeleton can also account for variations in digestive efficiency [
69]. The exoskeleton of a copepod is comprised of a thin, easily breakable, segmented cuticle constructed from a protein matrix containing lipids and chitin rods. Conversely, the cuticle forming the exoskeleton of
Artemia is thicker and more resistant to breaking [
70]. This difference constitutes a significant barrier to the digestion and assimilation of the contents of specific live prey [
65]. Additionally, the fact that
Artemia is not a natural prey item for seahorses adds complexity. For instance, [
18] discovered that
H.
subelongatus encountered difficulties in nutrient assimilation from the provided diet. [
71] observed
Artemia being excreted live during the first DPP when fed to juvenile
H.
guttulatus. Similarly, [
7] found that
H.
guttulatus newborns exhibited a limited ability to efficiently digest
Artemia until around 10 DPP, with significant an improvement only after 15 DPP [
65]. An additional explanation for the less effective use of
Artemia as food could be attributed not only to the development of the seahorse’s digestive system [
7,
64,
72] but also to the size of their oral cavity [
64,
73], which may limit its capacity to accommodate larger prey. In terms of prey size, since both prey types (
Artemia and copepods) were measured during the trials, and copepods were found to be almost twice the size of the
Artemia used, this hypothesis is not plausible, and the current results only suggest that the maturation of the digestive system is the most probable underlying cause. This idea is reinforced by the results of [
64], as their study did not establish a clear correlation between the mouth size of the juveniles and the size of the prey.
In contrast, the use of copepods as a preconditioning diet played a pivotal role in achieving the survival and growth of juvenile
H.
hippocampus. The preliminary use of a natural copepod diet appeared to facilitate the maturation of the digestive tract, subsequently enabling the ability to effectively digest other enriched crustacea diets with minimal mortality. Seahorses belong to the category of agastric teleost species, lacking a functional stomach. In these species, the primary site of digestion is the intestine [
74], which undergoes developmental changes during ontogeny, transitioning from a short, direct tube to an elongated, segmented duct. Within this context, the exocrine pancreas assumes the responsibility of synthesizing and releasing digestive enzymes, including proteases, glycosidases, and lipases, into the intestine. This biochemical process aids in the breakdown of dietary nutrients, transforming them into readily absorbable molecules [
75].
Given the effectiveness of employing copepods as the primary diet for most finfish species, their inclusion, often co-fed with other diets to address the challenges of their exclusive use, has the potential to significantly enhance the growth and survival of juvenile seahorses e.g., [
59,
64]. Therefore, considering the unsatisfactory performance of
Artemia in the preliminary trial, the second trial was conducted to test the beneficial use of limited copepod inclusion levels. During this trial, survival rates exhibited considerable fluctuation, yet the average survival rate across all dietary treatments reached 81%, with the lowest recorded at 72%. This promising outcome is noteworthy in comparison to findings from other studies [
17,
23,
70]. [
18] reported survival rates of >80% at 14 DPP for
H.
subelongatus juveniles fed copepods, compared to >40% for those fed enriched
Artemia. In the present study, considering the appropriateness of a copepod diet, one would anticipate a higher survival rate among fish fed this diet. However, contrary to this expectation, the opposite was observed, as fish fed the
Cop diet exhibited the lowest survival rate (72%) among the four tested groups. During the initial 7 days of the trial (0-7 DPP), all groups were provided with the same copepod diet, and only on the 8
th day on the diet was changed to the respective dietary treatments. Therefore, the initial mortality observed within the first 7 DPP cannot be attributed to the diet. Similarly, previous studies achieved reasonably high rates of survival and growth for seahorse juveniles fed copepod-based diets [
16,
18,
76].
Regarding the growth performance of fish fed various dietary treatments, it is noteworthy that the mean LG displayed greater homogeneity than the mean WG during the analysed time period. Furthermore, LG exhibited a more pronounced similarity among the groups. Once again, a recurring observation was made: smaller LG was associated with individuals fed
ArtDHA/EPA, whereas larger LG was evident among those fed on other dietary regimes, with the
Cop diet resulting in the highest measurements. Consequently, juvenile seahorses fed the enriched
Artemia diet (
ArtDHA/EPA) without any inclusion of copepods demonstrated the lowest MW gain at the conclusion of the experimental trial. As previously mentioned, this outcome likely resulted from the inadequate DHA/EPA ratio (0.04) identified in this particular diet, negatively impacting juvenile growth. Additionally, it was evident that when diets included either enriched
Artemia co-fed with copepods (
ArtDHA/EPA5% and
ArtDHA/EPA10%) or were exclusively comprised of copepods (
Cop), the MW gain increased significantly (P < 0.05). This consequently yielded substantially higher mean WG values, thereby contributing to elevated thermal-unit growth coefficient (TGC) values. These findings can also be attributed to the heightened HUFA content observed in these diets compared to that of
ArtDHA/EPA. This observation agrees with [
77], who demonstrated that optimal growth performance in
H.
erectus juveniles fed copepods was attributed to the abundant content of HUFAs.
In conclusion, the growth and survival of juvenile H. hippocampus are significantly enhanced when the initial diet consists exclusively of copepods, allowing for the maturation of the digestive tract. Subsequently, even a small inclusion of 5% to 10% copepods in the diet contributes to an improved fatty acid profile due to copepods’ high EFA content. This dietary adjustment aligns with the species’ requirements, translating into substantial benefits in terms of growth and survival.